Brune test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Brune test (named after the South African mathematician Otto Brune) is used to check the permissibility of the
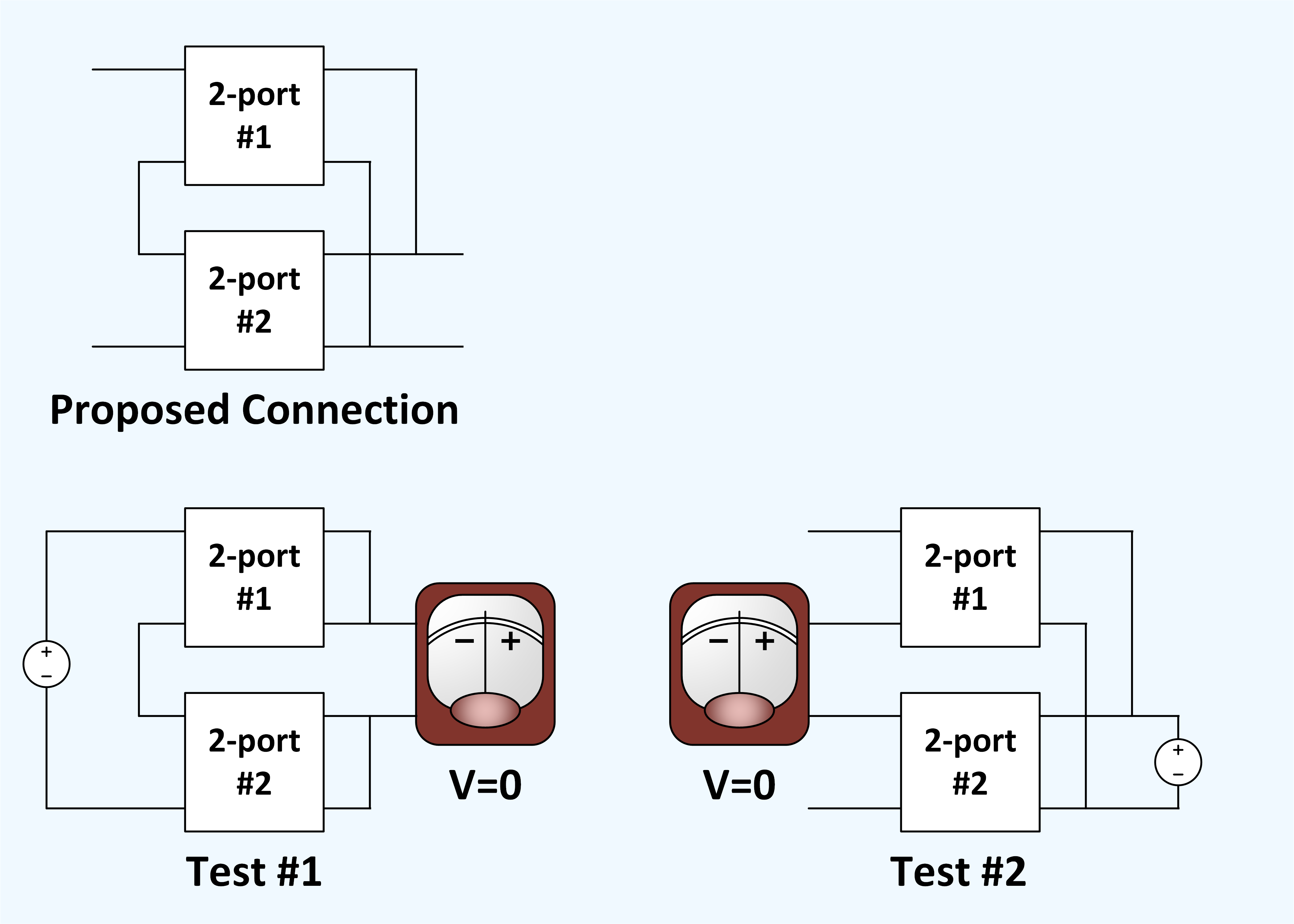
 To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a series-series configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in series, a voltage is applied to the input and the
To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a series-series configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in series, a voltage is applied to the input and the
File:Brune Test Series-Series Fail.png, Brune Test Series-Series Failure.
File:Brune Test Series-Series Pass.png, Brune test series-series pass with success obvious by inspection.
File:Brune Test Series-Series Pass Xfmr.png, Brune test series-series connection that passes because of transformer isolation.
The first example fails the series-series test because the through path between the lower terminals of 2-port #1 short-circuit part of the circuitry in 2-port #2. The second example passes the series-series test. The 2-ports are the same as in the first example, but 2-port #2 has been flipped or equivalently the choice of terminals to be placed in series has changed. The result is that the through path between the lower terminals of 2-port #1 simply provide a parallel path to the through path between the upper terminals of 2-port #2. The third example is the same as the first example, except that it passes the Brune test because ideal isolating transformers have been placed at the right side terminals which break the through paths.
 To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a parallel-parallel configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in parallel, a voltage is applied to the input and the
To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a parallel-parallel configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in parallel, a voltage is applied to the input and the
 A similar approach as above works for the hybrid connection (series-parallel connection) and the inverse hybrid connection (parallel-series connection).
{{-
A similar approach as above works for the hybrid connection (series-parallel connection) and the inverse hybrid connection (parallel-series connection).
{{-
combination
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are th ...
of two or more two-port network
A two-port network (a kind of four-terminal network or quadripole) is an electrical network (circuit) or device with two ''pairs'' of terminals to connect to external circuits. Two terminals constitute a port if the currents applied to them satis ...
s (or quadripoles) in electrical circuit analysis. The test determines whether the network still meets the port condition
In electrical circuit theory, a port is a pair of terminals connecting an electrical network or circuit to an external circuit, as a point of entry or exit for electrical energy. A port consists of two nodes (terminals) connected to an outside c ...
after the two-ports have been combined. The test is a sufficient, but not necessary, test.
Series-series connection
 To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a series-series configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in series, a voltage is applied to the input and the
To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a series-series configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in series, a voltage is applied to the input and the open-circuit voltage
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC) is the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of an electronic device when disconnected from any circuit. There is no external load connected. No external electric current fl ...
is measured/calculated between the output terminals to be connected. If there is a voltage drop, the two-port networks cannot be combined in series. The same test is repeated from the output side of the two-port networks (series connection of the output ports, application of a voltage to the output, measurement/calculation of the open-circuit voltage between the input terminals to be connected). Only if there is no voltage drop in both cases, a combination of the two-ports networks is permissible.
examples
Parallel-parallel connection
 To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a parallel-parallel configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in parallel, a voltage is applied to the input and the
To check if two two-port networks can be connected in a parallel-parallel configuration, first of all just the input ports are connected in parallel, a voltage is applied to the input and the open-circuit voltage
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC) is the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of an electronic device when disconnected from any circuit. There is no external load connected. No external electric current fl ...
is measured/calculated between the outputs that are short-circuited each. If there is a voltage drop, the two-port networks cannot be combined in parallel. The same test is repeated from the output side of the two-port networks (parallel connection of the output ports, application of a voltage to the output, measurement/calculation of the open-circuit voltage between the inputs that are short-circuited each). Only if there is no voltage drop in both cases, a combination of the two-ports networks is permissible.
Hybrid connection
 A similar approach as above works for the hybrid connection (series-parallel connection) and the inverse hybrid connection (parallel-series connection).
{{-
A similar approach as above works for the hybrid connection (series-parallel connection) and the inverse hybrid connection (parallel-series connection).
{{-
References