Blastema on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A blastema (
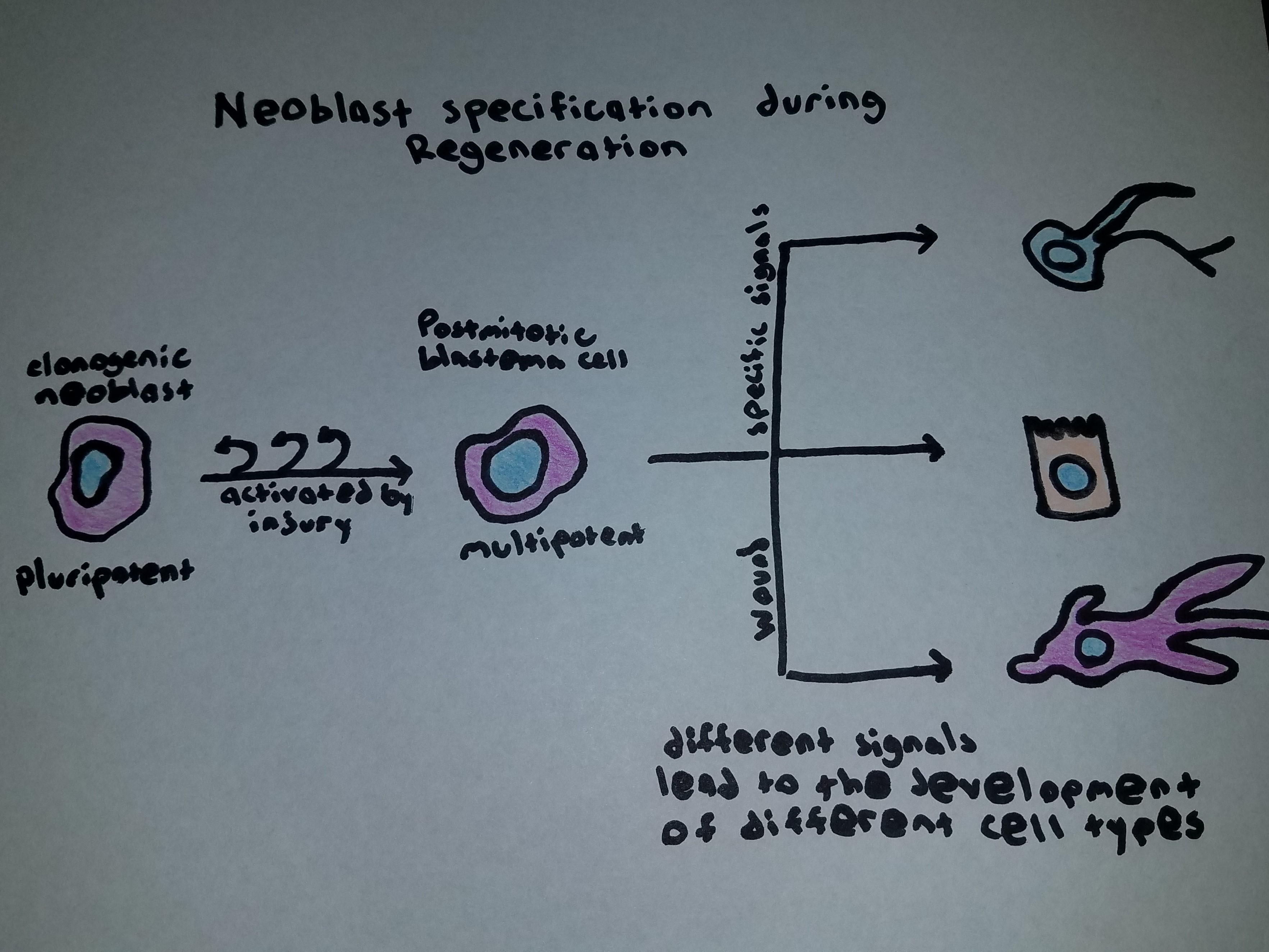 As stated above, there are several different types of organisms that can utilize a regenerative blastema as an adult. These organisms include urodele amphibians, zebrafish, and planarian flatworms as major creatures of study. In flatworms, the formation of a blastema needs adult stem cells that are called neoblasts for any type of regeneration to occur. Flatworms use these undifferentiated cells for regeneration after paracrine factors can provide signals from the surface of the wound. The cells in the blastema are also referred to as clonogenic neoblasts (cNeoblasts) that are able to move to the site of the wound and reform the tissue. In urodele amphibians, studies suggest that dedifferentiation of cells leads to the formation of a blastema that is able to form multiple tissue types after the amputation of their tails and wound healing occurs. In zebrafish, and in general, it seems as if experts are still uncertain of what truly forms the blastema. However, two common theories that have often been expressed are cell dedifferentiation and the recruitment of stem cells to the wound site.
As stated above, there are several different types of organisms that can utilize a regenerative blastema as an adult. These organisms include urodele amphibians, zebrafish, and planarian flatworms as major creatures of study. In flatworms, the formation of a blastema needs adult stem cells that are called neoblasts for any type of regeneration to occur. Flatworms use these undifferentiated cells for regeneration after paracrine factors can provide signals from the surface of the wound. The cells in the blastema are also referred to as clonogenic neoblasts (cNeoblasts) that are able to move to the site of the wound and reform the tissue. In urodele amphibians, studies suggest that dedifferentiation of cells leads to the formation of a blastema that is able to form multiple tissue types after the amputation of their tails and wound healing occurs. In zebrafish, and in general, it seems as if experts are still uncertain of what truly forms the blastema. However, two common theories that have often been expressed are cell dedifferentiation and the recruitment of stem cells to the wound site.
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''βλάστημα'', "offspring") is a mass of cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
s capable of growth and regeneration
Regeneration may refer to:
Science and technology
* Regeneration (biology), the ability to recreate lost or damaged cells, tissues, organs and limbs
* Regeneration (ecology), the ability of ecosystems to regenerate biomass, using photosynthesis
...
into organs or body parts. The changing definition of the word "blastema" has been reviewed by Holland (2021). A broad survey of how blastema has been used over time brings to light a somewhat involved history. The word entered the biomedical vocabulary in 1799 to designate a sinister acellular slime that was the starting point for the growth of cancers, themselves, at the time, thought to be acellular, as reviewed by Hajdu (2011, Cancer 118: 1155-1168). Then, during the early nineteenth century, the definition broadened to include growth zones (still considered acellular) in healthy, normally developing plant and animal embryos. Contemporaneously, cancer specialists dropped the term from their vocabulary, perhaps because they felt a term connoting a state of health and normalcy was not appropriate for describing a pathological condition. During the middle decades of the nineteenth century, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the cell theory, and Remak and Virchow insisted that cells can only be generated by division of existing ones. Consequently, the conception of the blastema changed from acellular to cellular. More specifically, the term came to designate a population of embryonic cells that gave rise to a particular tissue. In short, the term blastema started being used to refer to what modern embryologists increasingly began calling a rudiment or Anlage. Importantly, the term blastema did not yet refer to a mass of undifferentiated-looking cells that accumulates relatively early in a regenerating body part. For instance, Morgan (1900), does not use the term even once in his classic book, “Regeneration.” It was not until the eve of World War 1 that Fritsch (1911, Zool. Jb. Zool. Physiol. 30: 377-472) introduced the term blastema in the modern sense, as now used by contemporary students of regeneration.
During the last century, blastemas were thought to be composed of undifferentiated pluripotent Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
cells, but recent research indicates that in some organisms blastemas may retain memory of tissue origin. They are typically found in the early stages of an organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
's development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
such as in embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s, and in the regeneration of tissues, organs and bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
.
Some amphibians and certain species of fish and two species of African spiny mice can produce blastemas as adults. For example, salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten ...
s can regenerate many organs after their amputation, including their limbs, tail, retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
and intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
. Most animals, however, cannot produce blastemas.
Limb regeneration
When the limb of the salamander is cut off, a layer ofepidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
covers the surface of the amputation site. In the first few days after the injury, this wounded epidermis transforms into a layer of signaling cells called the Apical Epithelial Cap (AEC), which has a vital role in regeneration. In the meantime, fibroblasts
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells o ...
from the connective tissue migrate across the amputation surface to meet at the center of the wound. These fibroblasts multiply to form a blastema, the progenitor for a new limb.
Blastema cells can differentiate into any cell type with the exception of neurons. This means axons which are cut can be regrown by blastema cells, but if the soma of a neuron is damaged then a new neuron is unable to be created. As a result, neural organs cannot be regenerated.
Formation
 As stated above, there are several different types of organisms that can utilize a regenerative blastema as an adult. These organisms include urodele amphibians, zebrafish, and planarian flatworms as major creatures of study. In flatworms, the formation of a blastema needs adult stem cells that are called neoblasts for any type of regeneration to occur. Flatworms use these undifferentiated cells for regeneration after paracrine factors can provide signals from the surface of the wound. The cells in the blastema are also referred to as clonogenic neoblasts (cNeoblasts) that are able to move to the site of the wound and reform the tissue. In urodele amphibians, studies suggest that dedifferentiation of cells leads to the formation of a blastema that is able to form multiple tissue types after the amputation of their tails and wound healing occurs. In zebrafish, and in general, it seems as if experts are still uncertain of what truly forms the blastema. However, two common theories that have often been expressed are cell dedifferentiation and the recruitment of stem cells to the wound site.
As stated above, there are several different types of organisms that can utilize a regenerative blastema as an adult. These organisms include urodele amphibians, zebrafish, and planarian flatworms as major creatures of study. In flatworms, the formation of a blastema needs adult stem cells that are called neoblasts for any type of regeneration to occur. Flatworms use these undifferentiated cells for regeneration after paracrine factors can provide signals from the surface of the wound. The cells in the blastema are also referred to as clonogenic neoblasts (cNeoblasts) that are able to move to the site of the wound and reform the tissue. In urodele amphibians, studies suggest that dedifferentiation of cells leads to the formation of a blastema that is able to form multiple tissue types after the amputation of their tails and wound healing occurs. In zebrafish, and in general, it seems as if experts are still uncertain of what truly forms the blastema. However, two common theories that have often been expressed are cell dedifferentiation and the recruitment of stem cells to the wound site.
Signaling pathways
There are several different signaling pathways that have been shown to be involved with limb regeneration through the formation of the blastema. Inflatworms
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegment ...
, studies suggest that after using RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by o ...
Smad-beta-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcripti ...
-1 was found to set up the anterior-posterior axis. Inhibitions to this results in reversed polarity across the blastema. Urodeles
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten ...
use hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introducti ...
for dorsal-ventral patterning of their regenerating tail and its surrounding tissue. This was suggested by its inhibition leading to reduced blastemas. Zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family ( Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often ...
seem to use IGF signalling in limb regeneration as its inhibition led to clues of them being required for blastema function.
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Blastema Animal developmental biology