Breitspurbahn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Breitspurbahn (, translation: ''broad-gauge railway'') was a planned
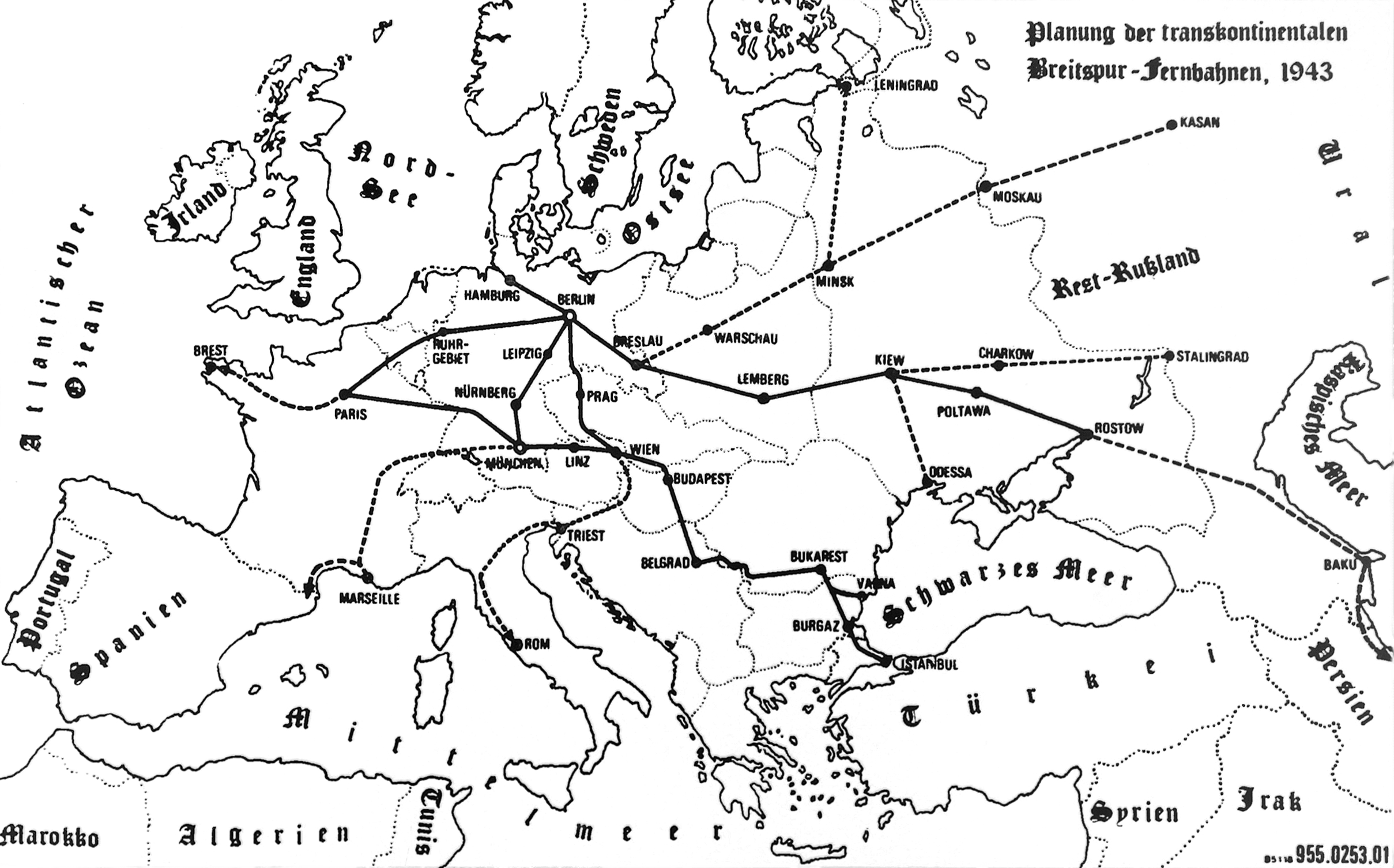 Early plans for routes considered India, Iran, Syria, Vladivostok and Canada (via Bering Strait) as the ultimate goals of the railways, but by 1943 the planning was focused exclusively on European cities. Ukraine and the Volga Basin were seen as especially important targets, as these areas were viewed as the future
Early plans for routes considered India, Iran, Syria, Vladivostok and Canada (via Bering Strait) as the ultimate goals of the railways, but by 1943 the planning was focused exclusively on European cities. Ukraine and the Volga Basin were seen as especially important targets, as these areas were viewed as the future
 Originally proposed to run on a track, the ''Breitspurbahn'' was ultimately developed with a
Originally proposed to run on a track, the ''Breitspurbahn'' was ultimately developed with a

Breitspurbahn.de
Pictures of the "Breitspurbahn"
epilog.de
Concept drawings and discussion of the Breitspurbahn {{Navbox track gauge Abandoned projects of Nazi Germany Rail infrastructure in Germany 3000 mm gauge railways 4000 mm gauge railways Track gauges Track gauges by name Standards of Germany
broad-gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union ( ...
railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
, proposed during the time of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, supposed to run with double-deck coach
Coach may refer to:
Guidance/instruction
* Coach (sport), a director of athletes' training and activities
* Coaching, the practice of guiding an individual through a process
** Acting coach, a teacher who trains performers
Transportation
* Coac ...
es between major cities of '' Grossdeutschland'', Hitler's expanded Germany,Puffert, Douglas J. (2009). ''Tracks across continents, paths through history: the economic dynamics of standardization in railway gauge''. Chicago : University of Chicago Press. . p 182 and neighbouring states.
History
Sincereparations
Reparation(s) may refer to:
Christianity
* Restitution (theology), the Christian doctrine calling for reparation
* Acts of reparation, prayers for repairing the damages of sin
History
*War reparations
**World War I reparations, made from ...
due after World War I had to be paid, the German railway company Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'', also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the German national railway system created after the end of World War I from the regiona ...
lacked money for appropriate expansion and sufficient maintenance of their track network and rolling stock.
Commercial and civilian traffic increased due to economic stimulation after the rise of the NSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
and Hitler's seizure of power
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with l ...
. Deutsche Reichsbahn was now faced with a serious capacity problem. As a result, in part driven by its military objectives, the government began to prepare plans to modernize the railway network and increase transport capacity. Hitler believed that the standard Stephenson gauge was obsolete and was too narrow for the full development of railways. Also, as Hitler envisioned the future German empire as essentially a land-based Empire, the new German railways were imagined as a land-based equivalent of the ocean liner
An ocean liner is a passenger ship primarily used as a form of transportation across seas or oceans. Ocean liners may also carry cargo or mail, and may sometimes be used for other purposes (such as for pleasure cruises or as hospital ships).
Ca ...
s and freighters connecting the maritime British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
.
Hitler embraced a suggestion from Fritz Todt
Fritz Todt (; 4 September 1891 – 8 February 1942) was a German construction engineer and senior Nazi who rose from the position of Inspector General for German Roadways, in which he directed the construction of the German autobahns (''Reich ...
to build a new high-capacity ''Reichsspurbahn'' (Imperial Gauge Railway) with notably increased gauge. Objections from railway experts – who foresaw difficulties in introducing a new, incompatible gauge (and proposed quadruple track standard gauge lines instead), and who could not imagine any use for the vast transport capacity of such a railway – were ignored, and Hitler ordered the ''Breitspurbahn'' to be built with initial lines between Hamburg, Berlin, Nuremberg, Munich and Linz.
The project engaged commercial partners Krauss-Maffei; Henschel
Henschel & Son (german: Henschel und Sohn) was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting v ...
; Borsig Borsig is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* (1867–1897), German entrepreneur
* August Borsig (1804–1854), German businessman
* Conrad von Borsig (1873–1945), German mechanical engineer
* Ernst Borsig
Ernst August Pau ...
;Brown, Boveri & Cie
Brown, Boveri & Cie. (Brown, Boveri & Company; BBC) was a Swiss group of electrical engineering companies.
It was founded in Zürich, in 1891 by Charles Eugene Lancelot Brown and Walter Boveri who worked at the Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon. In 19 ...
and Krupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krupp ...
, but did not develop beyond line planning and initial survey. Throughout World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, 100 officials and 80 engineers continued to work on the project.
Proposed routes
 Early plans for routes considered India, Iran, Syria, Vladivostok and Canada (via Bering Strait) as the ultimate goals of the railways, but by 1943 the planning was focused exclusively on European cities. Ukraine and the Volga Basin were seen as especially important targets, as these areas were viewed as the future
Early plans for routes considered India, Iran, Syria, Vladivostok and Canada (via Bering Strait) as the ultimate goals of the railways, but by 1943 the planning was focused exclusively on European cities. Ukraine and the Volga Basin were seen as especially important targets, as these areas were viewed as the future granaries
A granary is a storehouse or room in a barn for threshed grain or animal feed. Ancient or primitive granaries are most often made of pottery. Granaries are often built above the ground to keep the stored food away from mice and other animals ...
of Greater Germany, potentially through the "settlement strings", or ''Siedlungsperlen'' of the proposed Wehrbauer
''Wehrbauer'' (, ''defensive peasant''), plural ''Wehrbauern'', is a German term for settlers living on the marches of a realm, who were tasked with holding back foreign invaders until the arrival of proper military reinforcements. In turn, they w ...
settlements within the conquered territories, which would also be linked by the planned easternmost reaches of the Reichsautobahn
The ''Reichsautobahn'' system was the beginning of the German autobahns under Nazi Germany. There had been previous plans for controlled-access highways in Germany under the Weimar Republic, and two had been constructed, but work had yet to st ...
freeway network. Due to mountainous terrain, the initial phase routes of Aachen-Paris and Budapest-Bucharest were drawn via Antwerp instead of Liège, and via Belgrade instead of the Hungary/Romania border respectively.
*East-West: Rostov
Rostov ( rus, Росто́в, p=rɐˈstof) is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, one of the oldest in the country and a tourist center of the Golden Ring. It is located on the shores of Lake Nero, northeast of Moscow. Population:
While t ...
- Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: Names of European cities in different languages (C–D), cities' alternat ...
- Poltava
Poltava (, ; uk, Полтава ) is a city located on the Vorskla River in central Ukraine. It is the capital city of the Poltava Oblast (province) and of the surrounding Poltava Raion (district) of the oblast. Poltava is administratively ...
- Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
- Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine ...
- Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
- Katowice
Katowice ( , , ; szl, Katowicy; german: Kattowitz, yi, קאַטעוויץ, Kattevitz) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Upper Silesian metropolitan area. It is the 11th most popul ...
- Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
- Cottbus
Cottbus (; Lower Sorbian: ''Chóśebuz'' ; Polish: Chociebuż) is a university city and the second-largest city in Brandenburg, Germany. Situated around southeast of Berlin, on the River Spree, Cottbus is also a major railway junction with exten ...
- Welthauptstadt Germania
Welthauptstadt Germania () or World Capital Germania was the projected renewal of the German capital Berlin during the Nazi period, part of Adolf Hitler's vision for the future of Nazi Germany after the planned victory in World War II. It wa ...
(Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
) - Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
- Bielefeld
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Detmold and the ...
- Ruhrgebiet
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
- Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
- Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
- Saint-Quentin - Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
**Initially proposed the Flemish corridor as Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
- Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
- Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
- Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
*North-Southeast: Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
- Wittenberge
Wittenberge () is a town of eighteen thousand people on the middle Elbe in the district of Prignitz, Brandenburg, Germany.
Geography
Wittenberge is situated at the right (north-eastern) bank of the middle Elbe at its confluence with the Stepe ...
- Welthauptstadt Germania
Welthauptstadt Germania () or World Capital Germania was the projected renewal of the German capital Berlin during the Nazi period, part of Adolf Hitler's vision for the future of Nazi Germany after the planned victory in World War II. It wa ...
(Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
) - Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as wel ...
- Gotha
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the ...
- Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
- Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
- Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by popu ...
- Simbach am Inn
Simbach am Inn ( en, Simbach on the Inn) is a town on the river Inn in the Rottal-Inn district of Bavaria, Germany. The Austrian city Braunau am Inn lies on the opposite side of the river from Simbach.
History
Simbach was one of the first places ...
- Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846.
In 2009, it was a European Capital of ...
- Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
- Presburg
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approximately 140% of ...
- Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
- Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of ...
- Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
/Burgas
Burgas ( bg, Бургас, ), sometimes transliterated as ''Bourgas'', is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the fourth-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, and Varna, with a popu ...
- Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
**Initially proposed the Serbian corridor as Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
- Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
- Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of ...
*North-South-Parallel: Welthauptstadt Germania
Welthauptstadt Germania () or World Capital Germania was the projected renewal of the German capital Berlin during the Nazi period, part of Adolf Hitler's vision for the future of Nazi Germany after the planned victory in World War II. It wa ...
(Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
) - Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
- Aussig - Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
- Iglau
Jihlava (; german: Iglau) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 50,000 inhabitants. Jihlava is the capital of the Vysočina Region, situated on the Jihlava River on the historical border between Moravia and Bohemia.
Historically, Jihlava ...
- Znaim
Znojmo (; german: Znaim) is a town in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 33,000 inhabitants. Znojmo is the historical and cultural centre of southwestern Moravia and the second most populated town in the South Moravian R ...
- Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
- Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into provi ...
- Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
*East-West 2: Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by popu ...
- Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ' ...
- Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the ...
- Karlsruhe
Karlsruhe ( , , ; South Franconian: ''Kallsruh'') is the third-largest city of the German state (''Land'') of Baden-Württemberg after its capital of Stuttgart and Mannheim, and the 22nd-largest city in the nation, with 308,436 inhabitants. ...
- Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand E ...
- Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
- Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
- Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Franc ...
- Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
- Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
For further routes, ''see'' German version and Dutch version.
Tracks
track gauge
In rail transport, track gauge (in American English, alternatively track gage) is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many d ...
of , more than double the width of the common standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
track, and three times the width of the common semi-narrow metre gauge
Metre-gauge railways are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
The metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by European colonial powers, such as the French, British and German Empires. In Europe, la ...
track. Planning called for a ballastless track (much as was developed 30 years later for San Francisco BART
Bart is a masculine given name, usually a diminutive of Bartholomew, sometimes of Barton, Bartolomeo, etc.
Bart is a Dutch and Ashkenazi Jewish surname, and derives from the name ''Bartholomäus'', a German form of the biblical name ''Barthol ...
and 40 years later for German high-speed lines) which consisted of two parallel pre-stressed concrete "walls" sunk into the ground, joined at the top by a flat transverse slab. The rails were fixed on top of the "walls", with an elastic material between rail and concrete. Because it did not have conventional railway sleepers
''Sleepers'' is a 1996 American legal crime drama film written, produced, and directed by Barry Levinson, and based on Lorenzo Carcaterra's 1995 book of the same name. The film stars Kevin Bacon, Jason Patric, Brad Pitt, Robert De Niro, Dustin H ...
, this track would also have formed an ideal road for maintenance and military purposes. The rails would be either (Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
special; tall) rails or proposed (height-width ratio of 1:1) rails. The passing loop
A passing loop (UK usage) or passing siding (North America) (also called a crossing loop, crossing place, refuge loop or, colloquially, a hole) is a place on a single line railway or tramway, often located at or near a station, where trains or ...
length would be more than a mile (1 km).
The intended Russian territory included within Hitler's ''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperi ...
'' (sub-''Breitspurbahn'' system) plans had been using the slightly wider and Russian gauge
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
since the mid-19th century, barely half the width of the 3-meter gauge that was eventually chosen.
Vehicles

Locomotives
Forty-one different locomotive designs were suggested by the industry partners. These ranged from classical steam locomotives throughsteam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
, gas turbine-electric and diesel-hydraulic
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels ...
to electric locomotives. The designs ranged from 12 axles (UIC: 3′Fo3′, Whyte: 6-12-6) to 52 axles (UIC: 2′Fo′Fo′2′ + 5T5 + 5T5 + 2′Fo′Fo′2′, Whyte: 4-12-12-4 + 10-10 + 10-10 + 4-12-12-4). Power ranged from . All locomotives would have automatic couplers, ranged from Janney couplers to SA3 couplers. Several designs were short listed with passenger locomotives to be mainly electric and diesel-hydraulic with SA3 coupler
SA3 couplers (also known as СА3 or СА-3 couplers per the typical foundry stamp on top of these couplers, meaning "Советская Автосцепка, 3" in Russian or "Soviet Auto-latch 3" in English) or Willison coupler and Russia ...
s, and freight locomotives to be mainly conventional steam with Janney coupler
Janney couplers are a semi-automatic form of railway coupling that allow rail cars and locomotives to be securely linked together without rail workers having to get between the vehicles. They are also known as American, AAR, APT, ARA, MCB, knuck ...
s.
Multiple units
Diesel and electric multiple units of between five and eight coaches were proposed for shorter distance journeys. Despite being of somewhat lower standard, proposed designs included promenades, bars, lounges and large dining rooms.Carriages
The proposal was that high-performance locomotives should pull 8-axle double-floor carriages with a length of , width of and height of . The carriages would haveDutch door
A Dutch door (American English), stable door (British English), or half door (Hiberno-English), is a door divided in such a fashion that the bottom half may remain shut while the top half opens. They were known in early New England as double-hung ...
s (with retractable staircase). The trains would be fitted with a restaurant, theatre, swimming pool, barbershop and sauna. The whole train would have a length of about , allowing a capacity of between 2,000 and 4,000 passengers, travelling at speeds of . Designs included:
* 1st/2nd class day car: 48 first class seats in 12 compartments, 144 second class seats in 24 compartments, bar, lounge, reading room, luggage compartments, 12 toilets.
* 3rd class day car: 460 seats in 56 compartments, lounge, 12 toilets.
* 1st/2nd class dining car: 130 seats at 24 tables, kitchen, pantry.
* 3rd class day car with dining room: 244 seats in 28 compartments, 176 seat dining room, kitchen, pantry.
* 1st/2nd class sleeping car: 16 first class beds in 16 cabins, 41 second class beds in 19 cabins, breakfast room, kitchen, washrooms, 10 toilets.
* 2nd class sleeping car: 104 beds in 104 cabins, washrooms, 12 toilets.
* 3rd class sleeping car: 264 beds in 44 cabins, breakfast room, kitchen, shower rooms, 10 toilets.
* Day/night car for Ost-Arbeiter
:
' (, "Eastern worker") was a Nazi German designation for foreign slave workers gathered from occupied Central and Eastern Europe to perform forced labor in Germany during World War II. The Germans started deporting civilians at the beginning ...
: 480 seats in 52 cabins, kitchen, washrooms, staff room.
* Theatre car: 196-seat theatre.
* Observation car: 16 first class seats in four compartments, 32 second class seats in eight compartments, 160 third class seats in 20 compartments, galley, cold buffet, bar, observation deck.
* Mail car: mail storage and sorting, parcel space, crew room, space for 6 automobiles, dog kennels.
* Baggage car: baggage rooms, space for two automobiles, dog kennels, canteen, crew room, multiple 20 mm anti-aircraft guns, ammunition storage and gun crews.
Successors & similar plans
After Nazi Germany collapsed, several super-broad gauge railways were proposed, with track gauges ranging from . Locomotive options added nuclear-powered locomotives, and passenger carriages lengths ranging from . Most passenger carriages would haveDutch door
A Dutch door (American English), stable door (British English), or half door (Hiberno-English), is a door divided in such a fashion that the bottom half may remain shut while the top half opens. They were known in early New England as double-hung ...
s (with retractable staircase), with some exceptions being low-level-boarding-only designs.
In fiction
A ride on Breitspurbahn is featured in '' Wolfenstein: The New Order'' video game. The railway network is also mentioned in novels ''Fatherland
A homeland is a place where a cultural, national, or racial identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethn ...
'' and '' The Fuhrer's Orphans''.
An American version of the Breitspurbahn is depicted in the TV series '' Supertrain''.
In the television series Snowpiercer (TV series)
''Snowpiercer'' is an American post-apocalyptic dystopian thriller television series that premiered on TNT on May 17, 2020. It is based on both the 2013 film of the same name, directed by Bong Joon-ho and the 1982 French graphic novel ''Le Tra ...
, the titular train bears many similarities to the Breitspurbahn.
An upcoming Trainz
''Trainz'' is a series of 3D train simulator video games. The Australian studio Auran (since 2007 N3V Games) released the first game in 2001.
The simulators consist of route and session editors called ''Surveyor'', and the ''Driver'' module, ...
content called Project Germania based on the Breitspurbahn, going to be released in 2023.
See also
*Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
*Welthauptstadt Germania
Welthauptstadt Germania () or World Capital Germania was the projected renewal of the German capital Berlin during the Nazi period, part of Adolf Hitler's vision for the future of Nazi Germany after the planned victory in World War II. It wa ...
*Eurasian Land Bridge
The Eurasian Land Bridge (), sometimes called the New Silk Road (, ), is the rail transport route for moving freight and passengers overland between Pacific seaports in the Russian Far East and China and seaports in Europe. The route, a transc ...
*Bering Strait crossing
A Bering Strait crossing is a hypothetical bridge or tunnel that would span the relatively narrow and shallow Bering Strait between the Chukotka Peninsula in Russia and the Seward Peninsula in the U.S. state of Alaska. The crossing would prov ...
*Broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
*Dual gauge
In railway engineering, "gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to c ...
*Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
(Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
)
*Train on Train
__NOTOC__
is a concept for piggybacking (that is, carrying narrow-gauge wagons on broader-gauge flatwagons) by the trainload rather than one wagon at a time.
The need arose when Japan's Hokkaido Railway Company (JR Hokkaido) was planning f ...
* Trans-Asian Railway
*Transcontinental railway
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single ...
*Bilevel rail car
A bilevel car (American English) or double-decker coach (British English and Canadian English) is a type of rail car that has two levels of passenger accommodation, as opposed to one, increasing passenger capacity (in example cases of up to ...
References
Further reading
* ''Die Breitspurbahn'', Anton Joachimsthaler. Herbig, 1996. * ''Broader than Broad: Hitler's Great Dream: Three Meter Gauge Rails Across Europe'', Barnes, Robin. Locomotives International. 1998.External links
Breitspurbahn.de
Pictures of the "Breitspurbahn"
epilog.de
Concept drawings and discussion of the Breitspurbahn {{Navbox track gauge Abandoned projects of Nazi Germany Rail infrastructure in Germany 3000 mm gauge railways 4000 mm gauge railways Track gauges Track gauges by name Standards of Germany