Belle Époque on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Belle Époque or La Belle Époque (; French for "Beautiful Epoch") is a period of French and
 Two devastating world wars and their aftermath made the Belle Époque appear to be a time of ''
Two devastating world wars and their aftermath made the Belle Époque appear to be a time of '' Those who were able to benefit from the prosperity of the era were drawn towards new forms of light entertainment during the Belle Époque, and the Parisian bourgeoisie, or the successful industrialists called the '' nouveaux riches'', became increasingly influenced by the habits and fads of the city's elite social class, known popularly as ''
Those who were able to benefit from the prosperity of the era were drawn towards new forms of light entertainment during the Belle Époque, and the Parisian bourgeoisie, or the successful industrialists called the '' nouveaux riches'', became increasingly influenced by the habits and fads of the city's elite social class, known popularly as '' The
The
 The years between the Franco-Prussian War and World War I were characterised by unusual political stability in
The years between the Franco-Prussian War and World War I were characterised by unusual political stability in  Meanwhile, the international workers' movement also reorganised itself and reinforced pan-European, class-based identities among the classes whose labour supported the Belle Époque. The most notable transnational
Meanwhile, the international workers' movement also reorganised itself and reinforced pan-European, class-based identities among the classes whose labour supported the Belle Époque. The most notable transnational 
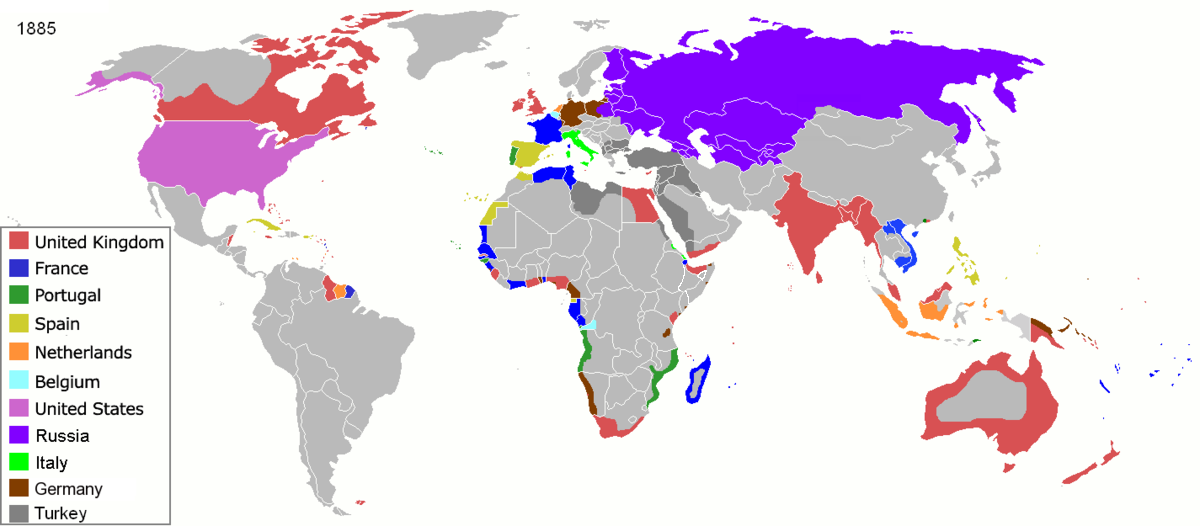
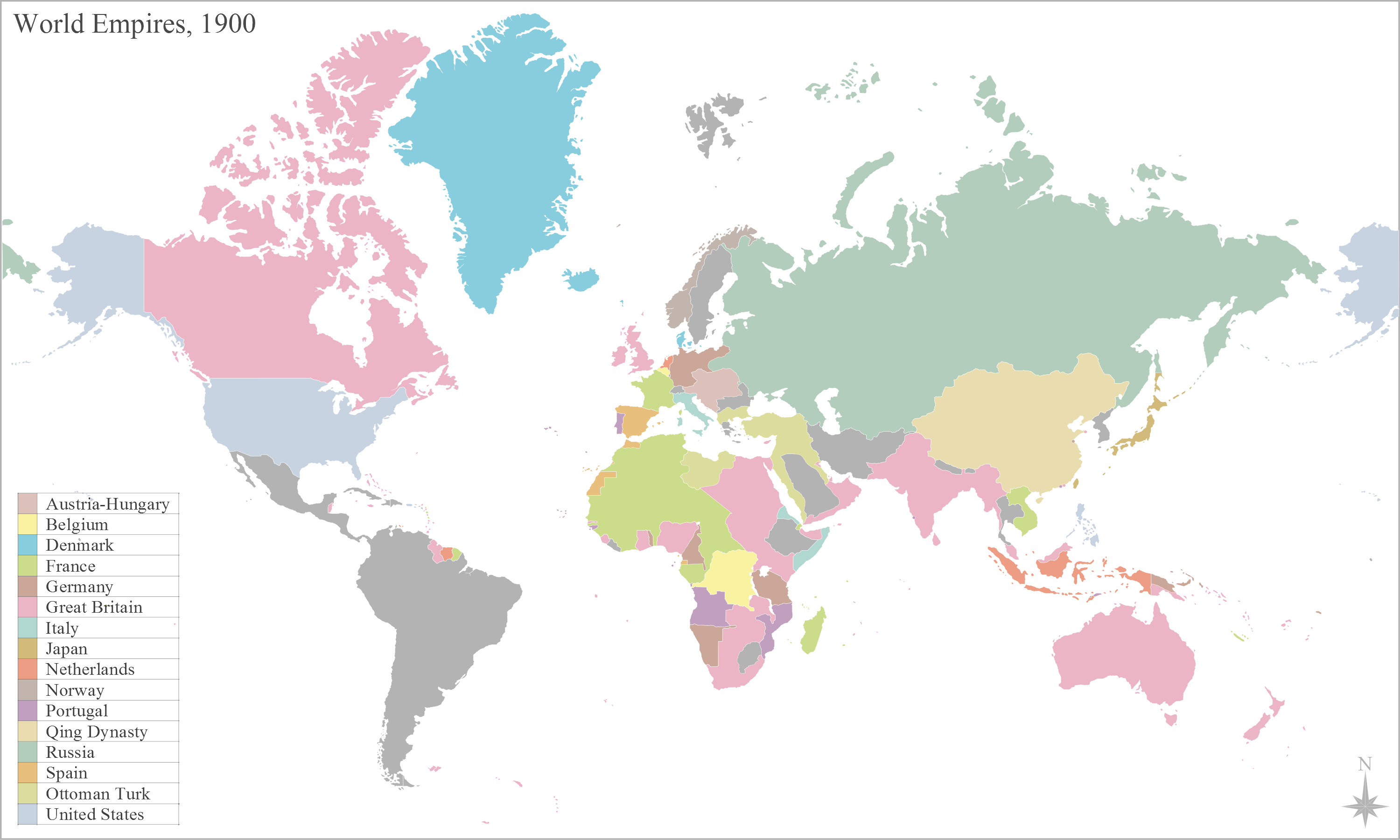 Most of the great powers (and some minor ones such as Belgium, the Netherlands, or Denmark) became involved in
Most of the great powers (and some minor ones such as Belgium, the Netherlands, or Denmark) became involved in
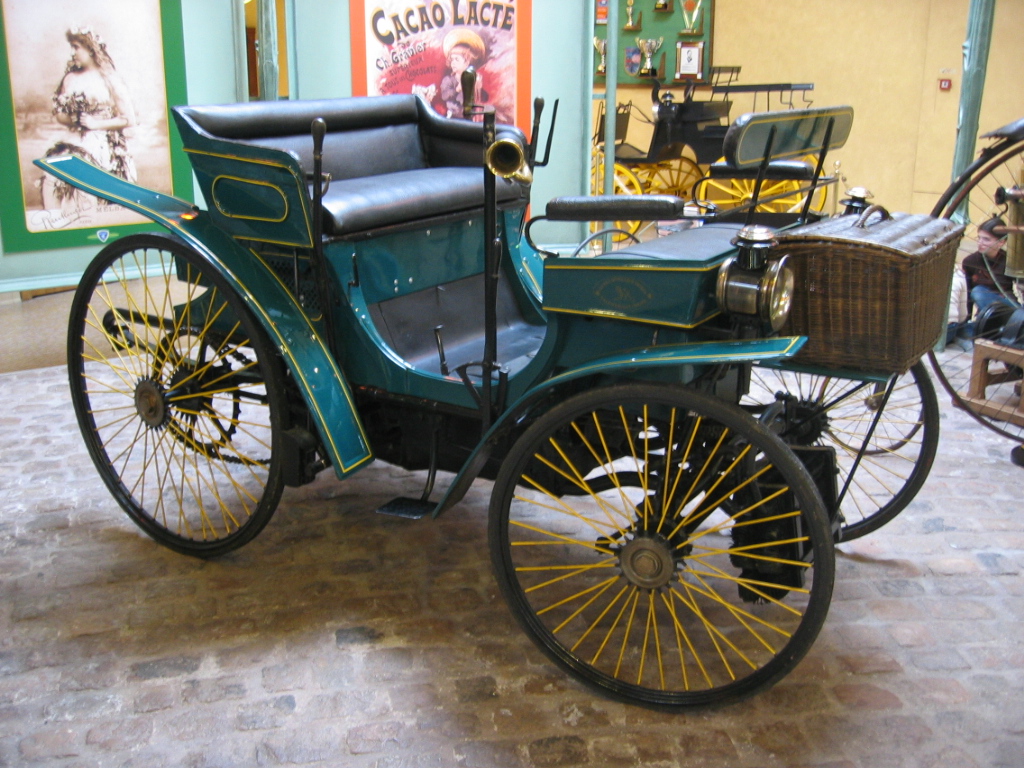



 The Belle Époque was an era of great scientific and technological advancement in Europe and the world in general. Inventions of the
The Belle Époque was an era of great scientific and technological advancement in Europe and the world in general. Inventions of the

 In 1890, Vincent van Gogh died. It was during the 1890s that his paintings achieved the admiration denied them during Van Gogh's life; first among other artists, then gradually among the public. Reactions against the ideals of the Impressionists characterised visual arts in Paris during the Belle Époque. Among the post-Impressionism, post-Impressionist movements in Paris were the Les Nabis, Nabis, the Salon de la Rose + Croix, the Symbolist movement (also in poetry, music, and visual art), Fauvism, and early Modernism. Between 1900 and 1914, Expressionism took hold of many artists in Paris and Vienna. Early works of Cubism and Abstraction were exhibited. Foreign influences were being strongly felt in Paris as well. The official art school in Paris, the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts, École des Beaux-Arts, held an exhibition of Japanese printmaking that changed approaches to graphic design, particular posters and book illustration (Aubrey Beardsley was influenced by a similar exhibit when he visited Paris during the 1890s). Exhibits of African tribal art also captured the imagination of Parisian artists at the turn of the 20th century.
Art Nouveau is the most popularly recognised art movement to emerge from the period. This largely decorative style (Jugendstil in central Europe), characterised by its curvilinear forms, and nature-inspired motifs became prominent from the mid-1890s and dominated progressive design throughout much of Europe. Its use in public art in Paris, such as Hector Guimard's
In 1890, Vincent van Gogh died. It was during the 1890s that his paintings achieved the admiration denied them during Van Gogh's life; first among other artists, then gradually among the public. Reactions against the ideals of the Impressionists characterised visual arts in Paris during the Belle Époque. Among the post-Impressionism, post-Impressionist movements in Paris were the Les Nabis, Nabis, the Salon de la Rose + Croix, the Symbolist movement (also in poetry, music, and visual art), Fauvism, and early Modernism. Between 1900 and 1914, Expressionism took hold of many artists in Paris and Vienna. Early works of Cubism and Abstraction were exhibited. Foreign influences were being strongly felt in Paris as well. The official art school in Paris, the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts, École des Beaux-Arts, held an exhibition of Japanese printmaking that changed approaches to graphic design, particular posters and book illustration (Aubrey Beardsley was influenced by a similar exhibit when he visited Paris during the 1890s). Exhibits of African tribal art also captured the imagination of Parisian artists at the turn of the 20th century.
Art Nouveau is the most popularly recognised art movement to emerge from the period. This largely decorative style (Jugendstil in central Europe), characterised by its curvilinear forms, and nature-inspired motifs became prominent from the mid-1890s and dominated progressive design throughout much of Europe. Its use in public art in Paris, such as Hector Guimard's  Among poets, the Symbolists such as Charles Baudelaire remained at the forefront. Although Baudelaire's poetry collection ''Les Fleurs du mal'' had been published in the 1850s, it exerted a strong influence on the next generation of poets and artists. The Decadent movement fascinated Parisians, intrigued by Paul Verlaine and above all Arthur Rimbaud, who became the archetypal ''enfant terrible'' of France. Rimbaud's ''Illuminations (poetry collection), Illuminations'' was published in 1886, and subsequently his other works were also published, influencing Surrealism, Surrealists and Modernism, Modernists during the Belle Époque and after. Rimbaud's poems were the first works of free verse seen by the French public. Free verse and typographic experimentation also emerged in ''Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard (Mallarmé), Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard'' by Stéphane Mallarmé, anticipating Dada and concrete poetry. Guillaume Apollinaire's poetry introduced themes and imagery from modern life to readers. ''Cosmopolis (magazine), Cosmopolis: An International Monthly Review'' had a far-reaching impact on European writers, and ran editions in London, Paris, Saint Petersburg, and Berlin.
Paris's popular bourgeois theatre was dominated by the light farces of Georges Feydeau and
Among poets, the Symbolists such as Charles Baudelaire remained at the forefront. Although Baudelaire's poetry collection ''Les Fleurs du mal'' had been published in the 1850s, it exerted a strong influence on the next generation of poets and artists. The Decadent movement fascinated Parisians, intrigued by Paul Verlaine and above all Arthur Rimbaud, who became the archetypal ''enfant terrible'' of France. Rimbaud's ''Illuminations (poetry collection), Illuminations'' was published in 1886, and subsequently his other works were also published, influencing Surrealism, Surrealists and Modernism, Modernists during the Belle Époque and after. Rimbaud's poems were the first works of free verse seen by the French public. Free verse and typographic experimentation also emerged in ''Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard (Mallarmé), Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard'' by Stéphane Mallarmé, anticipating Dada and concrete poetry. Guillaume Apollinaire's poetry introduced themes and imagery from modern life to readers. ''Cosmopolis (magazine), Cosmopolis: An International Monthly Review'' had a far-reaching impact on European writers, and ran editions in London, Paris, Saint Petersburg, and Berlin.
Paris's popular bourgeois theatre was dominated by the light farces of Georges Feydeau and
File:XDSC 7288-29-av-Rapp-paris-7.jpg, Art Nouveau building in Paris by architect Jules Lavirotte, sculptures by Jean-François Larrivé (1875–1928)
File:Henri Rousseau 011.jpg, ''La charmeuse de Serpents (The Snake-Charmer)'' (1907) by Henri Rousseau
File:Loie Fuller.jpg, Modern dance (and modern stage lighting) innovator Loie Fuller
File:Jules Massenet & Jean Richepin auteurs du Mage.jpg, Jules Massenet and Jean Richepin (the latter as Apollo Citharoedus), authors of ''Le mage'', premiered at the Opéra-Comique in Paris on 16 March 1891
online
* Bruna, D. ''Fashioning the body: An intimate history of the silhouette.'' (Yale University Press, 2015 )/. * Holmes, Diana, and Carrie Tarr, eds. ''A "Belle Epoque"? Women in French Society and Culture 1890–1914'' (Berghahn Books, 2006). * Dominique Kalifa, ''La Véritable histoire de la Belle Epoque'' (Paris: Fayard, 1917). * * Francaise, A. (14 November 2017). Fashion of the Belle Époque. Retrieved 24 September 2018, from http://learnfrenchchicago.com/2017/05/fashion-belle-epoque/ * Mostyn, Trevor. ''Egypt's Belle Époque: Cairo and the Age of the Hedonists'', Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2006. * Roberts, Mary Louise. '' Disruptive Acts: The New Woman in Fin-de-Siecle France'' (U of Chicago Press, 2002). * Wilcox, C. (2013). ''Fashion in detail'' 1700–2000. London: V & A. * Wires, Richard
"Paris: La Belle Époque"
''Conspectus of History'' 1.4 (1977): 60–72.
The ''Belle Époque'' in Europe
– many pictures of Art Nouveau architecture
Paris1900.lartnouveau.com
– The ''Belle Époque'' in Paris through postcards and documents
Dijon1900.blogspot.com
– The ''Belle Époque'' in Dijon through postcards
French Actress Postcards
{{DEFAULTSORT:Belle Epoque Belle Époque, 1871 establishments in France 1914 disestablishments in France 19th century 20th century Art Nouveau Gold standard Historical eras History of Europe by period Modern art Periodization European Cultural History
European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).
The first early ...
, usually considered to begin around 1871–1880 and to end with the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in 1914. Occurring during the era of the Third French Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940 ...
, it was a period characterised by optimism
Optimism is an attitude reflecting a belief or hope that the outcome of some specific endeavor, or outcomes in general, will be positive, favorable, and desirable. A common idiom used to illustrate optimism versus pessimism is a glass filled w ...
, regional peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
, economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
prosperity
Prosperity is the flourishing, thriving, good fortune and successful social status. Prosperity often produces profuse wealth including other factors which can be profusely wealthy in all degrees, such as happiness and health.
Competing notion ...
, colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
expansion, and technological
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
, scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, and cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
innovations
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entit ...
. In this era of France's cultural and artistic
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wh ...
climate (particularly within Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
), the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
markedly flourished, and numerous masterpieces of literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
, music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The perform ...
, and visual art
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, filmmaking, design, crafts and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile arts ...
gained extensive recognition.
The Belle Époque was so named in retrospect, when it began to be considered a continental European "Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during ...
" in contrast to the horrors of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
and World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The Belle Époque was a period in which, according to historian R. R. Palmer: " European civilisation achieved its greatest power in global politics, and also exerted its maximum influence upon peoples outside Europe."
Popular culture and fashions
 Two devastating world wars and their aftermath made the Belle Époque appear to be a time of ''
Two devastating world wars and their aftermath made the Belle Époque appear to be a time of ''joie de vivre
( , ; "joy of living") is a French phrase often used in English to express a cheerful enjoyment of life, an exultation of spirit.
It "can be a joy of conversation, joy of eating, joy of anything one might do… And ''joie de vivre'' may be ...
'' (joy of living) in contrast to 20th century hardships. It was also a period of stability that France enjoyed after the tumult of the early years of the Third Republic, featuring defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, the uprising of the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defended ...
, and the fall of General Georges Ernest Boulanger
Georges Ernest Jean-Marie Boulanger (29 April 1837 – 30 September 1891), nicknamed Général Revanche ("General Revenge"), was a French general and politician. An enormously popular public figure during the second decade of the Third Repub ...
. The defeat of Boulanger, and the celebrations tied to the 1889 World's Fair
The Exposition Universelle of 1889 () was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 5 May to 31 October 1889. It was the fourth of eight expositions held in the city between 1855 and 1937. It attracted more than thirty-two million visitors. The ...
in Paris, launched an era of optimism and affluence. French imperialism
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French Colonial Empire", that existe ...
was in its prime. It was a cultural center of global influence, its educational
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Vari ...
, scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
and medical
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
institutions were at the leading edge of Europe.
It was not entirely the reality of life in Paris or in France, however. France had a large economic underclass
The underclass is the segment of the population that occupies the lowest possible position in a class hierarchy, below the core body of the working class.
The general idea that a class system includes a population ''under'' the working class has ...
who never experienced much of the Belle Époque's wonders and entertainments. Poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
remained endemic in Paris's urban slums
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily in ...
and rural peasantry
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasants ...
for decades after the Belle Époque ended. Conflicts between the government and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
were regular during the period. Some of the artistic elite saw the Fin de siècle
() is a French term meaning "end of century,” a phrase which typically encompasses both the meaning of the similar English idiom "turn of the century" and also makes reference to the closing of one era and onset of another. Without context, ...
in a pessimistic light.
 Those who were able to benefit from the prosperity of the era were drawn towards new forms of light entertainment during the Belle Époque, and the Parisian bourgeoisie, or the successful industrialists called the '' nouveaux riches'', became increasingly influenced by the habits and fads of the city's elite social class, known popularly as ''
Those who were able to benefit from the prosperity of the era were drawn towards new forms of light entertainment during the Belle Époque, and the Parisian bourgeoisie, or the successful industrialists called the '' nouveaux riches'', became increasingly influenced by the habits and fads of the city's elite social class, known popularly as ''Tout-Paris
Le Tout-Paris ("everyone in Paris") is a French expression referring to the fashionable and affluent elite of the city, who frequent fashionable events and places, and establish trends in upper-class culture. It is equivalent to the "jet set" else ...
'' ("all of Paris", or "everyone in Paris"). The Casino de Paris
The Casino de Paris, located at 16, rue de Clichy, in the 9th arrondissement, is one of the well known music halls of Paris, with a history dating back to the 18th century. Contrary to what the name might suggest, it is a performance venue, not ...
opened in 1890. For Paris's less affluent public, entertainment was provided by cabaret
Cabaret is a form of theatrical entertainment featuring music, song, dance, recitation, or drama. The performance venue might be a pub, a casino, a hotel, a restaurant, or a nightclub with a stage for performances. The audience, often dining o ...
s, bistro
A bistro or bistrot , is, in its original Parisian incarnation, a small restaurant, serving moderately priced simple meals in a modest setting. Bistros are defined mostly by the foods they serve. French home-style cooking, and slow-cooked foods ...
s and music halls.
The Moulin Rouge
Moulin Rouge (, ; ) is a cabaret in Paris, on Boulevard de Clichy, at Place Blanche, the intersection of, and terminus of Rue Blanche.
In 1889, the Moulin Rouge was co-founded by Charles Zidler and Joseph Oller, who also owned the Paris Ol ...
cabaret is a Paris landmark still open for business today. The Folies Bergère
The Folies Bergère () is a cabaret music hall, located in Paris, France. Located at 32 Rue Richer in the 9th Arrondissement, the Folies Bergère was built as an opera house by the architect Plumeret. It opened on 2 May 1869 as the Folies Trév ...
was another landmark venue. Burlesque
A burlesque is a literary, dramatic or musical work intended to cause laughter by caricaturing the manner or spirit of serious works, or by ludicrous treatment of their subjects.
performance styles were more mainstream in Belle Époque Paris than in more staid cities of Europe and America. Liane de Pougy
Liane de Pougy (born Anne-Marie Chassaigne, 2 July 1869 – 26 December 1950), was a Folies Bergère vedette and dancer renowned as one of Paris's most beautiful and notorious courtesans.
Early life and marriage
Anne-Marie Chassaigne was bor ...
, dancer
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoi ...
, socialite and courtesan
Courtesan, in modern usage, is a euphemism for a "kept" mistress or prostitute, particularly one with wealthy, powerful, or influential clients. The term historically referred to a courtier, a person who attended the court of a monarch or other ...
, was well known in Paris as a headline performer at top cabarets. Belle Époque dancers and singers such as Polaire
Émilie Marie Bouchaud (14 May 1874 – 14 October 1939), better known by her stage name Polaire, was a French singer and actress. She was known for her wasp waist which, achieved through corsetry, reportedly measured less than 16 inches (41&nbs ...
, Mistinguett
Mistinguett (, born Jeanne Florentine Bourgeois; 5 April 1873 – 5 January 1956) was a French actress and singer. She was at one time the highest-paid female entertainer in the world.
Early life
The daughter of Antoine Bourgeois, a 31-year- ...
, Paulus, Eugénie Fougère, La Goulue
La Goulue (, meaning ''The Gourmand''), was the stage name of Louise Weber (12 July 1866 – 29 January 1929), a French can-can dancer who was a star of the Moulin Rouge, a popular cabaret in the Pigalle district of Paris, near Montmartre. Weber ...
and Jane Avril
Jane Avril (9 June 186817 January 1943) was a French can-can dancer made famous by Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec through his paintings. Extremely thin, "given to jerky movements and sudden contortions", she was nicknamed ''La Mélinite'', after a ...
were Paris celebrities, some of whom modelled for Toulouse-Lautrec
Comte Henri Marie Raymond de Toulouse-Lautrec-Monfa (24 November 1864 – 9 September 1901) was a French painter, printmaker, draughtsman, caricaturist and illustrator whose immersion in the colourful and theatrical life of Paris in the l ...
's iconic poster art. The Can-can dance was a popular 19th-century cabaret style that appears in Toulouse-Lautrec's posters from the era.
 The
The Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; french: links=yes, tour Eiffel ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower.
Locally nicknamed "'' ...
, built to serve as the grand entrance to the 1889 World's Fair
The Exposition Universelle of 1889 () was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 5 May to 31 October 1889. It was the fourth of eight expositions held in the city between 1855 and 1937. It attracted more than thirty-two million visitors. The ...
held in Paris, became the accustomed symbol of the city, to its inhabitants and to visitors from around the world. Paris hosted another successful World's Fair in 1900, the Exposition Universelle. Paris had been profoundly changed by the Second Empire Second Empire may refer to:
* Second British Empire, used by some historians to describe the British Empire after 1783
* Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396)
* Second French Empire (1852–1870)
** Second Empire architecture, an architectural styl ...
reforms to the city's architecture and public amenities. Haussmann's renovation of Paris
Haussmann's renovation of Paris was a vast public works programme commissioned by Emperor Napoleon III and directed by his prefect of Seine, Georges-Eugène Haussmann, between 1853 and 1870. It included the demolition of medieval neighbourh ...
changed its housing, street layouts, and green spaces. The walkable neighbourhoods were well-established by the Belle Époque.
Cheap coal and cheap labour contributed to the cult of the orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
and made possible the perfection of fruits grown under glass, as the apparatus of state dinner
A state banquet is an official banquet hosted by the head of state in his or her official residence for another head of state, or sometimes head of government, and other guests. Usually as part of a state visit or diplomatic conference, it is h ...
s extended to the upper classes. Exotic feathers and furs were more prominently featured in fashion than ever before, as '' haute couture'' was invented in Paris, the center of the Belle Époque, where fashion began to move in a yearly cycle. In Paris, restaurants such as Maxim's Paris
Maxim's is a restaurant in Paris, France, located at No. 3 rue Royale in the 8th . It is known for its Art Nouveau interior decor. In the mid 20th century Maxim's was regarded as the most famous restaurant in the world.
History
Early histor ...
achieved a new splendor and cachet as places for the rich to parade. Maxim's Paris was arguably the city's most exclusive restaurant. Bohemian
Bohemian or Bohemians may refer to:
*Anything of or relating to Bohemia
Beer
* National Bohemian, a brand brewed by Pabst
* Bohemian, a brand of beer brewed by Molson Coors
Culture and arts
* Bohemianism, an unconventional lifestyle, origin ...
lifestyles gained a different glamour, pursued in the cabaret
Cabaret is a form of theatrical entertainment featuring music, song, dance, recitation, or drama. The performance venue might be a pub, a casino, a hotel, a restaurant, or a nightclub with a stage for performances. The audience, often dining o ...
s of Montmartre
Montmartre ( , ) is a large hill in Paris's northern 18th arrondissement. It is high and gives its name to the surrounding district, part of the Right Bank. The historic district established by the City of Paris in 1995 is bordered by Rue Ca ...
.
Large public buildings such as the Opéra Garnier
The Palais Garnier (, Garnier Palace), also known as Opéra Garnier (, Garnier Opera), is a 1,979-seatBeauvert 1996, p. 102. opera house at the Place de l'Opéra in the 9th arrondissement of Paris, France. It was built for the Paris Opera from ...
devoted enormous spaces to interior designs as Art Nouveau show places. After the mid-19th century, railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
linked all the major cities of Europe to spa
A spa is a location where mineral-rich spring water (and sometimes seawater) is used to give medicinal baths. Spa towns or spa resorts (including hot springs resorts) typically offer various health treatments, which are also known as balneoth ...
towns like Biarritz, Deauville
Deauville () is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Major attractions include its harbour, race course, marinas, conference centre, villas, Grand Casino, and sumptuous hotels. The first Deauville Asian Film F ...
, Vichy
Vichy (, ; ; oc, Vichèi, link=no, ) is a city in the Allier department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of central France, in the historic province of Bourbonnais.
It is a spa and resort town and in World War II was the capital of ...
, Arcachon
Arcachon ( ; ) is a commune in the southwestern French department of Gironde. It is a popular seaside resort on the Atlantic coast southwest of Bordeaux, in the Landes forest. It has a sandy beach and a mild climate said to be favourable for i ...
and the French Riviera
The French Riviera (known in French as the ; oc, Còsta d'Azur ; literal translation " Azure Coast") is the Mediterranean coastline of the southeast corner of France. There is no official boundary, but it is usually considered to extend fro ...
. Their carriages were rigorously divided into first-class and second-class, but the super-rich now began to commission private railway coaches, as exclusivity as well as display was a hallmark of opulent luxury.
Politics
 The years between the Franco-Prussian War and World War I were characterised by unusual political stability in
The years between the Franco-Prussian War and World War I were characterised by unusual political stability in Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
. Although tensions between France and Germany persisted as a result of the French loss of Alsace-Lorraine to Germany in 1871, a series of diplomatic conferences managed to mediate disputes that threatened the general peace: the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at th ...
in 1878, the Berlin Congo Conference in 1884, and the Algeciras Conference in 1906. Indeed, for many Europeans during the Belle Époque, transnational, class-based affiliations were as important as national identities, particularly among aristocrats. An upper-class gentleman could travel through much of Western Europe without a passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that contains a person's identity. A person with a passport can travel to and from foreign countries more easily and access consular assistance. A passport certifies the personal ...
and even reside abroad with minimal bureaucratic regulation. World War I, mass transportation, the spread of literacy, and various citizenship concerns changed this.
The Belle Époque featured a class structure
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the upper, middle and lower classes. Membership in a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, inco ...
that ensured cheap labour. The Paris Métro
The Paris Métro (french: Métro de Paris ; short for Métropolitain ) is a rapid transit system in the Paris metropolitan area, France. A symbol of the Paris, city, it is known for its density within the capital's territorial limits, uniform ar ...
underground railway system joined the omnibus and streetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
in transporting the working population, including those servants who did not live in the wealthy centers of cities. One result of this commuting
Commuting is periodically recurring travel between one's place of residence and place of work or study, where the traveler, referred to as a commuter, leaves the boundary of their home community. By extension, it can sometimes be any regul ...
was suburbanisation allowing working-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
and upper-class neighbourhoods to be separated by large distances.
 Meanwhile, the international workers' movement also reorganised itself and reinforced pan-European, class-based identities among the classes whose labour supported the Belle Époque. The most notable transnational
Meanwhile, the international workers' movement also reorganised itself and reinforced pan-European, class-based identities among the classes whose labour supported the Belle Époque. The most notable transnational socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
organisation was the Second International
The Second International (1889–1916) was an organisation of socialist and labour parties, formed on 14 July 1889 at two simultaneous Paris meetings in which delegations from twenty countries participated. The Second International continued th ...
. Anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessari ...
of different affiliations were active during the period leading up to World War I. Political assassinations and assassination attempts were still rare in France (unlike in Russia) but there were some notable exceptions, including the killing of President Marie François Sadi Carnot
Marie François Sadi Carnot (; 11 August 1837 – 25 June 1894) was a French statesman, who served as the President of France from 1887 until his assassination in 1894.
Early life
Marie François Sadi Carnot was the son of the statesman Hippo ...
in 1894. A bomb was detonated in the Chamber of Deputies of France
Chamber of Deputies (french: Chambre des députés) was a parliamentary body in France in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries:
* 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy, the Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of ...
in 1893, causing injuries but no deaths. Terrorism against civilians also occurred in 1894, perpetrated by Émile Henry, who killed a cafe patron and wounded several others.
France enjoyed relative political stability at home during the Belle Époque. The sudden death of President Félix Faure
Félix François Faure (; 30 January 1841 – 16 February 1899) was the President of France from 1895 until his death in 1899. A native of Paris, he worked as a tanner in his younger years. Faure became a member of the Chamber of Deputies for ...
while in office took the country by surprise, but had no destabilising effect on the government. The most serious political issue to face the country during this period was the Dreyfus affair
The Dreyfus affair (french: affaire Dreyfus, ) was a political scandal that divided the French Third Republic from 1894 until its resolution in 1906. "L'Affaire", as it is known in French, has come to symbolise modern injustice in the Francop ...
. Captain Alfred Dreyfus was wrongly convicted of treason, with fabricated evidence from French government officials. Antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
directed at Dreyfus, and tolerated by the general French public in everyday society, was a central issue in the controversy and the court trials that followed. Public debate surrounding the Dreyfus Affair grew to an uproar after the publication of ''J'Accuse…!
"''J'Accuse...!''" (; "I Accuse...!") is an open letter that was published on 13 January 1898 in the newspaper ''L'Aurore'' by Émile Zola in response to the Dreyfus affair. Zola addressed President of France Félix Faure and accused his govern ...
'', an open letter sent to newspapers by prominent novelist Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of ...
, condemning government corruption and French antisemitism. The Dreyfus affair consumed the interest of the French for several years and it received heavy newspaper coverage.
European politics saw very few regime changes, the major exception being Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, which experienced a republican revolution in 1910. However, tensions between working-class socialist parties, bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
parties, and landed or aristocratic conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization i ...
parties did increase in many countries, and it has been claimed that profound political instability belied the calm surface of European politics in the era. In fact, militarism
Militarism is the belief or the desire of a government or a people that a state should maintain a strong military capability and to use it aggressively to expand national interests and/or values. It may also imply the glorification of the mili ...
and international tensions grew considerably between 1897 and 1914, and the immediate prewar years were marked by a general armaments competition in Europe. Additionally, this era was one of massive overseas colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
, known as the New Imperialism
In historical contexts, New Imperialism characterizes a period of colonial expansion by European powers, the United States, and Japan during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Com
The period featured an unprecedented pursuit of ove ...
. The most famous portion of this imperial expansion was the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
.
; Conflicts and wars

 Most of the great powers (and some minor ones such as Belgium, the Netherlands, or Denmark) became involved in
Most of the great powers (and some minor ones such as Belgium, the Netherlands, or Denmark) became involved in imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
, building their own overseas empires especially in Africa and Asia. Although there were numerous revolutions, civil wars and colonial insurrections, the most notable are: the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
(1877–1878), the War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific ( es, link=no, Guerra del Pacífico), also known as the Saltpeter War ( es, link=no, Guerra del salitre) and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought ...
(1879–1884), two Boer Wars (1880–1881 and 1899–1902), the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the po ...
(1894–1895), the First Italo-Ethiopian War
The First Italo-Ethiopian War, lit. ''Abyssinian War'' was fought between Italy and Ethiopia from 1895 to 1896. It originated from the disputed Treaty of Wuchale, which the Italians claimed turned Ethiopia into an Italian protectorate. Full-sc ...
(1895–1896), the Greco-Turkish War (1897), the Spanish-American War
Spanish Americans ( es, españoles estadounidenses, ''hispanoestadounidenses'', or ''hispanonorteamericanos'') are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly from Spain. They are the longest-established European American group in th ...
(1898), the Philippine-American War (1899–1902), the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
(1905), and the Italo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish or Turco-Italian War ( tr, Trablusgarp Savaşı, "Tripolitanian War", it, Guerra di Libia, "War of Libya") was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911, to 18 October 1912. As a result o ...
(1911–1912).
The First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
(1912–1913) and the Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies r ...
(1913) are considered prologues to the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918), whose level of material and human destruction at the industrial level marks the end of the ''Belle Époque''.
There were also notable diplomatic conflicts that could provoke world wars such as the 1890 British Ultimatum, the Fashoda Incident
The Fashoda Incident, also known as the Fashoda Crisis (French: ''Crise de Fachoda''), was an international incident and the climax of imperialist territorial disputes between Britain and France in East Africa, occurring in 1898. A French exped ...
(1898), the First Moroccan Crisis
The First Moroccan Crisis or the Tangier Crisis was an international crisis between March 1905 and May 1906 over the status of Morocco. Germany wanted to challenge France's growing control over Morocco, aggravating France and Great Britain. The ...
(1905-1906), and the Second Moroccan Crisis
The Agadir Crisis, Agadir Incident, or Second Moroccan Crisis was a brief crisis sparked by the deployment of a substantial force of French troops in the interior of Morocco in April 1911 and the deployment of the German gunboat to Agadir, a ...
(1911).
Science and technology



 The Belle Époque was an era of great scientific and technological advancement in Europe and the world in general. Inventions of the
The Belle Époque was an era of great scientific and technological advancement in Europe and the world in general. Inventions of the Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The Firs ...
that became generally common in this era include the perfection of lightly sprung, noiseless carriages in a multitude of new fashionable forms, which were superseded towards the end of the era by the automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
, which was for its first decade a luxurious experiment for the well-heeled. French automobile manufacturers such as Peugeot
Peugeot (, , ) is a French brand of automobiles owned by Stellantis.
The family business that preceded the current Peugeot companies was founded in 1810, with a steel foundry that soon started making hand tools and kitchen equipment, and the ...
were already pioneers in carriage manufacturing. Edouard Michelin invented removable pneumatic tires
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a Rim (wheel), wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide Traction (engineering), t ...
for bicycles and automobiles in the 1890s. The scooter and moped
A moped ( ) is a type of small motorcycle, generally having a less stringent licensing requirement than full motorcycles or automobiles. The term used to mean a similar vehicle except with both bicycle pedals and a motorcycle engine. Mopeds typ ...
are also Belle Époque inventions.
A number of French inventors patented products with a lasting impact on modern society. After the telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
joined the telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
as a vehicle for rapid communication, French inventor Édouard Belin
Édouard Belin (5 March 1876 – 4 March 1963) was a French photographer and inventor. In 1907 Belin invented a phototelegraphic apparatus called the Bélinographe (télestéréographe)—a system for receiving photographs over telephone ...
developed the Belinograph, or Wirephoto
Wirephoto, telephotography or radiophoto is the sending of pictures by telegraph, telephone or radio.
Édouard Belin's Bélinographe of 1913, which scanned using a photocell and transmitted over ordinary phone lines, formed the basis for the W ...
, to transmit photos by telephone. The electric light
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the soc ...
began to supersede gas lighting
Gas lighting is the production of artificial light from combustion of a gaseous fuel, such as hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, propane, butane, acetylene, ethylene, coal gas (town gas) or natural gas. The light is produced either directly ...
, and neon light
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode a ...
s were invented in France.
France was a leader of early cinema
Cinema may refer to:
Film
* Cinematography, the art of motion-picture photography
* Film or movie, a series of still images that create the illusion of a moving image
** Film industry, the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking
...
technology. The cinématographe
Cinematograph or kinematograph is an early term for several types of motion picture film mechanisms. The name was used for movie cameras as well as film projectors, or for complete systems that also provided means to print films (such as the Cin ...
was invented in France by Léon Bouly
Léon Guillaume Bouly (; 1872–1932) was a French inventor who created the word cinematograph.
Cinematograph
After devising chronophotography devices, Bouly applied a patent on a reversible device of photography and optics for the analysis and ...
and put to use by Auguste and Louis Lumière
The Lumière brothers (, ; ), Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas Lumière (19 October 1862 – 10 April 1954) and Louis Jean Lumière (5 October 1864 – 6 June 1948), were French manufacturers of photography equipment, best known for their ''Ciném ...
, brothers who held the first film screenings in the world. The Lumière brothers made many other innovations in cinematography
Cinematography (from ancient Greek κίνημα, ''kìnema'' "movement" and γράφειν, ''gràphein'' "to write") is the art of motion picture (and more recently, electronic video camera) photography.
Cinematographers use a lens to focu ...
. It was during this era that the motion pictures
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
were developed, though these did not become common until after World War I.
Although the aeroplane remained a fascinating experiment, France was a leader in aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
. France established the world's first national air force in 1910. Two French inventors, Louis Breguet and Paul Cornu, made independent experiments with the first flying helicopters in 1907.
Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity in 1896 while working with phosphorescent materials. His work confirmed and explained earlier observations regarding uranium salts by Abel Niépce de Saint-Victor in 1857.
It was during this era that biologists and physicians finally came to understand the germ theory of disease, and the field of bacteriology was established. Louis Pasteur was perhaps the most famous scientist in France during this time. Pasteur developed pasteurisation and a rabies vaccine. Mathematician and physicist Henri Poincaré made important contributions to pure and applied mathematics, and also published books for the general public on mathematical and scientific subjects. Marie Skłodowska-Curie worked in France, winning the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1903, and the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1911. Physicist Gabriel Lippmann invented integral imaging, still in use today.
Art and literature

 In 1890, Vincent van Gogh died. It was during the 1890s that his paintings achieved the admiration denied them during Van Gogh's life; first among other artists, then gradually among the public. Reactions against the ideals of the Impressionists characterised visual arts in Paris during the Belle Époque. Among the post-Impressionism, post-Impressionist movements in Paris were the Les Nabis, Nabis, the Salon de la Rose + Croix, the Symbolist movement (also in poetry, music, and visual art), Fauvism, and early Modernism. Between 1900 and 1914, Expressionism took hold of many artists in Paris and Vienna. Early works of Cubism and Abstraction were exhibited. Foreign influences were being strongly felt in Paris as well. The official art school in Paris, the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts, École des Beaux-Arts, held an exhibition of Japanese printmaking that changed approaches to graphic design, particular posters and book illustration (Aubrey Beardsley was influenced by a similar exhibit when he visited Paris during the 1890s). Exhibits of African tribal art also captured the imagination of Parisian artists at the turn of the 20th century.
Art Nouveau is the most popularly recognised art movement to emerge from the period. This largely decorative style (Jugendstil in central Europe), characterised by its curvilinear forms, and nature-inspired motifs became prominent from the mid-1890s and dominated progressive design throughout much of Europe. Its use in public art in Paris, such as Hector Guimard's
In 1890, Vincent van Gogh died. It was during the 1890s that his paintings achieved the admiration denied them during Van Gogh's life; first among other artists, then gradually among the public. Reactions against the ideals of the Impressionists characterised visual arts in Paris during the Belle Époque. Among the post-Impressionism, post-Impressionist movements in Paris were the Les Nabis, Nabis, the Salon de la Rose + Croix, the Symbolist movement (also in poetry, music, and visual art), Fauvism, and early Modernism. Between 1900 and 1914, Expressionism took hold of many artists in Paris and Vienna. Early works of Cubism and Abstraction were exhibited. Foreign influences were being strongly felt in Paris as well. The official art school in Paris, the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts, École des Beaux-Arts, held an exhibition of Japanese printmaking that changed approaches to graphic design, particular posters and book illustration (Aubrey Beardsley was influenced by a similar exhibit when he visited Paris during the 1890s). Exhibits of African tribal art also captured the imagination of Parisian artists at the turn of the 20th century.
Art Nouveau is the most popularly recognised art movement to emerge from the period. This largely decorative style (Jugendstil in central Europe), characterised by its curvilinear forms, and nature-inspired motifs became prominent from the mid-1890s and dominated progressive design throughout much of Europe. Its use in public art in Paris, such as Hector Guimard's Paris Métro
The Paris Métro (french: Métro de Paris ; short for Métropolitain ) is a rapid transit system in the Paris metropolitan area, France. A symbol of the Paris, city, it is known for its density within the capital's territorial limits, uniform ar ...
stations, has made it synonymous with the city.
Prominent artists in Paris during the Belle Époque included post-Impressionists such as Odilon Redon, Gustave Moreau, Maurice Denis, Pierre Bonnard, Édouard Vuillard, Paul Gauguin, Henri Matisse, Émile Bernard (painter), Émile Bernard, Henri Rousseau, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (whose reputation improved substantially after his death), Giuseppe Amisani, and a young Pablo Picasso. More modern forms in sculpture also began to dominate as in the works of Paris-native Auguste Rodin.
Although Impressionism in painting began well before the Belle Époque, it had initially been met with scepticism if not outright scorn by a public accustomed to the realist and representational art approved by the Academy. In 1890, Monet started his series ''Haystacks (Monet), Haystacks''. Impressionism, which had been considered the artistic avant-garde in the 1860s, did not gain widespread acceptance until after World War I. The academic painting style, associated with the Academy of Art in Paris, remained the most respected style among the public in Paris. Artists who appealed to the Belle Époque public include William-Adolphe Bouguereau, the English Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, Pre-Raphaelite's John William Waterhouse, and Frederic Leighton, 1st Baron Leighton, Lord Leighton and his depictions of idyllic Roman scenes. More progressive tastes patronised the Barbizon school ''plein-air'' painters. These painters were associates of the Pre-Raphaelites, who inspired a generation of aesthetic-minded "The Souls, Souls".
Many successful examples of Art Nouveau, with notable regional variations, were built in France, Germany, Belgium, Spain, Austria (the Vienna Secession), Hungary, Bohemia, Serbia, and Latvia. It soon spread around the world, including Peru, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, and the United States.
European literature underwent a major transformation during the Belle Époque. Literary realism and naturalism (literature), naturalism achieved new heights. Among the most famous French realist or naturalist authors are Guy de Maupassant and Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of ...
. Realism gradually developed into modernism, which emerged in the 1890s and came to dominate European literature during the Belle Époque's final years and throughout the Interwar period, interwar years. The Modernist classic ''In Search of Lost Time'' was begun by Marcel Proust in 1909, to be published after World War I. The works of German Thomas Mann had a huge impact in France as well, such as ''Death in Venice'', published in 1912. Colette shocked France with the publication of the sexually frank ''Claudine (book series), Claudine'' novel series, and other works. Joris-Karl Huysmans, who came to prominence in the mid-1880s, continued experimenting with themes and styles that would be associated with Symbolism (arts), Symbolism and the Decadent movement, mostly in his book ''à rebours''. André Gide, Anatole France, Alain-Fournier, and Paul Bourget are among France's most popular fiction writers of the era.
 Among poets, the Symbolists such as Charles Baudelaire remained at the forefront. Although Baudelaire's poetry collection ''Les Fleurs du mal'' had been published in the 1850s, it exerted a strong influence on the next generation of poets and artists. The Decadent movement fascinated Parisians, intrigued by Paul Verlaine and above all Arthur Rimbaud, who became the archetypal ''enfant terrible'' of France. Rimbaud's ''Illuminations (poetry collection), Illuminations'' was published in 1886, and subsequently his other works were also published, influencing Surrealism, Surrealists and Modernism, Modernists during the Belle Époque and after. Rimbaud's poems were the first works of free verse seen by the French public. Free verse and typographic experimentation also emerged in ''Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard (Mallarmé), Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard'' by Stéphane Mallarmé, anticipating Dada and concrete poetry. Guillaume Apollinaire's poetry introduced themes and imagery from modern life to readers. ''Cosmopolis (magazine), Cosmopolis: An International Monthly Review'' had a far-reaching impact on European writers, and ran editions in London, Paris, Saint Petersburg, and Berlin.
Paris's popular bourgeois theatre was dominated by the light farces of Georges Feydeau and
Among poets, the Symbolists such as Charles Baudelaire remained at the forefront. Although Baudelaire's poetry collection ''Les Fleurs du mal'' had been published in the 1850s, it exerted a strong influence on the next generation of poets and artists. The Decadent movement fascinated Parisians, intrigued by Paul Verlaine and above all Arthur Rimbaud, who became the archetypal ''enfant terrible'' of France. Rimbaud's ''Illuminations (poetry collection), Illuminations'' was published in 1886, and subsequently his other works were also published, influencing Surrealism, Surrealists and Modernism, Modernists during the Belle Époque and after. Rimbaud's poems were the first works of free verse seen by the French public. Free verse and typographic experimentation also emerged in ''Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard (Mallarmé), Un coup de dés jamais n'abolira le hasard'' by Stéphane Mallarmé, anticipating Dada and concrete poetry. Guillaume Apollinaire's poetry introduced themes and imagery from modern life to readers. ''Cosmopolis (magazine), Cosmopolis: An International Monthly Review'' had a far-reaching impact on European writers, and ran editions in London, Paris, Saint Petersburg, and Berlin.
Paris's popular bourgeois theatre was dominated by the light farces of Georges Feydeau and cabaret
Cabaret is a form of theatrical entertainment featuring music, song, dance, recitation, or drama. The performance venue might be a pub, a casino, a hotel, a restaurant, or a nightclub with a stage for performances. The audience, often dining o ...
performances. Theatre adopted new modern methods, including Expressionism, and many playwrights wrote plays that shocked contemporary audiences either with their frank depictions of everyday life and sexuality or with unusual artistic elements. Cabaret theatre also became popular.
Musically, the Belle Époque was characterised by salon music. This was not considered serious music but, rather, short pieces considered accessible to a general audience. In addition to works for piano solo or violin and piano, the Belle Époque was famous for its large repertory of songs (mélodies, romanze, etc.). The Italians were the greatest proponents of this type of song, its greatest champion being Francesco Paolo Tosti. Though Tosti's songs never completely left the repertoire, salon music generally fell into a period of obscurity. Even as encores, singers were afraid to sing them at serious recitals. In that period, waltzes also flourished. Operettas were also at the peak of their popularity, with composers such as Johann Strauss III, Emmerich Kálmán, and Franz Lehár. Many Belle Époque composers working in Paris are still popular today: Igor Stravinsky, Erik Satie, Claude Debussy, Lili Boulanger, Jules Massenet, César Franck, Camille Saint-Saëns, Gabriel Fauré and his pupil, Maurice Ravel. According to Fauré and Ravel, the favoured composer of the Belle Époch was Edvard Grieg, who enjoyed the height of his popularity in both Parisian concert and salon life (despite his stance on the accused in the Dreyfus affair). Ravel and Delius agreed that French music of this time was simply "Edvard Grieg plus the third act of ''Tristan''".
Modern dance began to emerge as a powerful artistic development in theatre. Dancer Loie Fuller appeared at popular venues such as the Folies Bergère
The Folies Bergère () is a cabaret music hall, located in Paris, France. Located at 32 Rue Richer in the 9th Arrondissement, the Folies Bergère was built as an opera house by the architect Plumeret. It opened on 2 May 1869 as the Folies Trév ...
, and took her eclectic performance style abroad as well. Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes brought fame to Vaslav Nijinsky and established modern ballet technique. The Ballets Russes launched several ballet masterpieces, including ''The Firebird'' and ''The Rite of Spring'' (sometimes causing audience riots at the same time).
Belle Époque by country


Africa
* In Khedivate of Egypt, Egypt, with the reigns of Isma'il Pasha, Tewfik Pasha, and Abbas II of Egypt, Abbas II Helmy. * In Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia, with the reigns of Yohannes IV and Menelik II.Americas
* In Argentina, with the period of the Generation of '80. * In Brazil, it began with the end of the Paraguayan War, during the reign of Pedro II of Brazil, Pedro II. * In Canada, it coincided with the beginnings of Canadian Confederation. * In Chile, it coincided with the Liberal Republic. * In Honduras, it coincided with the History of Honduras (1838–1932), Liberal Reform. * In Mexico, the period was known as the Porfiriato. * In Peru, with the period of the History of Peru#Reconstruction, the Aristocratic Republic, and Leguía's 11-year rule (1884–1930), Aristocratic Republic. * In the United States, emerging from the panic of 1873, ushering in the period known as ''Gilded Age'' and Progressive Era. * In Uruguay, the period was known as José Batlle y Ordóñez, Batllism.Asia
* In Qing dynasty, China, with the reigns of Tongzhi Emperor, Tongzhi, Guangxu Emperor, Guangxu, and the beginning of Puyi. * In Joseon, Korea, with the reign of Gojong of Korea, Gojong. * In Empire of Japan, Japan, with the reign of Emperor Meiji, Meiji. * In Kingdom of Nepal, Nepal, with the reigns of Surendra Bikram Shah, Prithvi Bir Bikram Shah, and the beginning of Tribhuvan of Nepal, Tribhuvan Bir Bikram Shah. * In Qajar Iran, Persia, with the reigns of Naser al-Din Shah Qajar, Naser al-Din Shah, Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar, Mozaffar ad-Din Shah, Mohammad Ali Shah Qajar, Mohammad Ali Shah, and the beginning of Ahmad Shah Qajar, Ahmad Shah. * In Rattanakosin Kingdom (1782–1932), Thailand, with the reign of Chulalongkorn and the beginning of Vajiravudh. * In Ottoman Empire, Turkey, with the reigns of Abdulaziz, Murad V, and the beginning of Abdul Hamid II.Europe
* In Austria-Hungary, with the reign of Franz Joseph I. * In Belgium, with the reign of Leopold II of Belgium, Leopold II and the beginning of Albert I of Belgium, Albert I. * In Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria, at the beginning of Ferdinand I of Bulgaria, Ferdinand I. * In Denmark, with the reigns of Christian IX and Frederick VIII of Denmark, Frederick VIII. * In France, with the French Third Republic. * In German Empire, Germany, it coincided with the reigns of William I, German Emperor, William I, Frederick III, German Emperor, Frederick III, and Wilhelminism of Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II. * In Kingdom of Greece, Greece, with the reign of George I of Greece, George I. * In Kingdom of Italy, Italy, with the reigns of Victor Emmanuel II, Umberto I, and the beginning of Victor Emmanuel III. * In Luxembourg, with the reigns of Adolphe, Grand Duke of Luxembourg, Adolphe and William IV, Grand Duke of Luxembourg, William IV. * In Kingdom of Montenegro, Montenegro, at the beginning of the reign of Nicholas I of Montenegro, Nicholas I. * In the Netherlands, with the reigns of William III of the Netherlands, William III and Wilhelmina of the Netherlands, Wilhelmina. * InPortugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, with the last period of the Kingdom of Portugal and the First Portuguese Republic.
* In Kingdom of Romania, Romania, with the reign of Carol I of Romania, Carol I.
* In Russian Empire, Russia, with the reign of Alexander III of Russia, Alexander III and the beginning of Nicholas II of Russia, Nicholas II.
* In Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, with the reign of Peter I of Serbia, Peter I.
* In Spain, with the reigns of Alfonso XII and Alfonso XIII.
* In Union between Sweden and Norway, Sweden-Norway, with the reign of Oscar II.
* In Switzerland, it coincided with the beginnings of the Swiss federal state from 1848.
* In the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, with the Victorian era and Edwardian era.
* In the Vatican City, Vatican, with the reign of Pope Leo XIII and the beginning of Pope Pius X.
Oceania
* In Australia, it coincided with the period known as the Australian gold rushes. * In Hawaiian Kingdom, Hawaii, with the reigns of Lunalilo, Kalākaua, and the beginning of Liliʻuokalani.Gallery
See also
* Paris in the Belle Époque * Paris architecture of the Belle Époque * Charles Ayrout, Belle Époque architect in Cairo, Egypt *Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The Firs ...
* Fin de siècle
() is a French term meaning "end of century,” a phrase which typically encompasses both the meaning of the similar English idiom "turn of the century" and also makes reference to the closing of one era and onset of another. Without context, ...
* Gay Nineties
* Gilded Age
* Edwardian era
* Succès de scandale
* ''Années folles''
Notes
Further reading
* Berlanstein, Lenard R. "Ready for progress? Opinion surveys on women's roles and opportunities in Belle Epoque France." ''French Politics, Culture and Society'' 27#1 (2009), p. 1+online
* Bruna, D. ''Fashioning the body: An intimate history of the silhouette.'' (Yale University Press, 2015 )/. * Holmes, Diana, and Carrie Tarr, eds. ''A "Belle Epoque"? Women in French Society and Culture 1890–1914'' (Berghahn Books, 2006). * Dominique Kalifa, ''La Véritable histoire de la Belle Epoque'' (Paris: Fayard, 1917). * * Francaise, A. (14 November 2017). Fashion of the Belle Époque. Retrieved 24 September 2018, from http://learnfrenchchicago.com/2017/05/fashion-belle-epoque/ * Mostyn, Trevor. ''Egypt's Belle Époque: Cairo and the Age of the Hedonists'', Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2006. * Roberts, Mary Louise. '' Disruptive Acts: The New Woman in Fin-de-Siecle France'' (U of Chicago Press, 2002). * Wilcox, C. (2013). ''Fashion in detail'' 1700–2000. London: V & A. * Wires, Richard
"Paris: La Belle Époque"
''Conspectus of History'' 1.4 (1977): 60–72.
External links
The ''Belle Époque'' in Europe
– many pictures of Art Nouveau architecture
Paris1900.lartnouveau.com
– The ''Belle Époque'' in Paris through postcards and documents
Dijon1900.blogspot.com
– The ''Belle Époque'' in Dijon through postcards
French Actress Postcards
{{DEFAULTSORT:Belle Epoque Belle Époque, 1871 establishments in France 1914 disestablishments in France 19th century 20th century Art Nouveau Gold standard Historical eras History of Europe by period Modern art Periodization European Cultural History