Bristol Centaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Centaurus was the final development of the
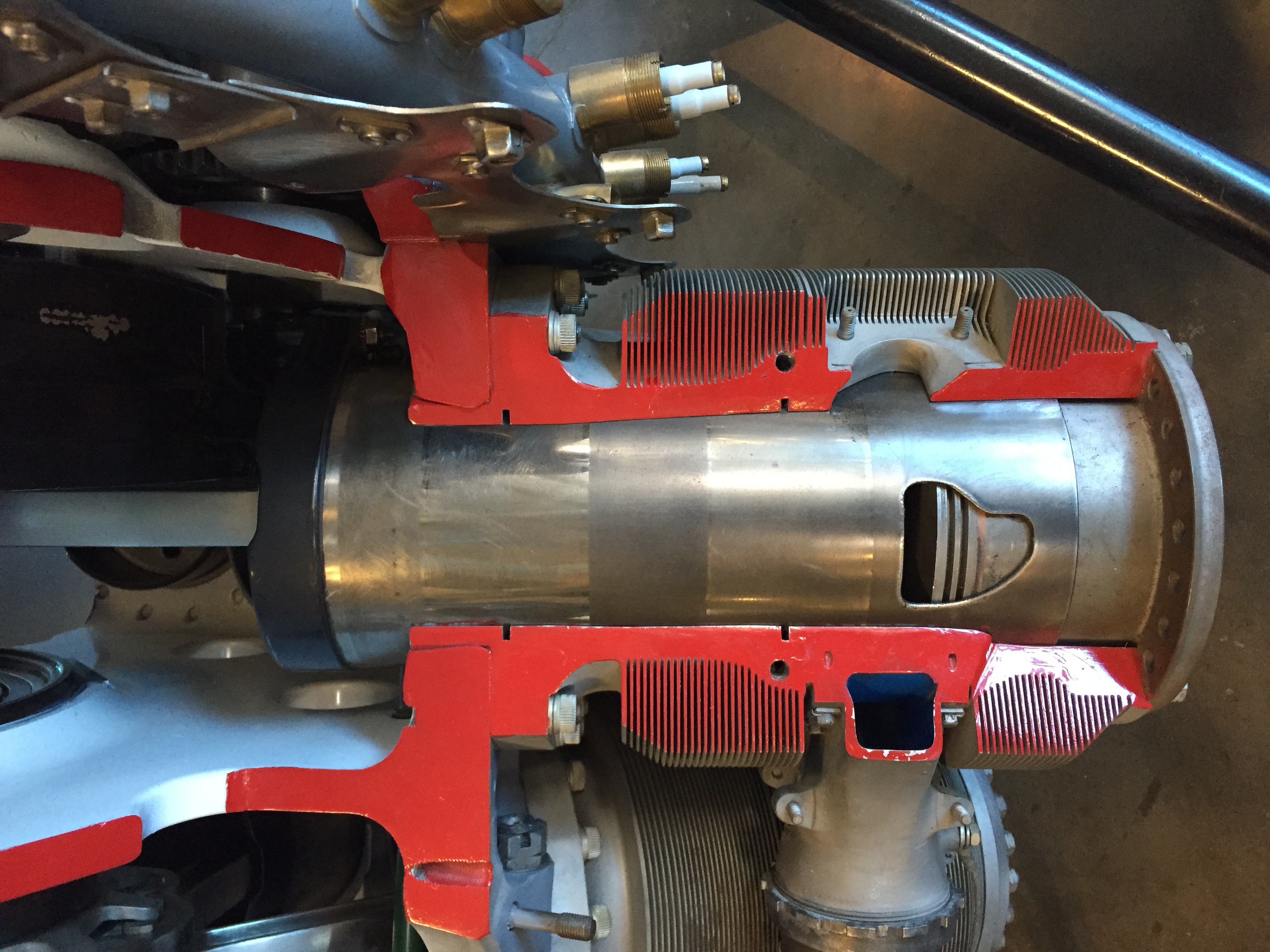 The Centaurus had a cylinder swept volume of , nearly as much as the American Wright R-3350 ''Duplex-Cyclone'' large radial, making the Centaurus one of the largest aircraft piston engines to enter production, while that of the Hercules was . The nearly 40 percent higher capacity was achieved by increasing the stroke from and by changing to two rows of nine cylinders instead of two rows of seven. The diameter of the Centaurus was only just over 6 percent greater than the Hercules in spite of its much greater swept volume.Bridgman (Jane's) 1998, p. 270.
The cylinder heads had an indentation like an inverted top hat, which was finned, but it was difficult to get air down into this hollow to adequately cool the head. During development, Bristol contacted ICI Metals Division, Birmingham, to enquire whether a copper-chromium alloy with higher thermal conductivity would have sufficient high temperature strength to be used for this purpose. With the same cylinder volume and using the new material, the horsepower per cylinder was raised from to .
Bristol maintained the Centaurus from type-testing in 1938, but production did not start until 1942, owing to the need to get the Hercules into production and improve the reliability of the entire engine line. Nor was there any real need for the larger engine at this early point in the war, when most military aircraft designs had a requirement for engines of about . The Hercules power of about was better suited to the existing airframes.
The Centaurus did not enter service until near the end of the war, first appearing on the
The Centaurus had a cylinder swept volume of , nearly as much as the American Wright R-3350 ''Duplex-Cyclone'' large radial, making the Centaurus one of the largest aircraft piston engines to enter production, while that of the Hercules was . The nearly 40 percent higher capacity was achieved by increasing the stroke from and by changing to two rows of nine cylinders instead of two rows of seven. The diameter of the Centaurus was only just over 6 percent greater than the Hercules in spite of its much greater swept volume.Bridgman (Jane's) 1998, p. 270.
The cylinder heads had an indentation like an inverted top hat, which was finned, but it was difficult to get air down into this hollow to adequately cool the head. During development, Bristol contacted ICI Metals Division, Birmingham, to enquire whether a copper-chromium alloy with higher thermal conductivity would have sufficient high temperature strength to be used for this purpose. With the same cylinder volume and using the new material, the horsepower per cylinder was raised from to .
Bristol maintained the Centaurus from type-testing in 1938, but production did not start until 1942, owing to the need to get the Hercules into production and improve the reliability of the entire engine line. Nor was there any real need for the larger engine at this early point in the war, when most military aircraft designs had a requirement for engines of about . The Hercules power of about was better suited to the existing airframes.
The Centaurus did not enter service until near the end of the war, first appearing on the
 ''Note:''
''Note:''
Royal Navy Historic Flight - Aircraft
Retrieved: 5 August 2009 until it was destroyed in an accident on 28 April 2021 whist attempting a forced landing following a failure and seizure of its Bristol Centaurus XVIII engine: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/628cd96cd3bf7f1f47c65ebc/Hawker_Sea_Fury_T_Mk_20_G-RNHF_07-22.pdf

Period advertisement for the Bristol Centaurus - ''Flight'', May 1949Video of a cutaway engine in motion illustrating its operation
{{Bristol aeroengines Aircraft air-cooled radial piston engines
Bristol Engine Company
The Bristol Aeroplane Company, originally the British and Colonial Aeroplane Company, was both one of the first and one of the most important British aviation companies, designing and manufacturing both airframes and aircraft engines. Notable ...
's series of sleeve valve
The sleeve valve is a type of valve mechanism for piston engines, distinct from the usual poppet valve. Sleeve valve engines saw use in a number of pre-World War II luxury cars and in the United States in the Willys-Knight car and light truck. ...
radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric), a line
* Radius, adjective form of
* Radial distance, a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system
* Radial set
* A bearing f ...
aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many ...
s. The Centaurus is an 18-cylinder, two-row design that eventually delivered over . The engine was introduced into service late in the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and was one of the most powerful aircraft piston engines to see service.
Design and development
Like other Bristol sleeve valve engines, the Centaurus was based on the design knowledge acquired from an earlier design, in this case theBristol Perseus
The Bristol Perseus was a British nine-cylinder, single-row, air-cooled radial aircraft engine produced by the Bristol Engine Company starting in 1932. It was the first production sleeve valve aero engine.
Design and development
In late 192 ...
cylinder. The Centaurus used 18 Perseus cylinders. The same cylinder was in use in the contemporary 14-cylinder Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
, which was being brought into production when the design of the Centaurus started.
Vickers Warwick
The Vickers Warwick was a multi-purpose twin-engined British aircraft developed and operated during the Second World War. In line with the naming convention followed by other RAF heavy bombers of the era, it was named after a British city or ...
. Other wartime, or postwar, uses included the Bristol Brigand
The Bristol Brigand was a British anti-shipping/ground attack/dive bomber aircraft, developed by the Bristol Aeroplane Company as a replacement for the Beaufighter. A total of 147 were built and were used by the Royal Air Force in Malaya duri ...
and Buckmaster, Hawker Tempest
The Hawker Tempest is a British fighter aircraft that was primarily used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) in the Second World War. The Tempest, originally known as the ''Typhoon II'', was an improved derivative of the Hawker Typhoon, intended to a ...
and Sea Fury and the Blackburn Firebrand
The Blackburn Firebrand was a British single-engine strike fighter for the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy designed during World War II by Blackburn Aircraft. Originally intended to serve as a pure fighter, its unimpressive performance and ...
and Beverley
Beverley is a market town, market and minster (church), minster town and a civil parishes in England, civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, of which it is the county town. The town centre is located south-east of York's centre ...
. The engine also entered service after the war in a civilian airliner, the Airspeed Ambassador
The Airspeed AS.57 Ambassador is a British twin piston-engined airliner that was designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Airspeed Ltd. It was one of the first postwar airliners to be produced.
The Ambassador was developed in ...
and was also used in the Bristol Brabazon
The Bristol Type 167 Brabazon was a large British piston-engined propeller-driven airliner designed by the Bristol Aeroplane Company to fly transatlantic routes between the UK and the United States. The type was named ''Brabazon'' after the ...
I Mark 1 prototype aircraft until the Brabazon trans-Atlantic airliner programme was cancelled. The eight Centaurus engines were to be replaced with eight Bristol Proteus gas turbines on the Mark II giving a 100 mph faster cruising speed at 10,000 ft higher altitude. By the end of the war in Europe, around 2,500 examples of the Centaurus had been produced by Bristol.
The 373 was the most powerful version of the Centaurus and was intended for the Blackburn Beverley transport aircraft. Using direct fuel injection, it achieved a remarkable , but was never fitted. A projected enlarged capacity version of the Centaurus was designed by Sir Roy Fedden
Sir Alfred Hubert Roy Fedden MBE, FRAeS (6 June 1885 – 21 November 1973) was an engineer who designed most of Bristol Engine Company's successful piston aircraft engine designs.
Early life
Fedden was born in the Bristol area to fairly weal ...
; cylinders were produced for this engine, but it was never built. Known as the Bristol Orion, a name used previously for a variant of the Jupiter engine and later re-used for a turboprop, this development was also a two-row, 18 cylinder sleeve valve engine, with the displacement increased to } (), nearly as large as the American Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major
The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II. First run in 1944, at , it is the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in ...
four-row, 28-cylinder radial, the largest displacement aviation radial engine ever placed in quantity production.
Variants
The Centaurus was produced in 34 variants, ranging from the Centaurus I to the final Centaurus 663 for theAirspeed Ambassador
The Airspeed AS.57 Ambassador is a British twin piston-engined airliner that was designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Airspeed Ltd. It was one of the first postwar airliners to be produced.
The Ambassador was developed in ...
airliner
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ...
. The most powerful variants to enter service were the Centaurus 170, 173, 660, 661 and 662.
Applications
 ''Note:''
''Note:''
Survivors
TheRoyal Navy Historic Flight
The Royal Navy Historic Flight (RNHF) was the historic flight of the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy up until its disbandment in March 2019. The RNHF maintained and flew a small number of aircraft that were important to British Naval aviation. ...
operated a Hawker Sea Fury powered by a Bristol Centaurus engineRetrieved: 5 August 2009 until it was destroyed in an accident on 28 April 2021 whist attempting a forced landing following a failure and seizure of its Bristol Centaurus XVIII engine: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/628cd96cd3bf7f1f47c65ebc/Hawker_Sea_Fury_T_Mk_20_G-RNHF_07-22.pdf
Engines on display
Preserved Bristol Centaurus engines are on public display at the following museums: * Aerospace Bristol *Aerospace Museum of California
The Aerospace Museum of California is a private non-profit aviation museum located in North Highlands, California, outside of Sacramento, California, on the grounds of the former McClellan Air Force Base. The museum has a 4.5-acre outdoor Air Pa ...
*Fleet Air Arm Museum
The Fleet Air Arm Museum is devoted to the history of British naval aviation. It has an extensive collection of military and civilian aircraft, aero engines, models of aircraft and Royal Navy ships (especially aircraft carriers), and paintin ...
*Imperial War Museum Duxford
Imperial War Museum Duxford is a branch of the Imperial War Museum near Duxford in Cambridgeshire, England. Britain's largest aviation museum, Duxford houses the museum's large exhibits, including nearly 200 aircraft, military vehicles, artill ...
*London Science Museum
The Science Museum is a major museum on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, London. It was founded in 1857 and is one of the city's major tourist attractions, attracting 3.3 million visitors annually in 2019.
Like other publicly funded ...
*Midland Air Museum
The Midland Air Museum (MAM) is situated just outside the village of Baginton in Warwickshire, England, and is adjacent to Coventry Airport. The museum includes the ''Sir Frank Whittle Jet Heritage Centre'' (named after the local aviation pionee ...
* Shuttleworth Collection, Old Warden
*Dumfries and Galloway Aviation Museum
The Dumfries and Galloway Aviation Museum is a volunteer-operated aviation museum located in and around the World War II-era watch tower (control tower) at the former RAF Dumfries, located two miles north east of the centre of Dumfries, Scotlan ...
*San Diego Air & Space Museum
San Diego Air & Space Museum (SDASM, formerly the San Diego Aerospace Museum) is an aviation and space exploration museum in San Diego, California, United States. The museum is located in Balboa Park and is housed in the former Ford Building, ...
Specifications (Centaurus VII)
See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
*Bridgman, L, (ed.) (1998) Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. Crescent. *Gunston, Bill. ''Development of Piston Aero Engines''. Cambridge, UK. Patrick Stephens, 2006. *Gunston, Bill. ''World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines: From the Pioneers to the Present Day''. 5th edition, Stroud, UK: Sutton, 2006. *Lumsden, Alec. ''British Piston Engines and Their Aircraft''. Marlborough, UK: Airlife Publishing, 2003. . *White, Graham. ''Allied Aircraft Piston Engines of World War II: History and Development of Frontline Aircraft Piston Engines Produced by Great Britain and the United States During World War II''. Warrendale, Pennsylvania: SAE International, 1995.External links
Period advertisement for the Bristol Centaurus - ''Flight'', May 1949
{{Bristol aeroengines Aircraft air-cooled radial piston engines
Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. ...
Sleeve valve engines
1930s aircraft piston engines