Bus and Tag on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Bus and Tag is an "IBM standard for a computer peripheral interface", and was commonly used to connect their mainframe computers to peripheral devices such as line printers,
Bus and Tag is an "IBM standard for a computer peripheral interface", and was commonly used to connect their mainframe computers to peripheral devices such as line printers,  Bus and Tag cables are " daisy chained"; and one interface can attach up to eight peripheral control units. The last control unit in the chain must have a terminator plug. Each control unit can attach a maximum number of devices, "sixteen is a typical number." There is an architectural limit of 256 devices per channel, and initially a limitation of , later extended to , between the mainframe and the control unit. Bus and Tag channels handle data rates up to 4.5 MB per second. Only one device can transfer data at a time.
Bus and Tag architecture was also used by other computer manufacturers to attach IBM peripherals to their systems. It was later published by the US National Technical Information Service (NTIS) as FIPS PUB 60-1, ''I/O Channel Interface''.
Bus and Tag was introduced with
Bus and Tag cables are " daisy chained"; and one interface can attach up to eight peripheral control units. The last control unit in the chain must have a terminator plug. Each control unit can attach a maximum number of devices, "sixteen is a typical number." There is an architectural limit of 256 devices per channel, and initially a limitation of , later extended to , between the mainframe and the control unit. Bus and Tag channels handle data rates up to 4.5 MB per second. Only one device can transfer data at a time.
Bus and Tag architecture was also used by other computer manufacturers to attach IBM peripherals to their systems. It was later published by the US National Technical Information Service (NTIS) as FIPS PUB 60-1, ''I/O Channel Interface''.
Bus and Tag was introduced with
 Bus and Tag is an "IBM standard for a computer peripheral interface", and was commonly used to connect their mainframe computers to peripheral devices such as line printers,
Bus and Tag is an "IBM standard for a computer peripheral interface", and was commonly used to connect their mainframe computers to peripheral devices such as line printers, disk storage
Disk storage (also sometimes called drive storage) is a general category of storage mechanisms where data is recorded by various electronic, magnetic, optical, or mechanical changes to a surface layer of one or more rotating disks. A disk drive is ...
, magnetic tape drives and IBM 3270
The IBM 3270 is a family of block oriented display and printer computer terminals introduced by IBM in 1971
and normally used to communicate with IBM mainframes. The 3270 was the successor to the IBM 2260 display terminal. Due to the text ...
display controllers. The technology uses two sets of thick, multi-connector copper cables, one set, carrying data, called the ''bus'', and the other set, carrying control information, called the ''tag''.
System/360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems that was announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. It was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applica ...
in 1964, and was also used with System/370. With the introduction of serial, fiber optic ESCON in the 1990s Bus and Tag channels were re-christened "parallel channels", and were gradually superseded. "Parallel channels are not available on the newest mainframes and are slowly being displaced on older systems." Equipment is available to allow connection of older devices using Bus and Tag to mainframe FICON or ESCON channels.
Evolution
Originally the System/360 had two types of channel; the byte multiplexor channel and the selector channel. Since that time there have been several extension to the channel architecture. In 1970, IBM announced the 2880 block multiplexor channel for the360/85
The IBM System/360 Model 85 is a high-end member of the System/360 family of computers, with many advanced features, and was announced in January 1968 and first shipped in December 1969. IBM built only about 30 360/85 systems because of "a recess ...
and 360/195
The IBM System/360 Model 195 is a discontinued IBM computer introduced on August 20, 1969. The Model 195 was a reimplementation of the IBM System/360 Model 91 design using monolithic integrated circuits. It offers "an internal processing speed ab ...
, in support of the IBM 2305
IBM manufactured magnetic disk storage devices from 1956 to 2003, when it sold its hard disk drive business to Hitachi. Both the hard disk drive (HDD) and floppy disk drive (FDD) were invented by IBM and as such IBM's employees were responsible ...
fixed head disk. This channel supports disconnected command chaining, which allows a high speed device to free the channel when performing a requested operation, without terminating the channel program. This channel also has an optional two-byte interface feature (bus extension feature), which allows a second bus cable in order to operate at 3.0 MB/S. In the same year, IBM announced the System/370, which included block multiplexor channels.
As DASD became faster, the original channel protocols could not support the required transfer rates and the two-byte interface was too expensive. As a solution, IBM offered data streaming initially supporting 3.0 MB/s and eventually supporting 4.5 MB/s.
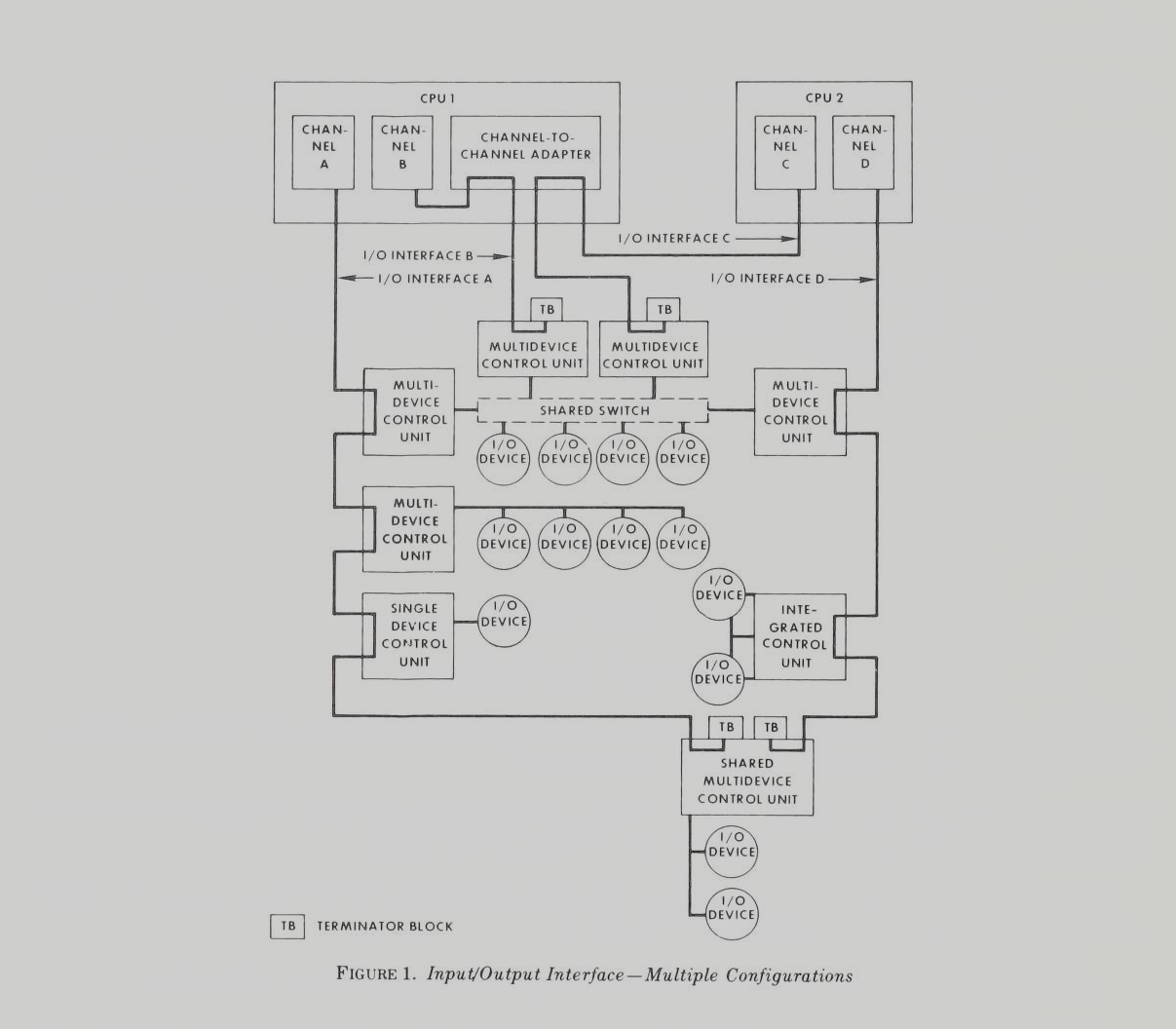
Example
The following schematic shows a complex system with two CPUs and multiple peripherals connected using bus and tag cabling.
Notes
References
External links
;OEMI : {{cite manual , title = IBM System/360 and System/370 I/O Interface Channel to Control Unit Original Equipment Manufacturers' Information , id = GA22-6974-4 , date = February 1988 , edition = Tenth , ref = {{sfnref, OEMI , url = http://bitsavers.org/pdf/ibm/370/channel/GA22-6974-9_360_370_IO_Interface_Channel_to_Control_Unit_OEM_Information_Feb88.pdf , accessdate = Sep 8, 2018 , publisher = IBM Corporation IBM System/360 mainframe line