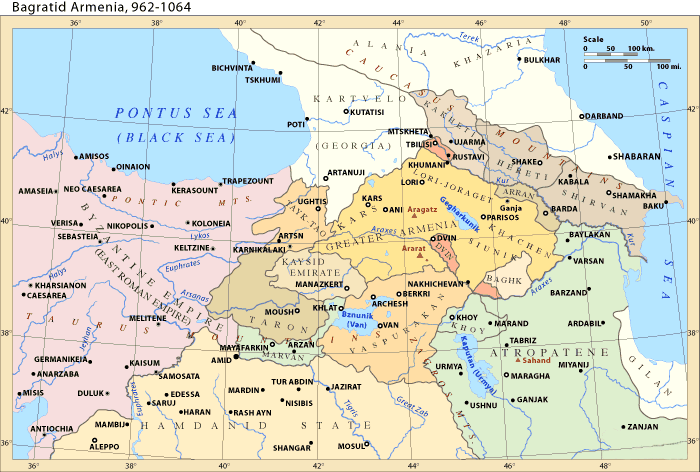
Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia, also known as Bagratid Armenia ( xcl, Բագրատունեաց Հայաստան, or , , 'kingdom of the Bagratunis'), was an independent
 The weakening of the Sassanian Empire during the 7th century led to the rise of another regional power, the Muslim Arabs. The Umayyad Arabs had conquered vast swaths of territory in the Middle East and, turning north, began to periodically launch raids into Armenia territory in 640.
The weakening of the Sassanian Empire during the 7th century led to the rise of another regional power, the Muslim Arabs. The Umayyad Arabs had conquered vast swaths of territory in the Middle East and, turning north, began to periodically launch raids into Armenia territory in 640.
 Armenian fortunes were reversed in 867 with the accession of the Armenian emperor of Byzantium
Armenian fortunes were reversed in 867 with the accession of the Armenian emperor of Byzantium
The Bagratids
" Iranica. Retrieved April 15, 2008. He secured the favor of both the Byzantines and Arabs but ultimately showed loyalty to Basil and chose to conclude an alliance with the Byzantines in 885. Ashot was not the sole Armenian prince of the region (other principalities existed in Syunik, Vaspurakan, and Taron) yet he commanded the full support of the other princes who recognized his authority in his becoming of king. With his status of king, his authority also carried over to the neighboring states of
 Smbat I was crowned king in 892, following a brief attempt by his uncle Abas to disrupt his succession to the throne. Smbat continued his father's policy of maintaining cordial relations with Byzantium but he remained mindful of the Arabs' fears of the Armeno-Byzantine alliance. Speaking with the Arab ostikan
Smbat I was crowned king in 892, following a brief attempt by his uncle Abas to disrupt his succession to the throne. Smbat continued his father's policy of maintaining cordial relations with Byzantium but he remained mindful of the Arabs' fears of the Armeno-Byzantine alliance. Speaking with the Arab ostikan
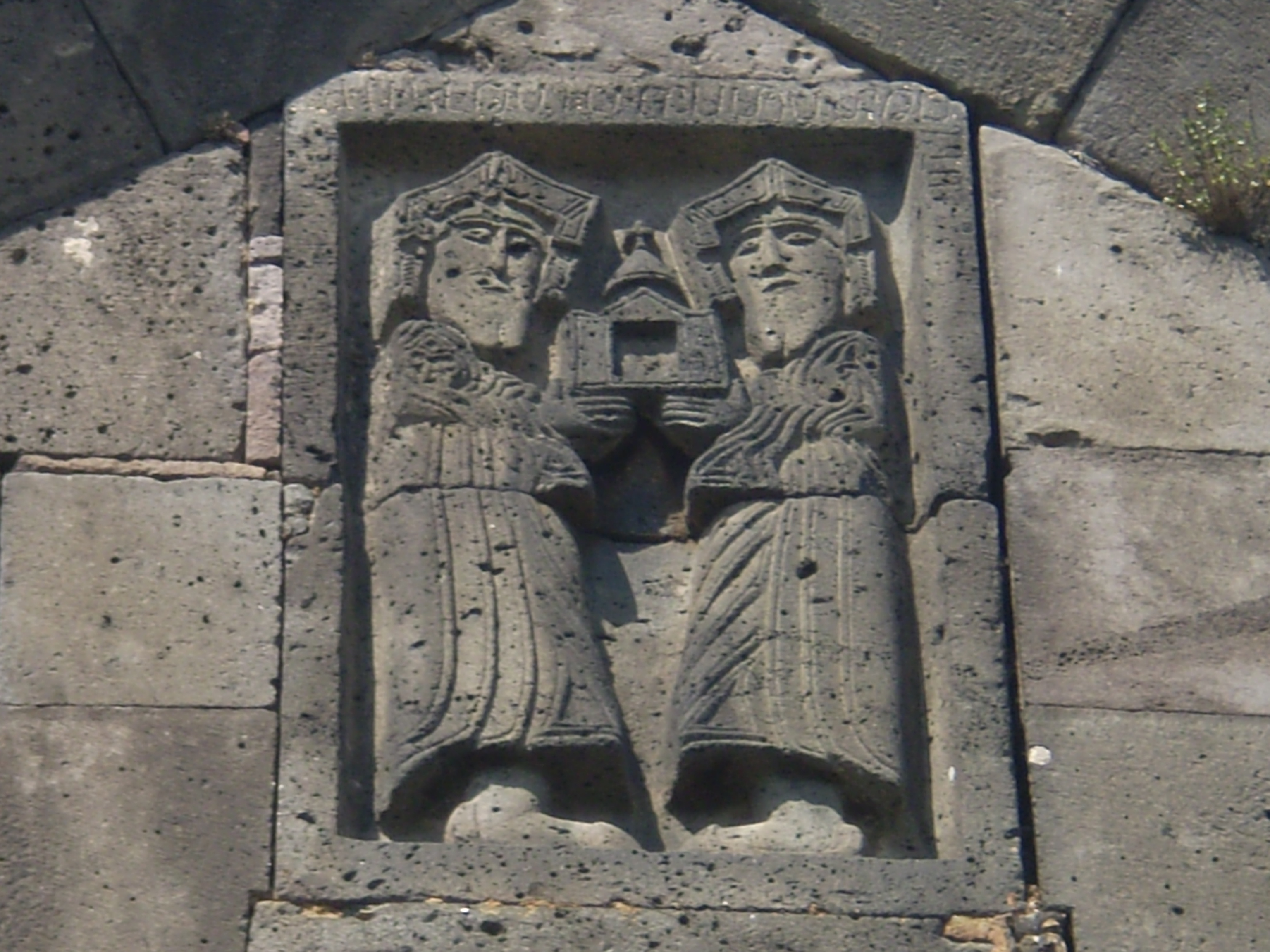



 Most Armenians belonged to the
Most Armenians belonged to the

 During the Bagratuni period, the great majority of the population of Armenia remained Armenian. 10th-century Arab sources attest that the cities of the Araxes valley remained predominantly Armenian and Christian despite Arab Muslim rule. In fact, the 10th-century Arab geographer
During the Bagratuni period, the great majority of the population of Armenia remained Armenian. 10th-century Arab sources attest that the cities of the Araxes valley remained predominantly Armenian and Christian despite Arab Muslim rule. In fact, the 10th-century Arab geographer
Arts_of_Armenia_[Architecture
/nowiki>.html" ;"title="rchitecture">Arts of Armenia [Architecture
/nowiki>">rchitecture">Arts of Armenia [Architecture
/nowiki>. Armenian Studies Program at Many churches and other forms of architecture suffered vandalism or outright destruction following the Seljuk invasions of the eleventh and twelfth centuries.
Armenian History; Tacentral.comVirtualANI: Dedicated to the Deserted Medieval Armenian City of Ani
On the architecture of Ani as well as general Armenian architecture.
Armenian Studies Program at
Notable societies of Europe, 900 A.D.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Armenia, Bagratid
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
state established by Ashot I Bagratuni of the Bagratuni dynasty
The Bagratuni or Bagratid dynasty ( hy, Բագրատունի, ) was an Armenian royal dynasty which ruled the medieval Kingdom of Armenia from c. 885 until 1045. Originating as vassals of the Kingdom of Armenia of antiquity, they rose to beco ...
in the early 880s following nearly two centuries of foreign domination of Greater Armenia under Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
Umayyad and Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
rule. With each of the two contemporary powers in the region—the Abbasids and Byzantines—too preoccupied to concentrate their forces in subjugating the region, and with the dissipation of several of the Armenian '' nakharar'' noble families, Ashot succeeded in asserting himself as the leading figure of a movement to dislodge the Arabs from Armenia.
Ashot's prestige rose as both Byzantine and Arab leader
Leadership, both as a research area and as a practical skill, encompasses the ability of an individual, group or organization to "lead", influence or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. The word "leadership" often gets view ...
s—eager to maintain a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
near their frontiers—courted him. The Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
recognized Ashot as "prince of princes" in 862 and, later on, as king (in 884 or 885). The establishment of the Bagratuni kingdom later led to the founding of several other Armenian principalities and kingdoms: Taron, Vaspurakan
Vaspurakan (, Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Vasbouragan'') was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeaster ...
, Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of K ...
, Khachen
The Principality of Khachen ( hy, Խաչենի իշխանություն, Khacheni ishkhanutyun) was a medieval Armenian principality on the territory of historical Artsakh (present-day Nagorno-Karabakh). The provinces of Artsakh and Utik we ...
and Syunik. Ter-Ghevondyan, Aram N. ''«Բագրատունիների Թագավորություն»'' (Bagratuni Kingdom). Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia
The ''Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia'' ( hy, Հայկական սովետական հանրագիտարան, ''Haykakan sovetakan hanragitaran''; ASE) publishing house was established in 1967 as a department of the Institute of History of the Armen ...
. vol. ii. Yerevan, Armenian SSR: Armenian Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia (NAS RA) ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետության գիտությունների ազգային ակադեմիա, ՀՀ ԳԱԱ, ''Hayastani Hanrapetut’yan gitut’yunneri az ...
, 1976, p. 202. During the reign of Ashot III
Ashot III ( hy, Աշոտ Գ) was a king of Armenia, ruling the medieval kingdom of Armenia from 952/53–77. Known as Ashot III the Merciful (Աշոտ Գ Ողորմած) and acknowledged by foreign rulers as the ''Shahanshah'' (king of kings) o ...
(952/53–77), Ani
Ani ( hy, Անի; grc-gre, Ἄνιον, ''Ánion''; la, Abnicum; tr, Ani) is a ruined medieval Armenian city now situated in Turkey's province of Kars, next to the closed border with Armenia.
Between 961 and 1045, it was the capital of the ...
became the kingdom's capital and grew into a thriving economic and cultural center.
The first half of the 11th century saw the decline and eventual collapse of the kingdom. The Byzantine emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar ...
() won a string of victories and annexed parts of southwestern Armenia; King Hovhannes-Smbat
Hovhannes-Smbat III was King of Ani (1020–1040). He succeeded his father Gagik I of Ani (989–1020) being the king's elder son and legal heir to the throne.
Life
His enthronement in 1020 was strongly opposed by his younger brother A ...
felt forced to cede his lands and in 1022 pledged that his kingdom would pass to the Byzantines following his death. However, after Hovhannes-Smbat's death in 1041, his successor, Gagik II
Gagik II ( hy, Գագիկ Բ; c. 1025 - May 5/November 24, 1079) was the last Armenian king of the Bagratuni dynasty. Known as Gagik II King of Ani (Ani being the capital of the kingdom at the time) he was enthroned as Gagik II and ruled for a bri ...
, refused to hand over Ani and continued resistance until 1045, when his kingdom, plagued by internal and external threats, was finally taken by Byzantine forces.
History
Background
 The weakening of the Sassanian Empire during the 7th century led to the rise of another regional power, the Muslim Arabs. The Umayyad Arabs had conquered vast swaths of territory in the Middle East and, turning north, began to periodically launch raids into Armenia territory in 640.
The weakening of the Sassanian Empire during the 7th century led to the rise of another regional power, the Muslim Arabs. The Umayyad Arabs had conquered vast swaths of territory in the Middle East and, turning north, began to periodically launch raids into Armenia territory in 640. Theodore Rshtuni
Theodore Rshtuni, also spelled Theodoros Ṛštuni (, ; AD 590–655 or 656), equated with Pasagnathes (Πασαγνάθης), the "''patrikios'' of the Armenians" from the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor,Curopalates
''Kouropalatēs'', Latinized as ''curopalates'' or ''curopalata'' ( el, κουροπαλάτης, from lat, cura palatii " he one incharge of the palace"). and Anglicized as curopalate, was a Byzantine court title, one of the highest from the ti ...
, signed a peace treaty with the Caliphate although the continuing war with the Arabs and Byzantines soon led to further destruction throughout Armenia. In 661, Armenian leaders agreed to submit under Muslim rule while the latter conceded to recognize Grigor Mamikonian from the powerful Mamikonian '' nakharar'' family as '' ishkhan'' (or prince) of Armenia. Known as "al-Arminiya" with its capital at Dvin, the province was headed by an '' ostikan'', or governor.
However, Umayyad rule in Armenia grew in cruelty in the early 8th century. Revolts against the Arabs spread throughout Armenia until 705, when under the pretext of meeting for negotiations, the Arab ostikan of Nakhichevan massacred almost all of the Armenian nobility. The Arabs attempted to conciliate with the Armenians but the levying of higher taxes, impoverishment of the country due to a lack of regional trade, and the Umayyads' preference of the Bagratuni family over the Mamikonians (other notable families included the Artsruni
The Artsruni ( hy, Արծրունի; also transliterated as Ardzruni) were an ancient noble (princely) family of Armenia.
Background and history
The Artsruni's claimed descent from Sennacherib, King of Assyria (705 BC–681 BC). Although ...
, Kamsarakan
Kamsarakan ( hy, Կամսարական) was an Armenian noble family that was an offshoot of the House of Karen, also known as the Karen-Pahlav. The Karens were one of the Seven Great Houses of Iran and were of Parthian origin.
In the Byzantine ...
, and Rshtuni
Rshtuni ( hy, Ռշտունի, also spelled Rashduni, Rshdouni, Reshdouni, Rashdouni, Rachdouni, Rachdoni, and Rushdoony) was an old Armenian noble house which ruled the region of Rshtuniq who were purportedly descendants of Rusas I of Urartu.
Th ...
) made this difficult to accomplish. Taking advantage of the overthrow of the Umayyads by the 'Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
, a second rebellion was conceived although it too was met with failure partly because of the frictional relationship between the Bagratuni and Mamikonian families. The rebellion's failure also resulted in the near disintegration of the Mamikonian house which lost most of the land it controlled (members of the Artstruni house were able to escape and settle in Vaspurakan
Vaspurakan (, Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Vasbouragan'') was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeaster ...
).
A third and final rebellion, stemming from similar grievances as the second, was launched in 774 under the leadership of Mushegh Mamikonian and with the support of other ''nakharars''. The Abbasid Arabs, however, marched into Armenia with an army of 30,000 men and decisively crushed the rebellion and its instigators at the battle of Bagrevand on April 24, 775, leaving a void for the sole largely intact family, the Bagratunis, to fill.
Rise of the Bagratids
The Bagratuni family had done its best to improve its relations with the Abbasid caliphs ever since they took power in 750. The Abbasids always treated the family's overtures with suspicion but by the early 770s, the Bagratunis had won them over and the relationship between the two drastically improved: the Bagratuni family members were soon viewed as leaders of the Armenians in the region. Following the end of the third rebellion, which the Bagratunis had wisely chosen not to participate in, and the dispersal of several of the princely houses, the family was left without any formidable rivals. Nevertheless, any immediate opportunities to take full control of the region was complicated by Arab immigration to Armenia and the caliph's appointment of '' emirs'' to rule in newly created administrative districts (''emirate
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalen ...
s''). But the number of Arabs residing in Armenia never grew in number to form a majority nor were the emirates fully subordinate to the Caliph. As historian George Bournoutian
George A. Bournoutian (; fa, جورج بورنوتیان, 25September 1943 – 22 August 2021) was an Iranian-American professor, historian, and author of Armenian descent. He was a Professor of History and the author of over 30 books, particu ...
observes, "this fragmentation of Arab authority provided the opportunity for the resurgence" of the Bagratuni family headed by Ashot Msaker (the "Meat-Eater").
Ashot began to annex the lands that formerly belonged to the Mamikonians and actively campaigned against the emirs as a sign of his allegiance to the Caliphate, who in 804 bestowed upon him the title of ''ishkhan''. Upon his death in 826, Ashot bequeathed his land to two of his sons: the eldest, Bagrat II Bagratuni Bagrat II Bagratuni ( hy, Բագրատ Բ Բագրատունի, Arabic: ''Buqrāṭ ibn Ashūṭ''; died after 851) was an Armenian noble of the Bagratid (Bagratuni) family and the presiding prince ("prince of princes") of Arab-ruled Armenia betw ...
received Taron and Sasun
Sason ( hy, Սասուն, translit=Sasun, ku, Qabilcewz, ar, قبل جوز; formerly known as Sasun or Sassoun) is a district and town in the Batman Province of Turkey. It was formerly part of the sanjak of Siirt, which was in Diyarbakır v ...
and inherited the prestigious title of ''ishkhanats ishkhan'', or prince of princes, whereas his brother, Smbat the Confessor, became the '' sparapet'' of Sper and Tayk.
The brothers, however, were unable to resolve their differences with one another nor able to form a unified front against the Muslims. A new Armenian rebellion against Arab rule broke out in 850 led by Bagrat and Ashot Artsruni of Vaspurakan but like previous rebellions, it failed: an Arab army led by the Turkic general Bugha al-Kabir
Bugha al-Kabir (), also known as Bugha al-Turki (), was a 9th-century Khazar general who served the Abbasid Caliphate.
He was of Khazar origin, and was acquired along with his sons as a military slave (''ghulam'') by al-Mu'tasim in 819/820.Gordo ...
captured Bagrat, Smbat, and other Armenian princes and brutally put down the rebellion.
Establishment of the kingdom
 Armenian fortunes were reversed in 867 with the accession of the Armenian emperor of Byzantium
Armenian fortunes were reversed in 867 with the accession of the Armenian emperor of Byzantium Basil I
Basil I, called the Macedonian ( el, Βασίλειος ὁ Μακεδών, ''Basíleios ō Makedṓn'', 811 – 29 August 886), was a Byzantine Emperor who reigned from 867 to 886. Born a lowly peasant in the theme of Macedonia, he rose in the ...
, whose successful military campaigns against the Arabs conclusively weakened Abbasid rule in Armenia. In 857, Smbat had been succeeded by his son Ashot I, who took a measured approach to gradually retake territories formerly held by the Arabs. He assumed the title prince of princes in 862 and appointed his brother Abas sparapet, as they began to push the Arabs out from their base in Tayk. His initial efforts to expel the ostikan of Arminiya failed, although this did not dissuade him in taking advantage of the Byzantine-Arab rivalry. Arakelyan, Babken N. ''«Աշոտ Ա»'' (''Ashot I''). Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia. vol. i. Yerevan: Armenian SSR: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1974, pp. 486-487.
Early on, he was courted by a Byzantium desperate to secure its eastern flank so as to direct its full strength against the Arabs; although Ashot avowed his loyalty to the empire, Byzantine leaders continued their long-standing demand that the Armenian Church
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
make religious concessions to the Eastern Orthodox Church. A synod of Armenian church leaders was convoked and a letter laden with equivocal wording sent to Constantinople was able to sustain a temporary agreement between the two churches. In any case, religious differences mattered little to the Byzantines in consideration of the menace the Arabs continued to pose. In 884, the Caliph Al-Mu'tamid
Abu’l-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Jaʿfar ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد بن جعفر; – 14 October 892), better known by his regnal name Al-Muʿtamid ʿalā ’llāh (, "Dependent on God"), was the Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate from 870 t ...
, reacting to the demands of Armenian princes and religious leaders and, more importantly, the security risks in allowing Armenia to fall under the Byzantine orbit, sent a crown to Ashot, recognizing him as king. This act was not lost on Basil who similarly sent a crown to Ashot. Ashot relocated his throne to the fortress-city of Bagaran and it was here where his coronation ceremony was held sometime in 884 or 885.
Thus, Ashot restored the Armenian monarchy and became Armenia's first king since 428. Toumanoff, Cyril.The Bagratids
" Iranica. Retrieved April 15, 2008. He secured the favor of both the Byzantines and Arabs but ultimately showed loyalty to Basil and chose to conclude an alliance with the Byzantines in 885. Ashot was not the sole Armenian prince of the region (other principalities existed in Syunik, Vaspurakan, and Taron) yet he commanded the full support of the other princes who recognized his authority in his becoming of king. With his status of king, his authority also carried over to the neighboring states of
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among ...
and several of the Arab emirates. Ashot's reign was brief and upon his death in 890, he was succeeded by his son Smbat I
Smbat I (; c. 850–912/14) was the second king of the medieval Kingdom of Armenia of the Bagratuni dynasty, and son of Ashot I. He is the father of Ashot II (known as Ashot Yerkat) and Abas I.
Rule
Smbat I was crowned king in 892 in Shirak ...
.
Smbat I
 Smbat I was crowned king in 892, following a brief attempt by his uncle Abas to disrupt his succession to the throne. Smbat continued his father's policy of maintaining cordial relations with Byzantium but he remained mindful of the Arabs' fears of the Armeno-Byzantine alliance. Speaking with the Arab ostikan
Smbat I was crowned king in 892, following a brief attempt by his uncle Abas to disrupt his succession to the throne. Smbat continued his father's policy of maintaining cordial relations with Byzantium but he remained mindful of the Arabs' fears of the Armeno-Byzantine alliance. Speaking with the Arab ostikan Muhammad Ibn Abi'l-Saj
Muhammad ibn Abi'l-Saj () also known as Muhammad al-Afshin (died 901), an Iranian appointed general of al-Mu'tadid, was the first Sajid amir of Azerbaijan, from 889 or 890 until his death. He was the son of Abi'l-Saj Devdad.
Early career
Like th ...
(Afshin), Smbat convinced him that the alliance would not only be for the dual benefit of Byzantium and Armenia but would also work to the economic favor of the Arabs. Smbat also achieved a major victory when on April 21, 892, he recaptured the historic city of Dvin from the Arabs.
Smbat's successes quickly came to a halt when Afshin decided that he could not countenance a powerful Armenia so close to his domains. He retook Dvin and managed to take Smbat's wife as a hostage until she was released in exchange for Smbat's son Mushegh, and his nephew, also named Smbat. The wars against Armenia continued even after Afshin's death in 901, when his brother Yusuf Ibn Abi'l-Saj became ostikan of Arminiya. While Yusuf's reign was not immediately hostile, Smbat committed a series of blunders which led to several of his allies to turn their backs on him: having sought to placate his eastern ally, Smbat of Syunik, by ceding to him Nakhichevan city, Smbat inadvertently drove Gagik Artsruni of Vaspurakan into Yusuf's arms since the city was a part of Gagik's domains. Yusuf took advantage of this feud by awarding Gagik a crown in 908, thus making him King Gagik I of Vaspurakan and creating an Armenian state opposed to the one led by Smbat.
As Yusuf began a new campaign against Smbat in conjunction with Gagik in 909, neither the Byzantines nor the Caliph sent aid to Smbat; several Armenian princes also chose to withhold their support. Those who did ally with Smbat were dealt brutally by Yusuf's powerful army: Smbat's son Mushegh, his nephew Smbat, and Grigor II of Western Syunik were all poisoned. Yusuf's army ravaged the rest of Armenia as it advanced towards Blue Fortress, where Smbat had taken refuge, and besieged it for some time. Smbat finally decided to surrender himself to Yusuf in 914 in hopes of ending the Arab onslaught; Yusuf, however, showed no compassion towards his prisoner as he tortured the Armenian king to death and put his headless body on display on a cross in Dvin.
Resurgence under Ashot Yerkat
Yusuf's invasion of Armenia had left the kingdom in ruins and this fact resonated among the Armenian princes who were left aghast in witnessing the Arab ostikan's brutality. Gagik I was especially shaken and he soon disavowed his loyalty to Yusuf and began to campaign against him. With Yusuf distracted by the resistance put up by his former ally, Smbat's sonAshot II
Ashot II the Iron ( hy, Աշոտ Բ; r. 914–929) was an Armenian king of the royal Bagratuni line. He was the son and successor of King Smbat I. His reign was filled with rebellions by vassals and pretenders to the throne, as well as foreign in ...
felt it appropriate to assume his father's throne. Ashot at once began to drive the Muslims out of his domains. Support for Ashot also arrived from the west: the Byzantine empress Zoe had watched the Arab invasion of Armenia unfold with consternation and so she ordered the Patriarch Nicholas Mystikos
Nicholas I Mystikos or Nicholas I Mysticus ( el, Νικόλαος Α΄ Μυστικός, ''Nikolaos I Mystikos''; 852 – 11 May 925) was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from March 901 to February 907 and from May 912 to his death ...
to write an official letter to the Armenian Catholicos
Catholicos, plural Catholicoi, is a title used for the head of certain churches in some Eastern Christian traditions. The title implies autocephaly and in some cases it is the title of the head of an autonomous church. The word comes from ancient ...
to form a new alliance with Armenia. The Catholicos responded amicably and in 914, Ashot accepted an invitation by Zoe to visit Constantinople. There, Ashot was well received, and a Byzantine force was created to assist Armenia in defeating the Arabs. The force, accompanying Ashot and led by the Domestic of the Schools Leo Phokas, moved out the next year and marched along Upper Euphrates, entering Taron with scant opposition from the Arabs.
Meanwhile, Yusuf's efforts to crush Gagik had failed miserably; instead, Yusuf turned his attention to Ashot and attempted to weaken his position by crowning Ashot's cousin, Ashot Shapuhyan, king of Armenia. Ashot Shapuhyan's and Yusuf's armies, though, were unable to stop the Byzantine advance, which stopped short of capturing Dvin due to the onset of winter. Nevertheless, the force had returned Ashot to a powerful position in Armenia and managed to inflict heavy casualties against the Arabs. This still left Ashot, the anti-king, in control in Dvin and civil war raged on from 918 to 920, when the pretender finally conceded defeat. Numerous other rebellions in Armenia also took place but Ashot was able to defeat each one of them. In 919, Yusuf had instigated a failed rebellion against the Caliph and was replaced by a far more well-disposed ostikan, Subuk Subuk (died 922?) was a ghulam who gained the governorship of Azerbaijan in 919 and held it for three years.
In 919, Subuk's master, the Sajid Yusuf Ibn Abu'l-Saj, was captured by forces of the caliph, with whom he had been at war. Acting in orde ...
. Subuk recognized Ashot as the legitimate ruler of Armenia and awarded him with the title of '' Shahanshah'', or "king of kings."
Ironically, the Byzantines were distressed with Ashot's close relations with the Arabs and dispatched a new force under the Armenian Domestic of the Schools John Kourkouas
John Kourkouas ( gr, Ἰωάννης Κουρκούας, Ioannes Kourkouas, ), also transliterated as Kurkuas or Curcuas, was one of the most important generals of the Byzantine Empire. His success in battles against the Muslim states in the Ea ...
to disrupt Ashot's position as king and to support the rebels fighting him. In 928, Kourkouas reached Dvin in an unsuccessful attempt to capture a city that was defended by both the Arabs and Ashot. In 923, the Caliph, facing troubles at home, released Yusuf, who traveled back to Armenia to unleash his fury against Armenia and especially Gagik I. He began demanding tribute from the Armenian rulers but faced considerable resistance by Ashot II. Time and again, Ashot was able to defeat and rout the Arab armies sent against him for several years. Finally, in 929, Yusuf died and an immense power struggle ensued between rival Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
and Kurdish families in Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
, thus reducing the Arab threat to Armenia. Byzantine emperor Romanos Lekapenos also turned his attention from the east to fight the Arabs in Syria. Ashot's efforts to preserve and defend the kingdom earned him the epithet "Yerkat", or Iron; he died in 929 and was succeeded by his brother, Abas I.
Stability under Abas
Abas I's reign was characterized with an unusual period of stability and prosperity that Armenia had not enjoyed for decades. His capital was based at the fortress-city ofKars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of K ...
and Abas achieved numerous successes on both the foreign and domestic fronts. In the same year that he became king, Abas traveled to Dvin, where he was able to convince the Arab governor there to release several Armenian hostages and turn over control of the pontifical palace back to Armenia. Conflict between the Arabs were minimal too, with the exception of a military defeat Abas suffered near the city of Vagharshapat. He was far less conciliatory towards the Byzantines, who had repeatedly demonstrated their unreliability as allies by attacking and annexing Armenian territories. Romanus of Byzantium was also more focused on fighting the Arab Hamdanids, leaving Abas virtually free to conduct his policies without foreign hindrance.
Another foreign threat that Abas steadfastly confronted was an invasion by king Ber of Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which ...
in 943: a new church had been completed in Kars under Abas' orders and prior to its consecration, Ber had appeared with an army along the river of the Araxes
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exc ...
, demanding that the new church be consecrated under Chalcedonian
Chalcedonian Christianity is the branch of Christianity that accepts and upholds theological and ecclesiological resolutions of the Council of Chalcedon, the Fourth Ecumenical Council, held in 451. Chalcedonian Christianity accepts the Christolo ...
rite. Abas refused to make any concessions and ambushed Ber's forces in a dawn assault. Several more skirmish
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They are usually deployed in a skirmish line, an ...
es took place, wherein Ber was finally captured by Abas' men. Abas took the king to his new church and told him that he would never see it again, blinding him and sending him back to Abkhazia. Abas died in 953, leaving his kingdom to his two sons, Ashot III and Mushegh.
Armenia's Golden Age
Ashot III
Ashot III ( hy, Աշոտ Գ) was a king of Armenia, ruling the medieval kingdom of Armenia from 952/53–77. Known as Ashot III the Merciful (Աշոտ Գ Ողորմած) and acknowledged by foreign rulers as the ''Shahanshah'' (king of kings) o ...
's official investiture as king of Armenia took place in 961, following the relocation of the Holy See of Cilicia from Vaspurakan to Argina, near the city of Ani
Ani ( hy, Անի; grc-gre, Ἄνιον, ''Ánion''; la, Abnicum; tr, Ani) is a ruined medieval Armenian city now situated in Turkey's province of Kars, next to the closed border with Armenia.
Between 961 and 1045, it was the capital of the ...
. In attendance were several contingents of the Armenian military, 40 bishops, the king of Caucasian Albania, as well as Catholicos Anania Mokatsi who crowned the king with the title of shahanshah. In that same year, Ashot had also relocated the capital from Kars to Ani. The Bagratuni kings had never chosen a city to settle in, alternating from Bagaran to Shirakavan
Shirakavan ( hy, Շիրակաւան); founded as Yerazgavors and later Yerazgavork, was a medieval Armenian city and one of the 13 historic capitals of Armenia, serving as a capital city between 890 and 929 during the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia.
...
to Kars; Kars never did reach a status where it could become a capital and Dvin was disregarded altogether, given its proximity to the hostile emirates. Ani's natural defenses were well suited Ashot's desire to secure an area which could withstand siege and fell on a trade route that passed from Dvin to Trebizond.
Owing to this trade route, the city quickly began to grow and became Bagratuni Armenia's chief political, cultural and economic center. Shops, markets, workshops, inns were established by the city's merchants and populace while the nakharar elite went on to sponsor the building of magnificent mansions and palaces. The construction was also complemented by the King Ashot's own philanthropy, including the building of the famed "Ashotashen" walls that were erected around Ani, monasteries, hospitals, schools, and almshouses (his wife Khosrovanuysh also founded the monastery complexes at Sanahin in 966 and Haghpat
Haghpat ( hy, Հաղպատ) is a village in the Lori Province of Armenia, located near the city of Alaverdi and the state border with Georgia.
It is notable for Haghpat Monastery, a religious complex founded in the 10th century and included in ...
in 976). Ashot's sponsorship of the construction of all these edifices earned him the nickname of "Voghormats", or "the Merciful." Ashot was also largely successful in foreign affairs. When a Byzantine army led by the Byzantine emperor John I Tzimiskes
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
entered Taron in 973, purportedly to avenge the death of his Domestic killed at the hands of the Arabs in Mosul, Ashot mobilized an 80,000 man army to meet and force its withdrawal. In the following year, he concluded an alliance with Tzimiskes and sent 10,000 Armenian troops to campaign with the emperor against the Muslim emirates in Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
and Mosul. Ashot also had unsuccessfully attempted to capture Dvin from the Shaddadid
The Shaddadids were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty. who ruled in various parts of Armenia and Arran from 951 to 1199 AD. They were established in Dvin. Through their long tenure in Armenia, they often intermarried with the Bagratuni royal fam ...
emir in 953; he had laid siege to it for quite some time but was forced to lift it after finding the city too well defended.
Sub-kingdoms
A new phenomenon that began under Ashot III's reign, and continued under his successors, was the establishment of sub-kingdoms throughout Bagratuni Armenia. Ashot III had sent his brother Mushegh I to rule in Kars (Vanand) and had allowed him to use the title of king. The administrative district of Dzoraget near Lake Sevan was given to Ashot's sonGurgen Gurgen or Gourgen (Armenian: Գուրգեն, Georgian: გურგენ) is an Armenian and Georgian masculine name of Middle Persian origin (''Gurgēn''), itself ultimately deriving from Old Iranian ''Vṛkaina-''. It may refer to:
Georgian m ...
, the progenitor of the Kyurikid line, in 966, who would later assume the title of king. The proliferation of so many kingdoms worked to the benefit of Armenia so long as the king in Ani remained strong and maintained his hegemony over other kings. Otherwise, the kings, as well their respective bishops who would claim the position of catholicos and formulate their own doctrines, would begin to test the limits of their autonomy.
Progress under Smbat and Gagik
This prosperous age which Armenia lived through continued unabated under the reign of Ashot's son and successor,Smbat II
Smbat II ( hy, Սմբատ Բ Տիեզերակալ, Smbat II Master of the Universe) reigned as King of Armenia from 977 to 989. He was of the Bagratuni line of kings, and the son of Ashot III, whom he succeeded.
Life
Smbat was crowned king on t ...
. Ani had grown so large by the time of Smbat's accession in 977, that a second set of walls, known as the Smbatashen walls, were ordered built by the new king.

Decline and Byzantine encroachment
The Byzantines had slowly been creeping eastward towards Armenia in the final decade of the 10th century. EmperorBasil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar ...
's numerous victories against the Arabs and internal Arab struggles helped clear a path towards the Caucasus. Constantinople's official policy was that no Christian ruler is equal to or independent of the Byzantine emperor, and even if it was at time masked with diplomatic compromises, the empire's ultimate goal was the complete annexation of the Armenian realms. By the middle of the 10th century, the Byzantine Empire lay along the full length of the western border of Armenia. Taron was the first Armenian region annexed by the Byzantine Empire. In a certain sense, the Byzantines considered the Bagratuni princes of Taron as their vassals, for they had consistently accepted titles, such as that of ''strategos'', and stipends from Constantinople. With the death of Ashot Bagratuni of Taron in 967 (not to be confused with Ashot III
Ashot III ( hy, Աշոտ Գ) was a king of Armenia, ruling the medieval kingdom of Armenia from 952/53–77. Known as Ashot III the Merciful (Աշոտ Գ Ողորմած) and acknowledged by foreign rulers as the ''Shahanshah'' (king of kings) o ...
), his sons Gregory and Bagrat were not able to withstand the pressure from the empire, which annexed their principality outright and converted it to a theme.
The Ardzruni
The Artsruni ( hy, Արծրունի; also transliterated as Ardzruni) were an ancient noble (princely) family of Armenia.
Background and history
The Artsruni's claimed descent from Sennacherib, King of Assyria (705 BC–681 BC). Although ...
kingdom of Vaspurakan was later annexed as well. In 1003, the last ruler of the kingdom Senekerim-Hovhannes
Senekerim-Hovhannes Artsruni ( hy, Սենեքերիմ-Հովհաննես Արծրունի), also known variously as Senekerim-John, Sennecherim or Sennacherib-John, known in Byzantine sources simply as Senachereim ( el, Σεναχηρείμ), was t ...
, son-in-law of King Gagik I of Ani, had brushed aside his nephews to become the sole king of Vaspurakan. His rule became even more precarious in the second decade of the 11th century with the plundering raids of various Turkmen groups. In 1016, Senekerim-Hovhannes thus offered Basil II the lands of Vaspurakan, including 72 fortresses and 3000-4000 villages, in exchange for a vast domain farther west on the Byzantine territory centered on the city of Sebastia to which he moved in 1021 together with his family and 14,000 retainers. Basil II had meanwhile already sent an army from the Balkans to Vaspurakan (which they also called Vasprakania, Asprakania, or Media) even before Senekerim-Hovhannes' offer and reduced it to another Byzantine theme with Van as regional capital. With the fall of the Ardzruni kingdom, Byzantine power was firmly established on the Armenian highlands, with only the Bagratuni and Eastern Syunik and Baghk kingdoms remaining independent.

Internal quarrels and fall
After the death of King Gagik I (in 1017 or 1020), the kingdom was split between his two sons,Hovhannes-Smbat
Hovhannes-Smbat III was King of Ani (1020–1040). He succeeded his father Gagik I of Ani (989–1020) being the king's elder son and legal heir to the throne.
Life
His enthronement in 1020 was strongly opposed by his younger brother A ...
who received the territory of Ani, and Ashot IV the Brave who kept a territory that should have included Dvin, but which he could not occupy because of its capture by the Shaddadid
The Shaddadids were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty. who ruled in various parts of Armenia and Arran from 951 to 1199 AD. They were established in Dvin. Through their long tenure in Armenia, they often intermarried with the Bagratuni royal fam ...
Abu'l-Aswar Shavur ibn Fadl
Abu'l-Aswar or Abu'l-Asvar Shavur ibn Fadl ibn Muhammad ibn Shaddad was a member of the Shaddadid dynasty. Between 1049 and 1067 he was the eighth Shaddadid ruler of Arran (today in western Azerbaijan) from Ganja. Prior to that, he ruled the ci ...
from Gandzak. The two brothers fought throughout their lives. In these tumultuous days, embroiled in territorial quarrels, the childless Hovhannes-Smbat sent the ''catholicos'' Petros Getadarts to Byzantium in order to negotiate a partial respite by leaving his kingdom to the empire after his death. Immediate results of this action were unknown, but after the death of the two brothers in 1040–41, the new Byzantine emperor and successor to Basil II claimed the kingdom of Bagratid Armenia. The son of Ashot, young Gagik II with the support of ''sparapet'' Vahram Pahlavouni and his followers, reigned only for a period of two years. Despite internal dissention led by pro-Byzantine overseer or stuard Sargis Haykazn, the Armenian king was able to repel a Turkmen attack. However, possibly with the persuasion of Sargis, he accepted the invitation of emperor Constantine IX
Constantine IX Monomachos ( grc-x-medieval, Κωνσταντῖνος Μονομάχος, translit=Kōnstantinos IX Monomachos; 1004 – 11 January 1055), reigned as Byzantine emperor from June 1042 to January 1055. Empress Zoë Porphyrogenita ...
to Constantinople, where he was obliged to cede his domain to the empire in exchange for a domain in Cappadocia. In 1044, the Byzantines twice invaded Ani but failed to conquer it. In view of this dire situation, catholicos Petros Getadarts, who governed Ani in the king's absence, surrendered Ani to the Byzantines in 1045. Ani was then annexed to the theme of Iberia
The theme of Iberia ( el, θέμα Ἰβηρίας) was an administrative and military unit – theme – within the Byzantine Empire carved by the Byzantine Emperors out of several Georgian lands in the 11th century. It was formed as a result ...
which was renamed "Iberia and Ani" or "Iberia and Armenia".
The Bagratid king of Kars, Gagik-Abas, still kept his throne even after 1064 when Ani fell to the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, but even he was constrained to cede his lands to the Byzantines and retreat to Anatolia, only to see Kars captured by the Turks in 1065. In Baghk and Eastern Syunik, only a few Armenian fortresses remained.
Culture and society
Government
The king of Bagratuni Armenia held unlimited powers and was the ultimate authority when it came to resolving questions on foreign and domestic affairs. The princes and nakharars were directly subordinate to the king and received and kept their lands only through his permission. Should certain nobles have disobeyed the king's orders, he would have the right to confiscate their lands and distribute them to other nobles. The concept of divine right, however, did not exist and insubordination by the nakharar elite could only be matched by the steadfastness of the king himself.Religion
Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
, but there were elements in Armenian society who also adhered to the Eastern Orthodox Church, the official religion of the Byzantine Empire. Byzantium repeatedly demanded for communion with the Armenian Church as prerequisite for sending aid to the Bagratunis but most attempts failed to bear any fruit.
In the mid-10th century, a new internal challenge to the authority of the Armenian Church and the kingdom arose when the Tondrakians
Tondrakians ( hy, Թոնդրակեաններ) were members of an anti-feudal, heretical Christian sect that flourished in medieval Armenia between the early 9th century and 11th century and centered on the district of Tondrak, north of Lake Va ...
experienced a revival. An anti-feudal and heretical Christian sect that had been crushed by the Arabs with the Armenian Church's support in the 9th century, the Tondrakian movement attracted many followers during this period. Ashot III had realized the danger the Tondrakians posed against the kingdom and this was of his reasons why he directly subjected the Church to him, gave it lands, and sponsored the construction of new monasteries and churches. The message of the Tondrakians, however, continued to spread and successive Armenian kings would work to suppress its expansion.
Economy
The Bagratuni kingdom was based on essentially two economies: one which was centered aroundagriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
based on feudalism and the other which was concentrated on mercantilism in towns and cities. Peasants (known as ''ramiks'') formed the lowest class in the economic stratum and largely busied themselves with raising livestock and farming
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. Many of them did not own land, and lived as tenants and worked as hired hands or even slaves on the lands owned by wealthy feudal magnates. Peasants were forced to pay heavy taxes to the government and the Armenian Apostolic Church in addition to their feudal lords. Most peasants remained poor and the massive tax burden they shouldered sometimes culminated in peasant uprisings which the state was forced to put down.
The Bagratuni kingdom did not mint any of its own coins, and used the currency found in Byzantium and the Arab Caliphate. The expanded trade between Byzantium and the Caliphate established several trades routes which ran across Armenia. The most important route began from Trebizond, in Byzantium, and from there it connected to the cities of Ani, Kars, and Artsn. The city of Kars allowed trade to move north, to ports on the Black Sea and to Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which ...
; other routes were connected to cities in Anatolia and Iran; and the main route leading from the Caliphate to Kievan Rus
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas o ...
was known as the "Great Armenian Highway." Ani did not lie along any previously important trade routes, but because of its size, power, and wealth it became an important trading hub. From Ani, Armenia exported textiles, metalwork, armor
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
, jewelry, horses, cattle, salt, wine, honey, timber, leather, and furs.Hewsen. ''Armenia'', p. 112. Its primary trading partners were the Byzantine Empire, the Arabs but also traded with Kievan Rus and Central Asia. Armenian-populated Dvin remained an important city on par with Ani, as evidenced in a vivid description by the Arab historian and geographer al-Mukadasi:
Dvin became famous throughout the Arab world for its wool and silk production and the export of pillows, rugs, curtains and covers. A village named Artashat near Dvin was so prominent a center for the production of Armenian cochineal
The Armenian cochineal (''Porphyrophora hamelii''), also known as the Ararat cochineal or Ararat scale, is a scale insect indigenous to the Ararat plain and Aras (Araks) River valley in the Armenian Highlands and in Turkey. It was formerly us ...
that it received the name ''vordan karmiri gyugh'' ("red-worm village") for the distinctive red dye that was derived from insects. Cochineal and other Armenian goods were extensively found throughout the caliphate and for their eminence were referred to by Arabs as "asfin al-Armani" ("Armenian products").

Demographics
 During the Bagratuni period, the great majority of the population of Armenia remained Armenian. 10th-century Arab sources attest that the cities of the Araxes valley remained predominantly Armenian and Christian despite Arab Muslim rule. In fact, the 10th-century Arab geographer
During the Bagratuni period, the great majority of the population of Armenia remained Armenian. 10th-century Arab sources attest that the cities of the Araxes valley remained predominantly Armenian and Christian despite Arab Muslim rule. In fact, the 10th-century Arab geographer Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
specified that Armenian was used in Dvin and Nakhichevan.Hovannisian. ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times, Volume I'', pp. 176–177. Regardless, there was a notable Muslim presence in certain regions of Armenia. For instance, the southern region of Aghdznik
Arzanene ( el, Ἀρζανηνή) or Aghdznik () was a historical region in the southwest of the ancient kingdom of Armenia. It was ruled by one of the four ''bdeashkhs'' (''bidakhsh'', ''vitaxa'') of Armenia, the highest ranking nobles below t ...
was heavily Arabized since earlier periods of Muslim dominance. On the north shore of Lake Van in the ninth and tenth centuries, there was also a considerable Muslim population that consisted of ethnic Arabs, and later Dailamites
The Daylamites or Dailamites (Middle Persian: ''Daylamīgān''; fa, دیلمیان ''Deylamiyān'') were an Iranian people inhabiting the Daylam—the mountainous regions of northern Iran on the southwest coast of the Caspian Sea, now compris ...
from Azerbaijan.
Art and literature
The Arab raids and invasion of Armenia as well as the devastation wrought upon the land during the Byzantine-Arab wars had largely stifled any expression of Armenian culture in fields such as historiography, literature andarchitecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
. These restrictions disappeared when the Bagratuni kingdom was established, ushering in a new golden age of Armenian culture.
The lack of a strong Arab presence saw a rise in the number of historians, who wrote and documented the relations between Armenia and other countries and described many events that took place from the seventh to eleventh centuries. Thanks to the patronage of the kings and nobles, monasteries became centers for the study and writing of literature throughout the kingdom. The monasteries of Haghpat
Haghpat ( hy, Հաղպատ) is a village in the Lori Province of Armenia, located near the city of Alaverdi and the state border with Georgia.
It is notable for Haghpat Monastery, a religious complex founded in the 10th century and included in ...
and Sanahin were well-known centers for higher learning. Notable figures in Armenian literature and philosophy during this period included the mystic Grigor Narekatsi
Grigor Narekatsi ( hy, Գրիգոր Նարեկացի; anglicized: Gregory of Narek) ( – 1003/1011) was an Armenian mystical and lyrical poet, monk, and theologian. He is venerated as a saint in the Armenian Apostolic and Catholic Churches an ...
and Grigor Magistros Grigor Magistros ( hy, Գրիգոր Մագիստրոս; "Gregory the ''magistros''"; ca. 990–1058) was an Armenian prince, linguist, scholar and public functionary. A layman of the princely Pahlavuni family that claimed descent from the dyna ...
.
The art of illuminated manuscripts and miniatures illustrations were also revived during this era. The relative period of peace between Byzantium and Armenia during the second half of the 10th century led to a great deal of interaction between Armenian artists and their Greek counterparts. Armenian manuscript authors tended either to stress the natural look of the human body in illustrations or to forgo it and instead concentrate on the aspect of decoration.
Armenian architecture during the Bagratuni era was especially prominent and "most of the surviving churches in present-day Armenia are from this period." The city of Ani, situated on the important trade intersection between the Byzantines, Arabs, and merchants of other countries, grew throughout the 9th century both commercially and culturally, earning renown for its "40 gates and 1,001 churches." The churches of this period expanded on 7th century designs; they were often steeper in elevation, introduced donor portraits in the round and incorporated ideas from Byzantine and Islamic architecture. Armenian churches were invariably built out of stone and had vaulted ceilings which supported a spherical dome.Kouymjian, Dickran/nowiki>.html" ;"title="rchitecture">
/nowiki>">rchitecture">
/nowiki>. Armenian Studies Program at
California State University, Fresno
California State University, Fresno (Fresno State) is a public university in Fresno, California. It is one of 23 campuses in the California State University system. The university had a fall 2020 enrollment of 25,341 students. It offers bache ...
. Accessed January 3, 2009.See also
*Bagrationi dynasty
The Bagrationi dynasty (; ) is a royal dynasty which reigned in Georgia from the Middle Ages until the early 19th century, being among the oldest extant Christian ruling dynasties in the world. In modern usage, the name of the dynasty is somet ...
* Bagratuni dynasty
The Bagratuni or Bagratid dynasty ( hy, Բագրատունի, ) was an Armenian royal dynasty which ruled the medieval Kingdom of Armenia from c. 885 until 1045. Originating as vassals of the Kingdom of Armenia of antiquity, they rose to beco ...
* Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of K ...
* Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
* Kingdom of Tashir-Dzoraget
The Kingdom of Tashir-Dzoraget ( hy, Տաշիր-Ձորագետի Թագավորություն ''Tashir-Dzorageti t'agavorut'yun''), alternatively known as the Kingdom of Lori or Kiurikian Kingdom by later historians, was a medieval Armenian kingd ...
* Kingdom of the Iberians
The Kingdom of the Iberians ( ka, ქართველთა სამეფო, tr) was a medieval Georgian monarchy under the Bagrationi dynasty which emerged circa 888 AD, succeeding the Principality of Iberia, in historical region of Tao ...
* Kingdom of Vaspurakan
The Kingdom of Vaspurakan (; also transliterated as Vasbouragan from Western Armenian) was a medieval Armenian kingdom centered on Lake Van, located in what is now eastern Turkey and northwestern Iran. It was named after Vaspurakan, a province ...
* Principality of Khachen
The Principality of Khachen ( hy, Խաչենի իշխանություն, Khacheni ishkhanutyun) was a medieval Armenian principality on the territory of historical Artsakh (present-day Nagorno-Karabakh). The provinces of Artsakh and Utik were ...
* Taron (historic Armenia)
References
Further reading
* Hovannisian, Richard G. (ed.) ''The Armenian People from Ancient to Modern Times, Volume I, The Dynastic Periods: From Antiquity to the Fourteenth Century''. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. . * Grousset, René. ''Histoire de l'Arménie: des origines à 1071''. Paris: Payot, 1947. * Ter-Ghevondyan, Aram N. ''Արաբական Ամիրայությունները Բագրատունյաց Հայաստանում'' (''The Arab Emirates in Bagratuni Armenia''). Yerevan, Armenian SSR: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1965. * Toumanoff, Cyril. "Armenia and Georgia." ''Cambridge Medieval History''. vol. vi: part 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1966. * Yuzbashyan, Karen. N. ''Армянские государства эпохи Багратидов и Византия, IX-XI вв'' (''The Armenian State in the Bagratuni and Byzantine Period, 9th-11th centuries''). Moscow, 1988.External links
Armenian History; Tacentral.com
On the architecture of Ani as well as general Armenian architecture.
Armenian Studies Program at
California State University, Fresno
California State University, Fresno (Fresno State) is a public university in Fresno, California. It is one of 23 campuses in the California State University system. The university had a fall 2020 enrollment of 25,341 students. It offers bache ...
.Notable societies of Europe, 900 A.D.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Armenia, Bagratid