Bacterial Vaginosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a disease of the
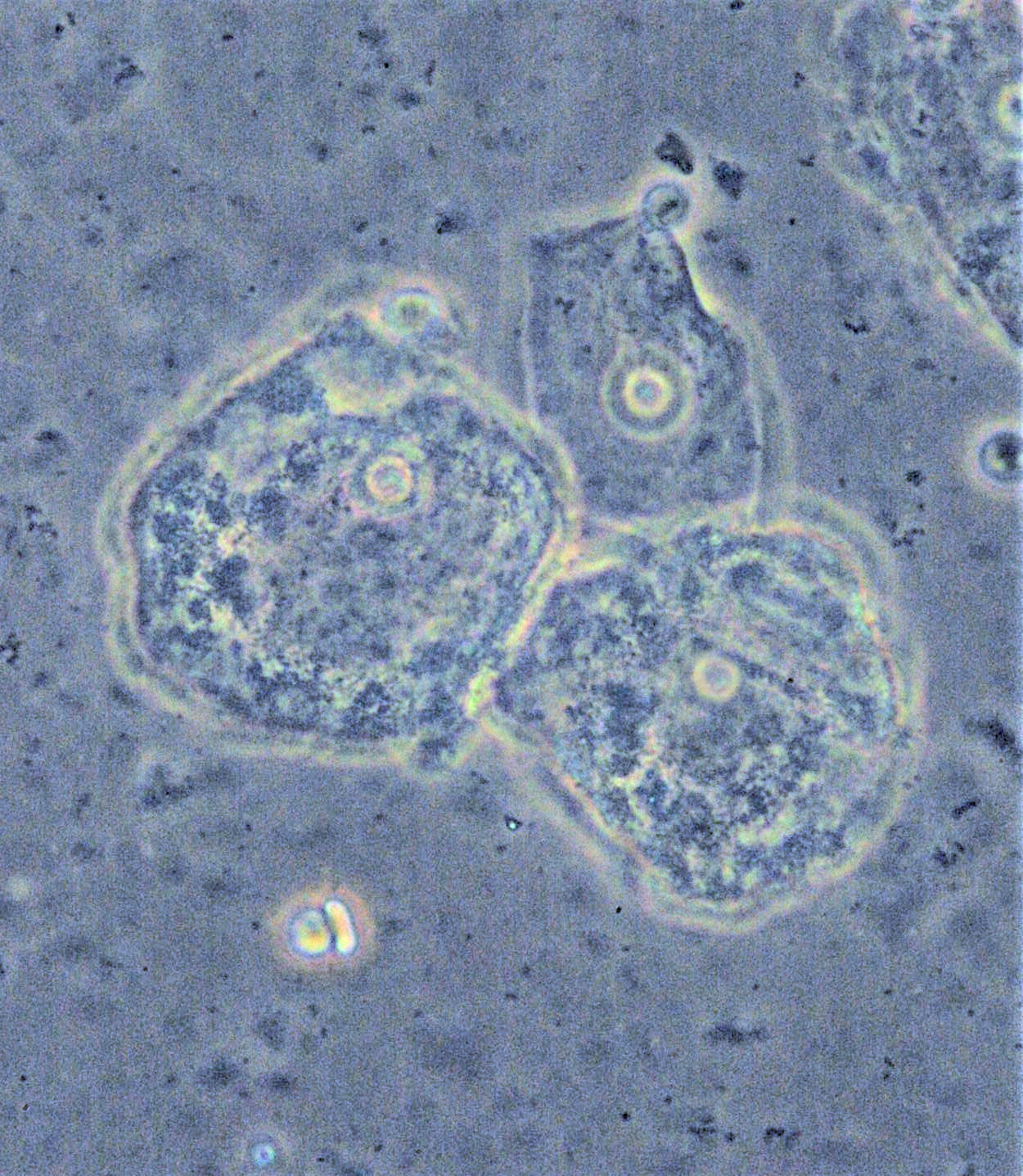

 To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*
To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*
vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, amou ...
that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination may occur. Itching is uncommon. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms. Having BV approximately doubles the risk of infection by a number of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women.
BV is caused by an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. There is a change in the most common type of bacteria and a hundred to thousand fold increase in total numbers of bacteria present. Typically, bacteria other than ''Lactobacilli'' become more common. Risk factors include douching
A douche is a device used to introduce a stream of water into the body for medical or hygienic reasons, or the stream of water itself. Douche usually refers to vaginal irrigation, the rinsing of the vagina, but it can also refer to the rinsing ...
, new or multiple sex partners
Multiple sex partners is the measure and incidence of engaging in sexual activities with two or more people within a specific time period. Sexual activity with MSP can happen simultaneously or serially. MSP includes sexual activity between people ...
, antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s, and using an intrauterine device, among others. However, it is not considered a sexually transmitted infection and, unlike gonorrhoea
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with ur ...
and chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several wee ...
, sexual partners are not treated. Diagnosis is suspected based on the symptoms, and may be verified by testing the vaginal discharge and finding a higher than normal vaginal pH, and large numbers of bacteria. BV is often confused with a vaginal yeast infection
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burn ...
or infection with ''Trichomonas''.
Usually treatment is with an antibiotic, such as clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infect ...
or metronidazole. These medications may also be used in the second or third trimesters of pregnancy. However, the condition often recurs following treatment. Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host i ...
s may help prevent re-occurrence. It is unclear if the use of probiotics or antibiotics affects pregnancy outcomes.
BV is the most common vaginal infection in women of reproductive age. The percentage of women affected at any given time varies between 5% and 70%. BV is most common in parts of Africa and least common in Asia and Europe. In the United States about 30% of women between the ages of 14 and 49 are affected. Rates vary considerably between ethnic groups within a country. While BV-like symptoms have been described for much of recorded history, the first clearly documented case occurred in 1894.
Signs and symptoms
Although about 50% of women with BV are asymptomatic, common symptoms include increasedvaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, amou ...
that usually smells like fish. The discharge is often white or gray in color. There may be burning with urination. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms.
The discharge coats the walls of the vagina, and is usually without significant irritation, pain, or erythema (redness), although mild itching can sometimes occur. By contrast, the normal vaginal discharge will vary in consistency and amount throughout the menstrual cycle and is at its clearest at ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
—about two weeks before the period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
starts. Some practitioners claim that BV can be asymptomatic in almost half of affected women, though others argue that this is often a misdiagnosis.
Complications
Although previously considered a mere nuisance infection, untreated bacterial vaginosis may cause increased susceptibility to sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, andpregnancy complication
Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal d ...
s.
It has been shown that HIV-infected women with bacterial vaginosis (BV) are more likely to transmit HIV to their sexual partners than those without BV.
There is evidence of an association between BV and increased rates of sexually transmitted infections such as HIV/AIDS. BV is associated with up to a six-fold increase in HIV shedding. BV is a risk factor for viral shedding and herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. BV may increase the risk of infection with or reactivation of human papillomavirus (HPV).
In addition, bacterial vaginosis as either pre-existing, or acquired, may increase the risk of pregnancy complications, most notably premature birth or miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
.
Pregnant women with BV have a higher risk of chorioamnionitis, miscarriage, preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, and postpartum endometritis. Women with BV who are treated with in vitro fertilization have a lower implantation rate and higher rates of early pregnancy loss.
Causes
Healthy vaginal microbiota consists of species that neither cause symptoms or infections, nor negatively affect pregnancy. It is dominated mainly by Lactobacillus species. BV is defined by the disequilibrium in the vaginal microbiota, with decline in the number of lactobacilli. While the infection involves a number of bacteria, it is believed that most infections start with '' Gardnerella vaginalis'' creating abiofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular p ...
, which allows other opportunistic bacteria to thrive.
One of the main risks for developing BV is douching
A douche is a device used to introduce a stream of water into the body for medical or hygienic reasons, or the stream of water itself. Douche usually refers to vaginal irrigation, the rinsing of the vagina, but it can also refer to the rinsing ...
, which alters the vaginal microbiota and predisposes women to developing BV. Douching is strongly discouraged by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and various medical authorities, for this and other reasons.
BV is a risk factor for pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be n ...
, HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and reproductive and obstetric disorders or negative outcomes. Although BV can be associated with sexual activity, there is no clear evidence of sexual transmission. It is possible for sexually inactive persons to develop bacterial vaginosis.
Also, subclinical iron deficiency may correlate with bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy. A longitudinal study published in February 2006, in the ''American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology'', showed a link between psychosocial stress and bacterial vaginosis persisted even when other risk factors were taken into account. Exposure to the spermicide nonoxynol-9 does not affect the risk of developing bacterial vaginosis.
Diagnosis


 To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*
To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a swab from inside the vagina should be obtained. These swabs can be tested for:
*Gram stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish ...
which shows the depletion of lactobacilli and overgrowth of '' Gardnerella vaginalis'' bacteria. Bacterial vaginosis is usually confirmed by a Gram stain of vaginal secretions.
* A characteristic "fishy" odor on wet mount
A microscope slide is a thin flat piece of glass, typically 75 by 26 mm (3 by 1 inches) and about 1 mm thick, used to hold objects for examination under a microscope. Typically the object is mounted (secured) on the slide, and then ...
. This test, called the ''whiff test'', is performed by adding a small amount of potassium hydroxide to a microscope slide
A microscope slide is a thin flat piece of glass, typically 75 by 26 mm (3 by 1 inches) and about 1 mm thick, used to hold objects for examination under a microscope. Typically the object is mounted (secured) on the slide, and then ...
containing the vaginal discharge. A characteristic fishy odor is considered a positive whiff test and is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis.
* Loss of acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
. To control bacterial growth, the vagina is normally slightly acidic with a pH of 3.8–4.2. A swab of the discharge is put onto litmus paper to check its acidity. A pH greater than 4.5 is considered alkaline and is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis.
* The presence of ''clue cell
Clue cells are epithelial cells of the vagina that get their distinctive stippled appearance by being covered with bacteria. The etymology behind the term "clue" cell derives from the original research article from Gardner and Dukes describing th ...
s'' on wet mount. Similar to the whiff test, the test for clue cells is performed by placing a drop of sodium chloride solution on a slide containing vaginal discharge. If present, clue cells can be visualized under a microscope. They are so-named because they give a clue to the reason behind the discharge. These are epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
cells that are coated with bacteria.
Differential diagnosis for bacterial vaginosis includes the following:
* Normal vaginal discharge.
* Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth ...
(thrush, or a yeast infection).
* Trichomoniasis, an infection caused by '' Trichomonas vaginalis''.
* Aerobic vaginitis
Aerobic vaginitis (AV) is a form of vaginitis first described by Donders et al. in 2002. It is characterized by a more or less severe disruption of the lactobacillary flora, along with inflammation, atrophy, and the presence of a predominantly a ...
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) defines STIs as "a variety of clinical syndromes and infections caused by pathogens that can be acquired and transmitted through sexual activity." But the CDC does not specifically identify BV as sexually transmitted infection.
Amsel criteria
In clinical practice BV can be diagnosed using the Amsel criteria: # Thin, white, yellow, homogeneous discharge #Clue cell
Clue cells are epithelial cells of the vagina that get their distinctive stippled appearance by being covered with bacteria. The etymology behind the term "clue" cell derives from the original research article from Gardner and Dukes describing th ...
s on microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of mic ...
# pH of vaginal fluid >4.5
# Release of a fishy odor on adding alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of ...
—10% potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution.
At least three of the four criteria should be present for a confirmed diagnosis.
A modification of the Amsel criteria accepts the presence of two instead of three factors and is considered equally diagnostic.
Gram stain
An alternative is to use a Gram-stained vaginal smear, with the Hay/Ison criteria or the Nugent criteria. The Hay/Ison criteria are defined as follows: * Grade 1 (Normal):Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically div ...
morphotypes predominate.
* Grade 2 (Intermediate): Some lactobacilli present, but ''Gardnerella'' or ''Mobiluncus'' morphotypes also present.
* Grade 3 (Bacterial Vaginosis): Predominantly ''Gardnerella'' and/or ''Mobiluncus'' morphotypes. Few or absent lactobacilli. (Hay et al., 1994)
''Gardnerella vaginalis'' is the main culprit in BV. ''Gardnerella vaginalis'' is a short, Gram-variable rod (coccobacillus). Hence, the presence of clue cells and gram variable coccobacilli are indicative or diagnostic of bacterial vaginosis.
Nugent score
The Nugent score is now rarely used by physicians due to the time it takes to read the slides and requires the use of a trained microscopist. A score of 0-10 is generated from combining three other scores. The scores are as follows: * 0–3 is considered negative for BV * 4–6 is considered intermediate * 7+ is considered indicative of BV. At least 10–20 high power (1000× oil immersion) fields are counted and an average determined. DNA hybridization testing with Affirm VPIII was compared to the Gram stain using the Nugent criteria. The Affirm VPIII test may be used for the rapid diagnosis of BV in symptomatic women but uses expensive proprietary equipment to read results, and does not detect other pathogens that cause BV, including ''Prevotella'' spp, ''Bacteroides'' spp, and ''Mobiluncus'' spp. The cervicovaginal microbiome measured using 16S rRNA sequencing has the capacity to increase throughput of the Nugent Score and has demonstrate to be directly comparable to clinical Nugent Score measurement.Screening
Screening during pregnancy is not recommended in the United States as of 2020.Prevention
Some steps suggested to lower the risk include: notdouching
A douche is a device used to introduce a stream of water into the body for medical or hygienic reasons, or the stream of water itself. Douche usually refers to vaginal irrigation, the rinsing of the vagina, but it can also refer to the rinsing ...
, avoiding sex, or limiting the number of sex partners.
One review concluded that probiotics may help prevent re-occurrence. Another review found that, while there is tentative evidence, it is not strong enough to recommend their use for this purpose.
Early evidence suggested that antibiotic treatment of male partners could re-establish the normal microbiota of the male urogenital tract and prevent the recurrence of infection. However, a 2016 Cochrane review found high-quality evidence that treating the sexual partners of women with bacterial vaginosis had no effect on symptoms, clinical outcomes, or recurrence in the affected women. It also found that such treatment may lead treated sexual partners to report increased adverse events.
Treatment
Antibiotics
Treatment is typically with theantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s metronidazole or clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infect ...
. They can be either given by mouth or applied inside the vagina with similar efficacy. About 10% to 15% of people, however, do not improve with the first course of antibiotics and recurrence rates of up to 80% have been documented. Recurrence rates are increased with sexual activity with the same pre-/posttreatment partner and inconsistent condom use although estrogen-containing contraceptives decrease recurrence. When clindamycin is given to pregnant women symptomatic with BV before 22 weeks of gestation the risk of pre-term birth before 37 weeks of gestation is lower.
Other antibiotics that may work include macrolides, lincosamide
Lincosamides are a class of antibiotics, which include lincomycin, clindamycin, and pirlimycin.
Structure
Lincosamides consist of a pyrrolidine ring linked to a pyranose moiety (methylthio-lincosamide) via an amide bond. Hydrolysis of lincosa ...
s, nitroimidazoles, and penicillins.
Bacterial vaginosis is not considered a sexually transmitted infection, and treatment of a male sexual partner of a woman with bacterial vaginosis is not recommended.
Probiotics
A 2009 Cochrane review found tentative but insufficient evidence for probiotics as a treatment for BV. A 2014 review reached the same conclusion. A 2013 review found some evidence supporting the use of probiotics during pregnancy. The preferred probiotics for BV are those containing high doses of lactobacilli (around 109 ) given in the vagina. Intravaginal administration is preferred to taking them by mouth. Prolonged repetitive courses of treatment appear to be more promising than short courses. The lack of effectiveness of commercially available ''Lactobacillus'' probiotics may be because most do not actually contain vaginal lactobacilli strains. LACTIN-V is a live biopharmaceutical medication containing the vaginally important ''Lactobacillus crispatus
''Lactobacillus crispatus'' is a common, rod-shaped species of genus ''Lactobacillus'' and is a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) producing beneficial microbiota species located in both the vagina, through vaginal discharge, and the vertebrate gastrointes ...
'' which is under development for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis and recurrent urinary tract infections. It has shown initial effectiveness in considerably reducing recurrence of bacterial vaginosis following antibiotic treatment. LACTIN-V is not yet Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved or commercially available.
Antiseptics
Topicalantiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putre ...
s, for example dequalinium
Dequalinium is a quaternary ammonium cation and bolaamphiphile commonly available as the dichloride salt. The bromide, iodide, acetate, and undecenoate salts are known as well. Dequalinium chloride is the active ingredient of several medications:
...
chloride, policresulen
Policresulen is the polycondensation product of ''meta''-cresolsulfonic acid and phenol. It is used as a topical hemostatic and antiseptic in infectious and other lesions of the mucous membranes, like gynecological infections, anal hemorrhoids ...
, hexetidine or povidone-iodine
Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may a ...
vaginal suppositories may be applied, if the risk of ascending infections is low (outside of pregnancy and in immunocompetent people without histories of upper genital tract infections). One study found that vaginal irrigations with hydrogen peroxide (3%) resulted in a slight improvement but this was much less than with the use of oral metronidazole. Intravaginal boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves ...
in conjunction with other medications may be helpful in the treatment of recurrent BV. TOL-463, a formulation of boric acid enhanced with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), is under development as an intravaginal medication for the treatment of BV and has shown preliminary effectiveness.
Epidemiology
BV is the most common infection of the vagina in women of reproductive age. The percentage of women affected at any given time varies between 5% and 70%. BV is most common in parts of Africa, and least common in Asia and Europe. In the United States, about 30% of those between the ages of 14 and 49 are affected. Rates vary considerably between ethnic groups within a country.References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bacterial Vaginosis Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organs Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Probiotics Mycoplasma