Busan–Geoje Bridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Busan–Geoje Fixed Link or Geoga Bridge () is an 8.2-kilometer (5.1-mi) bridge-tunnel
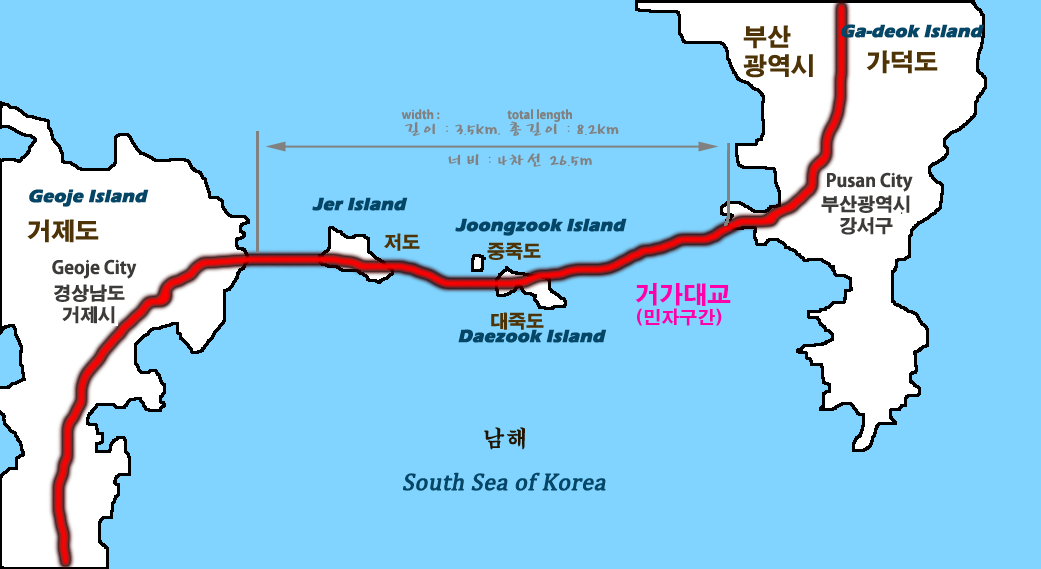 The route connects Busan, Korea's largest port city, to the shipbuilding industries and tourism destinations on Geoje Island. It replaces either a 210-minute journey by road or a 120-minute journey by ferry. The new route cuts travel time down to 40 minutes.
The fixed link starts on Geoje Island, crosses three
The route connects Busan, Korea's largest port city, to the shipbuilding industries and tourism destinations on Geoje Island. It replaces either a 210-minute journey by road or a 120-minute journey by ferry. The new route cuts travel time down to 40 minutes.
The fixed link starts on Geoje Island, crosses three
 When it opened, the tunnel became the world's deepest immersed roadway tunnel ( below mean water level) and the world's second-longest
When it opened, the tunnel became the world's deepest immersed roadway tunnel ( below mean water level) and the world's second-longest
Busan-Geoje Link
in the
fixed link
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somet ...
that connects the South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
n city of Busan
Busan (), officially Busan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's second list of cities in South Korea by population, most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.3 million as of 2024. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economi ...
to Geoje Island
Geojedo (), or Geoje Island, is the principal island of Geoje, South Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. It is joined to land by two bridges from nearby Tongyeong. Gohyeon is the largest town on the island.
Geojedo covers an area of , the second l ...
. The route opened on December 13, 2010 and shortens the travelling distance between Geoje Island and Busan by about 60 kilometers (37 mi). The new road has two lanes in each direction and carries National Road 58. Yeoward 2010, p. 26.
The fixed link opens Geoje Island to tourist-related development and saves US$300 million in costs related to traffic delays from the longer route. Cho 2009, p. 25.
Design and construction
The bridge was built under a public-private partnership. GK Fixed Link Corp, a consortium of seven Korean contractors, has a 40-year contract to build, operate and transfer the fixed link. The project is planned to cost US$1.8 billion. The government has provided only one-fourth of the cost; the rest is financed by the consortium to be repaid by tolls during the life of the contract. The lead contractor in the consortium is Daewoo Engineering & Construction, Co. Cho 2009, p. 24. Designers involved with the project includeCOWI A/S
COWI A/S is an international consulting group, specializing in engineering, environmental science and economics, with headquarters located in Lyngby, Denmark.
It has been involved in more than 50,000 projects in 175 countries and has approximat ...
(Denmark), Halcrow Group
Halcrow Group Limited was a British engineering consultancy company. It was one of the UK's largest consultancies, specialised in the provision of planning, design and management services for infrastructure development worldwide. With interests ...
(United Kingdom), Tunnel Engineering Consultants (Netherlands), Pihl and Son (Denmark), Arcadis US (USA), and Ben C. Gerwick (USA).
Route
 The route connects Busan, Korea's largest port city, to the shipbuilding industries and tourism destinations on Geoje Island. It replaces either a 210-minute journey by road or a 120-minute journey by ferry. The new route cuts travel time down to 40 minutes.
The fixed link starts on Geoje Island, crosses three
The route connects Busan, Korea's largest port city, to the shipbuilding industries and tourism destinations on Geoje Island. It replaces either a 210-minute journey by road or a 120-minute journey by ferry. The new route cuts travel time down to 40 minutes.
The fixed link starts on Geoje Island, crosses three islet
An islet ( ) is generally a small island. Definitions vary, and are not precise, but some suggest that an islet is a very small, often unnamed, island with little or no vegetation to support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/ ...
s (Jeo, Jungjuk and Daejuk) and ends on Gaduk Island. In addition to the tunnel between Daejuk and Gaduk islands, a bridge is used to cross each of the islets.
Bridge 1
The bridge between Jungjuk and Jeo islands includes acable-stayed bridge
A cable-stayed bridge has one or more ''towers'' (or ''pylons''), from which wire rope, cables support the bridge deck. A distinctive feature are the cables or wikt:stay#Etymology 3, stays, which run directly from the tower to the deck, norm ...
with a main span and side spans. This bridge provides of navigational clearance and has two diamond-shaped pylons. Fraser 2008.
Bridge 2
Between Geoje and Jeo islands, a bridge includes a three-pylon cable-stay bridge. This bridge has two mainspans of with side spans of . The pylons are tall and there is of clearance underneath the bridge.Tunnel
 When it opened, the tunnel became the world's deepest immersed roadway tunnel ( below mean water level) and the world's second-longest
When it opened, the tunnel became the world's deepest immersed roadway tunnel ( below mean water level) and the world's second-longest concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
immersed tunnel
An immersed tube (or immersed tunnel) is a kind of undersea tunnel composed of segments, constructed elsewhere and floated to the tunnel site to be sunk into place and then linked together. They are commonly used for road and rail crossings of r ...
, at . It is Korea's first immersed tunnel. Halcrow project video (wmv), 29 seconds. It became the second-deepest immersed vehicle tunnel after completion of the Marmaray
Marmaray () is a commuter rail line located in Istanbul, Turkey. The line runs from Halkalı, on the European side, to Gebze, on the Asian side, along the north shore of the Sea of Marmara. Mostly using the right-of-way of two existing com ...
(Bosphorus rail tunnel) in 2013. Rowson 2009.
The tunnel is made up of segments constructed in a dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
in Anjeon. Each segment was towed by barges and sunk into place. Cho 2009, p. 26.
Toll
(Since 2011)See also
*Transportation in South Korea
Transportation in South Korea is provided by extensive networks of railways, highways, bus routes, ferry services and air routes that traverse the country. South Korea is the third country in the world to operate a maglev train, which was an autom ...
* List of bridges in South Korea
This is a list of bridges and viaducts in South Korea, including those for pedestrians and vehicular traffic.
Historical and architectural interest bridges
Major road and railway bridges
This table presents the structures with spans greater ...
* List of bridge–tunnels
List of bridge–tunnels:
List
See also
*Transcontinental railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous rail transport, railroad trackage that crosses a continent, continental land mass and has terminals at d ...
* Lists of tunnels
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
* √òresund Bridge
The Øresund or Öresund Bridge is a combined List of road–rail bridges, railway and motorway cable-stayed bridge across the Øresund strait between Denmark and Sweden. It is the second longest bridge in Europe and combines both roadway and r ...
* Tokyo Bay Aqua-Line
The , also known as the Trans-Tokyo Bay Expressway, is an expressway that is mainly made up of a bridge–tunnel combination across Tokyo Bay in Japan. It connects the city of Kawasaki in Kanagawa Prefecture with the city of Kisarazu in Chiba P ...
* Undersea tunnel
An underwater tunnel is a tunnel which is partly or wholly constructed under the sea or a river. They are often used where building a bridge or operating a ferry link is unviable, or to provide competition or relief for existing bridges or ferry l ...
Notes and references
* * * * * *External links
Busan-Geoje Link
in the
Structurae
Structurae is an online database containing pictures and information about structural engineering, structural and civil engineering works, and their associated engineers, architects, and builders.
Overview
Structurae was founded in 1998 by Nico ...
database. Retrieved on 2009-02-22.
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Busan-Geoje Fixed Link
Bridges in Busan
Bridges in South Gyeongsang Province
Cable-stayed bridges in South Korea
Toll bridges in South Korea
Toll tunnels in Asia
Cross-sea bridges in Asia
Undersea tunnels in Asia
Immersed tube tunnels in Asia
Bridge–tunnels in Asia
Bridges completed in 2010
Tunnels completed in 2010
Infrastructure completed in 2010
2010 establishments in South Korea
Gangseo District, Busan
Geoje