Bow shock (aerodynamics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
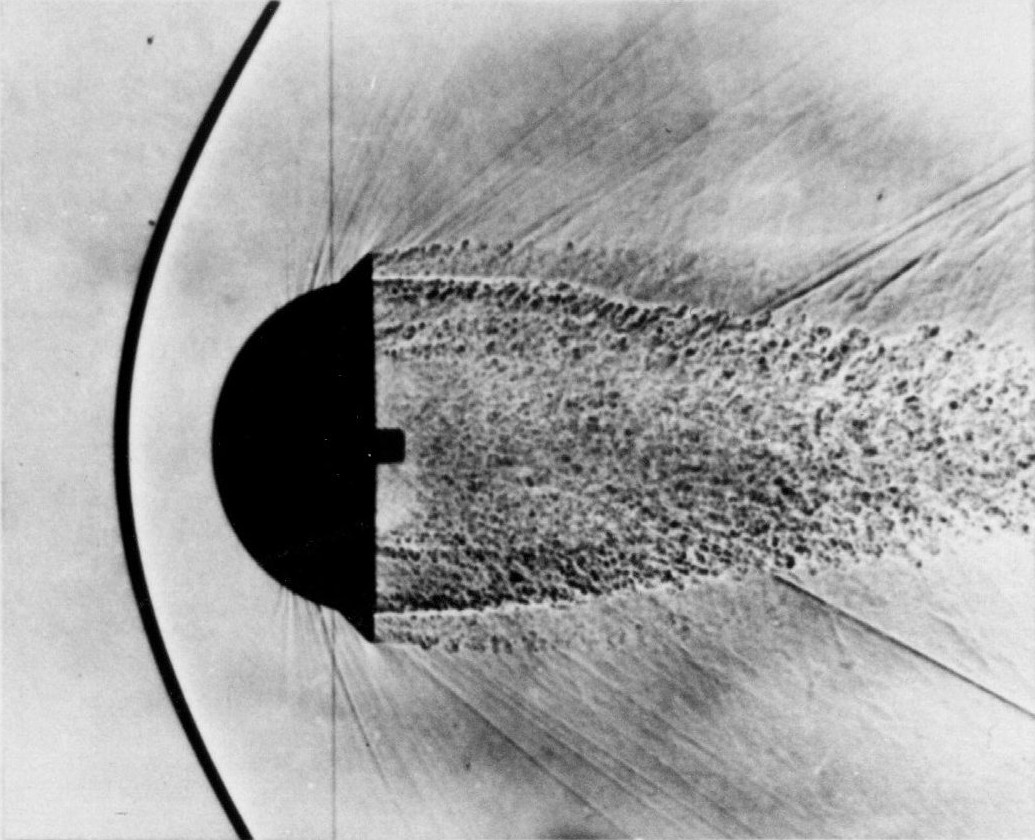 A bow shock, also called a detached shock or bowed normal shock, is a curved propagating disturbance wave characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in
A bow shock, also called a detached shock or bowed normal shock, is a curved propagating disturbance wave characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in
 A bow shock, also called a detached shock or bowed normal shock, is a curved propagating disturbance wave characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in
A bow shock, also called a detached shock or bowed normal shock, is a curved propagating disturbance wave characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
, temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
, and density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematicall ...
. It occurs when a supersonic flow
Choked flow is a compressible flow effect. The parameter that becomes "choked" or "limited" is the fluid velocity.
Choked flow is a fluid dynamic condition associated with the venturi effect. When a flowing fluid at a given pressure and temperatu ...
encounters a body, around which the necessary deviation angle of the flow is higher than the maximum achievable deviation angle for an attached oblique shock
An oblique shock wave is a shock wave that, unlike a normal shock, is inclined with respect to the incident upstream flow direction. It will occur when a supersonic flow encounters a corner that effectively turns the flow into itself and comp ...
(see detachment criterion). Then, the oblique shock
An oblique shock wave is a shock wave that, unlike a normal shock, is inclined with respect to the incident upstream flow direction. It will occur when a supersonic flow encounters a corner that effectively turns the flow into itself and comp ...
transforms in a curved detached shock wave. As bow shocks occur for high flow deflection angles, they are often seen forming around blunt bodies, because of the high deflection angle that the body impose to the flow around it.
The thermodynamic transformation across a bow shock is non-isentropic and the shock decreases the flow velocity from supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
velocity upstream to subsonic velocity downstream.
Applications
The bow shock significantly increases the drag in a vehicle traveling at a supersonic speed. This property was utilized in the design of the return capsules during space missions such as the Apollo program, which need a high amount of drag in order to slow down duringatmospheric reentry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the ...
.
Shock relations
As in normal shock andoblique shock
An oblique shock wave is a shock wave that, unlike a normal shock, is inclined with respect to the incident upstream flow direction. It will occur when a supersonic flow encounters a corner that effectively turns the flow into itself and comp ...
,
* The upstream static pressure
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure has several uses:
* In the design and operation of aircraft, ''static pressure'' is the air pressure in the aircraft's static pressure system.
* In fluid dynamics, many authors use the term ''static pres ...
s is lower than the downstream static pressure
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure has several uses:
* In the design and operation of aircraft, ''static pressure'' is the air pressure in the aircraft's static pressure system.
* In fluid dynamics, many authors use the term ''static pres ...
.
* The upstream static density is lower than the downstream static density.
* The upstream static temperature is lower than the downstream static temperature.
* The upstream total pressure is greater than the downstream total pressure.
* The upstream total density is lower than the downstream total density.
* The upstream total temperature is equal to the downstream total temperature, as the shock wave is supposed isenthalpic
An isenthalpic process or isoenthalpic process is a process that proceeds without any change in enthalpy, ''H''; or specific enthalpy, ''h''.
Overview
If a steady-state, steady-flow process is analysed using a control volume, everything outside ...
.
For a curved shock, the shock angle varies and thus has variable strength across the entire shock front. The post-shock flow velocity and vorticity can therefore be computed via the Crocco's theorem, which is independent of any EOS (equation of state
In physics, chemistry, and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation relating state variables, which describe the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions, such as pressure, volume, temperature, or intern ...
) assuming inviscid
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the in ...
flow.
See also
*Bow shock
In astrophysics, a bow shock occurs when the magnetosphere of an astrophysical object interacts with the nearby flowing ambient plasma such as the solar wind. For Earth and other magnetized planets, it is the boundary at which the speed of th ...
* Gas dynamics
Compressible flow (or gas dynamics) is the branch of fluid mechanics that deals with flows having significant changes in fluid density. While all flows are compressible, flows are usually treated as being incompressible when the Mach number (the ...
* Moving shock
* Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan
References
* * {{cite book , last = Courant , first = R. , author2=Friedrichs, K.O. , title = Supersonic Flow and Shock Waves , origyear = 1948 , publisher = Interscience Publishers , location = New York , year = 1956 Aerodynamics Shock waves