Battle of Aspern-Essling on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the Battle of Aspern-Essling (21–22 May 1809),
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
crossed the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
near Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, but the French and their allies were attacked and forced back across the river by the Austrians
, pop = 8–8.5 million
, regions = 7,427,759
, region1 =
, pop1 = 684,184
, ref1 =
, region2 =
, pop2 = 345,620
, ref2 =
, region3 =
, pop3 = 197,990
, ref3 ...
under Archduke Charles
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Laurentius of Austria, Duke of Teschen (german: link=no, Erzherzog Karl Ludwig Johann Josef Lorenz von Österreich, Herzog von Teschen; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian field-marshal, the third s ...
. It was the first time Napoleon had been personally defeated in a major battle, as well as his first defeat in a decade. Archduke Charles drove out the French but fell short of destroying their army. The Austrian artillery dominated the battlefield, firing 53,000 rounds compared to 24,300 French. The French lost over 20,000 men including one of Napoleon's ablest field commanders and closest friends, Marshal Jean Lannes
Jean Lannes, 1st Duke of Montebello, Prince of Siewierz (10 April 1769 – 31 May 1809), was a French military commander and a Marshal of the Empire who served during both the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He was one of Napoleon's ...
.
Background
At the time of the battle Napoleon was in possession ofVienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, the bridges over the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
had been broken, and the Archduke's army was near the Bisamberg
Bisamberg is a municipality in the district of Korneuburg in Austria.
Geography
It lies about 5 km northeast of Vienna in the Weinviertel in Lower Austria
Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''N ...
, a hill near Korneuburg
Korneuburg () is a town in Austria. It is located in the state Lower Austria and is the administrative center of the district of Korneuburg. Korneuburg is situated on the left bank of the Danube, opposite the city of Klosterneuburg, and is 12&n ...
, on the left bank of the river. The French wanted to cross the Danube. A first crossing attempt on the Schwarze Lackenau on 13 May was repulsed with some 700 French losses. Lobau, one of the numerous islands that divided the river into minor channels, was selected as the next point of crossing. Careful preparations were made, and on the night of 19–20 May the French bridged all the channels on the right bank to Lobau and occupied the island. By the evening of the 20th many men had been collected there and the last arm of the Danube, between Lobau and the left bank, had been bridged. Masséna's corps at once crossed to the left bank and dislodged the Austrian outposts. Undeterred by the news of heavy attacks on his rear from Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
and from Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
, Napoleon ferried all available troops to the bridges, and by daybreak on the 21st, 25,000 men were collected on the Marchfeld, the broad plain of the left bank, which was also to be the scene of the Battle of Wagram
The Battle of Wagram (; 5–6 July 1809) was a military engagement of the Napoleonic Wars that ended in a costly but decisive victory for Emperor Napoleon's French and allied army against the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles ...
.
The Archduke did not resist the passage. It was his intention, as soon as a large enough force had crossed, to attack it before the rest of the French army could come to its assistance. Napoleon had accepted the risk of such an attack, but he sought at the same time to minimize it by summoning every available battalion to the scene. His forces on the Marchfeld were drawn up in front of the bridges facing north, with their left in the village of Aspern
Aspern () is part of Donaustadt, the 22nd district of Vienna, Austria.
History
The area is known because of the Battle of Aspern-Essling, which was fought in the nearby Lobau on 21 and 22 May 1809. In that battle, the Austrian army, led by A ...
(Gross-Aspern) and their right in Essling
Essling
Essling entry in the Viennese government's history wiki (German) () is part of . Both places lay close to the Danube and could not therefore be turned; Aspern, indeed, is actually on the bank of one of the river channels. The French had to fill the gap between the villages, and also move forward to give room for the supporting units to form up. The corps led by
 ''Kaiserlich-Königliche Hauptarmee'', under the command of Charles of Austria:
* 1st Column (VI Corps),
''Kaiserlich-Königliche Hauptarmee'', under the command of Charles of Austria:
* 1st Column (VI Corps),
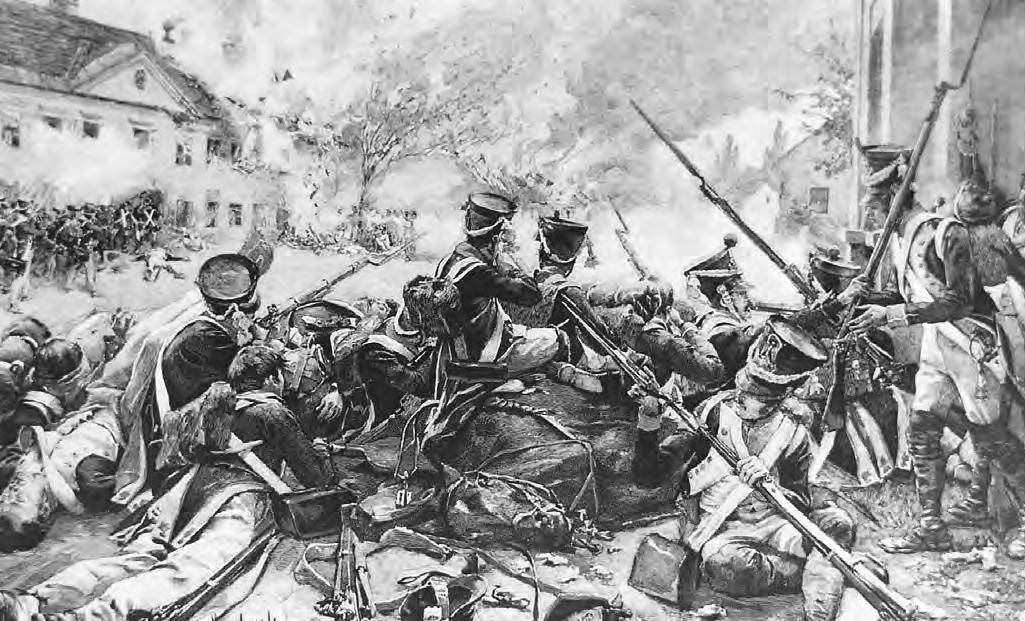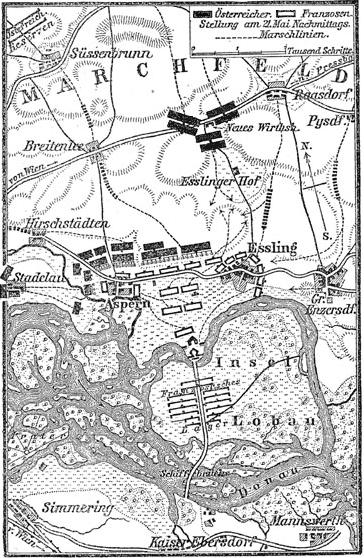
 The battle began at Aspern; Hiller carried the village at the first rush, but Masséna recaptured it, and held his ground with remarkable tenacity. The French infantry fought with the old stubborn bravery which it had failed to show in the earlier battles of the year. However, the Austrians also fought with fierceness and tenacity that surprised the French, including Napoleon himself.
The three Austrian columns were unable to capture more than half the village. The rest was still held by Masséna when night fell. Meanwhile, nearly all the French infantry between the two villages and in front of the bridges had been drawn into the fight on the flank. Napoleon therefore, to create a diversion, sent forward his center, now consisting only of cavalry, to charge the enemy's artillery, which was deployed in a long line and firing on Aspern. The first charge of the French was repulsed, but the second attempt was made by heavy masses of
The battle began at Aspern; Hiller carried the village at the first rush, but Masséna recaptured it, and held his ground with remarkable tenacity. The French infantry fought with the old stubborn bravery which it had failed to show in the earlier battles of the year. However, the Austrians also fought with fierceness and tenacity that surprised the French, including Napoleon himself.
The three Austrian columns were unable to capture more than half the village. The rest was still held by Masséna when night fell. Meanwhile, nearly all the French infantry between the two villages and in front of the bridges had been drawn into the fight on the flank. Napoleon therefore, to create a diversion, sent forward his center, now consisting only of cavalry, to charge the enemy's artillery, which was deployed in a long line and firing on Aspern. The first charge of the French was repulsed, but the second attempt was made by heavy masses of
 At early dawn of the 22nd the battle was resumed. Masséna swiftly cleared Aspern of the Austrians, but at the same time Rosenberg stormed Essling. Lannes, however, resisted desperately, and reinforced by St Hilaire's division, drove Rosenberg out. In Aspern, Masséna was driven out by a counter-attack of Hiller and Bellegarde.
Meanwhile, Napoleon had launched an attack on the Austrian center. The whole of the French center, with Lannes on the left and the cavalry in reserve, moved forward. The Austrian line was broken through, between Rosenberg's right and Hohenzollern's left, and the French squadrons poured into the gap. Victory was almost won when the Archduke brought up his last reserve, leading his soldiers with a colour in his hand. Lannes was checked, and with his repulse the impetus of the attack died out all along the line. Aspern had been lost, and graver news reached Napoleon at the critical moment. The Danube bridges, which had broken down once already, had been cut by heavy barges, which had been sent drifting down stream by the Austrians.
Napoleon at once suspended the attack. Essling now fell to another assault of Rosenberg, and the French drove him out again. Rosenberg then directed his efforts on the flank of the French center, slowly retiring on the bridges. The retirement was terribly costly, but Lannes stopped the French from being driven into the Danube. Complete exhaustion of both sides ended the fighting.
At early dawn of the 22nd the battle was resumed. Masséna swiftly cleared Aspern of the Austrians, but at the same time Rosenberg stormed Essling. Lannes, however, resisted desperately, and reinforced by St Hilaire's division, drove Rosenberg out. In Aspern, Masséna was driven out by a counter-attack of Hiller and Bellegarde.
Meanwhile, Napoleon had launched an attack on the Austrian center. The whole of the French center, with Lannes on the left and the cavalry in reserve, moved forward. The Austrian line was broken through, between Rosenberg's right and Hohenzollern's left, and the French squadrons poured into the gap. Victory was almost won when the Archduke brought up his last reserve, leading his soldiers with a colour in his hand. Lannes was checked, and with his repulse the impetus of the attack died out all along the line. Aspern had been lost, and graver news reached Napoleon at the critical moment. The Danube bridges, which had broken down once already, had been cut by heavy barges, which had been sent drifting down stream by the Austrians.
Napoleon at once suspended the attack. Essling now fell to another assault of Rosenberg, and the French drove him out again. Rosenberg then directed his efforts on the flank of the French center, slowly retiring on the bridges. The retirement was terribly costly, but Lannes stopped the French from being driven into the Danube. Complete exhaustion of both sides ended the fighting.
 The French lost over 20,000 men including one of Napoleon's ablest field commanders and closest friends, Marshal
The French lost over 20,000 men including one of Napoleon's ablest field commanders and closest friends, Marshal
Battle of Aspern-Essling
by David Johnson in journal Military History, April 2001. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Aspern-Essling Battles involving Austria Donaustadt Battles involving France Battles of the War of the Fifth Coalition Conflicts in 1809 1809 in the Austrian Empire 1809 in France 19th century in Vienna May 1809 events Austrian Empire–France relations Battles inscribed on the Arc de Triomphe
Essling entry in the Viennese government's history wiki (German) () is part of . Both places lay close to the Danube and could not therefore be turned; Aspern, indeed, is actually on the bank of one of the river channels. The French had to fill the gap between the villages, and also move forward to give room for the supporting units to form up. The corps led by
Johann von Hiller
Johann Baron von Hiller (13 October 1754 – 5 June 1819) was an Austrian general during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He held an important command during the 1809 campaign against France, playing a prominent role at the B ...
(VI), Heinrich Graf von Bellegarde
Count Heinrich von Bellegarde, Viceroy of Lombardy-Venetia (german: Heinrich Joseph Johannes, Graf von Bellegarde or sometimes ''Heinrich von Bellegarde''; 29 August 1756 – 22 July 1845), of a noble Savoyard family, was born in Saxony, joined the ...
(I) and Prince Friedrich of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (II) were to converge upon Aspern, while Prince Franz Seraph of Rosenberg-Orsini
Prince Franz Seraph von Orsini-Rosenberg (18 October 1761 – 4 August 1832) was born a member of Orsini-Rosenberg family, son of Prince Vinzenz Fererius von Orsini-Rosenberg and Maria Juliana, Countess von Stubenberg family, Stubenberg.
He ...
(IV) was to attack Essling. Prince Johann of Liechtenstein's Austrian reserve cavalry was in the center, ready to move out against any French cavalry attacking the heads of the columns. During the 21st the bridges became more and more unsafe, owing to the violence of the current, but the French crossed without intermission all day and during the night.
Order of battle
 ''Kaiserlich-Königliche Hauptarmee'', under the command of Charles of Austria:
* 1st Column (VI Corps),
''Kaiserlich-Königliche Hauptarmee'', under the command of Charles of Austria:
* 1st Column (VI Corps), Hiller Hiller may refer to:
* Hiller (surname)
* Hiller, Pennsylvania
* Hiller Aircraft Corporation:
** Hiller Hornet
** Hiller Flying Platform
** Tanner-Hiller Airport
** Hiller Aviation Museum
** Hiller X-18
** Fairchild Hiller FH-227
** YH-32 Hor ...
:
** Vanguard: Nordmann
** Div. Kottulinsky
** Div. Vincent
Vincent ( la, Vincentius) is a male given name derived from the Roman name Vincentius, which is derived from the Latin word (''to conquer'').
People with the given name Artists
*Vincent Apap (1909–2003), Maltese sculptor
*Vincent van Gogh ...
* 2nd Column (I Corps), Bellegarde:
** Div. Fresnel
** Div. Vogelsang
** Div. Ulm
** Div. Notitz
* 3rd Column (II Corps), Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen was a small principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to the Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty.
History
The County of Hohenzollern-Hechingen was created in 1576, upon the partition of the Co ...
:
** Advance Guard
** Div. Brady
** Div. Weber
* 4th Column (IV Corps), Rosenberg/Dedovich:
** Div. Klenau
** Div. Dedovich
* 5th Column (a part of IV Corps), Rosenberg/Hohenlohe:
** Vanguard: Rohan
** Div. Hohenlohe
The House of Hohenlohe () is a German princely dynasty. It ruled an immediate territory within the Holy Roman Empire which was divided between several branches. The Hohenlohes became imperial counts in 1450. The county was divided numerous tim ...
* Reserve Corps, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German language, German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constit ...
:
** Div. Hessen-Homburg
** Div. Kienmayer
** Div. of grenadier
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word ''grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited from ...
s, Lindenau
** Div. of grenadiers, d'Aspre
TOTAL: 99 000 men; 84 000 infantry, 14 250 cavalry, 288 guns
'' Armée d'Allemagne'', under the command of Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
:
* Imperial Guard
An imperial guard or palace guard is a special group of troops (or a member thereof) of an empire, typically closely associated directly with the Emperor or Empress. Usually these troops embody a more elite status than other imperial forces, i ...
:
** Div. 1 (Young Guard): Curial
** Div. 2 (Old Guard): Dorsenne
** Div. 3 (cavalry): Arrighi
* II Corps, Lannes † :
** Div. Tharreau
** Div. Claparède
** Div. Saint-Hilaire †
** Div. of reserve, Demont (unengaged)
* IV Corps, Masséna:
** Div. Legrand
** Div. Carra Saint-Cyr
** Div. Molitor
** Div. Boudet
** Brig. Marulaz (cavalry)
** Div. Lasalle (cavalry)
* Cavalry Reserve Corps, Bessières:
** Div. Nansouty
** Div. Saint-Sulpice
** Div. d'Espagne †
TOTAL: 77 000 men; 67 000 infantry, 10 000 cavalry, 152 guns
Battle
First day

 The battle began at Aspern; Hiller carried the village at the first rush, but Masséna recaptured it, and held his ground with remarkable tenacity. The French infantry fought with the old stubborn bravery which it had failed to show in the earlier battles of the year. However, the Austrians also fought with fierceness and tenacity that surprised the French, including Napoleon himself.
The three Austrian columns were unable to capture more than half the village. The rest was still held by Masséna when night fell. Meanwhile, nearly all the French infantry between the two villages and in front of the bridges had been drawn into the fight on the flank. Napoleon therefore, to create a diversion, sent forward his center, now consisting only of cavalry, to charge the enemy's artillery, which was deployed in a long line and firing on Aspern. The first charge of the French was repulsed, but the second attempt was made by heavy masses of
The battle began at Aspern; Hiller carried the village at the first rush, but Masséna recaptured it, and held his ground with remarkable tenacity. The French infantry fought with the old stubborn bravery which it had failed to show in the earlier battles of the year. However, the Austrians also fought with fierceness and tenacity that surprised the French, including Napoleon himself.
The three Austrian columns were unable to capture more than half the village. The rest was still held by Masséna when night fell. Meanwhile, nearly all the French infantry between the two villages and in front of the bridges had been drawn into the fight on the flank. Napoleon therefore, to create a diversion, sent forward his center, now consisting only of cavalry, to charge the enemy's artillery, which was deployed in a long line and firing on Aspern. The first charge of the French was repulsed, but the second attempt was made by heavy masses of cuirassiers
Cuirassiers (; ) were cavalry equipped with a cuirass, sword, and pistols. Cuirassiers first appeared in mid-to-late 16th century Europe as a result of armoured cavalry, such as men-at-arms and demi-lancers, discarding their lances and adopti ...
. The French horsemen drove off the Austrian gunners, rode round Hohenzollern's infantry square
An infantry square, also known as a hollow square, was a historic combat formation in which an infantry unit formed in close order, usually when it was threatened with cavalry attack. As a traditional infantry unit generally formed a line to adva ...
s, and resisted the cavalry of Lichtenstein, but they were unable to do more, and in the end they retired to their previous position.
Meanwhile, Essling had been the scene of fighting almost as desperate as that of Aspern. The French cuirassiers made heavy charges on the flank of Rosenberg's force, and delayed an assault. In the villages, Lannes with a single division resisted until night ended the battle. The two armies bivouacked, and in Aspern the French and Austrians lay within pistol shot of each other. The emperor was not discouraged, and renewed efforts to bring up every available man. All through the night more and more French troops came across.
Second day
 At early dawn of the 22nd the battle was resumed. Masséna swiftly cleared Aspern of the Austrians, but at the same time Rosenberg stormed Essling. Lannes, however, resisted desperately, and reinforced by St Hilaire's division, drove Rosenberg out. In Aspern, Masséna was driven out by a counter-attack of Hiller and Bellegarde.
Meanwhile, Napoleon had launched an attack on the Austrian center. The whole of the French center, with Lannes on the left and the cavalry in reserve, moved forward. The Austrian line was broken through, between Rosenberg's right and Hohenzollern's left, and the French squadrons poured into the gap. Victory was almost won when the Archduke brought up his last reserve, leading his soldiers with a colour in his hand. Lannes was checked, and with his repulse the impetus of the attack died out all along the line. Aspern had been lost, and graver news reached Napoleon at the critical moment. The Danube bridges, which had broken down once already, had been cut by heavy barges, which had been sent drifting down stream by the Austrians.
Napoleon at once suspended the attack. Essling now fell to another assault of Rosenberg, and the French drove him out again. Rosenberg then directed his efforts on the flank of the French center, slowly retiring on the bridges. The retirement was terribly costly, but Lannes stopped the French from being driven into the Danube. Complete exhaustion of both sides ended the fighting.
At early dawn of the 22nd the battle was resumed. Masséna swiftly cleared Aspern of the Austrians, but at the same time Rosenberg stormed Essling. Lannes, however, resisted desperately, and reinforced by St Hilaire's division, drove Rosenberg out. In Aspern, Masséna was driven out by a counter-attack of Hiller and Bellegarde.
Meanwhile, Napoleon had launched an attack on the Austrian center. The whole of the French center, with Lannes on the left and the cavalry in reserve, moved forward. The Austrian line was broken through, between Rosenberg's right and Hohenzollern's left, and the French squadrons poured into the gap. Victory was almost won when the Archduke brought up his last reserve, leading his soldiers with a colour in his hand. Lannes was checked, and with his repulse the impetus of the attack died out all along the line. Aspern had been lost, and graver news reached Napoleon at the critical moment. The Danube bridges, which had broken down once already, had been cut by heavy barges, which had been sent drifting down stream by the Austrians.
Napoleon at once suspended the attack. Essling now fell to another assault of Rosenberg, and the French drove him out again. Rosenberg then directed his efforts on the flank of the French center, slowly retiring on the bridges. The retirement was terribly costly, but Lannes stopped the French from being driven into the Danube. Complete exhaustion of both sides ended the fighting.
Aftermath
 The French lost over 20,000 men including one of Napoleon's ablest field commanders and closest friends, Marshal
The French lost over 20,000 men including one of Napoleon's ablest field commanders and closest friends, Marshal Jean Lannes
Jean Lannes, 1st Duke of Montebello, Prince of Siewierz (10 April 1769 – 31 May 1809), was a French military commander and a Marshal of the Empire who served during both the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He was one of Napoleon's ...
, who died after being mortally wounded by an Austrian cannonball in an attack on Johann von Klenau
Johann Josef Cajetan Graf von Klenau, Freiherr von Janowitz ( cs, Jan hrabě z Klenové, svobodný pán z Janovic; 13 April 1758 – 6 October 1819) was a field marshal in the Habsburg army. Klenau, the son of a Bohemian noble, joined the ...
's force at Aspern, which was backed up by 60 well-placed guns. French general Louis-Vincent-Joseph Le Blond de Saint-Hilaire
Louis-Vincent-Joseph Le Blond, comte de Saint-Hilaire (; 4 September 1766 – 5 June 1809) was a French general during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, described by Lejeune as "the pride of the army, as remarkable for his wit as for his m ...
also died as a result of injuries from the battle; his leg was torn off by a cannonball. The Austrians had also suffered similar casualties but had secured the first major victory against the French for over a decade. The victory demonstrated both the progress the Austrian army had made since the string of catastrophic defeats in 1800 and 1805, and the fact that Emperor Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
could still be defeated in battle, his last having been at Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial and US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square ...
, which coincidentally had occurred precisely ten years and one day before. The loss of Marshal Lannes was an especially severe blow to Napoleon, as he lost one of the few marshals who was capable of independent command, something that would haunt him dearly in the future.
The French forces were withdrawn to the island. On the night of the 22nd the last bridge was repaired, and the army awaited the arrival of reinforcements in Lobau. The Austrians, surprised by their victory, failed to capitalize on the situation, allowing the French to regroup. One month later, the French made a second attempt to cross the Danube where Napoleon gained a costly and decisive victory over the Austrians at the Battle of Wagram
The Battle of Wagram (; 5–6 July 1809) was a military engagement of the Napoleonic Wars that ended in a costly but decisive victory for Emperor Napoleon's French and allied army against the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles ...
.
The '' Löwe von Aspern'' (''Lion of Aspern''), a large stone sculpture in front of St. Martin's Church, is a monument commemorating the battle.
Accounts
Patrick Rambaud
Patrick Rambaud (born 21 April 1946) is a French writer.
Life
Born in Paris, France, with Michel-Antoine Burnier, he wrote forty pastiches, (satirical novels). They wrote ''Le Journalisme sans peine'' (Editions Plon, 1997). In 1970, he help foun ...
, a French author, wrote a fictionalized account of the conflict entitled "'' The Battle''" using many first-hand sources. Just looking from the French perspective, the novel provides a rather realistic description of combat in the Napoleonic era, as well as detailed depictions of famous commanders such as Napoleon, Massena, and Lannes. The concept and notes for the book originally came from noted French author Honoré de Balzac
Honoré de Balzac ( , more commonly , ; born Honoré Balzac;Jean-Louis Dega, La vie prodigieuse de Bernard-François Balssa, père d'Honoré de Balzac : Aux sources historiques de La Comédie humaine, Rodez, Subervie, 1998, 665 p. 20 May 179 ...
. Marcellin Marbot
Jean-Baptiste Antoine Marcelin Marbot ( , ; 18 August 1782 – 16 November 1854), known as Marcellin Marbot, was a French general, famous for his memoirs depicting the Napoleonic age of warfare. He belongs to a family that has distinguished it ...
, one of Marshal Lannes aide-de-camps, wrote in his memoirs of the battle, in which he had to observe the last moments of his close friends, and describes the amount of bloodshed and sadness which came to the Grande Armée after the crossing of the Danube.
The army surgeon Dominique-Jean Larrey
Baron Dominique Jean Larrey (; 8 July 1766 – 25 July 1842) was a French surgeon and military doctor, who distinguished himself in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. An important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, ...
also described the battle in his memoirs and mentions how he fed the wounded at Lobau with a bouillon of horse meat
Horse meat forms a significant part of the culinary traditions of many countries, particularly in Eurasia. The eight countries that consume the most horse meat consume about 4.3 million horses a year. For the majority of humanity's early existen ...
seasoned with gunpowder. Larrey is quoted in French by Dr Béraud
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * It referencesDominique-Jean Larrey
Baron Dominique Jean Larrey (; 8 July 1766 – 25 July 1842) was a French surgeon and military doctor, who distinguished himself in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. An important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, ...
, ''Mémoires de chirurgie militaire et campagnes'', III 281, Paris, Smith.
*
External links
Battle of Aspern-Essling
by David Johnson in journal Military History, April 2001. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Aspern-Essling Battles involving Austria Donaustadt Battles involving France Battles of the War of the Fifth Coalition Conflicts in 1809 1809 in the Austrian Empire 1809 in France 19th century in Vienna May 1809 events Austrian Empire–France relations Battles inscribed on the Arc de Triomphe