Battle of Mine Run on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Mine Run, also known as Payne's Farm, or New Hope Church, or the Mine Run campaign (November 27 – December 2, 1863), was conducted in
 After the
After the
Unlike Maj. Gen.
American Battlefield Trust "Mine Run Battlefield" page. Accessed May 29, 2018.
West Point website
* Salmon, John S. ''The Official Virginia Civil War Battlefield Guide''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2001. .
Mine Run Campaign in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
{{authority control 1863 in Virginia Mine Run Mine Run Mine Run Orange County, Virginia Mine Run Mine Run November 1863 events December 1863 events
Orange County, Virginia
Orange County is a county located in the Central Piedmont region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 36,254. Its county seat is Orange. Orange County includes Montpelier, the estate of James Madison, the ...
, in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
.
An unsuccessful attempt of the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confede ...
to defeat the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most oft ...
, it was marked by false starts and low casualties and ended hostilities in the Eastern Theater for the year.
Background


 After the
After the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
in July, Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee and his command retreated back across the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
into Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. Union commander Maj. Gen.
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
George G. Meade
George Gordon Meade (December 31, 1815 – November 6, 1872) was a United States Army officer and civil engineer best known for decisively defeating Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. H ...
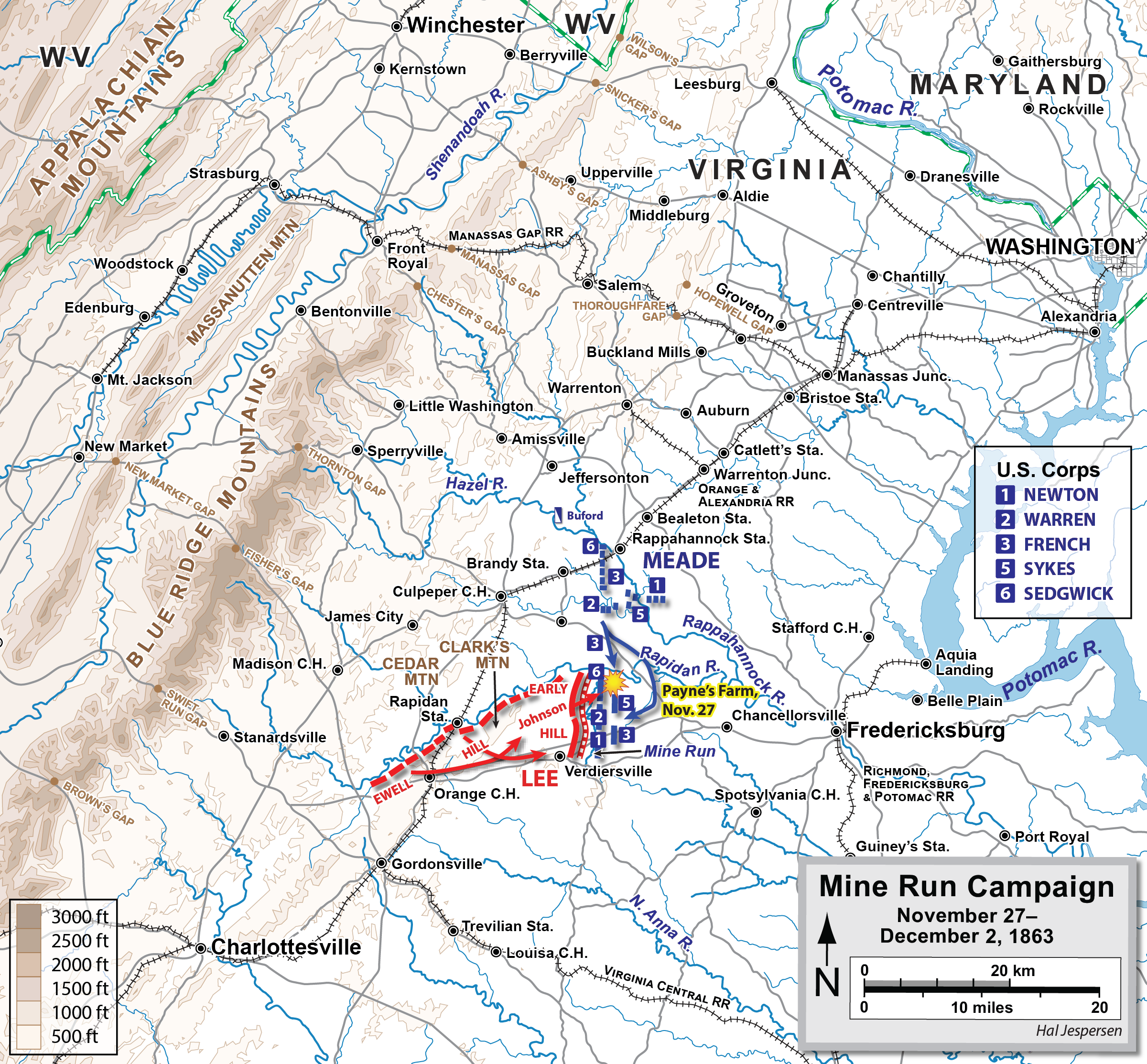
was widely criticized for failing to pursue aggressively and defeat Lee's army. Meade planned new offensives in Virginia for the fall. His first attempt was a series of inconclusive duels and maneuvers in October and November known as the Bristoe campaign.
In late November, Meade attempted to steal a march through the Wilderness of Spotsylvania and strike the right flank of the Confederate Army south of the Rapidan River. Meade had intelligence reports that Lee's army, half the size of Meade's Army of the Potomac (actually 48,000 to Meade's 81,000), was split in two, separated by Clark's Mountain, with the two flanks anchored at Mine Run and Liberty Mills, over thirty miles apart. His plan was to cross the Rapidan at points beyond Maj. Gen.
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
J.E.B. Stuart
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart (February 6, 1833May 12, 1864) was a United States Army officer from Virginia who became a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War. He was known to his friends as "Jeb,” from the initials of ...
's cavalry screen, overwhelm the right flank ( Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell's Second Corps) and then follow up with the remainder (Lt. Gen. A.P. Hill
Ambrose Powell Hill Jr. (November 9, 1825April 2, 1865) was a Confederate general who was killed in the American Civil War. He is usually referred to as A. P. Hill to differentiate him from another, unrelated Confederate general, Daniel Harvey H ...
's Third Corps).NPSUnlike Maj. Gen.
Joseph Hooker
Joseph Hooker (November 13, 1814 – October 31, 1879) was an American Civil War general for the Union, chiefly remembered for his decisive defeat by Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Chancellorsville in 1863.
Hooker had serv ...
's plan in the Chancellorsville campaign
The Battle of Chancellorsville, April 30 – May 6, 1863, was a major battle of the American Civil War (1861–1865), and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville campaign.
Chancellorsville is known as Lee's "perfect battle" because h ...
earlier that year on essentially the same ground, Meade planned no diversions; he intended a lightning strike with his entire army. The army marched on November 25 and got off to a good start, aided by fog on Clark's Mountain, which screened his movements from Confederate lookouts. However, Maj. Gen. William H. French's III Corps got mired in fording the river at Jacob's Ford, causing traffic jams when they moved their artillery to Germanna Ford, where other units were attempting to cross.
Opposing forces
Union
Confederate
Battle
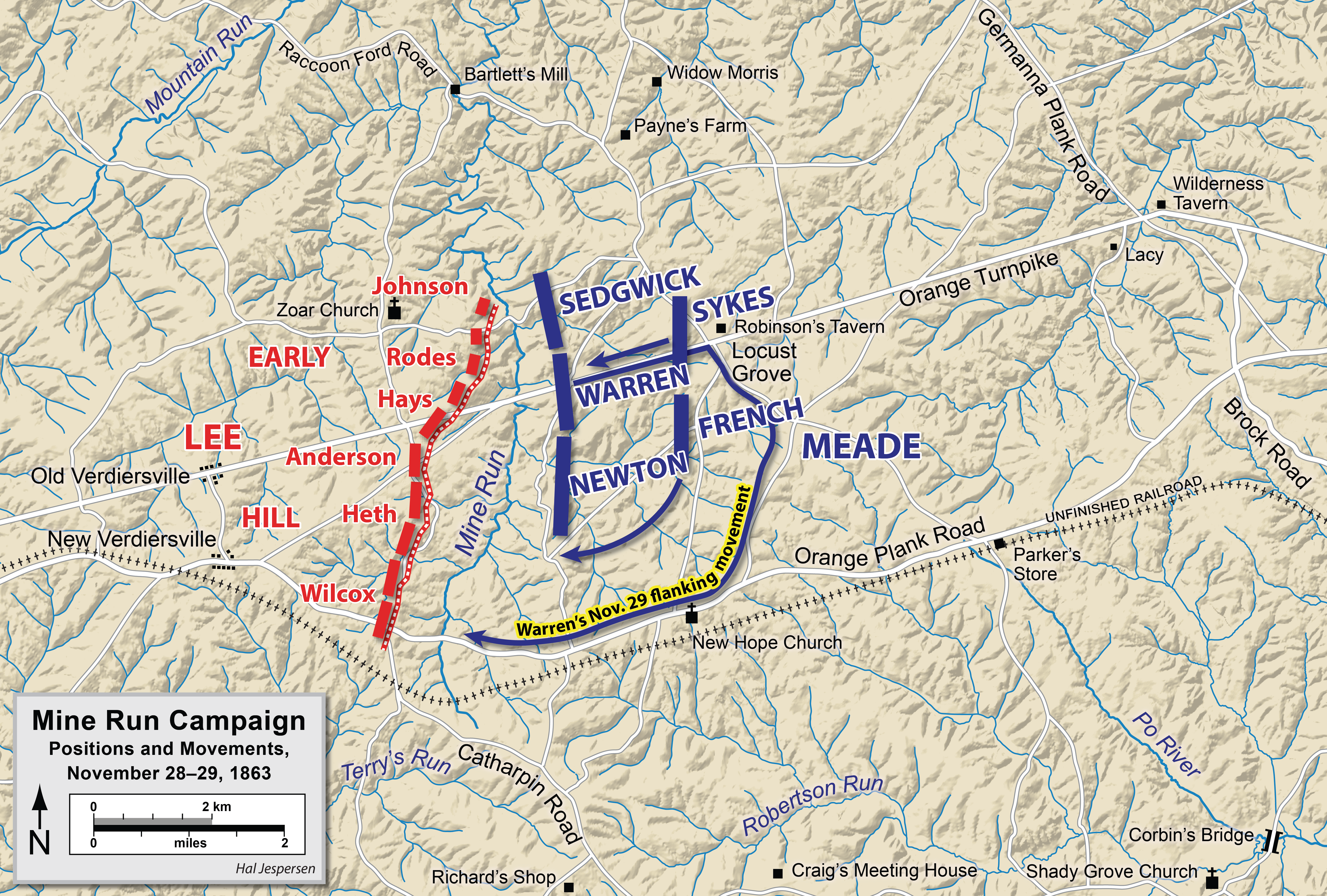
Speed had escaped Meade, who was furious with French, and this allowed Lee time to react. Lee ordered Maj. Gen. Jubal A. Early, in temporary command of Ewell's Second Corps, to march east on the Orange Turnpike to Locust Grove, where Early's men began skirmishing with advance Union elements. Maj. Gen. Edward "Allegheny" Johnson's division was marching along the Raccoon Ford Road to join Early when the head of Gen. French's III Corps made contact in the heavy wooded terrain along the Widow Morris Road. Johnson turned his division about and ordered what can only be described as a reckless double-envelopment assault against a mostly unseen enemy of unknown strength, throwing his 5,500 men against French and John Sedgwick's VI Corps (a combined 32,000). It was about 3:45 - 4:00 p.m. Johnson's assault fell apart quickly on the left, where Steuart lost control of his brigade, and quickly bogged down in the middle (Stonewall Brigade) and on the right (Stafford and Jones), but was strong enough to slow down the Union advance until nightfall, when Johnson left the field on his own accord, retreating with the rest of the army west behind the Mine Run Creek. The actual fighting consumed less than two and one-half hours and the losses were heavy. Johnson lost nearly 550 men (or 10% of his strength) and French's corps about 950 from all causes. The Battle of Payne's Farm was short, bloody, and important. Johnson's attack put French and his III Corps back on its heels, slowed the advance, and saved Lee's army. If Johnson had cleared the Widow Morris Road before the arrival of French and Sedgwick, or had been driven away in defeat, the 32,000 Federals could have marched behind Lee's left flank and into his rear. After dark, Lee withdrew to prepared fieldfortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
s along Mine Run. The next day the Union Army closed on the Confederate position. Meade planned a heavy artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
bombardment followed by Maj. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren
Gouverneur Kemble Warren (January 8, 1830 – August 8, 1882) was an American civil engineer and Union Army general during the American Civil War. He is best remembered for arranging the last-minute defense of Little Round Top during the Battle ...
's II Corps attack in the south, then Maj. Gen. John Sedgwick
John Sedgwick (September 13, 1813 – May 9, 1864) was a military officer and Union Army general during the American Civil War.
He was wounded three times at the Battle of Antietam while leading his division in an unsuccessful assault against Co ...
's VI Corps in the north an hour later. Lee planned an assault for December 2 that would have exploited the dangling left flank of the Union line, discovered the previous day by Maj. Gen. Wade Hampton's cavalry. Although the Union bombardment began on schedule, the major attack did not materialize; Meade concluded that the Confederate line was too strong to attack (although Warren is credited with getting the attack canceled) and retired during the night of December 1–2, ending the fall campaign. Lee was chagrined to find he had no one left in his front to attack.
Aftermath
The Army of the Potomac went into winter quarters atBrandy Station, Virginia
Brandy Station is an unincorporated area, unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Culpeper County, Virginia, Culpeper County, Virginia, United States. It was first listed as a CDP in the 2020 United States census, 2020 census ...
. Mine Run had been Meade's final opportunity to plan a strategic offensive before the arrival of Ulysses S. Grant as general-in-chief the following spring. Lee also regretted the inconclusive results. He was quoted as saying, "I am too old to command this army. We never should have permitted those people to get away." Confederate hopes of repeating their Chancellorsville triumph had been dashed.
The Mine Run Campaign was Meade's last and failed attempt in 1863 to destroy Lee's Army of Northern Virginia before winter halted military operations.
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator. His original works include " Paul Revere's Ride", '' The Song of Hiawatha'', and ''Evangeline''. He was the first American to completely tran ...
wrote the 1863 poem "Christmas Bells", which became the carol "I Heard the Bells on Christmas Day
"I Heard the Bells on Christmas Day" is a Christmas carol based on the 1863 poem "Christmas Bells" by American poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. The song tells of the narrator hearing Christmas bells during the American Civil War, but despairing ...
", in response to learning of his son Charles Appleton Longfellow being severely wounded in the battle.
Battlefield preservation
Attorney, historian, and publisher Theodore P. Savas, together with Paul Sacra of Richmond, Virginia, set out to locate and map the Payne's Farm battlefield in the early 1990s. Savas believed published articles and books had incorrectly located the fighting area and was determined to test his theory. Armed with extensive primary sources and battle reports, he and Sacra located what they believed was the field and, with the permission from several landowners, used metal detectors to prove it. Within a couple days Savas and Sacra had unearthed hundreds of artifacts, including bullets, a ramrod, bayonet socket, a partial harmonica, belt buckles, buttons, and much more. Savas drew maps of the field and the general location of the artifacts and delivered them to The Association for the Preservation of Civil War Sites (or APCWS), and its director, A. Wilson Greene, in Fredericksburg, Virginia. Greene, who had no idea the field was in such pristine condition, was excited by the find and affirmed its importance. Saving the land was a slow process for a variety of reasons, including the fact that the majority landowner wanted to develop the land. At that point, Savas and Sacra presented him with proof that the land contained at least one mass grave (which they had not detected or recovered anything from), and that to develop it would be a travesty. TheCivil War Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the American Civil War, the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812 through acquisition of battlefield land. T ...
(a division of the American Battlefield Trust) and its partners later acquired and preserved of the battlefield. The battlefield today features a wooded, 1.5-mile interpretive trail with historical wayside markers. It is located on Virginia highway 611 across from the Zoar Baptist Church about two miles north of Locust Grove.American Battlefield Trust "Mine Run Battlefield" page. Accessed May 29, 2018.
Notes
References
* David J. Eicher, Eicher, David J. ''The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. . * Esposito, Vincent J. ''West Point Atlas of American Wars''. New York: Frederick A. Praeger, 1959. . The collection of maps (without explanatory text) is available online at thWest Point website
* Salmon, John S. ''The Official Virginia Civil War Battlefield Guide''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2001. .
Further reading
* Gottfried, Bradley M. ''The Maps of the Bristoe Station and Mine Run Campaigns: An Atlas of the Battles and Movements in the Eastern Theater after Gettysburg, Including Rappahannock Station, Kelly's Ford, and Morton's Ford, July 1863 - February 1864''. Savas Beatie, 2013. * Graham, Martin F., and George F. Skoch. ''Mine Run: A Campaign of Lost Opportunities, October 21, 1863–May 1, 1864''. Lynchburg, VA: H. E. Howard, 1987. . * Mackowski, Chris. ''The Great Battle Never Fought: The Mine Run Campaign, November 26–December 2, 1863''. Emerging Civil War Series. El Dorado Hills, CA: Savas Beatie, 2018. .External links
Mine Run Campaign in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
{{authority control 1863 in Virginia Mine Run Mine Run Mine Run Orange County, Virginia Mine Run Mine Run November 1863 events December 1863 events