Battle Of Marchfeld on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava Field''; german: Schlacht auf dem Marchfeld; cs, Bitva na Moravském poli; hu, Morvamezei csata) at
 The deposition of Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen by Pope Innocent IV in 1245 created a grave crisis for the
The deposition of Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen by Pope Innocent IV in 1245 created a grave crisis for the
 Meanwhile, Rudolph was gathering allies and preparing for battle. He achieved two of these alliances through the classic Habsburg style – marriage. First, he married his son Albert to Elisabeth of Gorizia-Tyrol. In return, her father Count Meinhard II of Gorizia-Tyrol received the Duchy of Carinthia as a fief. Second, he established an — unstable — alliance with Duke Henry I of Lower Bavaria by offering Rudolph's daughter Katharina as wife for the Duke's son, Otto, in addition to the region of present-day Upper Austria as a pledge for her dowry. He also concluded an alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary, who intended to settle old scores with Ottokar.
Rudolph, so strengthened, besieged Ottokar at the Austrian capital
Meanwhile, Rudolph was gathering allies and preparing for battle. He achieved two of these alliances through the classic Habsburg style – marriage. First, he married his son Albert to Elisabeth of Gorizia-Tyrol. In return, her father Count Meinhard II of Gorizia-Tyrol received the Duchy of Carinthia as a fief. Second, he established an — unstable — alliance with Duke Henry I of Lower Bavaria by offering Rudolph's daughter Katharina as wife for the Duke's son, Otto, in addition to the region of present-day Upper Austria as a pledge for her dowry. He also concluded an alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary, who intended to settle old scores with Ottokar.
Rudolph, so strengthened, besieged Ottokar at the Austrian capital
 Surprised by Rudolph's maneuver, Ottokar quickly abandoned the siege at Laa, marched southwards, and on August 26 met the united German and Hungarian forces near Dürnkrut. When he arrived his enemies had already taken the opportunity to explore the topography of the future battleground. From the early morning, the left wing of the advancing Bohemian troops were embroiled in impetuous attacks by the Cuman forces, which the heavily armed knights could not ward off. Nevertheless, as the main armies collided and the battle wore on, Ottokar's outnumbering cavalry seemed to gain the upper hand, when even Rudolph's horse was stabbed under him and the 60-year-old narrowly escaped with his life, rescued by his liensmen.
After three hours of continuous fighting on a hot summer day, Ottokar's knights in their heavy armour were suffering from heat exhaustion and were not able to move. At noon Rudolph ordered a fresh heavy cavalry regiment he had concealed behind nearby hills and woods to attack the right flank of Ottokar's troops. Such ambushes were indeed commonly regarded as dishonourable in medieval warfare and Rudolph's commander Ulrich von Kapellen apologized to his own men in advance. Nevertheless, the attack prevailed in splitting and stampeding the Bohemian troops. Ottokar realized the surprise attack and tried to lead a remaining reserve contingent in the rear of von Kapellen's troops, a maneuver that was misinterpreted as a
Surprised by Rudolph's maneuver, Ottokar quickly abandoned the siege at Laa, marched southwards, and on August 26 met the united German and Hungarian forces near Dürnkrut. When he arrived his enemies had already taken the opportunity to explore the topography of the future battleground. From the early morning, the left wing of the advancing Bohemian troops were embroiled in impetuous attacks by the Cuman forces, which the heavily armed knights could not ward off. Nevertheless, as the main armies collided and the battle wore on, Ottokar's outnumbering cavalry seemed to gain the upper hand, when even Rudolph's horse was stabbed under him and the 60-year-old narrowly escaped with his life, rescued by his liensmen.
After three hours of continuous fighting on a hot summer day, Ottokar's knights in their heavy armour were suffering from heat exhaustion and were not able to move. At noon Rudolph ordered a fresh heavy cavalry regiment he had concealed behind nearby hills and woods to attack the right flank of Ottokar's troops. Such ambushes were indeed commonly regarded as dishonourable in medieval warfare and Rudolph's commander Ulrich von Kapellen apologized to his own men in advance. Nevertheless, the attack prevailed in splitting and stampeding the Bohemian troops. Ottokar realized the surprise attack and tried to lead a remaining reserve contingent in the rear of von Kapellen's troops, a maneuver that was misinterpreted as a
 Rudolph, to demonstrate his victory, had Ottokar's body displayed in Vienna. The "poor count" from Swabian Habsburg Castle assured his possession of the Duchies of Austria and Styria, the heartland and foundation of the rise of the
Rudolph, to demonstrate his victory, had Ottokar's body displayed in Vienna. The "poor count" from Swabian Habsburg Castle assured his possession of the Duchies of Austria and Styria, the heartland and foundation of the rise of the
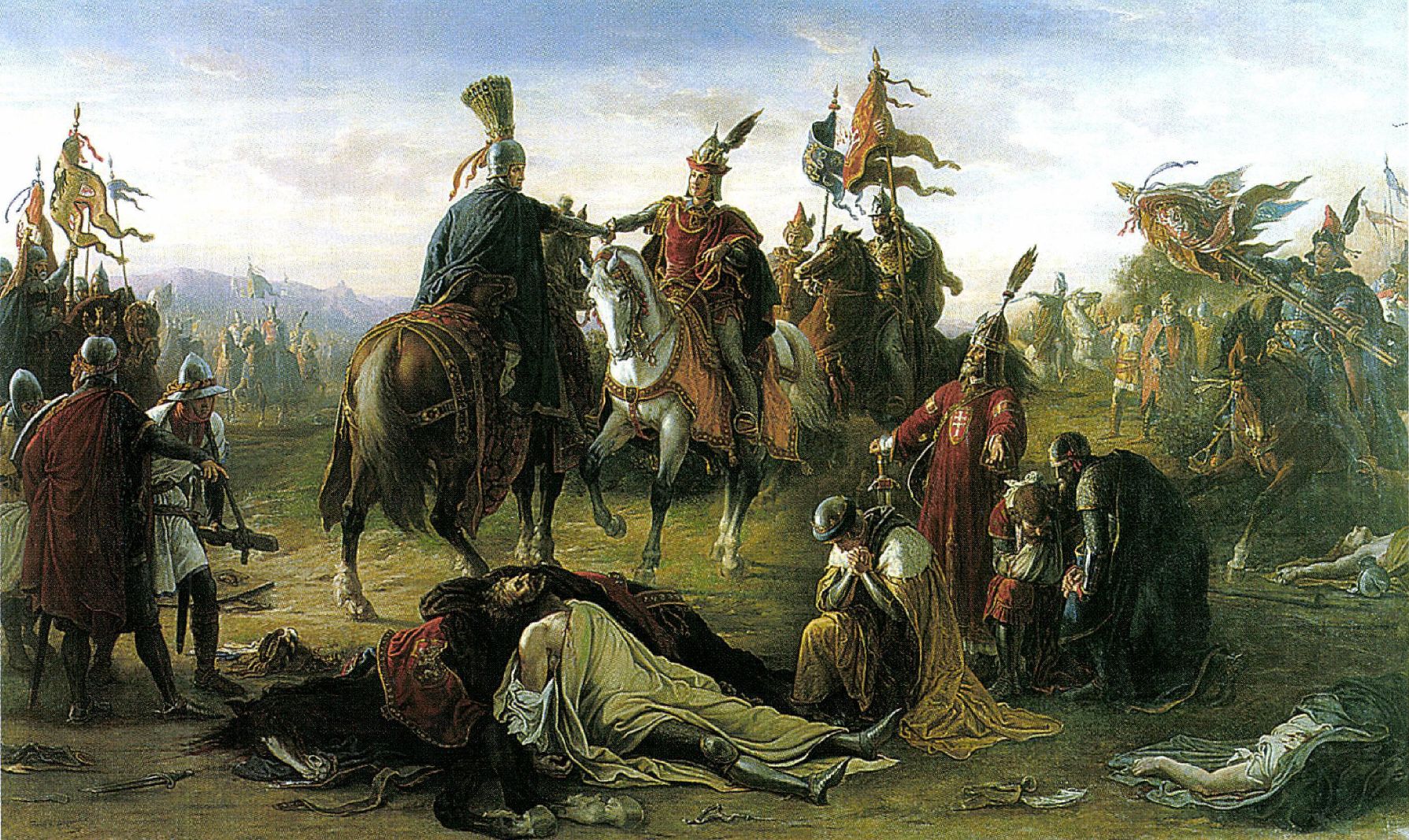 The battle was depicted in art especially during the rise of
The battle was depicted in art especially during the rise of
Bellum.cz – Battle on the Marchfeld 26 August 1278
{{Authority control 1278 in Europe Marchfeld 13th century in Hungary 13th century in Bohemia Lower Austria Marchfeld Marchfeld Marchfeld Marchfeld Conflicts in 1278 Ottokar II of Bohemia
Dürnkrut
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava Field''; german: Schlacht auf dem Marchfeld; cs, Bitva na Moravském poli; hu, Morvamezei csata) at Dürnkrut and Jedenspeigen took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history ...
and Jedenspeigen
Jedenspeigen is a town in the district of Gänserndorf in the Austrian state of Lower Austria.
Geography
Jedenspeigen lies in the Weinviertel
The ("wine quarter") or ("area below the ") is located in the northeast of Lower Austria.
In the ...
took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history of Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
for the following centuries. The opponents were a Bohemian
Bohemian or Bohemians may refer to:
*Anything of or relating to Bohemia
Beer
* National Bohemian, a brand brewed by Pabst
* Bohemian, a brand of beer brewed by Molson Coors
Culture and arts
* Bohemianism, an unconventional lifestyle, origin ...
(Czech) army led by the Přemyslid king Ottokar II of Bohemia
Ottokar II ( cs, Přemysl Otakar II.; , in Městec Králové, Bohemia – 26 August 1278, in Dürnkrut, Lower Austria), the Iron and Golden King, was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty who reigned as King of Bohemia from 1253 until his dea ...
and the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
army under the German king Rudolph I of Habsburg in alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary. With 15,300 mounted troops, it was one of the largest cavalry battles in Central Europe during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. The Hungarian cavalry played a significant role in the outcome of the battle.
King Ottokar II of Bohemia expanded his territories considerably from 1250 to 1273, but suffered a devastating defeat in November 1276, when the newly elected German king Rudolph I of Habsburg imposed the Imperial ban on Ottokar, declaring him an outlaw and took over Ottokar's holdings in Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carin ...
, Carniola, and Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered ...
. Ottokar was reduced to his possessions in Bohemia and Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The ...
, but was determined to regain his dominions, power, and influence. In 1278 he invaded Austria, where parts of the local population, especially in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, resented Habsburg rule. Rudolf allied himself with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
and mustered forces for a decisive confrontation.
Ottokar abandoned his siege of Laa an der Thaya and advanced to meet the allies near Dürnkrut, north of Vienna. Both armies were composed purely of cavalry and were divided into three divisions that attacked the enemy piecemeal. In the first phase of the battle, the Cuman
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many sough ...
horse archers in the Hungarian army outflanked and distracted the Bohemian left flank by launching arrows while the Hungarian light cavalry crashed into the Bohemians, driving them from the field. In the second phase, a great collision of knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the Christian denomination, church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood ...
s and heavy cavalry took place in the center, with Rudolf's forces being driven back. Rudolf's third division, led by the king personally, attacked and halted Ottokar's charge. Rudolf was unhorsed in the melee and nearly killed. At a decisive moment, a German cavalry force of 200 riders, commanded by Ulrich von Kapellen, ambush
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind moun ...
ed and attacked the Bohemian right flank from the rear. Assailed from two directions at once, Ottokar's army disintegrated into a rout, and Ottokar himself was killed in the confusion and slaughter. The Cumans pursued and killed the fleeing Bohemians with impunity.
The battle marked the beginning of the ascendancy of the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
in Austria and Central Europe. The influence of the Přemyslid kings of Bohemia was diminished and restricted to their inheritance in Bohemia and Moravia.
Background
 The deposition of Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen by Pope Innocent IV in 1245 created a grave crisis for the
The deposition of Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen by Pope Innocent IV in 1245 created a grave crisis for the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, as in the following decades several nobles were elected as ''Rex Romanorum
King of the Romans ( la, Rex Romanorum; german: König der Römer) was the title used by the king of Germany following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German k ...
'' and Emperor-to-be, none of whom were able to gain actual governing power upon the Emperor's death in 1250. That same year, Ottokar II, son of King Wenceslaus I of Bohemia, moved into the princeless Duchies of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered ...
. The last Babenberg duke Frederick II of Austria had been killed at the 1246 Battle of the Leitha River, in a border conflict he had picked with King Béla IV of Hungary. Ottokar II gained the support of the local nobility and was proclaimed Austrian and Styrian duke by the estates one year later.
In 1253, Ottokar II became Bohemian king upon the death of his father; the concentration of power on the western Hungarian border was viewed with suspicion by King Béla IV, who campaigned against Austria and Styria but was finally defeated at the 1260 Battle of Kressenbrunn
The Battle of Kressenbrunn was fought in July 1260 near Groissenbrunn in Lower Austria between the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Kingdom of Hungary for the possession of the duchies of Austria and Styria.''A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the ...
. In 1268 Ottokar signed a contract of inheritance with Ulrich III, the last Carinthian
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carint ...
duke of the House of Sponheim, and thus acquired Carinthia including the March of Carniola and the Windic March one year later. At the height of his power he aimed at the Imperial crown, but the Princes-Electors (''Kurfürsten''), distrustful of his steep rise, elected the "poor Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
n count" Rudolph of Habsburg King of the Romans on 29 September 1273.
Prelude
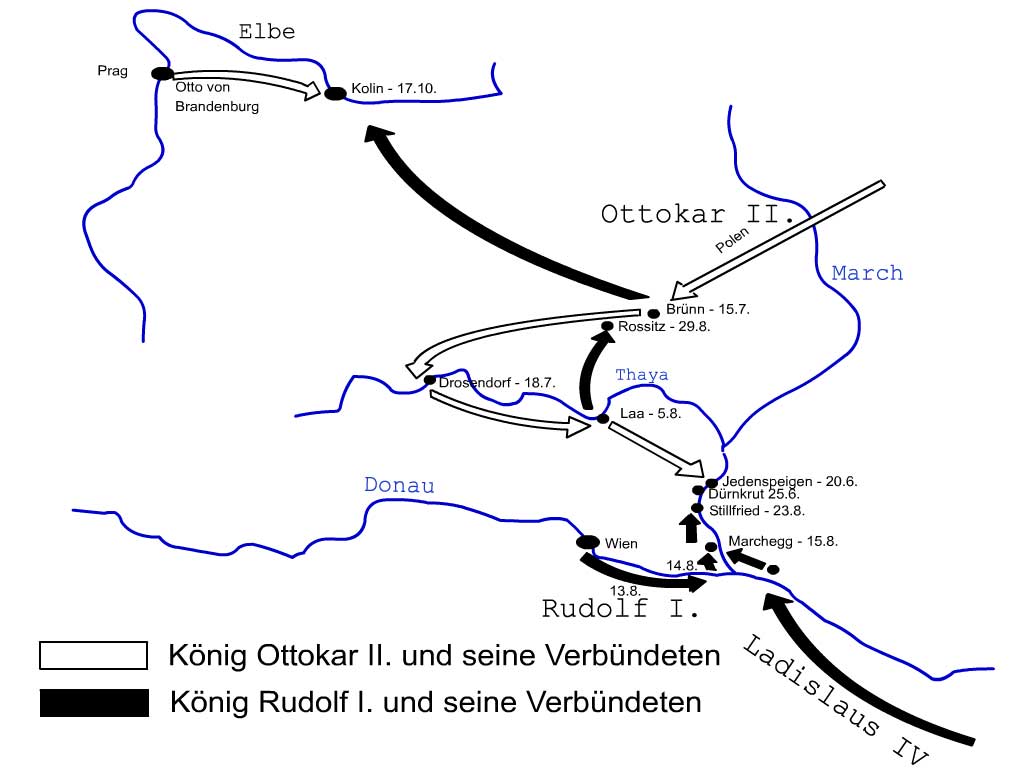
As the election had taken place in his absence, Ottokar did not acknowledge Rudolph as King. Rudolph himself had promised to regain the "alienated" territories which had to be conferred by the Imperial power with consent of the Prince-electors. He claimed the Austrian and Carinthian territories for the Empire and summoned Ottokar to the 1275 '' Reichstag'' at Würzburg. By not appearing before the Diet, Ottokar set the events of his demise in motion. He was placed under the Imperial ban and had all his territorial rights revoked, including even his Bohemian inheritance. Meanwhile, Rudolph was gathering allies and preparing for battle. He achieved two of these alliances through the classic Habsburg style – marriage. First, he married his son Albert to Elisabeth of Gorizia-Tyrol. In return, her father Count Meinhard II of Gorizia-Tyrol received the Duchy of Carinthia as a fief. Second, he established an — unstable — alliance with Duke Henry I of Lower Bavaria by offering Rudolph's daughter Katharina as wife for the Duke's son, Otto, in addition to the region of present-day Upper Austria as a pledge for her dowry. He also concluded an alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary, who intended to settle old scores with Ottokar.
Rudolph, so strengthened, besieged Ottokar at the Austrian capital
Meanwhile, Rudolph was gathering allies and preparing for battle. He achieved two of these alliances through the classic Habsburg style – marriage. First, he married his son Albert to Elisabeth of Gorizia-Tyrol. In return, her father Count Meinhard II of Gorizia-Tyrol received the Duchy of Carinthia as a fief. Second, he established an — unstable — alliance with Duke Henry I of Lower Bavaria by offering Rudolph's daughter Katharina as wife for the Duke's son, Otto, in addition to the region of present-day Upper Austria as a pledge for her dowry. He also concluded an alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary, who intended to settle old scores with Ottokar.
Rudolph, so strengthened, besieged Ottokar at the Austrian capital Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
in 1276. Ottokar was forced to surrender and to renounce all his acquisitions, receiving only Bohemia and Moravia as a fief from King Rudolph. Heavily deprived by this, he was determined to regain his territories and contracted an alliance with the Ascanian Margraves of Brandenburg
This article lists the Margraves and Electors of Brandenburg during the period of time that Brandenburg was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire.
The Mark, or ''March'', of Brandenburg was one of the primary constituent states of the Hol ...
and the Polish princes. In 1278 he campaigned against Austria, supported by Duke Henry I of Lower Bavaria, who had switched sides. Ottokar first laid siege to the towns of Drosendorf and Laa an der Thaya near the Austrian border, while Rudolph decided to leave Vienna and to face the Bohemian army in open battle in the Morava basin north of the capital, where the Cuman cavalry of King Ladislaus could easily join his forces.
Opposing forces
Ottakar fielded 6,000 cavalry, of which 1,000 were heavily armed and armored and 5,000 lightly equipped riders. Ottokar's heavy cavalry rode armored horses. Rudolf had 300 heavy cavalry and 4,000 light cavalry, of which an indeterminate number were Hungarians. Rudolf's force included a force of 5,000 Cuman horse archers.Battle
 Surprised by Rudolph's maneuver, Ottokar quickly abandoned the siege at Laa, marched southwards, and on August 26 met the united German and Hungarian forces near Dürnkrut. When he arrived his enemies had already taken the opportunity to explore the topography of the future battleground. From the early morning, the left wing of the advancing Bohemian troops were embroiled in impetuous attacks by the Cuman forces, which the heavily armed knights could not ward off. Nevertheless, as the main armies collided and the battle wore on, Ottokar's outnumbering cavalry seemed to gain the upper hand, when even Rudolph's horse was stabbed under him and the 60-year-old narrowly escaped with his life, rescued by his liensmen.
After three hours of continuous fighting on a hot summer day, Ottokar's knights in their heavy armour were suffering from heat exhaustion and were not able to move. At noon Rudolph ordered a fresh heavy cavalry regiment he had concealed behind nearby hills and woods to attack the right flank of Ottokar's troops. Such ambushes were indeed commonly regarded as dishonourable in medieval warfare and Rudolph's commander Ulrich von Kapellen apologized to his own men in advance. Nevertheless, the attack prevailed in splitting and stampeding the Bohemian troops. Ottokar realized the surprise attack and tried to lead a remaining reserve contingent in the rear of von Kapellen's troops, a maneuver that was misinterpreted as a
Surprised by Rudolph's maneuver, Ottokar quickly abandoned the siege at Laa, marched southwards, and on August 26 met the united German and Hungarian forces near Dürnkrut. When he arrived his enemies had already taken the opportunity to explore the topography of the future battleground. From the early morning, the left wing of the advancing Bohemian troops were embroiled in impetuous attacks by the Cuman forces, which the heavily armed knights could not ward off. Nevertheless, as the main armies collided and the battle wore on, Ottokar's outnumbering cavalry seemed to gain the upper hand, when even Rudolph's horse was stabbed under him and the 60-year-old narrowly escaped with his life, rescued by his liensmen.
After three hours of continuous fighting on a hot summer day, Ottokar's knights in their heavy armour were suffering from heat exhaustion and were not able to move. At noon Rudolph ordered a fresh heavy cavalry regiment he had concealed behind nearby hills and woods to attack the right flank of Ottokar's troops. Such ambushes were indeed commonly regarded as dishonourable in medieval warfare and Rudolph's commander Ulrich von Kapellen apologized to his own men in advance. Nevertheless, the attack prevailed in splitting and stampeding the Bohemian troops. Ottokar realized the surprise attack and tried to lead a remaining reserve contingent in the rear of von Kapellen's troops, a maneuver that was misinterpreted as a rout
A rout is a panicked, disorderly and undisciplined retreat of troops from a battlefield, following a collapse in a given unit's command authority, unit cohesion and combat morale (''esprit de corps'').
History
Historically, lightly-e ...
by the Bohemian forces. The following collapse resulted in a complete victory of Rudolph and his allies. Ottokar's camp was plundered, and he himself was found slain on the battlefield.''The Land Between: A History of Slovenia'', ed. Oto Luthar, (Peter Lang GmbH, 2008), 128.
Aftermath
 Rudolph, to demonstrate his victory, had Ottokar's body displayed in Vienna. The "poor count" from Swabian Habsburg Castle assured his possession of the Duchies of Austria and Styria, the heartland and foundation of the rise of the
Rudolph, to demonstrate his victory, had Ottokar's body displayed in Vienna. The "poor count" from Swabian Habsburg Castle assured his possession of the Duchies of Austria and Styria, the heartland and foundation of the rise of the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. At the 1282 Diet of Augsburg
The Diet of Augsburg were the meetings of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in the German city of Augsburg. Both an Imperial City and the residence of the Augsburg prince-bishops, the town had hosted the Estates in many such sessi ...
, he installed his sons Albert and Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Ho ...
as Austrian dukes; their descendants held the ducal dignity until 1918. However, in Bohemia, Rudolph acted cautiously and reached an agreement with the nobility and Ottokar's widow Kunigunda of Slavonia
Kunigunda Rostislavna (1245 – 9 September 1285; Czech: ''Kunhuta Uherská'' or ''Kunhuta Haličská'') was Queen consort of Bohemia and its regent from 1278 until her death. She was a member of the House of Chernigov, and a daughter of Rostis ...
on the succession of her son Wenceslaus II to the throne. On the same occasion he reconciled with the Brandenburg margraves, ceding them the guardianship over the minor heir apparent. King Ladislaus IV exerted himself in the christianization of the Cuman warriors, before he was assassinated in 1290.
Ottokar's son, the young king Wenceslaus II of Bohemia, turned out to be a capable ruler. In 1291 he acquired the Polish Seniorate Province
Seniorate Province, also known as the Senioral Province, , was a district principality in the Duchy of Poland that was formed in 1138, following the fragmentation of the state. Its ruler held the title of the High Duke, ruling all duchies wit ...
at Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
and was crowned King of Poland in 1300. He was even able to secure the Hungarian crown for his son Wenceslaus III, still a minor, who nevertheless was murdered in 1306, one year after his father's death, whereby the Přemyslid dynasty became extinct.
Casualties
No exact data on casualties is available, but Ottokar's losses were considerably higher than Rudolf's.In art and popular culture
 The battle was depicted in art especially during the rise of
The battle was depicted in art especially during the rise of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
in the 19th century, when it was viewed as the example of a traditional co-operation between Habsburg dynasty (Austria) and Kingdom of Hungary, from one side, and the traditional tension between Habsburg dynasty and Bohemia, from the Czech side.
The tragedy '' König Ottokars Glück und Ende'' written by Franz Grillparzer in 1823 is based on the rise and fall of king Ottokar II. The drama was originally inspired by the life of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, but Grillparzer, fearing Metternich's censorship, chose to write the play about Ottokar, in whose story he found many parallels. It nevertheless was immediately forbidden and could not be performed until 1825. Grillparzer perpetuated the legend of Ottokar's wife, Margaret of Babenberg, unsuccessfully trying to reconcile the opponents on the eve of the battle. In fact, Margaret had died in 1266.
The opera '' The Brandenburgers in Bohemia'', by the Czech composer Bedřich Smetana in 1863, was inspired by the battle and the following events.
See also
*Battle of Kressenbrunn
The Battle of Kressenbrunn was fought in July 1260 near Groissenbrunn in Lower Austria between the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Kingdom of Hungary for the possession of the duchies of Austria and Styria.''A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the ...
* List of battles 601–1400
* Battle of Rozgony
Citations
References
* * *Andreas Kusternig: 700 Jahre Schlacht bei Duernkrut und Jedenspeigen. Wien 1978. * * * *External links
Bellum.cz – Battle on the Marchfeld 26 August 1278
{{Authority control 1278 in Europe Marchfeld 13th century in Hungary 13th century in Bohemia Lower Austria Marchfeld Marchfeld Marchfeld Marchfeld Conflicts in 1278 Ottokar II of Bohemia