Battlefield Illumination Airborne System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Battlefield illumination is technology that improves visibility for military forces operating in difficult low-light conditions. The risks and dangers to armies fighting in poor light have been known since Ancient Chinese times. Prior to the advent of the electrical age, fire was used to improve visibility on the battlefield.
Modern armies use a variety of equipment and discharge devices to create artificial light. If natural light is not present
Battlefield illumination is technology that improves visibility for military forces operating in difficult low-light conditions. The risks and dangers to armies fighting in poor light have been known since Ancient Chinese times. Prior to the advent of the electrical age, fire was used to improve visibility on the battlefield.
Modern armies use a variety of equipment and discharge devices to create artificial light. If natural light is not present
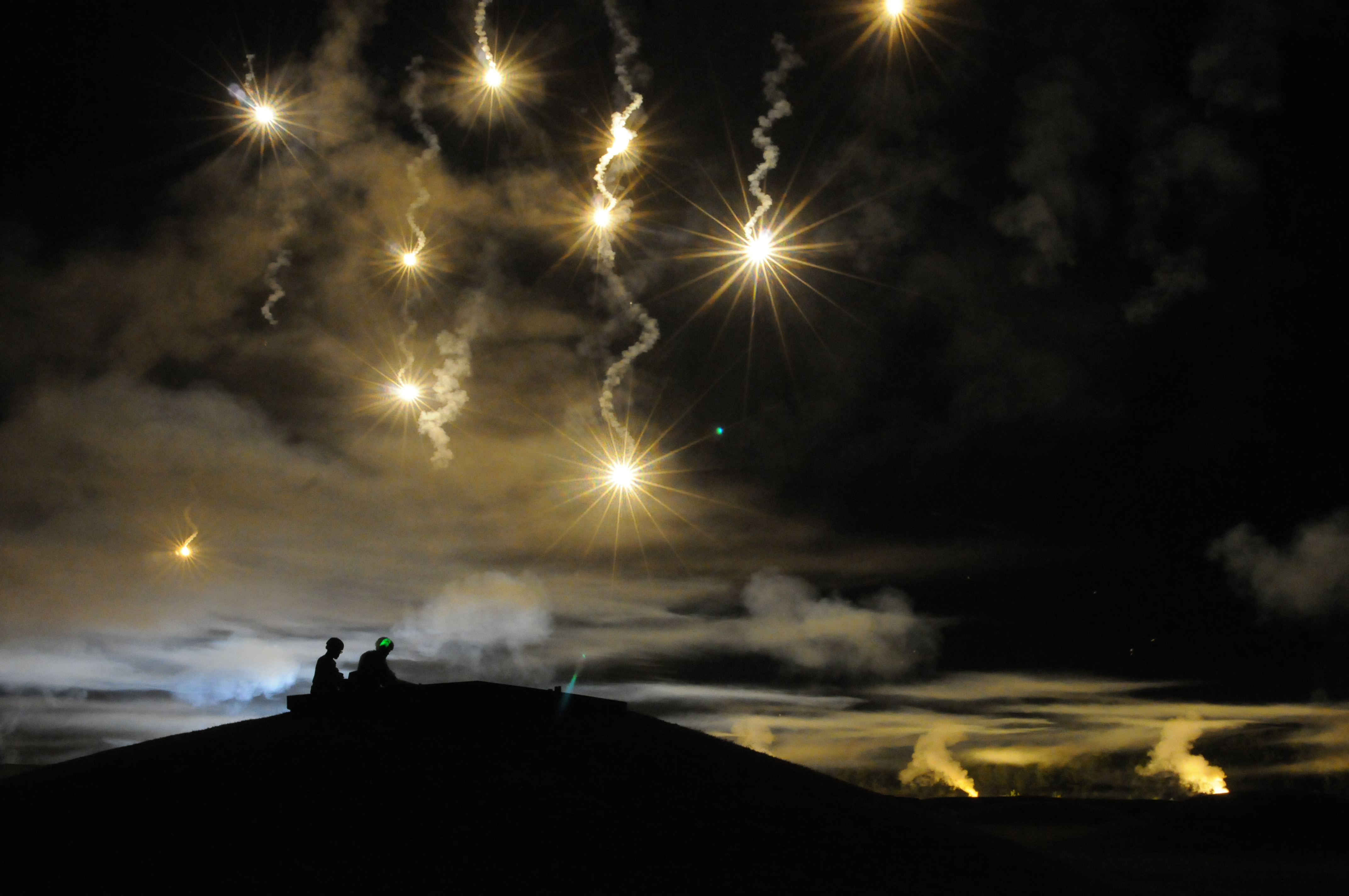 Ancient military strategists knew that
Ancient military strategists knew that
 In 1583, during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–90), the
In 1583, during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–90), the 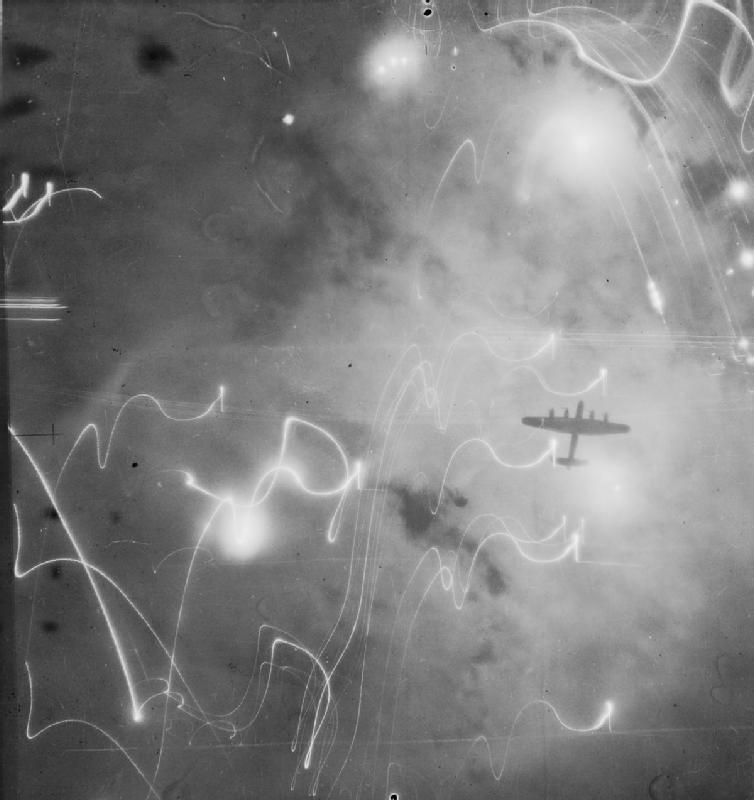
 Flares can be used to mark positions, usually for targeting, but
Flares can be used to mark positions, usually for targeting, but
 Battlefield illumination is technology that improves visibility for military forces operating in difficult low-light conditions. The risks and dangers to armies fighting in poor light have been known since Ancient Chinese times. Prior to the advent of the electrical age, fire was used to improve visibility on the battlefield.
Modern armies use a variety of equipment and discharge devices to create artificial light. If natural light is not present
Battlefield illumination is technology that improves visibility for military forces operating in difficult low-light conditions. The risks and dangers to armies fighting in poor light have been known since Ancient Chinese times. Prior to the advent of the electrical age, fire was used to improve visibility on the battlefield.
Modern armies use a variety of equipment and discharge devices to create artificial light. If natural light is not present searchlight
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a particular direc ...
s, whether using visible light or infrared, and flare
A flare, also sometimes called a fusée, fusee, or bengala in some Latin-speaking countries, is a type of pyrotechnic that produces a bright light or intense heat without an explosion. Flares are used for distress signaling, illumination, ...
s can be used. As light can be detected electronically, modern warfare has accordingly seen increased use of night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vi ...
through the use of infrared cameras
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
and image intensifier
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light proces ...
s.
Theory
 Ancient military strategists knew that
Ancient military strategists knew that natural light
Natural Light, sometimes Natty Light, is an American reduced-calorie light lager brewed by Anheuser-Busch since its introduction on July 31, 1977. Its ingredients are listed as water, barley malt, cereal grains, yeast, and hops. One serving cont ...
created shadows that can hide form while bright areas would expose a military force's size and number. Ancient armies would always prefer to fight with the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
behind them in order to use the visual glare to partially blind an opposing enemy. Backlight
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). As LCDs do not produce light by themselves—unlike, for example, cathode ray tube (CRT), plasma (PDP) or OLED displays—they need illumination ( ambient light or a ...
would also obscure movement and numbers making it more difficult for an enemy to react quickly to any tactical assault.
Adverse weather such as fog, rain and snow reduce both visibility and the usefulness of illumination. Enemy action in the form of smoke and shellfire, and the dust and smoke created by battle generally, further limit the effectiveness of illumination. Thermal imaging devices (using infrared) can however to some extent penetrate these obstacles.
History
 In 1583, during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–90), the
In 1583, during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–90), the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
used lanterns to defeat a Safavid army
The Military of Safavid Iran covers the military history of Safavid Iran from 1501 to 1736.
Foundation of the Safavid military
It was the first Safavid king (shah), Ismail I (1501–1524), who laid foundation to the Safavid military. Its ori ...
in a night time encounter, that became known as the Battle of Torches
The Battle of Torches ( tr, Meşaleler Savaşı) was fought in 1583 during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590). The name of the battle refers to torches used during night clashes. The battle resulted in an Ottoman victory, and had thereby se ...
.
In 1882 the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
used searchlights to prevent Egyptian forces from staffing artillery batteries at Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
during the Anglo-Egyptian War
The British conquest of Egypt (1882), also known as Anglo-Egyptian War (), occurred in 1882 between Egyptian and Sudanese forces under Ahmed ‘Urabi and the United Kingdom. It ended a nationalist uprising against the Khedive Tewfik Pasha. It ...
. Later that same year, the French and British forces landed troops under artificial light created by searchlights.
The Canal Defence Light
The Canal Defence Light (CDL) was a British "secret weapon" of the Second World War, based upon the use of a powerful carbon-arc searchlight mounted on a tank. It was intended to be used during night-time attacks, when the light would allow enem ...
was a British "secret weapon" of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. It was a tank fitted with a powerful carbon-arc searchlight
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a particular direc ...
to support night-time attacks. The War Office ordered 300 such lamps in 1940. During the latter stages of the war, the British Army created Moonlight Batteries, Royal Artillery
The Moonlight Batteries were Searchlight units of Britain's Royal Artillery that specialised in providing 'artificial moonlight', otherwise known as 'movement light' or 'Monty's moonlight', for ground operations during the latter stages of World Wa ...
that specialised in providing 'artificial moonlight', otherwise known as 'movement light' or ' Monty's moonlight' for ground operations.
Target indicator
Target indicators, also known as target markers or TI's for short, were flares used by the RAF's Bomber Command during World War II. TIs were normally dropped by Pathfinders onto the target, providing an easily seen visual aiming point for the ...
flares were widely used by the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
during the Second World War; these were dropped by a wave of Pathfinder Force
The Pathfinders were target-marking squadrons in RAF Bomber Command during World War II. They located and marked targets with flares, which a main bomber force could aim at, increasing the accuracy of their bombing. The Pathfinders were norma ...
aircraft ahead of the main force of bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
s to indicate the aiming point.

Types
Flares
 Flares can be used to mark positions, usually for targeting, but
Flares can be used to mark positions, usually for targeting, but laser-guided
Laser guidance directs a robotics system to a target position by means of a laser beam. The laser guidance of a robot is accomplished by projecting a laser light, image processing and communication to improve the accuracy of guidance. The key ide ...
and GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
weapons have reduced this function. GPS-guided bombs, for example, rely only on GPS signals, without any locally-provided target designation. Laser-guided bombs require a laser designator to guide them to the target, in turn requiring an observer (in the aircraft or on the ground) able to see the target and aim the laser designator.
During the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
and the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, US ground forces used the M127A1 White Star Signal Flare Parachute to light up the jungle in forward positions.
Searchlights
These are usually large portable devices that combine an extremely luminous source (usually acarbon arc lamp
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc).
The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, ...
) with a mirrored parabolic reflector
A parabolic (or paraboloid or paraboloidal) reflector (or dish or mirror) is a reflective surface used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is part of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface generated ...
to project a powerful beam of light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
of approximately parallel rays in a particular direction. They have been used to create "artificial moonlight" on battlefields.
Battlefield Illumination Airborne System (BIAS)
The Battlefield Illumination Airborne System (BIAS) was an illumination system consisting of a lamp assembly (consisting of a number of Xenon lamps), a power source, a heat exchanger pod and a control console. The system was intended to be installed on modified cargo aircraft, with the lamp assembly positioned on the rear cargo ramp, the other elements were to be installed in the main cargo area and mounted on the aircraft fuselage. TheUnited States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
(USAF) opened Operation Shed Light
Operation Shed Light was a crash development project in aerial warfare, initiated in 1966 by the United States Air Force to increase the ability to accurately strike at night or in adverse weather. During the 1960s the United States military w ...
as a development effort on 7 February 1966. Shed Light explored the deficiencies in attacking targets at night, particularly with visible light illumination. A single BIAS system was developed by LTV electro-Systems
LTV may refer to:
Television
* Lagos Television, a TV channel in Nigeria.
* Latvijas Televīzija, Latvian Television
* LRT televizija, formerly LTV, Lithuanian National Television
* LTV Ethiopia, a private satellite TV channel in Ethiopia
* Lumier ...
and installed on a Fairchild C-123B for the Special Air Warfare Center
Special or specials may refer to:
Policing
* Specials, Ulster Special Constabulary, the Northern Ireland police force
* Specials, Special Constable, an auxiliary, volunteer, or temporary; police worker or police officer
Literature
* Specials ( ...
at Eglin Air Force Base
Eglin Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.
The host unit at Eglin is the 96th Test Wing (formerly the 96th Air Base Wing). The ...
in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
by April 1966. Initially designated Airborne General Illumination Light (AGIL), the system weighed and had a lamp assembly with 28 Xenon lamps, heat exchanger and cooling system to prevent the lamps from overheating. Replacing the rear cargo ramp entirely, the AGIL created a 50° cone of light, shining vertically down, but able to rotate 50° to the side, illuminating at 0.04 Candela from , or at 0.4 Candela from .
Testing of the BIAS equipped C-123B in support of night strike, search and rescue, and ground operations was carried out eliciting positive feedback from USAF and United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
(US Army) observers. Ten C-123s were slated to receive the AGIL system under Southeast Asia Operational Requirement (SEAOR) 50, issued on 6 June 1966, the programme was changed to fit the system on 11 Lockheed JC-130A
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 ...
aircraft (re-designated RC-130S), but only two were completed and tested in South-East Asia, where it was found that the aircraft was, understandably, vulnerable to enemy anti-aircraft fire and was generally less effective than the emergent AC-130
The Lockheed AC-130 gunship is a heavily armed, long-endurance, attack aircraft, ground-attack variant of the C-130 Hercules transport, fixed-wing aircraft. It carries a wide array of ground-attack weapons that are integrated with sophisticate ...
gunships. The two BIAS equipped RC-130S, remained in SE Asia for an unknown length of time and were eventually returned to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
(US) and de-modified by 1974.
References
{{reflist Lighting Illumination