Block Design Test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
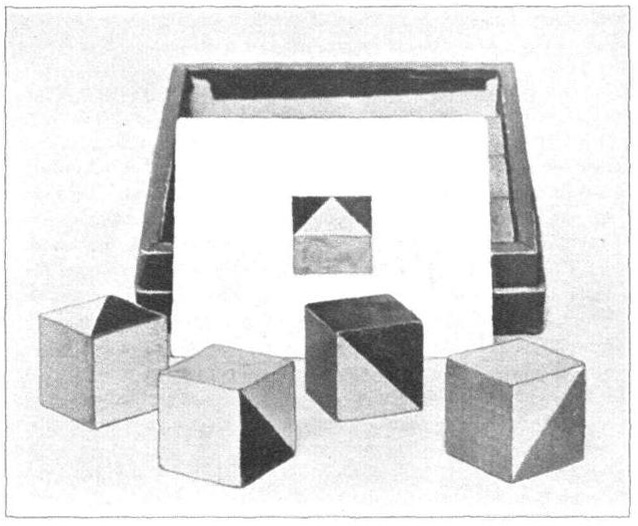 A block design test is a subtest on many IQ test batteries used as part of assessment of
A block design test is a subtest on many IQ test batteries used as part of assessment of
Index of Learning Styles Questionnaire
North Carolina State University
 A block design test is a subtest on many IQ test batteries used as part of assessment of
A block design test is a subtest on many IQ test batteries used as part of assessment of human intelligence
Human intelligence is the intellectual capability of humans, which is marked by complex cognitive feats and high levels of motivation and self-awareness. High intelligence is associated with better outcomes in life.
Through intelligence, humans ...
. It is thought to tap spatial visualization ability
Spatial visualization ability or visual-spatial ability is the ability to mentally manipulate 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional figures. It is typically measured with simple cognitive tests and is predictive of user performance with some kinds of u ...
and motor skill
A motor skill is a function that involves specific movements of the body's muscles to perform a certain task. These tasks could include walking, running, or riding a bike. In order to perform this skill, the body's nervous system, muscles, and br ...
. The test-taker uses hand movements to rearrange blocks that have various color patterns on different sides to match a pattern. The items in a block design test can be scored both by accuracy in matching the pattern and by speed in completing each item.
Historical background
David Wechsler
David Wechsler (; January 12, 1896 – May 2, 1981) was a Romanian-American psychologist. He developed well-known intelligence scales, such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC). A ...
adapted a block design subtest for his Wechsler-Bellevue test, the predecessor of his WAIS (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, as a revision of the ...
), from the Kohs block design test developed in 1920 at Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
by Samuel Calmin Kohs. A later revision of the Kohs test by Hutt incorporated the time taken to complete each item into the scoring of the test. Wechsler followed that practice in making both accuracy and speed factors in scoring the test.
Neuropsychological assessment
Good performance on the block design test is indicative of appropriate functioning of the parietal andfrontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove betwe ...
s. Head injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
, Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
, and stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
can severely reduce the performance of an individual on the block design test. Additional evidence suggests impairment in block design performance among schizophrenic
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdra ...
and bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
patient populations, though this represents only preliminary findings.
Spatial ability
The block design test is also a relatively accurate measure of spatial ability andspatial visualization ability
Spatial visualization ability or visual-spatial ability is the ability to mentally manipulate 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional figures. It is typically measured with simple cognitive tests and is predictive of user performance with some kinds of u ...
used in daily life. The block design test is considered one of the best measures of spatial ability, although it is subject to certain problems of administration, such as anxiety or over-cautious responding. Linda Kreger Silverman has proposed the block design subtest as the best putative measure of spatial ability among the Wechsler subtests.
Autism spectrum disorders
Uta Frith
Dame Uta Frith (''née'' Aurnhammer; born 25 May 1941) is a German-British developmental psychologist at the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London. She has pioneered much of the current research into autism and dysl ...
, in her book ''Autism: Explaining the Enigma'', addresses the superior performance of autistic individuals on the block design test. This was also addressed in an earlier paper. One article demonstrates the differences in construction time in the performance of the block design task by individuals with and without Asperger syndrome
Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's, is a former neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in Interpersonal relationship, social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted and re ...
. An essential point is that in an unsegmented version of the task, people with Asperger syndrome performed significantly faster than neurotypical
Neurotypical (NT, an abbreviation of neurologically typical) is a neologism widely used in the neurodiversity movement as a label for non-neurodivergent people. That is, anyone who has a typical neurotype, so excluding autistic people, those wit ...
individuals.
Science and engineering aptitude
Recent research has demonstrated a connection between spatial ability and math and science proficiency at the highest levels. A 2002 study in the Lancet demonstrated that high spatial ability was related to the performance of surgery. Additionally, although this is somewhat speculative, the grandfathers and fathers of autistic people were more likely to be engineers, and since it is known that autistic people have an ability peak in block design, it is possible that an inherited ability for block design performance may be responsible for the increased number of engineers and scientists among the relatives of autistic individuals.Spatial ability in pilots
In 1993, Dror et al. found that pilots' performance was superior to non-pilots on a test of the speed of mental rotation. Although the block design test is characterized as a test of spatial visualization, not mental rotation, spatial visualization ability as measured by the block design test is highly correlated to mental rotation ability.Research in an educational context
As performance on the block design test has been suggested as a predictive measure for performance in fields such as engineering and physics. Felder, atNorth Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
, has developed a learning style questionnaire that attempts to assess spatial ability in an educational context.Felder RM and
Soloman BAIndex of Learning Styles Questionnaire
North Carolina State University
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Block Design Test Intelligence tests