Battle Of Cross Keys on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Cross Keys was fought on June 8, 1862, in
; Krick, pp. 33–35. Two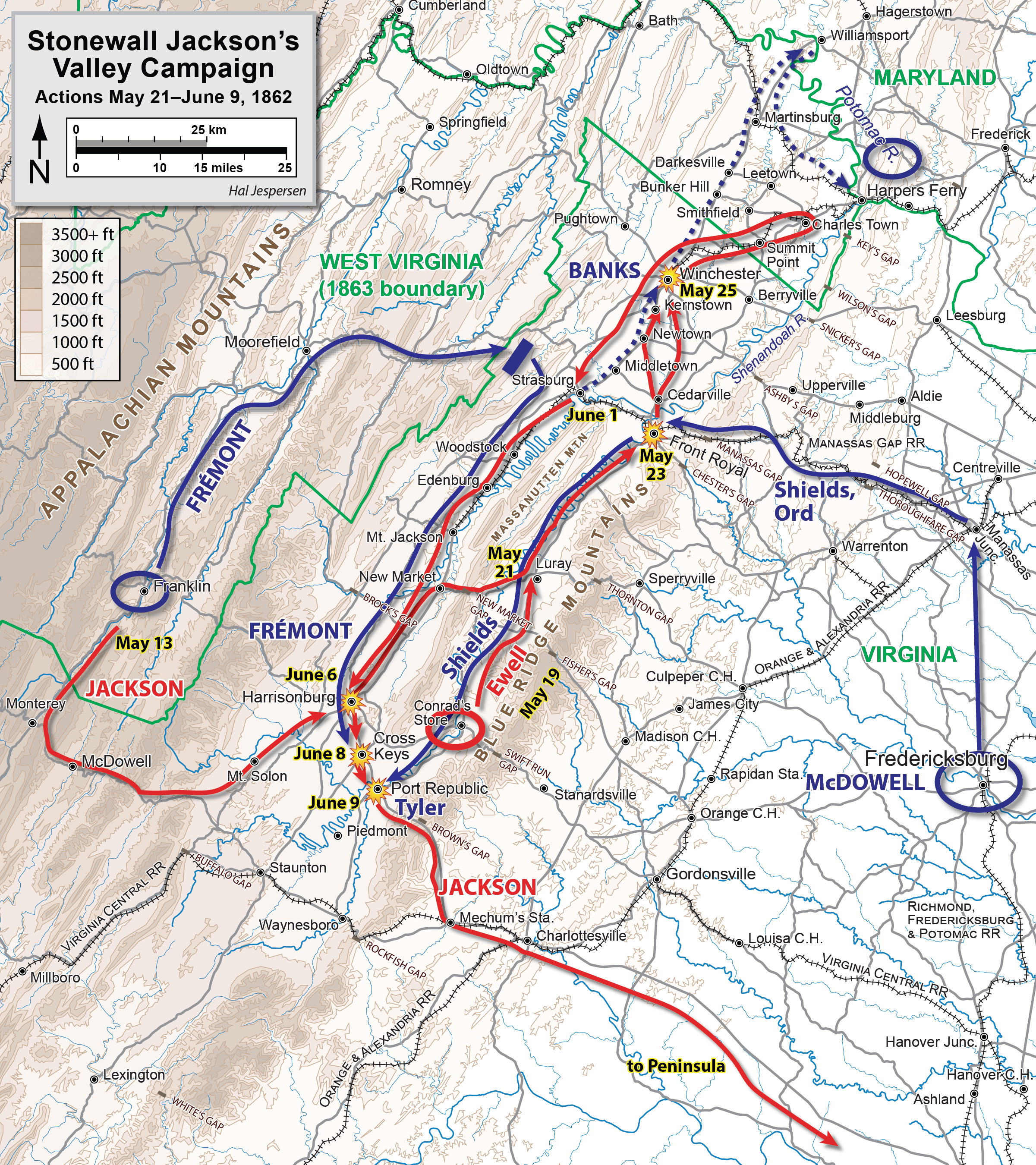
National Park Service battle description
CWSAC Report Update
Battle of Cross Keys in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
: Battle maps, history articles, and preservation news (
Animated history of Jackson's Valley Campaign
(Rough_sketch_of_the_battlefield_of_Cross_Keys,_Va.,_June_8,_1862,_compiled_by_Jed._Hotchkiss,_2d_Army_Corps..._-_NARA_-_305833.tif, Rough sketch of the Battlefield of Cross Keys, June 8, 1862, compiled by Jed. Hotchkiss
File:Cross_Keys_Battlefield_Virginia.jpg, Map of battlefield core and study areas by the American Battlefield Protection Program
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cross Keys
Cross Keys
Cross Keys
Cross Keys
Cross Keys
Rockingham County, Virginia
1862 in the American Civil War
1862 in Virginia
June 1862 events
Rockingham County, Virginia
Rockingham County is a county located in the U.S. state of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 83,757. Its county seat is the independent city of Harrisonburg.
Along with Harrisonburg, Rockingham County forms the Harrisonbur ...
, as part of Confederate Army Maj. Gen.
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's campaign through the Shenandoah Valley during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
. Together, the battles of Cross Keys and Port Republic the following day were the decisive victories in Jackson's Valley Campaign, forcing the Union armies
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
to retreat and leaving Jackson free to reinforce Gen. Robert E. Lee for the Seven Days Battles
The Seven Days Battles were a series of seven battles over seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia, during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, comman ...
outside Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
.
Background
The hamlet of Port Republic, Virginia, lies on a neck of land between the North and South Rivers, which conjoin to form theSouth Fork Shenandoah River
The Shenandoah River is the principal tributary of the Potomac River, long with two forks approximately long each,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 in t ...
. On June 6–7, 1862, Jackson's army, numbering about 16,000, bivouacked north of Port Republic, Maj. Gen. Richard S. Ewell
Richard Stoddert Ewell (February 8, 1817 – January 25, 1872) was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He achieved fame as a senior commander under Stonewall Jackson and Robert E. L ...
's division along the banks of Mill Creek near Goods Mill, and Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
Charles S. Winder
Charles Sidney Winder (October 18, 1829 – August 9, 1862), was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general officer in the American Civil War. He was killed in action during the Battle of Cedar Mountain.
Early life and car ...
's division on the north bank of North River near the bridge. The 15th Alabama Infantry regiment was left to block the roads at Union Church. Jackson's headquarters were in Madison Hall at Port Republic. The army trains were parked nearby.NPS report on battlefield condition; Krick, pp. 33–35. Two
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
columns converged on Jackson's position. The army of Maj. Gen. John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont or Fremont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was an American explorer, military officer, and politician. He was a U.S. Senator from California and was the first Republican nominee for president of the United States in 1856 ...
, about 15,000 strong, moved south on the Valley Pike and reached the vicinity of Harrisonburg on June 6. The division of Brig. Gen. James Shields, about 10,000, advanced south from Front Royal
Front Royal is the only incorporated town in Warren County, Virginia, United States. The population was 15,011 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Warren County.
History
The entire Shenandoah Valley including the area to become ...
in the Luray (Page) Valley, but was badly strung out because of the muddy Luray Road. At Port Republic, Jackson possessed the last intact bridge on the North River and the fords on the South River by which Frémont and Shields could unite. Jackson determined to check Frémont's advance at Mill Creek, while meeting Shields on the east bank of the South Fork of the Shenandoah River. A Confederate signal station on Massanutten monitored Union progress.
Early in the morning on June 8, Frémont's men encountered the Confederate advanced guard near Cross Keys Tavern. A few shots were fired and the Union cavalry fell back onto their main body, which was approaching. Darkness prevented further developments.

Opposing forces
Union
Confederate
Battle
ColonelSamuel S. Carroll
Samuel Sprigg "Red" Carroll (September 21, 1832 – January 28, 1893) was a career officer in the United States Army who rose to the rank of brigadier general of the Union during the American Civil War. The Maryland native was most known for h ...
, at the head of a regiment of Union cavalry, supported by an artillery battery and a brigade of infantry, was sent ahead by Shields to secure the North River Bridge at Port Republic. Shortly after dawn (June 8), Carroll scattered the Confederate pickets, forded the South River, and dashed into Port Republic. Jackson and his staff raced down the main street from headquarters and across the bridge, narrowly eluding capture (three members of his staff were captured: Col. Stapleton Crutchfield, Lt. Edward Willis, and Dr. Hunter McGuire
Hunter Holmes McGuire (October 11, 1835 – September 19, 1900) was a soldier, physician, teacher, and orator. McGuire was a surgeon in the Confederate Army attached to Stonewall Jackson's command, and he continued serving with the Army of Nor ...
). Carroll deployed one gun aimed at the bridge and brought up another. Jackson directed the defense, ordering Captain William T. Poague
William Thomas Poague (December 20, 1835 – September 8, 1914) was a Confederate States Army officer serving in the artillery during the American Civil War. He later served as Treasurer of the Virginia Military Institute.
Early life
Born in Ro ...
's battery to unlimber on the north bank. Captain James McD. Carrington brought up a gun from the vicinity of Madison Hall to rake the Main Street. Col. Samuel V. Fulkerson led his 37th Virginia Infantry
The 37th Virginia Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment raised in Virginia for service in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It fought mostly with the Army of Northern Virginia.
The 37th Virginia was organized in Wa ...
in a charge across the bridge, where the gun at the opposite end was firing on them with grape shot, to drive the Union cavalry out of the town. Carroll retreated in confusion, losing his two guns, before his infantry could come within range. Three Confederate batteries unlimbered on the bluffs east of Port Republic on the north bank of the South Fork and fired on the retreating Federals. Carroll retired several miles north on the Luray Road. Jackson stationed Brig. Gen. William B. Taliaferro's brigade in Port Republic and positioned the Stonewall Brigade
The Stonewall Brigade of the Confederate Army during the American Civil War, was a famous combat unit in United States military history. It was trained and first led by General Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, a professor from Virginia Military ...
near Bogota with the artillery to prevent any further surprises.
Meanwhile, Frémont, with Col. Gustave P. Cluseret's brigade in the lead, renewed his advance from the vicinity of Harrisonburg. After driving away the Confederate skirmishers, Cluseret reached and deployed his right flank along the Keezletown Road near Union Church. One by one, the Union brigades came into line: Brig. Gen. Robert C. Schenck
Robert Cumming Schenck (October 4, 1809 – March 23, 1890) was a Union Army general in the American Civil War, and American diplomatic representative to Brazil and the United Kingdom. He was at both battles of Bull Run and took part in Jack ...
on Cluseret's right, Brig. Gen. Robert H. Milroy on his left, and Brig. Gen. Julius H. Stahel on the far left, his left flank near Congers Creek. Brig. Gen. Henry Bohlen
Henry Bohlen (October 22, 1810 – August 22, 1862) was a German-American Union Army, Union Brigadier general (United States), Brigadier General of the American Civil War. Before becoming the first foreign-born Union general in the Civil War, he f ...
's and Col. John A. Koltes's brigades were held in reserve near the center of the line. A regiment of Union cavalry moved south on the road to secure the right flank. Batteries were brought to the front.
Ewell deployed his infantry division behind Mill Creek, Brig. Gen. Isaac R. Trimble's brigade on the right across the Port Republic Road, Brig. Gen. Arnold Elzey
Arnold Elzey Jones Jr. (December 18, 1816 – February 21, 1871), known for much of his life simply as Arnold Elzey, was a soldier in both the United States Army and the Confederate Army, serving as a major general in the American Civil War. At F ...
's in the center along the high bluffs. Ewell concentrated his artillery (4 batteries) at the center of the line. As Union troops deployed along Keezletown Road, Trimble advanced his brigade a quarter of a mile to Victory Hill and deployed Courtenay's (Latimer's) battery on a hill to his left supported by the 21st North Carolina Infantry. The 15th Alabama, which had been skirmishing near Union Church, rejoined the brigade. Trimble held his regiments out of sight behind the crest of the hill.
Frémont determined to advance his battle line with the evident intention of enveloping the Confederate position, assumed to be behind Mill Creek. This maneuver required an elaborate right wheel. Stahel's brigade on the far left had the farthest distance to cover and advanced first. Milroy moved forward on Stahel's right and rear. Union batteries were advanced with infantry lines south of Keezletown Road and engaged Confederate batteries. Stahel appeared oblivious to Trimble's advanced position. His battle line passed down into the valley, crossed the run, and began climbing Victory Hill. Suddenly, Trimble's men leaped up and fired all at once into Stahel's brigade. The Confederates were mostly armed with smoothbore muskets, which they loaded with buck and ball shot, and the effect at such close range was completely devastating; Stahel lost 300 men in a matter of moments and the remainder of the green, untested soldiers fled in panic. The Union brigade regrouped on the height opposite Victory Hill but made no effort to renew their assault. Different accounts of the battle place various estimates at how close Trimble was to Stahel when his men opened fire, but 40 yards seems to be a probable distance. The entire episode lasted no more than a minute as the amount of smoke from 1,300 muskets firing quickly made it impossible to see anything and most of the Confederates got off no more than one shot before Stahel's brigade broke and ran.
Stahel did not renew his attack but brought up a battery (Buell's) to support his position. Trimble moved the 15th Alabama by the right flank and up a ravine to get on the battery's left. In the meantime, Ewell sent two regiments ( 13th and 25th Virginia) along the ridge to Trimble's right, attracting a severe fire from the Union battery. With a shout, the 15th Alabama emerged from their ravine and began to climb the hill toward the battery, precipitating a melee. Trimble advanced his other two regiments ( 16th Mississippi Infantry on the left and 21st Georgia Infantry on the right) from their position on Victory Hill, forcing back the Union line. The Union battery limbered hastily and withdrew, saving its guns. A Union regiment counterattacked briefly, striking the left flank of the 16th Mississippi, but was forced back in desperate fighting.
Trimble continued advancing up the ravine on the Confederate right, outflanking successive Union positions. In the meantime, Milroy advanced on Stahel's right, supported by artillery. Milroy's line came within rifle-musket range of the Confederate center behind Mill Creek and opened fire. Union batteries continued to engage Confederate batteries in an artillery duel. Bohlen advanced on the far Union left to stiffen Stahel's crumbling defense. Milroy's left flank was endangered by Stahel's retreat, and Frémont ordered him to withdraw. Jackson brought Taylor's brigade forward to support Ewell if needed, but Taylor remained in reserve on the Port Republic Road near the Dunker Church.
Seemingly paralyzed by the decimation of Stahel's brigade on his left, Frémont was unable to mount a coordinated attack. He ordered Schenck's brigade forward to find the Confederate left flank south of Union Church. Ewell reinforced his left with elements of Elzey's brigade. Severe firing erupted along the line but quickly died down. Confederate Brig. Gen. Elzey and Brig. Gen. George H. Steuart were wounded in this exchange. Frémont withdrew his force to Keezletown Road, placing his artillery on the heights to his rear (Oak Ridge). Artillery firing continued.
Aftermath
Union casualties totaled 557 killed and wounded and 100 captured, while the Confederates lost fewer than 300 men. At dusk, Trimble pushed his battle line forward to within a quarter mile of the Union position, anticipating a night assault. Confederate accounts describe the Union soldiers going into camp, lighting fires, and making coffee. Schenck sent out a company to probe the Confederate positions after dark, but after a brief skirmish the company withdrew and no other engagements took place. During the night, Ewell ordered Trimble to withdraw without making the attack.Battlefield preservation
TheCivil War Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the American Civil War, the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812 through acquisition of battlefield land. T ...
(a division of the American Battlefield Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization ( 501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the American Civil War, the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812 through acquisition of battlefield land. Th ...
) and its partners have acquired and preserved of the battlefield. A key purchase was the 51-acre Widow Pence Farm in the heart of the battlefield. The Trust joined with a local retired surgeon, Irvin Hess, and his wife to purchase the property at auction. The couple has since fully restored the circa 1840 farmhouse. The land is protected through a conservation easement.
In March 2022, the " Talbot Boys" statue was relocated to the battlefield from Talbot County, Maryland
Talbot County is located in the heart of the Eastern Shore of Maryland in the U.S. state of Maryland. As of the 2020 census, the population was 37,526. Its county seat is Easton. The county was named for Lady Grace Talbot, the wife of Sir Rob ...
. The Confederate monument
In the United States, the public display of Confederate monuments, memorials and symbols has been and continues to be controversial. The following is a list of Confederate monuments and memorials that were established as public displays and symb ...
had stood in front of the Talbot County Courthouse since 1916, and was the last remaining Confederate monument on public grounds in Maryland when it was removed after years-long protests.
See also
*Nicolae Dunca
Nicolae Dunca (1837 – June 8, 1862) was a Romanian military officer who served in several conflicts in Europe and in the American Civil War.
Life and career
Dunca was born in 1837 in Iași, Moldavia.Eugene PiványHungarians in the American Civi ...
Notes/References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *National Park Service battle description
CWSAC Report Update
External links
Battle of Cross Keys in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
: Battle maps, history articles, and preservation news (
Civil War Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the American Civil War, the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812 through acquisition of battlefield land. T ...
)
Animated history of Jackson's Valley Campaign
Gallery