Breath Carbon Monitor Device on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving

 Ideally, air is breathed first out and secondly in through the nose. The
Ideally, air is breathed first out and secondly in through the nose. The
air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
into and from the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s to facilitate gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow, diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liqui ...
with the internal environment
The internal environment (or ''milieu intérieur'' in French) was a concept developed by Claude Bernard, a French physiologist in the 19th century, to describe the interstitial fluid and its physiological capacity to ensure protective stability f ...
, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
and bring in oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
.
All aerobic
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen.
Aerobic may also refer to
* Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity
* Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise
* Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of cellu ...
creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or "external respiration", brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* ...
through diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
. The body's circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
transports these gases to and from the cells, where "cellular respiration" takes place.
The breathing of all vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
s with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
and exhalation
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In animals, it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing.
This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, ...
through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is mea ...
, and is one of the four primary vital signs
Vital signs (also known as vitals) are a group of the four to six most crucial medical signs that indicate the status of the body's vital (life-sustaining) functions. These measurements are taken to help assess the general physical health of a ...
of life. Under normal conditions the breathing depth and rate is automatically, and unconsciously, controlled by several homeostatic mechanisms which keep the partial pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas ...
s of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
in the arterial blood constant. Keeping the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood unchanged under a wide variety of physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
circumstances, contributes significantly to tight control of the pH of the extracellular fluids
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
(ECF). Over-breathing (hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood. ...
) and under-breathing (hypoventilation
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia ...
), which decrease and increase the arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide respectively, cause a rise in the pH of ECF in the first case, and a lowering of the pH in the second. Both cause distressing symptoms.
Breathing has other important functions. It provides a mechanism for speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses Phonetics, phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if ...
, laughter
Laughter is a pleasant physical reaction and emotion consisting usually of rhythmical, often audible contractions of the diaphragm and other parts of the respiratory system. It is a response to certain external or internal stimuli. Laughter ...
and similar expressions of the emotions. It is also used for reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
es such as yawning
A yawn is a reflex lasting 4-7 seconds, and is characterized by a long inspiratory phase with gradual mouth gaping, followed by a brief climax (or acme) with muscle stretching, and a rapid expiratory phase with muscle relaxation. For fish an ...
, coughing
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three phas ...
and sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth and ...
. Animals that cannot thermoregulate
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
by perspiration
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distrib ...
, because they lack sufficient sweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial sur ...
s, may lose heat by evaporation through panting.
Mechanics
Thelung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s are not capable of inflating themselves, and will expand only when there is an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity. In humans, as in the other mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
, this is achieved primarily through the contraction of the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
, but also by the contraction of the intercostal muscles
Intercostal muscles are many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size ...
which pull the rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi- ...
upwards and outwards as shown in the diagrams on the right. During forceful inhalation (Figure on the right) the accessory muscles of inhalation, which connect the ribs and sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sh ...
to the cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
and base of the skull, in many cases through an intermediary attachment to the clavicles
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right ...
, exaggerate the pump handle and bucket handle movement
Bucket-handle is a movement of ribs that results in change in transverse diameter of the thorax.
Definition
One of the most important functions of ribs and diaphragm is the change in volume of thorax that helps inspiration and expiration. In g ...
s (see illustrations on the left), bringing about a greater change in the volume of the chest cavity. During exhalation (breathing out), at rest, all the muscles of inhalation relax, returning the chest and abdomen to a position called the "resting position", which is determined by their anatomical elasticity. At this point the lungs contain the functional residual capacity
Functional residual capacity (FRC) is the volume of air present in the lungs at the end of passive expiration. At FRC, the opposing elastic recoil forces of the lungs and chest wall are in equilibrium and there is no exertion by the diaphragm ...
of air, which, in the adult human, has a volume of about 2.5–3.0 liters.
During heavy breathing (hyperpnea
Hyperpnea, or hyperpnoea (forced respiration) is increased volume of air taken during breathing. It can occur with or without an increase in respiration rate. It is characterized by deep breathing. It may be physiologic—as when required by oxygen ...
) as, for instance, during exercise, exhalation is brought about by relaxation of all the muscles of inhalation, (in the same way as at rest), but, in addition, the abdominal muscles, instead of being passive, now contract strongly causing the rib cage to be pulled downwards (front and sides). This not only decreases the size of the rib cage but also pushes the abdominal organs upwards against the diaphragm which consequently bulges deeply into the thorax. The end-exhalatory lung volume is now less air than the resting "functional residual capacity". However, in a normal mammal, the lungs cannot be emptied completely. In an adult human, there is always still at least one liter of residual air left in the lungs after maximum exhalation.
Diaphragmatic breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, abdominal breathing, belly breathing, or deep breathing, is breathing that is done by contracting the diaphragm, a muscle located horizontally between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Air enters the lungs as the ...
causes the abdomen to rhythmically bulge out and fall back. It is, therefore, often referred to as "abdominal breathing". These terms are often used interchangeably because they describe the same action.
When the accessory muscles of inhalation are activated, especially during labored breathing Labored respiration or labored breathing is an abnormal respiration characterized by evidence of increased effort to breathe, including the use of accessory muscles of respiration, stridor, grunting, or nasal flaring.
Classification
Labored breath ...
, the clavicles are pulled upwards, as explained above. This external manifestation of the use of the accessory muscles of inhalation is sometimes referred to as clavicular breathing
Shallow breathing, thoracic breathing, costal breathing or chest breathing is the drawing of minimal Breathing, breath into the lungs, usually by drawing air into the Thoracic cavity, chest area using the intercostal muscles rather than throug ...
, seen especially during asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
attacks and in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
.
Passage of air

Upper airways

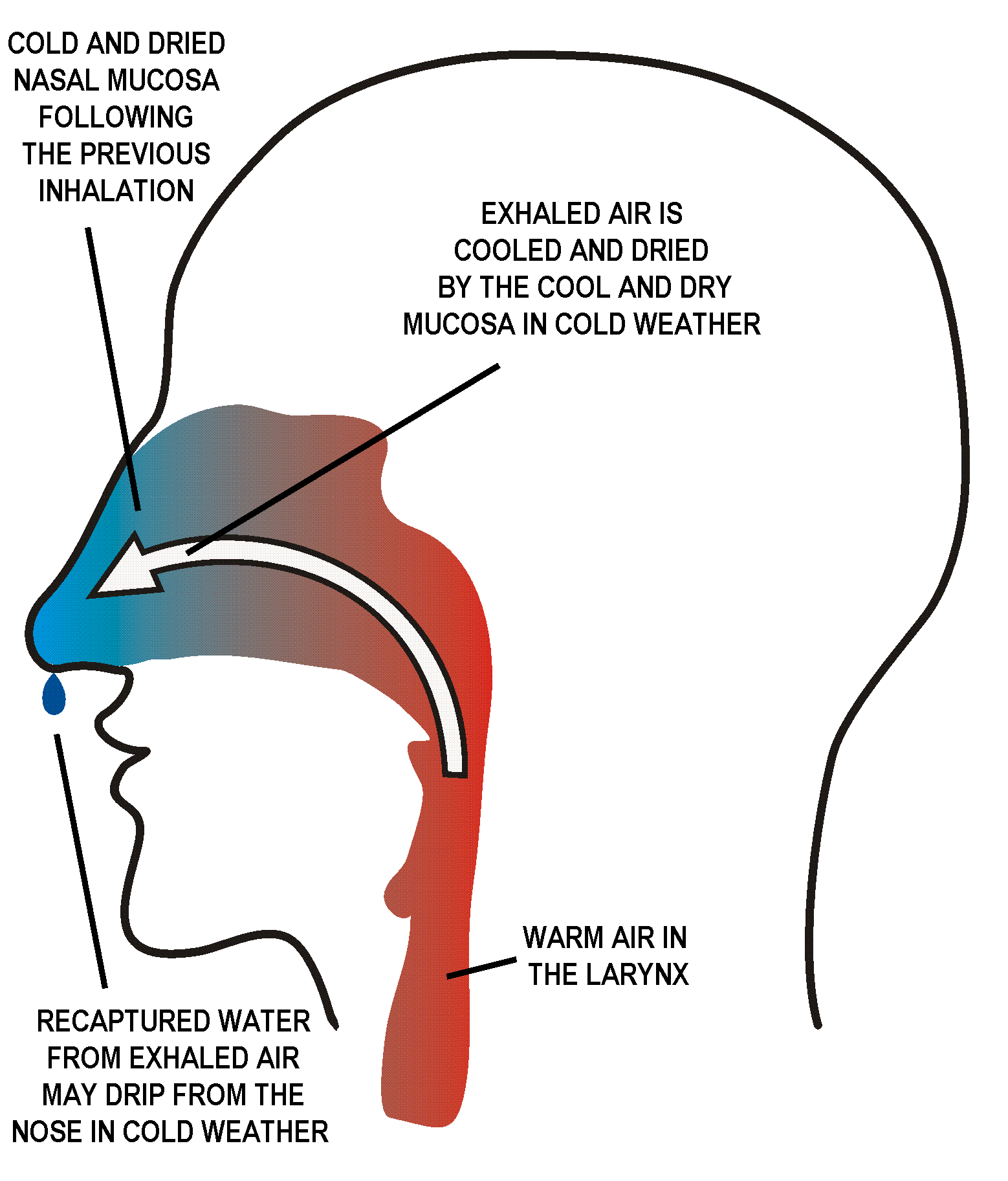
 Ideally, air is breathed first out and secondly in through the nose. The
Ideally, air is breathed first out and secondly in through the nose. The nasal cavities
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
(between the nostril
A nostril (or naris , plural ''nares'' ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbi ...
s and the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
) are quite narrow, firstly by being divided in two by the nasal septum
The nasal septum () separates the left and right airways of the Human nose, nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils.
It is Depression (kinesiology), depressed by the depressor septi nasi muscle.
Structure
The fleshy external end of the nasal ...
, and secondly by lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
*Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
*Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral cons ...
walls that have several longitudinal folds, or shelves, called
nasal concha
In anatomy, a nasal concha (), plural conchae (), also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various animals. The conchae are shaped like ...
e, thus exposing a large area of nasal mucous membrane to the air as it is inhaled (and exhaled). This causes the inhaled air to take up moisture from the wet mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
, and warmth from the underlying blood vessels, so that the air is very nearly saturated with water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
and is at almost body temperature by the time it reaches the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
. Part of this moisture and heat is recaptured as the exhaled air moves out over the partially dried-out, cooled mucus in the nasal passages, during exhalation. The sticky mucus also traps much of the particulate matter that is breathed in, preventing it from reaching the lungs.
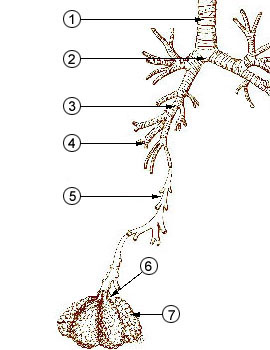
Lower airways
The anatomy of a typical mammalian respiratory system, below the structures normally listed among the "upper airways" (the nasal cavities, the pharynx, and larynx), is often described as a respiratory tree or tracheobronchial tree (figure on the left). Larger airways give rise to branches that are slightly narrower, but more numerous than the "trunk" airway that gives rise to the branches. The human respiratory tree may consist of, on average, 23 such branchings into progressively smaller airways, while the respiratory tree of themouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
has up to 13 such branchings. Proximal divisions (those closest to the top of the tree, such as the trachea and bronchi) function mainly to transmit air to the lower airways. Later divisions such as the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts and alveoli are specialized for gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow, diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liqui ...
.
The trachea and the first portions of the main bronchi are outside the lungs. The rest of the "tree" branches within the lungs, and ultimately extends to every part of the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s.
The alveoli are the blind-ended terminals of the "tree", meaning that any air that enters them has to exit the same way it came. A system such as this creates dead space
''Dead Space'' is a science fiction/horror fiction, horror media franchise created by Glen Schofield and Michael Condrey, developed by Visceral Games, and published and owned by Electronic Arts. The franchise's chronology is not presented in a lin ...
, a term for the volume of air that fills the airways at the end of inhalation, and is breathed out, unchanged, during the next exhalation, never having reached the alveoli. Similarly, the dead space is filled with alveolar air at the end of exhalation, which is the first air to breathed back into the alveoli during inhalation, before any fresh air which follows after it. The dead space volume of a typical adult human is about 150 ml.
Gas exchange
The primary purpose of breathing is to refresh air in the alveoli so thatgas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow, diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liqui ...
can take place in the blood. The equilibration of the partial pressures of the gases in the alveolar blood and the alveolar air occurs by diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
. After exhaling, adult human lungs still contain 2.5–3 L of air, their functional residual capacity
Functional residual capacity (FRC) is the volume of air present in the lungs at the end of passive expiration. At FRC, the opposing elastic recoil forces of the lungs and chest wall are in equilibrium and there is no exertion by the diaphragm ...
or FRC. On inhalation, only about 350 mL of new, warm, m