British Aerospace HS.748 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hawker Siddeley HS 748 is a medium-sized turboprop

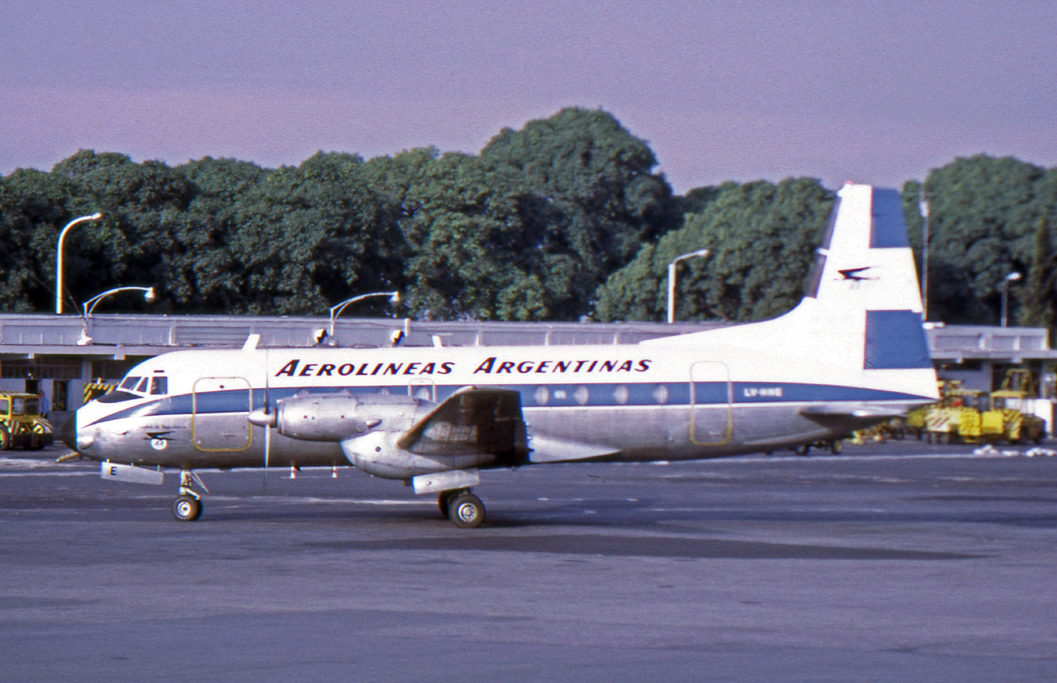 On 24 June 1960, the first Avro 748 made its maiden flight from the company's
On 24 June 1960, the first Avro 748 made its maiden flight from the company's
''BAE Systems'', Retrieved: 26 June 2019. Flight testing of the two prototypes quickly validated the type's short-field performance. Eighteen ''Avro 748 Series 1'' aircraft were produced; during April 1962, the first production aircraft were delivered to launch customer
''Flight International'', 18 November 1960. p. 783. During 1967, the series 2A was introduced, which was the same basic aircraft powered by ''Mk. 532'' engines along with a further increase in gross weight. From 1971 onwards, several new options were made available to customers, including a large freight door in the rear cabin and a strengthened cabin floor. During 1979, the Series 2B was introduced, which saw a 4-foot increase in wingspan, the adoption of ''Mk 536-2'' engines, along with a modernised passenger cabin, and various improvements to the fuel, water methanol injection system, and engine fire protection systems. During 1976, Eric Johnson, sales engineering manager of Hawker Siddeley Manchester, stated that the company was studying options for equipping a model of the HS 748 with turbofan engines, and that a preferred powerplant at that point was the Rolls-Royce/SNECMA M45H, as used on the VFW-Fokker 614 jetliner. Other changes would likely have been incorporated, including the addition of lift dumpers and adaptive brakes for better landing performance, while electrical, hydraulic and air conditioning systems would be redesigned; externally, a dihedral would have to be introduced to keep the tailplane clear of the jet exhaust. It was envisioned that the reengined aircraft could offers larger seating arrangements of up to 64 seats."HS.748 looks to the 1980s."
''Flight International'', 22 May 1976. p. 1342. In addition to the British production line, manufacture of the 748 was also performed overseas. Early on, India had placed orders for the type. Both the 748 Series 1 and Series 2 were licence-produced in Indian manufacturer Hindustan Aeronautics (HAL), aircraft produced by the company were designated ''HAL-748''. On 1 November 1961, the first Indian-assembled HAL-748 made its first flight. By the end of production, HAL had completed 89 Indian-built aircraft, 72 of which were for the
''Flight International'', 2 July 1970. pp. 12-13. Another key market for the HS 748 was the executive role; the type was repeatedly procured to serve as the designated aircraft for various heads of state, including of Argentina, Brazil, Chile, India, Venezuela, Zambia, Thailand and the United Kingdom. The HS 748 was one of the last planes to be flown by noted
'' Royal Australian Navy'', Retrieved: 26 June 2019. In a typical passenger configuration, the HS 748 can accommodate around 40–48 economy class seats in a four abreast layout; however, the majority of later-serving passenger HS 748s were typically operated as quick change ''combis''. These aircraft are fitted with a movable bulkhead that divides the main cabin, housing between 4 and 40 seats in the rear section while cargo is placed the forward section. The 748 has also been widely used as a pure freighter, having a typical max payload of about 12,000 lbs. Several carriers have used the 748 as a bulk fuel hauler, in which capacity it is normally with either seven or eight fixed tanks in the cabin, possessing a total capacity of about . The
 ;
* East Horizon Airlines
;
* Air Botswana
;
* LIAT Airlines
;
* Aerolíneas Argentinas
;
* Austrian Airlines (2)
;
* Bahamasair
;
* Bop Air (Operated one Aircraft)
;
* Varig (11) [one Avro 748 Series 2 prototype and 10 production aircraft]
British Virgin Islands
* Air BVI
;
* Air Gaspé
* Air Manitoba
* Austin Airways
* Calm Air
* First Air (9)
* Midwest Airlines
* Quebecair
* Transair (Canada)
* West Wind Aviation
;
* TACV
;
* LAN Chile
;
* Avianca
* Satena
* Intercontinental de Aviacion
;
* Fiji Airways
;
* Deutsche Flugsicherung
* Lufthansa CityLine, DLT Deutsche Luftverkehrsgesellschaft
;
* Guyana Airways (now defunct)
;
* Vayudoot (now defunct)
* Indian Airlines (now Air India)
* Hindustan Aeronautics Limited BH-572 Used by HAL Chairman
;
* Bouraq Indonesia Airlines (now defunct)
* Bali Air (now defunct) (4)
* Airfast Indonesia
;
* Ryan Air (2) 1986–1989 Inaugurating the Dublin-London (Luton) Service
;
* 748 Air Services
;
* Air Madagascar
;
* Air Malawi
;
* Air Marshall Islands
;
* Aeronaves de México (now Aeroméxico)
* Aerocaribe (1) (Bought From Atlantic Airlines de Honduras)
;
* Nepal Airlines
* Necon Air
;
* Mount Cook Airline
;
* Philippine Airlines
;
* SATA Air Açores
;
* Polynesian Airlines (2)
;
* Air Cape (South Africa)
* AirQuarius (Operated 6 aircraft)
* Executive Aerospace (Operated 13 aircraft)
* Intensive Air
* Stars Away Aviation
* South African Airways (Operated 5 aircraft 1970–1983)
;
* Aero Lanka (1)
* Air Ceylon (2)
* Lionair (Sri Lanka), Lionair (1)
;
* Bangkok Airways
* Thai Airways Company
;
* Trinidad and Tobago Air Service (TTAS)
;
* British Airways
* Dan Air
* Emerald Airways
* Janes Aviation (2)
*
;
* East Horizon Airlines
;
* Air Botswana
;
* LIAT Airlines
;
* Aerolíneas Argentinas
;
* Austrian Airlines (2)
;
* Bahamasair
;
* Bop Air (Operated one Aircraft)
;
* Varig (11) [one Avro 748 Series 2 prototype and 10 production aircraft]
British Virgin Islands
* Air BVI
;
* Air Gaspé
* Air Manitoba
* Austin Airways
* Calm Air
* First Air (9)
* Midwest Airlines
* Quebecair
* Transair (Canada)
* West Wind Aviation
;
* TACV
;
* LAN Chile
;
* Avianca
* Satena
* Intercontinental de Aviacion
;
* Fiji Airways
;
* Deutsche Flugsicherung
* Lufthansa CityLine, DLT Deutsche Luftverkehrsgesellschaft
;
* Guyana Airways (now defunct)
;
* Vayudoot (now defunct)
* Indian Airlines (now Air India)
* Hindustan Aeronautics Limited BH-572 Used by HAL Chairman
;
* Bouraq Indonesia Airlines (now defunct)
* Bali Air (now defunct) (4)
* Airfast Indonesia
;
* Ryan Air (2) 1986–1989 Inaugurating the Dublin-London (Luton) Service
;
* 748 Air Services
;
* Air Madagascar
;
* Air Malawi
;
* Air Marshall Islands
;
* Aeronaves de México (now Aeroméxico)
* Aerocaribe (1) (Bought From Atlantic Airlines de Honduras)
;
* Nepal Airlines
* Necon Air
;
* Mount Cook Airline
;
* Philippine Airlines
;
* SATA Air Açores
;
* Polynesian Airlines (2)
;
* Air Cape (South Africa)
* AirQuarius (Operated 6 aircraft)
* Executive Aerospace (Operated 13 aircraft)
* Intensive Air
* Stars Away Aviation
* South African Airways (Operated 5 aircraft 1970–1983)
;
* Aero Lanka (1)
* Air Ceylon (2)
* Lionair (Sri Lanka), Lionair (1)
;
* Bangkok Airways
* Thai Airways Company
;
* Trinidad and Tobago Air Service (TTAS)
;
* British Airways
* Dan Air
* Emerald Airways
* Janes Aviation (2)
*
 ;
* Military of Benin, Benin Air Force – One remains in service as of December 2017.
;
* Border Security Force Air Wing
*
;
* Military of Benin, Benin Air Force – One remains in service as of December 2017.
;
* Border Security Force Air Wing
*

 ;
*
;
*
 * HS 748 Srs2/228, c/n 1601 ex-
* HS 748 Srs2/228, c/n 1601 ex-
 * Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1587 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-831, at the Sri Lanka Air Force Museum, Ratmalana Airport, Colombo.
* HS 748 Srs2a/272, c/n 1691 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force SCM-3101, at Koggala Airport, SLAF Koggala, Galle.
* HS 748 Srs2a/301, c/n 1746 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-833, at Weerawila Airport, SLAF Weerawilla.
* Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1587 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-831, at the Sri Lanka Air Force Museum, Ratmalana Airport, Colombo.
* HS 748 Srs2a/272, c/n 1691 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force SCM-3101, at Koggala Airport, SLAF Koggala, Galle.
* HS 748 Srs2a/301, c/n 1746 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-833, at Weerawila Airport, SLAF Weerawilla.
 * HS 748 Srs2/243, c/n 1707 ex- Thai Airways HS-THH, at Jomtien Beach. Fuselage preserved where it crash landed in 1987. Painted in fictional camouflage.
* HS 748 Srs2a/243, c/n 1708 ex-Thai Airways HS-THI, at the Siam Country Club, Pattaya.
* HS 748 Srs2/243, c/n 1707 ex- Thai Airways HS-THH, at Jomtien Beach. Fuselage preserved where it crash landed in 1987. Painted in fictional camouflage.
* HS 748 Srs2a/243, c/n 1708 ex-Thai Airways HS-THI, at the Siam Country Club, Pattaya.
 * Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1543 ex-Emerald Airways G-BEJD, at Speke Aerodrome Heritage Group, Liverpool John Lennon Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2/225, c/n 1592 ex-Emerald Airways G-ATMI, nose and front fuselage at the RAF Millom, RAF Millom Museum, Cumbria.
* HS 748 Srs2/228, VH-AHL, c/n 1606 ex-Royal Australian Air Force A10-606, at the Skylark Hotel, adjacent to London Southend Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2a/266, c/n 1714 ex-Emerald Airways G-OPFW, cockpit at the South Yorkshire Aircraft Museum, Doncaster.
* HS 748 Srs2a/334, c/n 1756 ex-Emerald Airways G-ORAL, nose section at the Avro Heritage Museum, Woodford, Greater Manchester.
* HS 748 Srs2a/372, c/n 1777 ex-Emerald Airways G-BVOV, fuselage underwater at the Capernwray Diving Centre near Carnforth.
* Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1543 ex-Emerald Airways G-BEJD, at Speke Aerodrome Heritage Group, Liverpool John Lennon Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2/225, c/n 1592 ex-Emerald Airways G-ATMI, nose and front fuselage at the RAF Millom, RAF Millom Museum, Cumbria.
* HS 748 Srs2/228, VH-AHL, c/n 1606 ex-Royal Australian Air Force A10-606, at the Skylark Hotel, adjacent to London Southend Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2a/266, c/n 1714 ex-Emerald Airways G-OPFW, cockpit at the South Yorkshire Aircraft Museum, Doncaster.
* HS 748 Srs2a/334, c/n 1756 ex-Emerald Airways G-ORAL, nose section at the Avro Heritage Museum, Woodford, Greater Manchester.
* HS 748 Srs2a/372, c/n 1777 ex-Emerald Airways G-BVOV, fuselage underwater at the Capernwray Diving Centre near Carnforth.
"Flight Testing to Win."
''Lulu.com,'' 2005. . * * * * *
BAe/HS 748 AEW
{{Authority control 1960s British airliners Avro aircraft, HS 748 Hawker Siddeley aircraft, HS 748 Aircraft first flown in 1960 Low-wing aircraft Twin-turboprop tractor aircraft
airliner
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ...
originally designed and initially produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Avro
AVRO, short for Algemene Vereniging Radio Omroep ("General Association of Radio Broadcasting"), was a Dutch public broadcasting association operating within the framework of the Nederlandse Publieke Omroep system. It was the first public broad ...
. It was the last aircraft to be developed by Avro prior to its absorption by Hawker Siddeley.
The HS 748 was developed during the late 1950s as a move to re-orientate the company towards the civil and export markets. Powered by the popular Rolls-Royce Dart turboprop engine, it was specifically designed as a modern feederliner to act as a replacement for the aging Douglas DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner
manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper version ...
s then in widespread service. Originally intended to seat a smaller number of passengers, market research indicated that a seating capacity of around 40 passengers would be optimal for the type. As a means to differentiate the new airliner from competitors, it was designed to possess a high level of performance, including its short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities and overall ruggedness. First flying on 24 June 1960, the series 1 HS 748 entered revenue service during the following year.
Once in service, the HS 748 found itself a niche within the short-haul market. Several different models would be developed of the regional airliner, typical improvements being the adoption of increasingly powerful Dart engines and a higher gross weight. Perhaps the most distinct variant was the HS 780 Andover, a dedicated military transport model developed for the Royal Air Force (RAF) that featured a large rear loading ramp and a squatting main landing gear to assist in loading bulky freight items.
By 1988, the year in which production of the type was terminated, 380 aircraft had been produced between Hawker Siddeley
Hawker Siddeley was a group of British manufacturing companies engaged in aircraft production. Hawker Siddeley combined the legacies of several British aircraft manufacturers, emerging through a series of mergers and acquisitions as one of onl ...
(the owning company of Avro) and Indian aviation company Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). During the 1990s, a larger, stretched development of the HS 748, the BAe ATP
The British Aerospace ATP (Advanced Turbo-Prop) is an airliner designed and produced by British Aerospace. It was an evolution of the Hawker Siddeley HS 748, a fairly successful feederliner of the 1960s.
The ATP was developed during the 1980 ...
, was developed and had attempted to compete with market leaders such as the de Havilland Canada Dash 8 and ATR 42
The ATR 42 is a regional airliner produced by Franco-Italian manufacturer ATR, with final assembly in Toulouse, France.
On 4 November 1981, the aircraft was launched with ATR, as a joint venture between French Aérospatiale (now Airbus) and ...
, but saw only limited sales prior to production being terminated.
Development
Background
Following the release of the1957 Defence White Paper
The 1957 White Paper on Defence (Cmnd. 124) was a British white paper issued in March 1957 setting forth the perceived future of the British military. It had profound effects on all aspects of the defence industry but probably the most affected wa ...
, in which then- Minister of Defence Duncan Sandys announced that the termination of almost all manned military aircraft development, aircraft manufacturer Avro decided that it should place a greater emphasis upon the civilian market. Ten years prior, it had launched a civilian airliner, the Avro Tudor
The Avro Type 688 Tudor was a British piston-engined airliner based on Avro's four-engine Lincoln bomber, itself a descendant of the famous Lancaster heavy bomber, and was Britain's first pressurised airliner. Customers saw the aircraft as ...
series, but this had encountered few sales; thus, during 1958, it was decided to commence work upon a clean-sheet design, which would eventually become the HS 748. On 9 January 1959, the existence of the project, then referred to as the ''Avro 748'', was announced to the public.
By this point, the four-engined Vickers Viscount had already secured the larger end of the short-haul market, therefore Avro decided that it would design a smaller regional airliner, powered by a pair of Rolls-Royce Dart turboprop engines. It was envisioned that this aircraft would be a suitable replacement for the many DC-3 Dakotas that were by then reaching the end of their economic lifespan. According to aviation periodical Flight International, a major goal for the design team was to produce an aircraft that would be capable of operating from any airfield that the DC-3 could be.
Early intentions for the airliner was of a 20–30 seat aircraft, adopting a somewhat similar configuration to the future rival Fokker F27 Friendship; however, following discussions with several potential customers, the company opted for a low-wing 40-seat configuration. It was this latter arrangement that was chosen for the 748 project. Another important focus for the prospective airliner was compliance with both British and American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
standards of airworthiness; accordingly, it would be one of the first medium-sized aircraft to incorporate fail-safe design principles for its structure in place of the then-common safe-life principles being practiced. The airframe effectively lacked any imposed lifespan; during development, it was successfully tested using a water tank for up to the equivalent of 100,000 flight hours.
Avro was not the only company to see the potential for a DC-3 replacement and, by this point, work on the 748's direct competitor, the Dutch-built F27 Friendship, was well advanced. To differentiate itself from the competition, Avro decided to focus its efforts upon achieving a more rugged design that offered superior short takeoff and landing (STOL) performance, which enabled the prospective airliner to be operated from smaller and more austere airports, including those without modern runways. This STOL capability was accomplished via several features, including the adoption of a long, high lift wing, which was fitted with a unique single slot flap with a hinged flap tab at the trailing edge. This wing was mounted low on the fuselage with dihedral from the root, allowing for good overall ground clearance and the easy mounting of strong landing gear. Operationally, pilots were provided with a choice of three takeoff flap settings to select the level of STOL performance required.
Another supportive feature of the 748 was a design decision to adopt straightforward systems and use proven components where realistically possible. For operator convenience, the engines were provided with an internal ignition system; various other systems and structures throughout the airliner were designed to be easy to inspect and to perform repairs upon, even when at unprepared airstrips with limited equipment available. Likely as a consequence of these favourable qualities, the 748 quickly attracted the attention of a variety of airlines, particularly those that typically operated in remote areas, which has been attributed to its ability to operate from short rough fields without any ground service equipment while being capable of hauling payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of ...
s in excess of 10,000 lb.
Into flight

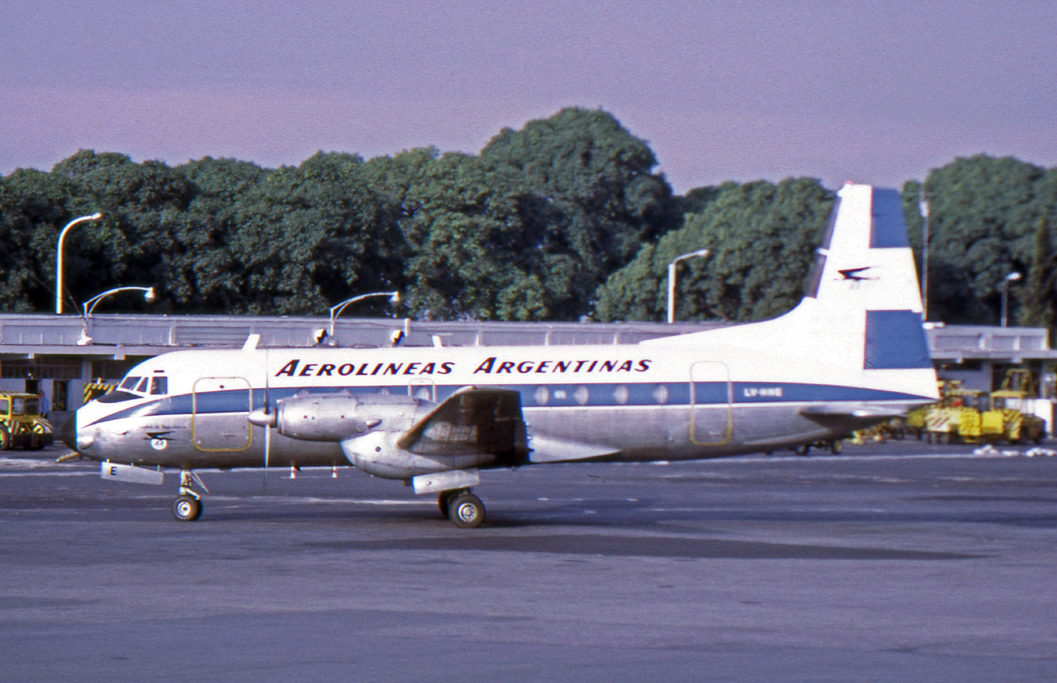 On 24 June 1960, the first Avro 748 made its maiden flight from the company's
On 24 June 1960, the first Avro 748 made its maiden flight from the company's Woodford, Cheshire
Woodford is a suburban village in the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport, Greater Manchester, England, south of Stockport, north-west of Macclesfield and south-east of Manchester. Woodford is the most southerly point of Greater Manchester and ...
aircraft factory."Avro 748 & Avro 748MF Andover."''BAE Systems'', Retrieved: 26 June 2019. Flight testing of the two prototypes quickly validated the type's short-field performance. Eighteen ''Avro 748 Series 1'' aircraft were produced; during April 1962, the first production aircraft were delivered to launch customer
Skyways Coach-Air Limited
Skyways Coach-Air Limited was the world's first low-cost airline.
Skyways launched the first commercial coach-air operation in late-September 1955, involving a coach trip from Central London to Lympne, a cross-Channel Lympne—Beauvais air secto ...
. However, the majority of the series 1 were export sales to operator Aerolíneas Argentinas. During the early 1960s, Avro's individual identity within the Hawker Siddeley
Hawker Siddeley was a group of British manufacturing companies engaged in aircraft production. Hawker Siddeley combined the legacies of several British aircraft manufacturers, emerging through a series of mergers and acquisitions as one of onl ...
Group was expunged, after which the airliner was marketed by the parent company as the ''HS 748''.
After the initial batch of series 1 aircraft was completed, production transitioned to the improved series 2. The series 2 was largely similar to its predecessor, principally benefiting from the adoption of more powerful ''Dart RDa 7 Mk 531'' engines and an increased gross weight. According to aviation periodical Flight International, during 1960, the basic price for a new Avro 748 Series 1 was £176,000, while that of the corresponding Avro 748 Series 2 was reportedly £196,000."Avro 748."''Flight International'', 18 November 1960. p. 783. During 1967, the series 2A was introduced, which was the same basic aircraft powered by ''Mk. 532'' engines along with a further increase in gross weight. From 1971 onwards, several new options were made available to customers, including a large freight door in the rear cabin and a strengthened cabin floor. During 1979, the Series 2B was introduced, which saw a 4-foot increase in wingspan, the adoption of ''Mk 536-2'' engines, along with a modernised passenger cabin, and various improvements to the fuel, water methanol injection system, and engine fire protection systems. During 1976, Eric Johnson, sales engineering manager of Hawker Siddeley Manchester, stated that the company was studying options for equipping a model of the HS 748 with turbofan engines, and that a preferred powerplant at that point was the Rolls-Royce/SNECMA M45H, as used on the VFW-Fokker 614 jetliner. Other changes would likely have been incorporated, including the addition of lift dumpers and adaptive brakes for better landing performance, while electrical, hydraulic and air conditioning systems would be redesigned; externally, a dihedral would have to be introduced to keep the tailplane clear of the jet exhaust. It was envisioned that the reengined aircraft could offers larger seating arrangements of up to 64 seats."HS.748 looks to the 1980s."
''Flight International'', 22 May 1976. p. 1342. In addition to the British production line, manufacture of the 748 was also performed overseas. Early on, India had placed orders for the type. Both the 748 Series 1 and Series 2 were licence-produced in Indian manufacturer Hindustan Aeronautics (HAL), aircraft produced by the company were designated ''HAL-748''. On 1 November 1961, the first Indian-assembled HAL-748 made its first flight. By the end of production, HAL had completed 89 Indian-built aircraft, 72 of which were for the
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
and 17 were delivered to national flag carrier Indian Airlines.
While the HS 748 was originally intended to be marketed principally towards the civilian market, numerous examples were sold to military customers around the world. Hawker Siddeley used the design as the basis for the HS 780 Andover, a military transport aircraft developed and produced for the Royal Air Force. In terms of its design, the HS 780 was broadly similar to the 748, differing primarily by its redesigned rear fuselage and empennage, which incorporated a large rear loading ramp and a squatting main landing gear to better facilitate the loading of bulky freight items.
During 1988, production of the HS 748 was terminated, while the last British-assembled aircraft made its first flight on 1 December of that year. According to BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
, a successor company to Hawker Siddeley, during the type's production life, a total of 381 aircraft had been produced, when including both the Andover and HAL-built examples.
Operational history
Within its first decade of its availability, sales of the HS 748 had reportedly been relatively brisk; by 1976, the sale of 312 aircraft had been recorded, of which 259 had been to export customers. Within ten years of its launch, India had emerged as the largest single market for the airliner, Indian Airlines being the largest HS 748 operator with a fleet of 26 aircraft. It had been popular with numerous commercial operators, across theCaribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
and Latin America alone, 63 HS 748s were in operation with 11 separate operators.
The HS 748 had been able to achieve some triumphs over competing rivals, including the F27 Friendship. Philippine Airlines had been the F27's largest operator prior to its decision to replace both it and its remaining DC-3s with the HS 748, which represented a significant sales coup for the latter. Other major civil operators included Aerolíneas Argentinas, VARIG, Thai Airways, LAN-Chile
LATAM Airlines Chile (formerly LAN Airlines and LAN-Chile) is an airline based in Santiago, Chile, one of the founders of LATAM Airlines Group, Latin America's largest airline holding company. The main hub is Arturo Merino Benítez International ...
, and Bouraq Airlines
Bouraq Indonesia Airlines, often shortened to Bouraq Airlines or just Bouraq, was an airline headquartered in Jakarta, Indonesia, which operated mostly domestic passenger flights out of its bases at Soekarno-Hatta International Airport and Sul ...
. Several of these operators would utilise its STOL capabilities in their services; according to Flight International, over one-third of all scheduled operations were reportedly involved operations from rough airstrips with minimalist facilities."The 748 is Ten."''Flight International'', 2 July 1970. pp. 12-13. Another key market for the HS 748 was the executive role; the type was repeatedly procured to serve as the designated aircraft for various heads of state, including of Argentina, Brazil, Chile, India, Venezuela, Zambia, Thailand and the United Kingdom. The HS 748 was one of the last planes to be flown by noted
aviator
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its Aircraft flight control system, directional flight controls. Some other aircrew, aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are al ...
and business magnate
A business magnate, also known as a tycoon, is a person who has achieved immense wealth through the ownership of multiple lines of enterprise. The term characteristically refers to a powerful entrepreneur or investor who controls, through perso ...
Howard Hughes. During 1972, Hughes performed several flights of the type, each time accompanied by Hawker Siddeley test pilot Tony Blackman, flying from the company's airport in Hatfield.
The Australian military purchased several aircraft; specifically, the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(RAAF) procured a fleet of ten HS 748s, the first of which arriving in 1968, for navigation training and transporting VIPs. The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) operated a pair of HS 748s starting in 1973 as a navigational trainer. Following Cyclone Tracy, relief aid was delivered across Darwin, Northern Territory
Darwin ( ; Larrakia: ) is the capital city of the Northern Territory, Australia. With an estimated population of 147,255 as of 2019, the city contains the majority of the residents of the sparsely populated Northern Territory.
It is the smalle ...
using the type; after being fitted with various electronic countermeasure
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting info ...
s (ECM) during the late 1970s, HS 748s were also used for electronic warfare training."Hawker Siddeley HS748."'' Royal Australian Navy'', Retrieved: 26 June 2019. In a typical passenger configuration, the HS 748 can accommodate around 40–48 economy class seats in a four abreast layout; however, the majority of later-serving passenger HS 748s were typically operated as quick change ''combis''. These aircraft are fitted with a movable bulkhead that divides the main cabin, housing between 4 and 40 seats in the rear section while cargo is placed the forward section. The 748 has also been widely used as a pure freighter, having a typical max payload of about 12,000 lbs. Several carriers have used the 748 as a bulk fuel hauler, in which capacity it is normally with either seven or eight fixed tanks in the cabin, possessing a total capacity of about . The
ICAO
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international a ...
designator as used in flight plan
Flight plans are documents filed by a pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider (e.g. the FAA in the United States) prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is ...
s is A748.
Variants
* 748 Series 1 – The original Avro 748 twin-engined short / medium-range airliner, powered by two Rolls-Royce Dart RDa 7 Mk 514 turboprop engines. 24 built. * – The Series 2 entered production in 1961 with a higher take-off weight and Mk 531 engines. 111 built. * – Introduced in 1967, with a further increase in take-off weight and Mk 532 or 534 engines. 157 built, making the 748 one of the more successful British airliners and the 2A the most popular variant. * 748 Series 2B – The main production model after Hawker-Siddeley was absorbed by British Aerospace, the 2B featured a 4-foot increase in wingspan, increased gross weight, Mk 536 engines, a modernized cabin, and systems improvements. 28 built. * 748 Series 5 – Version with overwing-mounted Rolls-Royce M-45H turbofans and a fuselage extension for 64 passengers. Not built. * Super 748 – Basically the same as the 2B but fitted with engine hush kits. 8 built. *Hawker Siddeley HS780 Andover
The Hawker Siddeley HS 780 Andover is a twin-engined turboprop military transport aircraft produced by Hawker Siddeley for the Royal Air Force (RAF), developed from the Avro-designed HS 748 airliner. The Andover was named after the Avro Andove ...
– Modified version of the 748 design for the Royal Air Force. Fitted with kneeling undercarriage, raised tail unit and rear loading ramp.
* Coastguarder – A maritime patrol version.
* 748 Andover – Military passenger transport versions of the 748.
* 748AEW – Airborne early warning variant to AST.400. Not built.
* 748AEW (FASS) – Version of 748AEW powered by four Avco Lycoming T53-21A turboprops. Not built.
* 748B – 36-seat variant. Not built.
* 748COD – Version for U.S. Navy for a deck-landing fleet support aircraft. Not built.
* 748CF – Civil version of Type 780. Not built.
*748E – Variant of Series 2 with fuselage extended to 76 feet to carry 52-60 passengers and wing from Type 780. Not built.
*748 Super E – Version of 748E with lower AGW and greater wingspan. Not built.
*748EW – AEW aircraft for Sweden with twin rudders and fins. Not built.
*748 Executive – Executive/VIP version of Series 2. Not built.
*748F – Freighter version of Series 2 with large freight door and strengthened floor. Not built, marketed as 748 Series 2 LFD.
*748J – Turbojet version with rear-mounted engines and a T-tail. Not built.
*748L – Large diameter (10'6") fuselage version of Series 2. Not built.
*748ML – Maritime reconnaissance version. Not built.
*748SFV – Version of Series 2A for US STOL requirement to carry 40 passengers. Not built.
*748STOL – STOL variant for U.S. airlines with four Avro Lycoming T53-21A engines. Not built.
*748X – Executive variant of Series 2 with increased fuel capacity. Not built.
*748-502 – Turbojet version with 2 Avco Lycoming ALF502 engines. Not built, developed into Series 5.
*757 – Version of Series 1 with strengthened floor and revised avionics for the Indian Air Force, not built. Also known as 748M.
*758 – High-wing version of 748. Not built. Also known as 748R.
* HAL 748 – Licence production by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited at Bangalore India. Indian aircraft were later modified for a variety of roles including a trials aircraft for an Airborne Early Warning version fitted with a large radome, known as the Airborne Surveillance Platform (ASP). 89 built.
* HAL 748 Series 2M – Production for the Indian Air Force (the last 20 built) were Series 2M aircraft with a large freight door.
Accidents and incidents
* On 10 July 1965, an Avro 748-101 Series 1 G-ARMV ofSkyways Coach-Air
Skyways Coach-Air Limited was the world's first low-cost airline.
Skyways launched the first commercial coach-air operation in late-September 1955, involving a coach trip from Central London to Lympne, a cross-Channel Lympne—Beauvais air secto ...
was written off in a landing accident at Lympne Airport. The 51 people on board survived. This was the first accident that resulted in a write-off on an Avro 748 / HS748.
* On 15 August 1967, two accidents involving HS-748-222 Series 2 aircraft of Channel Airways Limited, occurred roughly 90 minutes apart at Portsmouth Airport. In the first incident, G-ATEK, operating a scheduled service from Southend to Paris, via Portsmouth, landed in rainy conditions and was unable to stop in the available distance on the grass runway. The aircraft slid sideways, left the runway and stopped on an embankment. Some 90 minutes later, aircraft G-ATEH, operating a scheduled service from Jersey, via Guernsey to Portsmouth, landed and slid on the runway, crashed through a perimeter fence and came to rest on the main Eastern Road. There were no injuries in either accident, but both aircraft sustained serious damage. An AIB investigation reported that "both accidents were caused by inadequate braking which had resulted from the extremely low coefficient of friction provided by the very wet grass surface over the hard, dry and almost impermeable sub-soil".
* On 4 February 1970, Aerolíneas Argentinas Flight 707
Aerolíneas Argentinas Flight 707 was an international Asunción– Formosa–Corrientes– Rosario–Buenos Aires passenger service operated with an Avro 748-105 Srs. 1, registration LV-HGW, named "Ciudad de Bahía Blanca", that crashed on 4 Fe ...
, an Avro 748–105, crashed into the ground after the pilots lost control of the aircraft. The aircraft crashed at Loma Alta, Argentina and killed all 37 on board.
* On 9 December 1971, Indian Airlines, an HS 748, near Chinnamanur was descending into Madurai when it flew into high terrain about 50 mi (80 km) from the airport, killing the four crew members and 17 passengers. There were ten survivors among the passengers. The accident occurred in reduced visibility during daylight hours.
* 20 January 1976 – a TAME
Tame may refer to:
*Taming, the act of training wild animals
*River Tame, Greater Manchester
*River Tame, West Midlands and the Tame Valley
*Tame, Arauca, a Colombian town and municipality
* "Tame" (song), a song by the Pixies from their 1989 alb ...
HS 748-246 Series 2A registration HC-AUE crashed while flying over mountainous terrain at 10,000 feet. The aircraft struck trees with its right wing, lost control and crashed into the side of the mountain. The plane was en route from Loja to Simón Bolívar International Airport in Guayaquil, Ecuador. Six crewmembers and 28 passengers were killed; 8 passengers survived.
* 3 March 1978 – Línea Aeropostal Venezolana Hawker Siddeley HS 748 crashed on departure from Simón Bolívar International Airport, Venezuela, all 46 on board are killed.
* 7 September 1978 – Air Ceylon HS 748 4R-ACJ destroyed by fire while parked at Colombo-Ratmalana, resulting from detonation of bomb placed on board by terrorists. There were no fatalities.
* 31 July 1979 at Sumburgh Airport in the Shetland Islands, Scotland; Dan-Air Flight 0034
Dan-Air Flight 0034 was a fatal accident involving a Hawker Siddeley HS 748 series 1 turboprop aircraft operated by Dan-Air Services Limited on an oil industry charter flight from Sumburgh Airport, Shetland Islands, to Aberdeen Airport.
The ...
, an HS 748 series 1 (registration G-BEKF) operating an oil industry support flight crashed. The aircraft failed to become airborne and crashed into the sea. The accident was due to the elevator gust-lock having become re-engaged, preventing the aircraft from rotating into a flying attitude. The aircraft was destroyed and 17 persons died from drowning.
* 4 August 1979 - The Indian Airlines HAL-748 (VT-DXJ) was operating a scheduled flight from Pune to Bombay, India. The aircraft crashed in the Kiroli Hills near Panvel about 11 km east of Bombay. The aircraft was destroyed. All 45 persons on board were killed.
* 22 August 1979 – An aircraft mechanic (a former non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
of the Colombian Air Force), stole a military HS 748 ( FAC-1101) from a military hangar at the Eldorado International Airport
El Dorado International Airport is an international airport serving Bogotá, Colombia and its surrounding areas. The airport is located mostly in the Fontibón district of Bogotá, although it partially extends into the Engativá district ...
in Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the larges ...
, Colombia. According to the news, this person stole the aircraft with the intention of crashing it against his parents' house. After some minutes in the air, it ran out of fuel and crashed, killing the impromptu pilot and three people on the ground.
* 26 June 1981 – Dan-Air Flight 240
Dan-Air Flight 240 was a fatal accident involving a Hawker Siddeley HS 748 series 2A turboprop aircraft operated by Dan-Air, Dan Air Services Limited on the first stage of a night mail flight from London Gatwick Airport to East Midlands Airport. ...
, an HS 748 2A mail flight from Gatwick Airport to East Midlands Airport crashed at Nailstone killing the 3 crew members. While descending, the right-hand rear door detached, struck the horizontal tail plane and became lodged on its leading edge. Control was lost, and the aircraft entered a steep dive. During the dive, the wings and tail plane failed due to overstressing.
* 19 August 1981 – Indian Airlines Flight 557, an HAL 748 (VT-DXF) overshot the runway at Mangalore-Bajpe Airport in wet weather. The aircraft came to a halt just beyond the runway edge. There were no fatalities but the damaged aircraft was written off. One of the passengers on board was Veerappa Moily
Marpadi Veerappa Moily (born 12 January 1940) is an Indian politician belonging to the Indian National Congress from the state of Karnataka.
Moily was the former Chief Minister (and the first ethnic Tuluva CM) of the Indian state of Karnataka ...
ex-Cabinet Minister for Law, Justice and Company Affairs in the Government of India.
* 11 October 1983 – Air Illinois Flight 710
Air Illinois Flight 710 was a scheduled passenger flight from Chicago to Carbondale, Illinois. On the night of October 11, 1983, the Hawker Siddeley HS 748 operating the flight crashed near Pinckneyville, Illinois due to the flightcrew's mismanag ...
crashed at night in a thunderstorm between Pinckneyville and Tamaroa, IL. The flight originated at Chicago's Meigs Field and had stopped at Springfield, IL. The left generator had failed after takeoff and the first officer had mistakenly isolated the right generator. Attempts to restore the right generator were unsuccessful. The captain chose to continue to the destination rather than return to the nearby airport. The cloud base was at 2000 feet MSL, but ATC could not provide an IFR below 3,000 feet. Before the crash, the crew indicated a total loss of electrical power. The left generator drive shaft had sheared. All ten passengers and crew were killed.
* 27 June 1987 – Philippine Airlines Flight 206
Philippine Airlines Flight 206 (PR206) was the route designator of a domestic flight from the Manila Domestic Airport, Metro Manila, Philippines to Loakan Airport, Baguio. On June 26, 1987, the Hawker Siddeley HS 748 crashed onto a mountain en rou ...
crashed onto a mountain after poor visibility hampered the pilot's attempt to land at Loakan Airport in Baguio, Philippines. All 50 passengers and crew were killed.
*15 September 1988 - A Bradley Air Services HS-748 ( C-GFFA ) cargo plane crashed on approach to Ottawa International Airport, ON (YOW), Canada, killing both pilots. It had unloaded all cargo at Montreal-Dorval International Airport, QC (YUL) before departing at 09:58 for Ottawa on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan. At about 10:19, while in level cruise flight at 3000 feet at approximately 200 knots indicated airspeed (KIAS), the flight data recorder (FDR) recorded a full-up deflection of the left aileron and a full-down deflection of the right aileron, causing a sharp roll to the left. The right aileron was fully-deflected for three seconds before, over the next seven seconds, the deflection gradually decreased by about five degrees. Over the same 10-second period, the left aileron was nearly fully deflected for the first eight seconds, then decreased by about five degrees during the next two seconds. By this time, the aircraft had rolled through approximately 460 degrees and the nose had dropped 20 to 30 degrees below the horizon. The ailerons returned to a neutral position and remained there for the flight's last three seconds. The bank angle remained at approximately 90 degrees of left bank with a maximum vertical g of 4.7 recorded. The aircraft struck the ground at an airspeed of approximately 290 KIAS after a heading change of about 75 degrees left of the cruise heading. At impact, the bank angle was nearly 90 degrees left and the pitch angle was 41 degrees down. The time from initial aileron deflection to ground impact was approximately 18 seconds.
* 12 January 1989 - Bradley Air Services HS-748 (C-GDOV) The aircraft climbed to 1300 feet, turned right and descended into the ground after takeoff from Dayton International Airport Runway 24R. The aircraft became airborne again and continued 0,75 mile where it collided with trees. During several training flights and two check flights, the co-pilot demonstrated difficulty with instrument flight due to disorientation, narrow focus of attention, or lack of instrument scan especially during high workload.
* 10 November 1993 – Nothland Air Manitoba. Hawker Siddeley HS-748-234 Srs. 2A. Registration C-GQTH. Departure airport Sandy Lake Airport, Ontario (ZSJ/CZSJ), Canada "about 600 km northeast of Winnipeg.". The aircraft took off from runway 29 at Sandy Lake at approximately 1805 and entered a right turn. Witnesses indicate that the aircraft appeared to fly at a lower than normal height throughout the turn. After turning through approximately 120 degrees, the aircraft descended into 100-foot trees and crashed. The aircraft struck the ground about 1 nm northwest of the airport. Contributing factor was the loss of AC power to some of the flight instruments the reason for which could not be determined. All 3 crew members and 4 passengers perished.
* 28 April 1995 – Sri Lanka Air Force Avro 748 CR835
Sri Lanka Air Force Avro 748 CR835 was shot down on 28 April 1995 by a SA-7 missile fired by the LTTE. The plane, an Avro 748-334 Srs. 2A airliner, was en route to Ratmalana Airport and was shot down soon after take-off from SLAF Palaly. All 51 ...
an HS 748 serial CR835 (4R-HVB) was hit by an SA-7
The 9K32 Strela-2 (russian: Cтрела, "arrow"; NATO reporting name SA-7 Grail) is a light-weight, shoulder-fired, surface-to-air missile (or MANPADS) system. It is designed to target aircraft at low altitudes with passive infrared homing gui ...
missile fired by the LTTE
The Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE; ta, தமிழீழ விடுதலைப் புலிகள், translit=Tamiḻīḻa viṭutalaip pulikaḷ, si, දෙමළ ඊළාම් විමුක්ති කොටි, t ...
immediately after takeoff from Palaly. All 45 occupants were killed. Crew managed to return the aircraft for landing but the starboard wing collapsed on short finals 295 meters from threshold due to an extensive fire in No-2 engine.
* 11 January 1999 – ASTE HAL-748 ASP/H-2175, an HAL 748 crashed into the ground after the pilots lost control of the aircraft. The aircraft crashed at Attur, Tamil Nadu, India, killing the 2 crew and 6 passengers.
* 5 September 1999 – Necon Air Flight 128 from Pokhara to Kathmandu, a BAe 748-501 Super 2B (9N-AEG) collided with a communication tower of Nepal Telecommunication Corporation and crashed in a wooded area 25 km west of Kathmandu, while approaching Tribhuvan International Airport. All 10 passengers and 5 crew were killed.
* 1 June 2002 – Former South African cricket captain Hansie Cronje's scheduled flight home from Bloemfontein to George had been grounded, so he hitched a ride as the only passenger on a cargo flight in an HS 748. Near George airport, the pilots lost visibility in cloud, and were unable to land, partly due to unserviceable navigational equipment. While circling, the plane crashed into the Outeniqua mountains northeast of the airport. Cronje, aged 32, and the two pilots died. South Africa's High Court reached the conclusion that "the death of the deceased Wessel Johannes (Hansie) Cronje was brought about by an act or omission prima facie
''Prima facie'' (; ) is a Latin expression meaning ''at first sight'' or ''based on first impression''. The literal translation would be 'at first face' or 'at first appearance', from the feminine forms of ''primus'' ('first') and ''facies'' (' ...
amounting to an offence on the part of pilots." However, with Cronje's involvement in match-fixing, theories that Cronje was murdered on the orders of a cricket betting syndicate flourished after his death.
* 12 June 2012 – A Wasaya Airways Hawker Siddeley 748 caught fire during ground operations at Sandy Lake First Nation in Northwestern Ontario. No injuries were reported. The aircraft burned completely; only the left wing and nacelle survived.
* 17 February 2014 – an HS 748-371 Srs 2B 2014 748 Air Services HS 748 crash, crash landed at Rubkona airport in South Sudan killing one crew member and injuring the other three. The cargo plane was carrying humanitarian Aid to South Sudan.
* 14 November 2014 – A BAe HS-748 crashed on approach to Panyagor airstrip in South Sudan, killing two crew members and seriously injuring a third crew member. The cargo plane was on a charter flight for the Lutheran World Federation and carrying relief supplies from Juba, South Sudan.
Operators
Civil operators
As of July 2018 a total of 12 HS 748 aircraft (all variants) remained in airline service. As of September 2018 Transport Canada (TC) list 13 HS 748 in Canada with a current Certificate of Registration and 1 with a cancelled certificate. Current operators are: * Air Creebec (3) * Air Inuit (1 as per reference above, 4 as per TC) * Air North (1 as per reference above, 2 as per Air North, 4 as per TC) * Avro Express (1) * Bismillah Airlines (2) * Planes For Africa (2) * Safe Air Company (1) * Wasaya Airways (2 as per reference above, 3 as per TC)Former civil operators
 ;
* East Horizon Airlines
;
* Air Botswana
;
* LIAT Airlines
;
* Aerolíneas Argentinas
;
* Austrian Airlines (2)
;
* Bahamasair
;
* Bop Air (Operated one Aircraft)
;
* Varig (11) [one Avro 748 Series 2 prototype and 10 production aircraft]
British Virgin Islands
* Air BVI
;
* Air Gaspé
* Air Manitoba
* Austin Airways
* Calm Air
* First Air (9)
* Midwest Airlines
* Quebecair
* Transair (Canada)
* West Wind Aviation
;
* TACV
;
* LAN Chile
;
* Avianca
* Satena
* Intercontinental de Aviacion
;
* Fiji Airways
;
* Deutsche Flugsicherung
* Lufthansa CityLine, DLT Deutsche Luftverkehrsgesellschaft
;
* Guyana Airways (now defunct)
;
* Vayudoot (now defunct)
* Indian Airlines (now Air India)
* Hindustan Aeronautics Limited BH-572 Used by HAL Chairman
;
* Bouraq Indonesia Airlines (now defunct)
* Bali Air (now defunct) (4)
* Airfast Indonesia
;
* Ryan Air (2) 1986–1989 Inaugurating the Dublin-London (Luton) Service
;
* 748 Air Services
;
* Air Madagascar
;
* Air Malawi
;
* Air Marshall Islands
;
* Aeronaves de México (now Aeroméxico)
* Aerocaribe (1) (Bought From Atlantic Airlines de Honduras)
;
* Nepal Airlines
* Necon Air
;
* Mount Cook Airline
;
* Philippine Airlines
;
* SATA Air Açores
;
* Polynesian Airlines (2)
;
* Air Cape (South Africa)
* AirQuarius (Operated 6 aircraft)
* Executive Aerospace (Operated 13 aircraft)
* Intensive Air
* Stars Away Aviation
* South African Airways (Operated 5 aircraft 1970–1983)
;
* Aero Lanka (1)
* Air Ceylon (2)
* Lionair (Sri Lanka), Lionair (1)
;
* Bangkok Airways
* Thai Airways Company
;
* Trinidad and Tobago Air Service (TTAS)
;
* British Airways
* Dan Air
* Emerald Airways
* Janes Aviation (2)
*
;
* East Horizon Airlines
;
* Air Botswana
;
* LIAT Airlines
;
* Aerolíneas Argentinas
;
* Austrian Airlines (2)
;
* Bahamasair
;
* Bop Air (Operated one Aircraft)
;
* Varig (11) [one Avro 748 Series 2 prototype and 10 production aircraft]
British Virgin Islands
* Air BVI
;
* Air Gaspé
* Air Manitoba
* Austin Airways
* Calm Air
* First Air (9)
* Midwest Airlines
* Quebecair
* Transair (Canada)
* West Wind Aviation
;
* TACV
;
* LAN Chile
;
* Avianca
* Satena
* Intercontinental de Aviacion
;
* Fiji Airways
;
* Deutsche Flugsicherung
* Lufthansa CityLine, DLT Deutsche Luftverkehrsgesellschaft
;
* Guyana Airways (now defunct)
;
* Vayudoot (now defunct)
* Indian Airlines (now Air India)
* Hindustan Aeronautics Limited BH-572 Used by HAL Chairman
;
* Bouraq Indonesia Airlines (now defunct)
* Bali Air (now defunct) (4)
* Airfast Indonesia
;
* Ryan Air (2) 1986–1989 Inaugurating the Dublin-London (Luton) Service
;
* 748 Air Services
;
* Air Madagascar
;
* Air Malawi
;
* Air Marshall Islands
;
* Aeronaves de México (now Aeroméxico)
* Aerocaribe (1) (Bought From Atlantic Airlines de Honduras)
;
* Nepal Airlines
* Necon Air
;
* Mount Cook Airline
;
* Philippine Airlines
;
* SATA Air Açores
;
* Polynesian Airlines (2)
;
* Air Cape (South Africa)
* AirQuarius (Operated 6 aircraft)
* Executive Aerospace (Operated 13 aircraft)
* Intensive Air
* Stars Away Aviation
* South African Airways (Operated 5 aircraft 1970–1983)
;
* Aero Lanka (1)
* Air Ceylon (2)
* Lionair (Sri Lanka), Lionair (1)
;
* Bangkok Airways
* Thai Airways Company
;
* Trinidad and Tobago Air Service (TTAS)
;
* British Airways
* Dan Air
* Emerald Airways
* Janes Aviation (2)
* Skyways Coach-Air Limited
Skyways Coach-Air Limited was the world's first low-cost airline.
Skyways launched the first commercial coach-air operation in late-September 1955, involving a coach trip from Central London to Lympne, a cross-Channel Lympne—Beauvais air secto ...
(5)
;
* Air Illinois
* Air Virginia (AVAir)
* Cascade Airways
;
* Aeropostal
;
* Zambia Airways
Current military operators
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
: 57 remain in service as of December 2018.
;
* Nepalese Army Air Service – One in service as of December 2017.
;
* Republic of Korea Air Force: First used in April 1974.
;
* Royal Thai Air Force
Former military operators

Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
** School of Air Navigation RAAF/No. 32 Squadron RAAF – aircraft operated in navigation trainer configuration between 1968 and 2004
** No. 34 Squadron RAAF – aircraft operated in VIP configuration between 1967 and 1996
* Royal Australian Navy
** Fleet Air Arm (RAN) – operated between 1973 and 2000
*** No. 723 Squadron RAN
*** No. 851 Squadron RAN
;
* Belgian Air Force (Three operated from 1976, sold in 2001–2002 to Benin and replaced by four Embraer ERJ 145 family, Embraer Regional Jets)
** 21 Squadron (Belgium), 21 Squadron
;
* Brazilian Air Force
** Twelve aircraft operated between 1962 and 2005 as C-91.
;
* Royal Brunei Air Force
; ()
* Military of Burkina Faso - one aircraft
;
* Cameroon Air Force
;
* Colombian Air Force
;
* Ecuadorian Air Force
;
* Military of Madagascar
;
* Sri Lanka Air Force
;
* Tanzania Air Force Command - one aircraft
;
* Royal Air Force
;
* Venezuelan Air Force
* Venezuelan Navy
;
* Zambian Air Force - one aircraft
Specifications (Super 748)
Preserved aircraft
Australia
 * HS 748 Srs2/228, c/n 1601 ex-
* HS 748 Srs2/228, c/n 1601 ex-Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
A10-601, at the RAAF Museum, Point Cook, Victoria.
* HS 748 Srs2/228, c/n 1604 ex-Royal Australian Air Force A10-604, cockpit section at the Australian Aviation Museum, Bankstown Airport, New South Wales.
* HS 748 Srs2/229, c/n 1607 ex-Royal Australian Air Force A10-607, tail section at No. 32 Squadron RAAF, No. 32 Squadron HQ, RAAF Base East Sale, Victoria, Australia, Victoria.
* HS 748 Srs2/268, c/n 1709 ex- Royal Australian Navy N15-709, at the Australian Aviation Museum, Bankstown Airport, New South Wales.
Brazil
* HS 748 Srs2a/204, c/n 1554 ex-Brazilian Air Force 2504, at Museu Aeroespacial, Rio de Janeiro.Ecuador
* HS 748 Srs2a/285, c/n 1738 ex-Ecuadorian Air Force FAE738, at Museo Aeronáutico de la FAE, Mariscal Sucre International Airport, Quito.South Africa
* BAe-748-400 Srs2b, c/n 1796 ex-AirQuarius Aviation ZS-OLE, fuselage at Chartwell, Gauteng.Sri Lanka
 * Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1587 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-831, at the Sri Lanka Air Force Museum, Ratmalana Airport, Colombo.
* HS 748 Srs2a/272, c/n 1691 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force SCM-3101, at Koggala Airport, SLAF Koggala, Galle.
* HS 748 Srs2a/301, c/n 1746 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-833, at Weerawila Airport, SLAF Weerawilla.
* Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1587 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-831, at the Sri Lanka Air Force Museum, Ratmalana Airport, Colombo.
* HS 748 Srs2a/272, c/n 1691 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force SCM-3101, at Koggala Airport, SLAF Koggala, Galle.
* HS 748 Srs2a/301, c/n 1746 ex-Sri Lanka Air Force CR-833, at Weerawila Airport, SLAF Weerawilla.
Thailand
 * HS 748 Srs2/243, c/n 1707 ex- Thai Airways HS-THH, at Jomtien Beach. Fuselage preserved where it crash landed in 1987. Painted in fictional camouflage.
* HS 748 Srs2a/243, c/n 1708 ex-Thai Airways HS-THI, at the Siam Country Club, Pattaya.
* HS 748 Srs2/243, c/n 1707 ex- Thai Airways HS-THH, at Jomtien Beach. Fuselage preserved where it crash landed in 1987. Painted in fictional camouflage.
* HS 748 Srs2a/243, c/n 1708 ex-Thai Airways HS-THI, at the Siam Country Club, Pattaya.
United Kingdom
 * Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1543 ex-Emerald Airways G-BEJD, at Speke Aerodrome Heritage Group, Liverpool John Lennon Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2/225, c/n 1592 ex-Emerald Airways G-ATMI, nose and front fuselage at the RAF Millom, RAF Millom Museum, Cumbria.
* HS 748 Srs2/228, VH-AHL, c/n 1606 ex-Royal Australian Air Force A10-606, at the Skylark Hotel, adjacent to London Southend Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2a/266, c/n 1714 ex-Emerald Airways G-OPFW, cockpit at the South Yorkshire Aircraft Museum, Doncaster.
* HS 748 Srs2a/334, c/n 1756 ex-Emerald Airways G-ORAL, nose section at the Avro Heritage Museum, Woodford, Greater Manchester.
* HS 748 Srs2a/372, c/n 1777 ex-Emerald Airways G-BVOV, fuselage underwater at the Capernwray Diving Centre near Carnforth.
* Avro 748 Srs 1, c/n 1543 ex-Emerald Airways G-BEJD, at Speke Aerodrome Heritage Group, Liverpool John Lennon Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2/225, c/n 1592 ex-Emerald Airways G-ATMI, nose and front fuselage at the RAF Millom, RAF Millom Museum, Cumbria.
* HS 748 Srs2/228, VH-AHL, c/n 1606 ex-Royal Australian Air Force A10-606, at the Skylark Hotel, adjacent to London Southend Airport.
* HS 748 Srs2a/266, c/n 1714 ex-Emerald Airways G-OPFW, cockpit at the South Yorkshire Aircraft Museum, Doncaster.
* HS 748 Srs2a/334, c/n 1756 ex-Emerald Airways G-ORAL, nose section at the Avro Heritage Museum, Woodford, Greater Manchester.
* HS 748 Srs2a/372, c/n 1777 ex-Emerald Airways G-BVOV, fuselage underwater at the Capernwray Diving Centre near Carnforth.
See also
References
Citations
Bibliography
* Blackman, Tony"Flight Testing to Win."
''Lulu.com,'' 2005. . * * * * *
External links
BAe/HS 748 AEW
{{Authority control 1960s British airliners Avro aircraft, HS 748 Hawker Siddeley aircraft, HS 748 Aircraft first flown in 1960 Low-wing aircraft Twin-turboprop tractor aircraft