Burma Campaign (1944–45) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Burma campaign was a series of battles fought in the British colony of
 After the fall of
After the fall of
 The Japanese did not renew their offensive after the monsoon ended. They installed a nominally independent Burmese government under
The Japanese did not renew their offensive after the monsoon ended. They installed a nominally independent Burmese government under
 About the same time that SEAC was established, the Japanese created
About the same time that SEAC was established, the Japanese created
 In October 1943 the Chinese 38th Division led by
In October 1943 the Chinese 38th Division led by
 In Arakan, Indian XV Corps under Lieutenant General
In Arakan, Indian XV Corps under Lieutenant General
 IV Corps, under Lieutenant-General
IV Corps, under Lieutenant-General  By the end of the first week in April, IV Corps had concentrated in the Imphal plain. The Japanese launched several offensives during the month, which were repulsed. At the start of May, Slim and Scoones began a counter-offensive against the Japanese 15th Division north of Imphal. Progress was slow, as movement was made difficult by monsoon rains and IV Corps was short of supplies.
Also at the beginning of April, the Japanese 31st Division under Lieutenant-General Kotoku Sato reached Kohima. Instead of isolating the small British garrison there and pressing on with his main force to Dimapur, Sato chose to capture the
By the end of the first week in April, IV Corps had concentrated in the Imphal plain. The Japanese launched several offensives during the month, which were repulsed. At the start of May, Slim and Scoones began a counter-offensive against the Japanese 15th Division north of Imphal. Progress was slow, as movement was made difficult by monsoon rains and IV Corps was short of supplies.
Also at the beginning of April, the Japanese 31st Division under Lieutenant-General Kotoku Sato reached Kohima. Instead of isolating the small British garrison there and pressing on with his main force to Dimapur, Sato chose to capture the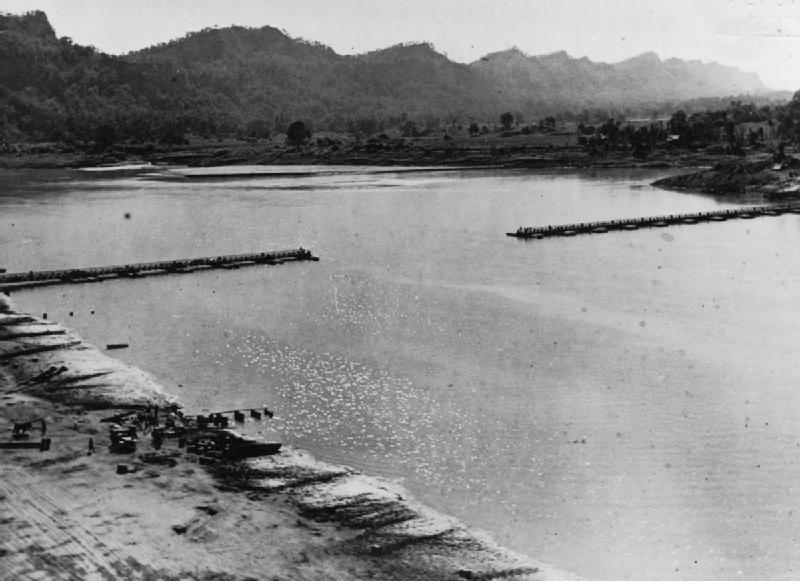  Mutaguchi (and Kawabe) continued to order renewed attacks. 33rd Division and Yamamoto Force made repeated efforts, but by the end of June they had suffered so many casualties both from battle and disease that they were unable to make any progress. The Imphal operation was finally broken off early in July, and the Japanese retreated painfully to the Chindwin River.
It was the greatest defeat to that date in Japanese history. They had suffered 50–60,000 dead,Despatch "Operations in Assam and Burma from 23RD June 1944 to 12TH November 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 3 March 1951, p. 1711. and 100,000 or more casualties.Despatch "Operations in Burma 12th November 1944 to 15th August 1945", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 6 April 1951, p. 1885. Most of these losses were the result of disease, malnutrition and exhaustion. The Allies suffered 12,500 casualties, including 2,269 killed.Despatch "Operations in Burma and North East India 16th November 1943 to 22nd June 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 13 March 1951, p. 1361. Mutaguchi had already relieved all his divisions' commanders, and was himself subsequently relieved of command.
During the monsoon from August to November, Fourteenth Army pursued the Japanese to the Chindwin River. While the
Mutaguchi (and Kawabe) continued to order renewed attacks. 33rd Division and Yamamoto Force made repeated efforts, but by the end of June they had suffered so many casualties both from battle and disease that they were unable to make any progress. The Imphal operation was finally broken off early in July, and the Japanese retreated painfully to the Chindwin River.
It was the greatest defeat to that date in Japanese history. They had suffered 50–60,000 dead,Despatch "Operations in Assam and Burma from 23RD June 1944 to 12TH November 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 3 March 1951, p. 1711. and 100,000 or more casualties.Despatch "Operations in Burma 12th November 1944 to 15th August 1945", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 6 April 1951, p. 1885. Most of these losses were the result of disease, malnutrition and exhaustion. The Allies suffered 12,500 casualties, including 2,269 killed.Despatch "Operations in Burma and North East India 16th November 1943 to 22nd June 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 13 March 1951, p. 1361. Mutaguchi had already relieved all his divisions' commanders, and was himself subsequently relieved of command.
During the monsoon from August to November, Fourteenth Army pursued the Japanese to the Chindwin River. While the
 The Allies launched a series of offensive operations into Burma during late 1944 and the first half of 1945. The command on the front was rearranged in November 1944. Eleventh Army Group HQ was replaced by
The Allies launched a series of offensive operations into Burma during late 1944 and the first half of 1945. The command on the front was rearranged in November 1944. Eleventh Army Group HQ was replaced by
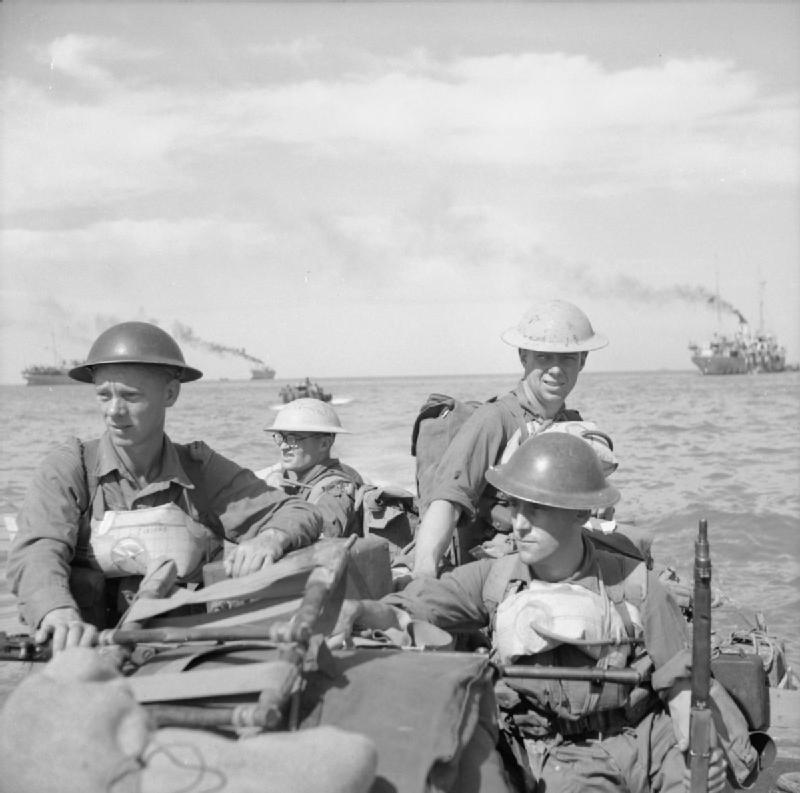 In Arakan, XV Corps resumed its advance on Akyab Island for the third year in succession. This time the Japanese were far weaker, and retreated before the steady Allied advance. They evacuated Akyab Island on 31 December 1944. It was occupied by XV Corps without resistance on 3 January 1945 as part of Operation Talon, the amphibious landing at Akyab.
Landing craft had now reached the theatre, and XV Corps launched amphibious attacks on the
In Arakan, XV Corps resumed its advance on Akyab Island for the third year in succession. This time the Japanese were far weaker, and retreated before the steady Allied advance. They evacuated Akyab Island on 31 December 1944. It was occupied by XV Corps without resistance on 3 January 1945 as part of Operation Talon, the amphibious landing at Akyab.
Landing craft had now reached the theatre, and XV Corps launched amphibious attacks on the
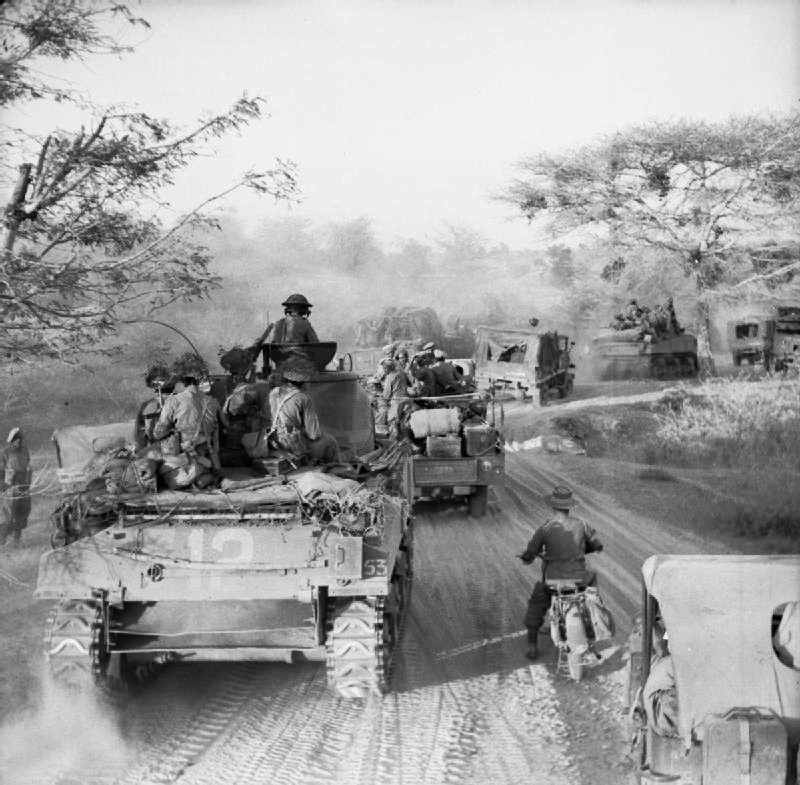 During January and February 1945, XXXIII Corps seized crossings over the Irrawaddy River near Mandalay. There was heavy fighting, which attracted Japanese reserves and fixed their attention. Late in February, the 7th Indian Division leading IV Corps, seized crossings at Nyaungu near Pakokku. 17th Indian Division and
During January and February 1945, XXXIII Corps seized crossings over the Irrawaddy River near Mandalay. There was heavy fighting, which attracted Japanese reserves and fixed their attention. Late in February, the 7th Indian Division leading IV Corps, seized crossings at Nyaungu near Pakokku. 17th Indian Division and
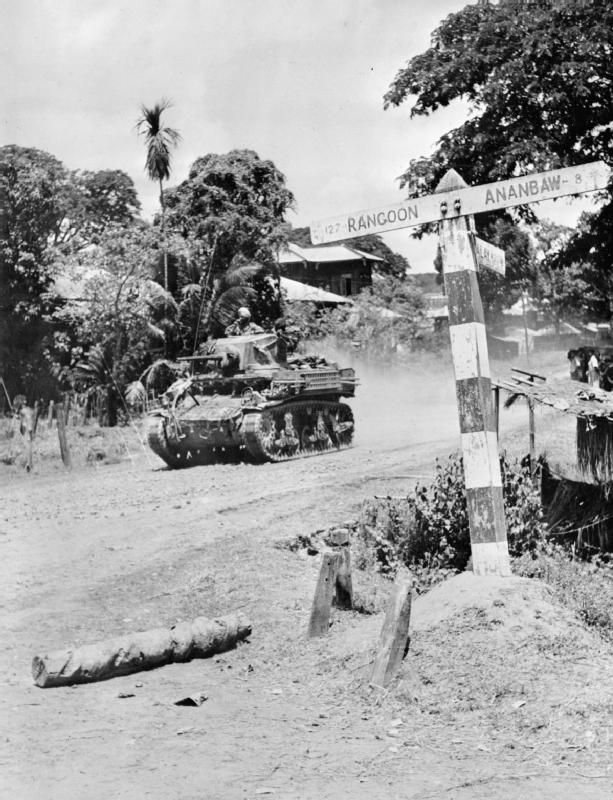 Though the Allied force had advanced successfully into central Burma, it was vital to capture the port of Rangoon before the monsoon to avoid a logistics crisis. In the spring of 1945, the other factor in the race for Rangoon was the years of preparation by the liaison organisation,
Though the Allied force had advanced successfully into central Burma, it was vital to capture the port of Rangoon before the monsoon to avoid a logistics crisis. In the spring of 1945, the other factor in the race for Rangoon was the years of preparation by the liaison organisation,
 The original conception of the plan to re-take Burma had envisaged XV Corps making an amphibious assault on Rangoon well before Fourteenth Army reached the capital, in order to ease supply problems. This operation, codenamed Operation Dracula, was postponed several times as the necessary landing craft were retained in Europe and finally dropped in favour of an attack on
The original conception of the plan to re-take Burma had envisaged XV Corps making an amphibious assault on Rangoon well before Fourteenth Army reached the capital, in order to ease supply problems. This operation, codenamed Operation Dracula, was postponed several times as the necessary landing craft were retained in Europe and finally dropped in favour of an attack on
 After the Allies captured Rangoon, a new Twelfth Army headquarters was created from XXXIII Corps HQ to take control of the formations which were to remain in Burma.
The Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army, after withdrawing from Arakan and resisting XXXIII Corps in the Irrawaddy valley, retreated into the
After the Allies captured Rangoon, a new Twelfth Army headquarters was created from XXXIII Corps HQ to take control of the formations which were to remain in Burma.
The Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army, after withdrawing from Arakan and resisting XXXIII Corps in the Irrawaddy valley, retreated into the
Burma Star Association
Imphal and Kohima, Britain's Greatest Battles, National Army Museum
Burma Summary
The Kohima Museum
A museum dedicated to the
Royal Engineers Museum
Engineers in the Burma Campaigns
Engineers with the Chindits
Canadian War Museum: Newspaper Articles on the Burma Campaigns, 1941–1945
World War II animated campaign maps
see this html version
* "Operations in Burma from 12 November 1944 to 15 August 1945" official despatch by Lieutenant General Sir
Siam goes to war
Canadians in south east Asia
{{Coord missing, Myanmar 1940s in Burma 1942 in Burma 1943 in Burma 1944 in Burma 1945 in Burma Battles and operations of World War II involving Nepal Campaigns of World War II Campaigns, operations and battles of World War II involving the United Kingdom Indian National Army Military history of India during World War II Military history of Thailand during World War II South-East Asian theatre of World War II World War II operations and battles of the Pacific theatre
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
. It was part of the South-East Asian theatre of World War II
The South-East Asian Theatre of World War II consisted of the campaigns of the Pacific War in the Philippines, Thailand, Indonesia, Indochina, Burma, India, Malaya and Singapore between 1941 to 1945.
Japan attacked British and American terri ...
and primarily involved forces of the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
(mainly from the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
and the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
, with support from the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
) against the invading forces of the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
. Imperial Japan was supported by the Thai
Thai or THAI may refer to:
* Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia
** Thai people, the dominant ethnic group of Thailand
** Thai language, a Tai-Kadai language spoken mainly in and around Thailand
*** Thai script
*** Thai (Unicode block ...
Phayap Army, as well as two collaborationist independence movements and armies. The first of these was the Burma Independence Army
The Burma Independence Army (BIA), was a collaborationist and revolutionary army that fought for the end of British rule in Burma by assisting the Japanese in their conquest of the country in 1942 during World War II. It was the first post-c ...
, which spearheaded the initial attacks against the country. The Indian National Army
The Indian National Army (INA; ''Azad Hind Fauj'' ; 'Free Indian Army') was a collaborationist armed force formed by Indian collaborators and Imperial Japan on 1 September 1942 in Southeast Asia during World War II. Its aim was to secure In ...
, led by Subhas C. Bose of the Free India movement, also collaborated with Imperial Japan, especially during Operation U-Go
The U Go offensive, or Operation C (ウ号作戦 ''U Gō sakusen''), was the Japanese offensive launched in March 1944 against forces of the British Empire in the northeast Indian regions of Manipur and the Naga Hills (then administered as part ...
in 1944. Nominally independent puppet states were established in the conquered areas and some territories were annexed by Thailand. In 1942 and 1943, the international Allied force in British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
launched several failed offensives to retake lost territories. Fighting intensified in 1944, and British Empire forces peaked at around 1 million land and air forces. These forces were drawn primarily from British India, with British Army forces (equivalent to eight regular infantry divisions and six tank regiments), 100,000 East and West African colonial troops, and smaller numbers of land and air forces from several other Dominions and Colonies. These additional forces allowed the Allied recapture of Burma in 1945.
The campaign had a number of notable features. The geographical characteristics of the region meant that weather, disease and terrain had a major effect on operations. The lack of transport infrastructure placed an emphasis on military engineering and air transport to move and supply troops, and evacuate wounded. The campaign was also politically complex, with the British, the United States and the Chinese all having different strategic priorities. It was also the only land campaign by the Western Allies in the Pacific Theatre which proceeded continuously from the start of hostilities to the end of the war. This was due to its geographical location. By extending from South East Asia to India, its area included some lands which the British lost at the outset of the war, but also included areas of India wherein the Japanese advance was eventually stopped. The climate of the region is dominated by the seasonal monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
rains, which allowed effective campaigning for only just over half of each year. This, together with other factors such as famine and disorder in British India and the priority given by the Allies to the defeat of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, prolonged the campaign and divided it into four phases: the Japanese invasion, which led to the expulsion of British, Indian and Chinese forces in 1942; failed attempts by the Allies to mount offensives into Burma, from late 1942 to early 1944; the 1944 Japanese invasion of India, which ultimately failed following the battles of Imphal and Kohima
Kohima (; Angami Naga: ''Kewhira'' ()), is the capital of the Northeastern Indian state of Nagaland. With a resident population of almost 100,000, it is the second largest city in the state. Originally known as ''Kewhira'', Kohima was founded ...
; and finally the successful Allied offensive which liberated Burma from late 1944 to mid-1945.
The campaign was also strongly affected from the political atmosphere which erupted in the South-East Asian regions occupied by Japan, who pursued the Pan-Asianist
Satellite photograph of Asia in orthographic projection.
Pan-Asianism (''also known as Asianism or Greater Asianism'') is an ideology aimed at creating a political and economic unity among Asian peoples. Various theories and movements of Pan-Asi ...
policy of a "Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
The , also known as the GEACPS, was a concept that was developed in the Empire of Japan and propagated to Asian populations which were occupied by it from 1931 to 1945, and which officially aimed at creating a self-sufficient bloc of Asian peo ...
". These led to a Japanese-sponsored revolution during the initial invasion and the establishment of the State of Burma
The State of Burma (; ja, ビルマ国, ''Biruma-koku'') was a List of World War II puppet states#Japan, Japanese puppet state created by Japan in 1943 during the Japanese occupation of Burma in World War II.
Background
During the early stage ...
, in which the Provisional Government of Free India
The Provisional Government of Free India (''Ārzī Hukūmat-e-Āzād Hind'') or, more simply, ''Azad Hind'', was an Indian provisional government established in Japanese occupied Singapore during World War II. It was created in October 1943 ...
, with its Indian National Army
The Indian National Army (INA; ''Azad Hind Fauj'' ; 'Free Indian Army') was a collaborationist armed force formed by Indian collaborators and Imperial Japan on 1 September 1942 in Southeast Asia during World War II. Its aim was to secure In ...
, was headquartered. The dominating attitude of the Japanese militarist who commanded the army stationed in the country, which ultimately doomed the co-prosperity sphere as a whole, led to local hopes for real Independence fade and the war-time established Burma National Army
The Burma Independence Army (BIA), was a collaborationist and revolutionary army that fought for the end of British rule in Burma by assisting the Japanese in their conquest of the country in 1942 during World War II. It was the first post-c ...
revolted in 1945. On the Allied side, political relations were mixed for much of the war. The China Burma India Theater
China Burma India Theater (CBI) was the United States military designation during World War II for the China and Southeast Asian or India–Burma (IBT) theaters. Operational command of Allied forces (including U.S. forces) in the CBI was officia ...
American-trained Chinese X Force
X Force was the name given to the portion of the National Revolutionary Army's Chinese Expeditionary Force that retreated from Burma into India in 1942. Chiang Kai-shek sent troops into Burma from Yunnan in 1942 to assist the British in hold ...
led to cooperation between the two countries, but the clashing strategies proposed by " Vinegar Joe" Stilwell and Chinese Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
would lead to Stilwell's eventual removal from his position as American Commander of the theater. On the other hand, China–India relations
China–India relations ( zh, 中国-印度关系; hi, भारत-चीन संबंध), also called Sino-Indian relations or Indo–Chinese relations, are the bilateral relations between the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and the ...
were positive from the cooperative Burma Road
The Burma Road () was a road linking Burma (now known as Myanmar) with southwest China. Its terminals were Kunming, Yunnan, and Lashio, Burma. It was built while Burma was a British colony to convey supplies to China during the Second Sino-J ...
, built to reach the Chinese Y Force
Y Force was the South East Asia Command designation given to Chinese National Revolutionary Army forces that re-entered Burma from Yunnan in 1944 as one of the Allies fighting in Burma Campaign of World War II. It consisted of 175,000 troops divide ...
and the Chinese war effort inside of China, as well as from the heroic missions over the extremely dangerous air route over the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
, nicknamed "The Hump
The Hump was the name given by Allied pilots in the Second World War to the eastern end of the Himalayan Mountains over which they flew military transport aircraft from India to China to resupply the Chinese war effort of Chiang Kai-shek and t ...
". The campaign would have a great impact on the independence struggle of Burma and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
in the post-war years.
Japanese conquest of Burma
Japanese objectives in Burma were initially limited to the capture ofRangoon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
(now known as Yangon), the capital and principal seaport. This would close the overland supply line to China and provide a strategic bulwark to defend Japanese gains in British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. U ...
and the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
. The Japanese Fifteenth Army
The was an army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. It was involved in the invasion of Burma in December 1941 and served in that country for most of its war service.
History
The Japanese 15th Army was formed on November 9, 1941 ...
under Lieutenant General Shōjirō Iida
was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II.
Biography
Iida was a native of Yamaguchi prefecture and a graduate of the 20th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1908 and the 27th class of the Army Staff College in Decemb ...
, initially consisting of only two infantry divisions, moved into northern Thailand (which had signed a treaty of friendship with Japan), and launched an attack over jungle-clad mountain ranges into the southern Burmese province of Tenasserim (now Tanintharyi Region
Tanintharyi Region ( my, တနင်္သာရီတိုင်းဒေသကြီး, ; Mon: or ; ms, Tanah Sari; formerly Tenasserim Division and subsequently Tanintharyi Division, th, ตะนาวศรี, RTGS: ''Tanao Si'', ...
) in January 1942.
In the face of the Japanese advances, huge numbers of Indians, Anglo-Indians, and Anglo-Burmese fled Burma, around 600,000 by the autumn of 1942, which was until then the largest mass migration in history. Perhaps 80,000 of those in flight would die from starvation, exhaustion and disease. Some of the worst massacres in Burma during World War II would be perpetrated not by the Japanese but by Burmese gangs linked to the Burma Independence Army.
The Japanese successfully attacked over the Kawkareik
Kawkareik (; my, ကော့ကရိတ်, ; ksw, ဒူဖျၢ်ယၢ်ဝ့ၢ်ဖိ) also spelled as Kawkarike, is a town in Karen State, Myanmar. It is the capital of Kawkaraik District and Kawkaraik Township.
History
The K ...
Pass and captured the port of Moulmein
Mawlamyine (also spelled Mawlamyaing; , ; th, เมาะลำเลิง ; mnw, မတ်မလီု, ), formerly Moulmein, is the fourth-largest city in Myanmar (Burma), ''World Gazetteer'' south east of Yangon and south of Thaton, at th ...
at the mouth of the Salween River
, ''Mae Nam Salawin'' (
, name_etymology =
, image = Sweet_View_of_Salween_River_in_Tang_Yan_Township,_Shan_State,_Myanmar.jpg
, image_size =
, image_caption = Salween River in Shan State, Myanmar
, map ...
after overcoming stiff resistance. They then advanced northwards, outflanking successive British defensive positions. Troops of the 17th Indian Infantry Division
The 17th Infantry Division is a formation of the Indian Army. Indian Army during World War II, During World War II, it had the distinction of being continually in combat during the three-year-long Burma Campaign (except for brief periods of refit ...
tried to retreat over the Sittaung River
The Sittaung River ( my, စစ်တောင်းမြစ် ; formerly, the Sittang or Sittounghttps://unstats.un.org/unsd/geoinfo/UNGEGN/docs/8th-uncsgn-docs/inf/8th_UNCSGN_econf.94_INF.75.pdf ) is a river in south central Myanmar in Bago ...
, but Japanese parties reached the vital bridge before they did. On 22 February, the bridge was demolished to prevent its capture, a decision that has since been extremely contentious.
The loss of two brigades of 17th Indian Division meant that Rangoon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
could not be defended. General Archibald Wavell, the commander-in-chief of the American-British-Dutch-Australian Command
The American-British-Dutch-Australian (ABDA) Command, or ABDACOM, was a short-lived, supreme command for all Allied forces in South East Asia in early 1942, during the Pacific War in World War II. The command consists of the forces of Australia ...
, nevertheless ordered Rangoon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
to be held as he was expecting substantial reinforcements from the Middle East. Although some units arrived, counterattacks failed and the new commander of Burma Army (General Harold Alexander
Harold Rupert Leofric George Alexander, 1st Earl Alexander of Tunis, (10 December 1891 – 16 June 1969) was a senior British Army officer who served with distinction in both the First and the Second World War and, afterwards, as Governor Ge ...
), ordered the city to be evacuated on 7 March after its port and oil refinery had been destroyed. The remnants of Burma Army broke out to the north, narrowly escaping encirclement.
On the eastern part of the front, in the Battle of Yunnan-Burma Road
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
, the Chinese 200th Division
The 200th Division ({{zh, t=第200師, s=第200师, w=Ti 200 Shih, p=Dì 200 Shī) was the first mechanised division in the National Revolutionary Army. It was created in 1938 by General Du Yuming, who was also its first commander. Its first act ...
held up the Japanese for a time around Toungoo
Taungoo (, ''Tauñngu myoú''; ; also spelled Toungoo) is a district-level city in the Bago Region of Myanmar, 220 km from Yangon, towards the north-eastern end of the division, with mountain ranges to the east and west. The main industr ...
, but after its fall the road was open for motorised troops of the Japanese 56th Division to shatter the Chinese Sixth Army to the east in the Karenni States
The Karenni States, also known as Red Karen States, was the name formerly given to the states inhabited mainly by the Red Karen, in the area of present-day Kayah State, eastern Burma. They were located south of the Federated Shan States and ea ...
and advance northward through the Shan States
The Shan States (1885–1948) were a collection of minor Shan kingdoms called ''muang'' whose rulers bore the title ''saopha'' in British Burma. They were analogous to the princely states of British India.
The term "Shan States" was firs ...
to capture Lashio
Lashio ( ; Shan: ) is the largest town in northern Shan State, Myanmar, about north-east of Mandalay. It is situated on a low mountain spur overlooking the valley of the Yaw River. Loi Leng, the highest mountain of the Shan Hills, is located ...
, outflanking the Allied defensive lines and cutting off the Chinese armies from Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
. With the effective collapse of the entire defensive line, there was little choice left other than an overland retreat to India or to Yunnan.
Japanese advance to the Indian frontier
 After the fall of
After the fall of Rangoon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
in March 1942, the Allies attempted to make a stand in the north of the country (Upper Burma), having been reinforced by a Chinese Expeditionary Force
The Chinese Expeditionary Force () was an expeditionary unit of Republic of China (1912-1949), China's National Revolutionary Army that was dispatched to British rule in Burma, Burma and British Raj, India in support of the Allies of World War II ...
. The Japanese had also been reinforced by two divisions made available by the capture of Singapore and defeated both the newly organised Burma Corps
The Burma Corps ('Burcorps') was an Army Corps of the Indian Army during the Second World War. It was formed in Prome, Burma, on 19 March 1942, took part in the retreat through Burma, and was disbanded on arrival in India in May 1942.
History
Bu ...
and the Chinese force. The Allies were also faced with growing numbers of Burmese insurgents and the civil administration broke down in the areas they still held. With their forces cut off from almost all sources of supply, the Allied commanders finally decided to evacuate their forces from Burma. On 16 April, in Burma, 7,000 British soldiers were encircled by the Japanese 33rd Division during the Battle of Yenangyaung
The Battle of Yenangyaung () was fought in Burma, now Myanmar, during the Burma Campaign in World War II. The battle of Yenaungyaung was fought in the vicinity of Yenangyaung and its oil fields.
Background
After the Japanese captured Rangoon in ...
and rescued by the Chinese 38th Division.
The retreat was conducted in very difficult circumstances. Starving refugees, disorganised stragglers, and the sick and wounded clogged the primitive roads and tracks leading to India. Burma Corps managed to make it most of the way to Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the fo ...
, in Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of Myanm ...
in India, just before the monsoon broke in May 1942, having lost most of their equipment and transport. There, they found themselves living out in the open under torrential rains in extremely unhealthy circumstances. The army and civil authorities in India were very slow to respond to the needs of the troops and civilian refugees.
Due to lack of communication, when the British retreated from Burma, almost none of the Chinese knew about the retreat. Realising that they could not win without British support, some of the X Force
X Force was the name given to the portion of the National Revolutionary Army's Chinese Expeditionary Force that retreated from Burma into India in 1942. Chiang Kai-shek sent troops into Burma from Yunnan in 1942 to assist the British in hold ...
committed by Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
made a hasty and disorganised retreat to India, where they were put under the command of the American General Joseph Stilwell
Joseph Warren "Vinegar Joe" Stilwell (March 19, 1883 – October 12, 1946) was a United States Army general who served in the China Burma India Theater during World War II. An early American popular hero of the war for leading a column walking ...
. After recuperating they were re-equipped and retrained by American instructors. The rest of the Chinese troops tried to return to Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
through remote mountainous forests and of these, at least half died.
Thai army enters Burma
In accordance with the Thai military alliance with Japan that was signed on 21 December 1941, on 21 March, the Thais and Japanese also agreed thatKarenni State
Kayah State ( my, ကယားပြည်နယ်, formerly Karenni State) is a state of Myanmar. Situated in eastern Myanmar, it is bounded on the north by Shan State, on the east by Thailand's Mae Hong Son Province, and on the south and wes ...
and Shan State
Shan State ( my, ရှမ်းပြည်နယ်, ; shn, မိူင်းတႆး, italics=no) also known by the Endonym and exonym, endonyms Shanland, Muang Tai, and Tailong, is a administrative divisions of Myanmar, state of Myanmar. ...
s were to be under Thai control. The rest of Burma was to be under Japanese control.
The leading elements of the Thai Phayap Army under General J. R. Seriroengrit crossed the border into the Shan States on 10 May 1942. Three Thai infantry division and one cavalry division, spearheaded by armoured reconnaissance groups and supported by the Royal Thai Air Force
"Royal Thai Air Force March"
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 9 April 1937 (Royal Thai Air Force Day)
, equipment =
, equipment_label =
, battles ...
, engaged the retreating Chinese 93rd Division. Kengtung
th , เชียงตุง
, other_name = Kyaingtong
, settlement_type = Town
, imagesize =
, image_caption =
, pushpin_map = Myanmar
, pushpin_label_position = left
, ...
, the main objective, was captured on 27 May. On 12 July, General Phin Choonhavan
Field Marshal Phin Choonhavan ( th, ผิน ชุณหะวัณ; ; August 14, 1891 – 26 January
1973) was a Thai military leader and Deputy Prime Minister of Thailand. Phin was a leader of several coups against the government, most nota ...
, who would become the Thai military governor of the occupied Shan State later in the war, ordered the 3rd Division of the Phayap Army from the southern part of the Shan State to occupy Karenni State and expel the Chinese 55th Division from Loikaw
Loikaw (, ) is the capital of Kayah State in Myanmar. It is located in the Karen Hills area, near the State's northern tip, just above an embayment on the Pilu River. The inhabitants are mostly Kayah (Karenni). Myanmar's largest hydropower plant ...
. The Chinese troops could not retreat because the routes to Yunnan were controlled by Axis forces and many Chinese soldiers were captured. The Thais remained in control of the Shan States for the remainder of the war. Their troops suffered from supply shortages and disease, but were not subjected to Allied attacks.
Allied setbacks, 1942–1943
 The Japanese did not renew their offensive after the monsoon ended. They installed a nominally independent Burmese government under
The Japanese did not renew their offensive after the monsoon ended. They installed a nominally independent Burmese government under Ba Maw
Ba Maw ( my, ဘမော်, ; 8 February 1893 – 29 May 1977) was a Burmese lawyer and political leader, active during the interwar and World War II periods. Dr. Ba Maw is a descendant of the Mon Dynasty. He was the first Burma Premier ...
, and reformed the Burma Independence Army
The Burma Independence Army (BIA), was a collaborationist and revolutionary army that fought for the end of British rule in Burma by assisting the Japanese in their conquest of the country in 1942 during World War II. It was the first post-c ...
on a more regular basis as the Burma National Army under General Aung San
Aung San (, ; 13 February 191519 July 1947) was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he was assassinated just six months before his go ...
. In practice, both government and army were strictly controlled by the Japanese authorities.
On the Allied side, operations in Burma over the remainder of 1942 and in 1943 were a study of military frustration. Britain could only maintain three active campaigns, and immediate offensives in both the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and Far East proved impossible through lack of resources. The Middle East was accorded priority, being closer to home and in accordance with the "Germany First" policy in London and Washington.
The Allied build up was also hampered by the disordered state of Eastern India at the time. There were violent "Quit India" protests in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
and Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
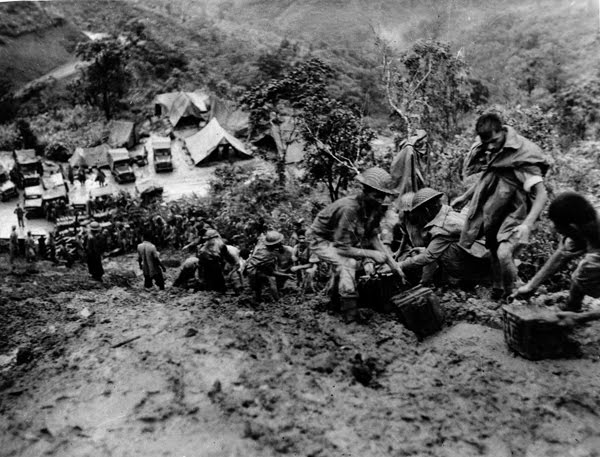
, which required large numbers of British troops to suppress. There was also a disastrous famine in Bengal, which may have led to 3 million deaths through starvation, disease and exposure. In such conditions of chaos, it was difficult to improve the inadequate lines of communication to the front line in Assam or make use of local industries for the war effort. Efforts to improve the training of Allied troops took time and in forward areas poor morale and endemic disease combined to reduce the strength and effectiveness of the fighting units.
Nevertheless, the Allies mounted two operations during the 1942–1943 dry season. The first was a small offensive into the coastal Arakan Province
Rakhine State (; , , ; formerly known as Arakan State) is a state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region to the east, the Bay of Benga ...
of Burma. The Indian Eastern Army intended to reoccupy the Mayu peninsula and Akyab Island, which had an important airfield. A division advanced to Donbaik, only a few miles from the end of the peninsula but was halted by a small but well entrenched Japanese force. At this stage of the war, the Allies lacked the means and tactical ability to overcome strongly constructed Japanese bunkers. Repeated British and Indian attacks failed with heavy casualties. Japanese reinforcements arrived from Central Burma and crossed rivers and mountain ranges which the Allies had declared to be impassable, to hit the Allies' exposed left flank and overrun several units. The exhausted British were unable to hold any defensive lines and were forced to abandon much equipment and fall back almost to the Indian frontier.
The second action was controversial. Under the command of Brigadier Orde Wingate
Major General Orde Charles Wingate, (26 February 1903 – 24 March 1944) was a senior British Army officer known for his creation of the Chindit deep-penetration missions in Japanese-held territory during the Burma Campaign of the Second World ...
, a long-range penetration unit known as the Chindits
The Chindits, officially as Long Range Penetration Groups, were special operations units of the British and Indian armies which saw action in 1943–1944 during the Burma Campaign of World War II.
The British Army Brigadier Orde Wingate form ...
infiltrated through the Japanese front lines and marched deep into Burma, with the initial aim of cutting the main north-south railway in Burma in an operation codenamed Operation ''Longcloth''. Some 3,000 men entered Burma in many columns. They damaged communications of the Japanese in northern Burma, cutting the railway for possibly two weeks but they suffered heavy casualties. Though the results were questioned the operation was used to propaganda effect, particularly to insist that British and Indian soldiers could live, move and fight as effectively as the Japanese in the jungle, doing much to restore morale among Allied troops.
The balance shifts 1943–1944
From December 1943 to November 1944 the strategic balance of the Burma campaign shifted decisively. Improvements in Allied leadership, training and logistics, together with greater firepower and growing Allied air superiority, gave Allied forces a confidence they had previously lacked. In the Arakan,XV Indian Corps
The XV Corps was a corps-sized formation of the British Indian Army, which was formed in India during the Second World War. It took part in the Burma Campaign and was disbanded after the end of the war. While part of the British Indian Army, it ...
withstood, and then broke, a Japanese counterstrike, while the Japanese invasion of India resulted in unbearably heavy losses and the ejection of the Japanese back beyond the Chindwin River ,
, image = Homalin aerial.jpg
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Chindwin at Homalin. The smaller, meandering Uyu River can be seen joining the Chindwin.
, map = Irrawaddyrivermap.jpg
, map_size =
, map_alt =
, map_caption ...
.

Allied plans
In August 1943, the Allies createdSouth East Asia Command
South East Asia Command (SEAC) was the body set up to be in overall charge of Allies of World War II, Allied operations in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II, South-East Asian Theatre during the World War II, Second World War.
Histo ...
(SEAC), a new combined command responsible for the South-East Asian Theatre, under Admiral Lord Louis Mountbatten
Louis Francis Albert Victor Nicholas Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (25 June 1900 – 27 August 1979) was a British naval officer, colonial administrator and close relative of the British royal family. Mountbatten, who was of Germa ...
. The training, equipment, health and morale of Allied troops under British Fourteenth Army
The British Fourteenth Army was a multi-national force comprising units from Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries during the World War II, Second World War. As well as British Army units, many of its units were from the British Indian ...
under Lieutenant General William Slim
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
was improving, as was the capacity of the lines of communication in North-eastern India. An innovation was the extensive use of aircraft to transport and supply troops.
SEAC had to accommodate several rival plans, many of which had to be dropped for lack of resources. Amphibious landings on the Andaman Islands (Operation "Pigstick") and in Arakan were abandoned when the landing craft assigned were recalled to Europe in preparation for the Normandy Landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
.
The major effort was intended to be by American-trained Chinese troops of Northern Combat Area Command
The Northern Combat Area Command (NCAC) was a subcommand of the Allied South East Asia Command (SEAC) during World War II. It controlled Allied ground operations in northern Burma. For most of its existence, NCAC was commanded by United States ...
(NCAC) under General Joseph Stilwell
Joseph Warren "Vinegar Joe" Stilwell (March 19, 1883 – October 12, 1946) was a United States Army general who served in the China Burma India Theater during World War II. An early American popular hero of the war for leading a column walking ...
, to cover the construction of the Ledo Road
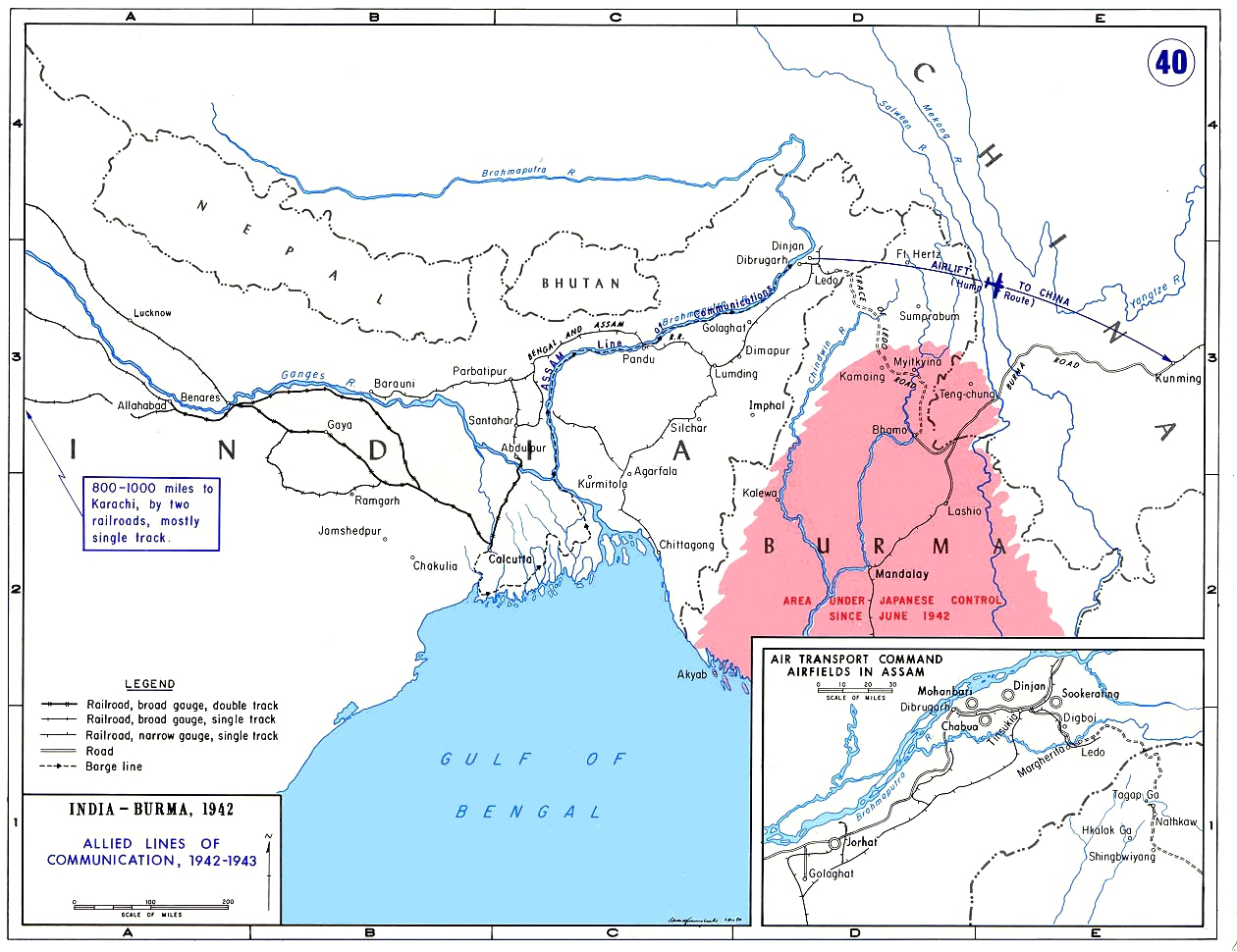
The Ledo Road (from Ledo, Assam, India to Kunming, Yunnan, China) was an overland connection between India and China, built during World War II to enable the Western Allies to deliver supplies to China and aid the war effort against Japan. ...
. Orde Wingate had controversially gained approval for a greatly expanded Chindit force, which was given the task of assisting Stilwell by disrupting the Japanese lines of supply to the northern front. Chiang Kai-shek had also agreed reluctantly to mount an offensive from the Yunnan.
Under British Fourteenth Army, the Indian XV Corps 15th Corps, Fifteenth Corps, or XV Corps may refer to:
*XV Corps (British India)
* XV Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army prior to and during World War I
* 15th Army Corps (Russian Empire), a unit in World War I
*XV Royal Bav ...
prepared to renew the advance in Arakan province, while IV Corps launched a tentative advance from Imphal in the centre of the long front to distract Japanese attention from the other offensives.
Japanese plans
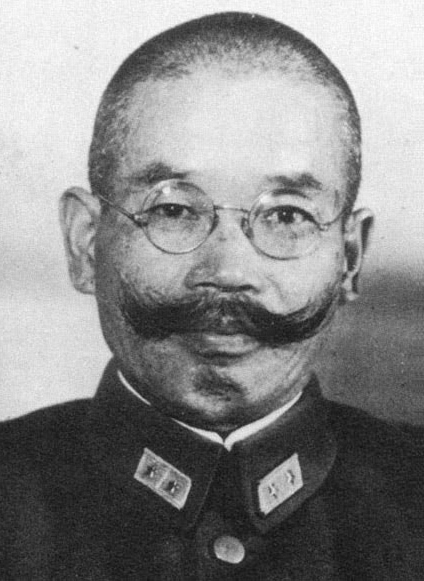
 About the same time that SEAC was established, the Japanese created
About the same time that SEAC was established, the Japanese created Burma Area Army
The was a field army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
History
The Japanese Burma Area Army was formed on 27 March 1943, under the control of the Southern Expeditionary Army Group as a garrison force to defend the nominally-ind ...
under Lieutenant General Masakazu Kawabe
was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army. He held important commands in the Imperial Japanese Army during the Second Sino-Japanese War, and during World War II in the Burma Campaign and defense of the Japanese homeland late in the war. He was ...
, which took under command the Fifteenth Army and the newly formed Twenty-Eighth Army.
The new commander of Fifteenth Army, Lieutenant General Renya Mutaguchi
was a Japanese military officer, lieutenant general in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II and field commander of the IJA forces during the Battle of Imphal.
Biography
Mutaguchi was a native of Saga Prefecture. He graduated from the 2 ...
was keen to mount an offensive against India. Burma Area Army originally quashed this idea, but found that their superiors at Southern Expeditionary Army Group
''Nanpō gun''
, image = 1938 terauchi hisaichi.jpg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = Japanese General Count Terauchi Hisaichi, right, commanding officer of the Southern Expeditiona ...
HQ in Singapore were keen on it. When the staff at Southern Expeditionary Army were persuaded that the plan was inherently risky, they in turn found that Imperial General Headquarters
The was part of the Supreme War Council and was established in 1893 to coordinate efforts between the Imperial Japanese Army and Imperial Japanese Navy during wartime. In terms of function, it was approximately equivalent to the United States ...
in Tokyo was in favour of Mutaguchi's plan.
The Japanese were influenced to an unknown degree by Subhas Chandra Bose
Subhas Chandra Bose ( ; 23 January 1897 – 18 August 1945
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*) was an Indian nationalist whose defiance of British authority in India made him a hero among Indians, but his wartime alliances with Nazi Germany and Imperia ...
, commander of the Indian National Army
The Indian National Army (INA; ''Azad Hind Fauj'' ; 'Free Indian Army') was a collaborationist armed force formed by Indian collaborators and Imperial Japan on 1 September 1942 in Southeast Asia during World War II. Its aim was to secure In ...
. This was composed largely of Indian soldiers who had been captured in Malaya or Singapore, and Indians (Tamils
The Tamil people, also known as Tamilar ( ta, தமிழர், Tamiḻar, translit-std=ISO, in the singular or ta, தமிழர்கள், Tamiḻarkaḷ, translit-std=ISO, label=none, in the plural), or simply Tamils (), are a Drav ...
) living in Malaya. At Bose's instigation, a substantial contingent of the INA joined in this Chalo Delhi ("March on Delhi"). Both Bose and Mutaguchi emphasised the advantages which would be gained by a successful attack into India. With misgivings on the part of several of Mutaguchi's superiors and subordinates, Operation U-Go
The U Go offensive, or Operation C (ウ号作戦 ''U Gō sakusen''), was the Japanese offensive launched in March 1944 against forces of the British Empire in the northeast Indian regions of Manipur and the Naga Hills (then administered as part ...
was launched.
Northern and Yunnan front 1943/44
Stilwell's forces (designatedX Force
X Force was the name given to the portion of the National Revolutionary Army's Chinese Expeditionary Force that retreated from Burma into India in 1942. Chiang Kai-shek sent troops into Burma from Yunnan in 1942 to assist the British in hold ...
) initially consisted of two American-equipped Chinese divisions with a Chinese-manned M3 Light Tank battalion and an American long-range penetration brigade known as "Merrill's Marauders
Merrill’s Marauders (named after Frank Merrill) or Unit ''Galahad'', officially named the 5307th Composite Unit (Provisional), was a United States Army long range penetration special operations jungle warfare unit, which fought in the Southe ...
".
In 1943 the Thai Phayap Army invasion headed to Xishuangbanna
Xishuangbanna, Sibsongbanna or Sipsong Panna ( Tham: , New Tai Lü script: ; ; th, สิบสองปันนา; lo, ສິບສອງພັນນາ; shn, သိပ်းသွင်ပၼ်းၼႃး; my, စစ်ဆောင်� ...
at China, but were driven back by the Chinese nationalist
Chinese nationalism () is a form of nationalism in the People's Republic of China (Mainland China) and the Republic of China on Taiwan which asserts that the Chinese people are a nation and promotes the cultural and national unity of all Chin ...
force.
 In October 1943 the Chinese 38th Division led by
In October 1943 the Chinese 38th Division led by Sun Li-jen
Sun Li-jen (; December 8, 1900November 19, 1990) was a Chinese Nationalist (KMT) general, a graduate of Virginia Military Institute, best known for his leadership in the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War. His military achie ...
began to advance from Ledo, Assam
Ledo is a small town in Tinsukia district, Assam, India. , the Ledo railway station is the easternmost broad gauge railway station in India. The town is also the starting point of Ledo Road, also known as Stilwell Road, a highway built during Wo ...
towards Myitkyina
Myitkyina (, ; (Eng; ''mitchinar'') Jinghpaw: ''Myitkyina'', ) is the capital city of Kachin State in Myanmar (Burma), located from Yangon, and from Mandalay. In Burmese it means "near the big river", and Myitkyina is on the west bank of the ...
and Mogaung
Mogaung ( my, မိုးကောင်း ; ( Shan: မိူင်းၵွင်း) is a town in Kachin State, Myanmar. It is situated on the Mandalay-Myitkyina railway line.
History
Mogaung or Möngkawng was the name and capital (roya ...
while American engineers and Indian labourers extended the Ledo Road
The Ledo Road (from Ledo, Assam, India to Kunming, Yunnan, China) was an overland connection between India and China, built during World War II to enable the Western Allies to deliver supplies to China and aid the war effort against Japan. ...
behind them. The Japanese 18th Division
The was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its tsūshōgō code name was the . The 18th Division was one of two infantry divisions newly raised by the Imperial Japanese Army immediately after the Russo-Japanese War (1904– ...
was repeatedly outflanked by the Marauders and threatened with encirclement.
In Operation Thursday
The Chindits, officially as Long Range Penetration Groups, were special operations units of the British and Indian armies which saw action in 1943–1944 during the Burma Campaign of World War II.
The British Army Brigadier Orde Wingate forme ...
, the Chindits
The Chindits, officially as Long Range Penetration Groups, were special operations units of the British and Indian armies which saw action in 1943–1944 during the Burma Campaign of World War II.
The British Army Brigadier Orde Wingate form ...
were to support Stilwell by interdicting Japanese communications in the region of Indaw
Indaw ( shn, ဝဵင်းဢၢင်းတေႃႇ)is a town in northern Burma, in Sagaing Division, Katha District, Indaw Township. It is located about 2 km south-east of Indaw Lake. The rail junction at Naba is located about 6 km ...
. A brigade began marching across the Patkai
The Pat-kai (Pron:pʌtˌkaɪ) or Patkai Bum ( Burmese: ''Kumon Taungdan'') are a series of mountains in the Indo-Myanmar border falling in the north-eastern Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Upper Burma region of Myanmar. They ...
mountains on 5 February 1944. In early March three other brigades were flown into landing zones behind Japanese lines by the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
and the USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
and established defensive strongholds around Indaw.
Meanwhile, the Chinese forces on the Yunnan front (Y Force
Y Force was the South East Asia Command designation given to Chinese National Revolutionary Army forces that re-entered Burma from Yunnan in 1944 as one of the Allies fighting in Burma Campaign of World War II. It consisted of 175,000 troops divide ...
) mounted an attack starting in the second half of April, with nearly 75,000 troops crossing the Salween river on a front. Soon some twelve Chinese divisions of 175,000 men, under General Wei Lihuang
Wei Lihuang () (16 February 1897 – 17 January 1960) was a Chinese general who served the Nationalist government throughout the Chinese Civil War and Second Sino-Japanese War as one of China's most successful military commanders.
First joinin ...
, were attacking the Japanese 56th Division. The Japanese forces in the North were now fighting on two fronts in northern Burma.
On 17 May, control of the Chindits passed from Slim to Stilwell. The Chindits now moved from the Japanese rear areas to new bases closer to Stilwell's front, and were given additional tasks by Stilwell for which they were not equipped. They achieved several objectives, but at the cost of heavy casualties. By the end of June, they had linked up with Stilwell's forces but were exhausted, and were withdrawn to India.
Also on 17 May, a force of two Chinese regiments, Unit Galahad (Merrill's Marauders) and Kachin guerrillas captured the airfield at Myitkyina
Myitkyina (, ; (Eng; ''mitchinar'') Jinghpaw: ''Myitkyina'', ) is the capital city of Kachin State in Myanmar (Burma), located from Yangon, and from Mandalay. In Burmese it means "near the big river", and Myitkyina is on the west bank of the ...
. The Allies did not immediately follow up this success and the Japanese were able to reinforce the town, which fell only after a siege that lasted until 3 August. The capture of Myitkyina airfield nevertheless immediately helped secure the air link from India to Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Romanization, alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality in Southwes ...
over the Hump
The Hump was the name given by Allied pilots in the Second World War to the eastern end of the Himalayan Mountains over which they flew military transport aircraft from India to China to resupply the Chinese war effort of Chiang Kai-shek and t ...
.
By the end of May, the Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
offensive, though hampered by the monsoon rains and lack of air support, succeeded in annihilating the garrison of Tengchong
Tengchong () is a county-level city of Baoshan City, western Yunnan province, People's Republic of China. It is well known for its volcanic activity. The city is named after the town of Tengchong which serves as its political center, previously kn ...
and eventually reached as far as Longling
Longling County () is a county in Baoshan City, in the west of Yunnan Province, China, bordering Burma's Shan State to the south.
Its capital is the large community Longshan ().
The site of the Songshan Battlefield () (1944 during the Second S ...
. Strong Japanese reinforcements then counterattacked and halted the Chinese advance.
Southern front 1943/44
 In Arakan, Indian XV Corps under Lieutenant General
In Arakan, Indian XV Corps under Lieutenant General Philip Christison
General Sir Alexander Frank Philip Christison, 4th Baronet, (17 November 1893 – 21 December 1993) was a British Army officer who served with distinction during the world wars. After service as a junior officer on the Western Front in the Fir ...
renewed the advance on the Mayu peninsula. Ranges of steep hills channelled the advance into three attacks each by an Indian or West African division. The 5th Indian Infantry Division captured the small port of Maungdaw
Maungdaw (, ) is a town in Rakhine State, in the western part of Myanmar (Burma). It is the administrative seat of Maungdaw Township and Maungdaw District. Maungdaw is a town of Myanmar and borders Bangladesh. Maungdaw is 16 miles north of Buthida ...
on 9 January 1944. The Corps then prepared to capture two railway tunnels linking Maungdaw with the Kalapanzin valley but the Japanese struck first. A strong force from the Japanese 55th Division infiltrated Allied lines to attack the 7th Indian Infantry Division
The 7th Infantry Division is a war-formed infantry division, part of the British Indian Army that saw service in the Burma Campaign.
History
The division was created on 1 October 1940 at Attock, under the command of Major General Arthur Wakely ...
from the rear, overrunning the divisional HQ.
Unlike previous occasions on which this had happened, the Allied forces stood firm against the attack and supplies were dropped to them by parachute. In the Battle of the Admin Box
The Battle of the Admin Box (sometimes referred to as the Battle of Ngakyedauk or the Battle of Sinzweya) took place on the southern front of the Burma campaign from 5 to 23 February 1944, in the South-East Asian Theatre of World War II.
Japa ...
from 5 to 23 February, the Japanese concentrated on XV Corps' Administrative Area, defended mainly by line of communication troops but they were unable to deal with tanks supporting the defenders, while troops from 5th Indian Division broke through the Ngakyedauk Pass
The Battle of the Admin Box (sometimes referred to as the Battle of Ngakyedauk or the Battle of Sinzweya) took place on the southern front of the Burma campaign from 5 to 23 February 1944, in the South-East Asian Theatre of World War II.
Japan ...
to relieve the defenders of the box. Although battle casualties were approximately equal, the result was a heavy Japanese defeat. Their infiltration and encirclement tactics had failed to panic Allied troops and as the Japanese were unable to capture enemy supplies, they starved.
Over the next few weeks, XV Corps' offensive ended as the Allies concentrated on the Central Front. After capturing the railway tunnels, XV Corps halted during the monsoon.
Japanese invasion of India 1944
 IV Corps, under Lieutenant-General
IV Corps, under Lieutenant-General Geoffry Scoones
General Sir Geoffry Allen Percival Scoones, (also spelt Geoffrey; 25 January 1893 – 19 September 1975) was a senior officer in the Indian Army during the Second World War.
Early life and education
Scoones was born in Karachi, British India, ...
, had pushed forward two divisions to the Chindwin River. One division was in reserve at Imphal. There were indications that a major Japanese offensive was building. Slim and Scoones planned to withdraw and force the Japanese to fight with their logistics stretched beyond the limit. However, they misjudged the date on which the Japanese were to attack, and the strength they would use against some objectives.
The Japanese Fifteenth Army consisted of three infantry divisions and a brigade-sized detachment ("Yamamoto Force"), and initially a regiment from the Indian National Army
The Indian National Army (INA; ''Azad Hind Fauj'' ; 'Free Indian Army') was a collaborationist armed force formed by Indian collaborators and Imperial Japan on 1 September 1942 in Southeast Asia during World War II. Its aim was to secure In ...
. Mutaguchi, the Army commander, planned to cut off and destroy the forward divisions of IV Corps before capturing Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the fo ...
, while the Japanese 31st Division
The was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the . The 31st Division was raised during World War II in Bangkok, Thailand, on March 22, 1943, out of Kawaguchi Detachment and parts of the 13th, 40th and 116th di ...
isolated Imphal by capturing Kohima
Kohima (; Angami Naga: ''Kewhira'' ()), is the capital of the Northeastern Indian state of Nagaland. With a resident population of almost 100,000, it is the second largest city in the state. Originally known as ''Kewhira'', Kohima was founded ...
. Mutaguchi intended to exploit the capture of Imphal by capturing the strategic city of Dimapur
Dimapur () is the largest city in the Indian state of Nagaland. As of 2011, the municipality had a population of 122,834. The city is the main gateway and commercial centre of Nagaland. Located near the border with Assam along the banks of the ...
, in the Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It ...
valley. If this could be achieved, the lines of communication to General Stilwell's forces and the airbases used to supply the Chinese over the Hump would be cut.
The Japanese troops crossed the Chindwin River on 8 March. Scoones (and Slim) were slow to order their forward troops to withdraw and the 17th Indian Infantry Division
The 17th Infantry Division is a formation of the Indian Army. Indian Army during World War II, During World War II, it had the distinction of being continually in combat during the three-year-long Burma Campaign (except for brief periods of refit ...
was cut off at Tiddim
Tedim (, , ( Zo: ''Tedim Khawpi'', pronounced ; is a town in and the administrative seat of Tedim Township, Chin State, in the north-western part of Burma. It is the second largest town in Chin State. The town's four major boroughs (''vengte'') ...
. It fought its way back to Imphal with aid from Scoones's reserve division, supplied by parachute drops. North of Imphal, 50th Indian Parachute Brigade was defeated at Sangshak by a regiment from the Japanese 31st Division on its way to Kohima. Imphal was thus left vulnerable to an attack by the Japanese 15th Division from the north but because the diversionary attack launched by Japanese in Arakan had already been defeated, Slim was able to move the 5th Indian Division by air to the Central Front. Two brigades went to Imphal, the other went to Dimapur from where it sent a detachment to Kohima.
 By the end of the first week in April, IV Corps had concentrated in the Imphal plain. The Japanese launched several offensives during the month, which were repulsed. At the start of May, Slim and Scoones began a counter-offensive against the Japanese 15th Division north of Imphal. Progress was slow, as movement was made difficult by monsoon rains and IV Corps was short of supplies.
Also at the beginning of April, the Japanese 31st Division under Lieutenant-General Kotoku Sato reached Kohima. Instead of isolating the small British garrison there and pressing on with his main force to Dimapur, Sato chose to capture the
By the end of the first week in April, IV Corps had concentrated in the Imphal plain. The Japanese launched several offensives during the month, which were repulsed. At the start of May, Slim and Scoones began a counter-offensive against the Japanese 15th Division north of Imphal. Progress was slow, as movement was made difficult by monsoon rains and IV Corps was short of supplies.
Also at the beginning of April, the Japanese 31st Division under Lieutenant-General Kotoku Sato reached Kohima. Instead of isolating the small British garrison there and pressing on with his main force to Dimapur, Sato chose to capture the hill station
A hill station is a town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The term was used mostly in colonial Asia (particularly in India), but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by European colonialists as refuges ...
. The siege lasted from 5 to 18 April, when the exhausted defenders were relieved. A new formation HQ, the Indian XXXIII Corps under Lieutenant-General Montagu Stopford
General Sir Montagu George North Stopford (16 November 1892 – 10 March 1971) was a senior British Army officer who fought during both World War I and World War II. The latter he served in with distinction, commanding XXXIII Indian Corps in t ...
, now took over operations on this front. The 2nd British Infantry Division began a counter-offensive and by 15 May, they had prised the Japanese off Kohima Ridge itself. After a pause during which more Allied reinforcements arrived, XXXIII Corps renewed its offensive.
By now, the Japanese were at the end of their endurance. Their troops (particularly 15th and 31st Divisions) were starving, and during the monsoon, disease rapidly spread among them. Lieutenant-General Sato had notified Mutaguchi that his division would withdraw from Kohima at the end of May if it were not supplied. In spite of orders to hold on, Sato did indeed retreat. The leading troops of IV Corps and XXXIII Corps met at Milestone 109 on the Dimapur-Imphal road on 22 June, and the siege of Imphal was raised.
 Mutaguchi (and Kawabe) continued to order renewed attacks. 33rd Division and Yamamoto Force made repeated efforts, but by the end of June they had suffered so many casualties both from battle and disease that they were unable to make any progress. The Imphal operation was finally broken off early in July, and the Japanese retreated painfully to the Chindwin River.
It was the greatest defeat to that date in Japanese history. They had suffered 50–60,000 dead,Despatch "Operations in Assam and Burma from 23RD June 1944 to 12TH November 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 3 March 1951, p. 1711. and 100,000 or more casualties.Despatch "Operations in Burma 12th November 1944 to 15th August 1945", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 6 April 1951, p. 1885. Most of these losses were the result of disease, malnutrition and exhaustion. The Allies suffered 12,500 casualties, including 2,269 killed.Despatch "Operations in Burma and North East India 16th November 1943 to 22nd June 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 13 March 1951, p. 1361. Mutaguchi had already relieved all his divisions' commanders, and was himself subsequently relieved of command.
During the monsoon from August to November, Fourteenth Army pursued the Japanese to the Chindwin River. While the
Mutaguchi (and Kawabe) continued to order renewed attacks. 33rd Division and Yamamoto Force made repeated efforts, but by the end of June they had suffered so many casualties both from battle and disease that they were unable to make any progress. The Imphal operation was finally broken off early in July, and the Japanese retreated painfully to the Chindwin River.
It was the greatest defeat to that date in Japanese history. They had suffered 50–60,000 dead,Despatch "Operations in Assam and Burma from 23RD June 1944 to 12TH November 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 3 March 1951, p. 1711. and 100,000 or more casualties.Despatch "Operations in Burma 12th November 1944 to 15th August 1945", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 6 April 1951, p. 1885. Most of these losses were the result of disease, malnutrition and exhaustion. The Allies suffered 12,500 casualties, including 2,269 killed.Despatch "Operations in Burma and North East India 16th November 1943 to 22nd June 1944", ''Supplement to the London Gazette'', 13 March 1951, p. 1361. Mutaguchi had already relieved all his divisions' commanders, and was himself subsequently relieved of command.
During the monsoon from August to November, Fourteenth Army pursued the Japanese to the Chindwin River. While the 11th East Africa Division
The 11th (East Africa) Infantry Division was a British Empire colonial unit formed in February 1943 during the Second World War.
Formation
In 1943, the 11th (East Africa) Division was formed primarily of troops from British East Africa. The divi ...
advanced down the Kabaw Valley
The Kabaw Valley also known as Kubo valley is a highland valley in Myanmar's western Sagaing division, close to the border with India's Manipur. The valley is located between Heerok or Yoma ranges of mountains, which constitute the present day bo ...
from Tamu, the 5th Indian Division advanced along the mountainous Tiddim road. By the end of November, Kalewa had been recaptured, and several bridgeheads were established on the east bank of the Chindwin.
Allied capture of Burma 1944–1945
 The Allies launched a series of offensive operations into Burma during late 1944 and the first half of 1945. The command on the front was rearranged in November 1944. Eleventh Army Group HQ was replaced by
The Allies launched a series of offensive operations into Burma during late 1944 and the first half of 1945. The command on the front was rearranged in November 1944. Eleventh Army Group HQ was replaced by Allied Land Forces South East Asia
The 11th Army Group was the main British Army force in Southeast Asia during the Second World War. Although a nominally British formation, it also included large numbers of troops and formations from the British Indian Army and from British African ...
and NCAC and XV Corps were placed directly under this new headquarters. Although the Allies were still attempting to complete the Ledo Road
The Ledo Road (from Ledo, Assam, India to Kunming, Yunnan, China) was an overland connection between India and China, built during World War II to enable the Western Allies to deliver supplies to China and aid the war effort against Japan. ...
, it was apparent that it would not materially affect the course of the war in China.
The Japanese also made major changes in their command. The most important was the replacement of General Kawabe at Burma Area Army by Hyotaro Kimura. Kimura threw Allied plans into confusion by refusing to fight at the Chindwin River. Recognising that most of his formations were weak and short of equipment, he withdrew his forces behind the Irrawaddy River
The Irrawaddy River ( Ayeyarwady River; , , from Indic ''revatī'', meaning "abounding in riches") is a river that flows from north to south through Myanmar (Burma). It is the country's largest river and most important commercial waterway. Origi ...
, forcing the Allies to greatly extend their lines of communication.
Southern front 1944/45
 In Arakan, XV Corps resumed its advance on Akyab Island for the third year in succession. This time the Japanese were far weaker, and retreated before the steady Allied advance. They evacuated Akyab Island on 31 December 1944. It was occupied by XV Corps without resistance on 3 January 1945 as part of Operation Talon, the amphibious landing at Akyab.
Landing craft had now reached the theatre, and XV Corps launched amphibious attacks on the
In Arakan, XV Corps resumed its advance on Akyab Island for the third year in succession. This time the Japanese were far weaker, and retreated before the steady Allied advance. They evacuated Akyab Island on 31 December 1944. It was occupied by XV Corps without resistance on 3 January 1945 as part of Operation Talon, the amphibious landing at Akyab.
Landing craft had now reached the theatre, and XV Corps launched amphibious attacks on the Myebon
Myebon ( my, မြေပုံမြို့ Myebon Township) is a town of Mrauk-U District in Rakhine State, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even ...
peninsula on 12 January 1945 and at Kangaw ten days later during the Battle of Hill 170
The Battle of Hill 170 was a battle between the British 3rd Commando Brigade and the Japanese 54th Division during the Second World War. The battle was fought in January 1945, as part of the Burma Campaign.
The 3rd Commando Brigade were giv ...
to cut off the retreating Japanese. There was severe fighting until the end of the month, in which the Japanese suffered heavy casualties.
An important objective for XV Corps was the capture of Ramree Island
Ramree Island ( my, ရမ်းဗြဲကျွန်း; also spelled Yanbye Island) is an island off the coast of Rakhine State, Myanmar (Burma). Ramree island is the largest island in the entire Rakhine Coast and in Myanmar. The area of t ...
and Cheduba Island
Cheduba Island ( my, မာန်အောင်ကျွန်း; also known as Manaung Island) is an island in the Bay of Bengal close to Ramree Island and belongs to Myanmar, formerly Burma. It has a maximum length of , with an area of approxi ...
to construct airfields which would support the Allies' operations in Central Burma. Most of the Japanese garrison died during the Battle of Ramree Island
The Battle of Ramree Island ( Burmese:ရမ်းဗြဲကျွန်း တိုက်ပွဲ, (also called Operation Matador) took place from 14 January to 22 February 1945, in the Second World War as part of the offensive on the Sout ...
. XV Corps operations on the mainland were curtailed to release transport aircraft to support Fourteenth Army.
Northern front 1944/45
NCAC resumed its advance late in 1944, although it was progressively weakened by the flyout of Chinese troops to the main front in China. On 10 December 1944, the 36th British Infantry Division on NCAC's right flank made contact with units of Fourteenth Army near Indaw in Northern Burma. Five days later, Chinese troops on the command's left flank captured the city ofBhamo
Bhamo ( my, ဗန်းမော်မြို့ ''ban: mau mrui.'', also spelt Banmaw; shn, မၢၼ်ႈမူဝ်ႇ; tdd, ᥛᥫᥒᥰ ᥛᥨᥝᥱ; zh, 新街, Hsinkai) is a city in Kachin State in northern Myanmar, south of the ...
.
NCAC made contact with Chiang Chiang may mean:
* a Chinese surname (蔣), alternatively spelt Jiang
** Chiang Kai-shek, former leader of the Republic of China
* Chi'ang, variant spelling of the ancient Qiang (historical people) (羌)
* Chi'ang, variant spelling of the modern ...
's Yunnan armies on 21 January 1945, and the Ledo road could finally be completed, although by this point in the war its value was uncertain. Chiang ordered the American General Daniel Isom Sultan
Daniel Isom Sultan (December 9, 1885 – January 14, 1947) was an American general. Sultan was born in Oxford, Mississippi, and graduated from the United States Military Academy in 1907. He entered the United States Army Corps of Engineers ...
, commanding NCAC, to halt his advance at Lashio
Lashio ( ; Shan: ) is the largest town in northern Shan State, Myanmar, about north-east of Mandalay. It is situated on a low mountain spur overlooking the valley of the Yaw River. Loi Leng, the highest mountain of the Shan Hills, is located ...
, which was captured on 7 March. This was a blow to British plans as it endangered the prospects of reaching Yangon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
before the onset of the monsoon, expected at the beginning of May. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
, British Prime Minister, appealed directly to American chief of staff George Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (December 31, 1880 – October 16, 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the US Army under Presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry ...
for the transport aircraft which had been assigned to NCAC to remain in Burma. From 1 April, NCAC's operations stopped, and its units returned to China and India. A US-led guerrilla force, OSS Detachment 101
Detachment 101 of the Office of Strategic Services (formed under the Office of the Coordinator of Information just weeks before it evolved into the OSS) operated in the China-Burma-India Theater of World War II. On 17 January 1956, it was ...
, took over the remaining military responsibilities of NCAC.
Central front 1944/45
The Fourteenth Army, now consisting of IV Corps and XXXIII Corps, made the main offensive effort into Burma. Although the Japanese retreat over the Irrawaddy forced the Allies to completely change their plans, such was the Allies' material superiority that this was done. IV Corps was switched in secret from the right to the left flank of the army and aimed to cross the Irrawaddy nearPakokku
Pakokku ( my, ပခုက္ကူမြို့, ) is the largest city in the Magway Region of Myanmar. It is situated about 30 km north-east of Bagan on the Irrawaddy River. It is the administration seat of Pakokku Township , Pakokku Distric ...
and seize the Japanese line-of-communication centre of Meiktila
Meiktila (; ) is a city in central Burma on the banks of Meiktila Lake in the Mandalay Region at the junctions of the Bagan-Taunggyi, Yangon-Mandalay and Meiktila-Myingyan highways. Because of its strategic position, Meiktila is home to Myanmar Ai ...
, while XXXIII Corps continued to advance on Mandalay
Mandalay ( or ; ) is the second-largest city in Myanmar, after Yangon. Located on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River, 631km (392 miles) (Road Distance) north of Yangon, the city has a population of 1,225,553 (2014 census).
Mandalay was fo ...
.
 During January and February 1945, XXXIII Corps seized crossings over the Irrawaddy River near Mandalay. There was heavy fighting, which attracted Japanese reserves and fixed their attention. Late in February, the 7th Indian Division leading IV Corps, seized crossings at Nyaungu near Pakokku. 17th Indian Division and
During January and February 1945, XXXIII Corps seized crossings over the Irrawaddy River near Mandalay. There was heavy fighting, which attracted Japanese reserves and fixed their attention. Late in February, the 7th Indian Division leading IV Corps, seized crossings at Nyaungu near Pakokku. 17th Indian Division and 255th Indian Tank Brigade
The 255th Indian Tank Brigade was an armoured brigade of the Indian Army during World War II. It was part of the Fourteenth Army and saw action in the Burma Campaign. The 255th Tank Brigade's tactical sign was a black bull, with yellow horns and ...
followed them across and struck for Meiktila. In the open terrain of Central Burma, this force outmanoeuvred the Japanese and fell on Meiktila on 1 March. The town was captured in four days, despite resistance to the last man.
The Japanese tried first to relieve the garrison at Meiktila and then to recapture the town and destroy its defenders. Their attacks were not properly coordinated and were repulsed. By the end of March the Japanese had suffered heavy casualties and lost most of their artillery, their chief anti-tank weapon. They broke off the attack and retreated to Pyawbwe.
XXXIII Corps had renewed its attack on Mandalay. It fell to 19th Indian Division on 20 March, though the Japanese held the former citadel which the British called Fort Dufferin
Fort Dufferin is a former Canadian government post near the Canada–United States border at Emerson, Manitoba. The fort was used during the 1870s as a base for the North American Boundary Commission and the North-West Mounted Police (NWMP), ...
for another week. Much of the historically and culturally significant portions of Mandalay were burned to the ground.
Race for Rangoon
 Though the Allied force had advanced successfully into central Burma, it was vital to capture the port of Rangoon before the monsoon to avoid a logistics crisis. In the spring of 1945, the other factor in the race for Rangoon was the years of preparation by the liaison organisation,
Though the Allied force had advanced successfully into central Burma, it was vital to capture the port of Rangoon before the monsoon to avoid a logistics crisis. In the spring of 1945, the other factor in the race for Rangoon was the years of preparation by the liaison organisation, Force 136
Force 136 was a far eastern branch of the British World War II intelligence organisation, the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Originally set up in 1941 as the India Mission with the cover name of GSI(k), it absorbed what was left of SOE's Or ...
, which resulted in a national uprising within Burma and the defection of the entire Burma National Army
The Burma Independence Army (BIA), was a collaborationist and revolutionary army that fought for the end of British rule in Burma by assisting the Japanese in their conquest of the country in 1942 during World War II. It was the first post-c ...
to the allied side. In addition to the allied advance, the Japanese now faced open rebellion behind their lines.
XXXIII Corps mounted Fourteenth Army's secondary drive down the Irrawaddy River valley against stiff resistance from the Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army. IV Corps made the main attack down the "Railway Valley", which was also followed by the Sittaung River
The Sittaung River ( my, စစ်တောင်းမြစ် ; formerly, the Sittang or Sittounghttps://unstats.un.org/unsd/geoinfo/UNGEGN/docs/8th-uncsgn-docs/inf/8th_UNCSGN_econf.94_INF.75.pdf ) is a river in south central Myanmar in Bago ...
. They began by striking at a Japanese delaying position (held by the remnants of the Japanese Thirty-Third Army) at Pyawbwe. The attackers were initially halted by a strong defensive position behind a dry waterway, but a flanking move by tanks and mechanised infantry struck the Japanese from the rear and shattered them.
From this point, the advance down the main road to Rangoon faced little organised opposition. An uprising by Karen guerillas prevented troops from the reorganised Japanese Fifteenth Army
The was an army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. It was involved in the invasion of Burma in December 1941 and served in that country for most of its war service.
History
The Japanese 15th Army was formed on November 9, 1941 ...
from reaching the major road centre of Taungoo
Taungoo (, ''Tauñngu myoú''; ; also spelled Toungoo) is a district-level city in the Bago Region of Myanmar, 220 km from Yangon, towards the north-eastern end of the division, with mountain ranges to the east and west. The main industry ...
before IV Corps captured it. The leading Allied troops met Japanese rearguards north of Bago
Bago may refer to:
Places Myanmar
* Bago, Myanmar, a city and the capital of the Bago Region
* Bago District, a district of the Bago Region
* Bago Region an administrative region
* Bago River, a river
* Bago Yoma or Pegu Range, a mountain rang ...
, north of Rangoon, on 25 April. Heitarō Kimura
was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army. He was convicted of war crimes and sentenced to death by hanging.
Biography
Kimura was born in Saitama prefecture, north of Tokyo, but was raised in Hiroshima prefecture, which he considered to be h ...
had formed the various service troops, naval personnel and even Japanese civilians in Yangon into the 105 Independent Mixed Brigade. This scratch formation held up the British advance until 30 April and covered the evacuation of the Rangoon area.
Operation Dracula
 The original conception of the plan to re-take Burma had envisaged XV Corps making an amphibious assault on Rangoon well before Fourteenth Army reached the capital, in order to ease supply problems. This operation, codenamed Operation Dracula, was postponed several times as the necessary landing craft were retained in Europe and finally dropped in favour of an attack on
The original conception of the plan to re-take Burma had envisaged XV Corps making an amphibious assault on Rangoon well before Fourteenth Army reached the capital, in order to ease supply problems. This operation, codenamed Operation Dracula, was postponed several times as the necessary landing craft were retained in Europe and finally dropped in favour of an attack on Phuket Island
Phuket (; th, ภูเก็ต, , ms, Bukit or ''Tongkah''; Hokkien:普吉; ) is one of the southern provinces (''changwat'') of Thailand. It consists of the island of Phuket, the country's largest island, and another 32 smaller islands of ...
, off the west coast of Thailand.
Slim feared that the Japanese would defend Rangoon to the last man through the monsoon, which would put Fourteenth Army in a disastrous supply situation. He therefore asked for Operation Dracula to be re-mounted at short notice. The naval forces for the attack on Phuket were diverted to Operation Dracula, and units of XV Corps were embarked from Akyab and Ramree.
On 1 May, a Gurkha parachute battalion was dropped on Elephant Point, and cleared Japanese rearguards from the mouth of the Yangon River
The Yangon River (also known as the Rangoon River or Hlaing River) is formed by the confluence of the Pegu and Myitmaka Rivers in Myanmar. It is a marine estuary that runs from Yangon (also known as Rangoon) to the Gulf of Martaban of the Andaman ...
. The 26th Indian Infantry Division
The 26th Indian Infantry Division, was an infantry division of the Indian Army during World War II. It fought in the Burma Campaign.
History
When the Japanese invaded Burma in 1942, the various units in training or stationed around Barrackpur n ...
landed by ship the next day. When they arrived they discovered that Kimura had ordered Rangoon to be evacuated, starting on 22 April. After the Japanese withdrawal, Yangon had experienced an orgy of looting and lawlessness similar to the last days of the British in the city in 1942. On the afternoon of 2 May 1945, the monsoon rains began in full force. The Allied drive to liberate Rangoon before the rains had succeeded with only a few hours to spare.
The leading troops of the 17th and 26th Indian divisions met at Hlegu, north of Rangoon, on 6 May.
Final operations
 After the Allies captured Rangoon, a new Twelfth Army headquarters was created from XXXIII Corps HQ to take control of the formations which were to remain in Burma.
The Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army, after withdrawing from Arakan and resisting XXXIII Corps in the Irrawaddy valley, retreated into the
After the Allies captured Rangoon, a new Twelfth Army headquarters was created from XXXIII Corps HQ to take control of the formations which were to remain in Burma.
The Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army, after withdrawing from Arakan and resisting XXXIII Corps in the Irrawaddy valley, retreated into the Pegu Yomas
The Pegu Range ( my, ပဲခူးရိုးမ; Pegu Yoma or Bago Yoma) is a range of low mountains or hillsSeekins, Donald M. (2006) ''Historical dictionary of Burma (Myanmar)'' Scarecrow Press, Lanham, Marylandpage 357 and uplands between ...
, a range of low jungle-covered hills between the Irrawaddy and Sittang rivers. They planned to break out and rejoin Burma Area Army. To cover this break-out, Kimura ordered Thirty-Third Army to mount a diversionary offensive across the Sittang, although the entire army could muster the strength of barely a regiment. On 3 July, they attacked British positions in the "Sittang Bend". On 10 July, after a battle for country which was almost entirely flooded, both the Japanese and the Allies withdrew.
The Japanese had attacked too early. Sakurai's Twenty-Eighth Army was not ready to start the break-out until 17 July. The break-out was a disaster. The British had placed ambushes or artillery concentrations on the routes the Japanese were to use. Hundreds of men drowned trying to cross the swollen Sittang on improvised bamboo floats and rafts. Burmese guerrillas and bandits killed stragglers east of the river. The break-out cost the Japanese nearly 10,000 men, half the strength of Twenty-Eighth Army. British and Indian casualties were minimal.
Fourteenth Army (now under Lieutenant General Miles Dempsey
General Sir Miles Christopher Dempsey, (15 December 1896 – 5 June 1969) was a senior British Army officer who served in both world wars. During the Second World War he commanded the Second Army in north west Europe. A highly professional an ...
) and XV Corps had returned to India to plan the next stage of the campaign to re-take Southeast Asia. A new corps, the Indian XXXIV Corps, under Lieutenant-General Ouvry Lindfield Roberts
General Sir Ouvry Lindfield Roberts, (3 April 1898 – 16 March 1986) was a senior officer of the British Army and the British Indian Army during the First and Second World Wars.
Military career
Educated at Cheltenham College, the Royal Mili ...
was raised and assigned to Fourteenth Army for further operations.
This was to be an amphibious assault on the western side of Malaya codenamed Operation Zipper
During World War II, Operation Zipper was a British plan to capture either Port Swettenham or Port Dickson, Malaya, as staging areas for the recapture of Singapore in Operation Mailfist. However, due to the end of the war in the Pacific, it wa ...
. The dropping of the atomic bombs forestalled this operation, but it was undertaken post-war as the quickest way of getting occupation troops into Malaya.
Results
Generally, the recovery of Burma is reckoned as a triumph for the British Indian Army and resulted in the greatest defeat the Japanese armies had suffered to that date. The attempted Japanese invasion of India in 1944 was launched on unrealistic premises as after the Singapore debacle and the loss of Burma in 1942, the British were bound to defend India at all costs. A successful invasion by Japanese Imperial forces would have been disastrous. The defence operations at Kohima and Imphal in 1944 have since taken on huge symbolic value as the turning of the tide in British fortunes in the war in the East. The American historian Raymond Callahan concluded "Slim's great victory ... helped the British, unlike the French, Dutch or, later, the Americans, to leave Asia with some dignity." After the war ended a combination of the pre-war agitation among the Bamar population for independence and the economic ruin of Burma during the four-year campaign made it impossible for the former regime to be resumed. Within three years both Burma and India were independent. American goals in Burma had been to aid the Nationalist Chinese regime. Apart from the "Hump" airlift, these bore no fruit until so near the end of the war that they made little contribution to the defeat of Japan. These efforts have also been criticised as fruitless because of the self-interest and corruption of Chiang Kai-Shek's regime.See also
*India in World War II
During the Second World War (1939–1945), India was a part of the British Empire. British Raj, India officially declared war on Nazi Germany in September 1939. India, as a part of the Allies of World War II, Allied Nations, sent over ...
* Japanese occupation of Burma
The Japanese occupation of Burma was the period between 1942 and 1945 during World War II, when Burma was occupied by the Empire of Japan. The Japanese had assisted formation of the Burma Independence Army, and trained the Thirty Comrades, who ...
* Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Th ...
* Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian strategic offensive operation (russian: Манчжурская стратегическая наступательная операция, Manchzhurskaya Strategicheskaya Nastu ...
References
Citations
Sources
* Allen, Louis, ''Burma: The Longest War'' * * Carew, Tim. ''The Longest Retreat'' * Calvert, Mike. ''Fighting Mad'' has content related to the 1944 Chindit campaign * * Dillon, Terence. ''Yangon to Kohima'' * * * * Fujino, Hideo. ''Singapore and Burma'' * Grant, Ian Lyall, & Tamayama, Kazuo, ''Burma 1942: The Japanese Invasion'' * Iida, Shojiro ''From the Battlefields'' * Ikuhiko Hata, ''Road to the Pacific War'' * * Hickey, Michael. ''The Unforgettable Army'' * Hodsun, J. L. ''War in the Sun'' * * * Latimer, Jon. ''Burma: The Forgotten War'' * Lunt, James. ''A Hell of a Licking' – The Retreat from Burma 1941–2'' London 1986 . Personal account by a British Burma Rifles officer, who later became an Oxford academic. * McLynn, Frank. ''The Burma Campaign: Disaster Into Triumph, 1942–45'' (Yale University Press; 2011), 532 pages; focus on William Slim, Orde Wingate, Louis Mountbatten, and Joseph Stilwell. * * * Ochi, Harumi. ''Struggle in Burma'' * Reynolds, E. Bruce. ''Thailand and Japan's Southern Advance'' * Rolo, Charles J. ''Wingate's Raiders'' * Sadayoshi Shigematsu, '' Fighting Around Burma'' * * Smyth John ''Before the Dawn'' * Sugita, Saiichi. ''Burma Operations'' * Thompson, Robert. ''Make for the Hills'' has content related to the 1944 Chindit campaign * Thompson, Julian. ''Forgotten Voices of Burma: The Second World War's Forgotten Conflict'' * Webster, Donovan. ''The Burma Road : The Epic Story of the China-Burma-India Theater in World War II'' * Williams, James Howard was Elephant Advisor to the Fourteenth Army, see his ''Elephant Bill'' (1950) and ''Bandoola'' (1953) * Young, Edward M. ''Aerial Nationalism: A History of Aviation in Thailand''Further reading
* Edwards, Roderick (2020). ''Should've Been With Me: The Wilfred Scull Story''. United States: KDP Books. * * * * * * * *External links
Associations
Burma Star Association
Imphal and Kohima, Britain's Greatest Battles, National Army Museum
Museums
Burma Summary
The Kohima Museum
A museum dedicated to the
Battle of Kohima
The Battle of Kohima proved the turning point of the Imperial Japan, Japanese Operation U-Go, U-Go offensive into British Raj, India in 1944 during the World War II, Second World War. The battle took place in three stages from 4 April to 22 June ...
Royal Engineers Museum
Engineers in the Burma Campaigns
Engineers with the Chindits
Canadian War Museum: Newspaper Articles on the Burma Campaigns, 1941–1945
Media
World War II animated campaign maps
Primary sources
* "Operations in Eastern Theatre, Based on India from March 1942 to December 31, 1942", official despatch byField Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
The Viscount Wavell
* "Operations in the Indo-Burma Theatre Based on India from 21 June 1943 to 15 November 1943" official despatch by Field Marshal Sir Claude E. Auchinleck, War Office. (osee this html version
* "Operations in Burma from 12 November 1944 to 15 August 1945" official despatch by Lieutenant General Sir
Oliver Leese
Lieutenant-General Sir Oliver William Hargreaves Leese, 3rd Baronet, (27 October 1894 – 22 January 1978) was a senior British Army officer who saw distinguished active service during both the world wars. He is probably most notable during the ...
History
Siam goes to war
Canadians in south east Asia
{{Coord missing, Myanmar 1940s in Burma 1942 in Burma 1943 in Burma 1944 in Burma 1945 in Burma Battles and operations of World War II involving Nepal Campaigns of World War II Campaigns, operations and battles of World War II involving the United Kingdom Indian National Army Military history of India during World War II Military history of Thailand during World War II South-East Asian theatre of World War II World War II operations and battles of the Pacific theatre