Bronzite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

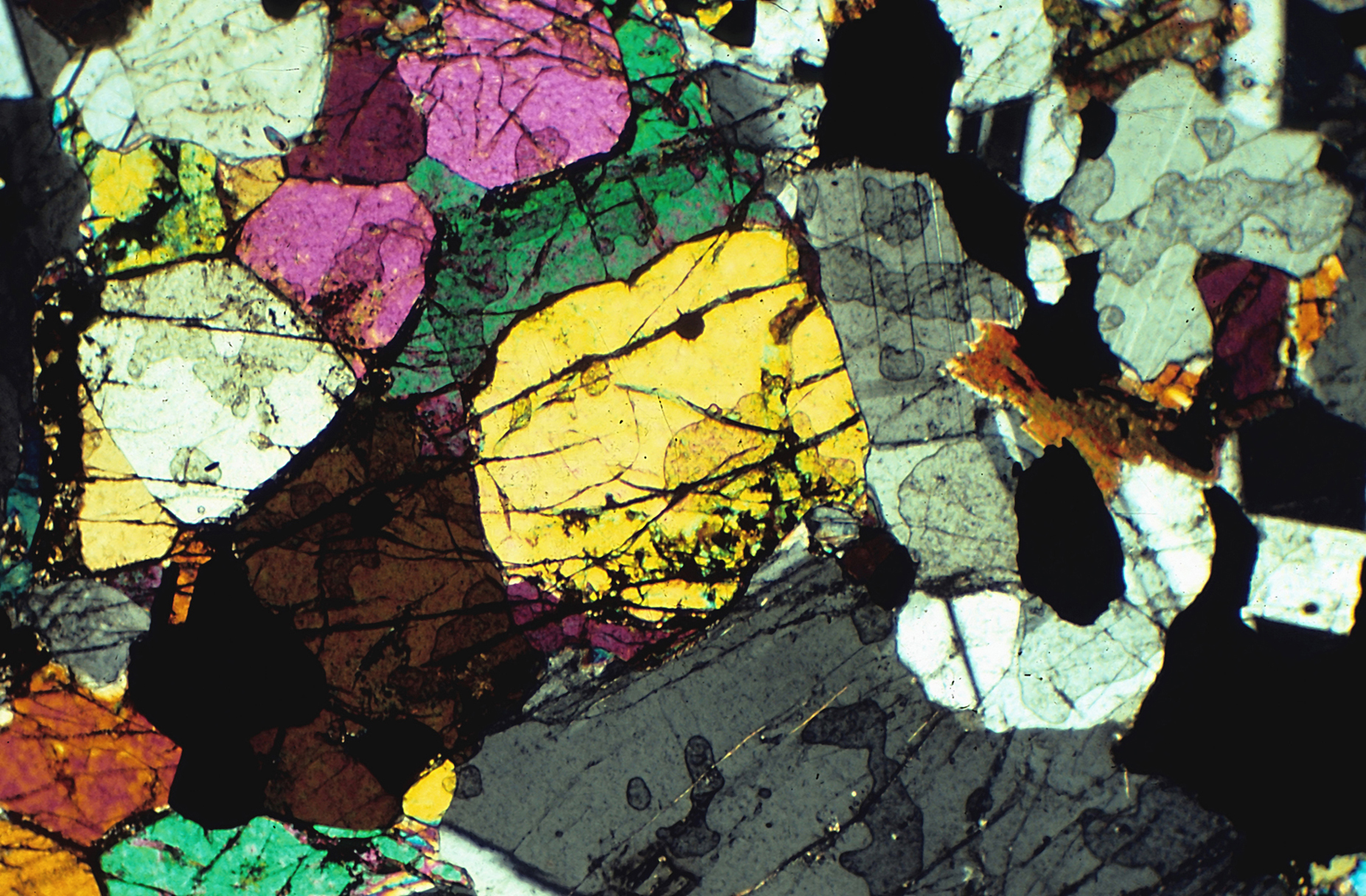 Bronzite is a member of the
Bronzite is a member of the

 Bronzite is a member of the
Bronzite is a member of the pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
group of mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
s, belonging with enstatite
Enstatite is a mineral; the magnesium endmember of the pyroxene silicate mineral series enstatite (MgSiO3) – ferrosilite (FeSiO3). The magnesium rich members of the solid solution series are common rock-forming minerals found in igneous and m ...
and hypersthene
Hypersthene is a common rock-forming inosilicate mineral belonging to the group of orthorhombic pyroxenes. Its chemical formula is . It is found in igneous and some metamorphic rocks as well as in stony and iron meteorites. Many references have f ...
to the orthorhombic series of the group. Rather than a distinct species, it is really a ferriferous variety of enstatite, which owing to partial alteration has acquired a bronze-like sub-metallic luster on the cleavage surfaces.
Enstatite is magnesium silicate, MgSiO3, with the magnesium partly replaced by small amounts (up to about 12%) of Fe+2. In the bronzite variety, (Mg,Fe)SiO3, the iron(II) oxide ranges from about 12 to 30%, and with still more iron there is a passage to hypersthene
Hypersthene is a common rock-forming inosilicate mineral belonging to the group of orthorhombic pyroxenes. Its chemical formula is . It is found in igneous and some metamorphic rocks as well as in stony and iron meteorites. Many references have f ...
.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius Hurlbut, Jr. (1985) ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' Wiley, 20th ed., The ferriferous varieties are liable to a particular kind of alteration, known as schillerization, which results in the separation of the iron as very fine films of oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
and hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. I ...
s along the cleavage cracks of the mineral. The cleavage surfaces therefore exhibit a metallic sheen or schiller, which is even more pronounced in hypersthene than in bronzite. The color of bronzite is green or brown; its specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water (molecule), wa ...
is about 3.3–3.4, varying with the amount of iron present. The refractive indices
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
and optic angle increase with iron content. The enstatite endmember has a positive optic sign A conoscopic interference pattern or interference figure is a pattern of Birefringence, birefringent colours crossed by dark bands (or ''isogyres''), which can be produced using a Geology, geological petrographic microscope for the purposes of miner ...
, whereas bronzite and hypersthene both show a negative optic sign.
Like enstatite, bronzite is a constituent of many mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
to ultramafic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
igneous rocks, such as, norite
Norite is a mafic intrusive igneous rock composed largely of the calcium-rich plagioclase labradorite, orthopyroxene, and olivine. The name ''norite'' is derived from ''Norge'', the Norwegian name for Norway.
Norite also known as orthopyrox ...
, gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is che ...
, and especially peridotite
Peridotite ( ) is a dense, coarse-grained igneous rock consisting mostly of the silicate minerals olivine and pyroxene. Peridotite is ultramafic, as the rock contains less than 45% silica. It is high in magnesium (Mg2+), reflecting the high prop ...
, and of the serpentinite
Serpentinite is a rock composed predominantly of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''ser ...
s which have been derived from them. It also occurs in some crystalline schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes o ...
. Bronzitite, a pyroxenite
Pyroxenite is an ultramafic igneous rock consisting essentially of minerals of the pyroxene group, such as augite, diopside, hypersthene, bronzite or enstatite. Pyroxenites are classified into clinopyroxenites, orthopyroxenites, and the we ...
of bronzite composition, is noted in the cumulate rocks of the Stillwater igneous complex
The Stillwater igneous complex is a large Layered intrusion, layered mafic intrusion (LMI) located in southern Montana in Stillwater County, Montana, Stillwater, Sweet Grass County, Montana, Sweet Grass and Park County, Montana, Park Counties. ...
of Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
.Jackson, Everett D., ''The Chromite Deposits of the Stillwater Complex, Montana'' in ''Ore Deposites of the Unitrd States, 1933-1967 (The Graton-Sales Volume)'' Vol. 2, pp. 1495-1509, 1968
Ornamental usage
Bronzite is sometimes cut and polished, usually in convex forms, for small ornamental objects, but its use for this purpose is less extensive than that of hypersthene{{Citation needed, date=August 2022. It often has a more-or-less distinct fibrous structure, and when this is pronounced the sheen has a certain resemblance to that of cats-eye. Masses sufficiently large for cutting are found in the norite of theKupferberg
Kupferberg () is a municipality in the district of Kulmbach, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated in the Frankenwald, 9 km northeast of Kulmbach.
Notable people
* Joseph Gabriel Findel Gottfried Joseph Gabriel Findel (born 21 October 1 ...
in the Fichtelgebirge
The Fichtel MountainsRandlesome, C. et al. (2011). ''Business Cultures in Europe'', 2nd ed., Routledge, Abingdon and New York, p. 52. . (german: Fichtelgebirge, cs, Smrčiny), form a small horseshoe-shaped mountain range in northeastern Bavaria ...
, and in the serpentine of Kraubat near Leoben in Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
. In this connection mention may be made of an altered form of enstatite or bronzite known as ''bastite'' or ''schiller spar''. Here, in addition to schillerization, the original enstatite has been altered by hydration and the product has the approximate composition of serpentine. In color bastite is brown or green with the same metallic sheen as bronzite. The typical locality is Baste in the Radauthal, Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
, where patches of pale greyish-green bastite are embedded in a darker-colored serpentine. This rock when cut and polished makes an effective decorative stone, although little used for that purpose.
References