Basilica di Sant'Andrea di Mantova on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Basilica of Sant'Andrea is a
Paolo Monti - Servizio fotografico (Mantova, 1972) - BEIC 6347241.jpg, Elements of the arches on the lateral façade. Photo by
 The purpose of the new building was to receive the pilgrims for the feast of Ascension when a vial, that the faithful believe contains the
The purpose of the new building was to receive the pilgrims for the feast of Ascension when a vial, that the faithful believe contains the
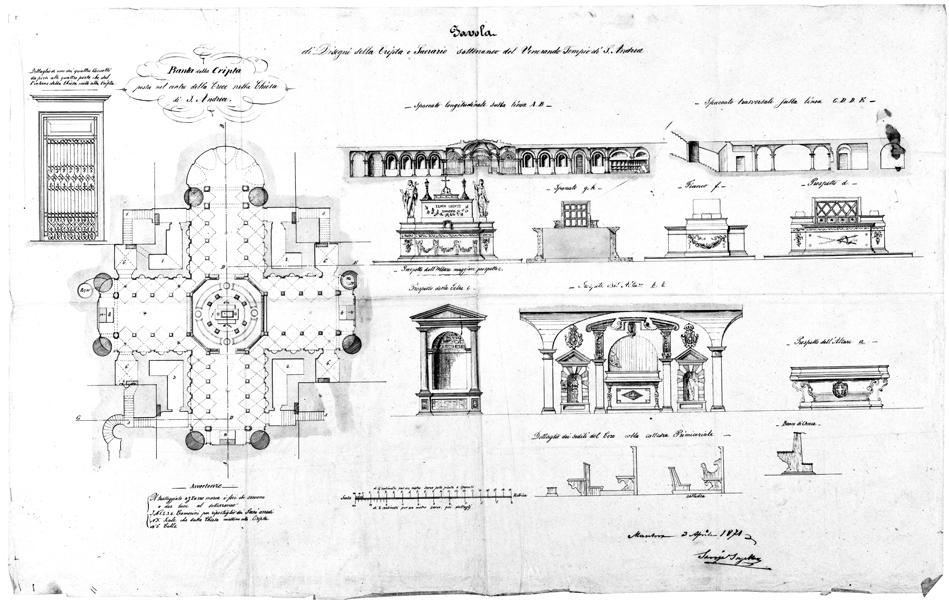 Alberti broke with basilican tradition by having multiple chapels branch off the nave instead of lining it with aisles—because the colonnades would block the view of ceremonies in the classic model. One of the chapels is known as the Mantegna funerary chapel, since it houses the tomb of the early Renaissance painter
Alberti broke with basilican tradition by having multiple chapels branch off the nave instead of lining it with aisles—because the colonnades would block the view of ceremonies in the classic model. One of the chapels is known as the Mantegna funerary chapel, since it houses the tomb of the early Renaissance painter
Alberti's Sant' Andrea in Mantua
Heather Horton, article at Smarthistory
Basilica Concattedrale di S. Andrea - complesso
Mantua tourist guide
Mantua tourist guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Basilica Di Sant'andrea Di Mantova Roman Catholic churches in Mantua Basilica churches in Lombardy Renaissance architecture in Mantua
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
co-cathedral and minor basilica
In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a designation given by the Pope to a church building. Basilicas are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building need not be a basilica in the architectural sense (a rectangular ...
in Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the Eur ...
, Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
(Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
). It is one of the major works of 15th-century Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought ...
in Northern Italy. Commissioned by Ludovico III Gonzaga
Ludovico III Gonzaga of Mantua, also spelled Lodovico (also Ludovico II; 5 June 1412 – 12 June 1478) was the ruler of the Italian city of Mantua from 1444 to his death in 1478.
Biography
Ludovico was the son of Gianfrancesco I Gonzaga an ...
, the church was begun in 1472 according to designs by Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. H ...
on a site occupied by a Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
monastery, of which the bell tower (1414) remains. The building, however, was only finished 328 years later. Though later changes and expansions altered Alberti's design, the church is still considered to be one of Alberti's most complete works. It looms over the Piazza Mantegna.
Architecture
The façade, built abutting a pre-existing bell tower (1414), is based on the scheme of the ancient Arch of Trajan at Ancona. It is largely a brick structure with hardened stucco used for the surface. It is defined by a large central arch, flanked by Corinthianpilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
s. There are smaller openings to the right and left of the arch. A novel aspect of the design was the integration of a lower order, comprising the fluted Corinthian columns, with a giant order
In classical architecture, a giant order, also known as colossal order, is an order whose columns or pilasters span two (or more) storeys. At the same time, smaller orders may feature in arcades or window and door framings within the storeys tha ...
, comprising the taller, unfluted pilasters. The whole is surmounted by a pediment and above that a vaulted structure, the purpose of which is not exactly known, but presumably to shade the window opening into the church behind it.
An important aspect of Alberti's design was the correspondence between the façade and the interior elevations, both elaborations of the triumphal arch motif, the arcades, like the facade, having alternating high arches and much lower square topped openings.
The nave is roofed by a barrel vault
A barrel vault, also known as a tunnel vault, wagon vault or wagonhead vault, is an architectural element formed by the extrusion of a single curve (or pair of curves, in the case of a pointed barrel vault) along a given distance. The curves are ...
, one of the first times such a form was used in such a monumental scale since antiquity, and probably modeled on the Basilica of Maxentius
The Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine ( it, Basilica di Massenzio), sometimes known as the Basilica Nova—meaning "new basilica"—or Basilica of Maxentius, is an ancient building in the Roman Forum, Rome, Italy. It was the largest building ...
in Rome. Alberti possibly planned for the vault to be coffer
A coffer (or coffering) in architecture is a series of sunken panels in the shape of a square, rectangle, or octagon in a ceiling, soffit or vault.
A series of these sunken panels was often used as decoration for a ceiling or a vault, also ...
ed, much like the shorter barrel vault of the entrance, but lack of funds led to the vault being constructed as a simple barrel vault with the coffers then being painted on. Originally, the building was planned without a transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building with ...
, and possibly even without a dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
. This phase of construction more or less ended in 1494.
In 1597, the lateral arms were added and the crypt finished. The massive dome (1732–1782) was designed by Filippo Juvarra
Filippo is an Italian language, Italian male given name, which is the equivalent of the English language, English name Philip (name), Philip, from the Greek language, Greek ''Philippos'', meaning "amante dei cavalli".''Behind the Name''"Given Name ...
, and the final decorations on the interior added under Paolo Pozzo and others in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Paolo Monti
Paolo Monti (11 August 1908 – 29 November 1982) was an Italian photographer, known for his architectural photography.
In his early period, Monti experimented with abstractionism as well as with effects such as blurring and diffraction. In 19 ...
Cupola Della Basilica di Sant'Andrea, Mantova.jpg, Dome
Lombardia Mantova5 tango7174.jpg, Interior
Relic of the Holy Blood
 The purpose of the new building was to receive the pilgrims for the feast of Ascension when a vial, that the faithful believe contains the
The purpose of the new building was to receive the pilgrims for the feast of Ascension when a vial, that the faithful believe contains the Blood of Christ
Blood of Christ, also known as the Most Precious Blood of Our Lord Jesus Christ, in Christian theology refers to (a) the physical blood actually shed by Jesus Christ primarily on the Cross, and the salvation which Christianity teaches was accomp ...
, is brought up from the crypt below through a hole in the floor located directly under the dome. The relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
, called ''Preziosissimo Sangue di Cristo'' ("Most Precious Blood
Blood of Christ, also known as the Most Precious Blood of Our Lord Jesus Christ, in Christian theology refers to (a) the physical blood actually shed by Jesus Christ primarily on the Cross, and the salvation which Christianity teaches was accomp ...
of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
"), which is preserved in Sacred Vessels. According to tradition the blood was brought to the city by the Roman centurion Longinus, who had scooped up the earth containing the blood at the foot of the cross.
In 804 Holy Roman emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
obtained authentication of the relic from Pope Leo III
Pope Leo III (died 12 June 816) was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 26 December 795 to his death. Protected by Charlemagne from the supporters of his predecessor, Adrian I, Leo subsequently strengthened Charlemagne's position ...
for its veneration. According to many scholars, this resulted in the creation of the Diocese of Mantua
The Diocese of Mantua ( la, Dioecesis Mantuana) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Italy. The diocese existed at the beginning of the 8th century, though the earliest attested bishop is Laiulfus (827). ...
and the construction of first portion of the Cathedral of St Andrew. The relic was "rediscovered" (''secunda inventio'') ca. 1049, in the presence of Matilda of Tuscany
Matilda of Tuscany ( it, Matilde di Canossa , la, Matilda, ; 1046 – 24 July 1115 or Matilda of Canossa after her ancestral castle of Canossa), also referred to as ("the Great Countess"), was a member of the House of Canossa (also known as ...
. Pope Leo IX recognized this relic as authentic in 1053, which became highly venerated during the Renaissance. The relic is displayed on Good Friday
Good Friday is a Christian holiday commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. It is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum. It is also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday (also Holy ...
, to the faithful, and in a procession on the city's streets.
Portions of the relic were extracted and taken by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
to the St Chapelle in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, and later to the Weingarten Abbey, to the Archbasilica of St. John Lateran in Rome, and to the Church of the Holy Cross in Guastalla
Guastalla ( Guastallese: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Reggio Emilia in Emilia-Romagna, Italy.
Geography
Guastalla is situated in the Po Valley, and lies on the banks of the Po River. Guastalla is located at around from the citie ...
(built on behalf of Beatrix of Canossa).
Other aspects
 Alberti broke with basilican tradition by having multiple chapels branch off the nave instead of lining it with aisles—because the colonnades would block the view of ceremonies in the classic model. One of the chapels is known as the Mantegna funerary chapel, since it houses the tomb of the early Renaissance painter
Alberti broke with basilican tradition by having multiple chapels branch off the nave instead of lining it with aisles—because the colonnades would block the view of ceremonies in the classic model. One of the chapels is known as the Mantegna funerary chapel, since it houses the tomb of the early Renaissance painter Andrea Mantegna
Andrea Mantegna (, , ; September 13, 1506) was an Italian painter, a student of Roman archeology, and son-in-law of Jacopo Bellini.
Like other artists of the time, Mantegna experimented with perspective, e.g. by lowering the horizon in orde ...
, with a bronze figure of him by Gianmarco Cavalli and Mantegna's own ''Holy Family''. Other artworks in the chapels include frescoes of Giulio Romano
Giulio Romano (, ; – 1 November 1546), is the acquired name of Giulio Pippi, who was an Italian painter and architect. He was a pupil of Raphael, and his stylistic deviations from High Renaissance classicism help define the sixteenth-cent ...
's school (a work by Giulio is currently a copy) and Correggio
Antonio Allegri da Correggio (August 1489 – 5 March 1534), usually known as just Correggio (, also , , ), was the foremost painter of the Parma school of the High Italian Renaissance, who was responsible for some of the most vigorous and sens ...
. In the belltower there are five bells (A, C#, E, F#, A) cast in the 19th century.
Burials
* Federico I Gonzaga, Marquess of MantuaNotes
See also
* List of tallest domes *Blood of Christ
Blood of Christ, also known as the Most Precious Blood of Our Lord Jesus Christ, in Christian theology refers to (a) the physical blood actually shed by Jesus Christ primarily on the Cross, and the salvation which Christianity teaches was accomp ...
References
* * * ''La reliquia del sangue di Cristo: Mantova, l'Italia e l'Europa ad tempo di Leone IX'', ed. Glauco Maria Cantarella, Verona: Scripta, 2012.External links
Alberti's Sant' Andrea in Mantua
Heather Horton, article at Smarthistory
Basilica Concattedrale di S. Andrea - complesso
Mantua tourist guide
Mantua tourist guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Basilica Di Sant'andrea Di Mantova Roman Catholic churches in Mantua Basilica churches in Lombardy Renaissance architecture in Mantua
Andrea
Andrea is a given name which is common worldwide for both males and females, cognate to Andreas, Andrej and Andrew.
Origin of the name
The name derives from the Greek word ἀνήρ (''anēr''), genitive ἀνδρός (''andrós''), that r ...
Church buildings with domes
Leon Battista Alberti church buildings
Filippo Juvarra buildings