Berkeley House, London on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Devonshire House in
Devonshire House in
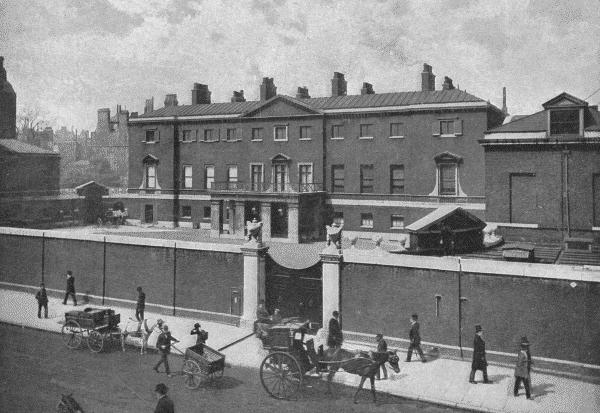
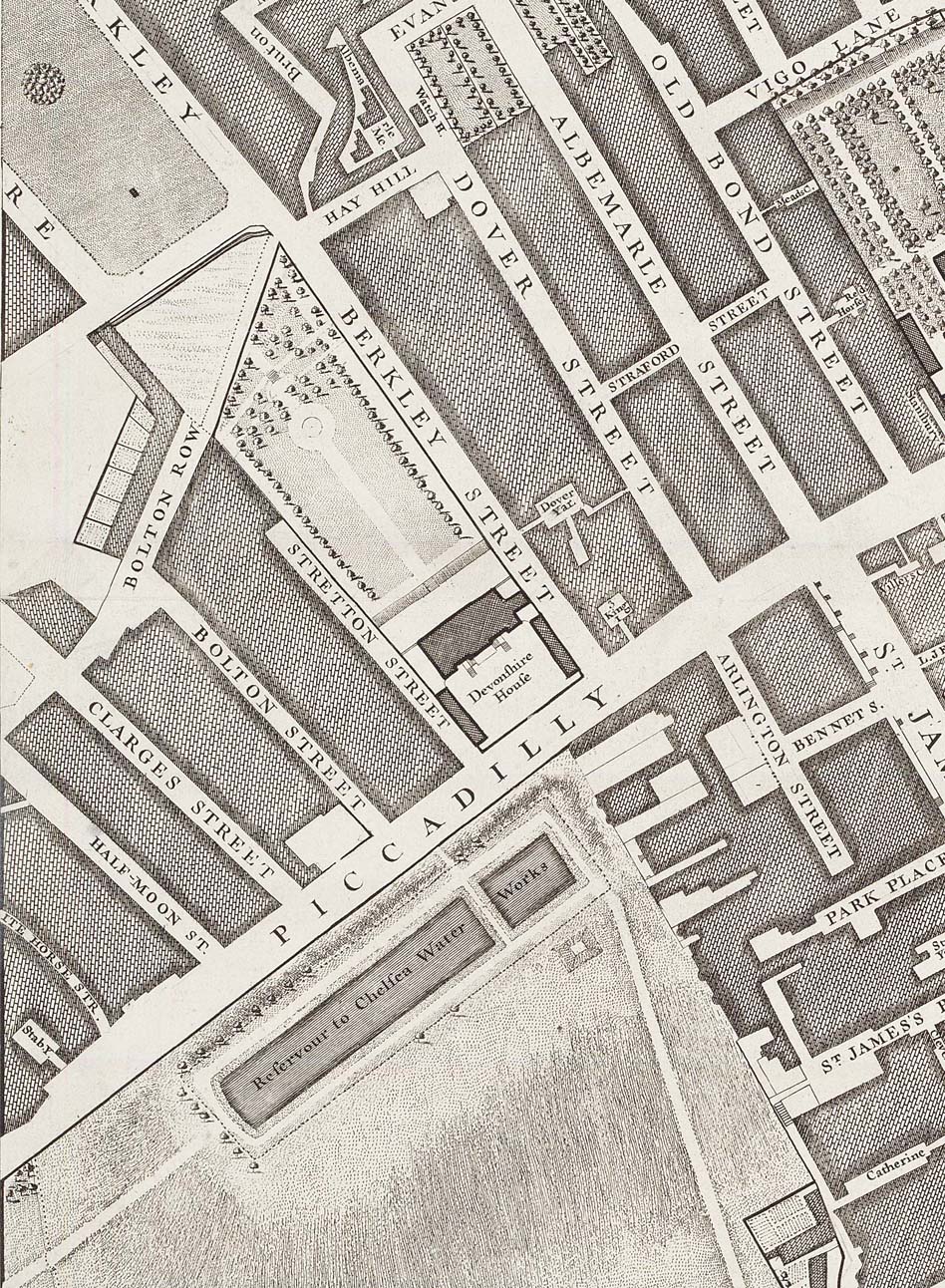 Devonshire House occupied the site of Berkeley House, which was built between 1665 and 1673 and at a cost of over £30,000, by John Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley of Stratton, of Bruton Priory in Somerset, following his return from service as Viceroy of Ireland. The site is memorialised today by
Devonshire House occupied the site of Berkeley House, which was built between 1665 and 1673 and at a cost of over £30,000, by John Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley of Stratton, of Bruton Priory in Somerset, following his return from service as Viceroy of Ireland. The site is memorialised today by
 In typical
In typical
 Alterations were made to Devonshire House by the architect
Alterations were made to Devonshire House by the architect
 During
During
accessed 4 Oct 2010
The reason for the abandonment was that the 9th Duke was the first of his family to suffer
 In 1924-1926
In 1924-1926
Official website for office building
{{Coord, 51.507270, -0.142756, type:landmark, display=title Buildings and structures in Mayfair Former houses in the City of Westminster Buildings and structures on Piccadilly Decimus Burton buildings William Kent buildings Georgian architecture in London
Piccadilly
Piccadilly () is a road in the City of Westminster, London, to the south of Mayfair, between Hyde Park Corner in the west and Piccadilly Circus in the east. It is part of the A4 road that connects central London to Hammersmith, Earl's Cour ...
, was the London townhouse
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence ...
of the Dukes of Devonshire during the 18th and 19th centuries. Following a fire in 1733 it was rebuilt by William Cavendish, 3rd Duke of Devonshire
William Cavendish, 3rd Duke of Devonshire, (26 September 1698 – 5 December 1755) was a British nobleman and Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1721 to 1729 when he inherited the Dukedom.
Life
Cavendish was the son of Will ...
, in the Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
style, to designs by William Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, bu ...
. Completed circa 1740, it stood empty after the First World War and was demolished in 1924.
Many of Britain's great noblemen maintained large London houses that bore their names. As a ducal house (only in mainland Europe were such houses referred to as palaces), Devonshire House was one of the largest and grandest, ranking alongside Burlington House
Burlington House is a building on Piccadilly in Mayfair, London. It was originally a private Neo-Palladian mansion owned by the Earls of Burlington and was expanded in the mid-19th century after being purchased by the British government. To ...
, Montague House, Lansdowne House, Londonderry House
Londonderry House was an aristocratic townhouse situated on Park Lane in the Mayfair district of London, England. The mansion served as the London residence of the Marquesses of Londonderry. It remained their home until 1962. In that year Londond ...
, Northumberland House
Northumberland House (also known as Suffolk House when owned by the Earls of Suffolk) was a large Jacobean townhouse in London, so-called because it was, for most of its history, the London residence of the Percy family, who were the Ear ...
, and Norfolk House
Norfolk House, 31 St James's Square, Westminster, was built between 1748 and 1752 as his London townhouse by Edward Howard, 9th Duke of Norfolk (1686–1777) to the design of Matthew Brettingham (1699–1769), "the Elder", and was demolishe ...
. All of these have long been demolished, except Burlington and Lansdowne, both of which have been substantially altered.
Today the site is occupied by a namesake modern office building.
The site
 Devonshire House occupied the site of Berkeley House, which was built between 1665 and 1673 and at a cost of over £30,000, by John Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley of Stratton, of Bruton Priory in Somerset, following his return from service as Viceroy of Ireland. The site is memorialised today by
Devonshire House occupied the site of Berkeley House, which was built between 1665 and 1673 and at a cost of over £30,000, by John Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley of Stratton, of Bruton Priory in Somerset, following his return from service as Viceroy of Ireland. The site is memorialised today by Berkeley Square
Berkeley Square is a garden square in the West End of London. It is one of the best known of the many squares in London, located in Mayfair in the City of Westminster. It was laid out in the mid 18th century by the architect William Ke ...
, Berkeley Street, Stratton Street and Bruton Street
Bruton Street is a street in London's Mayfair district.
It runs from Berkeley Square in the south-west to New Bond Street in the north-east, where it continues as Conduit Street.
Notable residents have included Field Marshal John Campbell, 2n ...
. The house was later occupied by Barbara Villiers, Duchess of Cleveland, one of the celebrated mistresses of King Charles II.
Berkeley House, a classical mansion built by Hugh May
Hugh May (1621 – 21 February 1684) was an English architect in the period after the Restoration of King Charles II. He worked in the era which fell between the first introduction of Palladianism into England by Inigo Jones, and the full flower ...
, having been purchased in 1696 by William Cavendish, 1st Duke of Devonshire
William Cavendish, 1st Duke of Devonshire, (25 January 164018 August 1707) was an English soldier, nobleman, and Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1661 to 1684 when he inherited his father's peerage as Earl of Devonshire. ...
, was renamed "Devonshire House". As part of the agreement, John Berkeley, 3rd Baron Berkeley of Stratton
Admiral John Berkeley, 3rd Baron Berkeley of Stratton (1663 – 27 February 1697) was an English admiral, of the Bruton branch of the Berkeley family.
Biography
He was the second son of John Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley of Stratton, and suc ...
(c. 1663–1697) undertook not to build on that part of the land he retained which lay directly behind the house to the north, so preserving the Duke's view. This covenant was still in force when the Berkeley land was developed after 1730, and the gardens
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate bot ...
of Berkeley Square
Berkeley Square is a garden square in the West End of London. It is one of the best known of the many squares in London, located in Mayfair in the City of Westminster. It was laid out in the mid 18th century by the architect William Ke ...
represent the northern termination of that undeveloped strip, combined in the south with the gardens of Lansdowne House.
On 16 October 1733, whilst undergoing refurbishment, the former Berkeley House was completely destroyed by fire, despite firefighting efforts by the Regiment of Guards
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscripted ...
, whose barracks were nearby, led by Willem van Keppel, 2nd Earl of Albemarle
Lieutenant-General Willem (or William) Anne van Keppel, 2nd Earl of Albemarle (5 June 1702 – 22 December 1754) was a British soldier, diplomat and courtier.
He held various roles in the household of George II (1683-1760), who was a personal fr ...
, and by other local troops led by Frederick, Prince of Wales
Frederick, Prince of Wales, (Frederick Louis, ; 31 January 170731 March 1751), was the eldest son and heir apparent of King George II of Great Britain. He grew estranged from his parents, King George and Queen Caroline. Frederick was the fa ...
. The cause was attributed to careless labourers. Ironically, the Duke's former London residence, Old Devonshire House
Old Devonshire House at 48 Boswell Street, was located between Theobald's Road in Bloomsbury, and Queen Square, London. William Cavendish, 3rd Earl of Devonshire had the house built in 1668 for his son, also called William Cavendish, who was MP ...
, at 48 Boswell Street, Bloomsbury
Bloomsbury is a district in the West End of London. It is considered a fashionable residential area, and is the location of numerous cultural, intellectual, and educational institutions.
Bloomsbury is home of the British Museum, the largest ...
, survived both its successors until The Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
Ethos
During the 18th century forms of entertainment began to change and large receptions came into fashion, often taking the form of concerts and balls. Initially, hosts hired one of the many new assembly rooms built to indulge the fashion. It was not long before the more dedicated and wealthy hosts began to add aballroom
A ballroom or ballhall is a large room inside a building, the primary purpose of which is holding large formal parties called balls. Traditionally, most balls were held in private residences; many mansions and palaces, especially historic ...
to their town houses
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
; the more wealthy still forsook their old-fashionedly proportioned town houses in favour of new and vast palaces designed purely for entertaining. The Duke of Devonshire, an owner of vast estates in Derbyshire and elsewhere, belonged to the latter category. Thus the fire at Devonshire House in 1733 provided the unforeseen opportunity to build one such palace during the height of the fashion.
The 3rd Duke chose the fashionable architect William Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, bu ...
, for whom this was a first commission for a London house. It was built between 1734 and about 1740. Kent was the protégé of the immensely cultivated 3rd Earl of Burlington and had worked on his Chiswick House
Chiswick House is a Neo-Palladian style villa in the Chiswick district of London, England. A "glorious" example of Neo-Palladian architecture in west London, the house was designed and built by Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington (1694– ...
, built in 1729, and also at Holkham Hall
Holkham Hall ( or ) is an 18th-century country house near the village of Holkham, Norfolk, England, constructed in the Neo-Palladian style for the 1st Earl of Leicester,The Earldom of Leicester has been, to date, created seven times. Thomas ...
, completed circa 1741, both in the Palladian style and considered the epitome of fashion and sophistication. Chiswick House later came, with other estates, into the possession of the Dukes of Devonshire through the marriage of the 4th Duke to Lady Charlotte Boyle, daughter and heiress of Lord Burlington.
Architecture
Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
style, Devonshire House consisted of a ''corps de logis
In architecture, a ''corps de logis'' () is the principal block of a large, (usually classical), mansion or palace. It contains the principal rooms, state apartments and an entry.Curl, James Stevens (2006). ''Oxford Dictionary of Architecture ...
'' flanked by service wing
Servants' quarters are those parts of a building, traditionally in a private house, which contain the domestic offices and staff accommodation. From the late 17th century until the early 20th century, they were a common feature in many large ...
s. The severity of the design - three storeys in eleven bays - caused one contemporary critic to liken the mansion to a warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of citie ...
, and a modern biographer of Kent to remark on its "plain severity". However, the curiously flat exterior concealed Kent's sumptuous interiors which housed a large part of the Devonshire art collection, considered one of the finest in the United Kingdom, and a renowned library, housed in a room 40 ft long and including amongst its treasures Claude Lorraine
Claude Lorrain (; born Claude Gellée , called ''le Lorrain'' in French; traditionally just Claude in English; c. 1600 – 23 November 1682) was a French painter, draughtsman and etcher of the Baroque era. He spent most of his life in It ...
's ''Liber Veritatis
The ''Liber Veritatis'', meaning ''Book of Truth'' in Latin, is a book of drawings recording his completed paintings made by Claude Lorrain, known in English as "Claude". Claude was a landscape painter in Rome, who began keeping this record in ...
'', his record in sketches of a lifetime of painting. In the Duke's sitting room a glass case over the chimneypiece contained the best of his collection of engraved gem
An engraved gem, frequently referred to as an intaglio, is a small and usually semi-precious gemstone that has been carved, in the Western tradition normally with images or inscriptions only on one face. The engraving of gemstones was a major lux ...
s and Renaissance and Baroque medallions. Such a prominent commission could hardly fail to be included in ''Vitruvius Britannicus
Colen Campbell (15 June 1676 – 13 September 1729) was a pioneering Scottish architect and architectural writer, credited as a founder of the Georgian style. For most of his career, he resided in Italy and England. As well as his architectura ...
''.
The plan of Devonshire House defines it as one of the earliest of the great 18th-century town houses
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
, then designed identically to grand country houses. Its purpose, too, was identical, to display wealth and consequently power. Thus a great town house, by its large size and design, accentuated its owner's power by its contrast with the monotony of the smaller terraced houses
In architecture and city planning, a terrace or terraced house ( UK) or townhouse ( US) is a form of medium-density housing that originated in Europe in the 16th century, whereby a row of attached dwellings share side walls. In the United State ...
surrounding it.
At Devonshire House, Kent's exterior stairs led up to a ''piano nobile
The ''piano nobile'' ( Italian for "noble floor" or "noble level", also sometimes referred to by the corresponding French term, ''bel étage'') is the principal floor of a palazzo. This floor contains the main reception and bedrooms of the ho ...
'', where the entrance hall was the only room that rose through two storeys. Inconspicuous pairs of staircases are tucked into modest sites at either side, for the upstairs was strictly private. Enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in de ...
s of interconnecting rooms, of which the largest space is devoted to the library, flank central halls, adjusting the traditions of the symmetrical Baroque state apartment
A state room in a large European mansion is usually one of a suite of very grand rooms which were designed for use when entertaining royalty. The term was most widely used in the 17th and 18th centuries. They were the most lavishly decorated in ...
s, a design which did not lend itself to large gatherings. A few years later architects such as Matthew Brettingham
Matthew Brettingham (1699 – 19 August 1769), sometimes called Matthew Brettingham the Elder, was an 18th-century Englishman who rose from humble origins to supervise the construction of Holkham Hall, and become one of the country's best-know ...
pioneered a more compact design, with a suite of connecting reception room
A drawing room is a room in a house where visitors may be entertained, and an alternative name for a living room. The name is derived from the 16th-century terms withdrawing room and withdrawing chamber, which remained in use through the 17th cent ...
s circling a central top-lit stair hall, which allowed guests to "circulate". Greeted at the head of the stairs, they then flowed in a convenient circuit, rather than retracing their steps. This design was first exemplified by the now-demolished Norfolk House
Norfolk House, 31 St James's Square, Westminster, was built between 1748 and 1752 as his London townhouse by Edward Howard, 9th Duke of Norfolk (1686–1777) to the design of Matthew Brettingham (1699–1769), "the Elder", and was demolishe ...
completed in 1756. Therefore, it seems that Devonshire House was old-fashioned and unsuited to its intended use almost from the moment of its completion. Thus from the late 18th century its interiors were vastly altered.
Usage
 Alterations were made to Devonshire House by the architect
Alterations were made to Devonshire House by the architect James Wyatt
James Wyatt (3 August 1746 – 4 September 1813) was an English architect, a rival of Robert Adam in the neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles. He was elected to the Royal Academy in 1785 and was its president from 1805 to 1806.
Early life
W ...
, over the long period 1776–90, and later by Decimus Burton
Decimus Burton (30 September 1800 – 14 December 1881) was one of the foremost English architects and landscapers of the 19th century. He was the foremost Victorian architect in the Roman revival, Greek revival, Georgian neoclassical and R ...
, who in 1843 constructed a new portico, entrance hall and grand staircase for the 6th Duke. At that time the external double staircase was swept away, allowing for formal entrance to be made into the ground floor through the new portico. Hitherto the ground floor had contained only secondary rooms and in 18th century fashion had been the domain of servants. The new staircase conveyed guests directly to the ''piano nobile'', from a low entrance hall, in a newly created recess formed by creating a convex bow at the centre of the rear garden facade. Known as the "Crystal Staircase", it had a glass handrail and newel posts. Burton amalgamated several of the principal rooms; he created a vast heavily gilded ballroom from two former drawing rooms and often created double height rooms at the expense of the bedrooms above, causing the house to become even more of a place for display and entertaining rather than for living.
Devonshire House was the setting for the brilliant social and political life of the circle around William Cavendish, 5th Duke of Devonshire
William Cavendish, 5th Duke of Devonshire, (14 December 1748 – 29 July 1811), was a British nobleman, aristocrat, and politician. He was the eldest son of William Cavendish, 4th Duke of Devonshire, by his wife, the heiress Lady Charlotte B ...
and his duchess, Lady Georgiana Spencer, Whig supporters of Charles James Fox
Charles James Fox (24 January 1749 – 13 September 1806), styled '' The Honourable'' from 1762, was a prominent British Whig statesman whose parliamentary career spanned 38 years of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He was the arch-ri ...
. The grand house was also the site for the much celebrated Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee
The Diamond Jubilee of Queen Victoria was officially celebrated on 22 June 1897 to mark the occasion of the 60th anniversary of Queen Victoria's accession on 20 June 1837. Queen Victoria was the first British monarch ever to celebrate a Diamond ...
with a lavish fancy dress
A costume party (American English) or fancy dress party (other varieties of English) is a type of party, common in contemporary Western culture, in which many of the guests are dressed in costume, usually depicting a fictional or stock cha ...
ball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but can sometimes be ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used f ...
, known as the Devonshire House Ball of 1897. The guests, including Albert Edward, Prince of Wales
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and ...
and the Princess of Wales
Princess of Wales (Welsh: ''Tywysoges Cymru'') is a courtesy title used since the 14th century by the wife of the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. The current title-holder is Catherine (née Middleton).
The title was fi ...
, were dressed as historical portraits come to life. The many portrait photographs taken at the ball have illustrated countless books on the social history of the late Victorian era.
Demolition
 During
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
Devonshire House was used by the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
, including for dealing with post. Gertrude Bacon
Gertrude Bacon (19 April 1874 – 22 December 1949) was an aeronautical pioneer. She achieved a considerable number of "firsts" for women in aeronautics, as well as making contributions in the areas of astronomy and botany. Bacon populari ...
was later in charge of this operation.
After the war, many aristocratic families gave up their London houses and Devonshire House was deserted in 1919. The demolition was mentioned nostalgically several times in literature and caused Virginia Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born i ...
's Clarissa Dalloway to think, as she passed down Piccadilly, of "Devonshire House without its gilt leopards", a reference to the house's gilded gates. It also inspired Siegfried Sassoon's "Monody on the Demolition of Devonshire House".Richard Davenport-Hines, "Cavendish, Victor Christian William, ninth Duke of Devonshire (1868–1938)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 200accessed 4 Oct 2010
The reason for the abandonment was that the 9th Duke was the first of his family to suffer
death duties
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an es ...
, which amounted to over £500,000. Additionally, he inherited the debts of the 7th Duke. This double burden prompted the sale of many of the family's valuables, including books printed by William Caxton
William Caxton ( – ) was an English merchant, diplomat and writer. He is thought to be the first person to introduce a printing press into England, in 1476, and as a printer to be the first English retailer of printed books.
His parentage a ...
, many 1st editions of Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
, and Devonshire House itself with its even more valuable three acres of gardens. The sale was finalised in 1920 at a price of £750,000 and the house was demolished. The two purchasers were Shurmer Sibthorpe and Lawrence Harrison, wealthy industrialists, who built on the site a hotel and block of flats. When told that the proposed demolition was an act of vandalism, Sibthorpe, echoing the building's 18th-century critics, replied: "Archaeologists have gathered round me and say I am a vandal, but personally I think the place is an eyesore."
Legacy
 In 1924-1926
In 1924-1926 Holland, Hannen & Cubitts
Holland, Hannen & Cubitts was a major building firm responsible for many of the great buildings of London.
History
The company was formed from the fusion of two well-established building houses that had competed throughout the later decades of ...
built a new office building on the site, fronting directly onto Piccadilly, also known as "Devonshire House". The building became the UK headquarters of the automobile manufacturer Citroën, with showrooms occupying the lower three floors. Citroën remained the chief occupant of the building until 1936. It was also the headquarters of The Rootes Group until the 1960s. During World War II it was occupied by the headquarters of the War Damage Commission.
Some of the paintings and furniture from Devonshire House survive at the Duke's principal seat, Chatsworth House in Derbyshire. The wrought-iron entrance gates, between piers with rusticated quoins and topped with seated sphinx
A sphinx ( , grc, σφίγξ , Boeotian: , plural sphinxes or sphinges) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of a falcon.
In Greek tradition, the sphinx has the head of a woman, the haunches of ...
es, have been re-erected on the south side of Piccadilly, to form an entrance to Green Park. The wine cellar is now the ticket office of Green Park Underground station. Other architectural salvage included furniture, doorways and mantelpieces which were relocated to Chatsworth. Some of these stored items were auctioned by Sotheby's on 5–7 October 2010, including five William Kent chimneypieces from Devonshire House described by the auctioneer Lord Dalmeny as being of special interest and value: "You can't buy them because they are all in listed buildings now. It's like being able to commission Rubens to paint your ceiling."
Most of the great detached houses of noblemen which existed in the West End of London, where even the grandest persons often lived in terraced house
In architecture and city planning, a terrace or terraced house ( UK) or townhouse ( US) is a form of medium-density housing that originated in Europe in the 16th century, whereby a row of attached dwellings share side walls. In the United State ...
s, including Devonshire House, Norfolk House
Norfolk House, 31 St James's Square, Westminster, was built between 1748 and 1752 as his London townhouse by Edward Howard, 9th Duke of Norfolk (1686–1777) to the design of Matthew Brettingham (1699–1769), "the Elder", and was demolishe ...
and Chesterfield House
Chesterfield may refer to:
Places Canada
* Rural Municipality of Chesterfield No. 261, Saskatchewan
* Chesterfield Inlet, Nunavut United Kingdom
*Chesterfield, Derbyshire, a market town in England
** Chesterfield (UK Parliament constituenc ...
, are today numbered amongst England's thousands of lost houses; Lansdowne House lost its front to a street-widening scheme. Just a few survive, but in corporate or state ownership. Marlborough House
Marlborough House, a Grade I listed mansion in St James's, City of Westminster, London, is the headquarters of the Commonwealth of Nations and the seat of the Commonwealth Secretariat. It was built in 1711 for Sarah Churchill, Duchess of Marl ...
passed to the crown in the 19th century. Apsley House
Apsley House is the London townhouse of the Dukes of Wellington. It stands alone at Hyde Park Corner, on the south-east corner of Hyde Park, facing south towards the busy traffic roundabout in the centre of which stands the Wellington Arch. I ...
remains a functioning possession of the Dukes of Wellington, but is mostly now a public museum on the edge of a busy roundabout, its gardens long gone (but not built over), with the family occupying the uppermost floor only. Spencer House Spencer House may refer to:
* Spencer House, Westminster, Greater London, England
United States
* Spencer House (Hartford, Connecticut), listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in Hartford County
* Spencer House in Columbus, Ge ...
is an event venue. Manchester House houses the Wallace Collection
The Wallace Collection is a museum in London occupying Hertford House in Manchester Square, the former townhouse of the Seymour family, Marquesses of Hertford. It is named after Sir Richard Wallace, who built the extensive collection, along ...
, a museum open to the public. Bridgewater House, Westminster
Bridgewater House is a townhouse located at 14 Cleveland Row in the St James's area of London, England. It is a Grade I listed building.
History
The earliest known house on the site was Berkshire House, built in about 1626–27 for Thomas Howa ...
by Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also respons ...
is now used as offices. Currently, Dudley House is the only one of London's surviving private palaces to be occupied and used as its design intended.A complete list (see Townhouse (Great Britain)
In British usage, the term townhouse originally referred to the town or city residence, in practice normally in London, of a member of the nobility or gentry, as opposed to their country seat, generally known as a country house or, colloquially ...
) would also include Melbourne House, remodelled as The Albany; Dover House in Whitehall, now government offices; Derby House in Stratford Place off Oxford Street; Crewe House,in Curzon Street; Bourdon House at the northeast end of Berkeley Square; Egremont House, Piccadilly, housing the Naval and Military Club; and Bath House. These are mentioned by Nikolaus Pevsner, ''London I: The Cities of London and Westminster'' (Buildings of England series) 1962. 78f.
See also
*List of demolished buildings and structures in London
This list of demolished buildings and structures in London includes buildings, structures and urban scenes of particular architectural and historical interest, scenic buildings which are preserved in old photographs, prints and paintings, but whic ...
* Destruction of country houses in 20th-century Britain
The destruction of country houses in 20th-century Britain was the result of a change in social conditions: many country houses of varying architectural merit were demolished by their owners. Collectively termed by several authors "the lost hous ...
References
Bibliography
*External links
Official website for office building
{{Coord, 51.507270, -0.142756, type:landmark, display=title Buildings and structures in Mayfair Former houses in the City of Westminster Buildings and structures on Piccadilly Decimus Burton buildings William Kent buildings Georgian architecture in London