The history of
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
stretches from its earliest settlement and its formation as a
stem duchy
A stem duchy (german: Stammesherzogtum, from '' Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Bavarians and Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the German Empire at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death of ...
in the 6th century through its inclusion in the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
to its status as an independent kingdom and finally as a large ''
Bundesland'' (state) of the Federal Republic of Germany. Originally settled by Celtic peoples such as the
Boii
The Boii ( Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul ( Northern Italy), Pannonia ( Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom ...
, by the 1st century BC it was eventually conquered and incorporated into the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
as the
provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
and
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nor ...
.
Early settlements and Roman Raetia
There have been numerous
palaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
discoveries in
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
.
The earliest known inhabitants that are mentioned in written sources were the
Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
s, participating in the widespread
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
, whom the
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
subdued just before the commencement of the
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
era, founding colonies among them and including their land in the provinces of
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
and
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nor ...
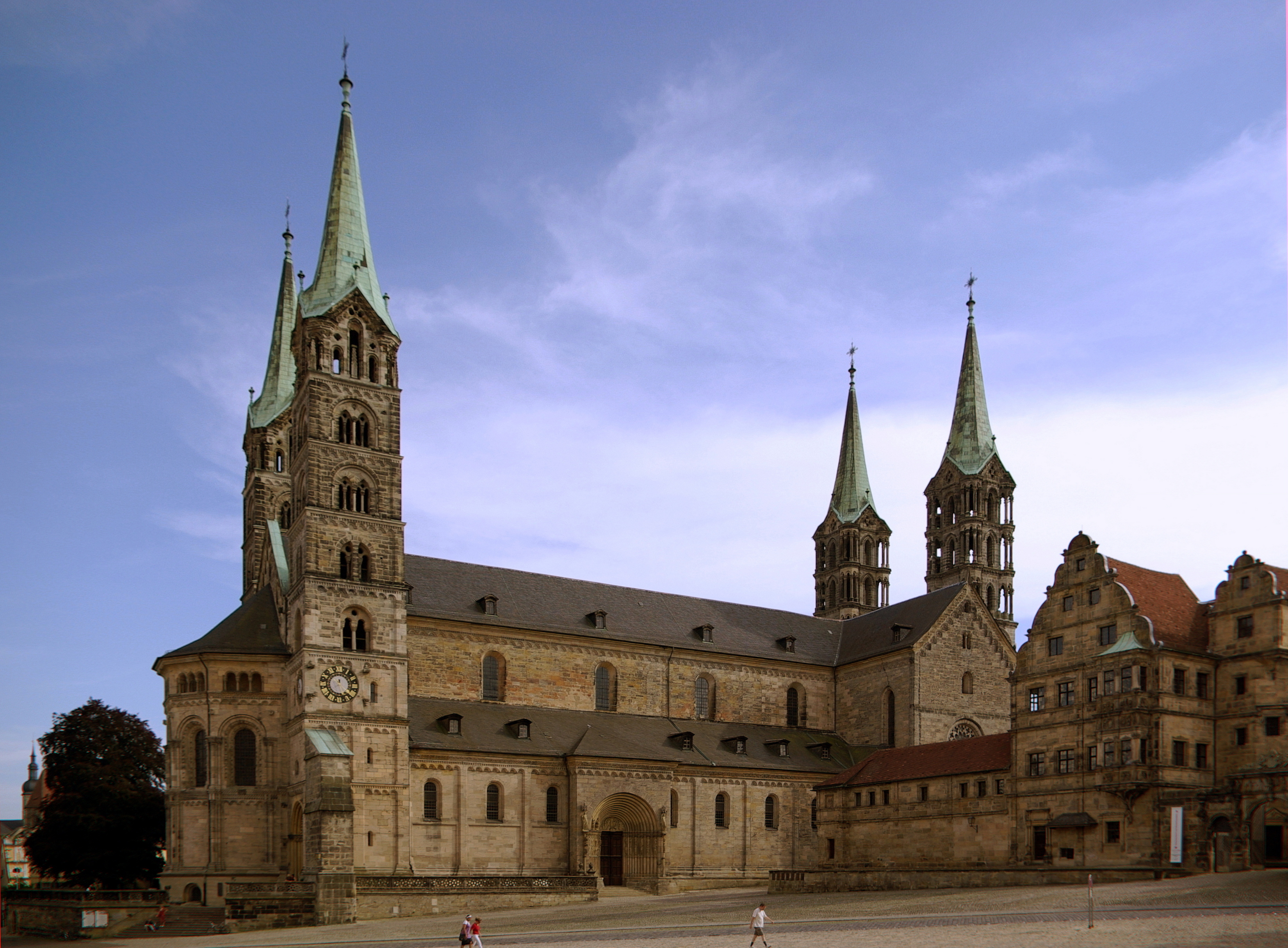
. The Roman center of administration for this area was ''Castra Regina'' (modern-day
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
).
Migrations and early medieval period
During the 5th century, the Romans in
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nor ...
and
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
, south of the
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, came under increasing pressure from people north of the Danube. This area had become inhabited by
Suebian groups from further north and was considered by Romans to be part of
Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-c ...
. The etymological origins of the name "Bavarian" (Latin ''Baiovarii'') are from the north of the Danube, outside the empire, coming from the
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
Boii
The Boii ( Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul ( Northern Italy), Pannonia ( Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom ...
, who lived there earlier. Their name was already used to refer to the part of this region in the time of
Maroboduus
Maroboduus (d. AD 37) was a king of the Marcomanni, who were a Germanic Suebian people. He spent part of his youth in Rome, and returning, found his people under pressure from invasions by the Roman empire between the Rhine and Elbe. He led the ...
who formed the
Germanic Marcomannic kingdom with its capital in this forested area. ''Boi'' became ''Bai'' according to typical Germanic linguistic changes happening at that time and a Germanic word similar to English "home" or modern German "''Heim''" was added.
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
therefore reports Boihaemum (Greek Βουίαιμον). Tacitus similarly reports that ''Boihaemum'' is the name given to the area where the Boii had lived. These forms led to modern
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
which lies to the east of modern Bavaria and completely to the north of the Danube, in the modern
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
. At some later stage, the ending "varii" was used in order to give a new name to specific people living in this geographical area who were then living on both sides of the Danube (similar Germanic ethnic names were created based on other regions:
Angrivarii and
Ampsivarii in northern Germany, Anglo-Saxon
Cantware,
Ripuarian Franks
Ripuarian or Rhineland Franks (Latin: ''Ripuarii'' or ''Ribuarii'') were one of the two main groupings of early Frankish people, and specifically it was the name eventually applied to the tribes who settled in the old Roman territory of the Ubii, ...
and so on).
Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importa ...
named both the "
Baenochaemae", living on the Upper
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
river and a "large people" known as the "'
Baimoi", living near the Danube.
In surviving records, the Bavarian name was first mentioned historically in a
Frankish list of peoples, prepared in c. 520 AD. The first document that also describes their location (east of the Swabians) is the ''History of the Goths'' by the historian
Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') an ...
dating from 551 AD. A remark by
Venantius Fortunatus
Venantius Honorius Clementianus Fortunatus ( 530 600/609 AD; french: Venance Fortunat), known as Saint Venantius Fortunatus (, ), was a Latin poet and hymnographer in the Merovingian Court, and a bishop of the Early Church who has been venerate ...
follows in his description of his travels from
Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
to
Tours
Tours ( , ) is one of the largest cities in the region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is the prefecture of the department of Indre-et-Loire. The commune of Tours had 136,463 inhabitants as of 2018 while the population of the whole metro ...
(565–571), in which he had crossed the lands of the Bavarians, referring to the dangers of travel in the region: 'If the road is clear and if the Bavarian does not stop you
..then travel across the Alps.'
Archaeological evidence dating from the 5th and 6th centuries points to social and cultural influences from several regions and peoples, such as
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pre ...
,
Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
,
Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into confl ...
,
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
,
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
n
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
and the local
Romanised
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and ...
population.
Recent research by Wolfram and Pohl (1990) has moved away from searching for specific geographical origins of the Bavarians. It is now thought that the tribal ethnicity was established by the process of
ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
, whereby an
ethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established fo ...
identity is formed because political and social pressures make a coherent identity necessary.
The stem duchy of Bavaria
Bavaria and the Agilolfings under Frankish overlordship
The Bavarians soon came under the dominion of the Franks, probably without a serious struggle. The Franks regarded this border area as a buffer zone against peoples to the east, such as the
Avars and the
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
, and as a source of manpower for the army. Sometime around 550 AD they put it under the administration of a duke - possibly Frankish or possibly chosen from amongst the local leading families - who was supposed to act as a regional governor for the
Frankish king. The first duke known was
Garibald I, a member of the powerful
Agilolfing family. This was the beginning of a series of Agilolfing dukes that was to last until 788 AD.
For a century and a half, a succession of dukes resisted the inroads of the
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
on their eastern frontier and by the time of
Duke Theodo I, who died in 717, had achieved complete independence from the feeble Frankish kings. When
Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesm ...
became the virtual ruler of the Frankish realm he brought the Bavarians into strict dependence and deposed two dukes successively for
contumacy
Contumacy is a stubborn refusal to obey authority or, particularly in law, the willful contempt of the order or summons of a court (see contempt of court). The term is derived from the Latin word ''contumacia'', meaning firmness or stubbornness.
I ...
. His son and successor
Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
likewise maintained Frankish authority. Several marriages took place between the family to which he belonged and the Agilolfings, who were united in a similar manner with the kings of the
Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
. The ease with which the Franks suppressed various risings gives colour to the supposition that family quarrels rather than the revolt of an oppressed people motivated the rebellions.
Bavarian law was committed to writing between the years 739 AD and 748 AD. Supplementary clauses, added afterward, bear evidence of Frankish influence. Thus, while the duchy belongs to the Agilolfing family, the duke must be chosen by the people and his election confirmed by the Frankish king, to whom he owes
fealty
An oath of fealty, from the Latin ''fidelitas'' (faithfulness), is a pledge of allegiance of one person to another.
Definition
In medieval Europe, the swearing of fealty took the form of an oath made by a vassal, or subordinate, to his lord. "Fea ...
. The
duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are r ...
has a fivefold
weregild
Weregild (also spelled wergild, wergeld (in archaic/historical usage of English), weregeld, etc.), also known as man price (blood money), was a precept in some archaic legal codes whereby a monetary value was established for a person's life, to b ...
, summons the nobles and clergy for purposes of deliberation, calls out the host, administers justice, and regulates finance. Five noble families exist, possibly representing former divisions of the people. Subordinate to the nobles we find the freeborn and then the freedmen. The law divided the country into ''gaits'' or counties, under their counts, assisted by judges responsible for declaring the law.
Christianity
Christianity had lingered in Bavaria from Roman times, but a new era set in when Bishop Rupert of
Worms Worms may refer to:
*Worm, an invertebrate animal with a tube-like body and no limbs
Places
*Worms, Germany
Worms () is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main. It had ...
came to the county at the invitation of Duke Theodo I in 696. He founded several monasteries, as did Bishop
Emmeran of
Poitiers
Poitiers (, , , ; Poitevin: ''Poetàe'') is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglome ...
, with the result that before long, most of the people professed Christianity and relations commenced between Bavaria and
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. The 8th century witnessed indeed a heathen reaction, but the arrival of
Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations o ...
in Bavaria during c. 734 AD checked
apostasy
Apostasy (; grc-gre, ἀποστασία , 'a defection or revolt') is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that ...
. Boniface organised the Bavarian church and founded or restored
bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
s at
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
,
Freising
Freising () is a university town in Bavaria, Germany, and the capital of the Freising ''Landkreis'' (district), with a population of about 50,000.
Location
Freising is the oldest town between Regensburg and Bolzano, and is located on the ...
,
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
and
Passau
Passau (; bar, label= Central Bavarian, Båssa) is a city in Lower Bavaria, Germany, also known as the Dreiflüssestadt ("City of Three Rivers") as the river Danube is joined by the Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north.
Passau's po ...
.
Tassilo III, who became duke of the Bavarians in 749, recognized the supremacy of the Frankish king,
Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
in 757 AD, but soon afterward refused to furnish a contribution to the war in
Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Janu ...
. Moreover, during the early years of the reign of
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
, Tassilo gave decisions in ecclesiastical and civil causes in his own name, refused to appear in the assemblies of the Franks, and in general acted as an independent ruler. His control of the Alpine passes, and his position as an ally of the
Avars and as a son-in-law of the Lombard king
Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born – died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Des ...
, became so troublesome to the Frankish kingdom that Charlemagne determined to crush him.
The details of this contest remain obscure. Tassilo appears to have done homage in 781 AD and again in 787 AD, probably owing to the presence of Frankish armies. But further trouble soon arose, and in 788 AD, the Franks summoned the duke to
Ingelheim
Ingelheim (), officially Ingelheim am Rhein ( en, Ingelheim upon Rhine), is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's west bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat ...
and sentenced him to death on a charge of treachery. The King, however, pardoned Tassilo who entered a monastery and formally renounced his duchy at
Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
in 794.
Gerold, a brother-in-law of Charlemagne, ruled Bavaria till his death in a battle with the Avars in 799, when Frankish counts took over the administration and assimilated the land with the rest of the
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
empire. Measures taken by Charlemagne for the intellectual progress and material welfare of his realm improved conditions. The Bavarians offered no resistance to the change which thus abolished their duchy. Their incorporation with the Frankish dominions, due mainly to the unifying influence of the church, appeared already so complete that Charlemagne did not find it necessary to issue more than two capitularies dealing especially with Bavarian affairs.
The Duchy during the Carolingian period

The history of Bavaria for the ensuing century intertwines with that of the
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
empire. Bavaria, given during the partition of 817 AD to the king of the
East Franks,
Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
, formed a part of the larger territories confirmed to him in 843 AD by the
Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
. Louis made Regensburg the center of his government and actively developed Bavaria, providing for its security by numerous campaigns against the Slavs. When he divided his possessions in 865 AD, it passed to his eldest son,
Carloman, who had already managed its administration, and after his death in 880 AD, it became a part of the extensive territories of the emperor,
Charles the Fat
Charles III (839 – 13 January 888), also known as Charles the Fat, was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 888. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandso ...
. This incompetent ruler left its defense to
Arnulf
Arnulf is a masculine German given name.
It is composed of the Germanic elements ''arn'' "eagle" and ''ulf'' "wolf".
The ''-ulf, -olf'' suffix was an extremely frequent element in Germanic onomastics and from an early time was perceived as a mere ...
, an illegitimate son of Carloman. Mainly due to the support of the Bavarians, Arnulf could take the field against Charles in 887 AD and secure his own election as a
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
king in the following year. In 899 AD, Bavaria passed to
Louis the Child, during whose reign continuous
Hungarian ravages occurred. Resistance to these inroads became gradually feebler, and tradition has it that on 5 July 907 almost the whole of the Bavarian tribe perished in the
Battle of Pressburg
The Battle of Pressburg (german: Schlacht von Pressburg) or Battle of Pozsony ( hu, Pozsonyi csata), or Battle of Bratislava ( sk, Bitka pri Bratislave) was a three-day-long battle, fought between 4–6 July 907, during which the East Francian arm ...
against these formidable enemies.
During the reign of Louis the Child,
Luitpold, Count of
Scheyern, who possessed large Bavarian domains, ruled the Mark of
Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carin ...
, created on the southeastern frontier for the defense of Bavaria. He died in the great battle of 907 AD, but his son
Arnulf
Arnulf is a masculine German given name.
It is composed of the Germanic elements ''arn'' "eagle" and ''ulf'' "wolf".
The ''-ulf, -olf'' suffix was an extremely frequent element in Germanic onomastics and from an early time was perceived as a mere ...
, surnamed the Bad, rallied the remnants of the tribe, in alliance with the Hungarians, became duke of the Bavarians in 911 AD, uniting Bavaria and Carinthia under his rule. The German king,
Conrad I, attacked Arnulf when the latter refused to acknowledge his royal supremacy but failed in the end.
Duchy during the Ottonian and Salian periods

In 920 AD, Conrad's successor was the German king,
Henry the Fowler
Henry the Fowler (german: Heinrich der Vogler or '; la, Henricus Auceps) (c. 876 – 2 July 936) was the Duke of Saxony from 912 and the King of East Francia from 919 until his death in 936. As the first non- Frankish king of East Francia, h ...
of the
Ottonian
The Ottonian dynasty (german: Ottonen) was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman Emperors named Otto, especially its first Emperor Otto I. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the ...
dynasty. Henry recognized Arnulf as duke, confirming his right to appoint bishops, coin money, and issue laws.
A similar conflict took place between Arnulf's son and successor
Eberhard Eberhard is an old Germanic name meaning the strength or courage of a wild boar.
People
First name
*Eberhard of Friuli (815–866), Duke and key figure in the Carolingian Empire
* Eberhard of Béthune (died 1212), Flemish grammarian
*Eberhard I, D ...
and Henry's son
Otto I the Great. Eberhard proved less successful than his father, and in 938 AD, fled from Bavaria, which Otto granted (with reduced privileges) to the late duke's uncle,
Bertold. Otto also appointed a
count palatine
A count palatine (Latin ''comes palatinus''), also count of the palace or palsgrave (from German ''Pfalzgraf''), was originally an official attached to a royal or imperial palace or household and later a nobleman of a rank above that of an ord ...
in the person of Eberhard's brother,
Arnulf
Arnulf is a masculine German given name.
It is composed of the Germanic elements ''arn'' "eagle" and ''ulf'' "wolf".
The ''-ulf, -olf'' suffix was an extremely frequent element in Germanic onomastics and from an early time was perceived as a mere ...
to watch the royal interests.
When Bertold died in 947 AD, Otto conferred the duchy upon his own brother
Henry, who had married Judith, a daughter of Duke Arnulf. The Bavarians disliked Henry, who spent his short reign mainly in disputes with his people.
The ravages of the Hungarians ceased after their defeat on the
Lechfeld (955 AD) and the area of the duchy was augmented for a time by the addition of certain adjacent districts in Italy.

In 955 AD, Henry's young son
Henry, surnamed the Quarrelsome, succeeded him, but in 974 AD he became involved in a conspiracy against King
Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (''der Rote''), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy ...
. The rising occurred because the king had granted the
Duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While the ...
to Henry's enemy,
Otto, a grandson of Emperor Otto the Great, and had given the new
Bavarian Eastern March
The Margraviate of Austria (german: Markgrafschaft Österreich) was a medieval frontier march, centered along the river Danube, between the river Enns and the Vienna Woods (''Wienerwald''), within the territory of modern Austrian provinces of U ...
, subsequently known as
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, to
Leopold of Babenberg. The revolt soon failed but Henry, who on his escape from prison renewed his plots, formally lost his Duchy of Bavaria in 976 AD to Otto, Duke of
Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
.
At the same time,
Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carin ...
was made a separate duchy, the office of Count Palatine was reestablished, and the Bavarian church became dependent on the king instead of on the duke.
Bavaria at this stage included the
Inn basin (including
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
and the
Salzach
The Salzach (Austrian: �saltsax ) is a river in Austria and Germany. It is in length and is a right tributary of the Inn, which eventually joins the Danube. Its drainage basin of comprises large parts of the Northern Limestone and Central ...
basin) and the
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
from
Donauwörth
Donauwörth () is a town and the capital of the Donau-Ries district in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is said to have been founded by two fishermen where the rivers Danube (Donau) and Wörnitz meet. The city is part of the scenic route called "Roman ...
(
Lech confluence) to
Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846.
In 2009, it was a European Capital ...
; the
March of Verona
The March of Verona and Aquileia was a vast Marches, march (frontier district) of the Holy Roman Empire in the northeastern Italian peninsula during the Middle Ages, centered on the cities of Verona and Aquileia. Seized by King Otto I, Holy Roman ...
(
South Tyrol
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol
, settlement_type = Autonomous province
, image_skyline =
, image_alt ...
) briefly fell to Bavaria (952 AD) before passing to Carinthia (976 AD).
The most important Bavarian cities at the time were
Freising
Freising () is a university town in Bavaria, Germany, and the capital of the Freising ''Landkreis'' (district), with a population of about 50,000.
Location
Freising is the oldest town between Regensburg and Bolzano, and is located on the ...
,
Passau
Passau (; bar, label= Central Bavarian, Båssa) is a city in Lower Bavaria, Germany, also known as the Dreiflüssestadt ("City of Three Rivers") as the river Danube is joined by the Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north.
Passau's po ...
,
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
and
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
.
Restored in 985 AD, Henry proved himself a capable ruler, establishing internal order, issuing important laws, and taking measures to reform the monasteries. In 1002 AD, his son and successor
Henry II gave Bavaria to his brother-in-law
Henry of
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, after whose death in 1026 AD it passed successively to Henry, afterward Emperor
Henry III, and then to another member of the family of Luxembourg, ruling as Duke
Henry VII. In 1061 AD,
Empress Agnes
Agnes of Poitou ( – 14 December 1077), was the queen of Germany from 1043 and empress of the Holy Roman Empire from 1046 until 1056 as the wife of Emperor Henry III. From 1056 to 1061, she ruled the Holy Roman Empire as regent during the ...
, mother and regent of the German king
Henry IV, entrusted the duchy to
Otto of Nordheim
Otto of Nordheim (c. 1020 – 11 January 1083) was Duke of Bavaria from 1061 until 1070. He was one of the leaders of the Saxon Rebellion in 1073-75 and the Great Saxon Revolt of 1077-88 against King Henry IV of Germany.
Life
Family
Otto was bor ...
.
Under the Welfs
In 1070 AD, King Henry IV deposed duke Otto, granting the duchy to Count
Welf, a member of an influential Bavarian family with roots in northern Italy.
In consequence of his support of
Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII ( la, Gregorius VII; 1015 – 25 May 1085), born Hildebrand of Sovana ( it, Ildebrando di Soana), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint ...
in his quarrel with Henry, Welf lost but subsequently regained Bavaria; two of his sons followed him in succession:
Welf II from 1101 AD and
Henry IX from 1120 AD. Both exercised considerable influence among the German princes.
Henry IX's son
Henry X, called the Proud, succeeded in 1126 AD and also obtained the
Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the C ...
in 1137 AD. Alarmed at his power, King
Conrad III
Conrad III (german: Konrad; it, Corrado; 1093 or 1094 – 15 February 1152) of the Hohenstaufen dynasty was from 1116 to 1120 Duke of Franconia, from 1127 to 1135 anti-king of his predecessor Lothair III and from 1138 until his death in 1152 ...
refused to allow two duchies to remain in the same hands and declared Henry deposed. He bestowed Bavaria upon
Leopold IV, Margrave of
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. When Leopold died in 1141, the king retained the duchy himself; but it continued to be the scene of considerable disorder, and in 1143 AD he entrusted it to
Henry, surnamed Jasomirgott, Margrave of Austria.
The struggle for its possession continued until 1156 AD, when
Emperor Frederick I, in his desire to restore peace to Germany, persuaded Henry to give up Bavaria to
Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
, duke of
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a ...
and son of Henry the Proud. In return, Austria was elevated from a margraviate to an independent duchy in the
Privilegium Minus
The is the denotation of a deed issued by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa on 17 September 1156. It included the elevation of the Bavarian frontier march of Austria () to a duchy, which was given as an inheritable fief to the House of B ...
. It was Henry the Lion who founded
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
.
Geographic fluctuations
During the years following the dissolution of the Carolingian empire the borders of Bavaria changed continuously and for a lengthy period after 955 AD, it finally started expanding. To the west, the
Lech still divided Bavaria from Swabia but on three other sides Bavaria took advantage of opportunities for expansion and the duchy occupied a considerable area north of the
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
. During the later years of the rule of the
Welfs, however, a contrary tendency operated, and the extent of Bavaria shrank.
In 1027 AD,
Conrad II
Conrad II ( – 4 June 1039), also known as and , was the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire from 1027 until his death in 1039. The first of a succession of four Salian emperors, who reigned for one century until 1125, Conrad ruled the kingdoms ...
split off the
Bishopric of Trent from the former Lombard
Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
. He attached it to the stem duchy of Bavaria, which was then under the rule of his son
Henry III. From the 12th century onwards, the counts residing in
Castle Tyrol near
Merano
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and '' comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeie ...
extended their territory over much of the region and came to surpass the power of the
bishops of Brixen
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
, of whom they were nominally vassals. After the deposition of
Henry X the Proud as Bavarian duke in 1138 AD, the Counts of
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
strengthened their independence from Bavaria under his son,
Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
. When the
House of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meus ...
was again given to the Bavarian duchy by
Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ...
at the 1154 AD
Reichstag of
Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the district of Goslar and located on the northwestern slopes of the Harz mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar and the Mi ...
, the
county of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised ...
was no longer counted as part of Bavaria.
Duke Henry the Lion focused on his northern duchy of Saxony rather than on his southern duchy of Bavaria, and when the dispute over the Bavarian succession ended in 1156 AD, the district between the
Enns and the
Inn became part of Austria.
The increasing importance of former Bavarian territories like the Mark of
Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered ...
(erected into a duchy in 1180 AD) and of the
county of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised ...
had diminished both the actual and the relative strength of Bavaria, which now on almost all sides lacked opportunities for expansion. The neighboring
Duchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial Sta ...
, the large territories of the
Archbishopric of Salzburg
The Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg (german: Fürsterzbistum Salzburg; Erzstift Salzburg; Erzbistum Salzburg) was an ecclesiastical principality and state of the Holy Roman Empire. It comprised the secular territory ruled by the archbishops o ...
, as well as a general tendency to claim more independence on the part of the nobles: all these causes limited Bavarian expansion.
Under the Wittelsbach dynasty
A new era began when, in consequence of Henry the Lion being placed under an imperial ban in 1180 AD, Emperor Frederick I awarded the duchy to
Otto, a member of the old Bavarian family of
Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
and a descendant of the counts of Scheyern. The Wittelsbach dynasty ruled Bavaria without interruption until 1918 AD. The
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
was also acquired by the Wittelsbachs in 1214 AD.
When Otto of Wittelsbach gained Bavaria at Altenburg in September 1180, the duchy's borders comprised the
Böhmerwald, the Inn, the Alps and the Lech; and the duke exercised practical power only over his extensive private domains around
Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
,
Kelheim
Kelheim () is a town and municipality in Bavaria, Germany. It is the capital of the district Kelheim and is situated at the confluence of the rivers Altmühl and Danube. Kelheim has a population of around 16,750 (2020).
History
Kelheim is ...
and
Straubing
Straubing () is an independent city in Lower Bavaria, southern Germany. It is seat of the district of Straubing-Bogen. Annually in August the Gäubodenvolksfest, the second largest fair in Bavaria, is held.
The city is located on the Danube for ...
.
Otto only enjoyed three years of rule over Bavaria. His son
Louis I Louis I may refer to:
* Louis the Pious, Louis I of France, "the Pious" (778–840), king of France and Holy Roman Emperor
* Louis I, Landgrave of Thuringia (ruled 1123–1140)
* Ludwig I, Count of Württemberg (c. 1098–1158)
* Louis I of Blois ...
succeeded him in 1183 AD, playing a leading part in German affairs during the early years of the reign of the emperor
Frederick II until Louis was assassinated at Kelheim in September 1231. His son
Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (''der Rote''), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy ...
, called the Illustrious, remained loyal to the
Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynas ...
emperors despite the Church placing Bavaria under an
interdict
In Catholic canon law, an interdict () is an ecclesiastical censure, or ban that prohibits persons, certain active Church individuals or groups from participating in certain rites, or that the rites and services of the church are banished from ...
and himself under a papal ban. Like his father, Otto II increased the area of his lands by purchases and considerably strengthened his hold upon the duchy. He died in November 1253.
Partitions

The efforts of the dukes to increase their power and to give unity to the duchy had met with a fair measure of success; but they were soon vitiated by partitions among different members of the family, which for 250 years made the history of Bavaria little more than a repetitive chronicle of territorial divisions bringing war and weakness in their wake.
The first of these divisions occurred in 1255.
Louis II and
Henry XIII, the sons of Duke Otto II, who for two years after their father's death had ruled Bavaria jointly, split their inheritance: Louis II obtained the western part of the duchy, afterward called Upper Bavaria, as well as the
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
, while Henry secured eastern or Lower Bavaria.
Lower Bavaria
Henry XIII of Lower Bavaria spent most of his time in quarrels with his brother, with Ottakar II of Bohemia and with various ecclesiastics. When he died in February 1290, the land fell to his three sons,
Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was Holy Roman Emperor from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of the Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was crowned as King of ...
, Louis III, and
Stephen I. The families of these three princes governed Lower Bavaria until 1333, when
Henry XV (son of Otto III) died, followed in 1334 by his cousin Otto IV; and as both died without sons the whole of Lower Bavaria then passed to
Henry XIV. Dying in 1339, Henry left an only son,
John I John I may refer to:
People
* John I (bishop of Jerusalem)
* John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople
* John of Antioch (died 441)
* Pope John I, Pope from 523 to 526
* John I (exarch) (died 615), Exarch of Ravenna
* John I ...
, who died childless in the following year, when the Wittelsbach emperor Louis IV, by securing Lower Bavaria for himself, united the whole of the duchy under his sway.
Upper Bavaria
In the course of a long reign, Louis II, called "the Stern", became the most powerful prince in
southern Germany
Southern Germany () is a region of Germany which has no exact boundary, but is generally taken to include the areas in which Upper German dialects are spoken, historically the stem duchies of Bavaria and Swabia or, in a modern context, Bavaria ...
. He served as the guardian of his nephew
Conradin
Conrad III (25 March 1252 – 29 October 1268), called ''the Younger'' or ''the Boy'', but usually known by the diminutive Conradin (german: link=no, Konradin, it, Corradino), was the last direct heir of the House of Hohenstaufen. He was Duke ...
of Hohenstaufen, and after Conradin's execution in Italy in 1268, Louis and his brother Henry inherited the domains of the Hohenstaufens in
Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
and elsewhere. He supported Count
Rudolph I of Habsburg, in his efforts to secure the German throne in 1273, married the new king's daughter Mechtild, and aided him in campaigns in Bohemia.

For some years after Louis' death in 1294, his sons
Rudolph I and
Louis, afterward the emperor Louis IV, ruled their duchy in common; but as their relations were never harmonious, a division of Upper Bavaria occurred in 1310, by which Rudolph received the land east of the
Isar
The Isar is a river in Tyrol, Austria, and Bavaria, Germany, which is not navigable for watercraft above raft size. Its source is in the Karwendel range of the Alps in Tyrol; it enters Germany near Mittenwald and flows through Bad Tölz, Mu ...
together with the town of
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
, and Louis the district between the Isar and the Lech. It was not long, however, before this arrangement led to war between the brothers, with the result that in 1317, three years after he had become German king, Louis compelled Rudolph to abdicate, and for twelve years ruled alone over the whole of Upper Bavaria. But in 1329 a series of events induced him to conclude the
Treaty of Pavia
The Treaty of Pavia was signed in Pavia on October 9, 1617, between representatives of the Spanish Empire and the Duchy of Savoy. Based on the terms of the accord, Savoy returned the Duchy of Montferrat to the Duchy of Mantua. Moreover, the treaty ...
with Rudolph's sons, Rudolph and Rupert, to whom he transferred the
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
(which the Wittelsbach family had owned since 1214) and also a portion of Bavaria north of the Danube, afterward called the
Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz, , ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, and is located in the east of Bavaria.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and numerous ponds and lak ...
(''Oberpfalz'').
At the same time, the two lines of the Wittelsbach family decided to exercise the electoral vote alternately, and that in the event of the extinction of either branch of the family, the surviving branch should inherit its possessions.
The consolidation of Bavaria under Louis IV lasted for seven years, during which the emperor was able to improve the condition of the country. When he died in 1347 he left six sons to share his possessions, who agreed upon a division of Bavaria in 1349. Its history, however, was complicated by its connections with
Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
,
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former Provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
,
Hainaut and
Tirol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
, all of which the emperor had also left to his sons. All the six brothers exercised some authority in Bavaria; but three alone left issue, and of these, the eldest,
Louis V, Duke of Bavaria
Louis V, called the Brandenburger (May 1315 – 18 September 1361), a member of the House of Wittelsbach, ruled as Margrave of Brandenburg from 1323 to 1351 and as Duke of Bavaria from 1347 until his death. From 1342 he also was co-ruling Cou ...
—also margrave of
Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
and count of
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
—died in 1361 and was followed to the grave two years later by his only son, the childless
Meinhard
Meinhard is a municipality in the Werra-Meißner-Kreis in Hesse, Germany.
Geography
Location
The community lies in the North Hesse Low Mountain Range landscape on the edge of the Werra valley, 3 km from the district seat of Eschwege.
Near ...
. Tyrol then passed to the Habsburgs. Brandenburg was lost in 1373.
The two remaining brothers,
Stephen II and
Albert I Albert I may refer to:
People Born before 1300
*Albert I, Count of Vermandois (917–987)
*Albert I, Count of Namur ()
* Albert I of Moha
*Albert I of Brandenburg (), first margrave of Brandenburg
*Albert I, Margrave of Meissen (1158–1195)
*Alber ...
, ruled over Bavaria-Landshut and Bavaria-Straubing respectively and when Stephen died in 1375 his three sons governed his portion of Bavaria jointly. In 1392, on the extinction of all the lines except those of Stephen and Albert, an important partition took place, which subdivided the greater part of the duchy amongst Stephen's three sons,
Stephen III,
Frederick and
John II, who founded respectively the lines of
Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area. Ingolstadt is the second largest city in Upper Ba ...
,
Landshut
Landshut (; bar, Landshuad) is a town in Bavaria in the south-east of Germany. Situated on the banks of the River Isar, Landshut is the capital of Lower Bavaria, one of the seven administrative regions of the Free State of Bavaria. It is also ...
and Munich.
The main result of the threefold division of 1392 proved to be a succession of civil wars which led to the temporary eclipse of Bavaria as a force in German politics. Neighboring states encroached upon its borders, and the nobles ignored the authority of the dukes, who, deprived of the electoral vote, were mainly occupied for fifty years with internal strife.
This condition of affairs, however, had some benefits. The government of the country and the control of the finances passed mainly into the hands of an assembly called the ''Landtag'' or ''Landschaft'', organized in 1392. The towns, assuming certain independence, became strong and wealthy as trade increased, and the citizens of Munich and Regensburg often proved formidable antagonists to the dukes. Thus, a period of disorder saw the growth of representative institutions and the establishment of a strong civic spirit.

Bavaria-Straubing
Albert I's duchy of
Bavaria-Straubing
Bavaria-Straubing denotes the widely scattered territorial inheritance in the Wittelsbach house of Bavaria that were governed by independent dukes of Bavaria-Straubing between 1353 and 1432; a map (''illustration'') of these marches and outliers ...
passed with Holland and Hainaut on his death in 1404 to his son
William II, and in 1417 to his younger son
John III, who resigned the
Bishopric of Liège
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
to take up his new position. When John died in 1425 this family became extinct, and after a contest between various claimants, the three remaining branches of the Wittelsbach family Ingolstadt, Landshut and Munich partitioned Bavaria-Straubing between themselves. However, Holland and Hainaut passed to Burgundy.
Bavaria-Ingolstadt
Stephen III, duke of
Bavaria-Ingolstadt
Bavaria-Ingolstadt ( or ') was a duchy which was part of the Holy Roman Empire from 1392 to 1447.
History
After the death of Stephen II in 1375, his sons Stephen III, Frederick, and John II jointly ruled Bavaria-Landshut. After seventeen yea ...
, was renowned as a soldier rather than as a statesman. His rule saw struggles with various towns and with his brother, John of Bavaria-Munich. On his death in 1413 his son
Louis VII
Louis VII (1120 – 18 September 1180), called the Younger, or the Young (french: link=no, le Jeune), was King of the Franks from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI (hence the epithet "the Young") and married Duchess ...
, called the Bearded, succeeded. Before his accession, this restless and quarrelsome prince had played an important part in the affairs of France, where his sister
Isabella had married King
Charles VI. About 1417 he became involved in a violent quarrel with his cousin,
Henry XVI of Bavaria-Landshut, fell under both the papal and the imperial ban, and in 1439 came under attack from his son, Louis VIII the Lame. This prince, who had married a daughter of
Frederick I of Hohenzollern, margrave of Brandenburg, resented the favor shown by his father to an illegitimate son. Aided by
Albert Achilles
Albrecht III (9 November 141411 March 1486) was Elector of Brandenburg from 1471 until his death, the third from the House of Hohenzollern. A member of the Order of the Swan, he received the cognomen '' Achilles'' because of his knightly qual ...
, afterward margrave of Brandenburg, he took the elder Louis prisoner and compelled him to abdicate in 1443. When Louis the Lame died in 1445 his father came into the power of his implacable enemy, Henry of Bavaria-Landshut, and died in prison in 1447.
Bavaria-Landshut
The duchy of Bavaria-Ingolstadt passed to Henry, who had succeeded his father Frederick as duke of
Bavaria-Landshut
Bavaria-Landshut (german: Bayern-Landshut) was a duchy in the Holy Roman Empire from 1353 to 1503.
History
The creation of the duchy was the result of the death of Emperor Louis IV the Bavarian. In the Treaty of Landsberg 1349, which divided ...
in 1393, and whose long reign comprised almost entirely family feuds. He died in July 1450, and his son,
Louis IX
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the House of Capet, Direct Capetians. He was Coronation of the French monarch, c ...
(called the Rich) succeeded. About this time Bavaria began to recover some of its former importance.
Louis IX expelled the Jews from his duchy, increased the security of traders, and improved both the administration of justice and the condition of the finances. In 1472 he founded the
University of Ingolstadt
The University of Ingolstadt was founded in 1472 by Louis the Rich, the Duke of Bavaria at the time, and its first Chancellor was the Bishop of Eichstätt. It consisted of five faculties: humanities, sciences, theology, law, and medicine, all o ...
, attempted to reform the monasteries, and successfully defeated Albert Achilles of Brandenburg. On the death of Louis IX in January 1479 his son
George, also called the Rich, succeeded; and when George, a faithful adherent of the German king Maximilian I, died without sons in December 1503, a war broke out for the possession of his duchy.
Bavaria-Munich

Bavaria-Munich
Bavaria-Munich (german: Bayern-München) was a duchy that was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1392 to 1505.
History
After the death of Stephen II in 1375, his sons Stephen III, Frederick, and John II jointly ruled Bavaria- ...
passed on after the death of John II in 1397 to his sons
Ernest
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
*Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
* Ernest, ...
and William III, but they only obtained possession of their lands after a struggle with Stephen of Bavaria-Ingolstadt. Both brothers then engaged in warfare with the other branches of the family and with the citizens of Munich. William III, a loyal servant of the emperor Sigismund, died in 1435, leaving an only son, Adolf, who died five years later; and Ernest, distinguished for his strength, died in 1438. In 1440 the whole of Bavaria-Munich came to Ernest's son
Albert III, who had become estranged from his father owing to his union with the commoner
Agnes Bernauer
Agnes Bernauer (c. 1410 – 12 October 1435) was the mistress and perhaps also the first wife of Albert, later Albert III, Duke of Bavaria. Because his father, Ernest, ruling Duke of Bavaria at the time, considered this liaison with a commone ...
. Albert, whose attempts to reform the monasteries earned him the surname of Pious, almost became the elected king of
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
in 1440. He died in 1460, leaving five sons, the two elder of whom,
John IV and
Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it '' Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
, reigned together until John's death in 1463. The third brother, Albert, who had been educated for the church, joined his brother in 1465, and when Sigismund abdicated two years later became sole ruler, in spite of the claims of his two younger brothers.
Albert IV, called the Wise, added the district of
Abensberg
Abensberg () is a town in the Lower Bavarian district of Kelheim, in Bavaria, Germany, lying around southwest of Regensburg, east of Ingolstadt, northwest of Landshut and north of Munich. It is situated on the river Abens, a tributary of t ...
to his possessions, and in 1504 became involved in the
Landshut War of Succession
The War of the Succession of Landshut resulted from a dispute between the duchies of Bavaria-Munich (''Bayern-München'' in German) and Bavaria-Landshut (''Bayern-Landshut''). An earlier agreement between the different Wittelsbach lines, the Tr ...
which broke out for the possession of Bavaria-Landshut on the death of George the Rich. Albert's rival was George's son-in-law Rupert, formerly bishop of
Freising
Freising () is a university town in Bavaria, Germany, and the capital of the Freising ''Landkreis'' (district), with a population of about 50,000.
Location
Freising is the oldest town between Regensburg and Bolzano, and is located on the ...
and also the successor of Philip as count palatine of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
. The emperor
Maximilian I, interested as archduke of
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and count of Tirol, interfered in the dispute. Rupert died in 1504, and the following year an arrangement was made at the Diet of
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
by which the emperor and Philip's grandson, Otto Henry, obtained certain outlying districts, while Albert by securing the bulk of George's possessions united Bavaria under his rule. In 1506 Albert decreed that the duchy should thenceforth pass according to the rules of primogeniture, and in other ways endeavored to consolidate Bavaria. He was partially successful in improving the condition of the country, and in 1500 Bavaria formed one of the six circles into which Germany was divided for the maintenance of peace. Albert died in March 1508 and was succeeded by his son,
William IV
William IV (William Henry; 21 August 1765 – 20 June 1837) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded h ...
, whose mother Kunigunde was the daughter of the emperor Frederick III.
Reunited duchy
Renaissance and Counter-Reformation
In spite of the decree of 1506, William IV was compelled to grant a share in the government in 1516 to his brother
Louis X Louis X may refer to:
* Louis X of France, "the Quarreller" (1289–1316).
* Louis X, Duke of Bavaria (1495–1545)
* Louis I, Grand Duke of Hesse
Louis I, Grand Duke of Hesse (14 June 1753 in Prenzlau – 6 April 1830 in Darmstadt) was '' ...
, an arrangement which lasted until the death of Louis in 1545.
William followed the traditional Wittelsbach policy of opposition to the Habsburgs until in 1534 he made a treaty at
Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846.
In 2009, it was a European Capital ...
with
Ferdinand
Ferdinand is a Germanic name composed of the elements "protection", "peace" (PIE "to love, to make peace") or alternatively "journey, travel", Proto-Germanic , abstract noun from root "to fare, travel" (PIE , "to lead, pass over"), and "co ...
, the king of
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
and
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
. This link strengthened in 1546, when the emperor
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infa ...
obtained the help of the duke during the war of the
league of Schmalkalden by promising him in certain eventualities the succession to the Bohemian throne, and the electoral dignity enjoyed by the
count palatine of the Rhine
The counts palatine of Lotharingia /counts palatine of the Rhine /electors of the Palatinate (german: Kurfürst von der Pfalz) ruled some part of Rhine area in the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire from 915 to 1803. The title was a kind ...
. William also did much at a critical period to secure Bavaria for
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The reformed doctrines had made considerable progress in the duchy when the duke obtained extensive rights over the bishoprics and monasteries from the pope. He then took measures to repress the reformers, many of whom were banished; while the
Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
, whom he invited into the duchy in 1541, made the
Jesuit College of Ingolstadt
The Jesuit College of Ingolstadt (german: Jesuitenkolleg Ingolstadt) was a Jesuit school in Ingolstadt, in the Duchy and Electorate of Bavaria, founded in 1556, that operated until the suppression of the Jesuit Order in 1773. The college was the ...
, their headquarters in Germany. William, whose death occurred in March 1550 and was succeeded by his son
Albert V, who had married a daughter of Ferdinand of Habsburg, afterward the emperor Ferdinand I. Early in his reign Albert made some concessions to the reformers, who were still strong in Bavaria; but about 1563 he changed his attitude, favored the decrees of the
Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
, and pressed forward the work of the
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
. As education passed by degrees into the hands of the Jesuits, the progress of
Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
was effectually arrested in Bavaria.
Albert V patronized art extensively. Artists of all kinds flocked to his court in Munich, and splendid buildings arose in the city, while Italy and elsewhere contributed to the collection of artistic works. The expenses of a magnificent court led the duke to quarrel with the ''Landschaft'' (the nobles), to oppress his subjects, and to leave a great burden of debt when he died in October 1579.

The succeeding duke, Albert's son,
William V William V may refer to:
* William V, Duke of Aquitaine (969–1030)
*William V of Montpellier (1075–1121)
* William V, Marquess of Montferrat (1191)
* William V, Count of Nevers (before 11751181)
*William V, Duke of Jülich (1299–1361)
* Willia ...
(called the Pious), had received a Jesuit education and showed keen attachment to Jesuit tenets. He secured the
Archbishopric of Cologne
The Archdiocese of Cologne ( la, Archidioecesis Coloniensis; german: Erzbistum Köln) is an archdiocese of the Catholic Church in western North Rhine-Westphalia and northern Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany.
History
The Electorate of Colo ...
for his brother
Ernest
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
*Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
* Ernest, ...
in 1583, and this dignity remained in the possession of the family for nearly 200 years. In 1597 he abdicated in favor of his son
Maximilian I, and retired to a monastery, where he died in 1626.
Thirty Years' War
Maximilian I found the duchy encumbered with debt and filled with disorder, but ten years of his vigorous rule effected a remarkable change. The finances and the judicial system were reorganized, a class of civil servants and a national militia founded, and several small districts were brought under the duke's authority. The result was unity and order in the duchy which enabled Maximilian to play an important part in the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
; during the earlier years of which he was so successful as to acquire the
Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz, , ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, and is located in the east of Bavaria.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and numerous ponds and lak ...
and the
electoral dignity
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the princ ...
which had been enjoyed since 1356 by the elder branch of the Wittelsbach family. In spite of subsequent reverses, Maximilian retained these gains at the
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pe ...
in 1648. During the later years of this war Bavaria, especially the northern part, suffered severely. In 1632 the
Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
invaded, and when Maximilian violated the treaty of
Ulm
Ulm () is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Danube on the border with Bavaria. The city, which has an estimated population of more than 126,000 (2018), forms an urban district of its own (german: link=no, ...
in 1647, the French and the Swedes ravaged the land. After repairing this damage to some extent, the elector died at
Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area. Ingolstadt is the second largest city in Upper Ba ...
in September 1651, leaving his duchy much stronger than he had found it. The recovery of the Upper Palatinate made Bavaria compact; the acquisition of the electoral vote made it influential, and the duchy was able to play a part in European politics which internal strife had rendered impossible for the past four hundred years.
Electorate of Bavaria
Absolutism
The international position won by
Maximilian I adds to the ducal house, on Bavaria itself its effect during the next two centuries were most dubious. Maximilian's son,
Ferdinand Maria (1651–1679), who was a minor when he succeeded, tried to repair the wounds caused by the Thirty Years' War, encouraging agriculture and industries and building or restoring numerous churches and monasteries. In 1669, moreover, he again called a meeting of the diet, which had been suspended since 1612.

His good work, however, was largely undone by his son
Maximilian II Emanuel
Maximilian, Maximillian or Maximiliaan (Maximilien in French) is a male given name.
The name "Max" is considered a shortening of "Maximilian" as well as of several other names.
List of people
Monarchs
*Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor (1459– ...
(1679–1726), whose far-reaching ambition set him warring against the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
and, on the side of France, in the great struggle of the
Spanish succession. He shared in the defeat at the
Battle of Blenheim
The Battle of Blenheim (german: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt, link=no; french: Bataille de Höchstädt, link=no; nl, Slag bij Blenheim, link=no) fought on , was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied ...
, near
Höchstädt, on 13 August 1704; his dominions were temporarily partitioned between Austria and the
elector palatine
The counts palatine of Lotharingia /counts palatine of the Rhine /electors of the Palatinate (german: Kurfürst von der Pfalz) ruled some part of Rhine area in the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire from 915 to 1803. The title was a kin ...
by the
Treaty of Ilbersheim, and only restored to him, harried and exhausted, at the
Treaty of Baden in 1714
The Treaty of Baden ended formal hostilities between Kingdom of France and the Holy Roman Empire, which had been at war since the start of the War of the Spanish Succession. The treaty was signed on 7 September 1714 in Baden, Switzerland, and com ...
; the first
Bavarian peasant insurrection, known as the ''
Bloody Christmas of Sendling'', having been crushed by the Austrian occupiers in 1706.
Untaught by Maximilian II Emmanuel's experience, his son,
Charles Albert
Charles Albert (; 2 October 1798 – 28 July 1849) was the King of Sardinia from 27 April 1831 until 23 March 1849. His name is bound up with the first Italian constitution, the Albertine Statute, and with the First Italian War of Independenc ...
(1726–1745), devoted all his energies to increasing the European prestige and power of his house. The death of the emperor
Charles VI proved his opportunity: he disputed the validity of the
Pragmatic Sanction
A pragmatic sanction is a sovereign's solemn decree on a matter of primary importance and has the force of fundamental law. In the late history of the Holy Roman Empire, it referred more specifically to an edict issued by the Emperor.
When used ...
which secured the Habsburg succession to
Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position '' suo jure'' (in her own right) ...
, allied himself with France, conquered Upper Austria, was crowned
king of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings beforehand, first gaining the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of the Holy Roman ...
at
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
and, in 1742, emperor at Frankfurt. The price he had to pay, however, was the occupation of Bavaria itself by Austrian troops; and, though the invasion of Bohemia in 1744 by
Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the S ...
enabled him to return to Munich, at his death on 20 January 1745 it was left to his successor to make what terms he could for the recovery of his dominions.
Maximilian III Joseph
Maximilian III Joseph, "the much beloved", (28 March 1727 – 30 December 1777) was a Prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire and Duke of Bavaria from 1745 to 1777.
Biography
Born in Munich, Maximilian was the eldest son of Holy Roman Empero ...
(1745–1777), called "Max the much-beloved", by the peace of
Füssen
Füssen is a town in Bavaria, Germany, in the district of Ostallgäu, situated one kilometre from the Austrian border. The town is known for violin manufacturing and as the closest transportation hub for the Neuschwanstein and Hohenschwangau ca ...
, signed on 22 April 1745, obtained the restitution of his dominions in return for a formal acknowledgment of the Pragmatic Sanction. He was a man of
enlightenment, did much to encourage agriculture, industries and the exploitation of the
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
wealth of the country, founded the
Academy of Sciences
An academy of sciences is a type of learned society or academy (as special scientific institution) dedicated to sciences that may or may not be state funded. Some state funded academies are tuned into national or royal (in case of the Unit ...
at Munich, and abolished the Jesuit censorship of the press. At the same time, the elector signed more death sentences than any of his predecessors ever had. On 30 December 1777, when he died, the Bavarian line of the Wittelsbachs became extinct, and the succession passed to
Charles Theodore, the elector palatine. After a separation of four and a half centuries, the
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
, to which the duchies of
Jülich
Jülich (; in old spellings also known as ''Guelich'' or ''Gülich'', nl, Gulik, french: Juliers, Ripuarian: ''Jöllesch'') is a town in the district of Düren, in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. As a border region betw ...
and
Berg Berg may refer to:
People
*Berg (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name)
*Berg Ng (born 1960), Hong Kong actor
* Berg (footballer) (born 1989), Brazilian footballer
Former states
* Berg (state), county and duchy of the Hol ...
had been added, was thus reunited with Bavaria.
Palatinate-Bavaria
Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods

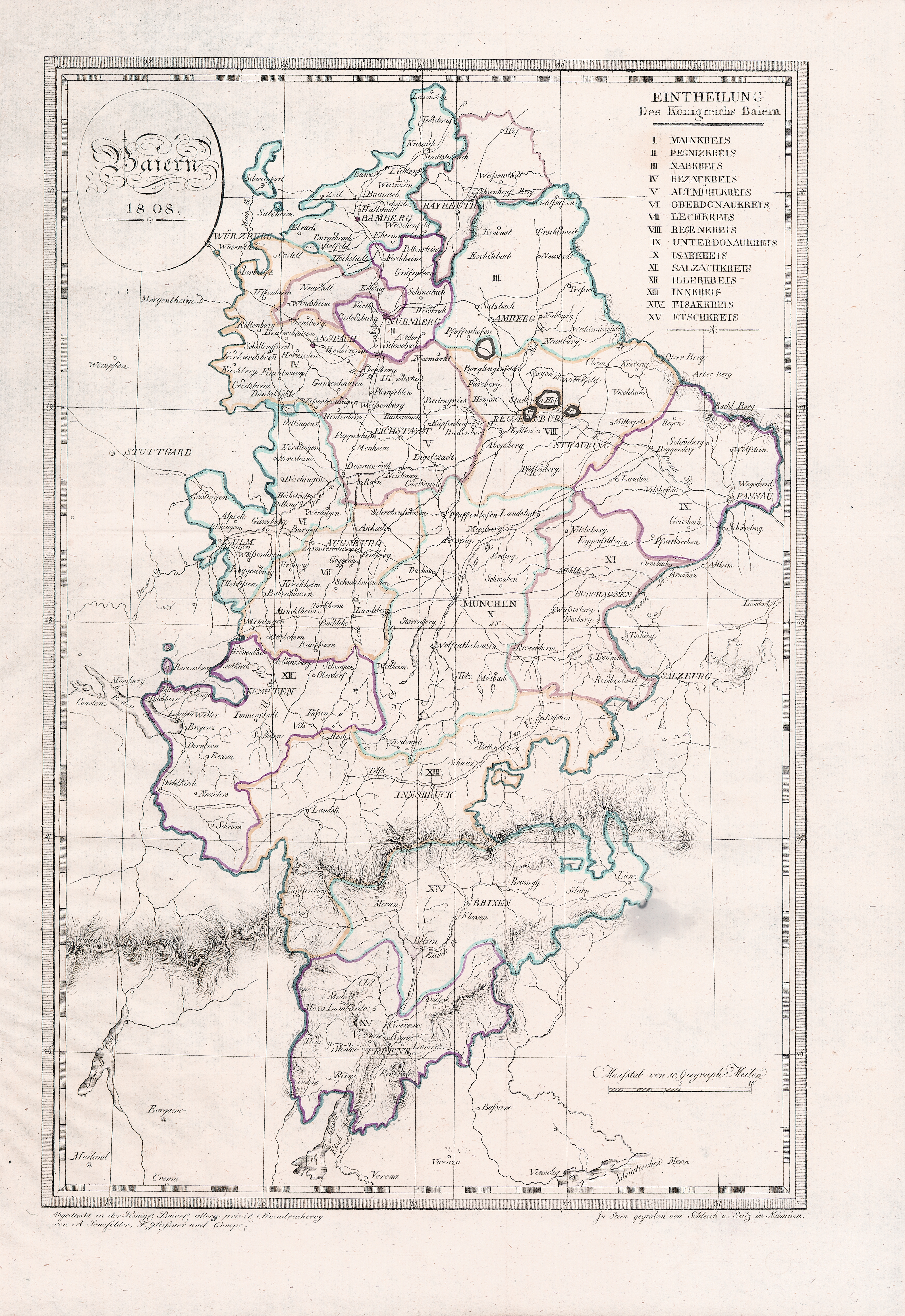
In 1792, French revolutionary armies overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under
Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself and advanced to Munich where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals, and laid siege to
Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area. Ingolstadt is the second largest city in Upper Ba ...
.
Charles Theodore, who had done nothing to prevent wars or to resist the invasion, fled to Saxony and abandoned a regency whose members signed a convention with Moreau, by which he granted an armistice in return for a heavy contribution (7 September 1796).
Between the French and the Austrians, Bavaria was now in a bad situation. Even before the death of Charles Theodore on 16 February 1799, the Austrians had again occupied the country, in preparation for renewing the war with France. The new elector,
Maximilian IV Joseph (of
Zweibrücken
Zweibrücken (; french: Deux-Ponts, ; Palatinate German: ''Zweebrigge'', ; literally translated as "Two Bridges") is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, on the Schwarzbach river.
Name
The name ''Zweibrücken'' means 'two bridges'; old ...
), succeeded to a difficult inheritance. Though both he and his all-powerful minister,
Maximilian von Montgelas
Maximilian Karl Joseph Franz de Paula Hieronymus de Garnerin de la Thuile, Count von Montgelas (german: Maximilian Karl Joseph Franz de Paula Hieronymus de Garnerin de la Thuille Graf von Montgelas; 12 September 1759 Munich – 14 June 1838 ...
sympathized more with France than Austria, the state of the Bavarian finances, and the fact that the Bavarian troops were scattered and disorganized, placed him helpless in the hands of Austria. On 2 December 1800, the Bavarian armies were involved in the
Austrian defeat at Hohenlinden, and Moreau once more occupied Munich. By the
Treaty of Lunéville
The Treaty of Lunéville (or Peace of Lunéville) was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville on 9 February 1801. The signatory parties were the French Republic and Emperor Francis II, who signed on his own behalf as ruler of the hereditary doma ...
(9 February 1801) Bavaria lost the Palatinate and the duchies of
Zweibrücken
Zweibrücken (; french: Deux-Ponts, ; Palatinate German: ''Zweebrigge'', ; literally translated as "Two Bridges") is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, on the Schwarzbach river.
Name
The name ''Zweibrücken'' means 'two bridges'; old ...
and
Jülich
Jülich (; in old spellings also known as ''Guelich'' or ''Gülich'', nl, Gulik, french: Juliers, Ripuarian: ''Jöllesch'') is a town in the district of Düren, in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. As a border region betw ...
.

In view of the scarcely disguised ambitions and intrigues of the Austrian court, Montgelas now believed that the interests of Bavaria lay in a frank alliance with the French Republic; he succeeded in overcoming the reluctance of Maximilian Joseph and on 24 August a separate treaty of peace and alliance with France was signed in
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
. By the third article of this the
First Consul
The Consulate (french: Le Consulat) was the top-level Government of France from the fall of the Directory in the coup of 18 Brumaire on 10 November 1799 until the start of the Napoleonic Empire on 18 May 1804. By extension, the term ''The Co ...
undertook to see that the compensation promised under the 7th article of the treaty of Lunéville for the territory ceded on the left bank of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
, should be carried out at the expense of the Empire in the manner most agreeable to Bavaria (see
de Martens, ''Recueil'', vol. vii. p. 365).
Thus in 1803, in accordance to this agreement, in the
territorial rearrangements consequent on Napoleon's suppression of the ecclesiastical states and of many
free cities of the Empire, Bavaria received the bishoprics of
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzburg ...
,
Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castl ...
,
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ' ...
and
Freisingen, part of that of
Passau
Passau (; bar, label= Central Bavarian, Båssa) is a city in Lower Bavaria, Germany, also known as the Dreiflüssestadt ("City of Three Rivers") as the river Danube is joined by the Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north.
Passau's po ...
, the territories of twelve abbeys, and seventeen cities and villages. The whole form a compact territory which more than compensated for the loss of her outlying provinces on the Rhine. Montgelas now aspired to raise Bavaria to the rank of a first-rate power and he pursued this object during the Napoleonic epoch with consummate skill, allowing fully for the preponderance of France – so long as it lasted – but never permitting Bavaria to sink, like so many of the states of the
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria a ...
, into mere French dependency. In the
war of 1805, in accordance with a treaty of alliance signed at
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzburg ...
on 23 September, Bavarian troops, for the first time since the days of
Charles VII, fought side by side with the French, and by the
Treaty of Pressburg, signed on 26 December, the
Principality of Eichstädt, the
Margraviate of Burgau, the Lordship of
Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with th ...
, the counties of
Hohenems and
Königsegg-Rothenfels
Königsegg-Rothenfels was a state in far southwestern Bavaria, Germany, located north of Austria and west of Baden-Württemberg. It was created as a partition of the Barony of Königsegg in 1622, and was raised to a county seven years later. It wa ...
, the lordships of
Argen
The Argen is a river in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It flows into Lake Constance between Kressbronn am Bodensee and Langenargen as the third largest tributary to the lake. It is long; if one includes the Obere Argen and its source river Seel ...
and
Tettnang
Tettnang is a town in the Bodensee district in southern Baden-Württemberg in a region of Germany known as Swabia.
It lies 7 kilometres from Lake Constance. The region produces significant quantities of Tettnang hop, an ingredient of beer, and ...
, and the city of
Lindau
Lindau (german: Lindau (Bodensee), ''Lindau am Bodensee''; ; Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Lindou'') is a major Town#Germany, town and Lindau (island), island on the eastern side of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German) in Bavaria, Ge ...
with its territory was to be added to Bavaria. On the other hand, Würzburg, obtained in 1803, was to be ceded by Bavaria to the elector of
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
in exchange for
Tirol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
. By the 1st article of the treaty, the emperor acknowledged the assumption by the elector of the title of king, as Maximilian I. The price which Maximilian had reluctantly to pay for this accession of dignity was the marriage of his daughter Augusta with
Eugène de Beauharnais
Eugène Rose de Beauharnais, Duke of Leuchtenberg (; 3 September 1781 – 21 February 1824) was a French nobleman, statesman, and military commander who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
Through the second ma ...
. On 15 March 1806 he ceded the Duchy of
Berg Berg may refer to:
People
*Berg (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name)
*Berg Ng (born 1960), Hong Kong actor
* Berg (footballer) (born 1989), Brazilian footballer
Former states
* Berg (state), county and duchy of the Hol ...
to Napoleon.
For the internal constitution of Bavaria also the French alliance had noteworthy consequences. Maximilian himself was an "
enlightened" prince of the 18th-century type, whose tolerant principles had already grievously offended his clerical subjects. Montgelas was a firm believer in drastic reform "from above", and, in 1803, had discussed with the rump of the old estates the question of reforms. But the revolutionary changes introduced by the constitution proclaimed on 1 May 1808 were due to the direct influence of Napoleon. A clean sweep was made of the medieval polity surviving in the somnolent local diets and corporations. In place of the old system of privileges and exemptions were set equality before the law, universal liability to taxation, the abolition of
serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which develop ...
, the security of person and property, liberty of conscience and of the press. A representative assembly was created on paper, based on a narrow franchise and with very limited powers, but was never summoned.

In 1809 Bavaria was again engaged in war with Austria on the side of France. The Tyroleans rose up against the Bavarian authority and succeeded three times in defeating Bavarian and French troops trying to retake the country. Austria lost the war of the
Fifth Coalition
The War of the Fifth Coalition was a European conflict in 1809 that was part of the Napoleonic Wars and the Coalition Wars. The main conflict took place in central Europe between the Austrian Empire of Francis I and Napoleon's French Empi ...
against France, and got even harsher terms in the
Treaty of Schönbrunn
The Treaty of Schönbrunn (french: Traité de Schönbrunn; german: Friede von Schönbrunn), sometimes known as the Peace of Schönbrunn or Treaty of Vienna, was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna on 14 October ...
in 1809. Often glorified as Tirol's national hero,
Andreas Hofer
Andreas Hofer (22 November 1767 – 20 February 1810) was a Tyrolean innkeeper and drover, who in 1809 became the leader of the Tyrolean Rebellion against the Napoleonic and Bavarian invasion during the War of the Fifth Coalition. He was subs ...
, the leader of the uprising, was executed in 1810 in
Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the Eur ...
, having lost a third and final battle against the French and Bavarian forces. By the treaty signed at Paris on 28 February 1810, Bavaria ceded southern Tirol to Italy and some small districts to
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württ ...
, receiving as compensation parts of Salzburg, the
Innviertel
The Innviertel (literally German for "Inn Quarter"; officially called the ''Innkreis''; ) is a traditional Austrian region southeast of the Inn river. It forms the western part of the state of Upper Austria and borders the German state of Bava ...
and
Hausruck and the principalities of
Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital o ...
and
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
. So far the policy of Montgelas had been brilliantly successful, but the star of Napoleon had now reached its zenith and already the astute opportunist had noted the signs of the coming change.
The events of 1812 followed; in 1813 Bavaria was summoned to join the alliance against Napoleon, the demand being passionately backed by the crown prince
Louis and by Marshal
Wrede
Wrede is a surname that includes two different noble families, the German princely one and Finnish-Swede noble family "von Wrede" that originated from Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern ...
; on 8 October the
treaty of Ried
The Treaty of Ried of 8 October 1813 was a treaty that was signed between the Kingdom of Bavaria and Austrian Empire. By this treaty, Bavaria left the Confederation of the Rhine which was allied with Napoleon, and agreed to join the Sixth Coalition ...
was signed, by which Bavaria threw in her lot with the Allies. Montgelas announced to the French ambassador that he had been compelled temporarily to bow before the storm, adding "Bavaria has need of France". (For Bavaria's share in the war see
Napoleonic Campaigns.)
Kingdom of Bavaria
Constitution and Revolution
Immediately after the
first peace of Paris (1814), Bavaria ceded to Austria the northern
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
and
Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with th ...
; during the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
it was decided that she was to add to these the greater part of
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
and the
Innviertel
The Innviertel (literally German for "Inn Quarter"; officially called the ''Innkreis''; ) is a traditional Austrian region southeast of the Inn river. It forms the western part of the state of Upper Austria and borders the German state of Bava ...
and . She received as compensation, besides
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzburg ...
and
Aschaffenburg
Aschaffenburg (; South Franconian German, South Franconian: ''Aschebersch'') is a town in northwest Bavaria, Germany. The town of Aschaffenburg is not part of the Aschaffenburg (district), district of Aschaffenburg, but is its administrative sea ...
, the
Palatinate (region)
The Palatinate (german: Pfalz; Palatine German: ''Palz'') is a region of Germany. In the Middle Ages it was known as the Rhenish Palatinate (''Rheinpfalz'') and Lower Palatinate (''Unterpfalz''), which strictly speaking designated only the wes ...
on the left bank of the Rhine and certain districts of
Hesse-Darmstadt
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Darmstadt) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a younger branch of the House of Hesse. It was formed in 1567 following the division of the Landgraviate of Hesse be ...
and of the former
Abbacy of Fulda. But with the collapse of France, the old fears and jealousies against Austria were revived in full force, and Bavaria only agreed to these cessions (
treaty of Munich, 16 April 1816) under the promise that, in the event of the powers ignoring her claim to the
Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
succession in favor of that of the line of the counts of
Hochberg, she should receive also the Palatinate on the right bank of the Rhine. The question was thus left open, the tension between the two powers remained high, and the war was only averted by the authority of the Grand Alliance . At the
Congress of Aix
A congress is a formal meeting of the Representative democracy, representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political party, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle Eng ...
(1818) the question of the Baden succession was settled in favor of the Hochberg line, without the compensation stipulated in the treaty of Munich; and by the treaty of Frankfurt, signed on behalf of the four great powers on 20 July 1819, the territorial issues between Bavaria and Austria were settled, in spite of the protests of the former, in the general sense of the arrangement made at Vienna. A small strip of territory was added, to connect Bavaria with the Palatinate, and Bavarian troops were to garrison the federal
fortress of Mainz
The Fortress of Mainz was a fortressed garrison town between 1620 and 1918. At the end of the Napoleonic Wars, under the term of the 1815 Peace of Paris, the control of Mainz passed to the German Confederation and became part of a chain of st ...
.
Meanwhile, on 1 February 1817, Montgelas had been dismissed; and Bavaria had entered on a new era of constitutional reform. This implied no breach with the European policy of the fallen minister. In the new German confederation, Bavaria had assumed the role of defender of the smaller states against the ambitions of Austria and Prussia. Montgelas had dreamed of a Bavarian hegemony in South Germany similar to that of Prussia in the north. It was to obtain popular support for this policy and for the Bavarian claims on Baden that the crown prince pressed for a liberal constitution, the reluctance of Montgelas to concede it is the cause of his dismissal.
On 26 May 1818, the constitution was proclaimed. The
parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
was to consist of two houses; the first comprising the great hereditary landowners, government officials, and nominees of the crown; the second, elected on a very narrow franchise, comprising representatives of the small land-owners, the towns, and the peasants. By additional articles the equality of religions was guaranteed and the rights of Protestants safeguarded, concessions which were denounced at
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
as a breach of the
Concordat
A concordat is a convention between the Holy See and a sovereign state that defines the relationship between the Catholic Church and the state in matters that concern both,René Metz, ''What is Canon Law?'' (New York: Hawthorn Books, 1960 st Edi ...
, which had been signed immediately before. The result of the constitutional experiment hardly justified the royal expectations; the parliament was hardly opened (5 February 1819) before the doctrinaire radicalism of some of its members, culminating in the demand that the army should swear allegiance to the constitution, so alarmed the king that he appealed to Austria and Germany, undertaking to carry out any repressive measures they might recommend. Prussia, however, refused to approve of any coup d'état; the parliament, chastened by the consciousness that its life depended on the goodwill of the king, moderated its tone; and Maximilian ruled till his death as a model constitutional monarch. On 13 October 1825, his son
Ludwig I succeeded him.

Ludwig proved an enlightened patron of the arts and sciences, who transferred the
University of Landshut
The University of Applied Sciences Landshut (''Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften Landshut'') is a Fachhochschule in Landshut, between Munich and Regensburg, with over 5000 students and over 100 professors. Its main focus areas are technol ...
to Munich, which, by his magnificent taste in building, he transformed into one of the most beautiful cities of the continent. The earlier years of his reign were marked by a liberal spirit and the reform, especially, of the financial administration; but the
revolutions of 1830 frightened him into reaction, which was accentuated by the opposition of the parliament to his expenditure on building and works of art. In 1837, the
Ultramontanes
Ultramontanism is a clerical political conception within the Catholic Church that places strong emphasis on the prerogatives and powers of the Pope. It contrasts with Gallicanism, the belief that popular civil authority—often represented by th ...
came into power with
Karl von Abel (1788–1859) as prime minister. The Jesuits now gained the upper hand; one by one the liberal provisions of the constitution were modified or annulled; the Protestants were harried and oppressed, and rigorous censorship forbade any free discussion of internal politics. The collapse of this régime was due, not to popular agitation, but to the resentment of Ludwig at the clerical opposition to the influence of his mistress,
Lola Montez
Eliza Rosanna Gilbert, Countess of Landsfeld (17 February 1821 – 17 January 1861), better known by the stage name Lola Montez (), was an Irish dancer and actress who became famous as a Spanish dancer, courtesan, and mistress of King Ludwig I ...
. On 17 February 1847, Abel was dismissed for publishing his memorandum against the proposal to naturalize Lola, who was an Irishwoman; and the Protestant
Georg Ludwig von Maurer took his place. The new ministry granted the certificate of naturalization; but riots, in which Ultramontane professors of the university took part, resulted. The professors were deprived, the parliament dissolved, and, on 27 November, the ministry dismissed. Lola Montez created Countess Landsfeld, became supreme in the state; and the new minister,
Prince Ludwig of Öttingen-Wallerstein (1791–1870), in spite of his efforts to enlist Liberal sympathy by appeals to pan-German patriotism, was powerless to form a stable government. His cabinet was known as the ''Lolaministerium''; in February 1848, stimulated by the news from Paris (
Revolution of 1848 in France), riots broke out against the countess; on 11 March the king dismissed Öttingen, and on 20 March, realizing the force of public opinion against him, abdicated in favor of his son,
Maximilian II.
Before his abdication Ludwig had issued, on 6 March 1848, a proclamation promising the zealous co-operation of the Bavarian government in the work of German freedom and unity (see
German revolutions of 1848–1849
The German revolutions of 1848–1849 (), the opening phase of which was also called the March Revolution (), were initially part of the Revolutions of 1848 that broke out in many European countries. They were a series of loosely coordinated pro ...
). To the spirit of this Maximilian was faithful, accepting the authority of the central government at Frankfurt and on 19 December the sanctioning of the official promulgation of the laws were passed by the German parliament. But Prussia was henceforth the enemy, not Austria. In refusing to agree to the offer of the imperial crown to
Frederick William IV, Maximilian had the support of his parliament. In withholding his assent to the new German constitution, by which Austria was excluded from the
Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical iss ...
, he ran indeed counter to the sentiment of his people; but by this time the back of the revolution was broken, and in the events which led to the humiliation of Prussia at
Olmütz
Olomouc (, , ; german: Olmütz; pl, Ołomuniec ; la, Olomucium or ''Iuliomontium'') is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 99,000 inhabitants, and its larger urban zone has a population of about 384,000 inhabitants (2019).
Located on th ...
in 1851, and the restoration of the old diet of the Confederation, Bavaria was safe in casting in her lot with Austria (see
History of Germany
The Germani tribes i.e. Germanic tribes are now considered to be related to the Jastorf culture before expanding and interacting with the other peoples.
The concept of a region for Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes is traced to time of Julius Ca ...
).
The guiding spirit in this anti-Prussian policy, which characterized Bavarian statesmanship up to the
war of 1866
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
, was
Baron Karl Ludwig von der Pfordten (1811–1880), who became minister for foreign affairs on 19 April 1849. His idea for the ultimate solution of the question of the balance of power in Germany was the so-called ''Trias'', i.e. a league of the Rhenish states as a counterpoise to the preponderance of Austria and Prussia. In internal affairs, his ministry was characterized by a reactionary policy less severe than elsewhere in Germany, which led none-the-less from 1854 onward to a struggle with the parliament, which ended in the dismissal of Pfordten's ministry on 27 March 1859. He was succeeded by
Karl Freiherr von Schrenk von Notzing (1806–1884), an official of Liberal tendencies who had been a Bavarian representative in the diet of the Confederation. Important reforms were now introduced, including the separation of the judicial and executive powers and the drawing up of a new criminal code. In foreign affairs Schrenk, like his predecessor, aimed at safeguarding the independence of Bavaria, and supported the idea of superseding the actual constitution of the Confederation by a supreme directory, in which Bavaria, as leader of the purely German states, would hold the balance between Prussia and Austria. Bavaria accordingly opposed the Prussian proposals for the reorganization of the Confederation, and one of the last acts of King Maximilian was to take a conspicuous part in the assembly of princes summoned to Frankfurt in 1863 by the emperor
Francis Joseph.
Maximilian was succeeded on 10 March 1864 by his son
Ludwig II, a youth of eighteen. The government was at first carried on by Schrenk and Pfordten in concert. Schrenk soon retired, when the Bavarian government found it necessary, in order to maintain its position in the Prussian
Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had b ...
, to become a party to the Prussian commercial treaty with France, signed in 1862. In the complicated
Schleswig-Holstein question
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schl ...
Bavaria, under Pfordten's guidance, consistently opposed Prussia, and headed the lesser states in their support of
Frederick of Augustenburg against the policy of the two great German powers. Finally, in the
war of 1866
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
, in spite of
Bismarck's efforts to secure her neutrality, Bavaria sided actively with Austria.
German Empire
The rapid victory of the Prussians and the wise moderation of Bismarck paved the way for a complete revolution in Bavaria's relation to Prussia and the German question. The
South German Confederation, contemplated by the 6th article of the
Treaty of Prague, never came into being; and, though Prussia, in order not to excite the alarm of France, opposed the suggestion that the southern states should join the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated st ...
, the bonds of Bavaria (as of the other southern states) with the north were strengthened by an offensive and defensive alliance with Prussia, as the result of Napoleon's demand for "compensation" in the Palatinate. This was signed at
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
on 22 August 1866, on the same day as the signature of the formal treaty of peace between the two countries. The separatist ambitions of Bavaria were thus formally given up; she had no longer "need of France"; and during the
Franco-Prussian War, the Bavarian army marched, under the command of the Prussian crown prince, against Germany's common enemy. It was on the proposal of King
Ludwig II that the imperial crown was offered to King
Wilhelm I
William I or Wilhelm I (german: Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 2 January 1861 and German Emperor from 18 January 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the ...
of Prussia.

This was preceded, on 23 November 1870, by the signature of a treaty between Bavaria and the North German Confederation. By this instrument, though Bavaria became an integral part of the new German empire, she reserved a larger measure of sovereign independence than any of the other constituent states. Thus she retained a separate diplomatic service, military administration, and postal, telegraph, and railway systems. The treaty was ratified by the Bavarian chambers on 21 January 1871, though not without considerable opposition on the part of the so-called Patriot Party. Their hostility was increased by the
Kulturkampf
(, 'culture struggle') was the conflict that took place from 1872 to 1878 between the Catholic Church in Germany, Catholic Church led by Pope Pius IX and the government of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia led by Otto von Bismarck. The main issues wer ...
, due to the promulgation in 1870 of the dogma of
papal infallibility
Papal infallibility is a dogma of the Catholic Church which states that, in virtue of the promise of Jesus to Peter, the Pope when he speaks '' ex cathedra'' is preserved from the possibility of error on doctrine "initially given to the apos ...
.
Munich University
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich or LMU; german: Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It is Germany's sixth-oldest university in continuous oper ...
, where
Ignaz von Döllinger
Johann Joseph Ignaz von Döllinger (; 28 February 179914 January 1890), also Doellinger in English, was a German theologian, Catholic priest and church historian who rejected the dogma of papal infallibility. Among his writings which proved con ...
was professor, became the center of the opposition to the new dogma, and the
Old Catholic
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches or Old Catholic movement designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the Great Chu ...
s were protected by the king and the government. The federal law expelling the Jesuits was proclaimed in Bavaria on 6 September 1871 and was extended to the
Redemptorist
The Redemptorists officially named the Congregation of the Most Holy Redeemer ( la, links=no, Congregatio Sanctissimi Redemptoris), abbreviated CSsR,is a Catholic clerical religious congregation of pontifical right for men (priests and brother ...
s in 1873. On 31 March 1871, moreover, the bonds with the rest of the empire had been drawn closer by the acceptance of a number of laws of the North German Confederation, of which the most important was the new criminal code, which was finally put into force in Bavaria in 1879. The opposition of the Patriot Party, however, reinforced by the strong Catholic sentiment of the country, continued and it was only the steady support given by the king to successive Liberal ministries that prevented its finding disastrous expression in the parliament, where it remained in a majority till 1887, and subsequently, as the
Centre Party, continued to form the most compact party.
Ludwig II, whose passion for building palaces and near-total neglect of his governmental duties were becoming a serious crisis, was declared insane and on 10 June 1886, his uncle, Prince
Luitpold, became the regent. Three days later on 13 June, Ludwig II was found dead in
Lake Starnberg
Lake Starnberg, or ''Starnberger See'' ) — called Lake Würm, or ''Würmsee'' , until 1962 — is Germany's second-largest body of fresh water, having great depth, and fifth-largest lake by area. It and its surroundings lie in three different Ba ...
. The question of whether his death was self-imposed, accidental or the result of malicious conspirators remains unanswered. However, it was reported at the time and today is widely accepted that it was a suicide. Due to the insanity of Ludwig's brother, King
Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
, Prince Luitpold continued as regent.
After 1871, Bavaria shared to the full in the rapid development of Germany; but her particularism, founded on traditional racial and religious antagonism to the Prussians, was by no means dead, though it exhibited itself in no more dangerous form than the prohibition, reissued in 1900, to display any but the Bavarian flag on public buildings on the emperor's birthday; a provision which was subsequently modified so as to allow the Bavarian and imperial flags to be hung side by side.
Following Prince Luitpold's death in 1912, his son, Prince Ludwig, became the regent. A year later, Ludwig deposed his cousin, Otto, and proclaimed himself King
Ludwig III of Bavaria
Ludwig III (Ludwig Luitpold Josef Maria Aloys Alfried; 7 January 1845 – 18 October 1921) was the last King of Bavaria, reigning from 1913 to 1918. Initially he served in the Bavarian military as a lieutenant and went on to hold the rank of Oberl ...
. During the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, Ludwig's eldest son, Crown Prince
Rupprecht, commanded the Bavarian army and became one of the leading German commanders on the Western Front.
Modern times
Bavaria during the
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a Constitutional republic, constitutional federal republic for the first time in ...

Republican institutions replaced royal ones in Bavaria during the upheavals of November 1918. Provisional National Council Minister-President
Kurt Eisner
Kurt Eisner (; 14 May 1867 21 February 1919)"Kurt Eisner – Encyclopædia Britannica" (biography), ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2006, Britannica.com webpageBritannica-KurtEisner. was a German politician, revolutionary, journalist, and theatre c ...
declared Bavaria to be a
free state on 8 November 1918. Eisner was assassinated on 21 February 1919 ultimately leading to a Communist revolt and the short lived
Bavarian Socialist Republic
The Bavarian Soviet Republic, or Munich Soviet Republic (german: Räterepublik Baiern, Münchner Räterepublik),Hollander, Neil (2013) ''Elusive Dove: The Search for Peace During World War I''. McFarland. p.283, note 269. was a short-lived unre ...
(''Bayerische Räterepublik'' or ''Münchner Räterepublik'') being proclaimed from 6 April 1919. After violent suppression by elements of the German Army and notably the
Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European military volunteer units, or paramilitary, that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenary or private armies, rega ...
, the Bavarian Socialist Republic fell on 3 May 1919. The
Bamberg Constitution (') was enacted on 14 August 1919 creating the Free State of Bavaria within the Weimar Republic.
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
became a hotbed of extremism: the 1919
Bavarian Soviet Republic
The Bavarian Soviet Republic, or Munich Soviet Republic (german: Räterepublik Baiern, Münchner Räterepublik),Hollander, Neil (2013) ''Elusive Dove: The Search for Peace During World War I''. McFarland. p.283, note 269. was a short-lived unre ...
and the 1923
Beer Hall Putsch
The Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch,Dan Moorhouse, ed schoolshistory.org.uk, accessed 2008-05-31.Known in German as the or was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party ( or NSDAP) leader Adolf Hitler, Erich Ludendorff and othe ...
involving
Erich Ludendorff
Erich Friedrich Wilhelm Ludendorff (9 April 1865 – 20 December 1937) was a German general, politician and military theorist. He achieved fame during World War I for his central role in the German victories at Liège and Tannenberg in 1914. ...
and
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
took place in the same city. For most of the
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a Constitutional republic, constitutional federal republic for the first time in ...
, though, Bavaria was dominated by the relatively mainstream conservative
Bavarian People's Party
The Bavarian People's Party (german: Bayerische Volkspartei; BVP) was the Bavarian branch of the Centre Party, a lay Roman Catholic party, which broke off from the rest of the party in 1918 to pursue a more conservative and more Bavarian parti ...
. The BPP was a Catholic party that represented the Bavarian tradition of particularist conservatism, through which monarchists and even separatist sentiments were conveyed. An attempt supported by a wide coalition of parties, to establish
Rupprecht, Crown Prince of Bavaria, as a ''Staatskommisar'' with dictatorial powers in 1932 to counter the Nazis failed due to the hesitant Bavarian government under
Heinrich Held.
Bavaria during
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
With the rise of the
Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
to power in 1933, the Bavarian parliament was dissolved without new elections. Instead, the seats were allocated according to the results in the national election of March 1933, giving the Nazis and its coalition partner, the
DNVP
The German National People's Party (german: Deutschnationale Volkspartei, DNVP) was a national-conservative party in Germany during the Weimar Republic. Before the rise of the Nazi Party, it was the major conservative and nationalist party in Wei ...
, a narrow two-seat majority due to the fact that the seats won by the
KPD were declared void. With this controlling power, the NSDAP was declared the only legal party and all other parties in Germany and Bavaria were dissolved. In 1934, the Bavarian parliament was, like all other state parliaments, dissolved too.
Shortly after, Bavaria itself was broken up during the reorganization of the ''Reich''. Instead of the states, ''
Reichsgau
A (plural ) was an administrative subdivision created in a number of areas annexed by Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945.
Overview
The term was formed from the words (realm, empire) and , the latter a deliberately medieval-sounding word w ...
e'' were established as administrative sub-divisions. Bavaria was split into six regions, the ''Reichsgaue'' ''
Schwaben
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
'', ''München-Oberbayern'', ''Bayerische Ostmark'', ''
Franken'', ''Main-Franken'' and'' Westmark''.

During the 12 years of Nazi rule, Bavaria was one of Hitler's favorite locations, and he spent much time in his residence at the
Obersalzberg
Obersalzberg is a mountainside retreat situated above the market town of Berchtesgaden in Bavaria, Germany. Located about south-east of Munich, close to the border with Austria, it is best known as the site of Adolf Hitler's former mountain resi ...
. The
KZ in
Dachau
Dachau () was the first concentration camp built by Nazi Germany, opening on 22 March 1933. The camp was initially intended to intern Hitler's political opponents which consisted of: communists, social democrats, and other dissidents. It is lo ...
, near Munich, was the first to be established. But Bavaria was also the scene of passive resistance to the regime, the most well known of this being the
White Rose
The White Rose (german: Weiße Rose, ) was a Nonviolence, non-violent, intellectual German resistance to Nazism, resistance group in Nazi Germany which was led by five students (and one professor) at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, ...
.
Nürnberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
, Bavaria's second-largest city, became the scene of massive rallies, the ''
Reichsparteitage
The Nuremberg Rallies (officially ', meaning ''Nazi Germany, Reich Party Congress'') refer to a series of celebratory events coordinated by the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, Germany. The first rally held took place in 1923. This rally was not part ...
''. Ironically, the last of those in 1939, titled ''Reichsparteitag des Friedens'' (''Reichsparteitag of peace''), was canceled due to the outbreak of the second world war. After the war, carefully chosen, for this reason, the city became the location of the war crimes trials, the
Nuremberg Military Tribunals
The subsequent Nuremberg trials were a series of 12 military tribunals for war crimes against members of the leadership of Nazi Germany between December 1946 and April 1949. They followed the first and best-known Nuremberg trial before the In ...
.
While Bavaria had approximately 54,000
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
people living in its borders at the turn of the 20th century, by 1933 still 41,000 lived in the state. By 1939, this number had shrunk to 16,000, and few of those survived the Nazi rule.
Bavaria during the Federal Republic of Germany
Following the end of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Bavaria was occupied by US forces, who reestablished the state on 19 September 1945. In 1946 Bavaria lost its district on the Rhine, the Palatinate. The destruction caused by
aerial bombing
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offici ...
s during the war, alongside the arrival of refugees from the parts of Germany now under
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
occupation, caused major problems for the authorities. By September 1950, 2,155,000 expellees had found refuge in Bavaria, or 23.6 percent of the population. Of these, 1,025,000 were
Sudeten Germans
German Bohemians (german: Deutschböhmen und Deutschmährer, i.e. German Bohemians and German Moravians), later known as Sudeten Germans, were ethnic Germans living in the Czech lands of the Bohemian Crown, which later became an integral part of ...
from Bohemia and Moravia and 459,000 were Germans from Polish-annexed
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
. A further large group were
German-speakers from Hungary. In the following decades, Sudeten Germans were acknowledged as Bavaria's fourth largest ethnic group, along with Bavarians, Franconians, and Swabians.
Bavaria is home to the
Bavarian Party, founded in 1946, whose goal is to establish an independent Bavarian state. For a time, the idea that Bavaria might become independent again was seriously entertained by the Allied occupation authorities, along with a possible union between Bavaria and Austria. With the onset of the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, support for Bavarian independence quickly lost support both within Bavaria and from the Western allies, and the state became a part of
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
.
The first post-World War II state elections were held on 30 June 1946, when 180 delegates were chosen. The main task of those delegates was to draft a new Bavarian constitution since the day-to-day running of the state still lay with the US authorities at this stage. The new constitution was accepted by a public vote on 1 December 1946, the same day the first post-war state parliament (German: ''Landtag'') was elected.
Bavaria was politically dominated by the
Christian Social Union (CSU), sister party of the
Christian Democratic Union, the main center-right party in Germany, until 1954. Bavaria was then governed by a coalition under the leadership of the
Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been ...
, returning to the CSU in 1957.
Since the 1960s Bavaria has seen a dynamic development to one of Europe's leading economic zones, the country is no longer mainly an agricultural region but hosts a variety of high tech industries.
After the CSU lost more than 17% of the votes in the
Bavarian state elections of 2008, incumbent Minister-President
Günther Beckstein
Günther Beckstein () (born 23 November 1943) is a German CSU politician from Bavaria and was the 17th Minister President of Bavaria from 9 October 2007 to 27 October 2008. He is well known for his outspoken views on law and order.
Biography ...
and Chairman of the CSU,
Erwin Huber, announced their resignations.
Horst Seehofer
Horst Lorenz Seehofer (born 4 July 1949) is a German politician who served as Minister of the Interior, Building and Community under Chancellor Angela Merkel from 2018 to 2021. A member of the Christian Social Union (CSU), he served as the 18 ...
was quickly proposed as their successor. At a party convention on 25 October, he was affirmed as the new Chairman of the CSU, and on 27 October he was elected Minister-President by the
Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non ...
with votes from the
Free Democratic Party, forming the first
coalition
A coalition is a group formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political or economical spaces.
Formation
According to ''A Gui ...
government in Bavaria since 1962.
In 2008, Bavaria became the first federal state of Germany to completely ban smoking in bars and restaurants. After this restriction was criticized as being "too harsh" by some members of the CSU, it was relaxed one year later. Supporters of smoking bans then brought about a public referendum on the issue, which led to even firmer restrictions than the initial ban. Thereafter, a more comprehensive ban was introduced in 2010.
See also
*
List of rulers of Bavaria
The following is a list of rulers during the history of Bavaria. Bavaria was ruled by several dukes and kings, partitioned and reunited, under several dynasties. Since 1949, Bavaria has been a democratic state in the Federal Republic of Germa ...
*
List of Premiers of Bavaria
*
Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria (german: Königreich Bayern; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German ...
*
History of Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken) is a region that is not precisely defined, but which lies in the north of the Free State of Bavaria, parts of Baden-Württemberg and South Thuringia and Hesse in Germany. It is characterised by its own cultural and lin ...
*
Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte: Museum
;History of cities in Bavaria
*
Timeline of Augsburg
Timeline of Augsburg, Bavaria, Germany.
Prior to 16th century
* 14 BCE – Roman colony established (approximate date).
* 5th century CE – Settlement sacked by Huns.
* 6th century CE - Catholic Diocese of Augsburg established.
* 778 – Simp ...
*
History of Munich
Events in the history of Munich in Germany.
Origin
The year 1158 is assumed to be the foundation date of Munich, which is only the earliest date the city is mentioned in a document. By that time the Guelph Henry the Lion, Duke of Saxony and Ba ...
and
Timeline of Munich
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Munich, Germany.
Prior to 17th century
* 1158 - Duke Henry the Lion builds bridge, mint, and salt-depot.
* 1175 - Munich gains official status as city.
* 1239 - Coat of arms of Munich ...
*
Timeline of Nuremberg
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Nuremberg, Germany.
Prior to 15th century
* 1030 – Nuremberg Castle built (approximate date).
* 1060 – Residence of the burgrave established.
* 1127 - Emperor Lothair assigns Nure ...
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Map of Bavaria 1789Bavarian Studies in History and Culture
History of the Bavarian Parliament - (Geschichte des Bayerischen Parliaments 1819 - 2003, in German)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bavaria (history)
Bavarian Circle
Boii
 The history of Bavaria for the ensuing century intertwines with that of the
The history of Bavaria for the ensuing century intertwines with that of the  In 955 AD, Henry's young son Henry, surnamed the Quarrelsome, succeeded him, but in 974 AD he became involved in a conspiracy against King
In 955 AD, Henry's young son Henry, surnamed the Quarrelsome, succeeded him, but in 974 AD he became involved in a conspiracy against King  For some years after Louis' death in 1294, his sons Rudolph I and Louis, afterward the emperor Louis IV, ruled their duchy in common; but as their relations were never harmonious, a division of Upper Bavaria occurred in 1310, by which Rudolph received the land east of the
For some years after Louis' death in 1294, his sons Rudolph I and Louis, afterward the emperor Louis IV, ruled their duchy in common; but as their relations were never harmonious, a division of Upper Bavaria occurred in 1310, by which Rudolph received the land east of the 

 The succeeding duke, Albert's son,
The succeeding duke, Albert's son,  His good work, however, was largely undone by his son
His good work, however, was largely undone by his son 
 In 1792, French revolutionary armies overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself and advanced to Munich where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals, and laid siege to
In 1792, French revolutionary armies overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself and advanced to Munich where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals, and laid siege to  In view of the scarcely disguised ambitions and intrigues of the Austrian court, Montgelas now believed that the interests of Bavaria lay in a frank alliance with the French Republic; he succeeded in overcoming the reluctance of Maximilian Joseph and on 24 August a separate treaty of peace and alliance with France was signed in
In view of the scarcely disguised ambitions and intrigues of the Austrian court, Montgelas now believed that the interests of Bavaria lay in a frank alliance with the French Republic; he succeeded in overcoming the reluctance of Maximilian Joseph and on 24 August a separate treaty of peace and alliance with France was signed in  In 1809 Bavaria was again engaged in war with Austria on the side of France. The Tyroleans rose up against the Bavarian authority and succeeded three times in defeating Bavarian and French troops trying to retake the country. Austria lost the war of the
In 1809 Bavaria was again engaged in war with Austria on the side of France. The Tyroleans rose up against the Bavarian authority and succeeded three times in defeating Bavarian and French troops trying to retake the country. Austria lost the war of the  Ludwig proved an enlightened patron of the arts and sciences, who transferred the
Ludwig proved an enlightened patron of the arts and sciences, who transferred the  During the 12 years of Nazi rule, Bavaria was one of Hitler's favorite locations, and he spent much time in his residence at the
During the 12 years of Nazi rule, Bavaria was one of Hitler's favorite locations, and he spent much time in his residence at the