Bristol Cathedral on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bristol Cathedral, the Cathedral Church of the Holy and Undivided Trinity, is the Church of England cathedral in the city of Bristol, England. Founded in 1140 and consecrated in 1148, it was originally St Augustine's Abbey but after the Dissolution of the Monasteries it became in 1542 the seat of the newly created Bishop of Bristol and the cathedral of the new Diocese of Bristol. It is a Grade I listed building.
The eastern end of the church includes fabric from the 12th century, with the Elder Lady Chapel which was added in the early 13th century. Much of the church was rebuilt in the English Decorated Gothic style during the 14th century despite financial problems within the abbey. In the 15th century the transept and central tower were added. The nave was incomplete at the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1539 and was demolished. In the 19th century

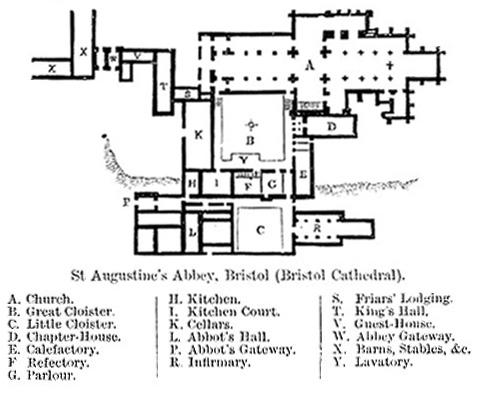
 Bristol Cathedral is a grade I listed building which shows a range of architectural styles and periods. Tim Tatton-Brown writes of the 14th century eastern arm as "one of the most interesting and splendid structures in this country".
Bristol Cathedral is a grade I listed building which shows a range of architectural styles and periods. Tim Tatton-Brown writes of the 14th century eastern arm as "one of the most interesting and splendid structures in this country".
 The eastern end of Bristol Cathedral is highly unusual for a number of reasons. Firstly, it was conceived as a " hall church", meaning that the aisles are the same height as the choir. While a feature of German Gothic architecture, this is rare in Britain, and Bristol cathedral is the most significant example. In the 19th century,
The eastern end of Bristol Cathedral is highly unusual for a number of reasons. Firstly, it was conceived as a " hall church", meaning that the aisles are the same height as the choir. While a feature of German Gothic architecture, this is rare in Britain, and Bristol cathedral is the most significant example. In the 19th century,  Because of the lack of a clerestory, the vault is comparatively low, being only about half the height of that at Westminster Abbey. The interior of the cathedral appears wide and spacious. The architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner wrote of the early 14th-century choir of Bristol that "from the point of view of spatial imagination" it is not only superior to anything else in England or Europe but "proves incontrovertibly that English design surpasses that of all other countries" at that date.
The choir has broad arches with two wave mouldings carried down the piers which support the ribs of the vaulting. These may have been designed by
Because of the lack of a clerestory, the vault is comparatively low, being only about half the height of that at Westminster Abbey. The interior of the cathedral appears wide and spacious. The architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner wrote of the early 14th-century choir of Bristol that "from the point of view of spatial imagination" it is not only superior to anything else in England or Europe but "proves incontrovertibly that English design surpasses that of all other countries" at that date.
The choir has broad arches with two wave mouldings carried down the piers which support the ribs of the vaulting. These may have been designed by
 Another feature of Bristol Cathedral is the vaulting of its various medieval spaces. The work that was carried out under Abbot Knowle is unique in this regard, with not one, but three unique vaults.
Another feature of Bristol Cathedral is the vaulting of its various medieval spaces. The work that was carried out under Abbot Knowle is unique in this regard, with not one, but three unique vaults.
 In vaulting a roof space using stone ribs and panels of infill, the bearing ribs all spring from columns along the walls. There is commonly a rib called the ridge rib which runs along the apex of the vault. There may be intermediate or " tierceron" ribs, which have their origin at the columns. In Decorated Gothic there are occasionally short lierne ribs connecting the bearing and tierceron ribs at angles, forming stellar patterns. This is the feature that appears at Bristol, at a very early date, and quite unlike the way that "lierne" ribs are used elsewhere. In this case, there is no ridge rib, and the lierne ribs are arranged to enclose a series of panels that extend the whole way along the centre of the choir roof, interacting with the large east window by reflecting the light from the smoothly arching surfaces. From the nave can be seen the intricate tracery of the east window echoed in the rich lierne pattern of the tower vault, which is scarcely higher than the choir, and therefore clearly visible. The two aisles of the choir both also have vaults of unique character, with open transverse arches and ribs above the stone bridges.
In vaulting a roof space using stone ribs and panels of infill, the bearing ribs all spring from columns along the walls. There is commonly a rib called the ridge rib which runs along the apex of the vault. There may be intermediate or " tierceron" ribs, which have their origin at the columns. In Decorated Gothic there are occasionally short lierne ribs connecting the bearing and tierceron ribs at angles, forming stellar patterns. This is the feature that appears at Bristol, at a very early date, and quite unlike the way that "lierne" ribs are used elsewhere. In this case, there is no ridge rib, and the lierne ribs are arranged to enclose a series of panels that extend the whole way along the centre of the choir roof, interacting with the large east window by reflecting the light from the smoothly arching surfaces. From the nave can be seen the intricate tracery of the east window echoed in the rich lierne pattern of the tower vault, which is scarcely higher than the choir, and therefore clearly visible. The two aisles of the choir both also have vaults of unique character, with open transverse arches and ribs above the stone bridges.
 The 13th-century East Lady Chapel is built of red sandstone in an Early English style, making it stand out from the rest of the building. It is four bays long and has a vaulted ceiling. The windows are supported by Blue Lias shafts matching those between the bays. Much of the chapel, including the piscina and sedilia, is decorated with stylised foliage, in a style known as "stiff-leaf".
The 13th-century East Lady Chapel is built of red sandstone in an Early English style, making it stand out from the rest of the building. It is four bays long and has a vaulted ceiling. The windows are supported by Blue Lias shafts matching those between the bays. Much of the chapel, including the piscina and sedilia, is decorated with stylised foliage, in a style known as "stiff-leaf".
 Street's design followed the form of the Gothic choir. On a plan or elevation it is not apparent that the work is of a different era. But Street designed an interior that respected the delicate proportions of the ribs and mouldings of the earlier work, but did not imitate their patterns. Street's nave is vaulted with a conservative vault with tierceron ribs, rising at the same pitch as the choir. Street's aisle vaults again echo their counterparts in the mediaeval chancel, using open vaulting above the stone bridges, but the transverse vaults are constructed differently.
Street's design followed the form of the Gothic choir. On a plan or elevation it is not apparent that the work is of a different era. But Street designed an interior that respected the delicate proportions of the ribs and mouldings of the earlier work, but did not imitate their patterns. Street's nave is vaulted with a conservative vault with tierceron ribs, rising at the same pitch as the choir. Street's aisle vaults again echo their counterparts in the mediaeval chancel, using open vaulting above the stone bridges, but the transverse vaults are constructed differently.
 Unlike many English Gothic cathedrals, Bristol's west facade has a rose window above the central doorway. The details, however, are clearly English, owing much to the Early English Gothic at Wells Cathedral and the Decorated Gothic at York Minster with a French Rayonnant style.
Unlike many English Gothic cathedrals, Bristol's west facade has a rose window above the central doorway. The details, however, are clearly English, owing much to the Early English Gothic at Wells Cathedral and the Decorated Gothic at York Minster with a French Rayonnant style.
 The late Norman
The late Norman
 The east window in the Lady Chapel was largely replaced and restored in the mid 19th century. However, it does contain some 14th-century
The east window in the Lady Chapel was largely replaced and restored in the mid 19th century. However, it does contain some 14th-century

 The south transept contains the important late Saxon stone panel of the Harrowing of Hell. It dates from before the Norman Conquest and may have been carved around 1050. Following a fire in 1831 it was found being used as a coffin lid under the Chapter House floor.
The high altar stone
The south transept contains the important late Saxon stone panel of the Harrowing of Hell. It dates from before the Norman Conquest and may have been carved around 1050. Following a fire in 1831 it was found being used as a coffin lid under the Chapter House floor.
The high altar stone  In addition there are notable monuments to local dignitaries of the 17th and 18th century. There is a perpendicular
In addition there are notable monuments to local dignitaries of the 17th and 18th century. There is a perpendicular
 The
The
, retrieved 1 March 2013 The Bristol Cathedral Concert Choir (formerly Bristol Cathedral Special Choir) was formed in 1954 and comprised sixty singers who presented large-scale works such as
Bristol Cathedral Website
Diocese of Bristol
Bristol Past: The Abbey Gatehouse
Panoramic tour of the cathedral
Panoramic interior picture of the cathedral
(Requires Flash) {{Good article Churches completed in 1332 Churches completed in 1888 Anglican cathedrals in England Augustinian monasteries in England Benedictine monasteries in England Church of England church buildings in Bristol Diocese of Bristol English Gothic architecture in Bristol Gothic Revival church buildings in England Grade I listed churches in Bristol Grade I listed cathedrals Monasteries in Bristol Music venues in Bristol English churches with Norman architecture Tourist attractions in Bristol G. E. Street buildings J. L. Pearson buildings 12th-century church buildings in England
Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
a new nave was built by George Edmund Street partially using the original plans. The western twin towers, designed by John Loughborough Pearson, were completed in 1888.
Located on College Green, the cathedral has tall Gothic windows and pinnacle
A pinnacle is an architectural element originally forming the cap or crown of a buttress or small turret, but afterwards used on parapets at the corners of towers and in many other situations. The pinnacle looks like a small spire. It was mainly ...
d skyline. The eastern end is a hall church in which the aisles are the same height as the Choir and share the Lierne vaults. The late Norman chapter house
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room that is part of a cathedral, monastery or collegiate church in which meetings are held. When attached to a cathedral, the cathedral chapter meets there. In monasteries, the whole communi ...
, situated south of the transept, contains some of the first uses of pointed arches in England. In addition to the cathedral's architectural features, it contains several memorials and an historic organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
. Little of the original stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
remains with some being replaced in the Victorian era and further losses during the Bristol Blitz.
History

Foundation and 12th century
Bristol Cathedral was founded as St Augustine's Abbey in 1140 by Robert Fitzharding, a wealthy local landowner and royal official who later became Lord Berkeley.J H Bettey, Bristol Cathedral the Rebuilding of the Nave, University of Bristol (Bristol branch of the Historical Association), 1993 As the name suggests, the monastic precinct housed Augustinian canons. The original abbey church, of which only fragments remain, was constructed between 1140 and 1148 in the Romanesque style, known in England as Norman. The Venerable Bede made reference toSt Augustine of Canterbury
Augustine of Canterbury (early 6th century – probably 26 May 604) was a monk who became the first Archbishop of Canterbury in the year 597. He is considered the "Apostle to the English" and a founder of the English Church.Delaney ''Di ...
visiting the site in 603ACE, and John Leland had recorded that it was a long-established religious shrine.J H Bettey, St Augustine's Abbey Bristol, University of Bristol (Bristol branch of the Historical Association), 1996 William Worcester recorded in his Survey of Bristol that the original Augustinian abbey church was further to the east of the current site, though that was rebuilt as the church of St Augustine the Less. That site was bombed during World War II and the site built on by the Royal Hotel, but archaeological finds were deposited with Bristol Museum and Art Gallery. The dedication ceremony was held on 11 April 1148, and was conducted by the Bishops of Worcester, Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
, Llandaff, and St Asaph.
Further stone buildings were erected on the site between 1148 and 1164. Three examples of this phase survive, the chapterhouse and the abbey gatehouse, now the diocesan office, together with a second Romanesque gateway, which originally led into the abbot's quarters. T.H.B. Burrough, a local architectural historian, describes the former as "the finest Norman chapter house still standing today". In 1154 King Henry II greatly increased the endowment and wealth of the abbey as reward to Robert Fitzharding, for his support during The Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legiti ...
which brought Henry II to the throne. By 1170 enough of the new church building was complete for it to be dedicated by four bishops – Worcester, Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
, Llandaff and St Asaph.
13th century
Under Abbot David (1216–1234) there was a new phase of building, notably the construction in around 1220 of a chapel dedicated to theBlessed Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother o ...
, abutting the northern side of the choir. This building, which still stands, was to become known as the "Elder Lady Chapel". The architect, referred to in a letter as 'L', is thought to have been Adam Lock
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as " ...
, master mason of Wells Cathedral. The stonework of the eastern window of this chapel is by William the Geometer, of about 1280. Abbot David argued with the convent and was deposed in 1234 to be replaced by William of Bradstone who purchased land from the mayor to build a quay and the Church of St Augustine the Less. The next abbot was William Longe, the Chamberlain of Keynsham
Keynsham ( ) is a town and civil parish located between Bristol and Bath in Somerset, England. It has a population of 16,000.
It was listed in the Domesday Book as ''Cainesham'' (as it is pronounced), which is believed to mean the home of Sai ...
, whose reign was found to have lacked discipline and had poor financial management. In 1280 he resigned and was replaced as abbot by Abbot Hugh who restored good order, with money being given by Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
.
14th–16th century
Under Abbot Edward Knowle (1306–1332), a major rebuilding of the Abbey church began despite financial problems. Between 1298 and 1332 the eastern part of the abbey church was rebuilt in the English Decorated Gothic style. He also rebuilt the cloisters, the canons' dining room, the King's Hall and the King's Chamber. TheBlack Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
is likely to have affected the monastery and when William Coke became abbot in 1353 he obtained a papal bull from Pope Urban V to allow him to ordain priests at a younger age to replace those who had died. Soon after the election of his successor, Henry Shellingford, in 1365 Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
took control of the monastery and made The 4th Baron Berkeley its commissioner to resolve the financial problems. In the late 14th and early 15th centuries Abbots Cernay and Daubeney restored the fortunes of the order, partly by obtaining the perpetual vicarage of several local parishes. These difficulties meant that little building work had been undertaken for nearly 100 years. However, in the mid-15th century, the number of Canons increased and the transept and central tower were constructed. Abbot John Newland, (1481–1515), also known as 'Nailheart' due to his rebus of a heart pierced by three nails, began the rebuilding of the nave, but it was incomplete at the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1539. Newland also rebuilt the cloisters, the upper part of the Gatehouse, the canons' dormitory and dining room, and the Prior's Lodging (parts of which remained until 1884 as they were built into Minster House).
The partly built nave was demolished and the remaining eastern part of the church closed until it reopened as a cathedral under the secular clergy. In an edict dated June 1542, Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
and Thomas Cranmer raised the building to rank of Cathedral of a new Diocese of Bristol. The new diocese was created from parts of the Diocese of Gloucester and the Diocese of Bath and Wells; Bristol had been, before the Reformation, and the erection of Gloucester diocese, part of the Diocese of Worcester. Paul Bush Paul Bush may refer to:
* Paul Bush (filmmaker) (1956–2023), British experimental film director and animator
* Paul Bush (Royal Navy officer) (1855–1930)
* Paul Bush (bishop) (1490–1558), English Augustinian and first bishop of Bristol
* Paul ...
, (died 1558) a former royal household chaplain, was created the first Bishop of Bristol. The new cathedral was dedicated to the Holy and Undivided Trinity.
19th century
In the1831 Bristol Riots
The 1831 Bristol riots took place on 29–31 October 1831 and were part of the 1831 reform riots in England. The riots arose after the second Reform Bill was voted down in the House of Lords, stalling efforts at electoral reform. The arrival ...
, a mob broke into the Chapter House, destroying a lot of the early records of the Abbey and damaging the building. The church itself was protected from the rioters by William Phillips, sub-sacrist, who barred their entry to the church at the cloister door.
Between the merger of the old Bristol diocese back into the Gloucester diocese on 5 October 1836 and the re-erection of the new independent Bristol diocese on 9 July 1897, Bristol Cathedral was a joint and equal cathedral of the Diocese of Gloucester and Bristol
The Diocese of Gloucester is a Church of England diocese based in Gloucester, covering the non-metropolitan county of Gloucestershire. The cathedral is Gloucester Cathedral and the bishop is the Bishop of Gloucester. It is part of the Provinc ...
.
Giles Gilbert Scott was consulted in 1860 and suggested removing the screen dated 1542 to provide 'a nave of the grandest possible capacity'. The work at this time also removed some of the more vulgar medieval misericords in the choir stalls. With the 19th century's Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
signalling renewed interest in Britain's ancient architectural heritage, a new nave, in a similar style to the eastern end, based on original 15th-century designs, was added between 1868 and 1877 by George Edmund Street, clearing the houses which had been built, crowded onto the site of the former nave, including Minster House. In 1829 leases for these houses were refused by the Dean and Chapter because the houses had become 'very notoriously a receptacle for prostitutes'. The rebuilding of the nave was paid for by public subscription including benefactors such as Greville Smyth of Ashton Court, The Miles family of Kings Weston House, the Society of Merchant Venturers
The Society of Merchant Venturers is a charitable organisation in the English city of Bristol.
The society can be traced back to a 13th-century guild which funded the voyage of John Cabot to Canada. In 1552, it gained a monopoly on sea trading ...
, Stuckey's Bank
Parr's Bank Limited was a bank that existed from 1782 to 1918. It was founded as Parr & Co. in Warrington, then in the county of Lancashire in the United Kingdom. In 1918 it was acquired by London County and Westminster Bank, and it was thus one ...
, William Gibbs of Tyntesfield, and many other Bristol citizens. The opening ceremony was on 23 October 1877. However, the west front with its twin towers, designed by John Loughborough Pearson, was only completed in 1888. The niches around the north porch originally held statues of St Gregory
Pope Gregory I ( la, Gregorius I; – 12 March 604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instigating the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregori ...
, St Ambrose, St Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is comm ...
and St Augustine, but their frivolous detail invoked letters of protest to their "Catholic" design. When the Dean, Gilbert Elliot, heard of the controversy, he employed a team of workmen without the knowledge of the architect or committee to remove the statues. The next edition of the Bristol Times reported that 'a more rough and open exhibition of iconoclasm has not been seen in Bristol since the days of Oliver Cromwell.' The sculptor, James Redfern, was made the scapegoat by the architect and the church, he retreated from the project, fell ill, and died later that year. As a result of Elliot's actions, the committee resigned ''en masse'' and the completion of the works was taken over by the Dean and Chapter. Elliot's drop in popularity meant that raising funds was a harder and slower process and the nave had to be officially opened before the two west towers were built.
Several of the bells in the north-west tower were cast in 1887 by John Taylor & Co. However, earlier bells include those from the 18th century by the Bilbie family and one by William III & Richard II Purdue made in 1658.
20th century
The full peal of eight bells was installed in the north-west tower, taken from the ruins of Temple Church after the bombing of World War II. In 1994, the ceremony took place in Bristol Cathedral for the first 32 women to be ordained as Church of England priests. Since the early 2000s, the cathedral's associations with the legacy of philanthropist and enslaver Edward Colston have been the subject of public debate, resulting in changes to annual commemoration services and memorials inside the cathedral.Architecture

 Bristol Cathedral is a grade I listed building which shows a range of architectural styles and periods. Tim Tatton-Brown writes of the 14th century eastern arm as "one of the most interesting and splendid structures in this country".
Bristol Cathedral is a grade I listed building which shows a range of architectural styles and periods. Tim Tatton-Brown writes of the 14th century eastern arm as "one of the most interesting and splendid structures in this country".
Specifications
Most of the medieval stonework, is made from limestone taken from quarries around Dundry and Felton withBath stone
Bath Stone is an oolitic limestone comprising granular fragments of calcium carbonate. Originally obtained from the Combe Down and Bathampton Down Mines under Combe Down, Somerset, England. Its honey colouring gives the World Heritage City of ...
being used in other areas. The two-bay Elder Lady Chapel, which includes some Purbeck Marble
Purbeck Marble is a fossiliferous limestone found in the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula in south-east Dorset, England. It is a variety of Purbeck stone that has been quarried since at least Roman times as a decorative building stone.
Geology
Strat ...
, lies to the north of the five-bay aisled chancel or presbytery. The Eastern Lady Chapel has two bays, the sacristy
A sacristy, also known as a vestry or preparation room, is a room in Christian churches for the keeping of vestments (such as the alb and chasuble) and other church furnishings, sacred vessels, and parish records.
The sacristy is usually located ...
one-bay and the Berkeley Chapel two bays. The exterior has deep buttresses with finial
A finial (from '' la, finis'', end) or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature.
In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the Apex (geometry), apex of a d ...
s to weathered tops and crenellated parapets with crocketed pinnacle
A pinnacle is an architectural element originally forming the cap or crown of a buttress or small turret, but afterwards used on parapets at the corners of towers and in many other situations. The pinnacle looks like a small spire. It was mainly ...
s below the Perpendicular crossing tower
A crossing, in ecclesiastical architecture, is the junction of the four arms of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church.
In a typically oriented church (especially of Romanesque and Gothic styles), the crossing gives access to the nave on the west, ...
.
The west front has two large flanking three-stage towers. On the rear outer corners of the towers are octagonal stair turrets with panels on the belfry stage. Between the towers is a deep entrance arch of six orders with decorative Purbeck Marble colonnettes and enriched mouldings to the arch. The tympanum of the arch contains an empty niche.
Hall Church
 The eastern end of Bristol Cathedral is highly unusual for a number of reasons. Firstly, it was conceived as a " hall church", meaning that the aisles are the same height as the choir. While a feature of German Gothic architecture, this is rare in Britain, and Bristol cathedral is the most significant example. In the 19th century,
The eastern end of Bristol Cathedral is highly unusual for a number of reasons. Firstly, it was conceived as a " hall church", meaning that the aisles are the same height as the choir. While a feature of German Gothic architecture, this is rare in Britain, and Bristol cathedral is the most significant example. In the 19th century, G. E. Street
George Edmund Street (20 June 1824 – 18 December 1881), also known as G. E. Street, was an English architect, born at Woodford in Essex. Stylistically, Street was a leading practitioner of the Victorian Gothic Revival. Though mainly an eccle ...
designed the nave along the same lines. The effect of this elevation means that there are no clerestory
In architecture, a clerestory ( ; , also clearstory, clearstorey, or overstorey) is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both.
Historically, ''clerestory'' denoted an upper l ...
windows to light the central space, as is usual in English Medieval churches. The north and south aisles employ a unique manner where the vaults rest on tie beam style bridges supported by pointed arches. All the internal light must come from the aisle windows which are accordingly very large. In the choir, the very large window of the Lady chapel is made to fill the entire upper part of the wall, so that it bathes the vault in daylight, particularly in the morning.
Thomas Witney
Thomas Witney or Thomas of Witney (''fl.'' 1292–1342) was an English master mason, probably born in Witney, Oxfordshire. The first record of his work is as a mason on the building of St Stephen's Chapel, London in the years following 1292.John H ...
or William Joy
William Joy ( fl. 1310 – 1348) was an English master mason, or architect, of the Decorated Gothic style, known for his work on several English cathedrals.
Joy's cathedral work shows influences of Bristol Cathedral, and he may have originated ...
as they are similar to the work at Wells Cathedral and St Mary Redcliffe
St Mary Redcliffe is an Anglican parish church located in the Redcliffe district of Bristol, England. The church is a short walk from Bristol Temple Meads station. The church building was constructed from the 12th to the 15th centuries, and it ...
. The choir is separated from the eastern Lady Chapel by a 14th-century reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for ex ...
which was damaged in The reformation and repaired in 1839 when the 17th-century altarpiece
An altarpiece is an artwork such as a painting, sculpture or relief representing a religious subject made for placing at the back of or behind the altar of a Christian church. Though most commonly used for a single work of art such as a painting o ...
was removed. The Lady Chapel was brightly painted in the late 19th and early 20th centuries following existing fragments of colour. To the south east of the choir and Lady Chapel is the Berkeley Chapel and an adjoining antechapel or sacristy
A sacristy, also known as a vestry or preparation room, is a room in Christian churches for the keeping of vestments (such as the alb and chasuble) and other church furnishings, sacred vessels, and parish records.
The sacristy is usually located ...
, which may have been added in the 14th century, possibly replacing an earlier structure.
Vaulting
 Another feature of Bristol Cathedral is the vaulting of its various medieval spaces. The work that was carried out under Abbot Knowle is unique in this regard, with not one, but three unique vaults.
Another feature of Bristol Cathedral is the vaulting of its various medieval spaces. The work that was carried out under Abbot Knowle is unique in this regard, with not one, but three unique vaults.
Eastern Lady Chapel
 The 13th-century East Lady Chapel is built of red sandstone in an Early English style, making it stand out from the rest of the building. It is four bays long and has a vaulted ceiling. The windows are supported by Blue Lias shafts matching those between the bays. Much of the chapel, including the piscina and sedilia, is decorated with stylised foliage, in a style known as "stiff-leaf".
The 13th-century East Lady Chapel is built of red sandstone in an Early English style, making it stand out from the rest of the building. It is four bays long and has a vaulted ceiling. The windows are supported by Blue Lias shafts matching those between the bays. Much of the chapel, including the piscina and sedilia, is decorated with stylised foliage, in a style known as "stiff-leaf".
Nave
 Street's design followed the form of the Gothic choir. On a plan or elevation it is not apparent that the work is of a different era. But Street designed an interior that respected the delicate proportions of the ribs and mouldings of the earlier work, but did not imitate their patterns. Street's nave is vaulted with a conservative vault with tierceron ribs, rising at the same pitch as the choir. Street's aisle vaults again echo their counterparts in the mediaeval chancel, using open vaulting above the stone bridges, but the transverse vaults are constructed differently.
Street's design followed the form of the Gothic choir. On a plan or elevation it is not apparent that the work is of a different era. But Street designed an interior that respected the delicate proportions of the ribs and mouldings of the earlier work, but did not imitate their patterns. Street's nave is vaulted with a conservative vault with tierceron ribs, rising at the same pitch as the choir. Street's aisle vaults again echo their counterparts in the mediaeval chancel, using open vaulting above the stone bridges, but the transverse vaults are constructed differently.
Fittings
The cathedral has two unusual and often-reproduced monuments, the Berkeley memorials. These are set into niches in the wall, and each is surrounded by a canopy of inverted cusped arches. Pearson's screen, completed in 1905, echoes these memorials in its three wide arches with flamboyant cusps.West front
 Unlike many English Gothic cathedrals, Bristol's west facade has a rose window above the central doorway. The details, however, are clearly English, owing much to the Early English Gothic at Wells Cathedral and the Decorated Gothic at York Minster with a French Rayonnant style.
Unlike many English Gothic cathedrals, Bristol's west facade has a rose window above the central doorway. The details, however, are clearly English, owing much to the Early English Gothic at Wells Cathedral and the Decorated Gothic at York Minster with a French Rayonnant style.
Chapter House
 The late Norman
The late Norman chapter house
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room that is part of a cathedral, monastery or collegiate church in which meetings are held. When attached to a cathedral, the cathedral chapter meets there. In monasteries, the whole communi ...
, situated south of the transept, contains some of the first uses of pointed arches in England. It also has a rich sculptural decoration, with a variety of Romanesque abstract motifs. In both of these aspects there are close similarities with the abbey gatehouse, supporting the view that the two structures were built around the same time in the 12th century, as put forward by Street in the 19th century.
The approach to the chapter house is through a rib-vaulted ante-room 3 bays wide, whose pointed arches provide a solution to that room's rectangular shape. Carved pointed arches also appear in the decoration of the chapter house itself. Here they arise from the intersections of the interlaced semicircular arcading, which runs continuously around the walls. The chapter house has a quadripartite ribbed vault high. The ribs, walls and columns display a complex interplay of carved patterns: chevron, spiral, nailhead, lozenge and zigzag.
The chapter house has 40 sedilia lining its walls, and may have originally provided seating for more when it was the meeting room for the abbey community. In 1714 it was refurbished to become a library, and its floor was raised by about 1 m (3 ft). Its east end was damaged in the Bristol riots
The Bristol riots refer to a number of significant riots in the city of Bristol in England.
Bristol Bridge riot, 1793
In 1794 the populace of Bristol were said to be "apt to collect in mobs on the slightest occasions; but have been seldom so spi ...
of 1831, requiring considerable restoration, and at that time or later the library furnishings were removed. In 1832, when the floor was lowered again, a Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
stone panel depicting the Harrowing of Hell was found underneath. The discovery of the stone provides strong evidence that there was a church or shrine on the site before Robert Fitzharding founded the Abbey in 1140.
Stained glass
 The east window in the Lady Chapel was largely replaced and restored in the mid 19th century. However, it does contain some 14th-century
The east window in the Lady Chapel was largely replaced and restored in the mid 19th century. However, it does contain some 14th-century stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
pieces, including male heads and heraldic symbols. Some of the early glass is also incorporated into the Tree of Jesse which goes across nine lights.
During the restoration led by Street, most of the work on the glass was by Hardman & Co.; these include the rose window and towers at the west end and the Magnificat in the Elder Lady Chapel.
Some of the most recent stained glass is by Bristolian Arnold Wathen Robinson
Arnold Wathen Robinson RWA, FMGP (1888–1955) was an English stained-glass artist. Although Robinson's family, on the paternal and maternal side were involved in local government, he sought a career as a stained-glass artist. During World ...
following damage during the Bristol Blitz of 1940 and 1941. These included depictions of local Civil Defence during World War II including St. John Ambulance
St John Ambulance is the name of a number of affiliated organisations in different countries which teach and provide first aid and emergency medical services, and are primarily staffed by volunteers. The associations are overseen by the internat ...
, the British Red Cross and the fire services along with air raid wardens, police officers, the Home Guard and the Women's Voluntary Service. The most recent glass is an abstract expressionist interpretation of the Holy Spirit designed by Keith New in 1965 and installed in the south choir.
A Victorian era window under the cathedral's clock, marked "to the glory of God and in memory of Edward Colston" and commemorating that 17th-century Royal African Company
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English mercantile (trade, trading) company set up in 1660 by the royal House of Stuart, Stuart family and City of London merchants to trade along the West Africa, west coast of Africa. It was led by the J ...
magnate and Bristol philanthropist, was ordered to be covered in June 2020 in advance of its eventual removal. The Diocese of Bristol also decided to remove from the cathedral other dedications to Colston after the toppling of the late 19th-century Statue of Edward Colston in the city centre on 7 June 2020, along with the removal of another stained glass window at St Mary Redcliffe
St Mary Redcliffe is an Anglican parish church located in the Redcliffe district of Bristol, England. The church is a short walk from Bristol Temple Meads station. The church building was constructed from the 12th to the 15th centuries, and it ...
. The cathedral dean previously considered removing the memorial window in 2017 but said in a radio broadcast in February it would cost "many, many thousands of pounds". The legacy of Colston became contentious because of his involvement in, and profit from, the transatlantic slave trade in enslaved Africans, and came to a head after the murder of George Floyd in May 2020.
Decoration, monuments and burials

 The south transept contains the important late Saxon stone panel of the Harrowing of Hell. It dates from before the Norman Conquest and may have been carved around 1050. Following a fire in 1831 it was found being used as a coffin lid under the Chapter House floor.
The high altar stone
The south transept contains the important late Saxon stone panel of the Harrowing of Hell. It dates from before the Norman Conquest and may have been carved around 1050. Following a fire in 1831 it was found being used as a coffin lid under the Chapter House floor.
The high altar stone reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for ex ...
are by John Loughborough Pearson of 1899. The three rows of choir stalls are mostly from the late 19th century with Flamboyant traceried ends. There are also 28 misericords dating from 1515 to 1526, installed by Robert Elyot, Abbot of St. Augustine's, with carvings largely based on Aesop's Fables. In the Berkeley chapel is a very rare candelabrum
A candelabra (plural candelabras) or candelabrum (plural candelabra or candelabrums) is a candle holder with multiple arms.
Although electricity has relegated candleholders to decorative use, interior designers continue to model light fixtures ...
of 1450 from the Temple church in Bristol.
The monuments within the cathedral include recumbent figures and memorials of several abbots and bishops: Abbot Walter Newbery
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
who died in 1473 and Abbot William Hunt
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
(died 1481) are within 14th-century recesses on the north side of the Lady Chapel, while the recumbent effigy of Abbot John Newland
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
(died 1515) is in a similar recess on the southern side. The coffin lid of Abbot David
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
(died 1234) is in the north transept. In the north choir aisle is a chest tomb to Bishop Bush (died 1558) which includes six fluted Ionic columns with an entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and ...
canopy. Also honoured are: Thomas Westfield, Bishop of Bristol (1642–1644), Thomas Howell (Bishop of Bristol) (1644–1645), Gilbert Ironside the elder, Bishop of Bristol (1661–1671), William Bradshaw (bishop)
William Bradshaw (10 April 1671 – 16 December 1732) was a Welsh churchman, who in the course of his career served as Dean of Christ Church, Oxford, and Bishop of Bristol.
Life
Bradshaw was born at Abergavenny in Monmouthshire on 10 April 16 ...
, Bishop of Bristol (1724–1732), Joseph Butler, Bishop of Bristol (1738–1750), John Conybeare, Bishop of Bristol (1750–1755) and Robert Gray (bishop of Bristol) (1827–1834), who is buried in graveyard attached to the cathedral. The Berkeley family as early benefactors are represented by Maurice de Berkeley (died 1281), * Thomas de Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley (died 1321), Lord Berkeley (died 1326) and Thomas Berkeley (died 1243) who are depicted in military effigies on the south side of the choir aisle, along with the chest tomb of Maurice Berkeley (died 1368).
 In addition there are notable monuments to local dignitaries of the 17th and 18th century. There is a perpendicular
In addition there are notable monuments to local dignitaries of the 17th and 18th century. There is a perpendicular reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for ex ...
showing figures kneeling at a prayer desk flanked by angels to Robert Codrington (died 1618) and his wife. Phillip Freke
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who populariz ...
(died 1729) is commemorated with a marble wall tablet in the north choir aisle. The oval wall tablet to Rowland Searchfield, English academic and Bishop of Bristol (died 1622) is made of slate. The Newton Chapel, which is between the Chapter House and south choir aisle contains a large dresser tomb of Henry Newton (died 1599) and a recumbent effigy of John Newton (died 1661), as well as a dresser tomb dedicated to Charles Vaughan who died in 1630.
Dame Joan Wadham (1533–1603) is buried, with her two husbands Sir Giles Strangways and Sir John Young, in an altar tomb at the entrance to Bristol Cathedral. She was one of the sisters and co-heiresses (through her issue) of Nicholas Wadham Nicholas Wadham may refer to:
* Nicholas Wadham (1531–1609)
Nicholas Wadham () (1531–1609) of Merryfield in the parish of Ilton, Somerset, and Edge in the parish of Branscombe, Devon, was a posthumous co-founder of Wadham College, Oxfo ...
(1531–1609) of Merryfield, Ilton Somerset and of Edge, Branscombe Devon, the co-founder with his wife Dorothy Wadham (1534–1618) of Wadham College, Oxford.
Dame Joan is represented in effigy lying beneath the armorials of Wadham and those of both her husbands, Giles Strangways
Giles Strangways (3 June 1615 – 20 July 1675) of Melbury House in Somerset, was an English politician who sat in the House of Commons variously between 1640 and 1675. He fought on the Royalist side during the Civil War
Origins
He was ...
MP (1528–1562) of Melbury Sampford
Melbury Sampford is a village and civil parish northwest of Dorchester, in the Dorset district, in the ceremonial county of Dorset, England. In 2001 the parish had a population of 33. The parish touches East Chelborough, Evershot, Melbury Bu ...
, with her the ancestor of the Earls of Ilchester, and John Young MP (1519–1589) with whom she built the Great House Bristol from 1568, of which only the Red Lodge, now the Red Lodge Museum, Bristol and completed by Dame Joan in 1590 after the death of her husband, remains today.
Queen Elizabeth I stayed with Joan and Sir John Young at The Great House when she visited Bristol in 1574, and the Red Lodge Museum with its Tudor panelled rooms and wood carvings is only a short walk from the cathedral.
The importance of exploration and trade to the city are reflected by a memorial tablet and representation in stained glass of Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Pri ...
(died 1616) is known for promoting the settlement of North America by the English through his works. He was a prebendary of the cathedral.
More recent monuments from the early 18th century to the 20th century include: Mrs Morgan (died 1767) by John Bacon to the design of James Stuart and a bust by Edward Hodges Baily to Robert Southey a Bristolian poet of the Romantic
Romantic may refer to:
Genres and eras
* The Romantic era, an artistic, literary, musical and intellectual movement of the 18th and 19th centuries
** Romantic music, of that era
** Romantic poetry, of that era
** Romanticism in science, of that e ...
school, one of the so-called " Lake Poets", and Poet laureate for 30 years from 1813 to his death in 1843. Baily also created the monument to William Brane Elwyn
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conques ...
(died 1841). The obelisk to local actor William Powell (died 1769) was made by James Paine. The memorial to Elizabeth Charlotte Stanhope
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
(died 1816) in the Newton Chapel is by Richard Westmacott. There is a memorial plaque to the education reformer Mary Carpenter (died 1877). The memorial to Emma Crawfuird
Emma may refer to:
* Emma (given name)
Film
* ''Emma'' (1932 film), a comedy-drama film by Clarence Brown
* ''Emma'' (1996 theatrical film), a film starring Gwyneth Paltrow
* ''Emma'' (1996 TV film), a British television film starring Kate Be ...
(died 1823) is by Francis Leggatt Chantrey while the effigy to Francis Pigou (Dean; died 1916) is by Newbury Abbot Trent. The most recent are of the biographer Alfred Ainger
Alfred Ainger (9 February 18378 February 1904) was an English biographer and critic.
Biography
The son of an architect in London, he was educated at University College School, King's College London and Trinity College, Cambridge, from where he ...
(died 1904) and the composer Walford Davies (died 1941).
In 1994 a plaque was installed to mark the first 32 women ordained as priests in the Church of England. In 2022 it was replaced with a new plaque that listed the names of these women, rather than only the names of the men who carried out the ceremony. Both plaques were carved in Welsh slate. The plaque is located on the north side of the nave where it meets the transept.
Dean and Chapter
As of 23 April 2022: * Dean – Mandy Ford (since 3 October 2020 installation) * Canon Pastor – Nicola Stanley (since 1 March 2014 installation) * Canon Missioner – Jonnie Parkin (since 22 August 2021 installation) * Diocesan Canon & Bishop's Chaplain – Martin Gainsborough (since 22 May 2019; previously Diocesan Canon, 2016–2019) * Diocesan Canon – vacant since 1 January 2019 (most recently Gainsborough as Canon Theologian and Diocesan Social Justice and Environmental Adviser)Music
Organ
 The
The organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
was originally built in 1685 by Renatus Harris at a cost of £500. This has been removed and repaired many times. However, some of the original work, including the case and pipes, is incorporated into the present instrument, which was built by J. W. Walkers & Sons in 1907, and which is to be found above the stalls on the north side of the choir. It was further restored in 1989.
Prior to the building of the main organ, the cathedral had a chair organ, which was built by Robert Taunton
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
in 1662, and before that one built by Thomas Dallam in 1630.
Organists
The earliest known appointment of an organist of Bristol Cathedral is Thomas Denny in 1542. Notable organists have included the writer and composer Percy Buck. The present Organist is Mark Lee and the Assistant Organist Paul Walton.Choirs
The first choir at Bristol probably dates from the Augustinian foundation of 1140. The present choir consists has twenty-eight choristers, six lay clerks and four choral scholars. The choristers include fourteen boys and fourteen girls, who are educated at Bristol Cathedral Choir School, the first government-funded choir academy in England. Choral evensong is sung daily during term.Bristol Cathedral Choirs, retrieved 1 March 2013 The Bristol Cathedral Concert Choir (formerly Bristol Cathedral Special Choir) was formed in 1954 and comprised sixty singers who presented large-scale works such as
Bach's
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the ''Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard wo ...
''St Matthew Passion
The ''St Matthew Passion'' (german: Matthäus-Passion, links=-no), BWV 244, is a '' Passion'', a sacred oratorio written by Johann Sebastian Bach in 1727 for solo voices, double choir and double orchestra, with libretto by Picander. It sets ...
''.; it was wound up in 2016. The Bristol Cathedral Consort is a voluntary choir drawn from young people of the city. They sing Evensong twice a month. Bristol Cathedral Chamber Choir was reformed in 2001 and is directed by assistant organist Paul Walton.
Burials in St Augustine's Abbey
* Harding of Bristol * Robert Fitzharding and his wife Eva * Maurice de Berkeley, Baron Berkeley * Maurice de Berkeley, 4th Baron Berkeley * Thomas de Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley * Margaret Mortimer, Baroness Berkeley, wife of Thomas de Berkeley, 3rd Baron Berkeley * William de Berkeley, 1st Marquess of BerkeleyIn popular culture
Bristol Cathedral was used as a location in the 1978 film '' The Medusa Touch'' under the guise of a fictional London place of worship called Minster Cathedral.Other cathedrals in Bristol
Bristol is also home to a Roman Catholic cathedral, Clifton Cathedral. The Church of England parish church ofSt. Mary Redcliffe
St Mary Redcliffe is an Anglican parish church located in the Redcliffe district of Bristol, England. The church is a short walk from Bristol Temple Meads station. The church building was constructed from the 12th to the 15th centuries, and it ...
is so grand as to be occasionally mistaken for a cathedral by visitors.
See also
* List of cathedrals in the United Kingdom * List of Gothic Cathedrals in Europe * Architecture of the medieval cathedrals of England * English Gothic architecture * Church of England * Grade I listed buildings in Bristol * Churches in Bristol *List of ecclesiastical restorations and alterations by J. L. Pearson
John Loughborough Pearson (1817–97) was an English architect whose works were mainly ecclesiastical. He was born in Brussels, Belgium, and spent his childhood in Durham, England, Durham. Pearson started his architectural training under Ignatiu ...
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Bristol Cathedral Website
Diocese of Bristol
Bristol Past: The Abbey Gatehouse
Panoramic tour of the cathedral
Panoramic interior picture of the cathedral
(Requires Flash) {{Good article Churches completed in 1332 Churches completed in 1888 Anglican cathedrals in England Augustinian monasteries in England Benedictine monasteries in England Church of England church buildings in Bristol Diocese of Bristol English Gothic architecture in Bristol Gothic Revival church buildings in England Grade I listed churches in Bristol Grade I listed cathedrals Monasteries in Bristol Music venues in Bristol English churches with Norman architecture Tourist attractions in Bristol G. E. Street buildings J. L. Pearson buildings 12th-century church buildings in England