Bulgaria Ethnic Map on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in

 Not long after the Slavic incursion,
Not long after the Slavic incursion,
 Byzantine domestic policies changed after Basil's death and a series of unsuccessful rebellions broke out, the largest being led by
Byzantine domestic policies changed after Basil's death and a series of unsuccessful rebellions broke out, the largest being led by
 The Ottomans were employed as mercenaries by the Byzantines in the 1340s but later became invaders in their own right. Sultan
The Ottomans were employed as mercenaries by the Byzantines in the 1340s but later became invaders in their own right. Sultan  The Western European Enlightenment in the 18th century influenced the initiation of a
The Western European Enlightenment in the 18th century influenced the initiation of a
 The Bulgarian principality won a war against Serbia and incorporated the semi-autonomous Ottoman territory of
The Bulgarian principality won a war against Serbia and incorporated the semi-autonomous Ottoman territory of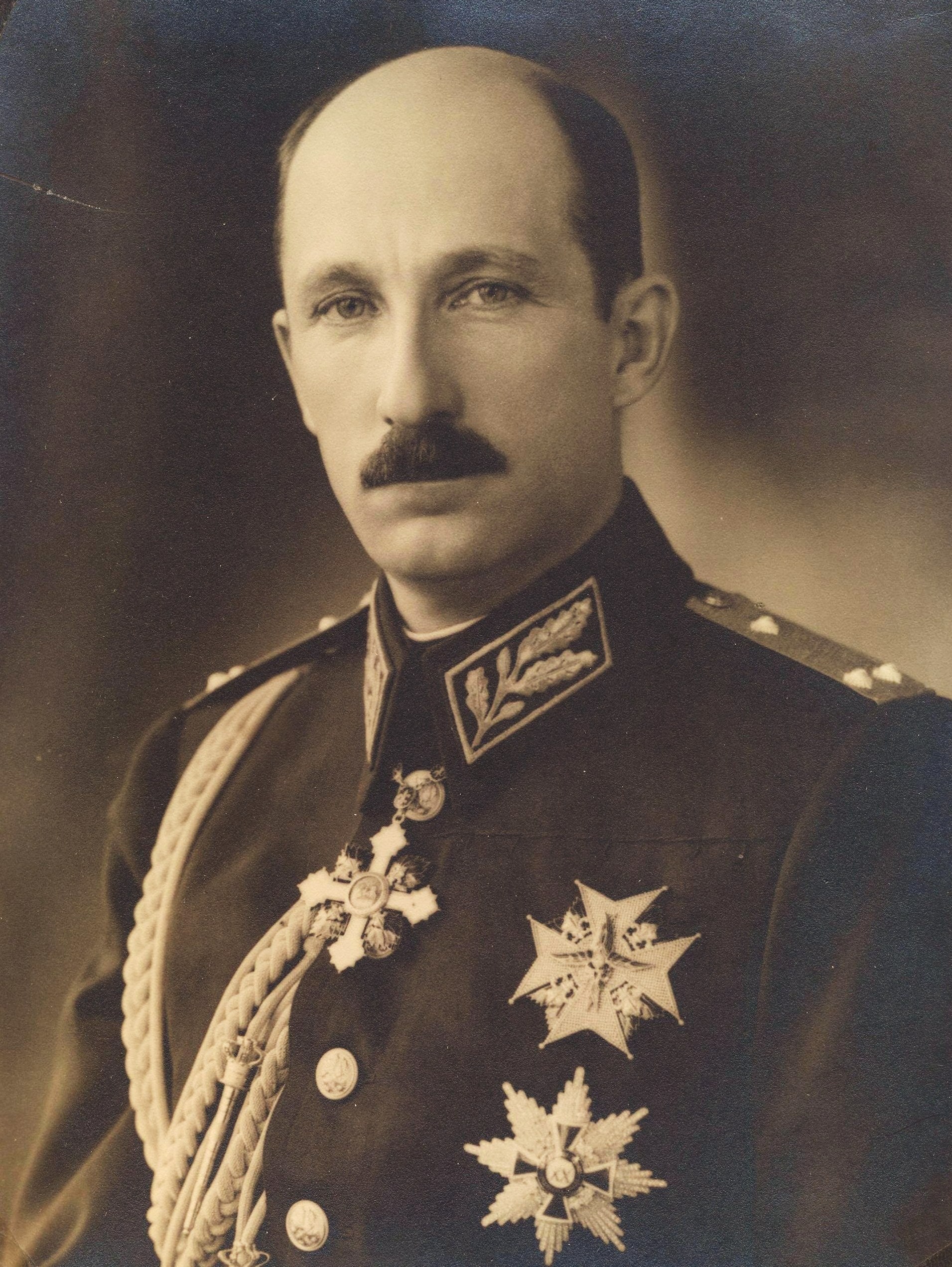  The resulting political unrest led to the establishment of a royal authoritarianism, authoritarian dictatorship by Tsar Boris III of Bulgaria, Boris III (1918–1943). Bulgaria entered World War II in 1941 as a member of Axis Powers, the Axis but declined to participate in Operation Barbarossa and Rescue of the Bulgarian Jews, saved its Jewish population from deportation to Nazi concentration camps, concentration camps. The sudden death of Boris III in mid-1943 pushed the country into political turmoil as the war turned against Germany, and the communist guerrilla movement gained momentum. The government of Bogdan Filov subsequently failed to achieve peace with the Allies. Bulgaria did not comply with Soviet demands to expel German forces from its territory, resulting in a declaration of war and an invasion by the USSR in September 1944. The communist-dominated Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power, ended participation in the Axis and joined the Allied side until the war ended. Bulgaria suffered little war damage and the Soviet Union demanded no reparations. But all wartime territorial gains, with the notable exception of Treaty of Craiova, Southern Dobrudzha, were lost.
The resulting political unrest led to the establishment of a royal authoritarianism, authoritarian dictatorship by Tsar Boris III of Bulgaria, Boris III (1918–1943). Bulgaria entered World War II in 1941 as a member of Axis Powers, the Axis but declined to participate in Operation Barbarossa and Rescue of the Bulgarian Jews, saved its Jewish population from deportation to Nazi concentration camps, concentration camps. The sudden death of Boris III in mid-1943 pushed the country into political turmoil as the war turned against Germany, and the communist guerrilla movement gained momentum. The government of Bogdan Filov subsequently failed to achieve peace with the Allies. Bulgaria did not comply with Soviet demands to expel German forces from its territory, resulting in a declaration of war and an invasion by the USSR in September 1944. The communist-dominated Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power, ended participation in the Axis and joined the Allied side until the war ended. Bulgaria suffered little war damage and the Soviet Union demanded no reparations. But all wartime territorial gains, with the notable exception of Treaty of Craiova, Southern Dobrudzha, were lost.
 The 1944 Bulgarian coup d'état, left-wing coup d'état of 9 September 1944 led to the abolition of the monarchy and People's Court (Bulgaria), the executions of some 1,000–3,000 dissidents, war criminals, and members of the former royal elite. But it was not until 1946 that a One-party state, one-party people's republic was instituted following a referendum. It fell into the Soviet sphere of influence under the leadership of Georgi Dimitrov (1946–1949), who established a repressive, rapidly industrialising Stalinist state. By the mid-1950s, standards of living rose significantly and political repression eased. The Soviet-style planned economy saw some experimental market-oriented policies emerging under Todor Zhivkov (1954–1989). Compared to wartime levels, national Gross domestic product, GDP increased five-fold and per capita GDP quadrupled by the 1980s, although severe debt spikes took place in 1960, 1977 and 1980. Zhivkov's daughter Lyudmila Zhivkova, Lyudmila bolstered national pride by promoting Bulgarian heritage, culture and arts worldwide. Facing declining birth rates among the ethnic Bulgarian majority, Zhivkov's government in 1984 forced the minority ethnic Bulgarian Turks, Turks to adopt Slavic names in an attempt to erase their identity and assimilate them. These policies resulted in the emigration of some 300,000 ethnic Turks to Turkey.
The Communist Party was forced to give up its political monopoly on 10 November 1989 under the influence of the Revolutions of 1989. Zhivkov resigned and Bulgaria embarked on a transition to a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy. The first free elections in June 1990 were won by the Communist Party, now rebranded as the Bulgarian Socialist Party. A Constitution of Bulgaria, new constitution that provided for a relatively weak elected president and for a prime minister accountable to the legislature was adopted in July 1991. The new system initially failed to improve living standards or create economic growth—the average quality of life and economic performance remained lower than under communism well into the early 2000s. After 2001, economic, political and geopolitical conditions improved greatly, and Bulgaria achieved high Human Development status in 2003. It became a member of
The 1944 Bulgarian coup d'état, left-wing coup d'état of 9 September 1944 led to the abolition of the monarchy and People's Court (Bulgaria), the executions of some 1,000–3,000 dissidents, war criminals, and members of the former royal elite. But it was not until 1946 that a One-party state, one-party people's republic was instituted following a referendum. It fell into the Soviet sphere of influence under the leadership of Georgi Dimitrov (1946–1949), who established a repressive, rapidly industrialising Stalinist state. By the mid-1950s, standards of living rose significantly and political repression eased. The Soviet-style planned economy saw some experimental market-oriented policies emerging under Todor Zhivkov (1954–1989). Compared to wartime levels, national Gross domestic product, GDP increased five-fold and per capita GDP quadrupled by the 1980s, although severe debt spikes took place in 1960, 1977 and 1980. Zhivkov's daughter Lyudmila Zhivkova, Lyudmila bolstered national pride by promoting Bulgarian heritage, culture and arts worldwide. Facing declining birth rates among the ethnic Bulgarian majority, Zhivkov's government in 1984 forced the minority ethnic Bulgarian Turks, Turks to adopt Slavic names in an attempt to erase their identity and assimilate them. These policies resulted in the emigration of some 300,000 ethnic Turks to Turkey.
The Communist Party was forced to give up its political monopoly on 10 November 1989 under the influence of the Revolutions of 1989. Zhivkov resigned and Bulgaria embarked on a transition to a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy. The first free elections in June 1990 were won by the Communist Party, now rebranded as the Bulgarian Socialist Party. A Constitution of Bulgaria, new constitution that provided for a relatively weak elected president and for a prime minister accountable to the legislature was adopted in July 1991. The new system initially failed to improve living standards or create economic growth—the average quality of life and economic performance remained lower than under communism well into the early 2000s. After 2001, economic, political and geopolitical conditions improved greatly, and Bulgaria achieved high Human Development status in 2003. It became a member of
 Bulgaria is a small country situated in Southeastern Europe, in the east of the Balkans. Its territory covers an area of , while land borders with its five neighbouring countries run a total length of , and its coastline is long. Bulgaria's geographic coordinates are 43rd parallel north, 43° N 25th meridian east, 25° E. The most notable topographical features of the country are the Danubian Plain (Bulgaria), Danubian Plain, the Balkan Mountains, the Thracian Plain, and the Rila-Rhodope Mountains, Rhodope massif. The southern edge of the Danubian Plain slopes upward into the foothills of the Balkans, while the Danube defines the border with Romania. The Thracian Plain is roughly triangular, beginning southeast of
Bulgaria is a small country situated in Southeastern Europe, in the east of the Balkans. Its territory covers an area of , while land borders with its five neighbouring countries run a total length of , and its coastline is long. Bulgaria's geographic coordinates are 43rd parallel north, 43° N 25th meridian east, 25° E. The most notable topographical features of the country are the Danubian Plain (Bulgaria), Danubian Plain, the Balkan Mountains, the Thracian Plain, and the Rila-Rhodope Mountains, Rhodope massif. The southern edge of the Danubian Plain slopes upward into the foothills of the Balkans, while the Danube defines the border with Romania. The Thracian Plain is roughly triangular, beginning southeast of  Bulgaria has a varied and changeable climate, which results from being positioned at the meeting point of the Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean, Oceanic climate, Oceanic and Continental climate, Continental air masses combined with the barrier effect of its mountains. Northern Bulgaria averages cooler, and registers more precipitation, than the regions south of the Balkan mountains. Temperature amplitudes vary significantly in different areas. The lowest recorded temperature is , while the highest is . Precipitation (meteorology), Precipitation averages about per year, and varies from in Dobrudja to more than in the mountains. Continental air masses bring significant amounts of snowfall during winter.
Bulgaria has a varied and changeable climate, which results from being positioned at the meeting point of the Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean, Oceanic climate, Oceanic and Continental climate, Continental air masses combined with the barrier effect of its mountains. Northern Bulgaria averages cooler, and registers more precipitation, than the regions south of the Balkan mountains. Temperature amplitudes vary significantly in different areas. The lowest recorded temperature is , while the highest is . Precipitation (meteorology), Precipitation averages about per year, and varies from in Dobrudja to more than in the mountains. Continental air masses bring significant amounts of snowfall during winter.
 Bulgaria is a parliamentary democracy where the Prime Minister of Bulgaria, prime minister is the head of government and the most powerful executive position. The political system has three branches—legislative, executive and judicial, with universal suffrage for citizens at least 18 years old. The Constitution of Bulgaria, Constitution also provides possibilities of direct democracy, namely petitions and national referendums. Elections are supervised by an independent Central Election Commission that includes members from all major political parties. Parties must register with the commission prior to participating in a national election. Normally, the prime minister-elect is the leader of the party receiving the most votes in parliamentary elections, although this is not always the case.
Unlike the prime minister, presidential domestic power is more limited. The directly elected President of Bulgaria, president serves as head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces, and has the authority to return a bill for further debate, although the parliament can override the presidential veto by a simple majority vote. Political parties gather in the National Assembly (Bulgaria), National Assembly, a body of 240 deputies elected to four-year terms by direct popular vote. The National Assembly has the power to enact laws, approve the budget, schedule presidential elections, select and dismiss the prime minister and other ministers, declare war, deploy troops abroad, and ratify international treaties and agreements.
Overall, Bulgaria displays a pattern of unstable governments. Boyko Borisov, the leader of the centre-right, pro-EU party GERB, served three terms as prime minister between 2009 and 2021.
It won 2009 Bulgarian parliamentary election, the 2009 general election and formed a minority government, which resigned in February 2013 after Protests against the Borisov cabinet, nationwide protests over the low living standards, corruption and the perceived failure of the democratic system.
The subsequent Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2013, snap elections in May resulted in a narrow win for GERB, but the Bulgarian Socialist Party eventually formed a government led by Plamen Oresharski after Borisov failed to secure parliamentary support. The Oresharski government resigned in July 2014 amid continuing 2013–14 Bulgarian protests against the Oresharski cabinet, large-scale protests.
The 2014 Bulgarian parliamentary election , October 2014 elections resulted in a third GERB victory. Borisov Second Borisov Government, formed a coalition with several right-wing parties, but resigned again after the candidate backed by his party failed to win the Bulgarian presidential election, 2016, 2016 Presidential election. The Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2017, March 2017 snap election was again won by GERB, but with 95 seats in Parliament. They formed a coalition with the far-right United Patriots, who held 27 seats.
Borisov's last cabinet saw a dramatic decrease in freedom of the press, and a number of corruption revelations that triggered 2020–2021 Bulgarian protests, yet another wave of mass protests in 2020. GERB came out first in the regular April 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, April 2021 election, but with its weakest result so far. All other parties refused to form a government, and after a brief deadlock, another election was called July 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, for July 2021. It too failed to break the stalemate, as no political party was able to form a coalition government.
Freedom House has reported a continuing deterioration of democratic governance after 2009, citing reduced media independence, stalled reforms, abuse of authority at the highest level and increased dependence of local administrations on the central government. Bulgaria is still Freedom in the World, listed as "Free", with a political system designated as a semi-consolidated democracy, albeit with deteriorating scores. The Democracy Index defines it as a "Flawed democracy". A 2018 survey by the Institute for Economics and Peace reported that less than 15% of respondents considered elections to be fair.
Bulgaria is a parliamentary democracy where the Prime Minister of Bulgaria, prime minister is the head of government and the most powerful executive position. The political system has three branches—legislative, executive and judicial, with universal suffrage for citizens at least 18 years old. The Constitution of Bulgaria, Constitution also provides possibilities of direct democracy, namely petitions and national referendums. Elections are supervised by an independent Central Election Commission that includes members from all major political parties. Parties must register with the commission prior to participating in a national election. Normally, the prime minister-elect is the leader of the party receiving the most votes in parliamentary elections, although this is not always the case.
Unlike the prime minister, presidential domestic power is more limited. The directly elected President of Bulgaria, president serves as head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces, and has the authority to return a bill for further debate, although the parliament can override the presidential veto by a simple majority vote. Political parties gather in the National Assembly (Bulgaria), National Assembly, a body of 240 deputies elected to four-year terms by direct popular vote. The National Assembly has the power to enact laws, approve the budget, schedule presidential elections, select and dismiss the prime minister and other ministers, declare war, deploy troops abroad, and ratify international treaties and agreements.
Overall, Bulgaria displays a pattern of unstable governments. Boyko Borisov, the leader of the centre-right, pro-EU party GERB, served three terms as prime minister between 2009 and 2021.
It won 2009 Bulgarian parliamentary election, the 2009 general election and formed a minority government, which resigned in February 2013 after Protests against the Borisov cabinet, nationwide protests over the low living standards, corruption and the perceived failure of the democratic system.
The subsequent Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2013, snap elections in May resulted in a narrow win for GERB, but the Bulgarian Socialist Party eventually formed a government led by Plamen Oresharski after Borisov failed to secure parliamentary support. The Oresharski government resigned in July 2014 amid continuing 2013–14 Bulgarian protests against the Oresharski cabinet, large-scale protests.
The 2014 Bulgarian parliamentary election , October 2014 elections resulted in a third GERB victory. Borisov Second Borisov Government, formed a coalition with several right-wing parties, but resigned again after the candidate backed by his party failed to win the Bulgarian presidential election, 2016, 2016 Presidential election. The Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2017, March 2017 snap election was again won by GERB, but with 95 seats in Parliament. They formed a coalition with the far-right United Patriots, who held 27 seats.
Borisov's last cabinet saw a dramatic decrease in freedom of the press, and a number of corruption revelations that triggered 2020–2021 Bulgarian protests, yet another wave of mass protests in 2020. GERB came out first in the regular April 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, April 2021 election, but with its weakest result so far. All other parties refused to form a government, and after a brief deadlock, another election was called July 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, for July 2021. It too failed to break the stalemate, as no political party was able to form a coalition government.
Freedom House has reported a continuing deterioration of democratic governance after 2009, citing reduced media independence, stalled reforms, abuse of authority at the highest level and increased dependence of local administrations on the central government. Bulgaria is still Freedom in the World, listed as "Free", with a political system designated as a semi-consolidated democracy, albeit with deteriorating scores. The Democracy Index defines it as a "Flawed democracy". A 2018 survey by the Institute for Economics and Peace reported that less than 15% of respondents considered elections to be fair.
 Bulgaria deployed significant numbers of both civilian and military advisors in Soviet-allied countries like Nicaraguan Revolution, Nicaragua and Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Libya during the Cold War. The first deployment of foreign troops on Bulgarian soil since World War II occurred in 2001, when the country hosted six KC-135 Stratotanker aircraft and 200 support personnel for the war effort in Afghanistan. International military relations were further expanded with accession to
Bulgaria deployed significant numbers of both civilian and military advisors in Soviet-allied countries like Nicaraguan Revolution, Nicaragua and Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Libya during the Cold War. The first deployment of foreign troops on Bulgarian soil since World War II occurred in 2001, when the country hosted six KC-135 Stratotanker aircraft and 200 support personnel for the war effort in Afghanistan. International military relations were further expanded with accession to

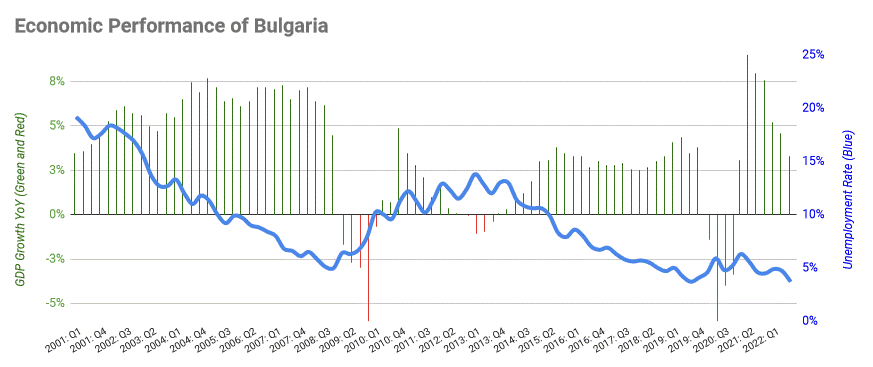 Bulgaria has an open, developing country, upper middle income range market economy where the private sector accounts for more than 70% of Gross domestic product, GDP. From a largely agricultural country with a predominantly rural population in 1948, by the 1980s Bulgaria had transformed into an industrial economy, with scientific and technological research at the top of its budgetary expenditure priorities. The loss of COMECON markets in 1990 and the subsequent "Shock therapy (economics), shock therapy" of the Planned economy, planned system caused a steep decline in industrial and agricultural production, ultimately followed by an economic collapse in 1997. The economy largely recovered during a period of rapid growth several years later, but the average salary of 1,036 leva ($615) per month remains the lowest in the EU. More than a fifth of the labour force work for a minimum wage of $1.16 per hour.
A balanced budget was achieved in 2003 and the country began running a budget surplus, surplus the following year. Expenditures amounted to $21.15 billion and revenues were $21.67 billion in 2017. Most government spending on institutions is earmarked for security. The ministries of defence, the interior and justice are allocated the largest share of the annual government budget, whereas those responsible for the environment, tourism and energy receive the least funding. Taxes form the bulk of government revenue at 30% of GDP. Bulgaria has some of the lowest corporate income Tax rates in Europe, tax rates in the EU at a flat 10% rate. The tax system is two-tier. Value added tax, excise duties, corporate and personal income tax are national, whereas real estate, inheritance, and vehicle taxes are levied by local authorities. Strong economic performance in the early 2000s reduced government debt from 79.6% in 1998 to 14.1% in 2008. It has since increased to 28.7% of GDP by 2016, but remains the third lowest in the EU.
The Yugozapaden First-level NUTS of the European Union, planning area is the most developed region with a per capita gross domestic product (Purchasing power parity, PPP) of $29,816 in 2018. It includes the capital city and the surrounding Sofia Province, which alone generate 42% of national gross domestic product despite hosting only 22% of the population. GDP per capita (in PPS) and the cost of living in 2019 stood at 53 and 52.8% of the EU average (100%), respectively. National PPP GDP was estimated at $143.1 billion in 2016, with a per capita value of $20,116. Economic growth statistics take into account illegal transactions from the informal economy, which is the largest in the EU as a percentage of economic output. The Bulgarian National Bank issues the national currency, Bulgarian lev, lev, which is pegged to the euro at a rate of 1.95583 levа per euro.
After several consecutive years of high growth, repercussions of the financial crisis of 2007–2008 resulted in a 3.6% contraction of GDP in 2009 and increased unemployment. Positive growth was restored in 2010 but intercompany debt exceeded $59 billion, meaning that 60% of all Bulgarian companies were mutually indebted. By 2012, it had increased to $97 billion, or 227% of GDP. The government implemented strict austerity measures with IMF and EU encouragement to some positive fiscal results, but the social consequences of these measures, such as increased economic inequality, income inequality and accelerated outward migration, have been "catastrophic" according to the International Trade Union Confederation.
Siphoning of public funds to the families and relatives of politicians from incumbent parties has resulted in fiscal and welfare losses to society. Bulgaria ranks 71st in the Corruption Perceptions Index and experiences the worst levels of corruption in the European Union, a phenomenon that remains a source of profound public discontent. Along with organised crime, corruption has resulted in a rejection of the country's Schengen Area application and withdrawal of foreign investment. Government officials reportedly engage in embezzlement, influence trading, government procurement violations and bribery with impunity. Government procurement in particular is a critical area in corruption risk. An estimated 10 billion leva ($5.99 billion) of state budget and Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund, European cohesion funds are spent on public tenders each year; nearly 14 billion ($8.38 billion) were spent on public contracts in 2017 alone. A large share of these contracts are awarded to a few politically connected companies amid widespread irregularities, procedure violations and tailor-made award criteria. Despite repeated criticism from the European Commission, EU institutions refrain from taking measures against Bulgaria because it supports Brussels on a number of issues, unlike Poland or Hungary.
Bulgaria has an open, developing country, upper middle income range market economy where the private sector accounts for more than 70% of Gross domestic product, GDP. From a largely agricultural country with a predominantly rural population in 1948, by the 1980s Bulgaria had transformed into an industrial economy, with scientific and technological research at the top of its budgetary expenditure priorities. The loss of COMECON markets in 1990 and the subsequent "Shock therapy (economics), shock therapy" of the Planned economy, planned system caused a steep decline in industrial and agricultural production, ultimately followed by an economic collapse in 1997. The economy largely recovered during a period of rapid growth several years later, but the average salary of 1,036 leva ($615) per month remains the lowest in the EU. More than a fifth of the labour force work for a minimum wage of $1.16 per hour.
A balanced budget was achieved in 2003 and the country began running a budget surplus, surplus the following year. Expenditures amounted to $21.15 billion and revenues were $21.67 billion in 2017. Most government spending on institutions is earmarked for security. The ministries of defence, the interior and justice are allocated the largest share of the annual government budget, whereas those responsible for the environment, tourism and energy receive the least funding. Taxes form the bulk of government revenue at 30% of GDP. Bulgaria has some of the lowest corporate income Tax rates in Europe, tax rates in the EU at a flat 10% rate. The tax system is two-tier. Value added tax, excise duties, corporate and personal income tax are national, whereas real estate, inheritance, and vehicle taxes are levied by local authorities. Strong economic performance in the early 2000s reduced government debt from 79.6% in 1998 to 14.1% in 2008. It has since increased to 28.7% of GDP by 2016, but remains the third lowest in the EU.
The Yugozapaden First-level NUTS of the European Union, planning area is the most developed region with a per capita gross domestic product (Purchasing power parity, PPP) of $29,816 in 2018. It includes the capital city and the surrounding Sofia Province, which alone generate 42% of national gross domestic product despite hosting only 22% of the population. GDP per capita (in PPS) and the cost of living in 2019 stood at 53 and 52.8% of the EU average (100%), respectively. National PPP GDP was estimated at $143.1 billion in 2016, with a per capita value of $20,116. Economic growth statistics take into account illegal transactions from the informal economy, which is the largest in the EU as a percentage of economic output. The Bulgarian National Bank issues the national currency, Bulgarian lev, lev, which is pegged to the euro at a rate of 1.95583 levа per euro.
After several consecutive years of high growth, repercussions of the financial crisis of 2007–2008 resulted in a 3.6% contraction of GDP in 2009 and increased unemployment. Positive growth was restored in 2010 but intercompany debt exceeded $59 billion, meaning that 60% of all Bulgarian companies were mutually indebted. By 2012, it had increased to $97 billion, or 227% of GDP. The government implemented strict austerity measures with IMF and EU encouragement to some positive fiscal results, but the social consequences of these measures, such as increased economic inequality, income inequality and accelerated outward migration, have been "catastrophic" according to the International Trade Union Confederation.
Siphoning of public funds to the families and relatives of politicians from incumbent parties has resulted in fiscal and welfare losses to society. Bulgaria ranks 71st in the Corruption Perceptions Index and experiences the worst levels of corruption in the European Union, a phenomenon that remains a source of profound public discontent. Along with organised crime, corruption has resulted in a rejection of the country's Schengen Area application and withdrawal of foreign investment. Government officials reportedly engage in embezzlement, influence trading, government procurement violations and bribery with impunity. Government procurement in particular is a critical area in corruption risk. An estimated 10 billion leva ($5.99 billion) of state budget and Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund, European cohesion funds are spent on public tenders each year; nearly 14 billion ($8.38 billion) were spent on public contracts in 2017 alone. A large share of these contracts are awarded to a few politically connected companies amid widespread irregularities, procedure violations and tailor-made award criteria. Despite repeated criticism from the European Commission, EU institutions refrain from taking measures against Bulgaria because it supports Brussels on a number of issues, unlike Poland or Hungary.
 The labour force is 3.36 million people, of whom 6.8% are employed in agriculture, 26.6% in industry and 66.6% in the services sector. Extraction of metals and minerals, production of chemical industry, chemicals, machinery industry, machine building, steel, biotechnology, tobacco, food processing and refined petroleum fuel, petroleum refining are among the major industrial activities. Mining alone employs 24,000 people and generates about 5% of the country's GDP; the number of employed in all mining-related industries is 120,000. Bulgaria is Europe's fifth-largest coal producer. Local deposits of coal, iron, copper and lead are vital for the manufacturing and energy sectors. The main destinations of Bulgarian exports outside the EU are Turkey, China and the United States, while Russia and Turkey are by far the largest import partners. Most of the exports are manufactured goods, machinery, chemicals, fuel products and food. Two-thirds of food and agricultural exports go to OECD countries.
Although cereal and vegetable output dropped by 40% between 1990 and 2008, output in grains has since increased, and the 2016–2017 season registered the biggest grain output in a decade. Maize, barley, oats and rice are also grown. Quality Turkish tobacco, Oriental tobacco is a significant industrial crop. Bulgaria is also the largest producer globally of lavender oil, lavender and rose oil, both widely used in fragrances. Within the services sector, Tourism in Bulgaria, tourism is a significant contributor to economic growth.
The labour force is 3.36 million people, of whom 6.8% are employed in agriculture, 26.6% in industry and 66.6% in the services sector. Extraction of metals and minerals, production of chemical industry, chemicals, machinery industry, machine building, steel, biotechnology, tobacco, food processing and refined petroleum fuel, petroleum refining are among the major industrial activities. Mining alone employs 24,000 people and generates about 5% of the country's GDP; the number of employed in all mining-related industries is 120,000. Bulgaria is Europe's fifth-largest coal producer. Local deposits of coal, iron, copper and lead are vital for the manufacturing and energy sectors. The main destinations of Bulgarian exports outside the EU are Turkey, China and the United States, while Russia and Turkey are by far the largest import partners. Most of the exports are manufactured goods, machinery, chemicals, fuel products and food. Two-thirds of food and agricultural exports go to OECD countries.
Although cereal and vegetable output dropped by 40% between 1990 and 2008, output in grains has since increased, and the 2016–2017 season registered the biggest grain output in a decade. Maize, barley, oats and rice are also grown. Quality Turkish tobacco, Oriental tobacco is a significant industrial crop. Bulgaria is also the largest producer globally of lavender oil, lavender and rose oil, both widely used in fragrances. Within the services sector, Tourism in Bulgaria, tourism is a significant contributor to economic growth.
 Despite the lack of funding, research in chemistry, materials science and physics remains strong. Antarctic research is actively carried out through the St. Kliment Ohridski Base on Livingston Island in Western Antarctica. The information and communication technologies (ICT) sector generates three per cent of economic output and employs 40,000 to 51,000 software engineers. Bulgaria was known as a "Communist Silicon Valley" during the Soviet era due to its key role in COMECON computing technology production. A concerted effort by the communist government to teach computing and IT skills in schools also indirectly made Bulgaria a major source of computer viruses in the 1980s and 90s. The country is a regional leader in supercomputer, high performance computing: it operates ''Avitohol'', the most powerful supercomputer in Southeast Europe, and will host one of the eight petascale computing, petascale European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking, EuroHPC supercomputers.
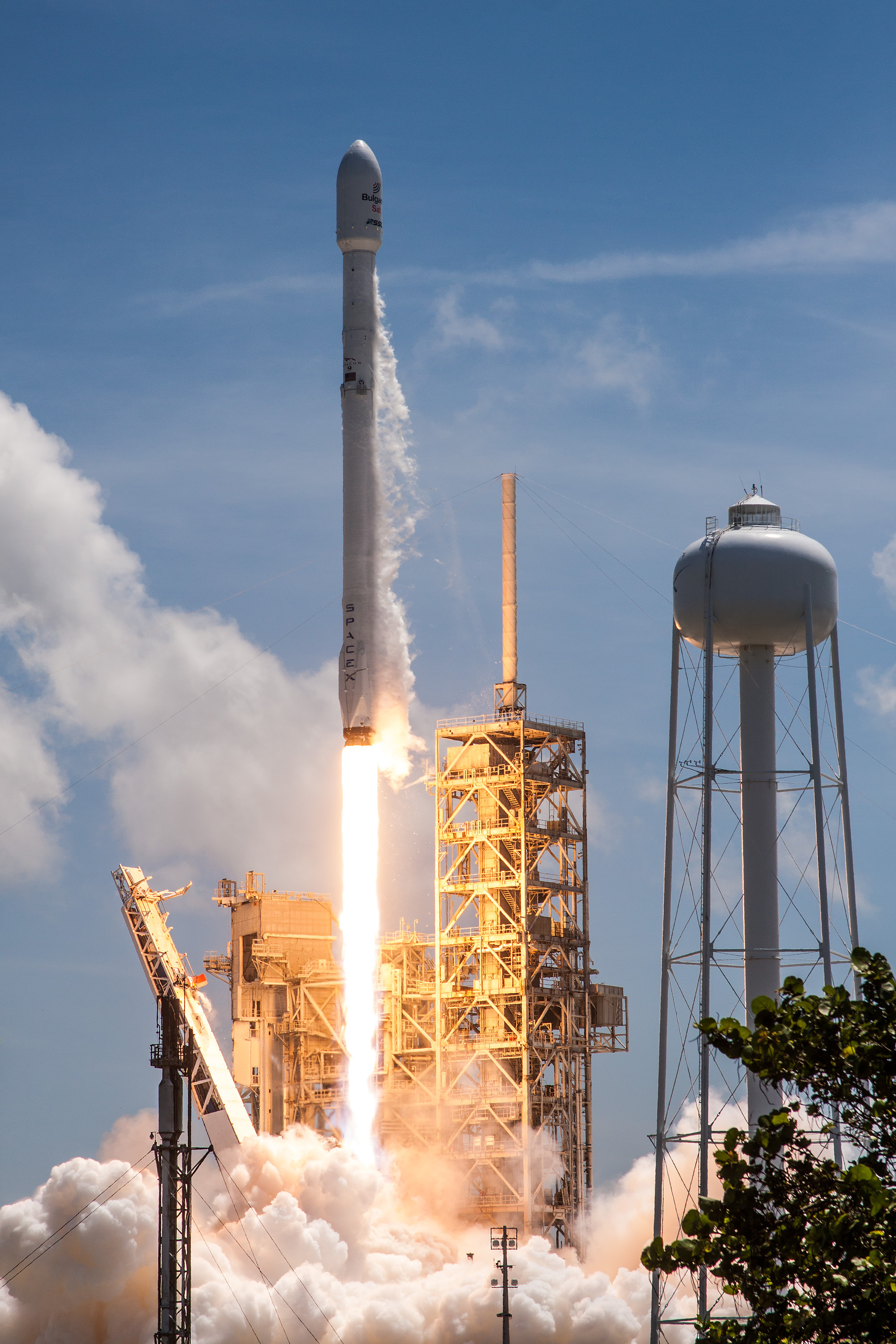
Bulgaria has made numerous contributions to space exploration. These include two scientific satellites, more than 200 payloads and 300 experiments in Earth orbit, as well as Bulgarian cosmonaut programme, two cosmonauts since 1971. Bulgaria was the first country to grow wheat and vegetables Plants in space, in space with its SVET plant growth system, Svet greenhouses on the Mir space station. It was involved in the development of the Granat Gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray observatory and the Vega program, particularly in modelling trajectories and guidance algorithms for both Vega probes. Bulgarian instruments have been used in the exploration of Mars, including a spectrometer that took the first high quality spectroscopy, spectroscopic images of Martian moon Phobos (moon), Phobos with the Phobos 2 probe. Cosmic ray, Cosmic radiation en route to and around the planet has been mapped by Liulin type instruments, Liulin-ML dosimeters on the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, ExoMars TGO. RADOM-7, Variants of these instruments have also been fitted on the International Space Station and the Chandrayaan-1 lunar probe. Another lunar mission, SpaceIL's ''Beresheet'', was also equipped with a Bulgarian-manufactured imaging payload. Bulgaria's first Geosynchronous satellite, geostationary communications satellite—BulgariaSat-1—was launched by SpaceX in 2017.
Despite the lack of funding, research in chemistry, materials science and physics remains strong. Antarctic research is actively carried out through the St. Kliment Ohridski Base on Livingston Island in Western Antarctica. The information and communication technologies (ICT) sector generates three per cent of economic output and employs 40,000 to 51,000 software engineers. Bulgaria was known as a "Communist Silicon Valley" during the Soviet era due to its key role in COMECON computing technology production. A concerted effort by the communist government to teach computing and IT skills in schools also indirectly made Bulgaria a major source of computer viruses in the 1980s and 90s. The country is a regional leader in supercomputer, high performance computing: it operates ''Avitohol'', the most powerful supercomputer in Southeast Europe, and will host one of the eight petascale computing, petascale European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking, EuroHPC supercomputers.
Bulgaria has made numerous contributions to space exploration. These include two scientific satellites, more than 200 payloads and 300 experiments in Earth orbit, as well as Bulgarian cosmonaut programme, two cosmonauts since 1971. Bulgaria was the first country to grow wheat and vegetables Plants in space, in space with its SVET plant growth system, Svet greenhouses on the Mir space station. It was involved in the development of the Granat Gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray observatory and the Vega program, particularly in modelling trajectories and guidance algorithms for both Vega probes. Bulgarian instruments have been used in the exploration of Mars, including a spectrometer that took the first high quality spectroscopy, spectroscopic images of Martian moon Phobos (moon), Phobos with the Phobos 2 probe. Cosmic ray, Cosmic radiation en route to and around the planet has been mapped by Liulin type instruments, Liulin-ML dosimeters on the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, ExoMars TGO. RADOM-7, Variants of these instruments have also been fitted on the International Space Station and the Chandrayaan-1 lunar probe. Another lunar mission, SpaceIL's ''Beresheet'', was also equipped with a Bulgarian-manufactured imaging payload. Bulgaria's first Geosynchronous satellite, geostationary communications satellite—BulgariaSat-1—was launched by SpaceX in 2017.
 Telephone services are widely available, and a central digital trunk line connects most regions. Vivacom (BTC) serves more than 90% of fixed lines and is one of the three operators providing mobile services, along with Mtel (Bulgaria), A1 and Telenor (Bulgaria), Telenor. Internet penetration stood at 69.2% of the population aged 16–74 and 78.9% of households in 2020.
Bulgaria's strategic geographic location and well-developed energy sector make it a key European energy centre despite its lack of significant fossil fuel deposits. Thermal power plants generate 48.9% of electricity, followed by nuclear power from the Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, Kozloduy reactors (34.8%) and renewable energy, renewable sources (16.3%). Equipment for a second nuclear power station at Belene Nuclear Power Plant, Belene has been acquired, but the fate of the project remains uncertain. Installed capacity amounts to 12,668 MW, allowing Bulgaria to exceed domestic demand and export energy.
The national road network has a total length of , of which are paved. Railroads are a major mode of freight transportation, although highways carry a progressively larger share of freight. Bulgaria has of railway track, with rail links available to Romania, Turkey, Greece, and Serbia, and express trains serving direct routes to Kyiv, Minsk, Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Sofia and Plovdiv are the country's air travel hubs, while Varna and Burgas are the principal maritime trade ports.
Telephone services are widely available, and a central digital trunk line connects most regions. Vivacom (BTC) serves more than 90% of fixed lines and is one of the three operators providing mobile services, along with Mtel (Bulgaria), A1 and Telenor (Bulgaria), Telenor. Internet penetration stood at 69.2% of the population aged 16–74 and 78.9% of households in 2020.
Bulgaria's strategic geographic location and well-developed energy sector make it a key European energy centre despite its lack of significant fossil fuel deposits. Thermal power plants generate 48.9% of electricity, followed by nuclear power from the Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, Kozloduy reactors (34.8%) and renewable energy, renewable sources (16.3%). Equipment for a second nuclear power station at Belene Nuclear Power Plant, Belene has been acquired, but the fate of the project remains uncertain. Installed capacity amounts to 12,668 MW, allowing Bulgaria to exceed domestic demand and export energy.
The national road network has a total length of , of which are paved. Railroads are a major mode of freight transportation, although highways carry a progressively larger share of freight. Bulgaria has of railway track, with rail links available to Romania, Turkey, Greece, and Serbia, and express trains serving direct routes to Kyiv, Minsk, Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Sofia and Plovdiv are the country's air travel hubs, while Varna and Burgas are the principal maritime trade ports.
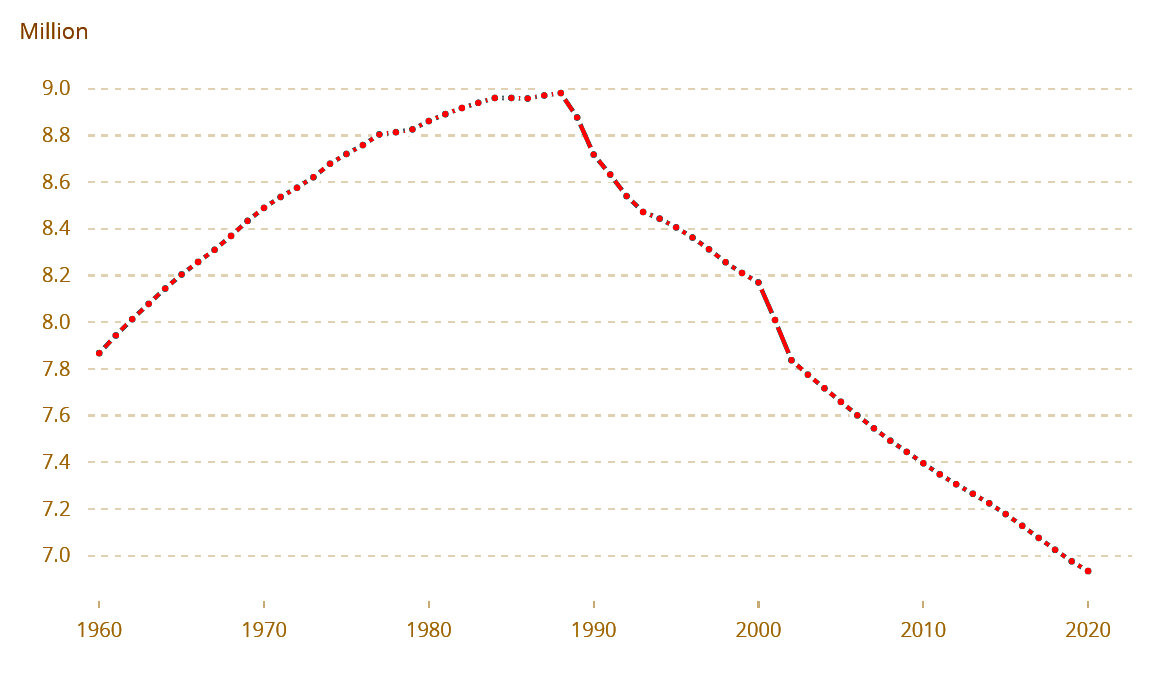
 The population of Bulgaria is 6,519,789 people according to the 2021 national census. The majority of the population, 72.5%, reside in urban areas. , Sofia is the most populated urban centre with 1,241,675 people, followed by Plovdiv (346,893),
The population of Bulgaria is 6,519,789 people according to the 2021 national census. The majority of the population, 72.5%, reside in urban areas. , Sofia is the most populated urban centre with 1,241,675 people, followed by Plovdiv (346,893),
 Public expenditures for education are far below the European Union average as well. Educational standards Education in Bulgaria, were once high, but have declined significantly since the early 2000s. Bulgarian students were among the highest-scoring in the world in terms of reading in 2001, performing better than their Canadian and German counterparts; by 2006, scores in reading, math and science had dropped. By 2018, Programme for International Student Assessment studies found 47% of pupils in the 9th grade to be functional illiteracy, functionally illiterate in reading and natural sciences. Average basic literacy stands high at 98.4% with no significant difference between sexes. The Ministry of Education and Science (Bulgaria), Ministry of Education and Science partially funds public schools, colleges and universities, sets criteria for textbooks and oversees the publishing process. Education in primary and secondary public schools is free and compulsory. The process spans 12 grades, in which grades one through eight are primary and nine through twelve are secondary level. Higher education consists of a 4-year Bachelor's degree, bachelor degree and a 1-year Master's degree, master's degree. Bulgaria's highest-ranked higher education institution is Sofia University.
Public expenditures for education are far below the European Union average as well. Educational standards Education in Bulgaria, were once high, but have declined significantly since the early 2000s. Bulgarian students were among the highest-scoring in the world in terms of reading in 2001, performing better than their Canadian and German counterparts; by 2006, scores in reading, math and science had dropped. By 2018, Programme for International Student Assessment studies found 47% of pupils in the 9th grade to be functional illiteracy, functionally illiterate in reading and natural sciences. Average basic literacy stands high at 98.4% with no significant difference between sexes. The Ministry of Education and Science (Bulgaria), Ministry of Education and Science partially funds public schools, colleges and universities, sets criteria for textbooks and oversees the publishing process. Education in primary and secondary public schools is free and compulsory. The process spans 12 grades, in which grades one through eight are primary and nine through twelve are secondary level. Higher education consists of a 4-year Bachelor's degree, bachelor degree and a 1-year Master's degree, master's degree. Bulgaria's highest-ranked higher education institution is Sofia University.
 Bulgaria is a secular state with guaranteed religious freedom by constitution, but Orthodoxy is designated as a traditional religion. More than three-quarters of Bulgarians subscribe to Eastern Orthodoxy. The Bulgarian Orthodox Church gained autocephalous status in AD 927, and has 12
Bulgaria is a secular state with guaranteed religious freedom by constitution, but Orthodoxy is designated as a traditional religion. More than three-quarters of Bulgarians subscribe to Eastern Orthodoxy. The Bulgarian Orthodox Church gained autocephalous status in AD 927, and has 12
 Contemporary Bulgarian culture blends the formal culture that helped forge a national consciousness towards the end of Ottoman rule with millennia-old folk traditions. An essential element of Bulgarian folklore is fire, used to banish evil spirits and illnesses. Many of these are personified as witches, whereas other creatures like Slavic dragon, zmey and samodiva (folklore), samodiva (Supernatural beings in Slavic religion, veela) are either benevolent guardians or ambivalent tricksters. Some rituals against evil spirits have survived and are still practised, most notably kukeri and survakane, survakari. Martenitsa is also widely celebrated. Nestinarstvo, a ritual fire-dance of Thracian origin, is included in the list of UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
List of World Heritage Sites in Bulgaria, Nine historical and natural objects are UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Pirin National Park, Srebarna Nature Reserve, Sreburna Nature Reserve, the Madara Rider, the Thracian tombs in Thracian Tomb of Sveshtari, Sveshtari and Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak, Kazanlak, the Rila Monastery, the Boyana Church, the Rock-hewn Churches of Ivanovo and the ancient city of Nesebar. The Rila Monastery was established by Saint John of Rila, Bulgaria's patron saint, whose life has been the subject of numerous literary accounts since Medieval times.
The establishment of the Preslav Literary School, Preslav and Ohrid Literary School, Ohrid literary schools in the 10th century is associated with a golden period in Bulgarian literature during the Middle Ages. The schools' emphasis on Christian religious text, scriptures made the Bulgarian Empire a centre of Slavic culture, bringing Slavs under the influence of Christianity and providing them with Old Church Slavonic, a written language. Its alphabet, Cyrillic script, was developed by the Preslav Literary School. The Tarnovo Literary School, on the other hand, is associated with a Silver age of literature defined by high-quality manuscripts on historical or mystical themes under the Asen dynasty, Asen and House of Shishman, Shishman dynasties. Many literary and artistic masterpieces were destroyed by the Ottoman conquerors, and artistic activities did not re-emerge until the Bulgarian National Revival, National Revival in the 19th century. The enormous body of work of Ivan Vazov (1850–1921) covered every genre and touched upon every facet of Bulgarian society, bridging pre-Liberation works with literature of the newly established state. Notable later works are ''Bay Ganyo'' by Aleko Konstantinov, the Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzschean poetry of Pencho Slaveykov, the Symbolism (arts), Symbolist poetry of Peyo Yavorov and Dimcho Debelyanov, the Marxism, Marxist-inspired works of Geo Milev and Nikola Vaptsarov, and the Socialist Realism, Socialist realism novels of Dimitar Dimov and Dimitar Talev. Tzvetan Todorov is a notable contemporary author, while Bulgarian-born Elias Canetti was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1981.
А religious visual arts heritage includes frescoes, murals and icons, many produced by the medieval Painting of the Tarnovo Artistic School, Tarnovo Artistic School. Like literature, it was not until the National Revival when Bulgarian visual arts began to reemerge. Zahari Zograf was a pioneer of the visual arts in the pre-Liberation era. After the Liberation, Ivan Mrkvička, Anton Mitov, Vladimir Dimitrov, Tsanko Lavrenov and Zlatyu Boyadzhiev introduced newer styles and substance, depicting scenery from Bulgarian villages, old towns and historical subjects. Christo is the most famous Bulgarian artist of the 21st century, known for his outdoor installations.
Folk music is by far the most extensive traditional art and has slowly developed throughout the ages as a fusion of Far Eastern, Oriental, medieval Eastern Orthodox and standard Western European tonalities and modes. Bulgarian folk music has a distinctive sound and uses a wide range of traditional instruments, such as gadulka, gaida, kaval and davul, tupan. A distinguishing feature is ''extended rhythmical time'', which has no equivalent in the rest of European music. The Bulgarian State Television Female Vocal Choir, State Television Female Vocal Choir won a Grammy Award in 1990 for its performances of Bulgarian folk music. Written musical composition can be traced back to the works of Yoan Kukuzel (c. 1280–1360), but modern classical music began with Emanuil Manolov, who composed the first Bulgarian opera in 1890. Pancho Vladigerov and Petko Staynov further enriched symphony, ballet and opera, which singers Ghena Dimitrova, Boris Christoff, Ljuba Welitsch and Nicolai Ghiaurov elevated to a world-class level.
Bulgarian performers have gained acclaim in other genres like electropop (Mira Aroyo), jazz (Milcho Leviev) and blends of jazz and folk (Ivo Papazov).
The Bulgarian National Radio, bTV (Bulgaria), bTV and daily newspapers ''Trud (Bulgarian newspaper), Trud'', ''Dnevnik (Bulgaria), Dnevnik'' and ''24 Chasa'' are some of the largest national media outlets. Media of Bulgaria, Bulgarian media were described as generally unbiased in their reporting in the early 2000s and print media had no legal restrictions. Since then, freedom of the press has deteriorated to the point where Bulgaria scores 111th globally in the World Press Freedom Index, lower than all European Union members and membership candidate states. The government has diverted EU funds to sympathetic media outlets and bribed others to be less critical on problematic topics, while attacks against individual journalists have increased. Collusion between politicians, oligarchs and the media is widespread.
Bulgarian cuisine is similar to that of other Balkan countries and demonstrates strong Turkish and Greek influences. Yogurt, lukanka, banitsa, shopska salad, lyutenitsa and kozunak are among the best-known local foods. Meat consumption is lower than the European average, given a cultural preference for a large variety of salads. Bulgaria was the world's second-largest wine exporter until 1989, but has since lost that position. The 2016 harvest yielded 128 million litres of wine, of which 62 million was exported mainly to Romania, Poland and Russia. Mavrud, Rubin, Siroka Melniska, Shiroka melnishka, Dimiat and Misket Cherven, Cherven Misket are the typical grapes used in Bulgarian wine. Rakia is a traditional fruit brandy that was consumed in Bulgaria as early as the 14th century.
Contemporary Bulgarian culture blends the formal culture that helped forge a national consciousness towards the end of Ottoman rule with millennia-old folk traditions. An essential element of Bulgarian folklore is fire, used to banish evil spirits and illnesses. Many of these are personified as witches, whereas other creatures like Slavic dragon, zmey and samodiva (folklore), samodiva (Supernatural beings in Slavic religion, veela) are either benevolent guardians or ambivalent tricksters. Some rituals against evil spirits have survived and are still practised, most notably kukeri and survakane, survakari. Martenitsa is also widely celebrated. Nestinarstvo, a ritual fire-dance of Thracian origin, is included in the list of UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
List of World Heritage Sites in Bulgaria, Nine historical and natural objects are UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Pirin National Park, Srebarna Nature Reserve, Sreburna Nature Reserve, the Madara Rider, the Thracian tombs in Thracian Tomb of Sveshtari, Sveshtari and Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak, Kazanlak, the Rila Monastery, the Boyana Church, the Rock-hewn Churches of Ivanovo and the ancient city of Nesebar. The Rila Monastery was established by Saint John of Rila, Bulgaria's patron saint, whose life has been the subject of numerous literary accounts since Medieval times.
The establishment of the Preslav Literary School, Preslav and Ohrid Literary School, Ohrid literary schools in the 10th century is associated with a golden period in Bulgarian literature during the Middle Ages. The schools' emphasis on Christian religious text, scriptures made the Bulgarian Empire a centre of Slavic culture, bringing Slavs under the influence of Christianity and providing them with Old Church Slavonic, a written language. Its alphabet, Cyrillic script, was developed by the Preslav Literary School. The Tarnovo Literary School, on the other hand, is associated with a Silver age of literature defined by high-quality manuscripts on historical or mystical themes under the Asen dynasty, Asen and House of Shishman, Shishman dynasties. Many literary and artistic masterpieces were destroyed by the Ottoman conquerors, and artistic activities did not re-emerge until the Bulgarian National Revival, National Revival in the 19th century. The enormous body of work of Ivan Vazov (1850–1921) covered every genre and touched upon every facet of Bulgarian society, bridging pre-Liberation works with literature of the newly established state. Notable later works are ''Bay Ganyo'' by Aleko Konstantinov, the Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzschean poetry of Pencho Slaveykov, the Symbolism (arts), Symbolist poetry of Peyo Yavorov and Dimcho Debelyanov, the Marxism, Marxist-inspired works of Geo Milev and Nikola Vaptsarov, and the Socialist Realism, Socialist realism novels of Dimitar Dimov and Dimitar Talev. Tzvetan Todorov is a notable contemporary author, while Bulgarian-born Elias Canetti was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1981.
А religious visual arts heritage includes frescoes, murals and icons, many produced by the medieval Painting of the Tarnovo Artistic School, Tarnovo Artistic School. Like literature, it was not until the National Revival when Bulgarian visual arts began to reemerge. Zahari Zograf was a pioneer of the visual arts in the pre-Liberation era. After the Liberation, Ivan Mrkvička, Anton Mitov, Vladimir Dimitrov, Tsanko Lavrenov and Zlatyu Boyadzhiev introduced newer styles and substance, depicting scenery from Bulgarian villages, old towns and historical subjects. Christo is the most famous Bulgarian artist of the 21st century, known for his outdoor installations.
Folk music is by far the most extensive traditional art and has slowly developed throughout the ages as a fusion of Far Eastern, Oriental, medieval Eastern Orthodox and standard Western European tonalities and modes. Bulgarian folk music has a distinctive sound and uses a wide range of traditional instruments, such as gadulka, gaida, kaval and davul, tupan. A distinguishing feature is ''extended rhythmical time'', which has no equivalent in the rest of European music. The Bulgarian State Television Female Vocal Choir, State Television Female Vocal Choir won a Grammy Award in 1990 for its performances of Bulgarian folk music. Written musical composition can be traced back to the works of Yoan Kukuzel (c. 1280–1360), but modern classical music began with Emanuil Manolov, who composed the first Bulgarian opera in 1890. Pancho Vladigerov and Petko Staynov further enriched symphony, ballet and opera, which singers Ghena Dimitrova, Boris Christoff, Ljuba Welitsch and Nicolai Ghiaurov elevated to a world-class level.
Bulgarian performers have gained acclaim in other genres like electropop (Mira Aroyo), jazz (Milcho Leviev) and blends of jazz and folk (Ivo Papazov).
The Bulgarian National Radio, bTV (Bulgaria), bTV and daily newspapers ''Trud (Bulgarian newspaper), Trud'', ''Dnevnik (Bulgaria), Dnevnik'' and ''24 Chasa'' are some of the largest national media outlets. Media of Bulgaria, Bulgarian media were described as generally unbiased in their reporting in the early 2000s and print media had no legal restrictions. Since then, freedom of the press has deteriorated to the point where Bulgaria scores 111th globally in the World Press Freedom Index, lower than all European Union members and membership candidate states. The government has diverted EU funds to sympathetic media outlets and bribed others to be less critical on problematic topics, while attacks against individual journalists have increased. Collusion between politicians, oligarchs and the media is widespread.
Bulgarian cuisine is similar to that of other Balkan countries and demonstrates strong Turkish and Greek influences. Yogurt, lukanka, banitsa, shopska salad, lyutenitsa and kozunak are among the best-known local foods. Meat consumption is lower than the European average, given a cultural preference for a large variety of salads. Bulgaria was the world's second-largest wine exporter until 1989, but has since lost that position. The 2016 harvest yielded 128 million litres of wine, of which 62 million was exported mainly to Romania, Poland and Russia. Mavrud, Rubin, Siroka Melniska, Shiroka melnishka, Dimiat and Misket Cherven, Cherven Misket are the typical grapes used in Bulgarian wine. Rakia is a traditional fruit brandy that was consumed in Bulgaria as early as the 14th century.
 Bulgaria appeared at the 1896 Summer Olympics, first modern Olympic games in 1896, when it was represented by Gymnastics at the 1896 Summer Olympics, gymnast Charles Champaud. Since then, Bulgarian athletes have won 55 gold, 90 silver, and 85 bronze medals, ranking 25th in the All-time Olympic Games medal table, all-time medal table. Olympic weightlifting, Weight-lifting is a signature sport of Bulgaria. Coach Ivan Abadjiev, Ivan Abadzhiev developed innovative training practices that have produced many Bulgarian world and Olympic champions in weight-lifting since the 1980s. Bulgarian athletes have also excelled in wrestling, boxing, gymnastics, volleyball and tennis. Stefka Kostadinova is the reigning List of world records in athletics, world record holder in the women's high jump at , achieved during the 1987 World Championships in Athletics, 1987 World Championships. Grigor Dimitrov is the first Bulgarian tennis player in the Top 3 ATP rankings#Current rankings, ATP rankings.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in the country by a substantial margin. The Bulgaria national football team, national football team's best performance was a semi-final at the 1994 FIFA World Cup, when the squad was spearheaded by forward Hristo Stoichkov. Stoichkov is the most successful Bulgarian player of all time; he was awarded the European Golden Shoe, Golden Boot and the Ballon d'Or, Golden Ball and was considered one of the best in the world while playing for FC Barcelona in the 1990s. PFC CSKA Sofia, CSKA and PFC Levski Sofia, Levski, both based in Sofia, are the most successful clubs domestically and Eternal derby of Bulgarian football, long-standing rivals. PFC Ludogorets Razgrad, Ludogorets is remarkable for having advanced from the local fourth division to the 2014–15 UEFA Champions League group stage in a mere nine years. Placed 39th in 2018, it is Bulgaria's highest-ranked club in UEFA.
Bulgaria appeared at the 1896 Summer Olympics, first modern Olympic games in 1896, when it was represented by Gymnastics at the 1896 Summer Olympics, gymnast Charles Champaud. Since then, Bulgarian athletes have won 55 gold, 90 silver, and 85 bronze medals, ranking 25th in the All-time Olympic Games medal table, all-time medal table. Olympic weightlifting, Weight-lifting is a signature sport of Bulgaria. Coach Ivan Abadjiev, Ivan Abadzhiev developed innovative training practices that have produced many Bulgarian world and Olympic champions in weight-lifting since the 1980s. Bulgarian athletes have also excelled in wrestling, boxing, gymnastics, volleyball and tennis. Stefka Kostadinova is the reigning List of world records in athletics, world record holder in the women's high jump at , achieved during the 1987 World Championships in Athletics, 1987 World Championships. Grigor Dimitrov is the first Bulgarian tennis player in the Top 3 ATP rankings#Current rankings, ATP rankings.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in the country by a substantial margin. The Bulgaria national football team, national football team's best performance was a semi-final at the 1994 FIFA World Cup, when the squad was spearheaded by forward Hristo Stoichkov. Stoichkov is the most successful Bulgarian player of all time; he was awarded the European Golden Shoe, Golden Boot and the Ballon d'Or, Golden Ball and was considered one of the best in the world while playing for FC Barcelona in the 1990s. PFC CSKA Sofia, CSKA and PFC Levski Sofia, Levski, both based in Sofia, are the most successful clubs domestically and Eternal derby of Bulgarian football, long-standing rivals. PFC Ludogorets Razgrad, Ludogorets is remarkable for having advanced from the local fourth division to the 2014–15 UEFA Champions League group stage in a mere nine years. Placed 39th in 2018, it is Bulgaria's highest-ranked club in UEFA.
Bulgaria
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''. * *
Bulgaria Profile
from Balkan Insight
President of The Republic of Bulgaria
{{Authority control Bulgaria, Balkan countries Bulgarian-speaking countries and territories Countries in Europe Eastern European countries Member states of NATO Member states of the European Union Member states of the Three Seas Initiative Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Republics Southeastern European countries States and territories established in 1908 States and territories established in the 680s
Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, and is bordered by Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
to the north, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
and North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
to the west, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
to the south, and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
is the nation's capital and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
and Burgas
Burgas ( bg, Бургас, ), sometimes transliterated as ''Bourgas'', is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the fourth-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, and Varna, with a pop ...
.
One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Karanovo culture
The Karanovo culture is a Neolithic culture (Karanovo I-III ca. 62nd to 55th centuries BC) named after the Bulgarian village of (Караново, Sliven Province ). The culture, which is part of the Danube civilization, is considered the lar ...
, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the S ...
. The Bulgars, led by Asparuh
Asparuh (also ''Ispor''; bg, Аспарух, Asparuh or (rarely) bg, Исперих, Isperih) was а ruler of Bulgars in the second half of the 7th century and is credited with the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681.
Early life
...
, attacked from the lands of Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria (Medieval Greek: Παλαιά Μεγάλη Βουλγαρία, ''Palaiá Megálē Voulgaría''), also often known by the Latin names ''Magna Bulgaria'' and ''Patria Onoguria'' (" Onogur land"), was a 7th- ...
and permanently invaded the Balkans in the late 7th century. They established First Bulgarian Empire, victoriously recognised by treaty in 681 AD by the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
. It dominated most of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
and significantly influenced Slavic cultures by developing the Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
. The First Bulgarian Empire lasted until the early 11th century, when Byzantine emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
conquered and dismantled it. A successful Bulgarian revolt in 1185 established a Second Bulgarian Empire, which reached its apex under Ivan Asen II
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II ( bg, Иван Асен II, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I one of the founders of the Second Bulgarian Empir ...
(1218–1241). After numerous exhausting wars and feudal strife, the empire disintegrated in 1396 and fell under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries.
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78 resulted in the formation of the third and current Bulgarian state. Many ethnic Bulgarians were left outside the new nation's borders, which stoked irredentist
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent st ...
sentiments that led to several conflicts with its neighbours and alliances with Germany in both world wars. In 1946, Bulgaria came under the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc and became a socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country, sometimes referred to as a workers' state or workers' republic, is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. The term '' communist state'' is of ...
. The ruling Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of ''The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. ...
gave up its monopoly on power after the revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Nat ...
and allowed multiparty
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coal ...
elections. Bulgaria then transitioned into a democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which people, the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation ("direct democracy"), or to choo ...
and a market-based economy. Since adopting a democratic constitution
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which people, the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation ("direct democracy"), or to choo ...
in 1991, Bulgaria has been a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigrou ...
parliamentary republic composed of 28 provinces, with a high degree of political, administrative, and economic centralisation.
Bulgaria is a developing country, with an upper-middle-income economy, ranking 68th in the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
. Its market economy is part of the European Single Market and is largely based on services, followed by industry—especially machine building and mining—and agriculture. Widespread corruption is a major socioeconomic issue; Bulgaria ranked as the most corrupt country in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
in 2018. The country also faces a demographic crisis, with its population slowly shrinking, down from a peak of nearly nine million in 1988, to roughly 6.5 million today. Bulgaria is a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, and the Council of Europe; it is also a founding member of the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, and has taken a seat on the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
three times.
Etymology
The name ''Bulgaria'' is derived from the '' Bulgars'', a tribe of Turkic origin that founded the First Bulgarian Empire. Their name is not completely understood and is difficult to trace back earlier than the 4th century AD, but it is possibly derived from theProto-Turkic
Proto-Turkic is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Turkic languages that was spoken by the Proto-Turks before their divergence into the various Turkic peoples. Proto-Turkic separated into Oghur (western) and Common Turk ...
word ''bulģha'' ("to mix", "shake", "stir") and its derivative ''bulgak'' ("revolt", "disorder"). The meaning may be further extended to "rebel", "incite" or "produce a state of disorder", and so, in the derivative, the "disturbers". Tribal groups in Inner Asia
Inner Asia refers to the northern and landlocked regions spanning North, Central and East Asia. It includes parts of western and northeast China, as well as southern Siberia. The area overlaps with some definitions of 'Central Asia', mostly the ...
with phonologically close names were frequently described in similar terms, as the Buluoji, a component of the " Five Barbarian" groups, which during the 4th century were portrayed as both: a "mixed race" and "troublemakers".
History
Prehistory and Antiquity

Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
remains dating to around 150,000 years ago, or the Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleoli ...
, are some of the earliest traces of human activity in the lands of modern Bulgaria. Remains from ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' found there are dated ''c.'' 47,000 years BP. This result represents the earliest arrival of modern humans in Europe. The Karanovo culture
The Karanovo culture is a Neolithic culture (Karanovo I-III ca. 62nd to 55th centuries BC) named after the Bulgarian village of (Караново, Sliven Province ). The culture, which is part of the Danube civilization, is considered the lar ...
arose circa 6,500 BC and was one of several Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
societies in the region that thrived on agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
. The Copper Age
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
Varna culture
The Varna culture is a Chalcolithic culture of northeastern Bulgaria, dated ca. 4500 BC, contemporary and closely related with Gumelnița in southern Romania, often considered as local variants.
It is characterized by polychrome pottery and r ...
(fifth millennium BC) is credited with inventing gold metallurgy. The associated Varna Necropolis treasure contains the oldest golden jewellery in the world with an approximate age of over 6,000 years. The treasure has been valuable for understanding social hierarchy and stratification in the earliest European societies.
The Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
, one of the three primary ancestral groups of modern Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understo ...
, appeared on the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
some time before the 12th century BC. The Thracians excelled in metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
and gave the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
the Orphean and Dionysian
The Apollonian and the Dionysian are philosophical and literary concepts represented by a duality between the figures of Apollo and Dionysus from Greek mythology. Its popularization is widely attributed to the work ''The Birth of Tragedy'' by Fri ...
cults, but remained tribal and stateless. The Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
conquered parts of present-day Bulgaria (in particular eastern Bulgaria) in the 6th century BC and retained control over the region until 479 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 479 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Rutilus (or, less frequently, year 275 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 479 BC for this year has ...
. The invasion became a catalyst for Thracian unity, and the bulk of their tribes united under king Teres
Teres may refer to:
Anatomy:
*Teres major muscle, a muscle of the upper limb; one of seven scapulohumeral muscles
*Teres minor muscle, a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff
*Pronator teres muscle, a muscle located mainly in the human fore ...
to form the Odrysian kingdom
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
in the 470s BC. It was weakened and vassalised by Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
in 341 BC, attacked by Celts in the 3rd century, and finally became a province of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in AD 45.
By the end of the 1st century AD, Roman governance was established over the entire Balkan Peninsula and Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
began spreading in the region around the 4th century. The Gothic Bible
The Gothic Bible or Wulfila Bible is the Christian Bible in the Gothic language spoken by the Eastern Germanic (Goths, Gothic) tribes in the early Middle Ages.
The translation was allegedly made by the Arianism, Arian bishop and missionary U ...
—the first Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, Engli ...
book—was created by Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
bishop Ulfilas
Ulfilas (–383), also spelled Ulphilas and Orphila, all Latinized forms of the unattested Gothic form *𐍅𐌿𐌻𐍆𐌹𐌻𐌰 Wulfila, literally "Little Wolf", was a Goth of Cappadocian Greek descent who served as a bishop and missionary ...
in what is today northern Bulgaria around 381. The region came under Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
control after the fall of Rome
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
in 476. The Byzantines were engaged in prolonged warfare against Persia and could not defend their Balkan territories from barbarian incursions. This enabled the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
to enter the Balkan Peninsula as marauders, primarily through an area between the Danube River and the Balkan Mountains known as Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
. Gradually, the interior of the peninsula became a country of the South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hu ...
, who lived under a democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which people, the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation ("direct democracy"), or to choo ...
. The Slavs assimilated the partially Hellenised
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek Greek culture, culture, Religion in Greece, religion, Greek language, language and Ethnic identity, identity by non-Greeks. In the Ancient Greece, ancient ...
, Romanised
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and ...
, and Gothicised Thracians in the rural areas.
First Bulgarian Empire
Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
was once again invaded, this time by the Bulgars under Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
Asparukh
Asparuh (also ''Ispor''; bg, Аспарух, Asparuh or (rarely) bg, Исперих, Isperih) was а ruler of Bulgars in the second half of the 7th century and is credited with the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681.
Early life
...
. Their horde was a remnant of Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria (Medieval Greek: Παλαιά Μεγάλη Βουλγαρία, ''Palaiá Megálē Voulgaría''), also often known by the Latin names ''Magna Bulgaria'' and ''Patria Onoguria'' (" Onogur land"), was a 7th- ...
, an extinct tribal confederacy situated north of the Black Sea in what is now Ukraine and southern Russia. Asparukh attacked Byzantine territories in Moesia and conquered the Slavic tribes there in 680. A peace treaty with the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
was signed in 681, marking the foundation of the First Bulgarian Empire. The minority Bulgars formed a close-knit ruling caste.
Succeeding rulers strengthened the Bulgarian state throughout the 8th and 9th centuries. Krum
Krum ( bg, Крум, el, Κροῦμος/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, Крум Страшни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territor ...
introduced a written code of law and checked a major Byzantine incursion at the Battle of Pliska
The Battle of Pliska or Battle of Vărbitsa Pass was a series of battles between troops, gathered from all parts of the Byzantine Empire, led by the Emperor Nicephorus I, and the First Bulgarian Empire, governed by Khan Krum. The Byzantines plu ...
, in which Byzantine emperor Nicephorus I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In r ...
was killed. Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
abolished paganism in favour of Eastern Orthodox Christianity
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
in 864. The conversion
Conversion or convert may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman''
* "Conversion" (''Stargate Atlantis''), an episode of the television series
* "The Conversion" ...
was followed by a Byzantine recognition of the Bulgarian church
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
and the adoption of the Cyrillic alphabet
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
, developed in the capital, Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
. The common language, religion and script strengthened central authority and gradually fused the Slavs and Bulgars into a unified people speaking a single Slavic language
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavs, Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic language, Proto ...
. A golden age began during the 34-year rule of Simeon the Great
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôto ...
, who oversaw the largest territorial expansion of the state.
After Simeon's death, Bulgaria was weakened by wars with Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic ...
and Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
and the spread of the Bogomil heresy. Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
was seized by the Byzantine army in 971 after consecutive Rus' and Byzantine invasions. The empire briefly recovered from the attacks under Samuil
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was ...
, but this ended when Byzantine emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
defeated the Bulgarian army at Klyuch in 1014. Samuil died shortly after the battle, and by 1018 the Byzantines had conquered the First Bulgarian Empire. After the conquest, Basil II prevented revolts by retaining the rule of local nobility, integrating them in Byzantine bureaucracy and aristocracy
Through the 5th century Hellenistic political systems, philosophies and theocratic Christian-Eastern concepts had gained power in the eastern Greek-speaking Mediterranean due to the intervention of Important religious figures there such as E ...
, and relieving their lands of the obligation to pay taxes in gold, allowing tax in kind Tax in kind or tax-in-kind usually refers to any taxation that is paid in kind, that is with goods or services rather than money, including:
* ''fisc'', in the Frankish kingdoms of the Medieval period
* food render, a ''feorm'' or tax-in-kind pro ...
instead. The Bulgarian Patriarchate
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
was reduced to an archbishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, but retained its autocephalous status and its diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, pro ...
s.
Second Bulgarian Empire
 Byzantine domestic policies changed after Basil's death and a series of unsuccessful rebellions broke out, the largest being led by
Byzantine domestic policies changed after Basil's death and a series of unsuccessful rebellions broke out, the largest being led by Peter Delyan
Petar II Delyan (reigned 1040–1041) ( bg, Петър II Делян, Greek: Πέτρος Δελεάνος) was the leader of an uprising against Byzantine rule in the Theme of Bulgaria during the summer of 1040. He was proclaimed Tsar of Bulgari ...
. The empire's authority declined after a catastrophic military defeat at Manzikert against Seljuk Seljuk or Saljuq (سلجوق) may refer to:
* Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia
* Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities
* Seljuk (warlord) (di ...
invaders, and was further disturbed by the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
. This prevented Byzantine attempts at Hellenisation
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the ...
and created fertile ground for further revolt. In 1185, Asen dynasty
The Asen dynasty ( bg, Асеневци, ''Asenevtsi'') founded and ruled a medieval Bulgarian state, called in modern historiography the Second Bulgarian Empire, between 1185 and 1280.
The Asen dynasty rose as the leaders of Bulgaria after a r ...
nobles Ivan Asen I
Ivan Asen I, also known as Asen I or John Asen I ( bg, Иван Асен I; died in 1196), was emperor or tsar of Bulgaria from 1187/1188 to 1196 as co-ruler with his elder brother, Peter II. Hailing from the Byzantine theme of Paristrion, his ...
and Peter IV organised a major uprising and succeeded in re-establishing the Bulgarian state. Ivan Asen and Peter laid the foundations of the Second Bulgarian Empire with its capital at Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
.
Kaloyan
Kaloyan or Kalojan, also known as Ioannitsa or Johannitsa ( bg, Калоян, Йоаница; 1170 – October 1207), was emperor or tsar of Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria from 1196 to 1207. He was the younger brother of Peter II of Bulgari ...
, the third of the Asen monarchs, extended his dominion to Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
and Ohrid
Ohrid ( mk, Охрид ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the List of cities in North Macedonia, eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording ...
. He acknowledged the spiritual supremacy of the pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
and received a royal crown from a papal legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title ''legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic ...
. The empire reached its zenith under Ivan Asen II
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II ( bg, Иван Асен II, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I one of the founders of the Second Bulgarian Empi ...
(1218–1241), when its borders expanded as far as the coast of Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, Serbia and Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinrich ...
, while commerce and culture flourished. Ivan Asen's rule was also marked by a shift away from Rome in religious matters.
The Asen dynasty became extinct in 1257. Internal conflicts and incessant Byzantine and Hungarian attacks followed, enabling the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
to establish suzerainty over the weakened Bulgarian state. In 1277, swineherd Ivaylo
Ivaylo (died 1281), also spelled Ivailo ( bg, Ивайло), was a rebel leader who ruled briefly as tsar of Bulgaria. In 1277, he spearheaded a peasant uprising and forced the Bulgarian nobility to accept him as emperor. He reigned as emperor fr ...
led a great peasant revolt that expelled the Mongols from Bulgaria and briefly made him emperor. He was overthrown in 1280 by the feudal landlords, whose factional conflicts caused the Second Bulgarian Empire to disintegrate into small feudal dominions by the 14th century. These fragmented rump state
A rump state is the remnant of a once much larger state, left with a reduced territory in the wake of secession, annexation, occupation, decolonization, or a successful coup d'état or revolution on part of its former territory. In the last case, ...
s—two tsardoms at Vidin
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as o ...
and Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
and the Despotate of Dobrudzha—became easy prey for a new threat arriving from the Southeast: the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
.
Ottoman rule
 The Ottomans were employed as mercenaries by the Byzantines in the 1340s but later became invaders in their own right. Sultan
The Ottomans were employed as mercenaries by the Byzantines in the 1340s but later became invaders in their own right. Sultan Murad I
Murad I ( ota, مراد اول; tr, I. Murad, Murad-ı Hüdavendigâr (nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'', from fa, خداوندگار, translit=Khodāvandgār, lit=the devotee of God – meaning "sovereign" in this context); 29 June 1326 – 15 Jun ...
took Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
from the Byzantines in 1362; Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
fell in 1382, followed by Shumen
Shumen ( bg, Шумен, also romanized as ''Shoumen'' or ''Šumen'', ) is the tenth largest city in Bulgaria and the administrative and economic capital of Shumen Province.
Etymology
The city was first mentioned as ''Šimeonis'' in 1153 by t ...
in 1388. The Ottomans completed their conquest of Bulgarian lands in 1393 when Tarnovo was sacked after a three-month siege and the Battle of Nicopolis
The Battle of Nicopolis took place on 25 September 1396 and resulted in the rout of an allied crusader army of Hungarian, Croatian, Bulgarian, Wallachian, French, Burgundian, German, and assorted troops (assisted by the Venetian navy) at ...
which brought about the fall of the Vidin Tsardom in 1396. Sozopol
Sozopol ( bg, Созопол , el, Σωζόπολη, translit=Sozopoli) is an ancient seaside town located 35 km south of Burgas on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Today it is one of the major seaside resorts in the country, known for the ...
was the last Bulgarian settlement to fall, in 1453. The Bulgarian nobility was subsequently eliminated and the peasantry was enserfed to Ottoman masters, while much of the educated clergy fled to other countries.
Bulgarians were subjected to heavy taxes (including Devshirme
Devshirme ( ota, دوشیرمه, devşirme, collecting, usually translated as "child levy"; hy, Մանկահավաք, Mankahavak′. or "blood tax"; hbs-Latn-Cyrl, Danak u krvi, Данак у крви, mk, Данок во крв, Danok vo krv ...
, or ''blood tax''), their culture was suppressed, and they experienced partial Islamisation
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurre ...
. Ottoman authorities established a religious administrative community called the Rum Millet
Rūm millet (millet-i Rûm), or "''Roman nation''", was the name of the Eastern Orthodox Christian community in the Ottoman Empire. Despite being subordinated within the Ottoman political system, the community maintained a certain internal aut ...
, which governed all Orthodox Christians regardless of their ethnicity. Most of the local population then gradually lost its distinct national consciousness, identifying only by its faith. The clergy remaining in some isolated monasteries kept their ethnic identity alive, enabling its survival in remote rural areas, and in the militant Catholic community in the northwest of the country.
As Ottoman power began to wane, Habsburg Austria and Russia saw Bulgarian Christians as potential allies. The Austrians
, pop = 8–8.5 million
, regions = 7,427,759
, region1 =
, pop1 = 684,184
, ref1 =
, region2 =
, pop2 = 345,620
, ref2 =
, region3 =
, pop3 = 197,990
, ref3 ...
first backed an uprising in Tarnovo in 1598, then a second one in 1686, the Chiprovtsi Uprising in 1688 and finally Karposh's Rebellion in 1689. The Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
also asserted itself as a protector of Christians in Ottoman lands with the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayna ...
in 1774.
national awakening of Bulgaria
The National awakening of Bulgaria refers to the Bulgarian nationalism that emerged in the early 19th century under the influence of western ideas such as liberalism and nationalism, which trickled into the country after the French revolution, mos ...
. It restored national consciousness and provided an ideological basis for the liberation struggle, resulting in the 1876 April Uprising
The April Uprising ( bg, Априлско въстание, Aprilsko vastanie) was an insurrection organised by the Bulgarians in the Ottoman Empire from April to May 1876. The regular Ottoman Army and irregular bashi-bazouk units brutally su ...
. Up to 30,000 Bulgarians were killed as Ottoman authorities put down the rebellion. The massacres prompted the Great Powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power in ...
to take action. They convened the Constantinople Conference
The 1876–77 Constantinople Conference ( tr, Tersane Konferansı "Shipyard Conference", after the venue ''Tersane Sarayı'' "Shipyard Palace") of the Great Powers (Austria-Hungary, Britain, France, Germany, Italy and Russia) was held in Constan ...
in 1876, but their decisions were rejected by the Ottomans. This allowed the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
to seek a military solution without risking confrontation with other Great Powers, as had happened in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
. In 1877, Russia declared war on the Ottomans and defeated them with the help of Bulgarian rebels, particularly during the crucial Battle of Shipka Pass
The Battle of Shipka Pass consisted of four battles that were fought between the Russian Empire, aided by Bulgarian volunteers known as opalchentsi, and the Ottoman Empire for control over the vital Shipka Pass during the Russo-Turkish War (1877� ...
which secured Russian control over the main road to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
.
Third Bulgarian state
TheTreaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-187 ...
was signed on 3 March 1878 by Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. It was to set up an autonomous Bulgarian principality spanning Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
, Macedonia and Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
, roughly on the territories of the Second Bulgarian Empire, and this day is now a public holiday called National Liberation Day. The other Great Powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power in ...
immediately rejected the treaty out of fear that such a large country in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
might threaten their interests. It was superseded by the Treaty of Berlin, signed on 13 July. It provided for a much smaller state, the Principality of Bulgaria
The Principality of Bulgaria ( bg, Княжество България, Knyazhestvo Balgariya) was a vassal state under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire. It was established by the Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
After the Russo-Turkish War ende ...
, only comprising Moesia and the region of Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, and leaving large populations of ethnic Bulgarians outside the new country. This significantly contributed to Bulgaria's militaristic foreign affairs approach during the first half of the 20th century.
 The Bulgarian principality won a war against Serbia and incorporated the semi-autonomous Ottoman territory of
The Bulgarian principality won a war against Serbia and incorporated the semi-autonomous Ottoman territory of Eastern Rumelia
Eastern Rumelia ( bg, Източна Румелия, Iztochna Rumeliya; ota, , Rumeli-i Şarkî; el, Ανατολική Ρωμυλία, Anatoliki Romylia) was an autonomous province (''oblast'' in Bulgarian, ''vilayet'' in Turkish) in the Otto ...
in 1885, proclaiming itself an independent state on 5 October 1908. In the years following independence, Bulgaria increasingly militarised and was often referred to as "the Balkan Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
". It became involved in three consecutive conflicts between 1912 and 1918—two Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
and World War I. After a disastrous defeat in the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria again found itself fighting on the losing side as a result of its alliance with the Central Powers in World War I. Despite fielding more than a quarter of its population in a 1,200,000-strong army and achieving several decisive victories at Battle of Doiran (1917), Doiran and Battle of Monastir (1917), Monastir, the country capitulated in 1918. The war resulted in significant territorial losses and a total of 87,500 soldiers killed. More than 253,000 refugees from the lost territories immigrated to Bulgaria from 1912 to 1929, placing additional strain on the already ruined national economy.
 The resulting political unrest led to the establishment of a royal authoritarianism, authoritarian dictatorship by Tsar Boris III of Bulgaria, Boris III (1918–1943). Bulgaria entered World War II in 1941 as a member of Axis Powers, the Axis but declined to participate in Operation Barbarossa and Rescue of the Bulgarian Jews, saved its Jewish population from deportation to Nazi concentration camps, concentration camps. The sudden death of Boris III in mid-1943 pushed the country into political turmoil as the war turned against Germany, and the communist guerrilla movement gained momentum. The government of Bogdan Filov subsequently failed to achieve peace with the Allies. Bulgaria did not comply with Soviet demands to expel German forces from its territory, resulting in a declaration of war and an invasion by the USSR in September 1944. The communist-dominated Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power, ended participation in the Axis and joined the Allied side until the war ended. Bulgaria suffered little war damage and the Soviet Union demanded no reparations. But all wartime territorial gains, with the notable exception of Treaty of Craiova, Southern Dobrudzha, were lost.
The resulting political unrest led to the establishment of a royal authoritarianism, authoritarian dictatorship by Tsar Boris III of Bulgaria, Boris III (1918–1943). Bulgaria entered World War II in 1941 as a member of Axis Powers, the Axis but declined to participate in Operation Barbarossa and Rescue of the Bulgarian Jews, saved its Jewish population from deportation to Nazi concentration camps, concentration camps. The sudden death of Boris III in mid-1943 pushed the country into political turmoil as the war turned against Germany, and the communist guerrilla movement gained momentum. The government of Bogdan Filov subsequently failed to achieve peace with the Allies. Bulgaria did not comply with Soviet demands to expel German forces from its territory, resulting in a declaration of war and an invasion by the USSR in September 1944. The communist-dominated Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power, ended participation in the Axis and joined the Allied side until the war ended. Bulgaria suffered little war damage and the Soviet Union demanded no reparations. But all wartime territorial gains, with the notable exception of Treaty of Craiova, Southern Dobrudzha, were lost.
 The 1944 Bulgarian coup d'état, left-wing coup d'état of 9 September 1944 led to the abolition of the monarchy and People's Court (Bulgaria), the executions of some 1,000–3,000 dissidents, war criminals, and members of the former royal elite. But it was not until 1946 that a One-party state, one-party people's republic was instituted following a referendum. It fell into the Soviet sphere of influence under the leadership of Georgi Dimitrov (1946–1949), who established a repressive, rapidly industrialising Stalinist state. By the mid-1950s, standards of living rose significantly and political repression eased. The Soviet-style planned economy saw some experimental market-oriented policies emerging under Todor Zhivkov (1954–1989). Compared to wartime levels, national Gross domestic product, GDP increased five-fold and per capita GDP quadrupled by the 1980s, although severe debt spikes took place in 1960, 1977 and 1980. Zhivkov's daughter Lyudmila Zhivkova, Lyudmila bolstered national pride by promoting Bulgarian heritage, culture and arts worldwide. Facing declining birth rates among the ethnic Bulgarian majority, Zhivkov's government in 1984 forced the minority ethnic Bulgarian Turks, Turks to adopt Slavic names in an attempt to erase their identity and assimilate them. These policies resulted in the emigration of some 300,000 ethnic Turks to Turkey.
The Communist Party was forced to give up its political monopoly on 10 November 1989 under the influence of the Revolutions of 1989. Zhivkov resigned and Bulgaria embarked on a transition to a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy. The first free elections in June 1990 were won by the Communist Party, now rebranded as the Bulgarian Socialist Party. A Constitution of Bulgaria, new constitution that provided for a relatively weak elected president and for a prime minister accountable to the legislature was adopted in July 1991. The new system initially failed to improve living standards or create economic growth—the average quality of life and economic performance remained lower than under communism well into the early 2000s. After 2001, economic, political and geopolitical conditions improved greatly, and Bulgaria achieved high Human Development status in 2003. It became a member of
The 1944 Bulgarian coup d'état, left-wing coup d'état of 9 September 1944 led to the abolition of the monarchy and People's Court (Bulgaria), the executions of some 1,000–3,000 dissidents, war criminals, and members of the former royal elite. But it was not until 1946 that a One-party state, one-party people's republic was instituted following a referendum. It fell into the Soviet sphere of influence under the leadership of Georgi Dimitrov (1946–1949), who established a repressive, rapidly industrialising Stalinist state. By the mid-1950s, standards of living rose significantly and political repression eased. The Soviet-style planned economy saw some experimental market-oriented policies emerging under Todor Zhivkov (1954–1989). Compared to wartime levels, national Gross domestic product, GDP increased five-fold and per capita GDP quadrupled by the 1980s, although severe debt spikes took place in 1960, 1977 and 1980. Zhivkov's daughter Lyudmila Zhivkova, Lyudmila bolstered national pride by promoting Bulgarian heritage, culture and arts worldwide. Facing declining birth rates among the ethnic Bulgarian majority, Zhivkov's government in 1984 forced the minority ethnic Bulgarian Turks, Turks to adopt Slavic names in an attempt to erase their identity and assimilate them. These policies resulted in the emigration of some 300,000 ethnic Turks to Turkey.
The Communist Party was forced to give up its political monopoly on 10 November 1989 under the influence of the Revolutions of 1989. Zhivkov resigned and Bulgaria embarked on a transition to a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy. The first free elections in June 1990 were won by the Communist Party, now rebranded as the Bulgarian Socialist Party. A Constitution of Bulgaria, new constitution that provided for a relatively weak elected president and for a prime minister accountable to the legislature was adopted in July 1991. The new system initially failed to improve living standards or create economic growth—the average quality of life and economic performance remained lower than under communism well into the early 2000s. After 2001, economic, political and geopolitical conditions improved greatly, and Bulgaria achieved high Human Development status in 2003. It became a member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in 2004 and participated in the War in Afghanistan (2001–present), War in Afghanistan. After several years of reforms, it joined the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and the European Single Market, single market in 2007, despite EU concerns over government corruption. Bulgaria hosted the 2018 Presidency of the Council of the European Union at the National Palace of Culture in Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
.
Geography
Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
and broadening as it reaches the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, Black Sea coast.
The Balkan mountains run laterally through the middle of the country from west to east. The mountainous southwest has two distinct Glacial landform, alpine type ranges—Rila and Pirin, which border the lower but more extensive Rhodope Mountains to the east, and various medium altitude mountains to west, northwest and south, like Vitosha, Osogovo and Belasitsa. Musala, at , is the highest point in both Bulgaria and the Balkans. The Black Sea coast is the country's lowest point. Plains occupy about one third of the territory, while plateaux and hills occupy 41%. Most rivers are short and with low water levels. The longest river located solely in Bulgarian territory, the Iskar (river), Iskar, has a length of . The Struma River, Struma and the Maritsa are two major rivers in the south.
 Bulgaria has a varied and changeable climate, which results from being positioned at the meeting point of the Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean, Oceanic climate, Oceanic and Continental climate, Continental air masses combined with the barrier effect of its mountains. Northern Bulgaria averages cooler, and registers more precipitation, than the regions south of the Balkan mountains. Temperature amplitudes vary significantly in different areas. The lowest recorded temperature is , while the highest is . Precipitation (meteorology), Precipitation averages about per year, and varies from in Dobrudja to more than in the mountains. Continental air masses bring significant amounts of snowfall during winter.
Bulgaria has a varied and changeable climate, which results from being positioned at the meeting point of the Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean, Oceanic climate, Oceanic and Continental climate, Continental air masses combined with the barrier effect of its mountains. Northern Bulgaria averages cooler, and registers more precipitation, than the regions south of the Balkan mountains. Temperature amplitudes vary significantly in different areas. The lowest recorded temperature is , while the highest is . Precipitation (meteorology), Precipitation averages about per year, and varies from in Dobrudja to more than in the mountains. Continental air masses bring significant amounts of snowfall during winter.
Biodiversity and environment
The interaction of climatic, hydrological, geological and topographical conditions has produced a relatively wide variety of plant and animal species. Bulgaria's biodiversity, one of the richest in Europe, List of protected areas of Bulgaria, is conserved in three national parks, 11 nature parks, 10 biosphere reserves and 565 protected areas. Ninety-three of the 233 mammal species of Europe are found in Bulgaria, along with 49% of butterfly and 30% of vascular plant species. Overall, 41,493 plant and animal species are present. Larger mammals with sizable populations include deer (106,323 individuals), wild boar (88,948), golden jackal (47,293) and red fox (32,326). Partridges number some 328,000 individuals, making them the most widespread Game (hunting), gamebird. A third of all nesting birds in Bulgaria can be found in Rila National Park, which also hosts Arctic and alpine species at high altitudes. Flora includes more than 3,800 vascular plant species of which 170 are Endemism, endemic and 150 are considered endangered. A checklist of larger fungi in Bulgaria by the Institute of Botany identifies more than 1,500 species. More than 35% of the land area is covered by forests. In 1998, the Bulgarian government adopted the National Biological Diversity Conservation Strategy, a comprehensive programme seeking the preservation of local ecosystems, protection of endangered species and conservation of genetic resources. Bulgaria has some of the largest Natura 2000 areas in Europe covering 33.8% of its territory. It also achieved its Kyoto Protocol objective of reducing carbon dioxide emissions by 30% from 1990 to 2009. Bulgaria ranks 30th in the 2018 Environmental Performance Index, but scores low on air quality. Particulates, Particulate levels are the highest in Europe, especially in urban areas affected by automobile traffic and coal-based power stations. One of these, the lignite-fired Maritsa Iztok Complex, Maritsa Iztok-2 station, is causing the highest damage to health and the environment in the European Union. Pesticide use in agriculture and antiquated industrial sewage systems produce extensive soil and water pollution. Water quality began to improve in 1998 and has maintained a trend of moderate improvement. Over 75% of surface rivers meet European standards for good quality.Politics
 Bulgaria is a parliamentary democracy where the Prime Minister of Bulgaria, prime minister is the head of government and the most powerful executive position. The political system has three branches—legislative, executive and judicial, with universal suffrage for citizens at least 18 years old. The Constitution of Bulgaria, Constitution also provides possibilities of direct democracy, namely petitions and national referendums. Elections are supervised by an independent Central Election Commission that includes members from all major political parties. Parties must register with the commission prior to participating in a national election. Normally, the prime minister-elect is the leader of the party receiving the most votes in parliamentary elections, although this is not always the case.
Unlike the prime minister, presidential domestic power is more limited. The directly elected President of Bulgaria, president serves as head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces, and has the authority to return a bill for further debate, although the parliament can override the presidential veto by a simple majority vote. Political parties gather in the National Assembly (Bulgaria), National Assembly, a body of 240 deputies elected to four-year terms by direct popular vote. The National Assembly has the power to enact laws, approve the budget, schedule presidential elections, select and dismiss the prime minister and other ministers, declare war, deploy troops abroad, and ratify international treaties and agreements.
Overall, Bulgaria displays a pattern of unstable governments. Boyko Borisov, the leader of the centre-right, pro-EU party GERB, served three terms as prime minister between 2009 and 2021.
It won 2009 Bulgarian parliamentary election, the 2009 general election and formed a minority government, which resigned in February 2013 after Protests against the Borisov cabinet, nationwide protests over the low living standards, corruption and the perceived failure of the democratic system.
The subsequent Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2013, snap elections in May resulted in a narrow win for GERB, but the Bulgarian Socialist Party eventually formed a government led by Plamen Oresharski after Borisov failed to secure parliamentary support. The Oresharski government resigned in July 2014 amid continuing 2013–14 Bulgarian protests against the Oresharski cabinet, large-scale protests.
The 2014 Bulgarian parliamentary election , October 2014 elections resulted in a third GERB victory. Borisov Second Borisov Government, formed a coalition with several right-wing parties, but resigned again after the candidate backed by his party failed to win the Bulgarian presidential election, 2016, 2016 Presidential election. The Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2017, March 2017 snap election was again won by GERB, but with 95 seats in Parliament. They formed a coalition with the far-right United Patriots, who held 27 seats.
Borisov's last cabinet saw a dramatic decrease in freedom of the press, and a number of corruption revelations that triggered 2020–2021 Bulgarian protests, yet another wave of mass protests in 2020. GERB came out first in the regular April 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, April 2021 election, but with its weakest result so far. All other parties refused to form a government, and after a brief deadlock, another election was called July 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, for July 2021. It too failed to break the stalemate, as no political party was able to form a coalition government.
Freedom House has reported a continuing deterioration of democratic governance after 2009, citing reduced media independence, stalled reforms, abuse of authority at the highest level and increased dependence of local administrations on the central government. Bulgaria is still Freedom in the World, listed as "Free", with a political system designated as a semi-consolidated democracy, albeit with deteriorating scores. The Democracy Index defines it as a "Flawed democracy". A 2018 survey by the Institute for Economics and Peace reported that less than 15% of respondents considered elections to be fair.
Bulgaria is a parliamentary democracy where the Prime Minister of Bulgaria, prime minister is the head of government and the most powerful executive position. The political system has three branches—legislative, executive and judicial, with universal suffrage for citizens at least 18 years old. The Constitution of Bulgaria, Constitution also provides possibilities of direct democracy, namely petitions and national referendums. Elections are supervised by an independent Central Election Commission that includes members from all major political parties. Parties must register with the commission prior to participating in a national election. Normally, the prime minister-elect is the leader of the party receiving the most votes in parliamentary elections, although this is not always the case.
Unlike the prime minister, presidential domestic power is more limited. The directly elected President of Bulgaria, president serves as head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces, and has the authority to return a bill for further debate, although the parliament can override the presidential veto by a simple majority vote. Political parties gather in the National Assembly (Bulgaria), National Assembly, a body of 240 deputies elected to four-year terms by direct popular vote. The National Assembly has the power to enact laws, approve the budget, schedule presidential elections, select and dismiss the prime minister and other ministers, declare war, deploy troops abroad, and ratify international treaties and agreements.
Overall, Bulgaria displays a pattern of unstable governments. Boyko Borisov, the leader of the centre-right, pro-EU party GERB, served three terms as prime minister between 2009 and 2021.
It won 2009 Bulgarian parliamentary election, the 2009 general election and formed a minority government, which resigned in February 2013 after Protests against the Borisov cabinet, nationwide protests over the low living standards, corruption and the perceived failure of the democratic system.
The subsequent Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2013, snap elections in May resulted in a narrow win for GERB, but the Bulgarian Socialist Party eventually formed a government led by Plamen Oresharski after Borisov failed to secure parliamentary support. The Oresharski government resigned in July 2014 amid continuing 2013–14 Bulgarian protests against the Oresharski cabinet, large-scale protests.
The 2014 Bulgarian parliamentary election , October 2014 elections resulted in a third GERB victory. Borisov Second Borisov Government, formed a coalition with several right-wing parties, but resigned again after the candidate backed by his party failed to win the Bulgarian presidential election, 2016, 2016 Presidential election. The Bulgarian parliamentary election, 2017, March 2017 snap election was again won by GERB, but with 95 seats in Parliament. They formed a coalition with the far-right United Patriots, who held 27 seats.
Borisov's last cabinet saw a dramatic decrease in freedom of the press, and a number of corruption revelations that triggered 2020–2021 Bulgarian protests, yet another wave of mass protests in 2020. GERB came out first in the regular April 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, April 2021 election, but with its weakest result so far. All other parties refused to form a government, and after a brief deadlock, another election was called July 2021 Bulgarian parliamentary election, for July 2021. It too failed to break the stalemate, as no political party was able to form a coalition government.
Freedom House has reported a continuing deterioration of democratic governance after 2009, citing reduced media independence, stalled reforms, abuse of authority at the highest level and increased dependence of local administrations on the central government. Bulgaria is still Freedom in the World, listed as "Free", with a political system designated as a semi-consolidated democracy, albeit with deteriorating scores. The Democracy Index defines it as a "Flawed democracy". A 2018 survey by the Institute for Economics and Peace reported that less than 15% of respondents considered elections to be fair.
Legal system
Bulgaria has a Civil law (legal system), civil law legal system. The judiciary is overseen by the Ministry of Justice. The Supreme Administrative Court and the Supreme Court of Cassation are the highest courts of appeal and oversee the application of laws in subordinate courts. The Supreme Judicial Council manages the system and appoints judges. The legal system is regarded by both domestic and international observers as one of Europe's most inefficient due to pervasive lack of transparency and corruption. Law enforcement is carried out by organisations mainly subordinate to the Ministry of Interior (Bulgaria), Ministry of the Interior. The National Police Service (Bulgaria), General Directorate of National Police (GDNP) combats general crime and maintains public order. GDNP fields 26,578 police officers in its local and national sections. The bulk of criminal cases are transport-related, followed by theft and drug-related crime; List of countries by intentional homicide rate, homicide rates are low. The Ministry of the Interior also heads the Border Police Service and the Gendarmerie (Bulgaria), National Gendarmerie—a specialised branch for anti-terrorist activity, crisis management and riot control. Counterintelligence and national security are the responsibility of the State Agency for National Security.Administrative divisions
Bulgaria is a unitary state. Since the 1880s, the number of territorial management units has varied from seven to 26. Between 1987 and 1999, the administrative structure consisted of nine provinces (''oblasti'', singular ''oblast''). A new administrative structure was adopted in parallel with the decentralisation of the economic system. It includes 27 provinces and a metropolitan capital province (Sofia-Grad). All areas take their names from their respective capital cities. The provinces are subdivided into 265 Municipalities of Bulgaria, municipalities. Municipalities are run by mayors, who are elected to four-year terms, and by directly elected municipal councils. Bulgaria is a highly centralisation, centralised state where the Government of Bulgaria, Council of Ministers directly appoints regional governors and all provinces and municipalities are heavily dependent on it for funding.Foreign relations and security
Bulgaria became a member of the United Nations in 1955 and since 1966 has been a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, Security Council three times, most recently from 2002 to 2003. It was also among the founding nations of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) in 1975. Euro-Atlantic integration has been a priority since the fall of communism, although the communist leadership also had aspirations of leaving the Warsaw Pact and joining the European Communities by 1987. Bulgaria signed the European Union Treaty of Accession 2005, Treaty of Accession on 25 April 2005, and became a full member of the European Union on 1 January 2007. In addition, it has a tripartite economic and diplomatic collaboration with Romania and Greece, good ties with China and Vietnam and a historical relationship with Russia. Bulgaria deployed significant numbers of both civilian and military advisors in Soviet-allied countries like Nicaraguan Revolution, Nicaragua and Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Libya during the Cold War. The first deployment of foreign troops on Bulgarian soil since World War II occurred in 2001, when the country hosted six KC-135 Stratotanker aircraft and 200 support personnel for the war effort in Afghanistan. International military relations were further expanded with accession to
Bulgaria deployed significant numbers of both civilian and military advisors in Soviet-allied countries like Nicaraguan Revolution, Nicaragua and Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Libya during the Cold War. The first deployment of foreign troops on Bulgarian soil since World War II occurred in 2001, when the country hosted six KC-135 Stratotanker aircraft and 200 support personnel for the war effort in Afghanistan. International military relations were further expanded with accession to NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in March 2004 and the US-Bulgarian Defence Cooperation Agreement signed in April 2006. Bezmer Air Base, Bezmer and Graf Ignatievo Air Base, Graf Ignatievo air bases, the Novo Selo Range, Novo Selo training range, and a logistics centre in Aytos Logistics Center, Aytos subsequently became List of joint US-Bulgarian military bases, joint military training facilities cooperatively used by the United States and Bulgarian militaries. Despite its active international defence collaborations, Bulgaria ranks as among the most peaceful countries globally, tying 6th alongside Iceland regarding domestic and international conflicts, and 26th on average in the Global Peace Index.
Domestic defence is the responsibility of the volunteer military, all-volunteer Bulgarian armed forces, composed of Bulgarian land forces, land forces, Bulgarian Navy, navy and an Bulgarian Air Force, air force. The land forces consist of two Mechanized infantry, mechanised brigades and eight independent regiments and battalions; the air force operates 106 aircraft and Anti-aircraft warfare, air defence systems across six air bases, and the navy operates various ships, helicopters and coastal defence weapons. Active troops dwindled from 152,000 in 1988 to 31,300 in 2017, supplemented by 3,000 reservists and 16,000 paramilitary troops. Military inventory mainly consists of Soviet equipment like Mikoyan MiG-29 and Sukhoi Su-25 jets, S-300 missile system, S-300PT air defence systems and SS-21 Scarab short-range ballistic missiles.
Economy
 Bulgaria has an open, developing country, upper middle income range market economy where the private sector accounts for more than 70% of Gross domestic product, GDP. From a largely agricultural country with a predominantly rural population in 1948, by the 1980s Bulgaria had transformed into an industrial economy, with scientific and technological research at the top of its budgetary expenditure priorities. The loss of COMECON markets in 1990 and the subsequent "Shock therapy (economics), shock therapy" of the Planned economy, planned system caused a steep decline in industrial and agricultural production, ultimately followed by an economic collapse in 1997. The economy largely recovered during a period of rapid growth several years later, but the average salary of 1,036 leva ($615) per month remains the lowest in the EU. More than a fifth of the labour force work for a minimum wage of $1.16 per hour.
A balanced budget was achieved in 2003 and the country began running a budget surplus, surplus the following year. Expenditures amounted to $21.15 billion and revenues were $21.67 billion in 2017. Most government spending on institutions is earmarked for security. The ministries of defence, the interior and justice are allocated the largest share of the annual government budget, whereas those responsible for the environment, tourism and energy receive the least funding. Taxes form the bulk of government revenue at 30% of GDP. Bulgaria has some of the lowest corporate income Tax rates in Europe, tax rates in the EU at a flat 10% rate. The tax system is two-tier. Value added tax, excise duties, corporate and personal income tax are national, whereas real estate, inheritance, and vehicle taxes are levied by local authorities. Strong economic performance in the early 2000s reduced government debt from 79.6% in 1998 to 14.1% in 2008. It has since increased to 28.7% of GDP by 2016, but remains the third lowest in the EU.
The Yugozapaden First-level NUTS of the European Union, planning area is the most developed region with a per capita gross domestic product (Purchasing power parity, PPP) of $29,816 in 2018. It includes the capital city and the surrounding Sofia Province, which alone generate 42% of national gross domestic product despite hosting only 22% of the population. GDP per capita (in PPS) and the cost of living in 2019 stood at 53 and 52.8% of the EU average (100%), respectively. National PPP GDP was estimated at $143.1 billion in 2016, with a per capita value of $20,116. Economic growth statistics take into account illegal transactions from the informal economy, which is the largest in the EU as a percentage of economic output. The Bulgarian National Bank issues the national currency, Bulgarian lev, lev, which is pegged to the euro at a rate of 1.95583 levа per euro.
After several consecutive years of high growth, repercussions of the financial crisis of 2007–2008 resulted in a 3.6% contraction of GDP in 2009 and increased unemployment. Positive growth was restored in 2010 but intercompany debt exceeded $59 billion, meaning that 60% of all Bulgarian companies were mutually indebted. By 2012, it had increased to $97 billion, or 227% of GDP. The government implemented strict austerity measures with IMF and EU encouragement to some positive fiscal results, but the social consequences of these measures, such as increased economic inequality, income inequality and accelerated outward migration, have been "catastrophic" according to the International Trade Union Confederation.
Siphoning of public funds to the families and relatives of politicians from incumbent parties has resulted in fiscal and welfare losses to society. Bulgaria ranks 71st in the Corruption Perceptions Index and experiences the worst levels of corruption in the European Union, a phenomenon that remains a source of profound public discontent. Along with organised crime, corruption has resulted in a rejection of the country's Schengen Area application and withdrawal of foreign investment. Government officials reportedly engage in embezzlement, influence trading, government procurement violations and bribery with impunity. Government procurement in particular is a critical area in corruption risk. An estimated 10 billion leva ($5.99 billion) of state budget and Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund, European cohesion funds are spent on public tenders each year; nearly 14 billion ($8.38 billion) were spent on public contracts in 2017 alone. A large share of these contracts are awarded to a few politically connected companies amid widespread irregularities, procedure violations and tailor-made award criteria. Despite repeated criticism from the European Commission, EU institutions refrain from taking measures against Bulgaria because it supports Brussels on a number of issues, unlike Poland or Hungary.
Bulgaria has an open, developing country, upper middle income range market economy where the private sector accounts for more than 70% of Gross domestic product, GDP. From a largely agricultural country with a predominantly rural population in 1948, by the 1980s Bulgaria had transformed into an industrial economy, with scientific and technological research at the top of its budgetary expenditure priorities. The loss of COMECON markets in 1990 and the subsequent "Shock therapy (economics), shock therapy" of the Planned economy, planned system caused a steep decline in industrial and agricultural production, ultimately followed by an economic collapse in 1997. The economy largely recovered during a period of rapid growth several years later, but the average salary of 1,036 leva ($615) per month remains the lowest in the EU. More than a fifth of the labour force work for a minimum wage of $1.16 per hour.
A balanced budget was achieved in 2003 and the country began running a budget surplus, surplus the following year. Expenditures amounted to $21.15 billion and revenues were $21.67 billion in 2017. Most government spending on institutions is earmarked for security. The ministries of defence, the interior and justice are allocated the largest share of the annual government budget, whereas those responsible for the environment, tourism and energy receive the least funding. Taxes form the bulk of government revenue at 30% of GDP. Bulgaria has some of the lowest corporate income Tax rates in Europe, tax rates in the EU at a flat 10% rate. The tax system is two-tier. Value added tax, excise duties, corporate and personal income tax are national, whereas real estate, inheritance, and vehicle taxes are levied by local authorities. Strong economic performance in the early 2000s reduced government debt from 79.6% in 1998 to 14.1% in 2008. It has since increased to 28.7% of GDP by 2016, but remains the third lowest in the EU.
The Yugozapaden First-level NUTS of the European Union, planning area is the most developed region with a per capita gross domestic product (Purchasing power parity, PPP) of $29,816 in 2018. It includes the capital city and the surrounding Sofia Province, which alone generate 42% of national gross domestic product despite hosting only 22% of the population. GDP per capita (in PPS) and the cost of living in 2019 stood at 53 and 52.8% of the EU average (100%), respectively. National PPP GDP was estimated at $143.1 billion in 2016, with a per capita value of $20,116. Economic growth statistics take into account illegal transactions from the informal economy, which is the largest in the EU as a percentage of economic output. The Bulgarian National Bank issues the national currency, Bulgarian lev, lev, which is pegged to the euro at a rate of 1.95583 levа per euro.
After several consecutive years of high growth, repercussions of the financial crisis of 2007–2008 resulted in a 3.6% contraction of GDP in 2009 and increased unemployment. Positive growth was restored in 2010 but intercompany debt exceeded $59 billion, meaning that 60% of all Bulgarian companies were mutually indebted. By 2012, it had increased to $97 billion, or 227% of GDP. The government implemented strict austerity measures with IMF and EU encouragement to some positive fiscal results, but the social consequences of these measures, such as increased economic inequality, income inequality and accelerated outward migration, have been "catastrophic" according to the International Trade Union Confederation.
Siphoning of public funds to the families and relatives of politicians from incumbent parties has resulted in fiscal and welfare losses to society. Bulgaria ranks 71st in the Corruption Perceptions Index and experiences the worst levels of corruption in the European Union, a phenomenon that remains a source of profound public discontent. Along with organised crime, corruption has resulted in a rejection of the country's Schengen Area application and withdrawal of foreign investment. Government officials reportedly engage in embezzlement, influence trading, government procurement violations and bribery with impunity. Government procurement in particular is a critical area in corruption risk. An estimated 10 billion leva ($5.99 billion) of state budget and Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund, European cohesion funds are spent on public tenders each year; nearly 14 billion ($8.38 billion) were spent on public contracts in 2017 alone. A large share of these contracts are awarded to a few politically connected companies amid widespread irregularities, procedure violations and tailor-made award criteria. Despite repeated criticism from the European Commission, EU institutions refrain from taking measures against Bulgaria because it supports Brussels on a number of issues, unlike Poland or Hungary.
Structure and sectors
Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, Plovdiv, Veliko Tarnovo, coastal resorts Albena, Golden Sands and Sunny Beach and winter resorts Bansko, Pamporovo and Borovets are some of the locations most visited by tourists. Most visitors are Romanian, Turkish, Greek and German. Tourism is additionally encouraged through the 100 Tourist Sites of Bulgaria, 100 Tourist Sites system.
Science and technology
Spending on research and development amounts to 0.78% of GDP, and the bulk of public R&D funding goes to the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS). Private businesses accounted for more than 73% of R&D expenditures and employed 42% of Bulgaria's 22,000 researchers in 2015. The same year, Bulgaria ranked 39th out of 50 countries in the Bloomberg Innovation Index, the highest score being in education (24th) and the lowest in value-added manufacturing (48th). Bulgaria was ranked 35th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, up from 40th in 2019. Chronic government underinvestment in research since 1990 has forced many professionals in science and engineering to leave Bulgaria. Despite the lack of funding, research in chemistry, materials science and physics remains strong. Antarctic research is actively carried out through the St. Kliment Ohridski Base on Livingston Island in Western Antarctica. The information and communication technologies (ICT) sector generates three per cent of economic output and employs 40,000 to 51,000 software engineers. Bulgaria was known as a "Communist Silicon Valley" during the Soviet era due to its key role in COMECON computing technology production. A concerted effort by the communist government to teach computing and IT skills in schools also indirectly made Bulgaria a major source of computer viruses in the 1980s and 90s. The country is a regional leader in supercomputer, high performance computing: it operates ''Avitohol'', the most powerful supercomputer in Southeast Europe, and will host one of the eight petascale computing, petascale European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking, EuroHPC supercomputers.
Bulgaria has made numerous contributions to space exploration. These include two scientific satellites, more than 200 payloads and 300 experiments in Earth orbit, as well as Bulgarian cosmonaut programme, two cosmonauts since 1971. Bulgaria was the first country to grow wheat and vegetables Plants in space, in space with its SVET plant growth system, Svet greenhouses on the Mir space station. It was involved in the development of the Granat Gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray observatory and the Vega program, particularly in modelling trajectories and guidance algorithms for both Vega probes. Bulgarian instruments have been used in the exploration of Mars, including a spectrometer that took the first high quality spectroscopy, spectroscopic images of Martian moon Phobos (moon), Phobos with the Phobos 2 probe. Cosmic ray, Cosmic radiation en route to and around the planet has been mapped by Liulin type instruments, Liulin-ML dosimeters on the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, ExoMars TGO. RADOM-7, Variants of these instruments have also been fitted on the International Space Station and the Chandrayaan-1 lunar probe. Another lunar mission, SpaceIL's ''Beresheet'', was also equipped with a Bulgarian-manufactured imaging payload. Bulgaria's first Geosynchronous satellite, geostationary communications satellite—BulgariaSat-1—was launched by SpaceX in 2017.
Despite the lack of funding, research in chemistry, materials science and physics remains strong. Antarctic research is actively carried out through the St. Kliment Ohridski Base on Livingston Island in Western Antarctica. The information and communication technologies (ICT) sector generates three per cent of economic output and employs 40,000 to 51,000 software engineers. Bulgaria was known as a "Communist Silicon Valley" during the Soviet era due to its key role in COMECON computing technology production. A concerted effort by the communist government to teach computing and IT skills in schools also indirectly made Bulgaria a major source of computer viruses in the 1980s and 90s. The country is a regional leader in supercomputer, high performance computing: it operates ''Avitohol'', the most powerful supercomputer in Southeast Europe, and will host one of the eight petascale computing, petascale European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking, EuroHPC supercomputers.
Bulgaria has made numerous contributions to space exploration. These include two scientific satellites, more than 200 payloads and 300 experiments in Earth orbit, as well as Bulgarian cosmonaut programme, two cosmonauts since 1971. Bulgaria was the first country to grow wheat and vegetables Plants in space, in space with its SVET plant growth system, Svet greenhouses on the Mir space station. It was involved in the development of the Granat Gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray observatory and the Vega program, particularly in modelling trajectories and guidance algorithms for both Vega probes. Bulgarian instruments have been used in the exploration of Mars, including a spectrometer that took the first high quality spectroscopy, spectroscopic images of Martian moon Phobos (moon), Phobos with the Phobos 2 probe. Cosmic ray, Cosmic radiation en route to and around the planet has been mapped by Liulin type instruments, Liulin-ML dosimeters on the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, ExoMars TGO. RADOM-7, Variants of these instruments have also been fitted on the International Space Station and the Chandrayaan-1 lunar probe. Another lunar mission, SpaceIL's ''Beresheet'', was also equipped with a Bulgarian-manufactured imaging payload. Bulgaria's first Geosynchronous satellite, geostationary communications satellite—BulgariaSat-1—was launched by SpaceX in 2017.
Infrastructure
 Telephone services are widely available, and a central digital trunk line connects most regions. Vivacom (BTC) serves more than 90% of fixed lines and is one of the three operators providing mobile services, along with Mtel (Bulgaria), A1 and Telenor (Bulgaria), Telenor. Internet penetration stood at 69.2% of the population aged 16–74 and 78.9% of households in 2020.
Bulgaria's strategic geographic location and well-developed energy sector make it a key European energy centre despite its lack of significant fossil fuel deposits. Thermal power plants generate 48.9% of electricity, followed by nuclear power from the Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, Kozloduy reactors (34.8%) and renewable energy, renewable sources (16.3%). Equipment for a second nuclear power station at Belene Nuclear Power Plant, Belene has been acquired, but the fate of the project remains uncertain. Installed capacity amounts to 12,668 MW, allowing Bulgaria to exceed domestic demand and export energy.
The national road network has a total length of , of which are paved. Railroads are a major mode of freight transportation, although highways carry a progressively larger share of freight. Bulgaria has of railway track, with rail links available to Romania, Turkey, Greece, and Serbia, and express trains serving direct routes to Kyiv, Minsk, Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Sofia and Plovdiv are the country's air travel hubs, while Varna and Burgas are the principal maritime trade ports.
Telephone services are widely available, and a central digital trunk line connects most regions. Vivacom (BTC) serves more than 90% of fixed lines and is one of the three operators providing mobile services, along with Mtel (Bulgaria), A1 and Telenor (Bulgaria), Telenor. Internet penetration stood at 69.2% of the population aged 16–74 and 78.9% of households in 2020.
Bulgaria's strategic geographic location and well-developed energy sector make it a key European energy centre despite its lack of significant fossil fuel deposits. Thermal power plants generate 48.9% of electricity, followed by nuclear power from the Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, Kozloduy reactors (34.8%) and renewable energy, renewable sources (16.3%). Equipment for a second nuclear power station at Belene Nuclear Power Plant, Belene has been acquired, but the fate of the project remains uncertain. Installed capacity amounts to 12,668 MW, allowing Bulgaria to exceed domestic demand and export energy.
The national road network has a total length of , of which are paved. Railroads are a major mode of freight transportation, although highways carry a progressively larger share of freight. Bulgaria has of railway track, with rail links available to Romania, Turkey, Greece, and Serbia, and express trains serving direct routes to Kyiv, Minsk, Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Sofia and Plovdiv are the country's air travel hubs, while Varna and Burgas are the principal maritime trade ports.
Demographics

Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
(336,505), Burgas
Burgas ( bg, Бургас, ), sometimes transliterated as ''Bourgas'', is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the fourth-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, and Varna, with a pop ...
(202,434) and Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse (142,902). Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understo ...
are the main ethnic group and constitute 84.8% of the population. Turks in Bulgaria, Turkish and Roma in Bulgaria, Roma minorities account for 8.8 and 4.9%, respectively; some 40 smaller minorities account for 0.7%, and 0.8% do not self-identify with an ethnic group. Former National Statistical Institute (Bulgaria), Statistics head Reneta Indzhova has disputed the 2011 census figures, suggesting the actual population is smaller than reported. The Roma minority is usually underestimated in census data and may represent up to 11% of the population. Population density is 65 per square kilometre, almost half the European Union average.
In 2018, the average total fertility rate (TFR) in Bulgaria was 1.56 children per woman, below the replacement rate of 2.1 and considerably below the historical high of 5.83 children per woman in 1905. Bulgaria thus has one of the oldest populations in the world, with an average age of 43 years.
Bulgaria is in a state of demographic crisis. It has had negative population growth since the early 1990s, when the economic collapse caused a long-lasting emigration wave. Some 937,000 to 1,200,000 people—mostly young adults—had left the country by 2005. The majority of children are born to unmarried women. Furthermore, a third of all households consist of only one person and 75.5% of families do not have children under the age of 16. The resulting birth rates are among the lowest in the world while death rates are among the highest.
Bulgaria scores high in gender equality, ranking 18th in the 2018 Global Gender Gap Report. Although women's suffrage was enabled relatively late, in 1937, women today have equal political rights, high workforce participation and legally mandated Equal pay for equal work, equal pay. In 2021, market research agency ''Reboot Online'' ranked Bulgaria as the best European country for women to work. Bulgaria has the highest ratio of female Information and communications technology, ICT researchers in the EU, as well as the second-highest ratio of females in the technology sector at 44.6% of the workforce. High levels of female participation are a Gender roles in post-communist Central and Eastern Europe, legacy of the Socialist era.
Largest cities
Health
High death rates result from a combination of an ageing population, high numbers of people at risk of poverty, and a weak Health system, healthcare system. Over 80% of deaths are due to cancer and cardiovascular conditions; nearly a fifth of those are avoidable. Although healthcare in Bulgaria is nominally universal, out-of-pocket expenses account for nearly half of all healthcare spending, significantly limiting access to medical care. Other problems disrupting care provision are the emigration of doctors due to low wages, understaffed and under-equipped regional hospitals, supply shortages and frequent changes to the basic service package for those insured. The 2018 Bloomberg Health Care Efficiency Index ranked Bulgaria last out of 56 countries. Average life expectancy is 74.8 years, compared with an EU average of 80.99 and a world average of 72.38.Education
 Public expenditures for education are far below the European Union average as well. Educational standards Education in Bulgaria, were once high, but have declined significantly since the early 2000s. Bulgarian students were among the highest-scoring in the world in terms of reading in 2001, performing better than their Canadian and German counterparts; by 2006, scores in reading, math and science had dropped. By 2018, Programme for International Student Assessment studies found 47% of pupils in the 9th grade to be functional illiteracy, functionally illiterate in reading and natural sciences. Average basic literacy stands high at 98.4% with no significant difference between sexes. The Ministry of Education and Science (Bulgaria), Ministry of Education and Science partially funds public schools, colleges and universities, sets criteria for textbooks and oversees the publishing process. Education in primary and secondary public schools is free and compulsory. The process spans 12 grades, in which grades one through eight are primary and nine through twelve are secondary level. Higher education consists of a 4-year Bachelor's degree, bachelor degree and a 1-year Master's degree, master's degree. Bulgaria's highest-ranked higher education institution is Sofia University.
Public expenditures for education are far below the European Union average as well. Educational standards Education in Bulgaria, were once high, but have declined significantly since the early 2000s. Bulgarian students were among the highest-scoring in the world in terms of reading in 2001, performing better than their Canadian and German counterparts; by 2006, scores in reading, math and science had dropped. By 2018, Programme for International Student Assessment studies found 47% of pupils in the 9th grade to be functional illiteracy, functionally illiterate in reading and natural sciences. Average basic literacy stands high at 98.4% with no significant difference between sexes. The Ministry of Education and Science (Bulgaria), Ministry of Education and Science partially funds public schools, colleges and universities, sets criteria for textbooks and oversees the publishing process. Education in primary and secondary public schools is free and compulsory. The process spans 12 grades, in which grades one through eight are primary and nine through twelve are secondary level. Higher education consists of a 4-year Bachelor's degree, bachelor degree and a 1-year Master's degree, master's degree. Bulgaria's highest-ranked higher education institution is Sofia University.
Language
Bulgarian language, Bulgarian is the only language with official status and native for % of the population. It belongs to the Slavic group of languages but has a number of grammatical peculiarities, shared with its closest relative Macedonian language, Macedonian, that set it apart from other Slavic languages: these include a complex verbal morphology (which also codes for distinctions in evidentiality), the absence of noun cases and infinitives, and the use of a suffixed definite article. Other significant languages spoken in Bulgaria are Turkish language, Turkish and Romani language, Romani, which according to the 2011 census were spoken natively by 9.1% and 4.2% of the population, respectively.Religion
diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, pro ...
s and over 2,000 priests.
Sunni Muslims are the second-largest religious community and constitute 10% of Bulgaria's overall religious makeup. A 2011 survey of 850 Muslims in Bulgaria found 30% self-professing as deeply religious and 50% as just religious. According to the study, some religious teachings, like Islamic funeral have been traditionally incorporated and are widely practiced while other major ones are less observed, like the Muslim prayer or abstaining from drinking alcohol, eating pork, and cohabitation.
Less than 3% of the population are affiliated with Religion in Bulgaria, other religions and 11.8% are Irreligion, irreligious or do not self-identify with a religion.
Culture
 Contemporary Bulgarian culture blends the formal culture that helped forge a national consciousness towards the end of Ottoman rule with millennia-old folk traditions. An essential element of Bulgarian folklore is fire, used to banish evil spirits and illnesses. Many of these are personified as witches, whereas other creatures like Slavic dragon, zmey and samodiva (folklore), samodiva (Supernatural beings in Slavic religion, veela) are either benevolent guardians or ambivalent tricksters. Some rituals against evil spirits have survived and are still practised, most notably kukeri and survakane, survakari. Martenitsa is also widely celebrated. Nestinarstvo, a ritual fire-dance of Thracian origin, is included in the list of UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
List of World Heritage Sites in Bulgaria, Nine historical and natural objects are UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Pirin National Park, Srebarna Nature Reserve, Sreburna Nature Reserve, the Madara Rider, the Thracian tombs in Thracian Tomb of Sveshtari, Sveshtari and Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak, Kazanlak, the Rila Monastery, the Boyana Church, the Rock-hewn Churches of Ivanovo and the ancient city of Nesebar. The Rila Monastery was established by Saint John of Rila, Bulgaria's patron saint, whose life has been the subject of numerous literary accounts since Medieval times.
The establishment of the Preslav Literary School, Preslav and Ohrid Literary School, Ohrid literary schools in the 10th century is associated with a golden period in Bulgarian literature during the Middle Ages. The schools' emphasis on Christian religious text, scriptures made the Bulgarian Empire a centre of Slavic culture, bringing Slavs under the influence of Christianity and providing them with Old Church Slavonic, a written language. Its alphabet, Cyrillic script, was developed by the Preslav Literary School. The Tarnovo Literary School, on the other hand, is associated with a Silver age of literature defined by high-quality manuscripts on historical or mystical themes under the Asen dynasty, Asen and House of Shishman, Shishman dynasties. Many literary and artistic masterpieces were destroyed by the Ottoman conquerors, and artistic activities did not re-emerge until the Bulgarian National Revival, National Revival in the 19th century. The enormous body of work of Ivan Vazov (1850–1921) covered every genre and touched upon every facet of Bulgarian society, bridging pre-Liberation works with literature of the newly established state. Notable later works are ''Bay Ganyo'' by Aleko Konstantinov, the Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzschean poetry of Pencho Slaveykov, the Symbolism (arts), Symbolist poetry of Peyo Yavorov and Dimcho Debelyanov, the Marxism, Marxist-inspired works of Geo Milev and Nikola Vaptsarov, and the Socialist Realism, Socialist realism novels of Dimitar Dimov and Dimitar Talev. Tzvetan Todorov is a notable contemporary author, while Bulgarian-born Elias Canetti was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1981.
А religious visual arts heritage includes frescoes, murals and icons, many produced by the medieval Painting of the Tarnovo Artistic School, Tarnovo Artistic School. Like literature, it was not until the National Revival when Bulgarian visual arts began to reemerge. Zahari Zograf was a pioneer of the visual arts in the pre-Liberation era. After the Liberation, Ivan Mrkvička, Anton Mitov, Vladimir Dimitrov, Tsanko Lavrenov and Zlatyu Boyadzhiev introduced newer styles and substance, depicting scenery from Bulgarian villages, old towns and historical subjects. Christo is the most famous Bulgarian artist of the 21st century, known for his outdoor installations.
Folk music is by far the most extensive traditional art and has slowly developed throughout the ages as a fusion of Far Eastern, Oriental, medieval Eastern Orthodox and standard Western European tonalities and modes. Bulgarian folk music has a distinctive sound and uses a wide range of traditional instruments, such as gadulka, gaida, kaval and davul, tupan. A distinguishing feature is ''extended rhythmical time'', which has no equivalent in the rest of European music. The Bulgarian State Television Female Vocal Choir, State Television Female Vocal Choir won a Grammy Award in 1990 for its performances of Bulgarian folk music. Written musical composition can be traced back to the works of Yoan Kukuzel (c. 1280–1360), but modern classical music began with Emanuil Manolov, who composed the first Bulgarian opera in 1890. Pancho Vladigerov and Petko Staynov further enriched symphony, ballet and opera, which singers Ghena Dimitrova, Boris Christoff, Ljuba Welitsch and Nicolai Ghiaurov elevated to a world-class level.
Bulgarian performers have gained acclaim in other genres like electropop (Mira Aroyo), jazz (Milcho Leviev) and blends of jazz and folk (Ivo Papazov).
The Bulgarian National Radio, bTV (Bulgaria), bTV and daily newspapers ''Trud (Bulgarian newspaper), Trud'', ''Dnevnik (Bulgaria), Dnevnik'' and ''24 Chasa'' are some of the largest national media outlets. Media of Bulgaria, Bulgarian media were described as generally unbiased in their reporting in the early 2000s and print media had no legal restrictions. Since then, freedom of the press has deteriorated to the point where Bulgaria scores 111th globally in the World Press Freedom Index, lower than all European Union members and membership candidate states. The government has diverted EU funds to sympathetic media outlets and bribed others to be less critical on problematic topics, while attacks against individual journalists have increased. Collusion between politicians, oligarchs and the media is widespread.
Bulgarian cuisine is similar to that of other Balkan countries and demonstrates strong Turkish and Greek influences. Yogurt, lukanka, banitsa, shopska salad, lyutenitsa and kozunak are among the best-known local foods. Meat consumption is lower than the European average, given a cultural preference for a large variety of salads. Bulgaria was the world's second-largest wine exporter until 1989, but has since lost that position. The 2016 harvest yielded 128 million litres of wine, of which 62 million was exported mainly to Romania, Poland and Russia. Mavrud, Rubin, Siroka Melniska, Shiroka melnishka, Dimiat and Misket Cherven, Cherven Misket are the typical grapes used in Bulgarian wine. Rakia is a traditional fruit brandy that was consumed in Bulgaria as early as the 14th century.
Contemporary Bulgarian culture blends the formal culture that helped forge a national consciousness towards the end of Ottoman rule with millennia-old folk traditions. An essential element of Bulgarian folklore is fire, used to banish evil spirits and illnesses. Many of these are personified as witches, whereas other creatures like Slavic dragon, zmey and samodiva (folklore), samodiva (Supernatural beings in Slavic religion, veela) are either benevolent guardians or ambivalent tricksters. Some rituals against evil spirits have survived and are still practised, most notably kukeri and survakane, survakari. Martenitsa is also widely celebrated. Nestinarstvo, a ritual fire-dance of Thracian origin, is included in the list of UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
List of World Heritage Sites in Bulgaria, Nine historical and natural objects are UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Pirin National Park, Srebarna Nature Reserve, Sreburna Nature Reserve, the Madara Rider, the Thracian tombs in Thracian Tomb of Sveshtari, Sveshtari and Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak, Kazanlak, the Rila Monastery, the Boyana Church, the Rock-hewn Churches of Ivanovo and the ancient city of Nesebar. The Rila Monastery was established by Saint John of Rila, Bulgaria's patron saint, whose life has been the subject of numerous literary accounts since Medieval times.
The establishment of the Preslav Literary School, Preslav and Ohrid Literary School, Ohrid literary schools in the 10th century is associated with a golden period in Bulgarian literature during the Middle Ages. The schools' emphasis on Christian religious text, scriptures made the Bulgarian Empire a centre of Slavic culture, bringing Slavs under the influence of Christianity and providing them with Old Church Slavonic, a written language. Its alphabet, Cyrillic script, was developed by the Preslav Literary School. The Tarnovo Literary School, on the other hand, is associated with a Silver age of literature defined by high-quality manuscripts on historical or mystical themes under the Asen dynasty, Asen and House of Shishman, Shishman dynasties. Many literary and artistic masterpieces were destroyed by the Ottoman conquerors, and artistic activities did not re-emerge until the Bulgarian National Revival, National Revival in the 19th century. The enormous body of work of Ivan Vazov (1850–1921) covered every genre and touched upon every facet of Bulgarian society, bridging pre-Liberation works with literature of the newly established state. Notable later works are ''Bay Ganyo'' by Aleko Konstantinov, the Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzschean poetry of Pencho Slaveykov, the Symbolism (arts), Symbolist poetry of Peyo Yavorov and Dimcho Debelyanov, the Marxism, Marxist-inspired works of Geo Milev and Nikola Vaptsarov, and the Socialist Realism, Socialist realism novels of Dimitar Dimov and Dimitar Talev. Tzvetan Todorov is a notable contemporary author, while Bulgarian-born Elias Canetti was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1981.
А religious visual arts heritage includes frescoes, murals and icons, many produced by the medieval Painting of the Tarnovo Artistic School, Tarnovo Artistic School. Like literature, it was not until the National Revival when Bulgarian visual arts began to reemerge. Zahari Zograf was a pioneer of the visual arts in the pre-Liberation era. After the Liberation, Ivan Mrkvička, Anton Mitov, Vladimir Dimitrov, Tsanko Lavrenov and Zlatyu Boyadzhiev introduced newer styles and substance, depicting scenery from Bulgarian villages, old towns and historical subjects. Christo is the most famous Bulgarian artist of the 21st century, known for his outdoor installations.
Folk music is by far the most extensive traditional art and has slowly developed throughout the ages as a fusion of Far Eastern, Oriental, medieval Eastern Orthodox and standard Western European tonalities and modes. Bulgarian folk music has a distinctive sound and uses a wide range of traditional instruments, such as gadulka, gaida, kaval and davul, tupan. A distinguishing feature is ''extended rhythmical time'', which has no equivalent in the rest of European music. The Bulgarian State Television Female Vocal Choir, State Television Female Vocal Choir won a Grammy Award in 1990 for its performances of Bulgarian folk music. Written musical composition can be traced back to the works of Yoan Kukuzel (c. 1280–1360), but modern classical music began with Emanuil Manolov, who composed the first Bulgarian opera in 1890. Pancho Vladigerov and Petko Staynov further enriched symphony, ballet and opera, which singers Ghena Dimitrova, Boris Christoff, Ljuba Welitsch and Nicolai Ghiaurov elevated to a world-class level.
Bulgarian performers have gained acclaim in other genres like electropop (Mira Aroyo), jazz (Milcho Leviev) and blends of jazz and folk (Ivo Papazov).
The Bulgarian National Radio, bTV (Bulgaria), bTV and daily newspapers ''Trud (Bulgarian newspaper), Trud'', ''Dnevnik (Bulgaria), Dnevnik'' and ''24 Chasa'' are some of the largest national media outlets. Media of Bulgaria, Bulgarian media were described as generally unbiased in their reporting in the early 2000s and print media had no legal restrictions. Since then, freedom of the press has deteriorated to the point where Bulgaria scores 111th globally in the World Press Freedom Index, lower than all European Union members and membership candidate states. The government has diverted EU funds to sympathetic media outlets and bribed others to be less critical on problematic topics, while attacks against individual journalists have increased. Collusion between politicians, oligarchs and the media is widespread.
Bulgarian cuisine is similar to that of other Balkan countries and demonstrates strong Turkish and Greek influences. Yogurt, lukanka, banitsa, shopska salad, lyutenitsa and kozunak are among the best-known local foods. Meat consumption is lower than the European average, given a cultural preference for a large variety of salads. Bulgaria was the world's second-largest wine exporter until 1989, but has since lost that position. The 2016 harvest yielded 128 million litres of wine, of which 62 million was exported mainly to Romania, Poland and Russia. Mavrud, Rubin, Siroka Melniska, Shiroka melnishka, Dimiat and Misket Cherven, Cherven Misket are the typical grapes used in Bulgarian wine. Rakia is a traditional fruit brandy that was consumed in Bulgaria as early as the 14th century.
Sports
 Bulgaria appeared at the 1896 Summer Olympics, first modern Olympic games in 1896, when it was represented by Gymnastics at the 1896 Summer Olympics, gymnast Charles Champaud. Since then, Bulgarian athletes have won 55 gold, 90 silver, and 85 bronze medals, ranking 25th in the All-time Olympic Games medal table, all-time medal table. Olympic weightlifting, Weight-lifting is a signature sport of Bulgaria. Coach Ivan Abadjiev, Ivan Abadzhiev developed innovative training practices that have produced many Bulgarian world and Olympic champions in weight-lifting since the 1980s. Bulgarian athletes have also excelled in wrestling, boxing, gymnastics, volleyball and tennis. Stefka Kostadinova is the reigning List of world records in athletics, world record holder in the women's high jump at , achieved during the 1987 World Championships in Athletics, 1987 World Championships. Grigor Dimitrov is the first Bulgarian tennis player in the Top 3 ATP rankings#Current rankings, ATP rankings.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in the country by a substantial margin. The Bulgaria national football team, national football team's best performance was a semi-final at the 1994 FIFA World Cup, when the squad was spearheaded by forward Hristo Stoichkov. Stoichkov is the most successful Bulgarian player of all time; he was awarded the European Golden Shoe, Golden Boot and the Ballon d'Or, Golden Ball and was considered one of the best in the world while playing for FC Barcelona in the 1990s. PFC CSKA Sofia, CSKA and PFC Levski Sofia, Levski, both based in Sofia, are the most successful clubs domestically and Eternal derby of Bulgarian football, long-standing rivals. PFC Ludogorets Razgrad, Ludogorets is remarkable for having advanced from the local fourth division to the 2014–15 UEFA Champions League group stage in a mere nine years. Placed 39th in 2018, it is Bulgaria's highest-ranked club in UEFA.
Bulgaria appeared at the 1896 Summer Olympics, first modern Olympic games in 1896, when it was represented by Gymnastics at the 1896 Summer Olympics, gymnast Charles Champaud. Since then, Bulgarian athletes have won 55 gold, 90 silver, and 85 bronze medals, ranking 25th in the All-time Olympic Games medal table, all-time medal table. Olympic weightlifting, Weight-lifting is a signature sport of Bulgaria. Coach Ivan Abadjiev, Ivan Abadzhiev developed innovative training practices that have produced many Bulgarian world and Olympic champions in weight-lifting since the 1980s. Bulgarian athletes have also excelled in wrestling, boxing, gymnastics, volleyball and tennis. Stefka Kostadinova is the reigning List of world records in athletics, world record holder in the women's high jump at , achieved during the 1987 World Championships in Athletics, 1987 World Championships. Grigor Dimitrov is the first Bulgarian tennis player in the Top 3 ATP rankings#Current rankings, ATP rankings.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in the country by a substantial margin. The Bulgaria national football team, national football team's best performance was a semi-final at the 1994 FIFA World Cup, when the squad was spearheaded by forward Hristo Stoichkov. Stoichkov is the most successful Bulgarian player of all time; he was awarded the European Golden Shoe, Golden Boot and the Ballon d'Or, Golden Ball and was considered one of the best in the world while playing for FC Barcelona in the 1990s. PFC CSKA Sofia, CSKA and PFC Levski Sofia, Levski, both based in Sofia, are the most successful clubs domestically and Eternal derby of Bulgarian football, long-standing rivals. PFC Ludogorets Razgrad, Ludogorets is remarkable for having advanced from the local fourth division to the 2014–15 UEFA Champions League group stage in a mere nine years. Placed 39th in 2018, it is Bulgaria's highest-ranked club in UEFA.
See also
*Outline of BulgariaExplanatory notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** * * * * * * *External links
*Bulgaria
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''. * *
Bulgaria Profile
from Balkan Insight
President of The Republic of Bulgaria
{{Authority control Bulgaria, Balkan countries Bulgarian-speaking countries and territories Countries in Europe Eastern European countries Member states of NATO Member states of the European Union Member states of the Three Seas Initiative Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Republics Southeastern European countries States and territories established in 1908 States and territories established in the 680s