Benefits Realisation Management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Benefits Realization Management (BRM) (also benefits management, benefits realisation or project benefits management) is one of the many ways of managing how time and resources are invested into making desirable
 The ''benefits dependency network'' has five types of object within maps.
;Investment Objectives :A small number of statements that define the focus of the project and how it links to investment drivers.
;Benefits :Advantages to specific individuals or groups of individuals.
;Business Changes :Changes required in the business to hit the Benefits.
;Enabling Changes :Changes required to allow the Business Changes to happen.
;IS/IT enablers :"The information systems and technology required to support the realization of identified benefits and allow the necessary changes to be undertaken."
The ''benefits dependency network'' has five types of object within maps.
;Investment Objectives :A small number of statements that define the focus of the project and how it links to investment drivers.
;Benefits :Advantages to specific individuals or groups of individuals.
;Business Changes :Changes required in the business to hit the Benefits.
;Enabling Changes :Changes required to allow the Business Changes to happen.
;IS/IT enablers :"The information systems and technology required to support the realization of identified benefits and allow the necessary changes to be undertaken."
 The ''benefits dependency map'' also has five types of object on the maps
;Bounding Objective :Measurable end goals which support the vision of what is being attempted.
;End Benefit :Independent Benefits (not interlinked) that achieve the objective.
;Intermediate Benefit :"An outcome of change which is perceived as positive by a stakeholder".
;Business Change :Changes to the business or environment of the business
;Enabler :Something developed / purchased to enable the realisation of benefit.
The ''benefits dependency map'' also has five types of object on the maps
;Bounding Objective :Measurable end goals which support the vision of what is being attempted.
;End Benefit :Independent Benefits (not interlinked) that achieve the objective.
;Intermediate Benefit :"An outcome of change which is perceived as positive by a stakeholder".
;Business Change :Changes to the business or environment of the business
;Enabler :Something developed / purchased to enable the realisation of benefit.
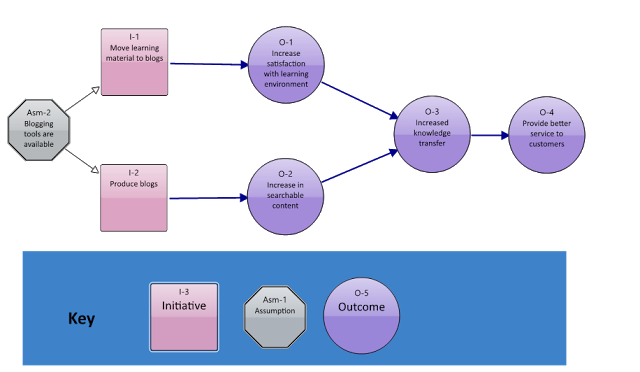 The ''results chain'' has four types of object on the maps.
;Outcome :The results being aimed at.
;Initiative :An action or activity that contributes to outcomes.
;Contribution :A measurable description of how an initiative is expected to contribute to an outcome.
;Assumption :Something believed to be required to realize outcomes or initiatives which the organisation has no or little control over.
The ''results chain'' has four types of object on the maps.
;Outcome :The results being aimed at.
;Initiative :An action or activity that contributes to outcomes.
;Contribution :A measurable description of how an initiative is expected to contribute to an outcome.
;Assumption :Something believed to be required to realize outcomes or initiatives which the organisation has no or little control over.
change
Change or Changing may refer to:
Alteration
* Impermanence, a difference in a state of affairs at different points in time
* Menopause, also referred to as "the change", the permanent cessation of the menstrual period
* Metamorphosis, or change, ...
s.
Benefits Realization Management has four main definitions. The first definition is to consider benefits management as an organisational change process. It is defined as "the process of organizing and managing, such that the potential benefits arising from the use of IT are actually realized". The second definition perceives it as a process. Benefits management is defined by the Association for Project Management
The Association for Project Management is a British professional organisation for project and programme management. It received a Royal Charter in 2017, and is a registered charity. It has over 37,500 individual and 550 corporate members, and ...
(APM) as the identification, definition, planning, tracking and realization of business benefits. The third definition is to apply this concept on project management level. Project benefits management is defined as "the initiating, planning, organizing, executing, controlling, transitioning and supporting of change in the organisation and its consequences as incurred by project management mechanisms to realize predefined project benefits". Finally, the last definition perceives benefits realization management as a set of processes structured to close the gap between strategy planning and execution by ensuring the implementation of the most valuable initiatives.
The popularity of BRM began in 1995 in the UK, when Scottish Widows created a Benefits Realisation method as part of its Project Management Handbook, and rolled its use out across the entire firm. It grew in the UK with the inclusion of BRM by the UK Government in their standardized approach to programmes, ''Managing Successful Programmes (MSP).''OGC (2003) ''Managing Successful Programmes'', London, The Stationery Office.
BRM practices aim to ensure the alignment between project outcomes and business strategies and has been shown to increase project success across different countries and industries. The Project Management Institute
The Project Management Institute (PMI, legally Project Management Institute, Inc.) is a U.S.-based not-for-profit professional organization for project management.
Overview
PMI serves more than five million professionals including over 680,00 ...
(PMI) identified that only one in five organizations report high maturity in benefits realization.
Overview
As with allproject management
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. Th ...
methodologies, BRM has clear roles and responsibilities, processes, principles and deliverables. The main roles are Business Change Managers (BCMs) who help the Benefits Owners (i.e. the main beneficiaries) identify, plan and review the expected benefits from the change and project managers who deliver the reliable capability on time and within budget. BRM is used to manage the investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing i ...
by organizations in procurement
Procurement is the method of discovering and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, Service (economics), services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. When a government agenc ...
, projects, programmes and portfolios. At the portfolio level, a value management framework should be put in place to monitor, track, and aggregate benefits from projects and programmes in order to track the overall value being delivered from all the components in the portfolio. BRM is also used to ensure the organization maintains a benefits focus during continuing business operations.
Outcomes are changes identified as important by stakeholders and can be strategic or non-strategic. A benefit is a measurable positive impact of change. A dis-benefit is a measurable negative impact of change.Thorp, J. (1998) The Information Paradox – realizing the business benefits of information technology, Toronto, Canada, McGraw-Hill. Successful BRM requires accountable people, relevant measures and proactive management.
A generic BRM process is to:
* Identify the investment outcomes
* Define benefit measures for each outcome
* Collect current benefit measure data to have a quantitative basis for decision making
* Agree to a tailored BRM approach for this investment
* Plan the new or changed capabilities necessary to realize the benefits
* Plan the investments needed to make the changes necessary to create or change the capabilities
* Optimize the plan to reduce waste and have acceptable levels of resource, risk, cost, quality and time
* Implement the plan
* Review the impact of the plan implementation on the Benefit Measures and use insights to improve
* On completion of the plan, ensure BRM continues to sustain the capabilities and realisation of benefits
To identify the investment outcomes, pictorial views of the outcomes of interest on an ''outcome map'' (also called a ''results chain'', ''benefits dependency network''Ward, J. and Murray, P.
(1997), Benefits Management: Best Practice Guidelines. Cranfield School of Management, Information Systems Research or ''benefit map''Bradley, G. (2006), Benefit Realisation Management – A practical guide to achieving benefits through change, Gower, Hampshire.) can be created. This technique supports agreement of the outcomes sought as it shows the outcomes and relationships between them on a single page. They can be agreed upon and communicated clearly as a result.
Data can then be captured either separately or within a suitable modelling tool for each outcome that will include the benefit measures used for each, ownership and accountability information and information to support realisation management.
Mapping styles
Constructing benefits maps or graphs is usually done from right to left, with what is attempting to be achieved (often called objectives, strategic outcomes etc.) being the start point, then moving through intermediate outcomes to the things required to cause these to happen at the very left.Benefits dependency networks (BDN)
 The ''benefits dependency network'' has five types of object within maps.
;Investment Objectives :A small number of statements that define the focus of the project and how it links to investment drivers.
;Benefits :Advantages to specific individuals or groups of individuals.
;Business Changes :Changes required in the business to hit the Benefits.
;Enabling Changes :Changes required to allow the Business Changes to happen.
;IS/IT enablers :"The information systems and technology required to support the realization of identified benefits and allow the necessary changes to be undertaken."
The ''benefits dependency network'' has five types of object within maps.
;Investment Objectives :A small number of statements that define the focus of the project and how it links to investment drivers.
;Benefits :Advantages to specific individuals or groups of individuals.
;Business Changes :Changes required in the business to hit the Benefits.
;Enabling Changes :Changes required to allow the Business Changes to happen.
;IS/IT enablers :"The information systems and technology required to support the realization of identified benefits and allow the necessary changes to be undertaken."
Benefits dependency map (BDM)
 The ''benefits dependency map'' also has five types of object on the maps
;Bounding Objective :Measurable end goals which support the vision of what is being attempted.
;End Benefit :Independent Benefits (not interlinked) that achieve the objective.
;Intermediate Benefit :"An outcome of change which is perceived as positive by a stakeholder".
;Business Change :Changes to the business or environment of the business
;Enabler :Something developed / purchased to enable the realisation of benefit.
The ''benefits dependency map'' also has five types of object on the maps
;Bounding Objective :Measurable end goals which support the vision of what is being attempted.
;End Benefit :Independent Benefits (not interlinked) that achieve the objective.
;Intermediate Benefit :"An outcome of change which is perceived as positive by a stakeholder".
;Business Change :Changes to the business or environment of the business
;Enabler :Something developed / purchased to enable the realisation of benefit.
Results chain
 The ''results chain'' has four types of object on the maps.
;Outcome :The results being aimed at.
;Initiative :An action or activity that contributes to outcomes.
;Contribution :A measurable description of how an initiative is expected to contribute to an outcome.
;Assumption :Something believed to be required to realize outcomes or initiatives which the organisation has no or little control over.
The ''results chain'' has four types of object on the maps.
;Outcome :The results being aimed at.
;Initiative :An action or activity that contributes to outcomes.
;Contribution :A measurable description of how an initiative is expected to contribute to an outcome.
;Assumption :Something believed to be required to realize outcomes or initiatives which the organisation has no or little control over.
See also
*Business case A business case captures the reasoning for initiating a project or task. It is often presented in a well-structured written document, but may also come in the form of a short verbal agreement or presentation. The logic of the business case is that, ...
* Cost-benefit analysis
* Value engineering
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, ...
References
{{reflist Organizational performance management