Barrow Island (Western Australia) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Barrow Island is a
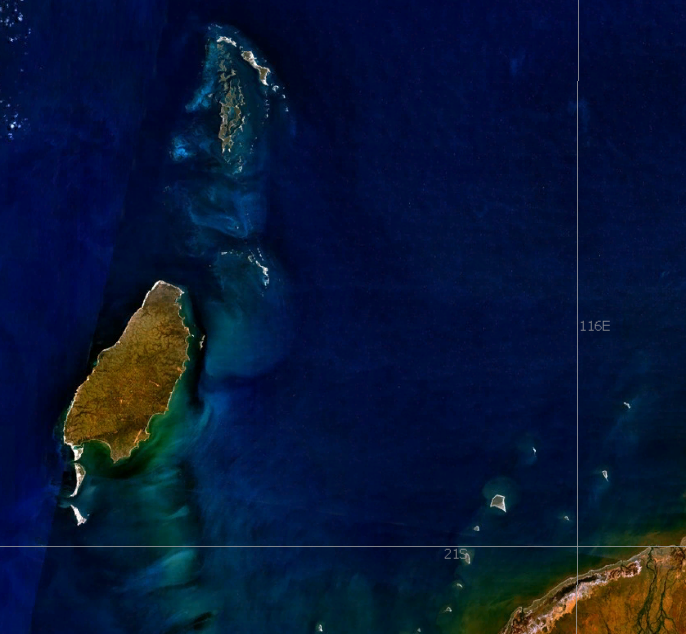 Barrow Island is noted for its flat spinifex
Barrow Island is noted for its flat spinifex , '' Liagoceradocus'' and other genera. These mostly inhabit an anchialine system, a 'lens' of fresh water above the saline ground water, which they share with cave fish species such as the blind cave eel (''
. World Meteorological Organization. The gust occurred on 10 April 1996, during Severe Tropical Cyclone Olivia.Courtney, J., et al. 2012
Documentation and verification of the world extreme wind gust record: 113.3 m/s on Barrow Island, Australia, during passage of tropical cyclone Olivia. ''Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal'' 62: 1-9. The previous record was a 372 km/h (231 mph) gust at Mount Washington, New Hampshire, United States in April 1934.
island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
northwest off the Pilbara
The Pilbara () is a large, dry, thinly populated region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Aboriginal peoples; its ancient landscapes; the red earth; and its vast mineral deposits, in particular iron ore. It is also a g ...
coast of Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
. The island is the second largest in Western Australia after Dirk Hartog Island
A dirk is a long bladed thrusting dagger.Chisholm, Hugh (ed.), ''Dagger'', The Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th ed., Vol. VII, New York, NY: Cambridge University Press (1910), p. 729 Historically, it gained its name from the Highland Dirk (Scot ...
.
Early history and European discovery
The island was visited byIndigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
approximately 4,000 or more years ago. It separated from the mainland approximately 6,800 years ago. Stone artefacts including several weathered flakes and fragments made of igneous and metamorphic rocks and chert were collected from Barrow Island in the 1960s. Thevenard Island also has evidence of Aboriginal visitation, and it is likely that the nearby Montebello Islands
The Montebello Islands, also rendered as the Monte Bello Islands, are an archipelago of around 174 small islands (about 92 of which are named) lying north of Barrow Island and off the Pilbara coast of north-western Australia. The islands f ...
were utilized as well; however, there have been no archaeological finds from these islands.
Navigators had noted its existence since the early 17th century, and Nicholas Baudin sighted it in 1803, mistakenly believing it to be part of mainland Australia. Phillip Parker King
Rear Admiral Phillip Parker King, FRS, RN (13 December 1791 – 26 February 1856) was an early explorer of the Australian and Patagonian coasts.
Early life and education
King was born on Norfolk Island, to Philip Gidley King and Ann ...
named the island in 1816 after Sir John Barrow
Sir John Barrow, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1764 – 23 November 1848) was an English geographer, linguist, writer and civil servant best known for term as the Second Secretary to the Admiralty from 1804 until 1845.
Early life
Barrow was born ...
, a Secretary of the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
and founder of the Royal Geographical Society.
Whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japa ...
s were known to operate in the area from about 1800 onwards. The first recorded visit by whalers was in 1842 with continued visits occurring until 1864. The island was used as a slave trading centre for Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Isl ...
during the 1870s by Captain William Cadell until he was arrested and removed from the colony in 1876. Slave labour was used in the nearby mainland pearling industry.
Guano was found on the island and mining began in 1883. It was mined for the remainder of the 1880s and sold to markets in Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth i ...
.
Environment
 Barrow Island is noted for its flat spinifex
Barrow Island is noted for its flat spinifex grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
s spotted with termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blatto ...
mounds. While the main feature of Barrow Island's geography is the undulating limestone uplands, the island is surrounded by a mixture of sandy beaches and rocky shores, low cliffs, dunes, salt flats, and reefs.
Due to its isolation from mainland Australia and protection afforded under its statutory status, Barrow Island is one of the most important conservation reserves in Western Australia. It is an "A-class" reserve, the highest level of conservation protection available for Crown land in Australia. Once a national park or class A nature reserve is made, mining leases and general purpose leases cannot be granted over them without the consent of both Houses of Parliament, and actual mining cannot take place within them without specific permission of the Minister for Environment. This occurred in 2003, when a portion of the reserve was excised in order to facilitate the Gorgon gas development program.
The island is known for its diversity of mammalian fauna, including several species now extinct or greatly reduced on mainland Australia. Thirteen mammal species exist on the island, including the spectacled hare-wallaby
The spectacled hare-wallaby (''Lagorchestes conspicillatus'') is a species of macropod found in Australia and New Guinea. In Australia, a small sub-population is found on Barrow Island, while the mainland type is widespread, though in decline, ...
, burrowing bettong
The boodie (''Bettongia lesueur''), also known as the burrowing bettong or Lesueur's rat-kangaroo, is a small, furry, rat-like mammal native to Australia. Once common throughout the continent, it is now restricted to a few coastal islands. A memb ...
, golden bandicoot
The golden bandicoot (''Isoodon auratus''; Yolngu: ''Wan'kurra'') is a short-nosed bandicoot found in northern Australia. It is the smallest of its genus.
The golden bandicoot is now a threatened species. It was once found throughout much o ...
, black-flanked rock-wallaby, Barrow Island euro and Barrow Island mouse (''Pseudomys
''Pseudomys'' is a genus of rodent that contains a wide variety of mice native to Australia and New Guinea. They are among the few terrestrial placental mammals that colonised Australia without human intervention.
Natural history
This genus con ...
nanus ferculinus''). The island is also home to 43 species of terrestrial reptiles including a variety of dragons, legless lizards, geckos, skinks, snakes and monitors. The most recognisable of these is probably the perentie
The perentie (''Varanus giganteus'') is the largest monitor lizard or goanna native to Australia. It is one of the largest living lizards on earth, after the Komodo dragon, Asian water monitor, crocodile monitor, and intersecting by size with ...
, Australia's biggest lizard and the island's top predator. The island represents important turtle nesting habitat for the green turtle
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exten ...
and flatback sea turtle
The Australian flatback sea turtle (''Natator depressus'') is a species of sea turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is endemic to the sandy beaches and shallow coastal waters of the Australian continental shelf. This turtle gets its ...
.
Some exotic species exist on the island (e.g. the American cockroach
The american cockroach (''Periplaneta americana'') is the largest species of common cockroach, and often considered a pest. In certain regions of the U.S. it is colloquially known as the waterbug, though it is not a true waterbug since it is not ...
) but the island fauna is largely intact. Black rats
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is n ...
(''Rattus rattus'') were discovered to have established in 1990, but were eradicated by the Department of Parks and Wildlife (then CALM). Current threats include invasive species (including weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. ...
s, feral cats, common house gecko
The common house gecko (''Hemidactylus frenatus'') is a gecko native to South and Southeast Asia. It is also known as the Asian house gecko, Pacific house gecko, wall gecko, house lizard, tayoto, chipkali or moon lizard.
Most geckos are nocturn ...
, etc.) establishing on the island, clearing for development, fire and disease.
Limestone caves on Barrow Island support subterranean ecological communities. These include endemic and vulnerable species. Invertebrate species include Stygofauna, amphipod crustaceans, of '' Nedsia''Ophisternon candidum
The blind cave eel (''Ophisternon candidum'') is a species of cavefish in the family Synbranchidae. It is the longest cavefish in Australia (up to ) and one of the only three vertebrates in Australia that is restricted to underground waters, the ...
''), and two blind cave gudgeons, '' Milyeringa veritas'' and '' Milyeringa justitia''. Troglofauna
Troglofauna are small cave-dwelling animals that have adapted to their dark surroundings. Troglofauna and stygofauna are the two types of subterranean fauna (based on life-history). Both are associated with subterranean environments – troglofa ...
have also been discovered within the cave systems; these include the schizomid '' Draculoides bramstokeri'' and perhaps the only troglobitic
A troglobite (or, formally, troglobiont) is an animal species, or population of a species, strictly bound to underground habitats, such as caves. These are separate from species that mainly live in above-ground habitats but are also able to live u ...
reptile—'' Anilios longissimus''. Hydrogen sulphide produced by the "Barrow fault" may sustain this diverse community through chemoautotrophic energy production.
Birds
Barrow Island has been classified by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area. Birds include the Barrow Island black-and-white fairy-wren (''Malurus leucopterus edouardi''), anendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
subspecies of the white-winged fairy-wren
The white-winged fairywren (''Malurus leucopterus'') is a species of passerine bird in the Australasian wren family, Maluridae. It lives in the drier parts of Central Australia; from central Queensland and South Australia across to Western Austr ...
which is regarded as vulnerable to extinction. The island also supports over 1% of the world populations of grey-tailed tattler, red-necked stint
The red-necked stint (''Calidris ruficollis'') is a small migratory wader. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'', a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific ''ruficollis'' is from ...
, pied oystercatcher
The pied oystercatcher (''Haematopus longirostris'') is a species of oystercatcher. It is a wading bird native to Australia and commonly found on its coastline. The similar South Island pied oystercatcher (''H. finschi'') occurs in New Zealand. ...
, and fairy tern
The fairy tern (''Sternula nereis'') is a small tern which is native to the southwestern Pacific. It is listed as " Vulnerable" by the IUCN and the New Zealand subspecies is " Critically Endangered".
There are three subspecies:
* Australian fai ...
, as well as an isolated population of the spinifexbird
The spinifexbird (''Poodytes carteri'') is endemic to inland Australia. Also known as Carter's desertbird, it is named after Thomas Carter, an English ornithologist and pastoralist active in Western Australia from 1887 to 1928.
Description
It h ...
.
Conservation
TheWestern Shield
Western Shield, managed by Western Australia's Department of Parks and Wildlife, is a nature conservation program safeguarding Western Australia's animals and protecting them from extinction. The program was set up in 1996 and as of 2009 was th ...
project has sought to reduce the impact of introduced species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived ther ...
to the region. Corporate and state government cooperation on programs has produced studies into the little-known subterranean fauna of the island.
Energy reserves
Oil
Oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
was discovered on the island in commercial quantities in 1964 by West Australian Petroleum Pty Ltd ( WAPET), and the first oil field was established shortly after. In 1995, there were 430 wells producing oil and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
across most of the southern half of the island. The site has been Australia's leading producer of oil.
Oil tanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk transport of oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined cru ...
s are filled by a submarine pipeline
Pipeline may refer to:
Electronics, computers and computing
* Pipeline (computing), a chain of data-processing stages or a CPU optimization found on
** Instruction pipelining, a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a s ...
that extends offshore. WAPET established a 200-room apartment complex for workers on the island. A private airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfa ...
facility known as Barrow Island Airport was also established to transport workers and equipment from Karratha and Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth i ...
.
Gas
In December 2009, a development consortium between the Australian subsidiaries ofChevron
Chevron (often relating to V-shaped patterns) may refer to:
Science and technology
* Chevron (aerospace), sawtooth patterns on some jet engines
* Chevron (anatomy), a bone
* '' Eulithis testata'', a moth
* Chevron (geology), a fold in rock ...
, ExxonMobil, and Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
received environmental approvals from the Government of Western Australia to develop natural gas reserves north of the island. Known as the Gorgon gas project
The Gorgon gas project is a multi-decade natural gas project in Western Australia, involving the development of the Greater Gorgon gas fields, subsea gas-gathering infrastructure, and a liquefied natural gas (LNG) plant on Barrow Island. The pr ...
, it was completed in 2017. Offering an estimated of gas makes it one of Australia's largest developments.
Climate
Highest wind record
TheWorld Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Intern ...
established Barrow Island as the location of the highest non- tornadic wind gust ever recorded, at 408 km/h (253 mph).World Record Wind Gust: 408 km/h. World Meteorological Organization. The gust occurred on 10 April 1996, during Severe Tropical Cyclone Olivia.
Documentation and verification of the world extreme wind gust record: 113.3 m/s on Barrow Island, Australia, during passage of tropical cyclone Olivia. ''Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal'' 62: 1-9. The previous record was a 372 km/h (231 mph) gust at Mount Washington, New Hampshire, United States in April 1934.
See also
* List of islands of Western Australia *Petroleum industry in Western Australia
The petroleum industry in Western Australia is the largest contributor to the country's oil exports. Western Australia's North West Shelf (NWS) is the primary location from which production originates. Oil exports are shipped from Port Hedland ...
References
Further reading
* Butler, Harry, (1982) ''Barrow Island'' (written by Harry Butler and compiled by Jacqueline Cox with assistance of other Wapet staff). Perth, W.A : West Australian Petroleum Pty Ltd. {{Authority control Islands of the Pilbara Oil fields of Australia Geology of Western Australia Important Bird Areas of Western Australia Energy in Western Australia North West Shelf