Bison Palaeosinensis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bison are large
 The American bison and the European bison (wisent) are the largest surviving terrestrial animals in North America and Europe. They are typical
The American bison and the European bison (wisent) are the largest surviving terrestrial animals in North America and Europe. They are typical
"American Bison", The National Wildlife Federation. and up to in heightSemenov U.A. of World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF-Russia, 2014, "The Wisents of Karachay-Cherkessia", Proceedings of the Sochi National Park (8), pp.23-24, , KMK Scientific Press and in length for European bison.Hendricks, K
"''Bison bonasus'', European bison"
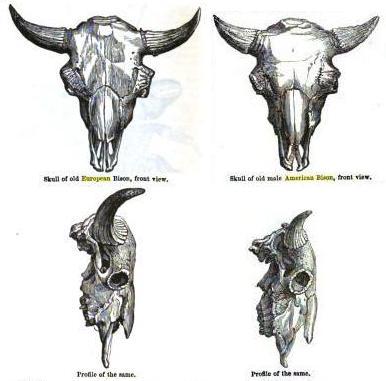
Animal Diversity Web, 2013. American bison can weigh from around and European bison can weigh from . European bison tend to be taller than American bison. Bison are nomadic grazers and travel in Although superficially similar, physical and behavioural differences exist between the American and European bison. The American species has 15 ribs, while the European bison has 14. The American bison has four lumbar vertebrae, while the European has five. (The difference in this case is that what would be the first lumbar vertebra has ribs attached to it in American bison and is thus counted as the 15th thoracic vertebra, compared to 14 thoracic vertebrae in wisent.) Adult American bison are less slim in build and have shorter legs. American bison tend to graze more, and browse less than their European relatives. Their anatomies reflect this behavioural difference; the American bison's head hangs lower than the European's. The body of the American bison is typically hairier, though its tail has less hair than that of the European bison. The horns of the European bison point through the plane of their faces, making them more adept at fighting through the interlocking of horns in the same manner as domestic cattle, unlike the American bison, which favours butting. American bison are more easily tamed than their European cousins, and breed with domestic cattle more readily.
Although superficially similar, physical and behavioural differences exist between the American and European bison. The American species has 15 ribs, while the European bison has 14. The American bison has four lumbar vertebrae, while the European has five. (The difference in this case is that what would be the first lumbar vertebra has ribs attached to it in American bison and is thus counted as the 15th thoracic vertebra, compared to 14 thoracic vertebrae in wisent.) Adult American bison are less slim in build and have shorter legs. American bison tend to graze more, and browse less than their European relatives. Their anatomies reflect this behavioural difference; the American bison's head hangs lower than the European's. The body of the American bison is typically hairier, though its tail has less hair than that of the European bison. The horns of the European bison point through the plane of their faces, making them more adept at fighting through the interlocking of horns in the same manner as domestic cattle, unlike the American bison, which favours butting. American bison are more easily tamed than their European cousins, and breed with domestic cattle more readily.
 During the population bottleneck, after the great slaughter of American bison during the 19th century, the number of bison remaining alive in North America declined to as low as 541. During that period, a handful of ranchers gathered remnants of the existing herds to save the species from extinction. These ranchers bred some of the bison with cattle in an effort to produce "cattleo" (today called "
During the population bottleneck, after the great slaughter of American bison during the 19th century, the number of bison remaining alive in North America declined to as low as 541. During that period, a handful of ranchers gathered remnants of the existing herds to save the species from extinction. These ranchers bred some of the bison with cattle in an effort to produce "cattleo" (today called "

nps.gov Their most obvious weapons are the horns borne by both males and females, but their massive heads can be used as battering rams, effectively using the momentum produced by what is a typical weight of moving at . The hind legs can also be used to kill or maim with devastating effect. In the words of early naturalists, they were dangerous, savage animals that feared no other animal and in prime condition could best any foe (except for wolves and brown bears). The rutting, or mating, season lasts from June through September, with peak activity in July and August. At this time, the older bulls rejoin the herd, and fights often take place between bulls. The herd exhibits much restlessness during breeding season. The animals are belligerent, unpredictable, and most dangerous.
 Bison are ruminants, which gives them the ability to ferment plants in a specialized stomach prior to digesting them. Bison were once thought to almost exclusively consume grasses and sedges, but are now known to consume a wide-variety of plants including woody plants and herbaceous eudicots. Over the course of the year, bison shift which plants they select in their diet based on which plants have the highest protein or energy concentrations at a given time and will reliably consume the same species of plants across years. Protein concentrations of the plants they eat tend to be highest in the spring and decline thereafter, reaching their lowest in the winter. In Yellowstone National Park, bison browsed willows and cottonwoods, not only in the winter when few other plants are available, but also in the summer. Bison are thought to migrate to optimize their diet, and will concentrate their feeding on recently burned areas due to the higher quality forage that regrows after the burn. Wisent tend to browse on shrubs and low-hanging trees more often than do the American bison, which prefer grass to shrubbery and trees.
Bison are ruminants, which gives them the ability to ferment plants in a specialized stomach prior to digesting them. Bison were once thought to almost exclusively consume grasses and sedges, but are now known to consume a wide-variety of plants including woody plants and herbaceous eudicots. Over the course of the year, bison shift which plants they select in their diet based on which plants have the highest protein or energy concentrations at a given time and will reliably consume the same species of plants across years. Protein concentrations of the plants they eat tend to be highest in the spring and decline thereafter, reaching their lowest in the winter. In Yellowstone National Park, bison browsed willows and cottonwoods, not only in the winter when few other plants are available, but also in the summer. Bison are thought to migrate to optimize their diet, and will concentrate their feeding on recently burned areas due to the higher quality forage that regrows after the burn. Wisent tend to browse on shrubs and low-hanging trees more often than do the American bison, which prefer grass to shrubbery and trees.
 Owing to their size, bison have few predators. Five notable exceptions are
Owing to their size, bison have few predators. Five notable exceptions are
 European settlers were almost exclusively accountable for the near-extinction of the American bison in the 1800s. At the beginning of the century, tens of millions of bison roamed North America. Pioneers and settlers slaughtered an estimated 50 million bison during the 19th century, although the causes of decline and the numbers killed are disputed and debated. Railroads were advertising "hunting by rail", where trains encountered large herds alongside or crossing the tracks. Men aboard fired from the train's roof or windows, leaving countless animals to rot where they died. This overhunting was in part motivated by the U.S. government's desire to limit the range and power of indigenous plains Indians whose diets and cultures depended on the buffalo herds. The overhunting of the bison reduced their population to hundreds.
The American bison's nadir came in 1889, with an estimated population of only 1,091 animals (both wild and captive). Repopulation attempts via enforced protection of government herds and extensive
European settlers were almost exclusively accountable for the near-extinction of the American bison in the 1800s. At the beginning of the century, tens of millions of bison roamed North America. Pioneers and settlers slaughtered an estimated 50 million bison during the 19th century, although the causes of decline and the numbers killed are disputed and debated. Railroads were advertising "hunting by rail", where trains encountered large herds alongside or crossing the tracks. Men aboard fired from the train's roof or windows, leaving countless animals to rot where they died. This overhunting was in part motivated by the U.S. government's desire to limit the range and power of indigenous plains Indians whose diets and cultures depended on the buffalo herds. The overhunting of the bison reduced their population to hundreds.
The American bison's nadir came in 1889, with an estimated population of only 1,091 animals (both wild and captive). Repopulation attempts via enforced protection of government herds and extensive
Conservation of North American bison: status and recommendations (PDF)
(Thesis). University of Calgary, Calgary, AB. – via Buffalo Field Campaign * Cunfer, Geoff and Bill Waiser. ''Bison and People on the North American Great Plains: A Deep Environmental History''. College Station, TX: Texas A&M University Press, 2016. * * *
History of Bison Blend Cattle
{{Authority control Holarctic fauna Mammal genera Extant Gelasian first appearances Taxa named by Charles Hamilton Smith
bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship betwe ...
s in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini
The tribe Bovini, or wild cattle, are medium to massive bovines that are native to North America, Eurasia, and Africa. These include the enigmatic, antelope-like saola, the African and Asiatic buffalos, and a clade that consists of bison and the ...
. Two extant
Extant is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extin ...
and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison
The American bison (''Bison bison'') is a species of bison native to North America. Sometimes colloquially referred to as American buffalo or simply buffalo (a different clade of bovine), it is one of two extant species of bison, alongside the ...
, ''B. bison'', found only in North America, is the more numerous. Although colloquially referred to as a buffalo in the United States and Canada, it is only distantly related to the true buffalo
Bubalina is a subtribe of wild cattle that includes the various species of true buffalo. Species include the African buffalo, the anoas, and the wild water buffalo (including the domesticated variant water buffalo). Buffaloes can be found na ...
. The North American species is composed of two subspecies, the Plains bison
The Plains bison (''Bison bison bison'') is one of two subspecies/ecotypes of the American bison, the other being the wood bison (''B. b. athabascae''). A natural population of Plains bison survives in Yellowstone National Park (the Yellowstone ...
, ''B. b. bison'', and the wood bison, ''B. b. athabascae'', which is the namesake of Wood Buffalo National Park in Canada. A third subspecies, the eastern bison (''B. b. pennsylvanicus'') is no longer considered a valid taxon, being a junior synonym of ''B. b. bison''. References to "woods bison" or "wood bison" from the eastern United States refer to this subspecies, not ''B. b. athabascae'', which was not found in the region. The European bison, ''B. bonasus'', or wisent, or zubr, or colloquially European buffalo, is found in Europe and the Caucasus, reintroduced after being extinct in the wild
A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due t ...
.
While bison species have been traditionally classified in their own genus, modern genetics indicates that they are nested within the genus ''Bos
''Bos'' (from Latin '' bōs'': cow, ox, bull) is the genus of wild and domestic cattle. ''Bos'' is often divided into four subgenera: ''Bos'', ''Bibos'', ''Novibos'', and ''Poephagus'', but including these last three divisions within the ge ...
,'' which includes, among others, cattle, yak
The domestic yak (''Bos grunniens''), also known as the Tartary ox, grunting ox or hairy cattle, is a species of long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Kachin Sta ...
s and gaur, being most closely related to yaks. Bison are sometimes bred with domestic cattle and produce offspring called beefalo
Beefalo constitute a hybrid offspring of domestic cattle (''Bos taurus''), usually a male in managed breeding programs, and the American bison (''Bison bison''), usually a female in managed breeding programs. The breed was created to combine the ...
or zubron.
Description
 The American bison and the European bison (wisent) are the largest surviving terrestrial animals in North America and Europe. They are typical
The American bison and the European bison (wisent) are the largest surviving terrestrial animals in North America and Europe. They are typical artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
(cloven hooved) ungulates, and are similar in appearance to other bovines such as cattle and true buffalo. They are broad and muscular with shaggy coats of long hair. Adults grow up to in height and in length for American bisonGennady G. Boeskorov, Olga R. Potapova, Albert V. Protopopov, Valery V. Plotnikov, Larry D. Agenbroad, Konstantin S. Kirikov, Innokenty S. Pavlov, Marina V. Shchelchkova, Innocenty N. Belolyubskii, Mikhail D. Tomshin, Rafal Kowalczyk, Sergey P. Davydov, Stanislav D. Kolesov, Alexey N. Tikhonov, Johannes van der Plicht, 2016, The Yukagir Bison: The exterior morphology of a complete frozen mummy of the extinct steppe bison, ''Bison priscus'' from the early Holocene of northern Yakutia, Russia, pp.7, Quaternary International
''Quaternary International'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal on quaternary science published by Elsevier on behalf of the International Union for Quaternary Research. The journal was established in 1989 and covers full spectrum of the physic ...
, Vol.406 (25 June 2016), Part B, pp.94-110"American Bison", The National Wildlife Federation. and up to in heightSemenov U.A. of World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF-Russia, 2014, "The Wisents of Karachay-Cherkessia", Proceedings of the Sochi National Park (8), pp.23-24, , KMK Scientific Press and in length for European bison.Hendricks, K
"''Bison bonasus'', European bison"
Animal Diversity Web, 2013. American bison can weigh from around and European bison can weigh from . European bison tend to be taller than American bison. Bison are nomadic grazers and travel in
herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called ''herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' i ...
s. The bulls leave the herds of females at two or three years of age, and join a herd of males, which are generally smaller than female herds. Mature bulls rarely travel alone. Towards the end of the summer, for the reproductive season, the sexes necessarily commingle.
American bison are known for living in the Great Plains, but formerly had a much larger range, including much of the eastern United States and parts of Mexico. Both species were hunted close to extinction during the 19th and 20th centuries, but have since rebounded. The wisent in part owes its survival to the Chernobyl disaster, as the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Zone of Alienation, Belarusian: Хона адчужэння Чарнобыльскай АЭС, ''Zona adčužennia Čarnobyĺskaj AES'', russian: Зона отчуждения Чернобыльской АЭС, ...
has become a kind of wildlife preserve for wisent and other rare megafauna such as the Przewalski's horse
Przewalski's horse (, , (Пржевальский ), ) (''Equus ferus przewalskii'' or ''Equus przewalskii''), also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered horse originally native to the steppes of ...
, though poaching has become a threat in recent years. The American Plains bison is no longer listed as endangered, but this does not mean the species is secure. Genetically pure ''B. b. bison'' currently number only about 20,000, separated into fragmented herds—all of which require active conservation measures. The wood bison is on the endangered species list in Canada and is listed as threatened in the United States, though numerous attempts have been made by beefalo
Beefalo constitute a hybrid offspring of domestic cattle (''Bos taurus''), usually a male in managed breeding programs, and the American bison (''Bison bison''), usually a female in managed breeding programs. The breed was created to combine the ...
ranchers to have it entirely removed from the Endangered Species List
On 29 January 2010, the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species identified 5220 (2754 animals, 1 fungus, 2464 plant, 1 protist) endangered species, subspecies and varieties, stocks and sub-populations.
For IUCN lists of endangered species by kingdom ...
.
 Although superficially similar, physical and behavioural differences exist between the American and European bison. The American species has 15 ribs, while the European bison has 14. The American bison has four lumbar vertebrae, while the European has five. (The difference in this case is that what would be the first lumbar vertebra has ribs attached to it in American bison and is thus counted as the 15th thoracic vertebra, compared to 14 thoracic vertebrae in wisent.) Adult American bison are less slim in build and have shorter legs. American bison tend to graze more, and browse less than their European relatives. Their anatomies reflect this behavioural difference; the American bison's head hangs lower than the European's. The body of the American bison is typically hairier, though its tail has less hair than that of the European bison. The horns of the European bison point through the plane of their faces, making them more adept at fighting through the interlocking of horns in the same manner as domestic cattle, unlike the American bison, which favours butting. American bison are more easily tamed than their European cousins, and breed with domestic cattle more readily.
Although superficially similar, physical and behavioural differences exist between the American and European bison. The American species has 15 ribs, while the European bison has 14. The American bison has four lumbar vertebrae, while the European has five. (The difference in this case is that what would be the first lumbar vertebra has ribs attached to it in American bison and is thus counted as the 15th thoracic vertebra, compared to 14 thoracic vertebrae in wisent.) Adult American bison are less slim in build and have shorter legs. American bison tend to graze more, and browse less than their European relatives. Their anatomies reflect this behavioural difference; the American bison's head hangs lower than the European's. The body of the American bison is typically hairier, though its tail has less hair than that of the European bison. The horns of the European bison point through the plane of their faces, making them more adept at fighting through the interlocking of horns in the same manner as domestic cattle, unlike the American bison, which favours butting. American bison are more easily tamed than their European cousins, and breed with domestic cattle more readily.
Evolution and genetic history
The bovine tribe (Bovini) split about 5 to 10 million years ago into the buffalos (''Bubalus
''Bubalus'' is a genus of Asiatic bovines that was proposed by Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. ''Bubalus'' and ''Syncerus'' form the subtribe Bubalina, the true buffaloes.
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and classification of ...
'' and ''Syncerus
''Syncerus'' is a genus of African bovid that contains the living Cape buffalo ''(Syncerus caffer)'', including the distinct African forest buffalo.
At least one extinct species belongs to this genus; ''Syncerus acoelotus''. The extinct giant ...
'') and a group leading to bison and taurine cattle. Genetic evidence from nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It ...
indicates that the closest living relatives of bison are yaks
The domestic yak (''Bos grunniens''), also known as the Tartary ox, grunting ox or hairy cattle, is a species of long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Kachin ...
, with bison being nested within the genus ''Bos
''Bos'' (from Latin '' bōs'': cow, ox, bull) is the genus of wild and domestic cattle. ''Bos'' is often divided into four subgenera: ''Bos'', ''Bibos'', ''Novibos'', and ''Poephagus'', but including these last three divisions within the ge ...
,'' rendering ''Bos'' without including bison paraphyletic. While nuclear DNA indicates that both extant bison species are each others closest living relatives, the mitochondrial DNA of European bison is more closely related to that of domestic cattle and aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius'') ( or ) is an extinct cattle species, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of the largest herbivores in the Holocene ...
(while the mitochondrial DNA of American bison is closely related to that of yaks). This discrepancy is either suggested to be the result of incomplete lineage sorting
Incomplete lineage sorting, also termed hemiplasy, deep coalescence, retention of ancestral polymorphism, or trans-species polymorphism, describes a phenomenon in population genetics when ancestral gene copies fail to coalesce (looking backwards i ...
or ancient introgression
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Intro ...
.Wang, K., Lenstra, J. A., Liu, L., Hu, Q., Ma, T., Qiu, Q., & Liu, J. (2018). Incomplete lineage sorting rather than hybridization explains the inconsistent phylogeny of the wisent. Communications biology, 1(1), 1-9. Bison are widely believed to have evolved from a lineage belonging to the extinct genus ''Leptobos
''Leptobos'' is an extinct genus of large bovine, known from the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene of Eurasia, extending from the Iberian Peninsula to northern China. Species of ''Leptobos'' reached a weight up to 320 kg. ''Leptobos'' is cons ...
'' during the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
in Asia. The earliest members of the bison lineage, known from the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of the Indian Subcontinent (''Bison sivalensis'') and China (''Bison palaeosinensis''), approximately 3.4-2.6 million years ago (Ma) are placed in the subgenus ''Bison'' (''Eobison'')''.'' The oldest remains of ''Eobison'' in Europe are those ''Bison georgicus'' found in Dmanisi, Georgia, dated to around 1.76 Ma. More derived
Derive may refer to:
*Derive (computer algebra system), a commercial system made by Texas Instruments
* ''Dérive'' (magazine), an Austrian science magazine on urbanism
*Dérive, a psychogeographical concept
See also
*
*Derivation (disambiguation ...
members of the genus are placed in the subgenus ''Bison'' (''Bison''), which first appeared towards the end of the Early Pleistocene, around 1.2 Ma, with early members of the subgenus including the widespread ''Bison schoetensacki
''Bison schoetensacki'', commonly as the Pleistocene woodland bison or Pleistocene wood bison, was a species of bison that lived until from the Early Pleistocene to at least the early Middle Pleistocene from western Europe to southern Siberia. It ...
''.
The steppe bison
The steppe bisonSeveral literatures address the species as ''primeval bison''. or steppe wisent (''Bison'' ''priscus'')
– Y ...
(''Bison priscus'') first appeared during the mid-– Y ...
Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. Th ...
in eastern Eurasia, and subsequently became widely distributed across Eurasia. During the late Middle Pleistocene, around 195,000-135,000 years ago, the steppe bison migrated across the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip o ...
into North America, becoming ancestral to modern American bison, as well as extinct forms such as the largest known bison, the long-horned ''Bison latifrons
''Bison latifrons'', also known as the giant bison or long-horned bison, is an extinct species of bison that lived in North America during the Pleistocene epoch ranging from Alaska to Mexico. It was the largest and heaviest bovid ever to live in ...
,'' and the smaller ''Bison antiquus
''Bison antiquus'', the antique bison or ancient bison, is an extinct species of bison that lived in Late Pleistocene North America until around 10,000 years ago. It was one of the most common large herbivores on the North American continent dur ...
,'' which became extinct at the end of the Late Pleistocene. Modern American bison are thought to have evolved from ''B. antiquus'' during the Late Pleistocene-Holocene transition via the intermediate form ''Bison occidentalis
''Bison occidentalis'' is an extinct species of bison that lived in North America, and in continental EurasiaC. G Van Zyll de Jong , 1986, A systematic study of recent bison, with particular consideration of the wood bison (Bison bison athabascae ...
''. The European bison, ''Bison bonasus,'' first appeared in Europe during the late Middle Pleistocene, where it existed in sympatry with the steppe bison. Its relationship with other extinct bison species is unclear, though it appears to be only distantly related to the steppe and American bisons, with possibly some interbreeding between the two lineages during the Middle Pleistocene. The steppe bison survived into the early-mid Holocene in Alaska-Yukon and eastern Siberia, before becoming extinct.
 During the population bottleneck, after the great slaughter of American bison during the 19th century, the number of bison remaining alive in North America declined to as low as 541. During that period, a handful of ranchers gathered remnants of the existing herds to save the species from extinction. These ranchers bred some of the bison with cattle in an effort to produce "cattleo" (today called "
During the population bottleneck, after the great slaughter of American bison during the 19th century, the number of bison remaining alive in North America declined to as low as 541. During that period, a handful of ranchers gathered remnants of the existing herds to save the species from extinction. These ranchers bred some of the bison with cattle in an effort to produce "cattleo" (today called "beefalo
Beefalo constitute a hybrid offspring of domestic cattle (''Bos taurus''), usually a male in managed breeding programs, and the American bison (''Bison bison''), usually a female in managed breeding programs. The breed was created to combine the ...
") Accidental crossings were also known to occur. Generally, male domestic bulls were crossed with bison cows, producing offspring of which only the females were fertile. The crossbred animals did not demonstrate any form of hybrid vigor, so the practice was abandoned. Wisent-American bison hybrids were briefly experimented with in Germany (and found to be fully fertile) and a herd of such animals is maintained in Russia. A herd of cattle-wisent crossbreeds ( zubron) is maintained in Poland. First-generation crosses do not occur naturally, requiring caesarean delivery. First-generation males are infertile. The U.S. National Bison Association has adopted a code of ethics that prohibits its members from deliberately crossbreeding bison with any other species. In the United States, many ranchers are now using DNA testing to cull the residual cattle genetics from their bison herds. The proportion of cattle DNA that has been measured in introgressed individuals and bison herds today is typically quite low, ranging from 0.56 to 1.8%.
There are also remnant purebred American bison herds on public lands in North America. Herds of importance are found in Yellowstone National Park, Wind Cave National Park in South Dakota, Blue Mounds State Park
Blue Mounds State Park is a state park of Minnesota, USA, in Rock County near the town of Luverne. It protects an American bison herd which grazes on one of the state's largest prairie remnants.
The state park is named after a linear escarpm ...
in Minnesota, Elk Island National Park
Elk Island National Park is a national park in Alberta, Canada, that played an important part in the conservation of the Plains bison. The park is administered by the Parks Canada Agency. This "island of conservation" is east of Edmonton, alon ...
in Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Terri ...
, and Grasslands National Park
Grasslands National Park (French: ') is a Canadian national park located near the village of Val Marie, Saskatchewan, and one of 44 national parks and park reserves in Canada's national park system (though one of only two in Saskatchewan it ...
in Saskatchewan. In 2015, a purebred herd of 350 individuals was identified on public lands in the Henry Mountains of southern Utah via genetic testing of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA. This study, published in 2015, also showed the Henry Mountains bison herd
The Henry Mountains bison herd, numbering 250 to 400 bison, is one of only four free-roaming and genetically-pure herds on public lands in North America. The other three herds are the Yellowstone Park bison herd which was the ancestral herd for th ...
to be free of brucellosis
Brucellosis is a highly contagious zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.
Th ...
, a bacterial disease that was imported with non-native domestic cattle to North America.
In 2021, the American Society of Mammalogists
The American Society of Mammalogists (ASM) was founded in 1919. Its primary purpose is to encourage the study of mammals, and professions studying them. There are over 4,500 members of this society, and they are primarily professional scientists w ...
considered ''Bison'' to be a subgenus, and placed both bison species back into ''Bos
''Bos'' (from Latin '' bōs'': cow, ox, bull) is the genus of wild and domestic cattle. ''Bos'' is often divided into four subgenera: ''Bos'', ''Bibos'', ''Novibos'', and ''Poephagus'', but including these last three divisions within the ge ...
''.
Behavior

Wallowing Wallowing in animals is comfort behaviour during which an animal rolls about or lies in mud, water or snow. Some definitions include rolling about in dust, however, in ethology this is usually referred to as dust bathing. Wallowing is often combi ...
is a common behavior of bison. A ''bison wallow'' is a shallow depression in the soil, either wet or dry. Bison roll in these depressions, covering themselves with mud or dust. Possible explanations suggested for wallowing behavior include grooming behavior associated with moulting, male-male interaction (typically rutting behavior), social behavior for group cohesion, play behavior, relief from skin irritation due to biting insects, reduction of ectoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
load (tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s and lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result o ...
), and thermoregulation. In the process of wallowing, bison may become infected by the fatal disease anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
, which may occur naturally in the soil.
Bison temperament is often unpredictable. They usually appear peaceful, unconcerned, even lazy, yet they may attack anything, often without warning or apparent reason. They can move at speeds up to and cover long distances at a lumbering gallop.American Bisonnps.gov Their most obvious weapons are the horns borne by both males and females, but their massive heads can be used as battering rams, effectively using the momentum produced by what is a typical weight of moving at . The hind legs can also be used to kill or maim with devastating effect. In the words of early naturalists, they were dangerous, savage animals that feared no other animal and in prime condition could best any foe (except for wolves and brown bears). The rutting, or mating, season lasts from June through September, with peak activity in July and August. At this time, the older bulls rejoin the herd, and fights often take place between bulls. The herd exhibits much restlessness during breeding season. The animals are belligerent, unpredictable, and most dangerous.
Habitat
American bison
The American bison (''Bison bison'') is a species of bison native to North America. Sometimes colloquially referred to as American buffalo or simply buffalo (a different clade of bovine), it is one of two extant species of bison, alongside the ...
live in river valleys and on prairies and plains. Typical habitat is open or semiopen grasslands, as well as sagebrush, semiarid lands, and scrublands. Some lightly wooded areas are also known historically to have supported bison. They also graze in hilly or mountainous areas where the slopes are not steep. Although not particularly known as high-altitude animals, bison in the Yellowstone Park bison herd
The Yellowstone Park bison herd is a bison herd in Yellowstone National Park. It is probably the oldest and largest public bison herd in the United States, estimated in 2020 to be 4,800 bison. The bison in the Yellowstone Park bison herd are Am ...
are frequently found at elevations above . The Henry Mountains bison herd
The Henry Mountains bison herd, numbering 250 to 400 bison, is one of only four free-roaming and genetically-pure herds on public lands in North America. The other three herds are the Yellowstone Park bison herd which was the ancestral herd for th ...
is found on the plains around the Henry Mountains, Utah, as well as in mountain valleys of the Henry Mountains to an altitude of .
European bison most commonly live in lightly wooded to fully wooded areas as well as areas with increased shrubs and bushes. European bison can sometimes be found living on grasslands and plains as well.
Restrictions
Throughout most of their historical range, landowners have sought restrictions on free-ranging bison. Herds on private land are required to be fenced in. In the state of Montana, free-ranging bison on public lands may be shot, due to concerns about transmission of disease to cattle and damage to public property. In 2013, Montana legislative measures concerning the bison were proposed and passed the legislature, but opposed by Native American tribes as they impinged on sovereign tribal rights. Three such bills were vetoed by Steve Bullock, the governor of Montana. The bison's circumstances remain an issue of contention between Native American tribes and private landowners.Diet
 Bison are ruminants, which gives them the ability to ferment plants in a specialized stomach prior to digesting them. Bison were once thought to almost exclusively consume grasses and sedges, but are now known to consume a wide-variety of plants including woody plants and herbaceous eudicots. Over the course of the year, bison shift which plants they select in their diet based on which plants have the highest protein or energy concentrations at a given time and will reliably consume the same species of plants across years. Protein concentrations of the plants they eat tend to be highest in the spring and decline thereafter, reaching their lowest in the winter. In Yellowstone National Park, bison browsed willows and cottonwoods, not only in the winter when few other plants are available, but also in the summer. Bison are thought to migrate to optimize their diet, and will concentrate their feeding on recently burned areas due to the higher quality forage that regrows after the burn. Wisent tend to browse on shrubs and low-hanging trees more often than do the American bison, which prefer grass to shrubbery and trees.
Bison are ruminants, which gives them the ability to ferment plants in a specialized stomach prior to digesting them. Bison were once thought to almost exclusively consume grasses and sedges, but are now known to consume a wide-variety of plants including woody plants and herbaceous eudicots. Over the course of the year, bison shift which plants they select in their diet based on which plants have the highest protein or energy concentrations at a given time and will reliably consume the same species of plants across years. Protein concentrations of the plants they eat tend to be highest in the spring and decline thereafter, reaching their lowest in the winter. In Yellowstone National Park, bison browsed willows and cottonwoods, not only in the winter when few other plants are available, but also in the summer. Bison are thought to migrate to optimize their diet, and will concentrate their feeding on recently burned areas due to the higher quality forage that regrows after the burn. Wisent tend to browse on shrubs and low-hanging trees more often than do the American bison, which prefer grass to shrubbery and trees.
Reproduction
Female bison typically do not reproduce until three years of age and can reproduce to at least 19 years of age. Female bison can produce calves annually as long as their nutrition is sufficient, but will not give birth to a calf after years where weight gain was too low. A mother's probability of reproduction the following year is strongly dependent on the mother's mass and age. Heavier female bison produce heavier calves (weighed in the fall at weaning) than light mothers, while the weight of calves is lower for older mothers (after age 8).Predators
 Owing to their size, bison have few predators. Five notable exceptions are
Owing to their size, bison have few predators. Five notable exceptions are humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, grey wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly u ...
, cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large cat native to the Americas. Its range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. ...
s, grizzly bear
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America.
In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horr ...
s, and coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological n ...
s. Wolves generally take down a bison while in a pack, but cases of a single wolf killing bison have been reported. Grizzly bears also consume bison, often by driving off the pack and consuming the wolves' kill. Grizzly bears and coyotes also prey on bison calves. Historically and prehistorically, lions, cave lions, tigers, dire wolves
The dire wolf (''Aenocyon dirus'' ) is an extinct canine. It is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores in North America, along with its extinct competitor ''Smilodon''. The dire wolf lived in the Americas and eastern Asia during the Lat ...
, ''Smilodon
''Smilodon'' is a genus of the extinct machairodont subfamily of the felids. It is one of the most famous prehistoric mammals and the best known saber-toothed cat. Although commonly known as the saber-toothed tiger, it was not closely relat ...
'', '' Homotherium'', cave hyena
The cave hyena (''Crocuta crocuta spelaea''), also known as the Ice Age spotted hyena, was a paleosubspecies of spotted hyena which ranged from the Iberian Peninsula to eastern Siberia. It is one of the best known mammals of the Ice Age and is w ...
s, and Neanderthals
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While ...
posed threats to bison.
Infections and illness
For the American bison, the main cause of illness is malignant catarrhal fever, thoughbrucellosis
Brucellosis is a highly contagious zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.
Th ...
is a serious concern in the Yellowstone Park bison herd. Bison in the Antelope Island bison herd are regularly inoculated against brucellosis, parasites, ''Clostridium'' infection, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, and bovine vibriosis.
The major concerns for illness in European bison are foot-and-mouth disease and balanoposthitis
Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. When the foreskin is also affected, the proper term is balanoposthitis. Balanitis on boys still in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis. The word ''balanitis'' i ...
, which affects the male sex organs; a number of parasitic diseases have also been cited as threats. The inbreeding of the species caused by the small population plays a role in a number of genetic defects and immunity to diseases, which in turn poses greater risks to the population.
Name
The term "buffalo" is sometimes considered to be amisnomer
A misnomer is a name that is incorrectly or unsuitably applied. Misnomers often arise because something was named long before its correct nature was known, or because an earlier form of something has been replaced by a later form to which the name ...
for this animal, as it is only distantly related to either of the two "true buffalo", the Asian water buffalo and the African buffalo. Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; Fichier OrigineFor a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December 1635) was a Fr ...
applied the French term ''buffle'' to the bison in 1616 (published 1619), after seeing skins and a drawing shown to him by members of the Nipissing First Nation
Nipissing First Nation ( oj, Niipsing, meaning place of the elms) is a long-standing community of Nishnaabeg peoples located along the shorelines of Lake Nipissing in northern Ontario. They are referred to by many names in European historical re ...
, who said they travelled 40 days (from east of Lake Huron) to trade with another nation who hunted the animals. Though "bison" might be considered more scientifically correct, "buffalo" is also considered correct as a result of standard usage in American English, and is listed in many dictionaries as an acceptable name for American buffalo or bison. Buffalo has a much longer history than bison, which was first recorded in 1774.
Human impact
Bison was a significant resource forindigenous peoples of North America
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Am ...
for food and raw materials until near extinction in the late 19th century. For the indigenous peoples of the Plains, it was their principal food source. Native Americans highly valued their relationship with the bison and saw them as sacred, treating them respectfully to ensure their abundance and longevity. In his biography, Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
teacher and elder John Fire Lame Deer
John Fire Lame Deer (in Lakota ''Tȟáȟča Hušté''; March 17, 1903 – December 14, 1976, also known as Lame Deer, John Fire and John (Fire) Lame Deer) was a Lakota holy man, member of the Heyoka society, grandson of the Miniconjou head man L ...
describes the relationship as such:
 European settlers were almost exclusively accountable for the near-extinction of the American bison in the 1800s. At the beginning of the century, tens of millions of bison roamed North America. Pioneers and settlers slaughtered an estimated 50 million bison during the 19th century, although the causes of decline and the numbers killed are disputed and debated. Railroads were advertising "hunting by rail", where trains encountered large herds alongside or crossing the tracks. Men aboard fired from the train's roof or windows, leaving countless animals to rot where they died. This overhunting was in part motivated by the U.S. government's desire to limit the range and power of indigenous plains Indians whose diets and cultures depended on the buffalo herds. The overhunting of the bison reduced their population to hundreds.
The American bison's nadir came in 1889, with an estimated population of only 1,091 animals (both wild and captive). Repopulation attempts via enforced protection of government herds and extensive
European settlers were almost exclusively accountable for the near-extinction of the American bison in the 1800s. At the beginning of the century, tens of millions of bison roamed North America. Pioneers and settlers slaughtered an estimated 50 million bison during the 19th century, although the causes of decline and the numbers killed are disputed and debated. Railroads were advertising "hunting by rail", where trains encountered large herds alongside or crossing the tracks. Men aboard fired from the train's roof or windows, leaving countless animals to rot where they died. This overhunting was in part motivated by the U.S. government's desire to limit the range and power of indigenous plains Indians whose diets and cultures depended on the buffalo herds. The overhunting of the bison reduced their population to hundreds.
The American bison's nadir came in 1889, with an estimated population of only 1,091 animals (both wild and captive). Repopulation attempts via enforced protection of government herds and extensive ranching
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are most ofte ...
began in 1910 and have continued (with excellent success) to the present day, with some caveats. Extensive farming has increased the bison's population to nearly 150,000, and it is officially no longer considered an endangered species. However, from a genetic standpoint, most of these animals are actually hybrids with domestic cattle and only two populations in Yellowstone National Park, USA and Elk Island National Park
Elk Island National Park is a national park in Alberta, Canada, that played an important part in the conservation of the Plains bison. The park is administered by the Parks Canada Agency. This "island of conservation" is east of Edmonton, alon ...
, Canada remain as genetically pure bison. These genetically-pure animals account for only ~5% of the currently extant American bison population, reflecting the loss of most of the species' genetic diversity.
As of July 2015, an estimated 4,900 bison lived in Yellowstone National Park, the largest U.S. bison population on public land. During 1983–1985 visitors experienced 33 bison-related injuries (range = 10–13/year), so the park implemented education campaigns. After years of success, five injuries associated with bison encounters occurred in 2015, because visitors did not maintain the required distance of 75 ft (23 m) from bison while hiking or taking pictures.
Nutrition
Bison is an excellent source of complete protein and a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value, DV) of multiple vitamins, including riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12, and is also a rich source of minerals, including iron, phosphorus, and zinc. Additionally, bison is a good source (10% or more of the DV) of thiamine.Livestock
The earliest plausible accounts of captive bison are those of the zoo at Tenochtitlan, theAztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
capital, which held an animal the Spaniards called "the Mexican bull". In 1552, Francisco Lopez de Gomara
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name ''Franciscus''.
Nicknames
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed "Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comunitatis'' (father of ...
described Plains Indians
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
herding and leading bison like cattle in his controversial book, '' Historia general de las Indias''. Gomara, having never visited the Americas himself, likely misinterpreted early ethnographic accounts as the more familiar pastoralist relationship of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
. Today, bison are increasingly raised for meat, hides, wool, and dairy products. The majority of bison in the world are raised for human consumption or fur clothing. Bison meat is generally considered to taste very similar to beef, but is lower in fat and cholesterol, yet higher in protein than beef, which has led to the development of beefalo
Beefalo constitute a hybrid offspring of domestic cattle (''Bos taurus''), usually a male in managed breeding programs, and the American bison (''Bison bison''), usually a female in managed breeding programs. The breed was created to combine the ...
, a fertile hybrid of bison and domestic cattle. A market even exists for kosher bison meat; these bison are slaughtered at one of the few kosher mammal slaughterhouses in the U.S. and Canada, and the meat is then distributed worldwide.Terry Kremeniuk. "Bison Farming". ''Canadian Encyclopedia''. Historica-Dominion. 2012. Retrieved 18 June 2013, from HighBeam Research:
In America, the commercial industry for bison has been slow to develop despite individuals, such as Ted Turner
Robert Edward "Ted" Turner III (born November 19, 1938) is an American entrepreneur, television producer, media proprietor, and philanthropist. He founded the Cable News Network (CNN), the first 24-hour cable news channel. In addition, he fo ...
, who have long marketed bison meat. In the 1990s, Turner found limited success with restaurants for high-quality cuts of meat, which include bison steaks and tenderloin.Haddad, Charles. "Bison Meat Slow to Catch On, But Turner Sees Promise". ''Knight Ridder/Tribune Business News''. McClatchy-Tribune Information Services. 1999. Retrieved 18 June 2013, from HighBeam Research: Lower-quality cuts suitable for hamburger and hot dogs have been described as "almost nonexistent". This created a marketing problem for commercial farming because the majority of usable meat, about 400 pounds for each bison, is suitable for these products. In 2003, the United States Department of Agriculture purchased $10 million worth of frozen overstock to save the industry, which would later recover through better use of consumer marketing.Bone, Eugenia. "Bison's back: bravo for buffalo. We're saving the Western icon by eating it (again).(The next frontier)." ''Sunset''. Sunset Publishing Corp. 2008. Restaurants have played a role in popularizing bison meat, like Ted's Montana Grill, which added bison to their menus. Ruby Tuesday first offered bison on their menus in 2005.
In Canada, commercial bison farming began in the mid-1980s, concerning an unknown number of animals then. The first census of the bison occurred in 1996, which recorded 45,235 bison on 745 farms, and grew to 195,728 bison on 1,898 farms for the 2006 census.
Several pet food companies use bison as a red meat alternative in dog foods. The companies producing these formulas include Natural Balance Pet Foods
Dick Van Patten's Natural Balance Pet Foods is an American pet food manufacturer with its headquarters located in Burbank, Los Angeles, California. Established in 1989 by actor Dick Van Patten, the company markets itself as "Food For a Lifetime" ...
, Freshpet
Freshpet is an American pet food company. Its cat food and dog food products are marketed as fresh, and need to be kept refrigerated. It is listed on the Nasdaq exchange with the ticker symbol FRPT.
History
Freshpet was founded in Secaucu ...
, the Blue Buffalo Company, Solid Gold, Canidae, and Taste of the Wild (made by Diamond Pet Foods, Inc., owned by Schell and Kampeter, Inc.).
See also
*Bison hunting
Bison hunting (hunting of the American bison, also commonly known as the American buffalo) was an activity fundamental to the economy and society of the Plains Indians peoples who inhabited the vast grasslands on the Interior Plains of Nort ...
* Gaur
* National Bison Day
National Bison Day is an annual celebration of the significance of the American bison. A campaign is underway to pass federal legislation officially recognizing National Bison Day. Although the legislation has so far failed to pass, the Senate has ...
(1 November in the United States)
* Regina, Saskatchewan
Regina () is the capital city of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The city is the second-largest in the province, after Saskatoon, and is a commercial centre for southern Saskatchewan. As of the 2021 census, Regina had a city population ...
: ''Pile of Bones'' was the original name for Regina, Saskatchewan in reference to bison bones found nearby.
* Yellowstone Park bison herd
The Yellowstone Park bison herd is a bison herd in Yellowstone National Park. It is probably the oldest and largest public bison herd in the United States, estimated in 2020 to be 4,800 bison. The bison in the Yellowstone Park bison herd are Am ...
References
Bibliography
* Boyd, Delaney P. (April 2003)Conservation of North American bison: status and recommendations (PDF)
(Thesis). University of Calgary, Calgary, AB. – via Buffalo Field Campaign * Cunfer, Geoff and Bill Waiser. ''Bison and People on the North American Great Plains: A Deep Environmental History''. College Station, TX: Texas A&M University Press, 2016. * * *
External links
History of Bison Blend Cattle
{{Authority control Holarctic fauna Mammal genera Extant Gelasian first appearances Taxa named by Charles Hamilton Smith