Blaise Pascal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Blaise Pascal ( , , ; ; 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French
 Pascal was born in
Pascal was born in
 In 1642, in an effort to ease his father's endless, exhausting calculations, and recalculations, of taxes owed and paid (into which work the young Pascal had been recruited), Pascal, not yet 19, constructed a mechanical calculator capable of addition and subtraction, called '' Pascal's calculator'' or the ''Pascaline''. Of the eight Pascalines known to have survived, four are held by the Musée des Arts et Métiers in Paris and one more by the Zwinger museum in
In 1642, in an effort to ease his father's endless, exhausting calculations, and recalculations, of taxes owed and paid (into which work the young Pascal had been recruited), Pascal, not yet 19, constructed a mechanical calculator capable of addition and subtraction, called '' Pascal's calculator'' or the ''Pascaline''. Of the eight Pascalines known to have survived, four are held by the Musée des Arts et Métiers in Paris and one more by the Zwinger museum in
 Pascal's ''Traité du triangle arithmétique'', written in 1654 but published posthumously in 1665, described a convenient tabular presentation for
Pascal's ''Traité du triangle arithmétique'', written in 1654 but published posthumously in 1665, described a convenient tabular presentation for
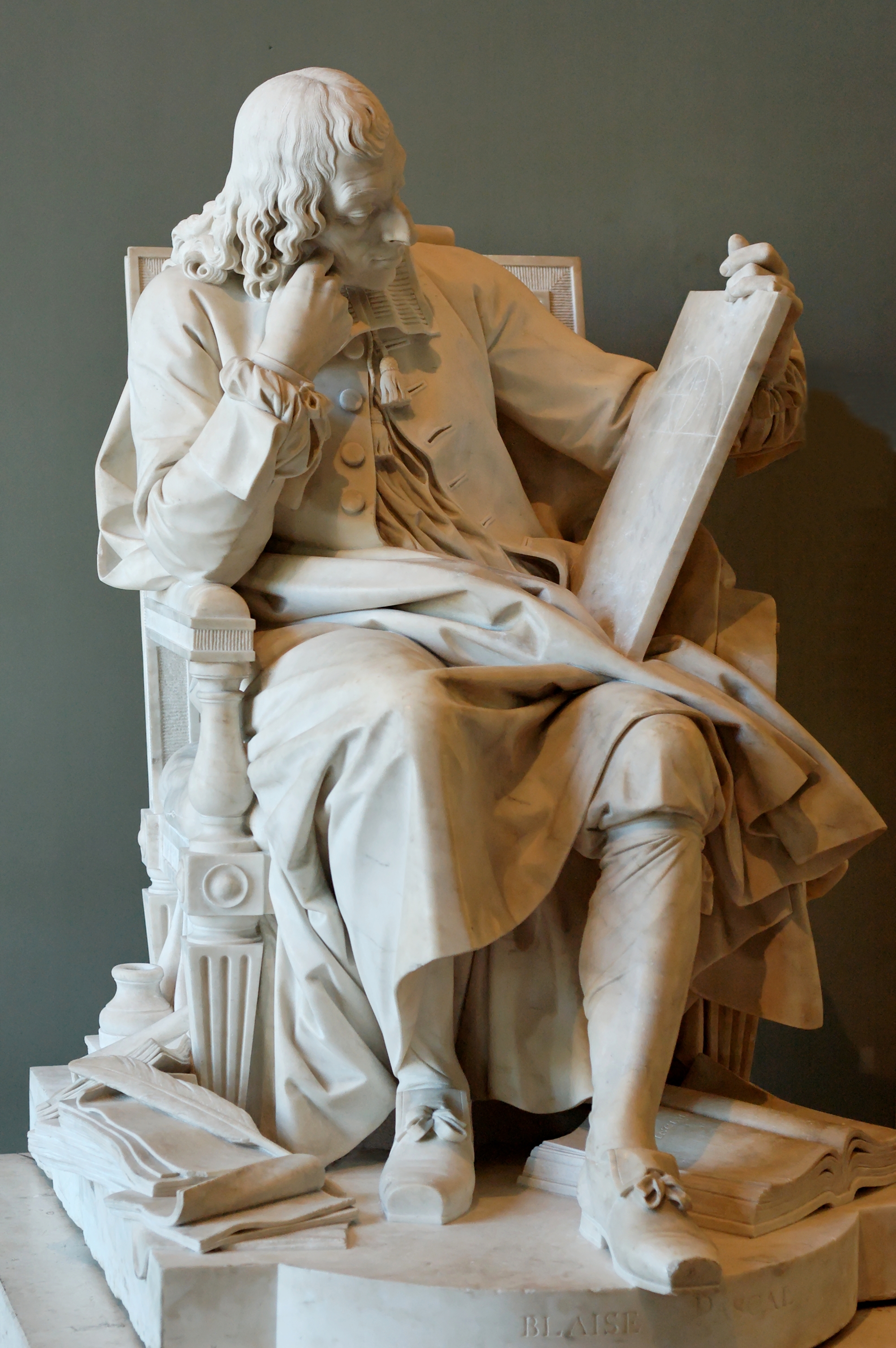 In 1658, Pascal, while suffering from a toothache, began considering several problems concerning the cycloid. His toothache disappeared, and he took this as a heavenly sign to proceed with his research. Eight days later he had completed his essay and, to publicize the results, proposed a contest.
Pascal proposed three questions relating to the
In 1658, Pascal, while suffering from a toothache, began considering several problems concerning the cycloid. His toothache disappeared, and he took this as a heavenly sign to proceed with his research. Eight days later he had completed his essay and, to publicize the results, proposed a contest.
Pascal proposed three questions relating to the
 Pascal contributed to several fields in physics, most notably the fields of fluid mechanics and pressure. In honour of his scientific contributions, the name ''Pascal'' has been given to the SI unit of pressure and Pascal's law (an important principle of hydrostatics). He introduced a primitive form of roulette and the roulette wheel in his search for a
Pascal contributed to several fields in physics, most notably the fields of fluid mechanics and pressure. In honour of his scientific contributions, the name ''Pascal'' has been given to the SI unit of pressure and Pascal's law (an important principle of hydrostatics). He introduced a primitive form of roulette and the roulette wheel in his search for a
 Following more experimentation in this vein, in 1647 Pascal produced ''Experiences nouvelles touchant le vide'' ("New experiments with the vacuum"), which detailed basic rules describing to what degree various liquids could be supported by
Following more experimentation in this vein, in 1647 Pascal produced ''Experiences nouvelles touchant le vide'' ("New experiments with the vacuum"), which detailed basic rules describing to what degree various liquids could be supported by
 In the winter of 1646, Pascal's 58-year-old father broke his hip when he slipped and fell on an icy street of Rouen; given the man's age and the state of medicine in the 17th century, a
In the winter of 1646, Pascal's 58-year-old father broke his hip when he slipped and fell on an icy street of Rouen; given the man's age and the state of medicine in the 17th century, a
 In literature, Pascal is regarded as one of the most important authors of the French Classical Period and is read today as one of the greatest masters of French prose. His use of satire and wit influenced later
In literature, Pascal is regarded as one of the most important authors of the French Classical Period and is read today as one of the greatest masters of French prose. His use of satire and wit influenced later
 Pascal's most influential theological work, referred to posthumously as the ''Pensées'' ("Thoughts") is widely considered to be a masterpiece, and a landmark in ''French prose''. When commenting on one particular section (Thought #72),
Pascal's most influential theological work, referred to posthumously as the ''Pensées'' ("Thoughts") is widely considered to be a masterpiece, and a landmark in ''French prose''. When commenting on one particular section (Thought #72),
''Seventeenth Century''
p. 174 (2009 reprint). Will Durant hailed the Pensées as "the most eloquent book in French prose".'' The Story of Civilization: Volume 8, "The Age of Louis XIV"'' by Will & Ariel Durant, chapter II, Subsection 4.4, p. 66 The ''Pensées'' was not completed before his death. It was to have been a sustained and coherent examination and defense of the
 T. S. Eliot described him during this phase of his life as "a man of the world among ascetics, and an ascetic among men of the world." Pascal's ascetic lifestyle derived from a belief that it was natural and necessary for a person to suffer. In 1659, Pascal fell seriously ill. During his last years, he frequently tried to reject the ministrations of his doctors, saying, "Sickness is the natural state of Christians."Muir, Jane
T. S. Eliot described him during this phase of his life as "a man of the world among ascetics, and an ascetic among men of the world." Pascal's ascetic lifestyle derived from a belief that it was natural and necessary for a person to suffer. In 1659, Pascal fell seriously ill. During his last years, he frequently tried to reject the ministrations of his doctors, saying, "Sickness is the natural state of Christians."Muir, Jane
''Of Men and Numbers''
(New York: Dover Publications, Inc, 1996). , p. 104. Louis XIV suppressed the Jansenist movement at Port-Royal in 1661. In response, Pascal wrote one of his final works, ''Écrit sur la signature du formulaire'' ("Writ on the Signing of the Form"), exhorting the Jansenists not to give in. Later that year, his sister Jacqueline died, which convinced Pascal to cease his polemics on Jansenism. Pascal's last major achievement, returning to his mechanical genius, was inaugurating perhaps the first bus line, the carrosses à cinq sols, moving passengers within Paris in a carriage with many seats. Pascal also designated the operation principles which were later used to plan public transportation: The carriages has a fixed route, fixed price, and left even if there were no passengers. It is widely considered that the idea of public transportation was well ahead of time. The lines were not commercially successful, and the last one closed by 1675. In 1662, Pascal's illness became more violent, and his emotional condition had severely worsened since his sister's death. Aware that his health was fading quickly, he sought a move to the hospital for incurable diseases, but his doctors declared that he was too unstable to be carried. In Paris on 18 August 1662, Pascal went into convulsions and received extreme unction. He died the next morning, his last words being "May God never abandon me," and was buried in the cemetery of
''Of Men and Numbers''
(New York: Dover Publications, Inc, 1996). , p. 103. The headaches which affected Pascal are generally attributed to his brain
 One of the Universities of
One of the Universities of
"Pascal's Views on Mathematics and the Divine,"
''Mathematics and the Divine: A Historical Study'' (eds. T. Koetsier and L. Bergmans. Amsterdam: Elsevier 2005), pp. 407–21. * Broome, J.H. ''Pascal''. (London: E. Arnold, 1965). * Campe, Rüdiger, "Numbers and Calculation in Context: The Game of Decision - Pascal" in The ''Game of Probability. Literature and Calculation from Pascal and Kleist'', Stanford University Press, 2012 *Davidson, Hugh M. ''Blaise Pascal''. (Boston: Twayne Publishers), 1983. * * Farrell, John. "Pascal and Power". Chapter seven of ''Paranoia and Modernity: Cervantes to Rousseau'' (Cornell UP, 2006). * Goldmann, Lucien, ''The hidden God; a study of tragic vision in the Pensees of Pascal and the tragedies of Racine'' (original ed. 1955, Trans. Philip Thody. London: Routledge, 1964). * Groothuis, Douglas. ''On Pascal''. (Belmont: Wadsworth, 2002). * Jordan, Jeff. ''Pascal's Wager: Pragmatic Arguments and Belief in God''. (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 2006). * Landkildehus, Søren. "Kierkegaard and Pascal as kindred spirits in the Fight against Christendom" in ''Kierkegaard and the Renaissance and Modern Traditions'' (ed. Jon Stewart. Farnham: Ashgate Publishing, 2009). * Mackie, John Leslie. ''The Miracle of Theism: Arguments for and against the Existence of God''. (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1982). * Stafford Harry Northcote, Viscount Saint Cyres, ''Pascal'' (London: Smith, Elder & Company, 1909; New York: E. P. Dutton) * Pugh, Anthony R. ''The Composition of Pascal's Apologia'', (University of Toronto Press, 1984). * * * * Tobin, Paul. "The Rejection of Pascal's Wager: A Skeptic's Guide to the Bible and the Historical Jesus". authorsonline.co.uk, 2009. * Yves Morvan, ''Pascal à Mirefleurs ? Les dessins de la maison de Domat'', Impr. Blandin, 1985. (FRBNF40378895)
Oeuvres complètes, volume 2
(1858) Paris: Libraire de L Hachette et Cie, link from
The Correspondence of Blaise Pascal
i
EMLO
* * * * ''Pensées de Blaise Pascal''. Renouard, Paris 1812 (2 vols.) ()
Discussion of the Pascaline, its history, mechanism, surviving examples, and modern replicas at http://things-that-count.net
in orig. French/Latin and modern English, trans. Elizabeth T. Knuth.
(in French) *
BBC Radio 4. In Our Time: Pascal.
* ttp://www.intratext.com/Catalogo/Autori/Aut852.htm Blaise Pascal's works text, concordances and frequency lists * * Etext of Pascal's
Pensées
' (English, in various formats) * Etext of Pascal's
' (English) * Etext of a number of Pascal'
minor works
(English translation) including, ''De l'Esprit géométrique'' and ''De l'Art de persuader''. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Pascal, Blaise 1623 births 1662 deaths Writers from Clermont-Ferrand French Roman Catholic writers 17th-century French writers 17th-century male writers 17th-century French mathematicians 17th-century philosophers Aphorists Christian apologists Christian humanists Roman Catholic mystics Critics of atheism Converts to Roman Catholicism Fluid dynamicists French mathematicians French philosophers French physicists 17th-century French theologians 17th-century Christian mystics Hypochondriacs Jansenists Probability theorists Catholic philosophers 17th-century Roman Catholics Burials at Saint-Étienne-du-Mont Cartesianism Scientists from Clermont-Ferrand
mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
, physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
, inventor, philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
, and Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
writer.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
. Pascal's earliest mathematical work was on conic section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a ...
s; he wrote a significant treatise on the subject of projective geometry at the age of 16. He later corresponded with Pierre de Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (; between 31 October and 6 December 1607 – 12 January 1665) was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he ...
on probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set ...
, strongly influencing the development of modern economics and social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of s ...
. In 1642, while still a teenager, he started some pioneering work on calculating machines (called Pascal's calculators and later Pascalines), establishing him as one of the first two inventors of the mechanical calculator
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or (historically) a simulation such as an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators w ...
.
Like his contemporary René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Ma ...
, Pascal was also a pioneer in the natural and applied sciences. Pascal wrote in defense of the scientific method
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientifi ...
and produced several controversial results. He made important contributions to the study of fluids, and clarified the concepts of pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
and vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often ...
by generalising the work of Evangelista Torricelli
Evangelista Torricelli ( , also , ; 15 October 160825 October 1647) was an Italian physicist and mathematician, and a student of Galileo. He is best known for his invention of the barometer, but is also known for his advances in optics and wo ...
. Following Torricelli and Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He ...
, he rebutted the likes of Aristotle and Descartes who insisted that nature abhors a vacuum in 1647.
In 1646, he and his sister Jacqueline identified with the religious movement within Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
known by its detractors as Jansenism. Following a religious experience in late 1654, he began writing influential works on philosophy and theology. His two most famous works date from this period: the '' Lettres provinciales'' and the ''Pensées
The ''Pensées'' ("Thoughts") is a collection of fragments written by the French 17th-century philosopher and mathematician Blaise Pascal. Pascal's religious conversion led him into a life of asceticism, and the ''Pensées'' was in many ways hi ...
'', the former set in the conflict between Jansenists and Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
. The latter contains Pascal's Wager, known in the original as the ''Discourse on the Machine'', a fideistic probabilistic argument for God's existence. In that year, he also wrote an important treatise on the arithmetical triangle. Between 1658 and 1659, he wrote on the cycloid and its use in calculating the volume of solids.
Throughout his life, Pascal was in frail health, especially after the age of 18; he died just two months after his 39th birthday.
Life
Early life and education
 Pascal was born in
Pascal was born in Clermont-Ferrand
Clermont-Ferrand (, ; ; oc, label= Auvergnat, Clarmont-Ferrand or Clharmou ; la, Augustonemetum) is a city and commune of France, in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, with a population of 146,734 (2018). Its metropolitan area (''aire d'attrac ...
, which is in France's Auvergne region, by the Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,0 ...
. He lost his mother, Antoinette Begon, at the age of three. His father, Étienne Pascal (1588–1651), who also had an interest in science and mathematics, was a local judge and member of the " Noblesse de Robe". Pascal had two sisters, the younger Jacqueline
Jacqueline may refer to:
People
* Jacqueline (given name), including a list of people with the name
* Jacqueline Moore (born 1964), ring name "Jacqueline", American professional wrestler
Arts and entertainment
* ''Jacqueline'' (1923 film), ...
and the elder Gilberte.
In 1631, five years after the death of his wife, Étienne Pascal moved with his children to Paris. The newly arrived family soon hired Louise Delfault, a maid who eventually became a key member of the family. Étienne, who never remarried, decided that he alone would educate his children, for they all showed extraordinary intellectual ability, particularly his son Blaise. The young Pascal showed an amazing aptitude for mathematics and science.
"Essay on Conics"
Particularly of interest to Pascal was a work ofDesargues
Girard Desargues (; 21 February 1591 – September 1661) was a French mathematician and engineer, who is considered one of the founders of projective geometry. Desargues' theorem, the Desargues graph, and the crater Desargues on the Moo ...
on conic section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a ...
s. Following Desargues' thinking, the 16-year-old Pascal produced, as a means of proof, a short treatise on what was called the "Mystic Hexagram", "Essai pour les coniques" ("Essay on Conics") and sent it—his first serious work of mathematics—to Père Mersenne in Paris; it is known still today as Pascal's theorem. It states that if a hexagon is inscribed in a circle (or conic) then the three intersection points of opposite sides lie on a line (called the Pascal line).
Pascal's work was so precocious that René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Ma ...
was convinced that Pascal's father had written it. When assured by Mersenne that it was, indeed, the product of the son and not the father, Descartes dismissed it with a sniff: "I do not find it strange that he has offered demonstrations about conics more appropriate than those of the ancients," adding, "but other matters related to this subject can be proposed that would scarcely occur to a 16-year-old child."
Leaving Paris
In France at that time offices and positions could be—and were—bought and sold. In 1631, Étienne sold his position as second president of the '' Cour des Aides'' for 65,665livres
The (; ; abbreviation: ₶.) was one of numerous currencies used in medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in Early Modern France.
The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 g ...
. The money was invested in a government bond which provided, if not a lavish, then certainly a comfortable income which allowed the Pascal family to move to, and enjoy, Paris. But in 1638 Richelieu, desperate for money to carry on the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
, defaulted on the government's bonds. Suddenly Étienne Pascal's worth had dropped from nearly 66,000 livres to less than 7,300.
Like so many others, Étienne was eventually forced to flee Paris because of his opposition to the fiscal policies of Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, Duke of Richelieu (; 9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French clergyman and statesman. He was also known as ''l'Éminence rouge'', or "the Red Eminence", a term derived from the ...
, leaving his three children in the care of his neighbour Madame Sainctot, a great beauty with an infamous past who kept one of the most glittering and intellectual salons in all France. It was only when Jacqueline performed well in a children's play with Richelieu in attendance that Étienne was pardoned. In time, Étienne was back in good graces with the cardinal and in 1639 had been appointed the king's commissioner of taxes in the city of Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
—a city whose tax records, thanks to uprisings, were in utter chaos.
Pascaline
 In 1642, in an effort to ease his father's endless, exhausting calculations, and recalculations, of taxes owed and paid (into which work the young Pascal had been recruited), Pascal, not yet 19, constructed a mechanical calculator capable of addition and subtraction, called '' Pascal's calculator'' or the ''Pascaline''. Of the eight Pascalines known to have survived, four are held by the Musée des Arts et Métiers in Paris and one more by the Zwinger museum in
In 1642, in an effort to ease his father's endless, exhausting calculations, and recalculations, of taxes owed and paid (into which work the young Pascal had been recruited), Pascal, not yet 19, constructed a mechanical calculator capable of addition and subtraction, called '' Pascal's calculator'' or the ''Pascaline''. Of the eight Pascalines known to have survived, four are held by the Musée des Arts et Métiers in Paris and one more by the Zwinger museum in Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
, Germany, exhibit two of his original mechanical calculators.
Although these machines are pioneering forerunners to a further 400 years of development of mechanical methods of calculation, and in a sense to the later field of computer engineering
Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer engineers n ...
, the calculator failed to be a great commercial success. Partly because it was still quite cumbersome to use in practice, but probably primarily because it was extraordinarily expensive, the Pascaline became little more than a toy, and a status symbol, for the very rich both in France and elsewhere in Europe. Pascal continued to make improvements to his design through the next decade, and he refers to some 50 machines that were built to his design. He built 20 finished machines over the following 10 years.
Mathematics
Probability
Pascal's development ofprobability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set ...
was his most influential contribution to mathematics. Originally applied to gambling, today it is extremely important in economics, especially in actuarial science. John Ross writes, "Probability theory and the discoveries following it changed the way we regard uncertainty, risk, decision-making, and an individual's and society's ability to influence the course of future events." However, Pascal and Fermat, though doing important early work in probability theory, did not develop the field very far. Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists o ...
, learning of the subject from the correspondence of Pascal and Fermat, wrote the first book on the subject. Later figures who continued the development of the theory include Abraham de Moivre
Abraham de Moivre FRS (; 26 May 166727 November 1754) was a French mathematician known for de Moivre's formula, a formula that links complex numbers and trigonometry, and for his work on the normal distribution and probability theory.
He move ...
and Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarize ...
.
In 1654, prompted by his friend the Chevalier de Méré, he corresponded with Pierre de Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (; between 31 October and 6 December 1607 – 12 January 1665) was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he ...
on the subject of gambling problems, and from that collaboration was born the mathematical theory of probabilities
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, ...
. The specific problem was that of two players who want to finish a game early and, given the current circumstances of the game, want to divide the stakes fairly, based on the chance each has of winning the game from that point. From this discussion, the notion of expected value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean of a ...
was introduced. Pascal later (in the ''Pensées'') used a probabilistic argument, Pascal's wager, to justify belief in God and a virtuous life. The work done by Fermat and Pascal into the calculus of probabilities laid important groundwork for Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of ma ...
' formulation of the calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
.
''Treatise on the Arithmetical Triangle''
 Pascal's ''Traité du triangle arithmétique'', written in 1654 but published posthumously in 1665, described a convenient tabular presentation for
Pascal's ''Traité du triangle arithmétique'', written in 1654 but published posthumously in 1665, described a convenient tabular presentation for binomial coefficient
In mathematics, the binomial coefficients are the positive integers that occur as coefficients in the binomial theorem. Commonly, a binomial coefficient is indexed by a pair of integers and is written \tbinom. It is the coefficient of the t ...
s which he called the arithmetical triangle, but is now called Pascal's triangle. The triangle can also be represented:
He defined the numbers in the triangle by recursion
Recursion (adjective: ''recursive'') occurs when a thing is defined in terms of itself or of its type. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematic ...
: Call the number in the (''m'' + 1)th row and (''n'' + 1)th column ''t''''mn''. Then ''t''''mn'' = ''t''''m''–1,''n'' + ''t''''m'',''n''–1, for ''m'' = 0, 1, 2, ... and ''n'' = 0, 1, 2, ... The boundary conditions are ''t''''m'',−1 = 0, ''t''−1,''n'' = 0 for ''m'' = 1, 2, 3, ... and ''n'' = 1, 2, 3, ... The generator ''t''00 = 1. Pascal concluded with the proof,
:
In the same treatise, Pascal gave an explicit statement of the principle of mathematical induction
Mathematical induction is a method for proving that a statement ''P''(''n'') is true for every natural number ''n'', that is, that the infinitely many cases ''P''(0), ''P''(1), ''P''(2), ''P''(3), ... all hold. Informal metaphors help ...
. In 1654, he proved ''Pascal's identity'' relating the sums of the ''p''-th powers of the first ''n'' positive integers for ''p'' = 0, 1, 2, ..., ''k''.
That same year, Pascal had a religious experience, and mostly gave up work in mathematics.
Cycloid
 In 1658, Pascal, while suffering from a toothache, began considering several problems concerning the cycloid. His toothache disappeared, and he took this as a heavenly sign to proceed with his research. Eight days later he had completed his essay and, to publicize the results, proposed a contest.
Pascal proposed three questions relating to the
In 1658, Pascal, while suffering from a toothache, began considering several problems concerning the cycloid. His toothache disappeared, and he took this as a heavenly sign to proceed with his research. Eight days later he had completed his essay and, to publicize the results, proposed a contest.
Pascal proposed three questions relating to the center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
, area and volume of the cycloid, with the winner or winners to receive prizes of 20 and 40 Spanish doubloon
The doubloon (from Spanish ''doblón'', or "double", i.e. ''double escudo'') was a two-''escudo'' gold coin worth approximately $4 (four Spanish dollars) or 32 '' reales'',
and weighing 6.766 grams (0.218 troy ounce) of 22-karat gold (or 0.917 fi ...
s. Pascal, Gilles de Roberval and Pierre de Carcavi were the judges, and neither of the two submissions (by John Wallis
John Wallis (; la, Wallisius; ) was an English clergyman and mathematician who is given partial credit for the development of infinitesimal calculus. Between 1643 and 1689 he served as chief cryptographer for Parliament and, later, the royal ...
and Antoine de Lalouvère) were judged to be adequate. While the contest was ongoing, Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren PRS FRS (; – ) was one of the most highly acclaimed English architects in history, as well as an anatomist, astronomer, geometer, and mathematician-physicist. He was accorded responsibility for rebuilding 52 church ...
sent Pascal a proposal for a proof of the rectification
Rectification has the following technical meanings:
Mathematics
* Rectification (geometry), truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points
* Rectifiable curve, in mathematics
* Recti ...
of the cycloid; Roberval claimed promptly that he had known of the proof for years. Wallis published Wren's proof (crediting Wren) in Wallis's ''Tractus Duo'', giving Wren priority for the first published proof.
Physics
 Pascal contributed to several fields in physics, most notably the fields of fluid mechanics and pressure. In honour of his scientific contributions, the name ''Pascal'' has been given to the SI unit of pressure and Pascal's law (an important principle of hydrostatics). He introduced a primitive form of roulette and the roulette wheel in his search for a
Pascal contributed to several fields in physics, most notably the fields of fluid mechanics and pressure. In honour of his scientific contributions, the name ''Pascal'' has been given to the SI unit of pressure and Pascal's law (an important principle of hydrostatics). He introduced a primitive form of roulette and the roulette wheel in his search for a perpetual motion
Perpetual motion is the motion of bodies that continues forever in an unperturbed system. A perpetual motion machine is a hypothetical machine that can do work infinitely without an external energy source. This kind of machine is impossible, a ...
machine.
Fluid dynamics
His work in the fields ofhydrodynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) a ...
and hydrostatics centered on the principles of hydraulic fluid
A hydraulic fluid or hydraulic liquid is the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water. Examples of equipment that might use hydraulic fluids are excavators and backhoe ...
s. His inventions include the hydraulic press (using hydraulic pressure to multiply force) and the syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside ...
. He proved that hydrostatic pressure depends not on the weight of the fluid but on the elevation difference. He demonstrated this principle by attaching a thin tube to a barrel full of water and filling the tube with water up to the level of the third floor of a building. This caused the barrel to leak, in what became known as Pascal's barrel experiment.
Vacuum
By 1647, Pascal had learned ofEvangelista Torricelli
Evangelista Torricelli ( , also , ; 15 October 160825 October 1647) was an Italian physicist and mathematician, and a student of Galileo. He is best known for his invention of the barometer, but is also known for his advances in optics and wo ...
's experimentation with barometers. Having replicated an experiment that involved placing a tube filled with mercury upside down in a bowl of mercury, Pascal questioned what force kept some mercury in the tube and what filled the space above the mercury in the tube. At the time, most scientists including Descartes believed in a plenum, i. e. some invisible matter filled all of space, rather than a vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often ...
. " Nature abhors a vacuum." This was based on the Aristotelian notion that everything in motion was a substance, moved by another substance. Furthermore, light passed through the glass tube, suggesting a substance such as aether rather than vacuum filled the space.
 Following more experimentation in this vein, in 1647 Pascal produced ''Experiences nouvelles touchant le vide'' ("New experiments with the vacuum"), which detailed basic rules describing to what degree various liquids could be supported by
Following more experimentation in this vein, in 1647 Pascal produced ''Experiences nouvelles touchant le vide'' ("New experiments with the vacuum"), which detailed basic rules describing to what degree various liquids could be supported by air pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars ...
. It also provided reasons why it was indeed a vacuum above the column of liquid in a barometer tube. This work was followed by ''Récit de la grande expérience de l'équilibre des liqueurs'' ("Account of the great experiment on equilibrium in liquids") published in 1648.
The Torricellian vacuum found that air pressure is equal to the weight of 30 inches of mercury. If air has a finite weight, Earth's atmosphere must have a maximum height. Pascal reasoned that if true, air pressure on a high mountain must be less than at a lower altitude. He lived near the Puy de Dôme
Puy de Dôme (, ; oc, label=Auvergnat, Puèi Domat or ) is a lava dome and one of the youngest volcanoes in the region of Massif Central in central France. This chain of volcanoes including numerous cinder cones, lava domes and maars is ...
mountain, tall, but his health was poor so could not climb it. On 19 September 1648, after many months of Pascal's friendly but insistent prodding, Florin Périer, husband of Pascal's elder sister Gilberte, was finally able to carry out the fact-finding mission vital to Pascal's theory. The account, written by Périer, reads:
Pascal replicated the experiment in Paris by carrying a barometer up to the top of the bell tower at the church of Saint-Jacques-de-la-Boucherie, a height of about 50 metres. The mercury dropped two lines.
In a reply to the plenist Estienne Noel, Pascal wrote, echoing contemporary notions of science and falsifiability: "In order to show that a hypothesis is evident, it does not suffice that all the phenomena follow from it; instead, if it leads to something contrary to a single one of the phenomena, that suffices to establish its falsity."
Blaise Pascal Chairs are given to outstanding international scientists to conduct their research in the Ile de France region.
Adult life: religion, literature, and philosophy
Religious conversion
 In the winter of 1646, Pascal's 58-year-old father broke his hip when he slipped and fell on an icy street of Rouen; given the man's age and the state of medicine in the 17th century, a
In the winter of 1646, Pascal's 58-year-old father broke his hip when he slipped and fell on an icy street of Rouen; given the man's age and the state of medicine in the 17th century, a broken hip
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone). Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.
They most often occur as a res ...
could be a very serious condition, perhaps even fatal. Rouen was home to two of the finest doctors in France, Deslandes and de la Bouteillerie. The elder Pascal "would not let anyone other than these men attend him...It was a good choice, for the old man survived and was able to walk again..." But treatment and rehabilitation took three months, during which time La Bouteillerie and Deslandes had become regular visitors.
Both men were followers of Jean Guillebert, proponent of a splinter group from Catholic teaching known as Jansenism. This still fairly small sect was making surprising inroads into the French Catholic community at that time. It espoused rigorous Augustinism
Augustinianism is the philosophical and theological system of Augustine of Hippo and its subsequent development by other thinkers, notably Boethius, Anselm of Canterbury and Bonaventure. Among Augustine's most important works are ''The City of God ...
. Blaise spoke with the doctors frequently, and after their successful treatment of his father, borrowed from them works by Jansenist authors. In this period, Pascal experienced a sort of "first conversion" and began to write on theological subjects in the course of the following year.
Pascal fell away from this initial religious engagement and experienced a few years of what some biographers have called his "worldly period" (1648–54). His father died in 1651 and left his inheritance to Pascal and his sister Jacqueline, for whom Pascal acted as conservator. Jacqueline announced that she would soon become a postulant in the Jansenist convent of Port-Royal Port Royal is the former capital city of Jamaica.
Port Royal or Port Royale may also refer to:
Institutions
* Port-Royal-des-Champs, an abbey near Paris, France, which spawned influential schools and writers of the 17th century
** Port-Royal Ab ...
. Pascal was deeply affected and very sad, not because of her choice, but because of his chronic poor health; he needed her just as she had needed him.
By the end of October in 1651, a truce had been reached between brother and sister. In return for a healthy annual stipend, Jacqueline signed over her part of the inheritance to her brother. Gilberte had already been given her inheritance in the form of a dowry. In early January, Jacqueline left for Port-Royal. On that day, according to Gilberte concerning her brother, "He retired very sadly to his rooms without seeing Jacqueline, who was waiting in the little parlor..."
In early June 1653, after what must have seemed like endless badgering from Jacqueline,
Pascal formally signed over the whole of his sister's inheritance to Port-Royal, which, to him, "had begun to smell like a cult." With two-thirds of his father's estate now gone, the 29-year-old Pascal was now consigned to genteel poverty.
For a while, Pascal pursued the life of a bachelor. During visits to his sister at Port-Royal in 1654, he displayed contempt for affairs of the world but was not drawn to God.Richard H. Popkin, Paul Edwards (ed.), ''Encyclopedia of Philosophy'', 1967 edition, s.v. "Pascal, Blaise.", vol. 6, p. 52–55, New York: Macmillan
=The ''Memorial''
= On the 23 of November, 1654, between 10:30 and 12:30 at night, Pascal had an intense religious experience and immediately wrote a brief note to himself which began: "Fire. God of Abraham, God of Isaac, God of Jacob, not of the philosophers and the scholars..." and concluded by quoting Psalm 119:16: "I will not forget thy word. Amen." He seems to have carefully sewn this document into his coat and always transferred it when he changed clothes; a servant discovered it only by chance after his death.Pascal, Blaise. ''Oeuvres complètes''. (Paris: Seuil, 1960), p. 618 This piece is now known as the ''Memorial''. The story of a carriage accident as having led to the experience described in the ''Memorial'' is disputed by some scholars. His belief and religious commitment revitalized, Pascal visited the older of two convents atPort-Royal Port Royal is the former capital city of Jamaica.
Port Royal or Port Royale may also refer to:
Institutions
* Port-Royal-des-Champs, an abbey near Paris, France, which spawned influential schools and writers of the 17th century
** Port-Royal Ab ...
for a two-week retreat in January 1655. For the next four years, he regularly travelled between Port-Royal and Paris. It was at this point immediately after his conversion when he began writing his first major literary work on religion, the ''Provincial Letters''.
Literature
 In literature, Pascal is regarded as one of the most important authors of the French Classical Period and is read today as one of the greatest masters of French prose. His use of satire and wit influenced later
In literature, Pascal is regarded as one of the most important authors of the French Classical Period and is read today as one of the greatest masters of French prose. His use of satire and wit influenced later polemic
Polemic () is contentious rhetoric intended to support a specific position by forthright claims and to undermine the opposing position. The practice of such argumentation is called ''polemics'', which are seen in arguments on controversial topic ...
ists.
The ''Provincial Letters''
Beginning in 1656–57, Pascal published his memorable attack on casuistry, a popular ethical method used byCatholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
thinkers in the early modern period (especially the Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
, and in particular Antonio Escobar). Pascal denounced casuistry as the mere use of complex reasoning to justify moral laxity and all sorts of sins. The 18-letter series was published between 1656 and 1657 under the pseudonym Louis de Montalte and incensed Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
. The king ordered that the book be shredded and burnt in 1660. In 1661, in the midsts of the formulary controversy, the Jansenist school at Port-Royal was condemned and closed down; those involved with the school had to sign a 1656 papal bull condemning the teachings of Jansen as heretical. The final letter from Pascal, in 1657, had defied Alexander VII
Pope Alexander VII ( it, Alessandro VII; 13 February 159922 May 1667), born Fabio Chigi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 April 1655 to his death in May 1667.
He began his career as a vice-papal legate, an ...
himself. Even Pope Alexander, while publicly opposing them, nonetheless was persuaded by Pascal's arguments.
Aside from their religious influence, the ''Provincial Letters'' were popular as a literary work. Pascal's use of humor, mockery, and vicious satire in his arguments made the letters ripe for public consumption, and influenced the prose of later French writers like Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his '' nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—e ...
and Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
.
It is in the ''Provincial Letters'' that Pascal made his oft-quoted apology for writing a long letter, as he had not had time to write a shorter one.
From Letter XVI, as translated by Thomas M'Crie:
'Reverend fathers, my letters were not wont either to be so prolix, or to follow so closely on
one another. Want of time must plead my excuse for both of these faults. The present letter is
a very long one, simply because I had no leisure to make it shorter.'
Charles Perrault wrote of the ''Letters'': "Everything is there—purity of language, nobility of thought, solidity in reasoning, finesse in raillery, and throughout an ''agrément'' not to be found anywhere else."
Philosophy
Pascal is arguably best known as a philosopher, considered by some the second greatest French mind behindRené Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Ma ...
. He was a dualist following Descartes. However, he is also remembered for his opposition to both the rationalism
In philosophy, rationalism is the epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification".Lacey, A.R. (1996), ''A Dictionary of Philosophy' ...
of the likes of Descartes and simultaneous opposition to the main countervailing epistemology, empiricism
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological theory that holds that knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience. It is one of several views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empir ...
, preferring fideism
Fideism () is an epistemological theory which maintains that faith is independent of reason, or that reason and faith are hostile to each other and faith is superior at arriving at particular truths (see natural theology). The word ''fideism'' c ...
.
He cared above all about the philosophy of religion. Pascalian theology has grown out of his perspective that humans are, according to Wood, "born into a duplicitous world that shapes us into duplicitous subjects and so we find it easy to reject God continually and deceive ourselves about our own sinfulness".
Philosophy of mathematics
Pascal's major contribution to thephilosophy of mathematics
The philosophy of mathematics is the branch of philosophy that studies the assumptions, foundations, and implications of mathematics. It aims to understand the nature and methods of mathematics, and find out the place of mathematics in people' ...
came with his ''De l'Esprit géométrique'' ("Of the Geometrical Spirit"), originally written as a preface to a geometry textbook for one of the famous Petites écoles de Port-Royal ("Little Schools of Port-Royal"). The work was unpublished until over a century after his death. Here, Pascal looked into the issue of discovering truths, arguing that the ideal of such a method would be to found all propositions on already established truths. At the same time, however, he claimed this was impossible because such established truths would require other truths to back them up—first principles, therefore, cannot be reached. Based on this, Pascal argued that the procedure used in geometry was as perfect as possible, with certain principles assumed and other propositions developed from them. Nevertheless, there was no way to know the assumed principles to be true.
Pascal also used ''De l'Esprit géométrique'' to develop a theory of definition. He distinguished between definitions which are conventional labels defined by the writer and definitions which are within the language and understood by everyone because they naturally designate their referent. The second type would be characteristic of the philosophy of essentialism
Essentialism is the view that objects have a set of attributes that are necessary to their identity. In early Western thought, Plato's idealism held that all things have such an "essence"—an "idea" or "form". In ''Categories'', Aristotle sim ...
. Pascal claimed that only definitions of the first type were important to science and mathematics, arguing that those fields should adopt the philosophy of formalism
Formalism may refer to:
* Form (disambiguation)
* Formal (disambiguation)
* Legal formalism, legal positivist view that the substantive justice of a law is a question for the legislature rather than the judiciary
* Formalism (linguistics)
* Scien ...
as formulated by Descartes.
In ''De l'Art de persuader'' ("On the Art of Persuasion"), Pascal looked deeper into geometry's axiomatic method
In mathematics and logic, an axiomatic system is any set of axioms from which some or all axioms can be used in conjunction to logically derive theorems. A theory is a consistent, relatively-self-contained body of knowledge which usually contai ...
, specifically the question of how people come to be convinced of the axioms upon which later conclusions are based. Pascal agreed with Montaigne that achieving certainty in these axioms and conclusions through human methods is impossible. He asserted that these principles can be grasped only through intuition, and that this fact underscored the necessity for submission to God in searching out truths.
Pensées
:::::Blaise Pascal, ''Pensées'' No. 200 Pascal's most influential theological work, referred to posthumously as the ''Pensées'' ("Thoughts") is widely considered to be a masterpiece, and a landmark in ''French prose''. When commenting on one particular section (Thought #72),
Pascal's most influential theological work, referred to posthumously as the ''Pensées'' ("Thoughts") is widely considered to be a masterpiece, and a landmark in ''French prose''. When commenting on one particular section (Thought #72), Sainte-Beuve
Charles Augustin Sainte-Beuve (; 23 December 1804 – 13 October 1869) was a French literary critic.
Early life
He was born in Boulogne, educated there, and studied medicine at the Collège Charlemagne in Paris (1824–27). In 1828, he s ...
praised it as the finest pages in the French language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in N ...
.Sainte-Beuve''Seventeenth Century''
p. 174 (2009 reprint). Will Durant hailed the Pensées as "the most eloquent book in French prose".'' The Story of Civilization: Volume 8, "The Age of Louis XIV"'' by Will & Ariel Durant, chapter II, Subsection 4.4, p. 66 The ''Pensées'' was not completed before his death. It was to have been a sustained and coherent examination and defense of the
Christian faith
Christianity is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism, monotheistic religion based on the Life of Jesus in the New Testament, life and Teachings of Jesus, teachings of Jesus, Jesus of Nazareth. It is the Major religious groups, world's ...
, with the original title ''Apologie de la religion Chrétienne'' ("Defense of the Christian Religion"). The first version of the numerous scraps of paper found after his death appeared in print as a book in 1669 titled ''Pensées de M. Pascal sur la religion, et sur quelques autres sujets'' ("Thoughts of M. Pascal on religion, and on some other subjects") and soon thereafter became a classic.
One of the ''Apologie''s main strategies was to use the contradictory philosophies of Pyrrhonism
Pyrrhonism is a school of philosophical skepticism founded by Pyrrho in the fourth century BCE. It is best known through the surviving works of Sextus Empiricus, writing in the late second century or early third century CE.
History
Pyrrho of ...
and Stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asserting tha ...
, personalized by Montaigne on one hand, and Epictetus on the other, in order to bring the unbeliever to such despair and confusion that he would embrace God.
Last works and death
''Of Men and Numbers''
(New York: Dover Publications, Inc, 1996). , p. 104. Louis XIV suppressed the Jansenist movement at Port-Royal in 1661. In response, Pascal wrote one of his final works, ''Écrit sur la signature du formulaire'' ("Writ on the Signing of the Form"), exhorting the Jansenists not to give in. Later that year, his sister Jacqueline died, which convinced Pascal to cease his polemics on Jansenism. Pascal's last major achievement, returning to his mechanical genius, was inaugurating perhaps the first bus line, the carrosses à cinq sols, moving passengers within Paris in a carriage with many seats. Pascal also designated the operation principles which were later used to plan public transportation: The carriages has a fixed route, fixed price, and left even if there were no passengers. It is widely considered that the idea of public transportation was well ahead of time. The lines were not commercially successful, and the last one closed by 1675. In 1662, Pascal's illness became more violent, and his emotional condition had severely worsened since his sister's death. Aware that his health was fading quickly, he sought a move to the hospital for incurable diseases, but his doctors declared that he was too unstable to be carried. In Paris on 18 August 1662, Pascal went into convulsions and received extreme unction. He died the next morning, his last words being "May God never abandon me," and was buried in the cemetery of
Saint-Étienne-du-Mont
Saint-Étienne-du-Mont is a church in Paris, France, on the Montagne Sainte-Geneviève in the 5th arrondissement, near the Panthéon. It contains the shrine of St. Geneviève, the patron saint of Paris. The church also contains the tombs of ...
.
An autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any d ...
performed after his death revealed grave problems with his stomach and other organs of his abdomen, along with damage to his brain. Despite the autopsy, the cause of his poor health was never precisely determined, though speculation focuses on tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
, stomach cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Ly ...
, or a combination of the two.Muir, Jane''Of Men and Numbers''
(New York: Dover Publications, Inc, 1996). , p. 103. The headaches which affected Pascal are generally attributed to his brain
lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
.
Legacy
=Cultural references
= One of the Universities of
One of the Universities of Clermont-Ferrand
Clermont-Ferrand (, ; ; oc, label= Auvergnat, Clarmont-Ferrand or Clharmou ; la, Augustonemetum) is a city and commune of France, in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, with a population of 146,734 (2018). Its metropolitan area (''aire d'attrac ...
, France – Université Blaise Pascal – is named after him. Établissement scolaire français Blaise-Pascal in Lubumbashi
Lubumbashi (former names: (French), ( Dutch)) is the second-largest city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, located in the country's southeasternmost part, along the border with Zambia. The capital and principal city of the Haut-Katan ...
, Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
is named after Pascal.
The 1969 Eric Rohmer film '' My Night at Maud's'' is based on the work of Pascal. Roberto Rossellini
Roberto Gastone Zeffiro Rossellini (8 May 1906 – 3 June 1977) was an Italian film director, producer, and screenwriter. He was one of the most prominent directors of the Italian neorealist cinema, contributing to the movement with films such ...
directed a filmed biopic, ''Blaise Pascal'', which originally aired on Italian television in 1971. Pascal was a subject of the first edition of the 1984 BBC Two
BBC Two is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network owned and operated by the BBC. It covers a wide range of subject matter, with a remit "to broadcast programmes of depth and substance" in contrast to the more mainstream a ...
documentary, '' Sea of Faith'', presented by Don Cupitt. The chameleon in the film '' Tangled'' is named for Pascal
Pascal, Pascal's or PASCAL may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Pascal (given name), including a list of people with the name
* Pascal (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
** Blaise Pascal, Frenc ...
.
A programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language.
The description of a programming ...
is named for Pascal. In 2014, Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
announced its new Pascal microarchitecture, which is named for Pascal. The first graphics cards featuring Pascal were released in 2016.
The 2017 game '' Nier: Automata'' has multiple characters named after famous philosophers; one of these is a sentient pacifistic machine named Pascal, who serves as a major supporting character. Pascal creates a village for machines to live peacefully with the androids they're at war with and acts as a parental figure for other machines trying to adapt to their newly-found individuality.
The otter in the '' Animal Crossing'' series is named for Pascal.
Minor planet 4500 Pascal is named in his honor.
Pope Paul VI
Pope Paul VI ( la, Paulus VI; it, Paolo VI; born Giovanni Battista Enrico Antonio Maria Montini, ; 26 September 18976 August 1978) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City, Vatican City State from 21 June 1963 to his ...
, in encyclical '' Populorum progressio'', quotes Pascal's ''Pensées'':
Works
* "Essai pour les coniques" ssay on conics(1639) * ''Experiences nouvelles touchant le vide'' ew experiments with the vacuum(1647) * ''Récit de la grande expérience de l'équilibre des liqueurs'' ccount of the great experiment on equilibrium in liquids(1648) * ''Traité du triangle arithmétique'' reatise on the arithmetical triangle(written c. 1654; publ. 1665) * '' Lettres provinciales'' he provincial letters(1656–57) * ''De l'Esprit géométrique'' n the geometrical spirit(1657 or 1658) * ''Écrit sur la signature du formulaire'' (1661) * ''Pensées
The ''Pensées'' ("Thoughts") is a collection of fragments written by the French 17th-century philosopher and mathematician Blaise Pascal. Pascal's religious conversion led him into a life of asceticism, and the ''Pensées'' was in many ways hi ...
'' houghts(incomplete at death; publ. 1670)
* " Discourse on the Passion of Love"
* " On the Conversion of the Sinner"
See also
*Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean of a ...
* Gambler's ruin
The gambler's ruin is a concept in statistics. It is most commonly expressed as follows: A gambler playing a game with negative expected value will eventually go broke, regardless of their betting system.
The concept was initially stated: A pers ...
* Pascal's barrel
* Pascal distribution
* Pascal's mugging
* Pascal's pyramid
* Pascal's simplex
* Problem of points
* Scientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transforme ...
* List of pioneers in computer science
* List of works by Eugène Guillaume
References
Further reading
* Adamson, Donald. ''Blaise Pascal: Mathematician, Physicist, and Thinker about God'' (1995) * Adamson, Donald"Pascal's Views on Mathematics and the Divine,"
''Mathematics and the Divine: A Historical Study'' (eds. T. Koetsier and L. Bergmans. Amsterdam: Elsevier 2005), pp. 407–21. * Broome, J.H. ''Pascal''. (London: E. Arnold, 1965). * Campe, Rüdiger, "Numbers and Calculation in Context: The Game of Decision - Pascal" in The ''Game of Probability. Literature and Calculation from Pascal and Kleist'', Stanford University Press, 2012 *Davidson, Hugh M. ''Blaise Pascal''. (Boston: Twayne Publishers), 1983. * * Farrell, John. "Pascal and Power". Chapter seven of ''Paranoia and Modernity: Cervantes to Rousseau'' (Cornell UP, 2006). * Goldmann, Lucien, ''The hidden God; a study of tragic vision in the Pensees of Pascal and the tragedies of Racine'' (original ed. 1955, Trans. Philip Thody. London: Routledge, 1964). * Groothuis, Douglas. ''On Pascal''. (Belmont: Wadsworth, 2002). * Jordan, Jeff. ''Pascal's Wager: Pragmatic Arguments and Belief in God''. (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 2006). * Landkildehus, Søren. "Kierkegaard and Pascal as kindred spirits in the Fight against Christendom" in ''Kierkegaard and the Renaissance and Modern Traditions'' (ed. Jon Stewart. Farnham: Ashgate Publishing, 2009). * Mackie, John Leslie. ''The Miracle of Theism: Arguments for and against the Existence of God''. (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1982). * Stafford Harry Northcote, Viscount Saint Cyres, ''Pascal'' (London: Smith, Elder & Company, 1909; New York: E. P. Dutton) * Pugh, Anthony R. ''The Composition of Pascal's Apologia'', (University of Toronto Press, 1984). * * * * Tobin, Paul. "The Rejection of Pascal's Wager: A Skeptic's Guide to the Bible and the Historical Jesus". authorsonline.co.uk, 2009. * Yves Morvan, ''Pascal à Mirefleurs ? Les dessins de la maison de Domat'', Impr. Blandin, 1985. (FRBNF40378895)
External links
Oeuvres complètes, volume 2
(1858) Paris: Libraire de L Hachette et Cie, link from
HathiTrust
HathiTrust Digital Library is a large-scale collaborative repository of digital content from research libraries including content digitized via Google Books and the Internet Archive digitization initiatives, as well as content digitized locall ...
.
*
*
*The Correspondence of Blaise Pascal
i
EMLO
* * * * ''Pensées de Blaise Pascal''. Renouard, Paris 1812 (2 vols.) ()
Discussion of the Pascaline, its history, mechanism, surviving examples, and modern replicas at http://things-that-count.net
in orig. French/Latin and modern English, trans. Elizabeth T. Knuth.
(in French) *
BBC Radio 4. In Our Time: Pascal.
* ttp://www.intratext.com/Catalogo/Autori/Aut852.htm Blaise Pascal's works text, concordances and frequency lists * * Etext of Pascal's
Pensées
' (English, in various formats) * Etext of Pascal's
' (English) * Etext of a number of Pascal'
minor works
(English translation) including, ''De l'Esprit géométrique'' and ''De l'Art de persuader''. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Pascal, Blaise 1623 births 1662 deaths Writers from Clermont-Ferrand French Roman Catholic writers 17th-century French writers 17th-century male writers 17th-century French mathematicians 17th-century philosophers Aphorists Christian apologists Christian humanists Roman Catholic mystics Critics of atheism Converts to Roman Catholicism Fluid dynamicists French mathematicians French philosophers French physicists 17th-century French theologians 17th-century Christian mystics Hypochondriacs Jansenists Probability theorists Catholic philosophers 17th-century Roman Catholics Burials at Saint-Étienne-du-Mont Cartesianism Scientists from Clermont-Ferrand