British 3rd Infantry Division on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 3rd (United Kingdom) Division is a
 The 3rd Division was also present at the
The 3rd Division was also present at the
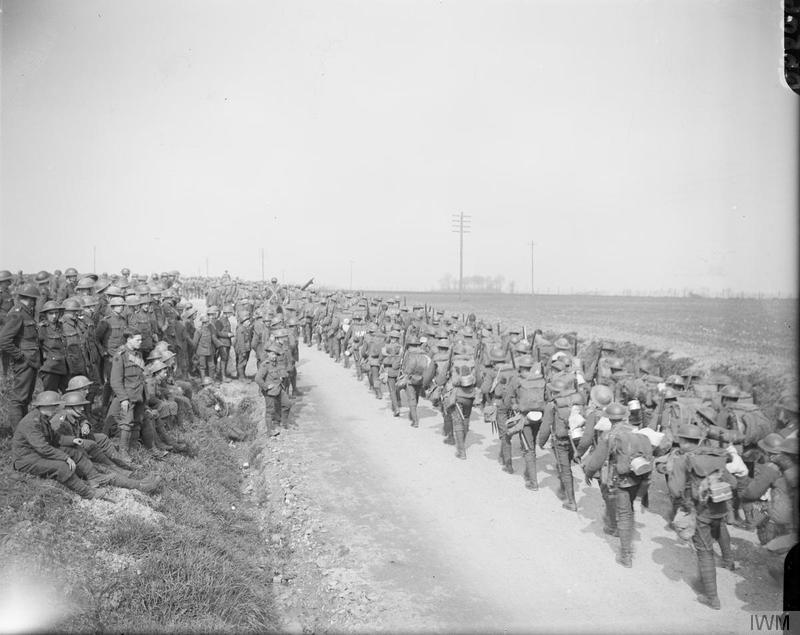 During the
During the
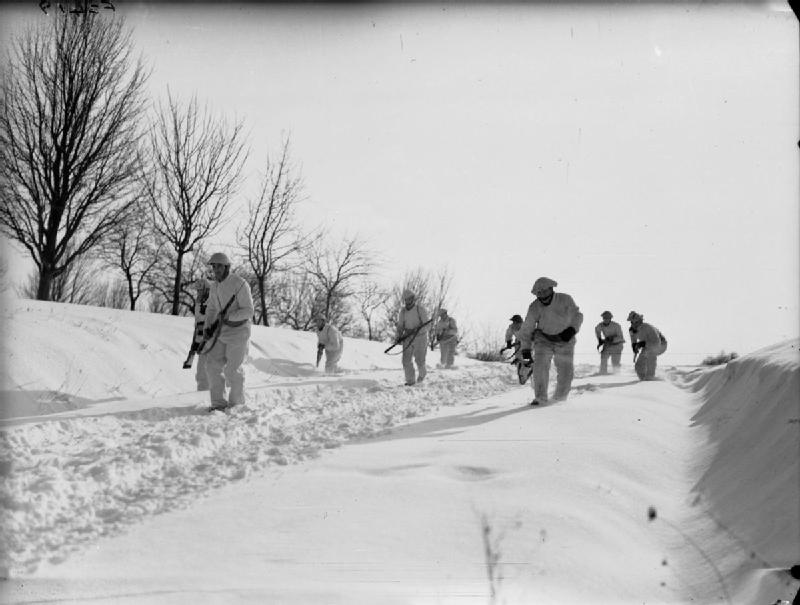 The 3rd Infantry Division, under the command of Major General
The 3rd Infantry Division, under the command of Major General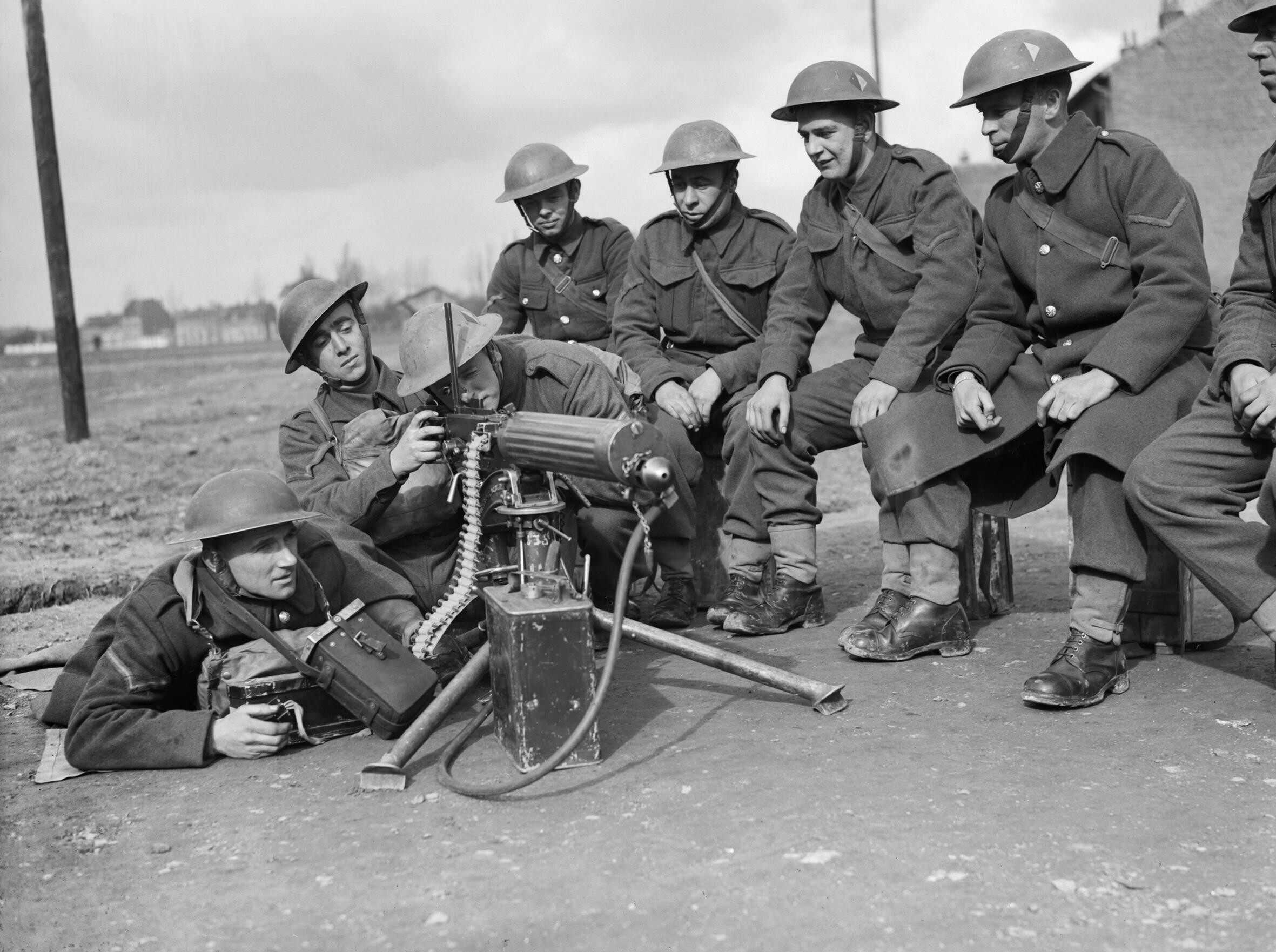  In May 1940, after several months of relative inactivity, the
In May 1940, after several months of relative inactivity, the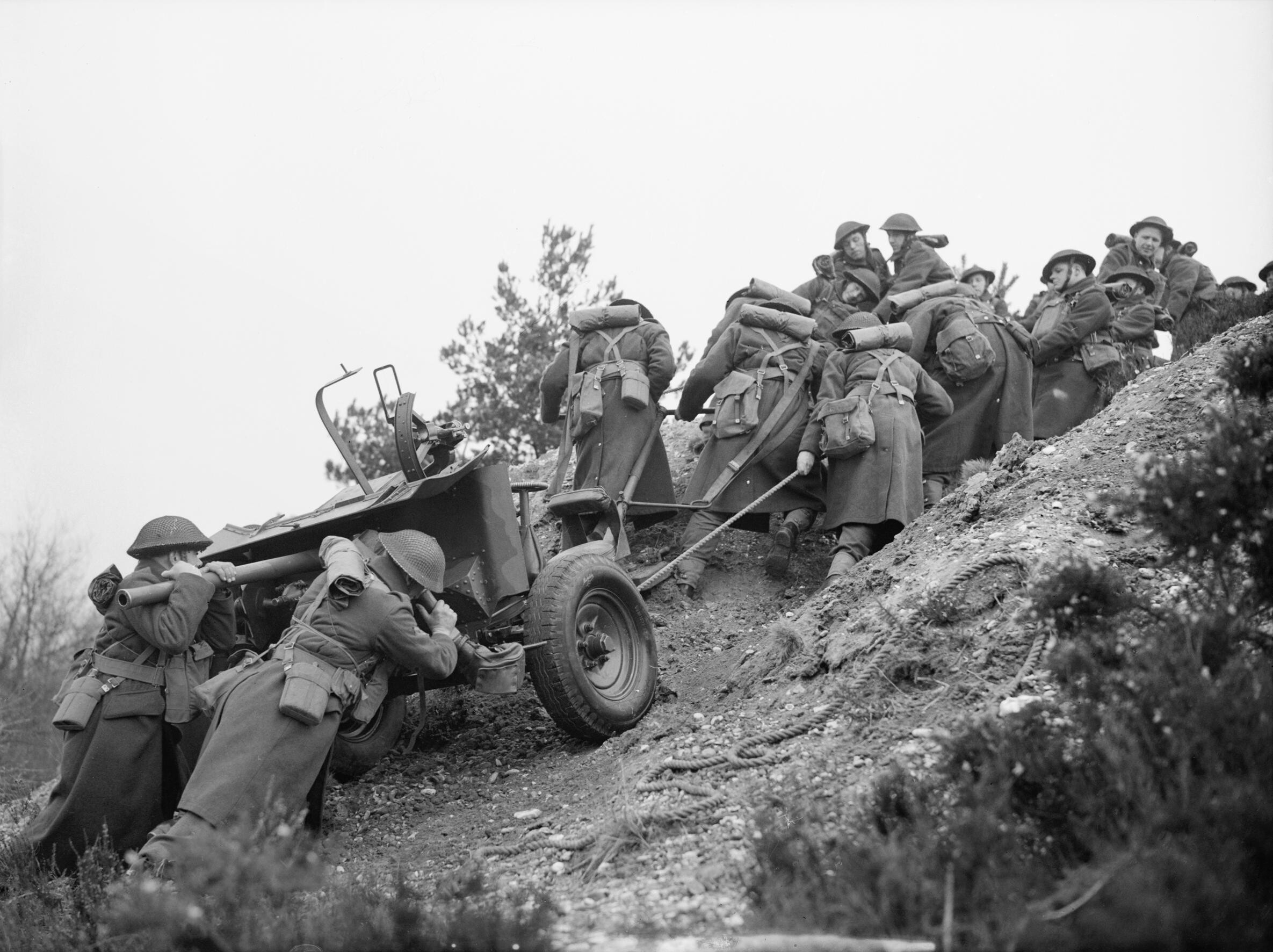  For over a year after Dunkirk the composition of 3rd Division remained largely unchanged (except that the motorcycle battalion was converted into 3rd (RNF) Reconnaissance Regiment,
For over a year after Dunkirk the composition of 3rd Division remained largely unchanged (except that the motorcycle battalion was converted into 3rd (RNF) Reconnaissance Regiment,
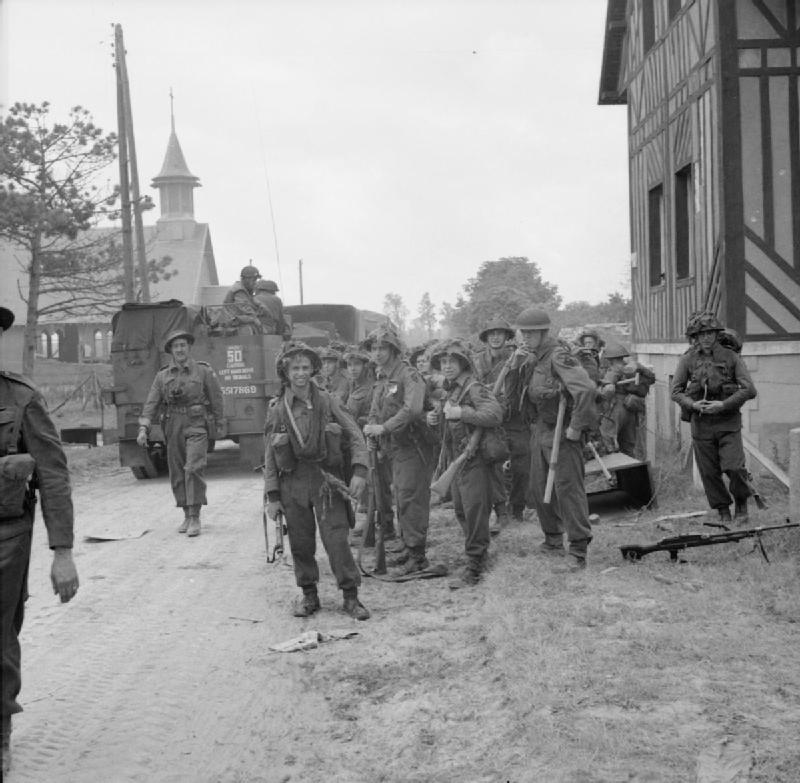 The 3rd British Infantry Division was the first British formation to land at
The 3rd British Infantry Division was the first British formation to land at
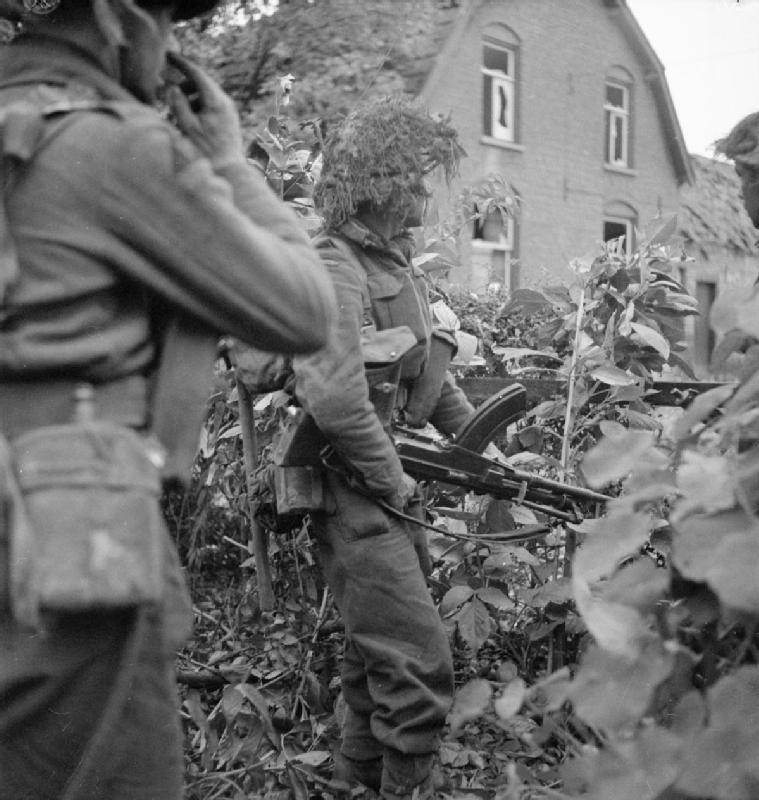 After D-Day the 3rd Infantry Division fought through the
After D-Day the 3rd Infantry Division fought through the
 ;3rd (UK) Mechanised Division (1990s)British Army Units
;3rd (UK) Mechanised Division (1990s)British Army Units
/ref> * 1st Mechanized Brigade * 4th Mechanized Brigade * 12th Mechanized Brigade * 3rd Division Headquarters and Signal Regiment * 5 Regiment Army Air Corps (Lynx) * 36 Engineer Regiment,
* indicates a posthumous award
3rd (UK) Division
on British Army official website
British Military History: 3 Division (1930 - 1938)
British Military History: 3 Infantry Division (1939)
British Military History: 3 Infantry Division (1940)
British Military History: 3 Infantry Division (1944-45)
{{DEFAULTSORT:03 Infantry Division Infantry divisions of the British Army in World War I Infantry divisions of the British Army in World War II Military units and formations established in 1809 1809 establishments in the United Kingdom Military units and formations of the United Kingdom in the Peninsular War
regular army
A regular army is the official army of a state or country (the official armed forces), contrasting with irregular forces, such as volunteer irregular militias, private armies, mercenaries, etc. A regular army usually has the following:
* a standi ...
division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gur ...
. It was created in 1809 by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, as part of the Anglo-Portuguese Army
The Anglo-Portuguese Army was the combined British and Portuguese army that participated in the Peninsular War, under the command of Arthur Wellesley. The Army is also referred to as the British-Portuguese Army and, in Portuguese, as the ''Ex� ...
, for service in the Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spai ...
, and was known as the Fighting 3rd under Sir Thomas Picton during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
. The division fought at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
, as well as during the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
and the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
. As a result of bitter fighting in 1916, during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the division became referred to as the 3rd (Iron) Division, or the Iron Division or Ironsides. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the division (now known as the 3rd Infantry Division) fought in the Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second Wor ...
including a rearguard action during the Dunkirk Evacuation
The Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of more than 338,000 Allied soldiers during the Second World War from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the ...
, and played a prominent role in the D-Day landings of 6 June 1944. The division was to have been part of a proposed Commonwealth Corps
The Commonwealth Corps was the name given to a proposed British Commonwealth army formation, which was scheduled to take part in the planned Allied invasion of Japan during 1945 and 1946. The corps was never formed, however, as the Japanese surr ...
, formed for a planned invasion of Japan in 1945–46, and later served in the British Mandate of Palestine British Mandate of Palestine or Palestine Mandate most often refers to:
* Mandate for Palestine: a League of Nations mandate under which the British controlled an area which included Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan.
* Mandatory P ...
. During the Second World War, the insignia became the "pattern of three" — a black triangle trisected by an inverted red triangle, created by Bernard Montgomery to instil pride in his troops.
Napoleonic Wars
The division was part of the Allied British and Portuguese forces that took part in thePeninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spai ...
. It fought at the Battle of Bussaco in September 1810, the Battle of Fuentes de Oñoro
In the Battle of Fuentes de Oñoro (3–5 May 1811), the British–Portuguese Army under Wellington checked an attempt by the French Army of Portugal under Marshal André Masséna to relieve the besieged city of Almeida.
A bloody stalem ...
in May 1811 and the Battle of El Bodón in September 1811, before further combat at the Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo in January 1812, the Siege of Badajoz in March 1812 and the Battle of Salamanca
The Battle of Salamanca (in French and Spanish known as the Battle of Arapiles) on 22July 1812 was a battle in which an Anglo-Portuguese army under the Earl of Wellington defeated Marshal Auguste Marmont's French forces at Arapiles, s ...
in July 1812. It also fought at the Siege of Burgos
At the siege of Burgos, from 19 September to 21 October 1812, the Anglo-Portuguese Army led by General Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington tried to capture the castle of Burgos from its French garrison under the command of General of ...
in September 1812 and the Battle of Vitoria
At the Battle of Vitoria (21 June 1813) a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leading ...
in June 1813.Cannon, p. 81 It then pursued the French army into France and saw action at the Battle of the Pyrenees
The Battle of the Pyrenees was a large-scale offensive (the author David Chandler recognises the 'battle' as an offensive) launched on 25 July 1813 by Marshal Nicolas Jean de Dieu Soult from the Pyrénées region on Emperor Napoleon’s or ...
in July 1813, the Battle of Nivelle
The Battle of Nivelle (10 November 1813) took place in front of the river Nivelle near the end of the Peninsular War (1808–1814). After the Allied siege of San Sebastian, Wellington's 80,000 British, Portuguese and Spanish troops (20, ...
in November 1813 and the Battle of the Nive
The Battles of the Nive (9–13 December 1813) were fought towards the end of the Peninsular War. Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington's Anglo-Portuguese and Spanish army defeated Marshal Nicolas Soult's French army on French soil ...
in December 1813. After that it fought at the Battle of Orthez
The Battle of Orthez (27 February 1814) saw the Anglo-Spanish-Portuguese Army under Field Marshal Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington attack an Imperial French army led by Marshal Nicolas Soult in southern France. The outnumbered F ...
in February 1814 and the Battle of Toulouse in April 1814.
According to Picton, the fighting by the 3rd was so intense at the Battle of Vitoria
At the Battle of Vitoria (21 June 1813) a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leading ...
, that the division lost 1,800 men (over one third of all Allied losses at the battle) having taken a key bridge and village, where they were subjected to fire by 40 to 50 cannons
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during ...
, and a counter-attack on the right flank (which was open because the rest of the army had not kept pace). The 3rd held their ground and pushed on with other divisions to capture the village of Arinez.
Battle of Quatre Bras
The Battle of Quatre Bras was fought on 16 June 1815, as a preliminary engagement to the decisive Battle of Waterloo that occurred two days later. The battle took place near the strategic crossroads of Quatre Bras and was contested between el ...
and the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
in the Waterloo campaign
The Waterloo campaign (15 June – 8 July 1815) was fought between the French Army of the North and two Seventh Coalition armies, an Anglo-allied army and a Prussian army. Initially the French army was commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte, but he ...
under the command of Lieutenant-General Sir Charles Alten K.C.B. (Count Carl von Alten).
Crimean War
The 3rd Division took part in theCrimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
and fought in the Battle of Alma
The Battle of the Alma (short for Battle of the Alma River) was a battle in the Crimean War between an allied expeditionary force (made up of French, British, and Ottoman forces) and Russian forces defending the Crimean Peninsula on 20Septemb ...
and the Siege of Sevastopol. It was under the command of Lieutenant-General Sir Richard England.
Second Boer War
During theSecond Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
(1899–1902) the division began under the command of General Gatacre Gatacre may refer to:
* Galfry Gatacre or Gataker (1907–1983), Australian naval officer
* Thomas Gatacre, 16th-century English politician and cleric
* William Gatacre (MP) (died 1577), English politician
*William Forbes Gatacre (1843–1906), Br ...
. In 1902 the army was restructured, and a 3rd Infantry division was established permanently at Bordon
Bordon is a town in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. It lies in the interior of the royal Woolmer Forest, about southeast of Alton. The town forms a part of the civil parish of Whitehill which is one of two contiguous villag ...
as part of the 1st Army Corps, comprising the 5th
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five.
Fifth or The Fifth may refer to:
* Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth"
* Fifth column, a political term
* Fifth disease, a contagious rash th ...
and 6th Infantry Brigades.
First World War
 During the
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
the 3rd Division was a permanently established Regular Army
A regular army is the official army of a state or country (the official armed forces), contrasting with irregular forces, such as volunteer irregular militias, private armies, mercenaries, etc. A regular army usually has the following:
* a standi ...
division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
that was amongst the first to be sent to France at the outbreak of the war as part of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF). The 3rd Division served on the Western Front in France and Belgium for four years, from 1914 to 1918. During this time, it was nicknamed "The Iron Division". Its first commander during the war, Major-General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Hubert Hamilton, was killed by shellfire near Béthune
Béthune ( ; archaic and ''Bethwyn'' historically in English) is a city in northern France, sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department.
Geography
Béthune is located in the former province of Artois. It is situated south-east of Calais, ...
in October 1914. The division served in many major battles of the war, including the Battle of Mons
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
and the subsequent Great Retreat
The Great Retreat (), also known as the retreat from Mons, was the long withdrawal to the River Marne in August and September 1914 by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army. The Franco-British forces on the Western F ...
, and later the First Battle of Ypres
The First Battle of Ypres (french: Première Bataille des Flandres; german: Erste Flandernschlacht – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the F ...
.
Inter-War Period
After the end of the First World War, the division was stationed in southern England where it formed part ofSouthern Command
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
. In 1937, one of its brigades, the 9th Infantry Brigade, was commanded by Brigadier
Brigadier is a military rank, the seniority of which depends on the country. In some countries, it is a senior rank above colonel, equivalent to a brigadier general or commodore, typically commanding a brigade of several thousand soldiers. In ...
Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and th ...
. He assumed command of the 3rd Division shortly before Britain declared war on Germany in September 1939.
Second World War
 The 3rd Infantry Division, under the command of Major General
The 3rd Infantry Division, under the command of Major General Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and th ...
, was sent overseas to France in late September 1939, just under a month after the outbreak of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.Joslen, p. 43-44 There the division became part of Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Alan Brooke
Field Marshal Alan Francis Brooke, 1st Viscount Alanbrooke, (23 July 1883 – 17 June 1963), was a senior officer of the British Army. He was Chief of the Imperial General Staff (CIGS), the professional head of the British Army, during the Sec ...
's II Corps of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF). However, unlike in the First World War, where the division was almost immediately engaged in desperate fighting, there was no action. Montgomery instantly began training the men of his division in a tough training regime. As with most of the rest of the BEF, training was severely hampered by a shortage of modern equipment.
 In May 1940, after several months of relative inactivity, the
In May 1940, after several months of relative inactivity, the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwa ...
launched its attack in the west which resulted in the BEF being split up from the French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Forc ...
, evacuated from Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Brigadier
Brigadier is a military rank, the seniority of which depends on the country. In some countries, it is a senior rank above colonel, equivalent to a brigadier general or commodore, typically commanding a brigade of several thousand soldiers. In ...
Kenneth Anderson took temporary control of the division before, in July, Major General James Gammell assumed command.
 For over a year after Dunkirk the composition of 3rd Division remained largely unchanged (except that the motorcycle battalion was converted into 3rd (RNF) Reconnaissance Regiment,
For over a year after Dunkirk the composition of 3rd Division remained largely unchanged (except that the motorcycle battalion was converted into 3rd (RNF) Reconnaissance Regiment, Reconnaissance Corps
The Reconnaissance Corps, or simply Recce Corps, was a corps of the British Army, formed during the Second World War whose units provided reconnaissance for infantry divisions. It was formed from infantry brigade reconnaissance groups on 14 Janua ...
). Then, in September 1941, the 7th Guards Brigade was transferred to help create the Guards Armoured Division
The Guards Armoured Division was an armoured division of the British Army during the Second World War. The division was created in the United Kingdom on 17 June 1941 during the Second World War from elements of the Guards units, the Grenadier ...
, and, in November, the 37th Infantry Brigade Group joined the 3rd Division and was renumbered 7th Brigade with the following composition:Joslen, pp. 43–4. The brigade anti-tank companies were disbanded during 1941 and 92nd (Loyals) Light Anti-Aircraft Regiment, Royal Artillery, formerly the 7th Battalion, Loyal Regiment (North Lancashire)
The Loyal Regiment (North Lancashire) (until 1921 known as the Loyal North Lancashire Regiment) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army that was in existence from 1881 to 1970. In 1970, the regiment was amalgamated with the Lancashire Re ...
, joined the division in March 1942. In June 1942, 3rd Infantry Division was reorganised as a 'Mixed' Division, with 33rd Tank Brigade replacing 7th Infantry Brigade. By early 1943, the experiment with 'mixed' divisions was abandoned, and division reverted to being an infantry formation, 33rd Tank Brigade being replaced by 185th Infantry Brigade.
D-Day
 The 3rd British Infantry Division was the first British formation to land at
The 3rd British Infantry Division was the first British formation to land at Sword Beach
Sword, commonly known as Sword Beach, was the code name given to one of the five main landing areas along the Normandy coast during the initial assault phase, Operation Neptune, of Operation Overlord. The Allied invasion of German-occupied Fra ...
on D-Day, 6 June 1944, as part of the invasion of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norm ...
, part of the larger Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norm ...
. For the assault landing, 3rd British Division was organised as a Division Group, with other formations temporarily under its command. These included 27th Armoured Brigade ( Sherman DD amphibious tanks) and 22nd Dragoons
The 22nd Dragoons was the title held by five separate Cavalry regiments of the British Army raised and disbanded between 1716 and 1945. The last regiment of this name existed during the Second World War, from 1 December 1940 until 30 November ...
( Sherman Crab flail tanks), 1st Special Service Brigade
The 1st Special Service Brigade was a commando brigade of the British Army. Formed during the Second World War, it consisted of elements of the British Army (including British Commandos) and the Royal Marines. The brigade's component units saw a ...
and No. 41 (Royal Marine) Commando, 5th Royal Marine Independent Armoured Support Battery ( Centaur IV close support tanks), 77 and 79 Assault Squadrons of 5th Assault Regiment, Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the '' Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is head ...
( Churchill AVREs).
The division's own artillery were all self-propelled (field regiments: M7 Priest
The 105 mm Howitzer Motor Carriage M7 was an American self-propelled gun vehicle produced during World War II. It was given the official service name 105 mm Self Propelled Gun, Priest by the British Army, due to the pulpit-like machine ...
; anti-tank regiment: M10 tank destroyer
The M10 tank destroyer was an American tank destroyer of World War II. After US entry into World War II and the formation of the Tank Destroyer Force, a suitable vehicle was needed to equip the new battalions. By November 1941, the Army requeste ...
) and the SP field guns and RM Centaurs were able to fire from their landing craft during the run-in to the beach. In addition, 3rd British Division had 101 Beach Sub-Area HQ and Nos 5 and 6 Beach groups under command for the assault phase: these included additional engineers, transport, pioneers, medical services and vehicle recovery sections.Ellis, pp. 173, 184–6.
The 3rd Division's brigades were organised as brigade group
Brigade Enterprises Limited is a real estate and property development company that is based in Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. The Brigade Group also has operations in Mangalore, Mysore, Chennai, Kochi, Hyderabad, Chikmagalur, Ahmedabad and a ...
s for the assault, with 8 Brigade Group making the first landing, followed by 185 Brigade Group and 9 Brigade Group in succession during the morning and early afternoon.
After D-Day
 After D-Day the 3rd Infantry Division fought through the
After D-Day the 3rd Infantry Division fought through the Battle for Caen
The Battle for Caen (June to August 1944) is the name given to fighting between the British Second Army and the German in the Second World War for control of the city of Caen and its vicinity during the larger Battle of Normandy. The battles ...
, in Operation Charnwood
Operation Charnwood was an Anglo-Canadian offensive that took place from 8 to 9 July 1944, during the Battle for Caen, part of the larger Operation Overlord (code-name for the Battle of Normandy) in the Second World War. The operation was int ...
and Operation Goodwood
Operation Goodwood was a British offensive during the Second World War, which took place between 18 and 20 July 1944 as part of the larger battle for Caen in Normandy, France. The objective of the operation was a limited attack to the sout ...
. With the fighting in Normandy over after the Battle of the Falaise Gap, the division also participated in the Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine
The Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine, also known as the Siegfried Line campaign, was a phase in the Western European campaign of World War II.
This phase spans from the end of the Battle of Normandy, or Operation Overlord, (25 August 194 ...
and fought in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Neth ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the ...
and later the Allied invasion of Germany. For the campaign in Normandy, the division was commanded by Major-General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Tom Rennie until he was wounded on 13 June 1944; Major-General 'Bolo' Whistler, a highly popular commander, took command on 23 June 1944. During the campaign in Normandy, the division won its first Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
of the Second World War, awarded in August 1944 to Corporal
Corporal is a military rank in use in some form by many militaries and by some police forces or other uniformed organizations. The word is derived from the medieval Italian phrase ("head of a body"). The rank is usually the lowest ranking non- ...
Sidney Bates of 1st Battalion, Royal Norfolk Regiment
The Royal Norfolk Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army until 1959. Its predecessor regiment was raised in 1685 as Henry Cornwall's Regiment of Foot. In 1751, it was numbered like most other British Army regiments and named ...
, part of the 185th Brigade. Private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* "In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorded ...
James Stokes of the 2nd Battalion, King's Shropshire Light Infantry
The King's Shropshire Light Infantry (KSLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army, formed in the Childers Reforms of 1881, but with antecedents dating back to 1755. It served in the Second Boer War, World War I and World War II. In 196 ...
, also of the 185th Brigade, was the second recipient awarded the Victoria Cross in March 1945.
During the often intense fighting from Sword Beach to Bremen, the 3rd Division suffered 2,586 killed with over 12,000 wounded.
Cold War
Postwar, the division was reformed on 1 April 1951, in theSuez Canal Zone
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
, under the command of Sir Hugh Stockwell. The division became part of Middle East Land Forces. It consisted of three recently reraised brigades, the 32nd Guards, the 19th Infantry, and the 39th Infantry. It served in the UK for many years and was part of Army Strategic Command
The Army Strategic Reserves Command ( id, Komando Cadangan Strategis Angkatan Darat; abbreviated ) is a combined-arms formation of the Indonesian Army. Kostrad is a Corps level command which has up to 35,000 troops. It also supervises operation ...
in 1968. It had elements of 5th, 19th, and 24th Brigades attached to it.
During the 1970s the division consisted of two "square" brigades, the 6th Armoured Brigade and 33rd Armoured Brigade. It became 3rd Armoured Division in 1976 and served with I (BR) Corps being based at St Sebastian Barracks in Soest near the Möhne Dam from 1977. After being briefly reorganised into two "task forces" ("Echo" and "Foxtrot") in the late 1970s, it consisted of the 4th Armoured Brigade, the 6th Airmobile Brigade and the 19th Infantry Brigade in the 1980s.
Post–Cold War
In September 1992, the headquarters of 3rd Armoured Division was relocated from Germany to Bulford, Wiltshire in the UK, where it became 3rd Mechanised Division. It provided the headquarters for Multi-National Division (South-West) inBosnia-Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
in 1995 / 1996 and again in 1998. In early 2002, the division headquarters and its GOC, Major General John McColl, formed the initial basis of the headquarters of the International Security Assistance Force
' ps, کمک او همکاري '
, allies = Afghanistan
, opponents = Taliban Al-Qaeda
, commander1 =
, commander1_label = Commander
, commander2 =
, commander2_label =
, commander3 =
, command ...
in Kabul, Afghanistan.
On 1 September 1999 the division was freed from its administrative and regional responsibilities and became a deployable or "fly-away" division. As 3rd (UK) Mechanised Division it was the only division at continual operational readiness in the United Kingdom (the other at operational readiness being 1st (UK) Armoured Division in Germany). It was based at Picton Barracks, Bulford Camp, and reported to the Commander Land Forces
Commander-in-Chief, Land Forces (CINCLAND), was a senior officer in the British Army. CINCLAND commanded HQ Land Forces, an administrative apparatus that had responsibility for all of the army's fighting units in the United Kingdom (excluding N ...
at Andover.
On 11 July 2003, the division deployed to Iraq to replace the British 1st Armoured Division, signalling the start of Operation Telic
Operation Telic (Op TELIC) was the codename under which all of the United Kingdom's military operations in Iraq were conducted between the start of the invasion of Iraq on 19 March 2003 and the withdrawal of the last remaining British forces on ...
II. The 3rd Division also controlled numerous other coalition forces in southeast Iraq, including contingents from the Czech Republic, Denmark, Italy, Lithuania, the Netherlands, New Zealand and Norway.
Under Army 2020
Army 2020, was the name given to the restructuring of the British Army, in light of the 2010 Strategic Defence and Security Review.
Background
The British Government gave an indication of its proposals for the future structure of the Army in ea ...
, the division was renamed as 3rd (United Kingdom) Division and continued to be based at Bulford Camp and to command the Reaction Force. In 2015, Brigadier General Mike Tarsa of the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
was assigned as deputy commanding general of the division. He was replaced in May 2016 by Brigadier General Doug Crissman. Crissman was replaced by Brigadier General Matthew J. Van Wagenen in April 2018. This was part of a growing practice for senior officers of the British Army and the United States Army to be assigned as deputy commanders (and effectively liaison officers) in each other's operational units.
Future
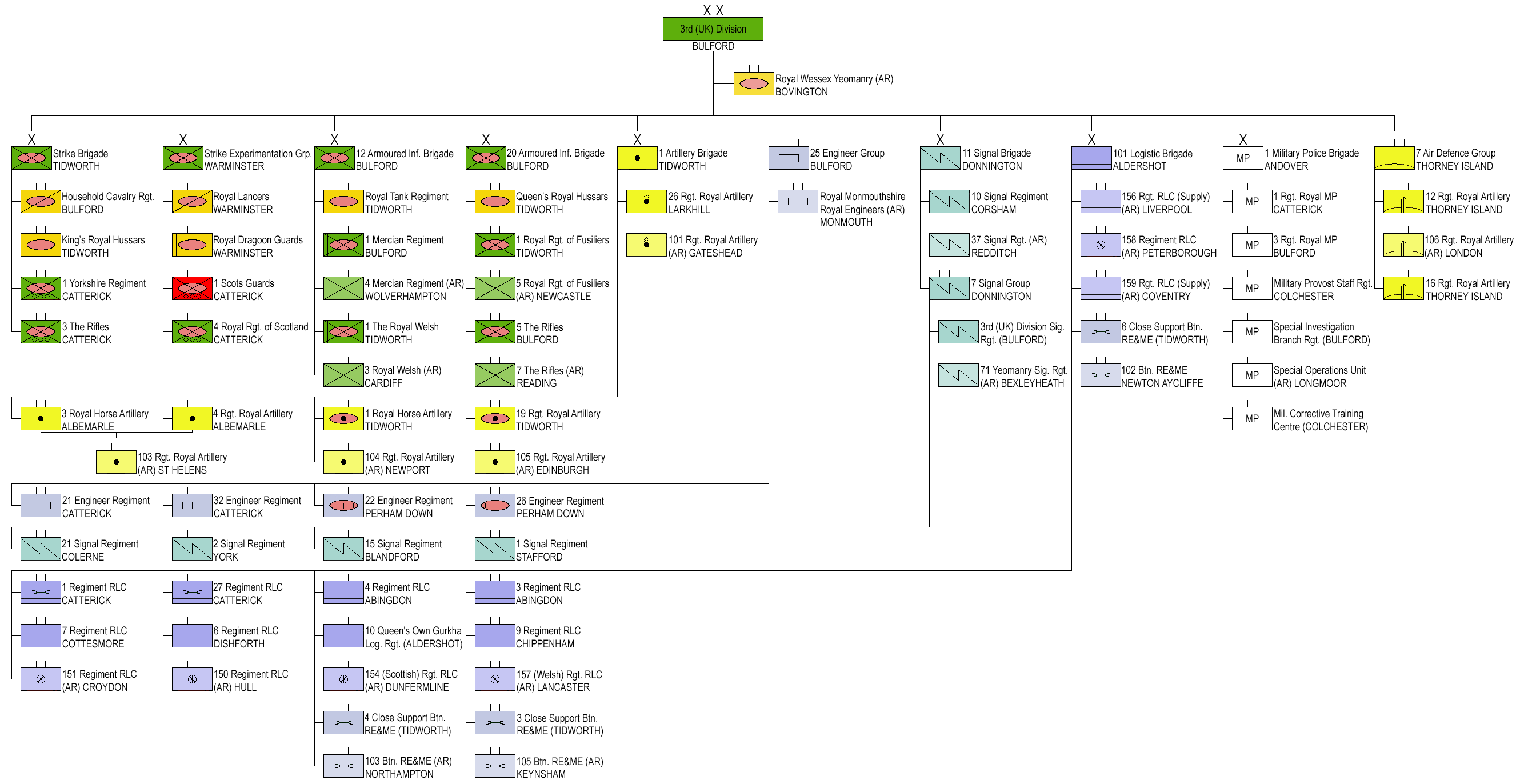
Under the Future Soldier programme, the division will be re-structured with the 1st Armoured Infantry Brigade becoming the '' Deep Reconnaissance Strike Brigade Combat Team'', the 12th Armoured Infantry Brigade becoming ''12th Armoured Brigade Combat Team'', 20th Armoured Infantry Brigade becoming ''20th Armoured Brigade Combat Team'', 11th Signal Brigade reduced to just 7th Signals Group, and 1st Artillery Brigade disbanding.Order of battle
 ;3rd (UK) Mechanised Division (1990s)British Army Units
;3rd (UK) Mechanised Division (1990s)British Army Units/ref> * 1st Mechanized Brigade * 4th Mechanized Brigade * 12th Mechanized Brigade * 3rd Division Headquarters and Signal Regiment * 5 Regiment Army Air Corps (Lynx) * 36 Engineer Regiment,
Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the '' Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is head ...
* 3 Regiment, Royal Military Police
The Royal Military Police (RMP) is the corps of the British Army responsible for the policing of army service personnel, and for providing a military police presence both in the UK and while service personnel are deployed overseas on operations ...
* The Royal Wessex Yeomanry
;3rd (United Kingdom) Division (2019–present)
* 1st Armoured Infantry Brigade
* 12th Armoured Infantry Brigade
* 20th Armoured Infantry Brigade
* 101 Logistic Brigade
* 1st Artillery Brigade
* 11th Signal Brigade
* 1st Military Police Brigade -tactical command
* 7 Air Defence Group
7th Air Defence Group (7 AD Gp) is a formation of the British Army and part of 3rd (United Kingdom) Division. It is responsible for all the army's ground based air defence assets. All of the organisation's subordinate units are drawn from the Roy ...
* 25 (Close Support) Engineer Group
Recipients of the Victoria Cross
See also
* List of commanders of the British 3rd Division * List of British divisions in World War I * List of British divisions in World War II * British Army Order of Battle (September 1939) *Units of the Royal Corps of Signals This is a list of units of the British Army's Royal Corps of Signals.
Brigades
* 1st Signal Brigade (1982—1987)
** 1st Signal Group (1968—1982)
* 1st (United Kingdom) Signal Brigade (1995—Present)
* 2nd (National Communications) Signal Brig ...
* Death of Baha Mousa Baha Mousa was an Iraqi man who died while in British Army custody in Basra, Iraq, in September 2003. The inquiry into his death found that Mousa's death was caused by "factors including lack of food and water, heat, exhaustion, fear, previous inju ...
Notes
Footnotes CitationsReferences
* * Blaxland, Gregory (1971) ''The Regiments Depart: A History of the British Army 1945–70'', London: William Kimber. * *Chappel M., (1986) ''British Battle Insignia (1). 1914–18'' Osprey Publishing * * Delaforce, Patrick (1995) ''Monty's Iron Sides'', Stroud: Alan Sutton, , * Ellis, Major L.F. (2004) ''History of the Second World War: United Kingdom Military Series: Victory in the West'', Volume I: ''The Battle of Normandy'', London: HMSO, 1962/Uckfield: Naval & Military, . * * Horrocks, Lt-Gen Sir Brian, (1960) ''A Full Life'', London: Collins. * * Keegan, John (1991), ''Churchill's Generals'', London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. * Montgomery, Field Marshal Viscount, (1958) ''Memoirs'', London: Collins. * * Scarfe, Norman (2006) 947 Assault Division: A History of the 3rd Division from the Invasion of Normandy to the Surrender of Germany. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Spellmount. .External links
3rd (UK) Division
on British Army official website
British Military History: 3 Division (1930 - 1938)
British Military History: 3 Infantry Division (1939)
British Military History: 3 Infantry Division (1940)
British Military History: 3 Infantry Division (1944-45)
{{DEFAULTSORT:03 Infantry Division Infantry divisions of the British Army in World War I Infantry divisions of the British Army in World War II Military units and formations established in 1809 1809 establishments in the United Kingdom Military units and formations of the United Kingdom in the Peninsular War