Banknote seal (China) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A cash seal (; "''Baochao''" means "valuable money", "''Yin''" means "
A cash seal (; "''Baochao''" means "valuable money", "''Yin''" means "

 The economy of China during the
The economy of China during the
The anti-counterfeiting techniques of Ming Dynasty cash
{{DEFAULTSORT:Banknote Seal (China) Banknotes of China Chinese inventions Economic history of China Seals (insignia)
 A cash seal (; "''Baochao''" means "valuable money", "''Yin''" means "
A cash seal (; "''Baochao''" means "valuable money", "''Yin''" means "seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to imp ...
") is a type of seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to imp ...
used as an anti-counterfeiting measure on paper money
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
or banknote
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
s. The cash seal first appeared during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
in China.
The short name is ''Chao Yin'' (), and the full name is Seal of Baochao (), or ''Baochao Yinjian'' (). The name can also be simply translated as "money seal" or "banknote seal".
History

 The economy of China during the
The economy of China during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
outpaced the supply of traditional coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
age, leading the government to issue banknote
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
s (''Jiaozi
''Jiaozi'' (; ; pinyin: jiǎozi) are Chinese dumplings commonly eaten in China and other parts of East Asia. ''Jiaozi'' are folded to resemble Chinese sycee and have great cultural significance attached to them within China. ''Jiaozi'' are ...
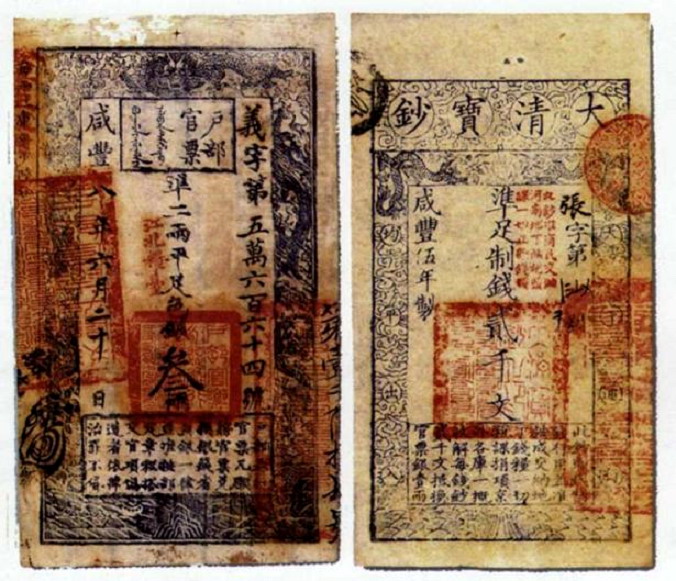
'' (交子)) to increase the money supply. Subsequently, a government department was created to manage cash affairs, with its responsibilities including producing and issuing cash, and combating counterfeiting. The cash seal was developed as an anti-counterfeiting measure; official banknotes received a red, sometimes black or purple, stamp at their centres. This forced counterfeiters to attempt to replicate the seal, presumably leading to distinguishable lower quality stamps. Severe punishments, including the death penalty, were given to counterfeiters.
The Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
and Qing dynasties also stamped banknotes. The Ming government department responsible for cash affairs and the use of the cash seal was the Baochao Bureau ().
Modern time
The use of cash seals is no longer restricted to governments. Seals or private individuals and organizations may be used in the same manner on private banknotes to represent the parties' trust, credit, or authority. In the era of the Republic of China, these seal stamps could also be called ''Yinhang Yin'' (銀行印/银行印; direct translation: the seal stamp of bank, or just "bank seal"). In Japan, ''ginkō-in'' (Japanese: 銀行印) seals have similar functions. InSingapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, a seal has been present in all Singapore dollar
The Singapore dollar (sign: S$; code: SGD) is the official currency of the Republic of Singapore. It is divided into 100 cents. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or S$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencie ...
banknotes since its first series, bearing the chairman of the Monetary Authority of Singapore
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is the central bank and financial regulatory authority of Singapore. It administers the various statutes pertaining to money, banking, insurance, securities and the financial sector in general, as well ...
(MAS) or the Board of Commissioners of Currency Singapore (BCCS).
Typical seals
In late imperial China: * 大明寳鈔之印 / 大明宝钞之印 (traditional/simplified Chinese); ''The Seal of Cash of the Great Ming''. * 大清寳鈔之印 / 大清宝钞之印; ''The Seal of Cash of the Great Qing''.See also
*Seal (East Asia)
A seal, in an East and Southeast Asian context, is a general name for printing stamps and impressions thereof which are used in lieu of signatures in personal documents, office paperwork, contracts, art, or any item requiring acknowledgeme ...
* Banknote
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
* Cash
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-im ...
* Economy of the Song Dynasty
The economy of the Song dynasty (960–1279) in China was the wealthiest economy in the world during its time. The dynasty moved away from the top-down command economy of the Tang dynasty (618-907) and made extensive use of market mechanisms as na ...
References
External links
The anti-counterfeiting techniques of Ming Dynasty cash
{{DEFAULTSORT:Banknote Seal (China) Banknotes of China Chinese inventions Economic history of China Seals (insignia)