Bridge Transformer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A hybrid transformer (also known as a bridge transformer, hybrid coil, or just hybrid) is a type of directional coupler which is designed to be configured as a
A hybrid transformer (also known as a bridge transformer, hybrid coil, or just hybrid) is a type of directional coupler which is designed to be configured as a
 The primary use of a voiceband hybrid transformer is to convert between
The primary use of a voiceband hybrid transformer is to convert between
 For use in
For use in
Modelling Telephony Hybrids as 2 × 2 Matrices
{{FS1037C MS188 Electric transformers Telecommunications equipment
 A hybrid transformer (also known as a bridge transformer, hybrid coil, or just hybrid) is a type of directional coupler which is designed to be configured as a
A hybrid transformer (also known as a bridge transformer, hybrid coil, or just hybrid) is a type of directional coupler which is designed to be configured as a circuit
Circuit may refer to:
Science and technology
Electrical engineering
* Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current
** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels
** Balanced circu ...
having four ports that are conjugate in pairs, implemented using one or more transformers. It is a particular case of the more general concept of a hybrid coupler
Power dividers (also power splitters and, when used in reverse, power combiners) and directional couplers are Passivity (engineering), passive devices used mostly in the field of radio technology. They couple a defined amount of the electromagne ...
.
A signal arriving at one port is divided equally between the two adjacent ports but does not appear at the opposite port. In the schematic diagram, the signal into W splits between X and Z, and no signal passes to Y. Similarly, signals into X split to W and Y with none to Z, etc.
Correct operation requires matched characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance (usually written Z0) of a uniform transmission line is the ratio of the amplitudes of voltage and current of a single wave propagating along the line; that is, a wave travelling in one direction in ...
at all four ports. Forms of hybrid other than transformer coils are possible; any format of directional coupler can be designed to be a hybrid. These formats include transmission lines and waveguides.
Motivation
 The primary use of a voiceband hybrid transformer is to convert between
The primary use of a voiceband hybrid transformer is to convert between 2-wire In telecommunication, a two-wire circuit is characterized by supporting transmission in two directions simultaneously, as opposed to four-wire circuits, which have separate pairs for transmit and receive. The subscriber local loop from the telco tel ...
and 4-wire
In telecommunication, a four-wire circuit is a two-way circuit using two paths so arranged that the respective signals are transmitted in one direction only by one path and in the other direction by the other path. The four-wire circuit gets its n ...
operation in sequential sections of a communications circuit, for example in a four-wire terminating set A four-wire terminating set (4WTS) is a balanced transformer used to perform a conversion between four-wire and two-wire operation in telecommunication systems.
For example, a 4-wire circuit may, by means of a 4-wire terminating set, be connecte ...
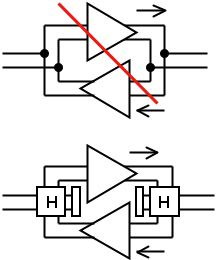
. Such conversion was necessary when repeaters were introduced in a 2-wire circuit, a frequent practice at early 20th century telephony. Without hybrids, the output of one amplifier feeds directly into the input of the other, resulting in uncontrollable feedback oscillation (upper diagram). By using hybrids, the outputs and inputs are isolated, resulting in correct 2-wire repeater operation. Late in the century, this practice became rare but hybrids continued in use in line cards.
Implementations
Hybrids are realized using transformers. Two versions of transformer hybrids were used, the single transformer version providing unbalanced outputs with one end grounded, and the double transformer version providing balanced ports.Single transformer
 For use in
For use in 2-wire In telecommunication, a two-wire circuit is characterized by supporting transmission in two directions simultaneously, as opposed to four-wire circuits, which have separate pairs for transmit and receive. The subscriber local loop from the telco tel ...
repeaters, the single transformer version suffices, since amplifiers in the repeaters have grounded inputs and outputs. X, Y, and Z share a common ground. As shown at left, signal into W, the 2-wire port, will appear at X and Z. But since Y is bridged from center of coil to center of X and Z, no signal appears. Signal into X will appear at W and Y. But signal at Z is the difference of what appears at Y and, through the transformer coil, at W, which is zero. Similar reasoning proves both pairs, W & Y, X & Z, are conjugates.
Double transformer
When both the2-wire In telecommunication, a two-wire circuit is characterized by supporting transmission in two directions simultaneously, as opposed to four-wire circuits, which have separate pairs for transmit and receive. The subscriber local loop from the telco tel ...
and the 4-wire circuits must be balanced, double transformer hybrids are used, as shown at right. Signal into port W splits between X and Z, but due to reversed connection to the windings, cancel at port Y. Signal into port X goes to W and Y. But due to reversed connection to ports W and Y, Z gets no signal. Thus the pairs, W & Y, X & Z, are conjugates.
Applications
Telephone hybrids are used intelephone exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital syst ...
s to convert the 4-wire appearance to the 2-wire last mile
Last mile may refer to:
* Last mile (telecommunications), the final leg of the telecommunications networks that deliver services to retail end-users
* Last mile (transportation), the final leg the movement of people and goods from a transportation ...
connection to the subscriber's telephone. A different kind of hybrid is used in telephone handsets to convert the four wires of the transmitter (earpiece) and receiver (microphone) to the 2-wire line connection. This kind of hybrid is more commonly called an "induction coil" due to its derivation from high-voltage induction coil
An induction coil or "spark coil" (archaically known as an inductorium or Ruhmkorff coil after Heinrich Rühmkorff) is a type of electrical transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current (DC) supply. p.98 To ...
s. It does not produce a high voltage, but like the high-voltage variety, it is a step-up transformer in order to impedance match the low-impedance carbon button transmitter to the higher impedance parts of the system. The simple induction coil later evolved into a form of hybrid as a sidetone reduction measure, or volume of microphone output that was fed back to the earpiece. Without this, the phone user's own voice would be louder in the earpiece than the other party's.Lewis Coe, ''The Telephone and Its Several Inventors: A History'', pp. 124, 173, McFarland, 2006 . Today, the transformer version of the hybrid has been replaced by resistor networks and compact IC versions, which use integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
electronics to do the job of the hybrid coil.
Radio-frequency hybrids are used to split radio signals, including television. The splitter divides the antenna
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves
* Antennae Galaxies, the name of two collid ...
signal to feed multiple receivers.
See also
* Magic tee * Rat-race couplerReferences
External links
* Douglas Rice (2008Modelling Telephony Hybrids as 2 × 2 Matrices
{{FS1037C MS188 Electric transformers Telecommunications equipment