British West India Islands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
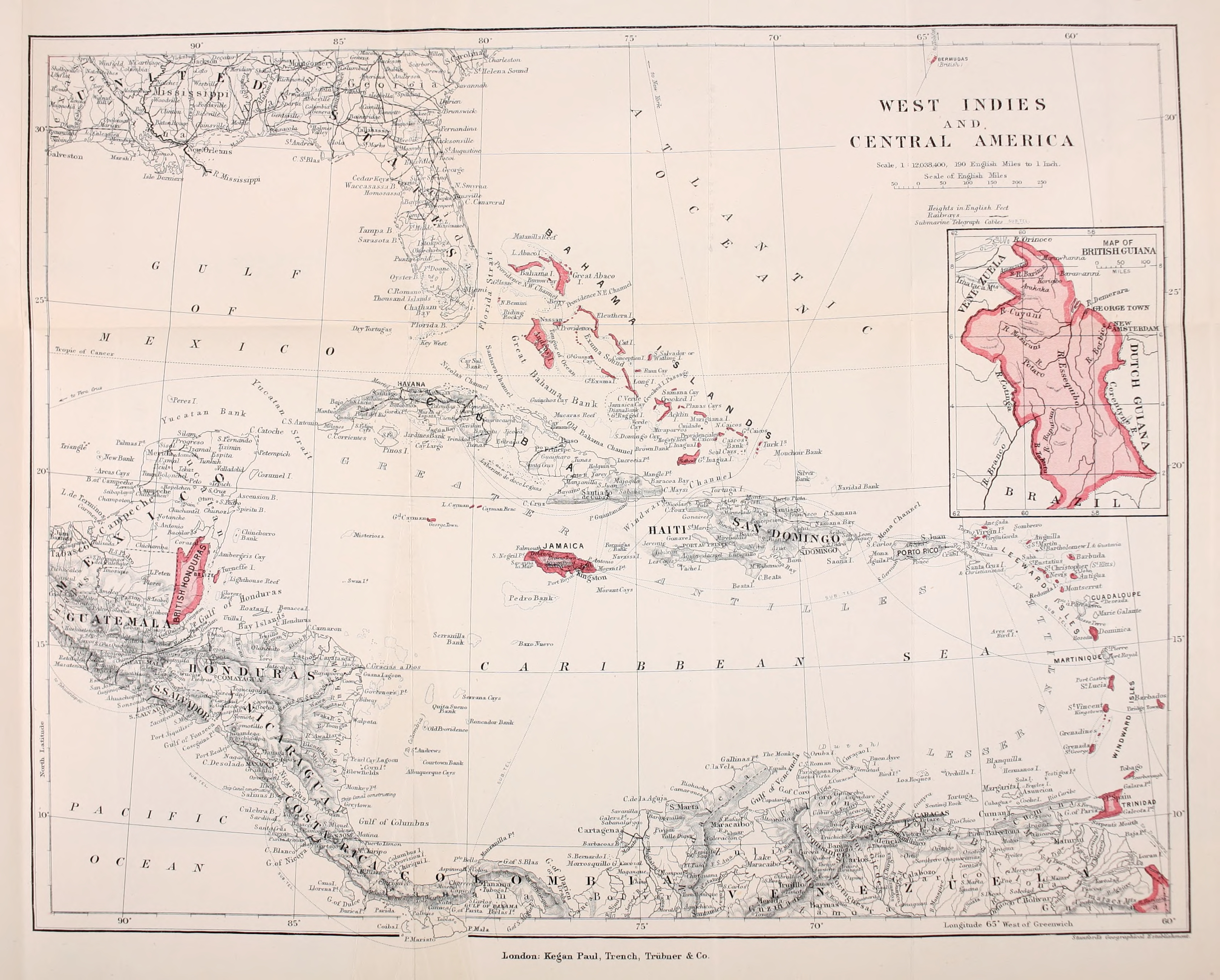 The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British
Books.google.com (12 August 2008). Retrieved on 17 July 2013. Following the independence of most of the territories from the United Kingdom, the term Commonwealth Caribbean is now used. In 1912, the British government divided their territories into different colonies: The Bahamas, Barbados,
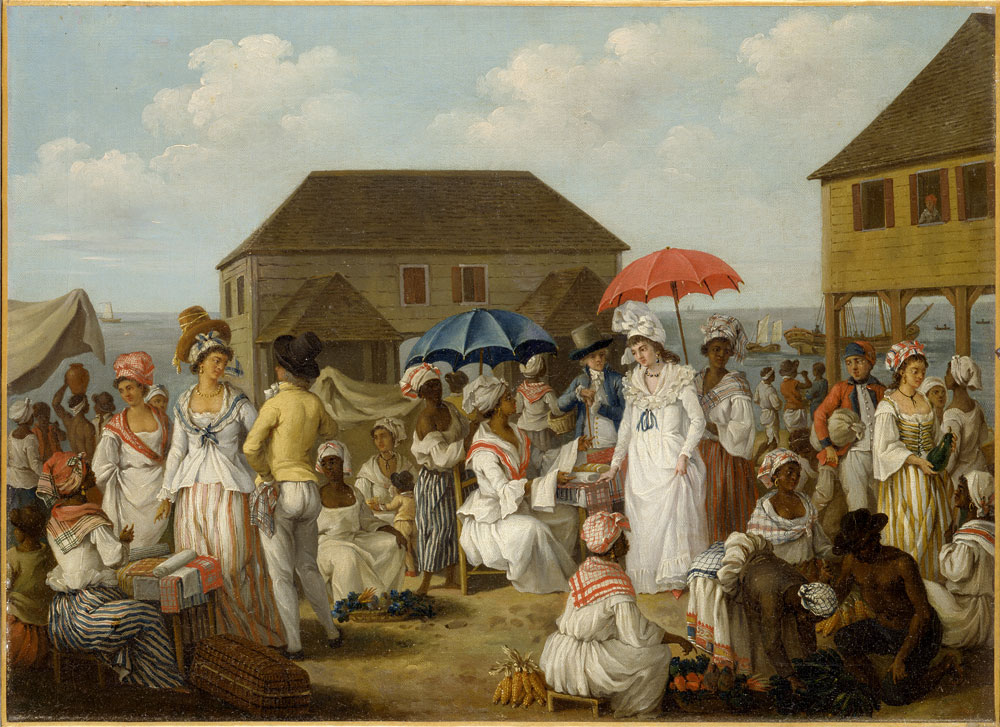 Sir William Stapleton established the first federation in the British West Indies in 1674. He set up a General Assembly of the
Sir William Stapleton established the first federation in the British West Indies in 1674. He set up a General Assembly of the
Antigua Termination of Association Order
UK Parliamentary Hansard debate of the bill
 Although most of the British West Indies seceded from British rule and were granted independence, several opted to remain British territories. Those territories include:
* Anguilla
* Bermuda (sometimes included as part of the BWI)
* British Virgin Islands
*
Although most of the British West Indies seceded from British rule and were granted independence, several opted to remain British territories. Those territories include:
* Anguilla
* Bermuda (sometimes included as part of the BWI)
* British Virgin Islands
*
 The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda (, ) is a sovereign country in the West Indies. It lies at the juncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles, at 17°N latitude. The country consists of two maj ...
, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
, Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindian ...
, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first European to encounter Guiana was S ...
(now Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
) and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories include Bermuda, and the former British Honduras (now Belize). The colonies were also at the center of the transatlantic slave trade, around 2.3 million slaves were brought to the British Caribbean. Before the decolonisation period in the later 1950s and 1960s the term was used to include all British colonies in the region as part of the British Empire.The British West Indies: Their History, Resources and Progress – Sir Algernon Edward Aspinall – Google BoekenBooks.google.com (12 August 2008). Retrieved on 17 July 2013. Following the independence of most of the territories from the United Kingdom, the term Commonwealth Caribbean is now used. In 1912, the British government divided their territories into different colonies: The Bahamas, Barbados,
British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first European to encounter Guiana was S ...
, British Honduras, Jamaica (with its dependencies the Turks and Caicos Islands and the Cayman Islands), Trinidad and Tobago, the Windward Islands, and the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
. Between 1958 and 1962, all of the island territories except the British Virgin Islands, the Bahamas and Bermuda were organised into the West Indies Federation. It was hoped that the Federation would become independent as a single nation, but it had limited powers and faced many practical problems. Consequently, the West Indies Federation was dissolved in 1962.
The territories are now fully independent sovereign states, except for five – Anguilla, the British Virgin Islands, the Cayman Islands, Montserrat, and the Turks and Caicos Islands – which remain British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remna ...
, as does Bermuda. All remain within the Commonwealth of Nations. They also established the Caribbean Community, and many of the nations have joined various international bodies, such as the Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 April ...
, the Association of Caribbean States, the World Trade Organization, the United Nations, and the Caribbean Development Bank among others.
Territories
The territories that were originally part of the British West Indies are (date of independence, where applicable, in brackets): * The Bahamas (1973) * Barbados (1966) * Belize (formerly British Honduras) (1981) * Bermuda (British overseas territory) * British Leeward Islands ** Anguilla (British overseas territory) **Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda (, ) is a sovereign country in the West Indies. It lies at the juncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles, at 17°N latitude. The country consists of two maj ...
(1981)
** British Virgin Islands (British overseas territory)
** Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
(1978)
** Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
(British overseas territory)
** Saint Kitts and Nevis (1983)
* British Windward Islands
** Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
(1974)
** Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindian ...
(1979)
** Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (1979)
* Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
(British overseas territory)
* Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
(formerly British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first European to encounter Guiana was S ...
) (1966)
* Jamaica (formerly Colony of Jamaica) (1962)
* Trinidad and Tobago (1962)
* Turks and Caicos Islands (British overseas territory)
History
The origins of the British West Indies lie in outposts established to support English pirates and privateers who were involved in raidingSpanish treasure fleets
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to ...
, and merchants interested in trade. Charles Leigh, an English merchant, established a short-lived settlement on the Wiapoco River
The Oyapock or Oiapoque (; ; ) is a long river in South America that forms most of the border between the French overseas department of French Guiana and the Brazilian state of Amapá.
Course
The Oyapock runs through the Guianan moist for ...
in 1604 (now the Oyapock, which forms the border between French Guiana and Brazil). This was followed by failed attempts to established settlements in Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindian ...
in 1605 and Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
in 1609. The first permanent settlement was established in St. Christopher (St. Kitts) by Thomas Warner. This was followed by settlements in Barbados in 1627, Nevis in 1628, and Montserrat and Antigua in 1632. Providence Island was colonised by English Puritans in 1630, but the colony was destroyed by the Spanish in 1641. The capture of Jamaica in 1655 expanded British control beyond these small islands in the Lesser Antilles.
Leeward Islands
 Sir William Stapleton established the first federation in the British West Indies in 1674. He set up a General Assembly of the
Sir William Stapleton established the first federation in the British West Indies in 1674. He set up a General Assembly of the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
in St. Kitts. Stapleton's Federation was active between 1674 and 1685, during his term as governor, and the General Assembly met regularly until 1711.
By the 18th century, each island had kept its own Assembly and made its own laws. The islands continued to share one Governor and one Attorney-General. Although unpopular, Stapleton's Federation was never really dissolved but simply replaced by other arrangements.
Between 1816 and 1833, the Leewards were divided into two groups: St. Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla and Antigua-Barbuda-Montserrat, each with its own Governor. In 1833 all the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
were brought together, and Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
was added, remaining as part of the group until 1940.
In 1869, Governor Benjamin Pine was assigned to organise a federation of Antigua-Barbuda, Dominica, Montserrat, Nevis, St. Kitts, Anguilla and the British Virgin Islands. St. Kitts and Nevis opposed sharing their government funds with Antigua and Montserrat, which were bankrupt. Governor Pine told the Colonial Office that the scheme had failed due to "local prejudice and self-interest". His only achievement was to give the Leewards a single Governor. All laws and ordinances, however, had to be approved by each island council.
In 1871 the British government passed the Leeward Islands Act, by which all the islands were under one Governor and one set of laws. The Federal Colony was composed of all islands organised under Governor Pine's previous attempt. Each island was called a "Presidency" under its own Administrator or Commissioner. Like earlier groupings, this federation was unpopular but it continued until 1956, when it was redefined as the Territory of the Leeward Islands. In 1958 the Federation of the West Indies was organised, of which the Leeward Islands became a part.
Windward Islands
In 1833 the Windward Islands became a formal union called the Windward Islands Colony. In 1838, Trinidad (acquired in 1802) andSt. Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerin ...
(acquired in 1814) were brought into the Windward Islands Colony, but were not given their own assemblies (having previously been Crown Colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
). In 1840 Trinidad left the Colony. Barbados wished to retain its separate identity and ancient institutions, and the other colonies did not want to associate with it. The individual islands resisted British attempts at closer union. Barbados in particular fought to retain its own Assembly and left the union in 1884. Power for the union was then transferred to Grenada as overseer of the bloc.
From 1885 to 1958, the Windward Islands Colony included Grenada and the Grenadines, St. Vincent and St. Lucia during the entire period. Tobago left in 1889, forming a union with Trinidad. Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
joined the Windward Islands Colony in 1940, after having been transferred from the Leewards, and remained in the Colony until 1958. After 1885 the Windward Islands Colony was under one Governor-General in Grenada, and each island had its own Lieutenant-Governor and its own assembly (as before). Attempts to create a Federal Colony, as in the Leewards, were always resisted. The Windward Islands Colony broke up in 1958 when each island chose to join the new Federation of the West Indies as a separate unit.
Jamaica and dependencies
TheCayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
and Turks and Caicos Islands were grouped under Jamaica out of convenience and sometimes for historical and/or geographical reasons. British Honduras (later Belize) was surrounded by hostile Spanish colonies and needed the protection afforded by the Jamaican Army and Navy. In addition, British Honduras had been founded by loggers. It increased in population partly by the settlement of Englishmen migrating from Jamaica in the late 17th and early 18th centuries (settlers also immigrated directly from England; others were born in the colony.) From 1742, British Honduras was a dependency directly under the Governor of Jamaica. In 1749 the Governors of Jamaica appointed Administrators for British Honduras.
In 1862 British Honduras became a Crown Colony; it was placed under the Governor of Jamaica with its own Lieutenant-Governor. In 1884 it finally broke all administrative ties with Jamaica and wanted self governance, as did Cayman Islands and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation was a short-lived federation that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. It consisted of several Caribbean colonies of the United Kingdom. The Federation's purpose was to create a political unit that would become independent from Britain as a single state, similar to theFederation of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia (which also governed what is now the Northern Territory), and Western A ...
or Canadian Confederation. However, the Federation collapsed due to internal political conflicts over how it would be governed before that could develop.
West Indies Associated States
In 1967, following the termination of the West Indies Federation, a number of Eastern Caribbean islands formed a free association form of government along with the United Kingdom called the West Indies Associated States. The arrangement was created through the British House of Commons passing the ''West Indies Act (1967)'' (also known as the ''Associated States Act''). As part of the arrangement more sovereignty was granted to the bloc of West Indies countries with the United Kingdom maintaining responsibility for defence and external affairs only.UK Parliamentary Hansard debate of the bill
Territories today
Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
* Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
* Turks and Caicos Islands
Sport
Cricket
Cricket has traditionally been the main sport in the British West Indies (though others sports such asfootball
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
have challenged its dominance since the 1990s). Most of the countries and territories listed above field a combined cricket team called the West Indies, which is one of the twelve elite international teams that play at Test match level. The West Indies hosted the 2007 Cricket World Cup
The 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup was the ninth Cricket World Cup, a One Day International (ODI) cricket tournament that took place in the West Indies from 13 March to 28 April 2007. There were a total of 51 matches played, three fewer than at the ...
of ODI Cricket and the 2010 ICC World Twenty20
The 2010 ICC World Twenty20 was the third ICC World Twenty20 competition, an international Twenty20 cricket tournament that was held in the West Indies between 30 April and 16 May 2010. It was won by England, who defeated Australia in the fina ...
.
See also
*British colonization of the Americas
The British colonization of the Americas was the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by England, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. C ...
* British North America
* BWIA West Indies Airways
* Crown Dependencies
* Foreign and Commonwealth Office
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) is a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom. Equivalent to other countries' Ministry of Foreign Affairs, ministries of fore ...
* Indo-Caribbean
Indo-Caribbeans or Indian-Caribbeans are Indian people in the Caribbean who are descendants of the Jahaji Indian indentured laborers brought by the British, Dutch, and French during the colonial era from the mid-19th century to the early 20th c ...
* Right of abode
* University of the West Indies
The University of the West Indies (UWI), originally University College of the West Indies, is a public university system established to serve the higher education needs of the residents of 17 English-speaking countries and territories in th ...
* British West Indies Regiment
The British West Indies Regiment was a unit of the British Army during the First World War, formed from volunteers from British colonies in the West Indies.
Formation
In 1915 the British Army formed a second West Indies regiment from Caribbean ...
* West Indies (Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
- Dutch - French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
- Spanish)
References
Further reading
* * * {{Coord, 24.0000, N, 71.0000, W, source:wikidata, display=title Colonial government in the West Indies Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former countries in the Caribbean Former colonies in North America West Indies Jamaica–United Kingdom relations Bahamas–United Kingdom relations 1674 establishments in the British Empire 1674 establishments in North America