Breast Cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin.
Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ducts with milk. Cancers developing from the ducts are known as Invasive ductal carcinoma, ductal carcinomas, while those developing from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas. There are more than 18 other sub-types of breast cancer. Some, such as ductal carcinoma in situ, develop from pre-invasive lesions. The diagnosis of breast cancer is confirmed by taking a Breast biopsy, biopsy of the concerning tissue. Once the diagnosis is made, further tests are carried out to determine if the cancer has spread beyond the breast and which treatments are most likely to be effective.
The balance of benefits versus harms of breast cancer screening is controversial. A 2013 Cochrane review found that it was unclear whether mammographic screening does more harm than good, in that a large proportion of women who test positive turn out not to have the disease. A 2009 review for the US Preventive Services Task Force found evidence of benefit in those 40 to 70 years of age, and the organization recommends screening every two years in women 50 to 74 years of age. The medications tamoxifen or raloxifene may be used in an effort to prevent breast cancer in those who are at high risk of developing it. Preventive mastectomy, Surgical removal of both breasts is another preventive measure in some high risk women. In those who have been diagnosed with cancer, a number of treatments may be used, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, Hormonal therapy (oncology), hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy. Types of surgery vary from breast-conserving surgery to mastectomy. Breast reconstruction may take place at the time of surgery or at a later date. In those in whom the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, treatments are mostly aimed at improving quality of life and comfort.
Outcomes for breast cancer vary depending on the cancer type, the Cancer staging, extent of disease, and the person's age. The five-year survival rates in England and the United States are between 80 and 90%. In developing countries, five-year survival rates are lower. Worldwide, breast cancer is the leading type of cancer in women, accounting for 25% of all cases. In 2018, it resulted in two million new cases and 627,000 deaths. It is more common in developed countries, and is more than 100 times more common in women than Male breast cancer, in men. For transgender individuals on gender-affirming hormone therapy, breast cancer is 5 times more common in cisgender women than in transgender men, and 46 times more common in transgender women than in cisgender men.
 Most people with breast cancer have no symptoms at the time of diagnosis; their tumor is detected by a breast cancer screening test. For those who do have symptoms, a new breast lump, lump in the breast is most common. Most breast lumps are not cancer, though lumps that are painless, hard, and with irregular edges are more likely to be cancerous. Other symptoms include swelling or pain in the breast; dimpling, thickening, redness, or dryness of the breast skin; and pain, or inversion of the nipple. Some may experience unusual discharge from the breasts, or swelling of the lymph nodes under the arms or along the collar bone.
Some less common forms of breast cancer cause distinctive symptoms. Up to 5% of people with breast cancer have inflammatory breast cancer, where cancer cells block the lymph vessels of one breast, causing the breast to substantially swell and redden over three to six months. Up to 3% of people with breast cancer have Paget's disease of the breast, with eczema-like red, scaly irritation on the nipple and areola.
Advanced tumors can spread (metastasize) beyond the breast, most commonly to the bones, liver, lungs, and brain. Bone metastases can cause swelling, progressive bone pain, and weakening of the bones that leads to bone fracture, fractures. Liver metastases can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and skin problems – rash, itchy skin, or yellowing of the skin (jaundice). Those with lung metastases experience chest pain, shortness of breath, and regular coughing. Metastases in the brain can cause persistent headache, seizures, nausea, vomiting, and disruptions to the affected person's speech, vision, memory, and regular behavior.
Most people with breast cancer have no symptoms at the time of diagnosis; their tumor is detected by a breast cancer screening test. For those who do have symptoms, a new breast lump, lump in the breast is most common. Most breast lumps are not cancer, though lumps that are painless, hard, and with irregular edges are more likely to be cancerous. Other symptoms include swelling or pain in the breast; dimpling, thickening, redness, or dryness of the breast skin; and pain, or inversion of the nipple. Some may experience unusual discharge from the breasts, or swelling of the lymph nodes under the arms or along the collar bone.
Some less common forms of breast cancer cause distinctive symptoms. Up to 5% of people with breast cancer have inflammatory breast cancer, where cancer cells block the lymph vessels of one breast, causing the breast to substantially swell and redden over three to six months. Up to 3% of people with breast cancer have Paget's disease of the breast, with eczema-like red, scaly irritation on the nipple and areola.
Advanced tumors can spread (metastasize) beyond the breast, most commonly to the bones, liver, lungs, and brain. Bone metastases can cause swelling, progressive bone pain, and weakening of the bones that leads to bone fracture, fractures. Liver metastases can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and skin problems – rash, itchy skin, or yellowing of the skin (jaundice). Those with lung metastases experience chest pain, shortness of breath, and regular coughing. Metastases in the brain can cause persistent headache, seizures, nausea, vomiting, and disruptions to the affected person's speech, vision, memory, and regular behavior.
 Breast cancer screening refers to testing otherwise-healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to diagnose breast tumors early when treatments are more successful. The most common screening test for breast cancer is low-dose X-ray imaging of the breast, called mammography. Each breast is pressed between two plates and imaged. Tumors can appear unusually dense within the breast, distort the shape of surrounding tissue, or cause small dense flecks called microcalcifications. Radiologists generally report mammogram results on a standardized scale – the six-point Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is the most common globally – where a higher number corresponds to a greater risk of a cancerous tumor.
A mammogram also reveals breast density; dense breast tissue appears opaque on a mammogram and can obscure tumors. BI-RADS categorizes breast density into four categories. Mammography can detect around 90% of breast tumors in the least dense breasts (called "fatty" breasts), but just 60% in the most dense breasts (called "extremely dense"). Women with particularly dense breasts can instead be screened by ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or tomosynthesis, all of which more sensitively detect breast tumors.
Breast cancer screening refers to testing otherwise-healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to diagnose breast tumors early when treatments are more successful. The most common screening test for breast cancer is low-dose X-ray imaging of the breast, called mammography. Each breast is pressed between two plates and imaged. Tumors can appear unusually dense within the breast, distort the shape of surrounding tissue, or cause small dense flecks called microcalcifications. Radiologists generally report mammogram results on a standardized scale – the six-point Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is the most common globally – where a higher number corresponds to a greater risk of a cancerous tumor.
A mammogram also reveals breast density; dense breast tissue appears opaque on a mammogram and can obscure tumors. BI-RADS categorizes breast density into four categories. Mammography can detect around 90% of breast tumors in the least dense breasts (called "fatty" breasts), but just 60% in the most dense breasts (called "extremely dense"). Women with particularly dense breasts can instead be screened by ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or tomosynthesis, all of which more sensitively detect breast tumors.
 Regular screening mammography reduces breast cancer deaths by at least 20%. Most medical guidelines recommend annual screening mammograms for women aged 50–70. Screening also reduces breast cancer mortality in women aged 40–49, and some guidelines recommend annual screening in this age group as well. For women at high risk for developing breast cancer, most guidelines recommend adding MRI screening to mammography, to increase the chance of detecting potentially dangerous tumors. Regularly feeling one's own breasts for lumps or other abnormalities, called breast self-examination, does not reduce a person's chance of dying from breast cancer. Clinical breast exams, where a health professional feels the breasts for abnormalities, are common; whether they reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer is not known. Regular breast cancer screening is commonplace in most wealthy nations, but remains uncommon in the world's poorer countries.
Regular screening mammography reduces breast cancer deaths by at least 20%. Most medical guidelines recommend annual screening mammograms for women aged 50–70. Screening also reduces breast cancer mortality in women aged 40–49, and some guidelines recommend annual screening in this age group as well. For women at high risk for developing breast cancer, most guidelines recommend adding MRI screening to mammography, to increase the chance of detecting potentially dangerous tumors. Regularly feeling one's own breasts for lumps or other abnormalities, called breast self-examination, does not reduce a person's chance of dying from breast cancer. Clinical breast exams, where a health professional feels the breasts for abnormalities, are common; whether they reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer is not known. Regular breast cancer screening is commonplace in most wealthy nations, but remains uncommon in the world's poorer countries.
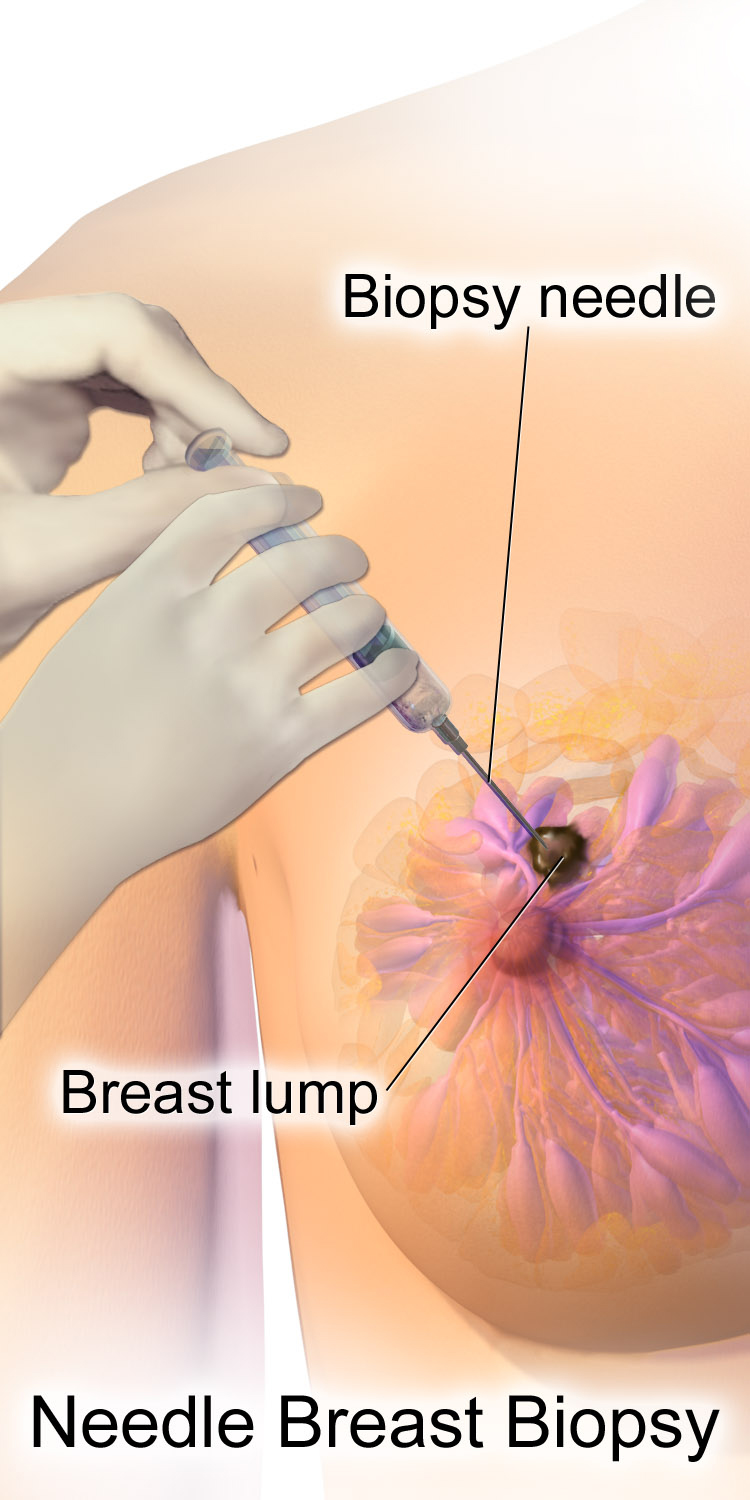 Those who have a suspected tumor from a mammogram or physical exam first undergo additional imaging – typically a second "diagnostic" mammogram and ultrasound – to confirm its presence and location. A breast biopsy, biopsy is then taken of the suspected tumor. Breast biopsy is typically done by core needle biopsy, with a hollow needle used to collect tissue from the area of interest. Suspected tumors that appear to be filled with fluid are often instead sampled by fine-needle aspiration. Around 10–20% of breast biopsies are positive for cancer. Most biopsied breast masses are instead caused by fibrocystic breast changes, a term that encompasses benign pockets of fluid, cell growth, or fibrous tissue.
Those who have a suspected tumor from a mammogram or physical exam first undergo additional imaging – typically a second "diagnostic" mammogram and ultrasound – to confirm its presence and location. A breast biopsy, biopsy is then taken of the suspected tumor. Breast biopsy is typically done by core needle biopsy, with a hollow needle used to collect tissue from the area of interest. Suspected tumors that appear to be filled with fluid are often instead sampled by fine-needle aspiration. Around 10–20% of breast biopsies are positive for cancer. Most biopsied breast masses are instead caused by fibrocystic breast changes, a term that encompasses benign pockets of fluid, cell growth, or fibrous tissue.
File:Invasive Ductal Carcinoma 40x.jpg, High-grade invasive ductal carcinoma, with minimal tubule formation, marked pleomorphism (cytology), pleomorphism, and prominent Breast cancer classification#Mitotic count, mitoses, 40x field
File:Mamma-CA.jpg, F-18 FDG PET/CT: A breast cancer metastasis to the right scapula
File:Diagram showing stage T1 breast cancer CRUK 244.svg, Stage T1 breast cancer
File:Diagram showing stage T2 breast cancer CRUK 252.svg, Stage T2 breast cancer
File:Diagram showing stage T3 breast cancer CRUK 259.svg, Stage T3 breast cancer
File:Stage 4 of Breast Cancer.jpg, Metastatic or stage 4 breast cancer
 Those whose tumors have not spread beyond the breast often undergo surgery to remove the tumor and some surrounding breast tissue. The surgery method is typically chosen to spare as much healthy breast tissue as possible, removing just the tumor (lumpectomy) or a larger part of the breast (partial mastectomy). Those with large or multiple tumors, high genetic risk of subsequent cancers, or who are unable to receive radiotherapy, radiation therapy may instead opt for full removal of the affected breast(s) (full mastectomy). To reduce the risk of cancer spreading, women will often have the nearest lymph node removed in a procedure called sentinel lymph node biopsy. Dye is injected near the tumor site, and several hours later the lymph node the dye accumulates in is removed.
After surgery, many undergo radiotherapy to decrease the chance of cancer recurrence. Those who had lumpectomies receive radiation to the whole breast. Those who had a mastectomy and are at elevated risk of tumor spread – tumor greater than five centimeters wide, or cancerous cells in nearby lymph nodes – receive radiation to the mastectomy scar and chest wall. If cancerous cells have spread to nearby lymph nodes, those lymph nodes will be irradiated as well. Radiation is typically given five days per week, for up to seven weeks. Radiotherapy for breast cancer is typically delivered via external beam radiotherapy, where a device focuses radiation beams onto the targeted parts of the body. Instead, some undergo brachytherapy, where radioactive material is placed into a device inserted at the surgical site the tumor was removed from. Fresh radioactive material is added twice a day for five days, then the device is removed. Surgery plus radiation typically eliminates a person's breast tumor. Less than 5% of those treated have their breast tumor grow back. After surgery and radiation, the breast can be breast reconstruction, surgically reconstructed, either by adding a breast implant or transferring excess tissue from another part of the body.
Chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurring in the next ten years by around a third. However, 1-2% of those on chemotherapy experience life-threatening or permanent side effects. To balance these benefits and risks, chemotherapy is typically offered to those with a higher risk of cancer recurrence. There is no established risk cutoff for offering chemotherapy; determining who should receive chemotherapy is controversial. Chemotherapy drugs are typically given in two- to three-week cycles, with periods of drug treatment interspersed with rest periods to recover from the therapies' side effects. Four to six cycles are given in total. Many classes of chemotherapeutic agents are effective for breast cancer treatment, including the Alkylating antineoplastic agent, DNA alkylating drugs (cyclophosphamide), anthracyclines (doxorubicin and epirubicin), antimetabolites (fluorouracil, capecitabine, and methotrexate), taxanes (docetaxel and paclitaxel), and platinum-based chemotherapy, platinum-based chemotherapies (cisplatin and carboplatin).
Chemotherapies from different classes are typically given in combination, with particular chemotherapy drugs selected based on the affected person's health and the different chemotherapeutics' side effects. Anthrocyclines and cyclophosphamide cause leukemia in up to 1% of those treated. Anthrocyclines also cause congestive heart failure in around 1% of people treated. Taxanes cause peripheral neuropathy, which is permanent in up to 5% of those treated. The same chemotherapy agents can be given before surgery – called neoadjuvant therapy – to shrink tumors, making them easier to safely remove.
For those whose tumors are HER2-positive, adding the HER2-targeted antibody trastuzumab to chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurrence and death by at least a third. Trastuzumab is given weekly or every three weeks for twelve months. Adding a second HER2-targeted antibody, pertuzumab slightly enhances treatment efficacy. In rare cases, trastuzumab can disrupt heart function, and so it is typically not given in conjunction with anthracyclines, which can also damage the heart.
After their chemotherapy course, those whose tumors are ER-positive or PR-positive benefit from endocrine therapy, which reduces the levels of estrogens and progesterones that hormone receptor-positive breast cancers require to survive. Tamoxifen treatment blocks the ER in the breast and some other tissues, and reduces the risk of breast cancer death by around 40% over the next ten years. Chemically blocking estrogen production with GnRH-targeted drugs (goserelin, leuprolide, or triptorelin) and aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane) slightly improves survival, but has more severe side effects. Side effects of estrogen depletion include hot flashes, vaginal discomfort, and muscle and joint pain. Endocrine therapy is typically recommended for at least five years after surgery and chemotherapy, and is sometimes continued for 10 years or longer.
Women with breast cancer who had a lumpectomy or a mastectomy and kept their other breast have similar survival rates to those who had a double mastectomy. There seems to be no survival advantage to removing the other breast, with only a 7% chance of cancer occurring in the other breast over 20 years.
Those whose tumors have not spread beyond the breast often undergo surgery to remove the tumor and some surrounding breast tissue. The surgery method is typically chosen to spare as much healthy breast tissue as possible, removing just the tumor (lumpectomy) or a larger part of the breast (partial mastectomy). Those with large or multiple tumors, high genetic risk of subsequent cancers, or who are unable to receive radiotherapy, radiation therapy may instead opt for full removal of the affected breast(s) (full mastectomy). To reduce the risk of cancer spreading, women will often have the nearest lymph node removed in a procedure called sentinel lymph node biopsy. Dye is injected near the tumor site, and several hours later the lymph node the dye accumulates in is removed.
After surgery, many undergo radiotherapy to decrease the chance of cancer recurrence. Those who had lumpectomies receive radiation to the whole breast. Those who had a mastectomy and are at elevated risk of tumor spread – tumor greater than five centimeters wide, or cancerous cells in nearby lymph nodes – receive radiation to the mastectomy scar and chest wall. If cancerous cells have spread to nearby lymph nodes, those lymph nodes will be irradiated as well. Radiation is typically given five days per week, for up to seven weeks. Radiotherapy for breast cancer is typically delivered via external beam radiotherapy, where a device focuses radiation beams onto the targeted parts of the body. Instead, some undergo brachytherapy, where radioactive material is placed into a device inserted at the surgical site the tumor was removed from. Fresh radioactive material is added twice a day for five days, then the device is removed. Surgery plus radiation typically eliminates a person's breast tumor. Less than 5% of those treated have their breast tumor grow back. After surgery and radiation, the breast can be breast reconstruction, surgically reconstructed, either by adding a breast implant or transferring excess tissue from another part of the body.
Chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurring in the next ten years by around a third. However, 1-2% of those on chemotherapy experience life-threatening or permanent side effects. To balance these benefits and risks, chemotherapy is typically offered to those with a higher risk of cancer recurrence. There is no established risk cutoff for offering chemotherapy; determining who should receive chemotherapy is controversial. Chemotherapy drugs are typically given in two- to three-week cycles, with periods of drug treatment interspersed with rest periods to recover from the therapies' side effects. Four to six cycles are given in total. Many classes of chemotherapeutic agents are effective for breast cancer treatment, including the Alkylating antineoplastic agent, DNA alkylating drugs (cyclophosphamide), anthracyclines (doxorubicin and epirubicin), antimetabolites (fluorouracil, capecitabine, and methotrexate), taxanes (docetaxel and paclitaxel), and platinum-based chemotherapy, platinum-based chemotherapies (cisplatin and carboplatin).
Chemotherapies from different classes are typically given in combination, with particular chemotherapy drugs selected based on the affected person's health and the different chemotherapeutics' side effects. Anthrocyclines and cyclophosphamide cause leukemia in up to 1% of those treated. Anthrocyclines also cause congestive heart failure in around 1% of people treated. Taxanes cause peripheral neuropathy, which is permanent in up to 5% of those treated. The same chemotherapy agents can be given before surgery – called neoadjuvant therapy – to shrink tumors, making them easier to safely remove.
For those whose tumors are HER2-positive, adding the HER2-targeted antibody trastuzumab to chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurrence and death by at least a third. Trastuzumab is given weekly or every three weeks for twelve months. Adding a second HER2-targeted antibody, pertuzumab slightly enhances treatment efficacy. In rare cases, trastuzumab can disrupt heart function, and so it is typically not given in conjunction with anthracyclines, which can also damage the heart.
After their chemotherapy course, those whose tumors are ER-positive or PR-positive benefit from endocrine therapy, which reduces the levels of estrogens and progesterones that hormone receptor-positive breast cancers require to survive. Tamoxifen treatment blocks the ER in the breast and some other tissues, and reduces the risk of breast cancer death by around 40% over the next ten years. Chemically blocking estrogen production with GnRH-targeted drugs (goserelin, leuprolide, or triptorelin) and aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane) slightly improves survival, but has more severe side effects. Side effects of estrogen depletion include hot flashes, vaginal discomfort, and muscle and joint pain. Endocrine therapy is typically recommended for at least five years after surgery and chemotherapy, and is sometimes continued for 10 years or longer.
Women with breast cancer who had a lumpectomy or a mastectomy and kept their other breast have similar survival rates to those who had a double mastectomy. There seems to be no survival advantage to removing the other breast, with only a 7% chance of cancer occurring in the other breast over 20 years.
 Many breast cancer therapies have side effects that can be alleviated with appropriate supportive care. Chemotherapy causes alopecia, hair loss, nausea, and vomiting in nearly everyone who receives it. Antiemetic drugs can alleviate nausea and vomiting; cooling the scalp with a cold cap during chemotherapy treatments may reduce hair loss. Many complain of Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, cognitive issues during chemotherapy treatment. These usually resolve within a few months of the end of chemotherapy treatment. Those on endocrine therapy often experience hot flashes, muscle and joint pain, and vaginal dryness/discomfort that can lead to issues having sex. Around half of women have their hot flashes alleviated by taking antidepressants; pain can be treated with physical therapy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; counseling and use of personal lubricants can improve sexual issues.
In women with non-metastatic breast cancer, psychological interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy can have positive effects on outcomes such as cognitive impairment, anxiety, depression and mood disturbance, and can also improve the quality of life. Physical activity interventions, yoga and meditation may also have beneficial effects on health related quality of life, cognitive impairment, anxiety, fitness and physical activity in women with breast cancer following adjuvant therapy.
Many breast cancer therapies have side effects that can be alleviated with appropriate supportive care. Chemotherapy causes alopecia, hair loss, nausea, and vomiting in nearly everyone who receives it. Antiemetic drugs can alleviate nausea and vomiting; cooling the scalp with a cold cap during chemotherapy treatments may reduce hair loss. Many complain of Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, cognitive issues during chemotherapy treatment. These usually resolve within a few months of the end of chemotherapy treatment. Those on endocrine therapy often experience hot flashes, muscle and joint pain, and vaginal dryness/discomfort that can lead to issues having sex. Around half of women have their hot flashes alleviated by taking antidepressants; pain can be treated with physical therapy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; counseling and use of personal lubricants can improve sexual issues.
In women with non-metastatic breast cancer, psychological interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy can have positive effects on outcomes such as cognitive impairment, anxiety, depression and mood disturbance, and can also improve the quality of life. Physical activity interventions, yoga and meditation may also have beneficial effects on health related quality of life, cognitive impairment, anxiety, fitness and physical activity in women with breast cancer following adjuvant therapy.
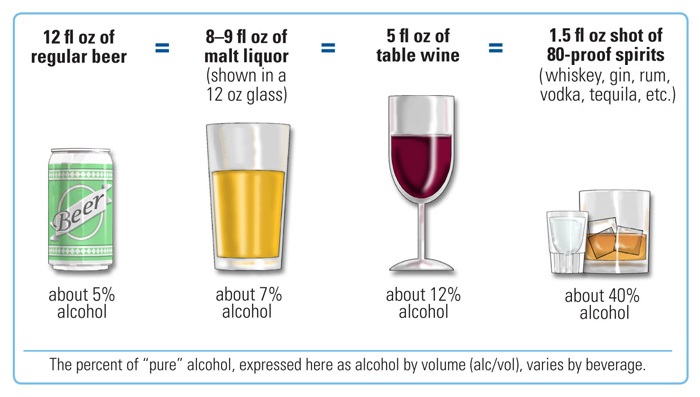 Drinking alcoholic beverages increases the risk of breast cancer, even among very light drinkers (women drinking less than half of one alcoholic drink per day). The risk is highest among heavy drinkers. Globally, about one in ten cases of breast cancer is caused by women drinking alcoholic beverages. Alcohol use is among the most common modifiable risk factors.
Obesity and diabetes increase the risk of breast cancer. A high body mass index (BMI) causes 7% of breast cancers while diabetes is responsible for 2%. At the same time the correlation between obesity and breast cancer is not at all linear. Studies show that those who rapidly gain weight in adulthood are at higher risk than those who have been overweight since childhood. Likewise, excess fat in the midriff seems to induce a higher risk than excess weight carried in the lower body. Dietary factors that may increase risk include a high-fat diet and obesity-related high cholesterol levels.
Dietary iodine deficiency may also play a role in the development of breast cancer.
Smoking tobacco appears to increase the risk of breast cancer, with the greater the amount smoked and the earlier in life that smoking began, the higher the risk. In those who are long-term smokers, the relative risk is increased by 35% to 50%.
A lack of physical activity has been linked to about 10% of cases. Sitting regularly for prolonged periods is associated with higher mortality from breast cancer. The risk is not negated by regular exercise, though it is lowered.
Actions to prevent breast cancer include not drinking alcoholic beverages, maintaining a healthy body composition, avoiding smoking and eating Healthy diet, healthy food. Combining all of these (leading the healthiest possible lifestyle) would make almost a quarter of breast cancer cases worldwide preventable. The remaining three-quarters of breast cancer cases cannot be prevented through lifestyle changes.
Other risk factors include circadian disruptions related to shift-work and routine late-night eating. A number of chemicals have also been linked, including polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and organic solvents. Although the radiation from mammography is a low dose, it is estimated that yearly screening from 40 to 80 years of age will cause approximately 225 cases of fatal breast cancer per million women screened.
Drinking alcoholic beverages increases the risk of breast cancer, even among very light drinkers (women drinking less than half of one alcoholic drink per day). The risk is highest among heavy drinkers. Globally, about one in ten cases of breast cancer is caused by women drinking alcoholic beverages. Alcohol use is among the most common modifiable risk factors.
Obesity and diabetes increase the risk of breast cancer. A high body mass index (BMI) causes 7% of breast cancers while diabetes is responsible for 2%. At the same time the correlation between obesity and breast cancer is not at all linear. Studies show that those who rapidly gain weight in adulthood are at higher risk than those who have been overweight since childhood. Likewise, excess fat in the midriff seems to induce a higher risk than excess weight carried in the lower body. Dietary factors that may increase risk include a high-fat diet and obesity-related high cholesterol levels.
Dietary iodine deficiency may also play a role in the development of breast cancer.
Smoking tobacco appears to increase the risk of breast cancer, with the greater the amount smoked and the earlier in life that smoking began, the higher the risk. In those who are long-term smokers, the relative risk is increased by 35% to 50%.
A lack of physical activity has been linked to about 10% of cases. Sitting regularly for prolonged periods is associated with higher mortality from breast cancer. The risk is not negated by regular exercise, though it is lowered.
Actions to prevent breast cancer include not drinking alcoholic beverages, maintaining a healthy body composition, avoiding smoking and eating Healthy diet, healthy food. Combining all of these (leading the healthiest possible lifestyle) would make almost a quarter of breast cancer cases worldwide preventable. The remaining three-quarters of breast cancer cases cannot be prevented through lifestyle changes.
Other risk factors include circadian disruptions related to shift-work and routine late-night eating. A number of chemicals have also been linked, including polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and organic solvents. Although the radiation from mammography is a low dose, it is estimated that yearly screening from 40 to 80 years of age will cause approximately 225 cases of fatal breast cancer per million women screened.

 The major causes of sporadic breast cancer are associated with hormone levels. Breast cancer is promoted by estrogen. This hormone activates the development of breast throughout puberty, menstrual cycles and pregnancy. The imbalance between estrogen and progesterone during the menstrual phases causes cell proliferation. Moreover, oxidative metabolites of estrogen can increase DNA damage and mutations. Repeated cycling and the impairment of repair process can transform a normal cell into pre-malignant and eventually malignant cell through mutation. During the pre-malignant stage, high proliferation of Stromal cell, stromal cells can be activated by estrogen to support the development of breast cancer. During the ligand binding activation, the ER can regulate gene expression by interacting with estrogen response elements within the promotor of specific genes. The expression and activation of ER due to lack of estrogen can be stimulated by extracellular signals. Interestingly, the ER directly binding with the several proteins, including growth factor receptors, can promote the expression of genes related to cell growth and survival.
Breast cancer, like other cancers, occurs because of an interaction between an environmental (external) factor and a genetically susceptible host. Normal cells divide as many times as needed, and stop. They attach to other cells and stay in place in tissues. Cells become cancerous when they lose their ability to stop dividing, to attach to other cells, to stay where they belong, and to die at the proper time.
Normal cells will self-destruct (apoptosis, programmed cell death) when they are no longer needed. Until then, cells are protected from programmed death by several protein clusters and pathways. One of the protective pathways is the PI3K/AKT pathway; another is the Ras (protein), RAS/Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, MEK/Extracellular signal-regulated kinases, ERK pathway. Sometimes the genes along these protective pathways are mutated in a way that turns them permanently "on", rendering the cell incapable of self-destructing when it is no longer needed. This is one of the steps that causes cancer in combination with other mutations. Normally, the PTEN (gene), ''PTEN'' protein turns off the PI3K/AKT pathway when the cell is ready for programmed cell death. In some breast cancers, the gene for the ''PTEN'' protein is mutated, so the PI3K/AKT pathway is stuck in the "on" position, and the cancer cell does not self-destruct.
Mutations that can lead to breast cancer have been experimentally linked to estrogen exposure. Additionally, G-protein coupled estrogen receptors have been associated with various cancers of the female reproductive system including breast cancer.
Abnormal growth factor signaling in the interaction between stromal cells and epithelial cells can facilitate malignant cell growth. In breast adipose tissue, overexpression of leptin leads to increased cell proliferation and cancer.
Some mutations associated with cancer, such as p53, ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'', occur in mechanisms to correct errors in DNA. The inherited mutation in ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' genes can interfere with repair of Crosslinking of DNA, DNA crosslinks and double-strand breaks (known functions of the encoded protein). These carcinogens cause DNA damage such as DNA crosslinks and double-strand breaks that often require repairs by pathways containing ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2''.
GATA-3 directly controls the expression of estrogen receptor (ER) and other genes associated with epithelial differentiation, and the loss of GATA-3 leads to loss of differentiation and poor prognosis due to cancer cell invasion and metastasis.
The major causes of sporadic breast cancer are associated with hormone levels. Breast cancer is promoted by estrogen. This hormone activates the development of breast throughout puberty, menstrual cycles and pregnancy. The imbalance between estrogen and progesterone during the menstrual phases causes cell proliferation. Moreover, oxidative metabolites of estrogen can increase DNA damage and mutations. Repeated cycling and the impairment of repair process can transform a normal cell into pre-malignant and eventually malignant cell through mutation. During the pre-malignant stage, high proliferation of Stromal cell, stromal cells can be activated by estrogen to support the development of breast cancer. During the ligand binding activation, the ER can regulate gene expression by interacting with estrogen response elements within the promotor of specific genes. The expression and activation of ER due to lack of estrogen can be stimulated by extracellular signals. Interestingly, the ER directly binding with the several proteins, including growth factor receptors, can promote the expression of genes related to cell growth and survival.
Breast cancer, like other cancers, occurs because of an interaction between an environmental (external) factor and a genetically susceptible host. Normal cells divide as many times as needed, and stop. They attach to other cells and stay in place in tissues. Cells become cancerous when they lose their ability to stop dividing, to attach to other cells, to stay where they belong, and to die at the proper time.
Normal cells will self-destruct (apoptosis, programmed cell death) when they are no longer needed. Until then, cells are protected from programmed death by several protein clusters and pathways. One of the protective pathways is the PI3K/AKT pathway; another is the Ras (protein), RAS/Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, MEK/Extracellular signal-regulated kinases, ERK pathway. Sometimes the genes along these protective pathways are mutated in a way that turns them permanently "on", rendering the cell incapable of self-destructing when it is no longer needed. This is one of the steps that causes cancer in combination with other mutations. Normally, the PTEN (gene), ''PTEN'' protein turns off the PI3K/AKT pathway when the cell is ready for programmed cell death. In some breast cancers, the gene for the ''PTEN'' protein is mutated, so the PI3K/AKT pathway is stuck in the "on" position, and the cancer cell does not self-destruct.
Mutations that can lead to breast cancer have been experimentally linked to estrogen exposure. Additionally, G-protein coupled estrogen receptors have been associated with various cancers of the female reproductive system including breast cancer.
Abnormal growth factor signaling in the interaction between stromal cells and epithelial cells can facilitate malignant cell growth. In breast adipose tissue, overexpression of leptin leads to increased cell proliferation and cancer.
Some mutations associated with cancer, such as p53, ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'', occur in mechanisms to correct errors in DNA. The inherited mutation in ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' genes can interfere with repair of Crosslinking of DNA, DNA crosslinks and double-strand breaks (known functions of the encoded protein). These carcinogens cause DNA damage such as DNA crosslinks and double-strand breaks that often require repairs by pathways containing ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2''.
GATA-3 directly controls the expression of estrogen receptor (ER) and other genes associated with epithelial differentiation, and the loss of GATA-3 leads to loss of differentiation and poor prognosis due to cancer cell invasion and metastasis.

 Because of its visibility, breast cancer was the form of cancer most often described in ancient documents. Because autopsies were rare, cancers of the internal organs were essentially invisible to ancient medicine. Breast cancer, however, could be felt through the skin, and in its advanced state often developed into fungating lesions: the tumor would become necrotic (die from the inside, causing the tumor to appear to break up) and Ulcer (dermatology), ulcerate through the skin, weeping fetid, dark fluid.
The oldest discovered evidence of breast cancer is from Egypt and dates back 4200 years, to the Sixth Dynasty. The study of a woman's remains from the necropolis of Qubbet el-Hawa showed the typical destructive damage due to metastatic spread. The Edwin Smith Papyrus describes eight cases of tumors or ulcers of the breast that were treated by cauterization. The writing says about the disease, "There is no treatment." For centuries, physicians described similar cases in their practices, with the same conclusion. Ancient medicine, from the time of the Greeks through the 17th century, was based on humoralism, and thus believed that breast cancer was generally caused by imbalances in the fundamental fluids that controlled the body, especially an excess of black bile. Alternatively it was seen as divine punishment.
Mastectomy for breast cancer was performed at least as early as AD 548, when it was proposed by the court physician Aetios of Amida to Theodora (wife of Justinian I), Theodora. It was not until doctors achieved greater understanding of the circulatory system in the 17th century that they could link breast cancer's spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit. In the early 18th century the French surgeon Jean Louis Petit performed total mastectomies that included removing the axillary lymph nodes, as he recognized that this reduced recurrence. Petit's work built on the methods of the surgeon Bernard Peyrilhe, who in the 17th century additionally removed the pectoralis major, pectoral muscle underlying the breast, as he judged that this greatly improved the prognosis. But poor results and the considerable risk to the patient meant that physicians did not share the opinion of surgeons such as Nicolaes Tulp, who in the 17th century proclaimed "the sole remedy is a timely operation." The eminent surgeon Richard Wiseman (surgeon), Richard Wiseman documented in the mid-17th century that following 12 mastectomies, two patients died during the operation, eight patients died shortly after the operation from progressive cancer and only two of the 12 patients were cured. Physicians were conservative in the treatment they prescribed in the early stages of breast cancer. Patients were treated with a mixture of Detoxification (alternative medicine), detox purges, blood letting and traditional remedies that were supposed to lower acidity, such as the alkaline arsenic.
When in 1664 Anne of Austria was diagnosed with breast cancer, the initial treatment involved compresses saturated with Conium, hemlock juice. When the lumps increased the King's physician commenced a treatment with arsenic ointments. The royal patient died 1666 in atrocious pain. Each failing treatment for breast cancer led to the search for new treatments, spurring a market in remedies that were advertised and sold by quackery, quacks, herbalists, chemists and apothecaries. The lack of anesthesia and antiseptics made mastectomy a painful and dangerous ordeal. In the 18th century, a wide variety of anatomical discoveries were accompanied by new theories about the cause and growth of breast cancer. The investigative surgeon John Hunter (surgeon), John Hunter claimed that neural fluid generated breast cancer. Other surgeons proposed that milk within the mammary ducts led to cancerous growths. Theories about trauma to the breast as cause for malignant changes in breast tissue were advanced. The discovery of breast lumps and swellings fueled controversies about hard tumors and whether lumps were benign stages of cancer. Medical opinion about necessary immediate treatment varied. The surgeon Benjamin Bell advocated removal of the entire breast, even when only a portion was affected.
Because of its visibility, breast cancer was the form of cancer most often described in ancient documents. Because autopsies were rare, cancers of the internal organs were essentially invisible to ancient medicine. Breast cancer, however, could be felt through the skin, and in its advanced state often developed into fungating lesions: the tumor would become necrotic (die from the inside, causing the tumor to appear to break up) and Ulcer (dermatology), ulcerate through the skin, weeping fetid, dark fluid.
The oldest discovered evidence of breast cancer is from Egypt and dates back 4200 years, to the Sixth Dynasty. The study of a woman's remains from the necropolis of Qubbet el-Hawa showed the typical destructive damage due to metastatic spread. The Edwin Smith Papyrus describes eight cases of tumors or ulcers of the breast that were treated by cauterization. The writing says about the disease, "There is no treatment." For centuries, physicians described similar cases in their practices, with the same conclusion. Ancient medicine, from the time of the Greeks through the 17th century, was based on humoralism, and thus believed that breast cancer was generally caused by imbalances in the fundamental fluids that controlled the body, especially an excess of black bile. Alternatively it was seen as divine punishment.
Mastectomy for breast cancer was performed at least as early as AD 548, when it was proposed by the court physician Aetios of Amida to Theodora (wife of Justinian I), Theodora. It was not until doctors achieved greater understanding of the circulatory system in the 17th century that they could link breast cancer's spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit. In the early 18th century the French surgeon Jean Louis Petit performed total mastectomies that included removing the axillary lymph nodes, as he recognized that this reduced recurrence. Petit's work built on the methods of the surgeon Bernard Peyrilhe, who in the 17th century additionally removed the pectoralis major, pectoral muscle underlying the breast, as he judged that this greatly improved the prognosis. But poor results and the considerable risk to the patient meant that physicians did not share the opinion of surgeons such as Nicolaes Tulp, who in the 17th century proclaimed "the sole remedy is a timely operation." The eminent surgeon Richard Wiseman (surgeon), Richard Wiseman documented in the mid-17th century that following 12 mastectomies, two patients died during the operation, eight patients died shortly after the operation from progressive cancer and only two of the 12 patients were cured. Physicians were conservative in the treatment they prescribed in the early stages of breast cancer. Patients were treated with a mixture of Detoxification (alternative medicine), detox purges, blood letting and traditional remedies that were supposed to lower acidity, such as the alkaline arsenic.
When in 1664 Anne of Austria was diagnosed with breast cancer, the initial treatment involved compresses saturated with Conium, hemlock juice. When the lumps increased the King's physician commenced a treatment with arsenic ointments. The royal patient died 1666 in atrocious pain. Each failing treatment for breast cancer led to the search for new treatments, spurring a market in remedies that were advertised and sold by quackery, quacks, herbalists, chemists and apothecaries. The lack of anesthesia and antiseptics made mastectomy a painful and dangerous ordeal. In the 18th century, a wide variety of anatomical discoveries were accompanied by new theories about the cause and growth of breast cancer. The investigative surgeon John Hunter (surgeon), John Hunter claimed that neural fluid generated breast cancer. Other surgeons proposed that milk within the mammary ducts led to cancerous growths. Theories about trauma to the breast as cause for malignant changes in breast tissue were advanced. The discovery of breast lumps and swellings fueled controversies about hard tumors and whether lumps were benign stages of cancer. Medical opinion about necessary immediate treatment varied. The surgeon Benjamin Bell advocated removal of the entire breast, even when only a portion was affected.
 Breast cancer was uncommon until the 19th century, when improvements in sanitation and control of deadly infectious diseases resulted in dramatic increases in lifespan. Previously, most women had died too young to have developed breast cancer. In 1878, an article in ''Scientific American'' described historical treatment by pressure intended to induce local ischemia in cases when surgical removal were not possible. William Stewart Halsted started performing radical mastectomies in 1882, helped greatly by advances in general surgical technology, such as aseptic technique and anesthesia. The Halsted radical mastectomy often involved removing both breasts, associated lymph nodes, and the underlying chest muscles. This often led to long-term pain and disability, but was seen as necessary to prevent the cancer from recurring. Before the advent of the Halsted radical mastectomy, 20-year survival rates were only 10%; Halsted's surgery raised that rate to 50%.
Cancer staging, Breast cancer staging systems were developed in the 1920s and 1930s to determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. The first case-controlled study on breast cancer epidemiology was done by Janet Lane-Claypon, who published a comparative study in 1926 of 500 breast cancer cases and 500 controls of the same background and lifestyle for the British Ministry of Health. Radical mastectomies remained the standard of care in the USA until the 1970s, but in Europe, breast-sparing procedures, often followed by radiation therapy, were generally adopted in the 1950s. In 1955 George Crile Jr. published ''Cancer and Common Sense'' arguing that cancer patients needed to understand available treatment options. Crile became a close friend of the environmentalist Rachel Carson, who had undergone a Halsted radical mastectomy in 1960 to treat her malign breast cancer. The US oncologist Jerome Urban promoted super radical mastectomies, taking even more tissue, until 1963, when the ten-year survival rates proved equal to the less-damaging radical mastectomy. Carson died in 1964 and Crile went on to published a wide variety of articles, both in the popular press and in medical journals, challenging the widespread use of the Halsted radical mastectomy. In 1973 Crile published ''What Women Should Know About the Breast Cancer Controversy''. When in 1974 Betty Ford was diagnosed with breast cancer, the options for treating breast cancer were openly discussed in the press. During the 1970s, a new understanding of metastasis led to perceiving cancer as a systemic illness as well as a localized one, and more sparing procedures were developed that proved equally effective.
In the 1980s and 1990s, thousands of women who had successfully completed standard treatment then demanded and received high-dose bone marrow transplants, thinking this would lead to better long-term survival. However, it proved completely ineffective, and 15–20% of women died because of the brutal treatment. The 1995 reports from the Nurses' Health Study and the 2002 conclusions of the Women's Health Initiative trial conclusively proved that Hormone replacement therapy, HRT significantly increased the incidence of breast cancer.
Breast cancer was uncommon until the 19th century, when improvements in sanitation and control of deadly infectious diseases resulted in dramatic increases in lifespan. Previously, most women had died too young to have developed breast cancer. In 1878, an article in ''Scientific American'' described historical treatment by pressure intended to induce local ischemia in cases when surgical removal were not possible. William Stewart Halsted started performing radical mastectomies in 1882, helped greatly by advances in general surgical technology, such as aseptic technique and anesthesia. The Halsted radical mastectomy often involved removing both breasts, associated lymph nodes, and the underlying chest muscles. This often led to long-term pain and disability, but was seen as necessary to prevent the cancer from recurring. Before the advent of the Halsted radical mastectomy, 20-year survival rates were only 10%; Halsted's surgery raised that rate to 50%.
Cancer staging, Breast cancer staging systems were developed in the 1920s and 1930s to determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. The first case-controlled study on breast cancer epidemiology was done by Janet Lane-Claypon, who published a comparative study in 1926 of 500 breast cancer cases and 500 controls of the same background and lifestyle for the British Ministry of Health. Radical mastectomies remained the standard of care in the USA until the 1970s, but in Europe, breast-sparing procedures, often followed by radiation therapy, were generally adopted in the 1950s. In 1955 George Crile Jr. published ''Cancer and Common Sense'' arguing that cancer patients needed to understand available treatment options. Crile became a close friend of the environmentalist Rachel Carson, who had undergone a Halsted radical mastectomy in 1960 to treat her malign breast cancer. The US oncologist Jerome Urban promoted super radical mastectomies, taking even more tissue, until 1963, when the ten-year survival rates proved equal to the less-damaging radical mastectomy. Carson died in 1964 and Crile went on to published a wide variety of articles, both in the popular press and in medical journals, challenging the widespread use of the Halsted radical mastectomy. In 1973 Crile published ''What Women Should Know About the Breast Cancer Controversy''. When in 1974 Betty Ford was diagnosed with breast cancer, the options for treating breast cancer were openly discussed in the press. During the 1970s, a new understanding of metastasis led to perceiving cancer as a systemic illness as well as a localized one, and more sparing procedures were developed that proved equally effective.
In the 1980s and 1990s, thousands of women who had successfully completed standard treatment then demanded and received high-dose bone marrow transplants, thinking this would lead to better long-term survival. However, it proved completely ineffective, and 15–20% of women died because of the brutal treatment. The 1995 reports from the Nurses' Health Study and the 2002 conclusions of the Women's Health Initiative trial conclusively proved that Hormone replacement therapy, HRT significantly increased the incidence of breast cancer.
 A pink ribbon is the most prominent symbol of breast cancer awareness. Pink ribbons, which can be made inexpensively, are sometimes sold as fundraisers, much like Poppy day#Poppies, poppies on Remembrance Day. They may be worn to honor those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, or to identify products that the manufacturer would like to sell to consumers that are interested in breast cancer. In the 1990s, breast cancer awareness campaigns were launched by US-based corporations. As part of these cause-related marketing campaigns, corporations donated to a variety of breast cancer initiatives for every pink ribbon product that was purchased. The ''Wall Street Journal'' noted that "the strong emotions provoked by breast cancer translate to a company's bottom line". While many US corporations donated to existing breast cancer initiatives, others such as Avon Products, Avon established their own breast cancer foundations on the back of pink ribbon products.
Wearing or displaying a pink ribbon has been criticized by the opponents of this practice as a kind of slacktivism, because it has no practical positive effect. It has also been criticized as hypocrisy, because some people wear the pink ribbon to show good will towards women with breast cancer, but then oppose these women's practical goals, like patient rights and anti-pollution legislation. Critics say that the feel-good nature of pink ribbons and pink consumption distracts society from the lack of progress on preventing and curing breast cancer. It is also criticized for reinforcing gender stereotypes and objectifying women and their breasts. Breast Cancer Action launched the "Think Before You Pink" campaign in 2002 against Pinkwashing (breast cancer), pinkwashing, to target businesses that have co-opted the pink campaign to promote products that cause breast cancer, such as alcoholic beverages.
A pink ribbon is the most prominent symbol of breast cancer awareness. Pink ribbons, which can be made inexpensively, are sometimes sold as fundraisers, much like Poppy day#Poppies, poppies on Remembrance Day. They may be worn to honor those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, or to identify products that the manufacturer would like to sell to consumers that are interested in breast cancer. In the 1990s, breast cancer awareness campaigns were launched by US-based corporations. As part of these cause-related marketing campaigns, corporations donated to a variety of breast cancer initiatives for every pink ribbon product that was purchased. The ''Wall Street Journal'' noted that "the strong emotions provoked by breast cancer translate to a company's bottom line". While many US corporations donated to existing breast cancer initiatives, others such as Avon Products, Avon established their own breast cancer foundations on the back of pink ribbon products.
Wearing or displaying a pink ribbon has been criticized by the opponents of this practice as a kind of slacktivism, because it has no practical positive effect. It has also been criticized as hypocrisy, because some people wear the pink ribbon to show good will towards women with breast cancer, but then oppose these women's practical goals, like patient rights and anti-pollution legislation. Critics say that the feel-good nature of pink ribbons and pink consumption distracts society from the lack of progress on preventing and curing breast cancer. It is also criticized for reinforcing gender stereotypes and objectifying women and their breasts. Breast Cancer Action launched the "Think Before You Pink" campaign in 2002 against Pinkwashing (breast cancer), pinkwashing, to target businesses that have co-opted the pink campaign to promote products that cause breast cancer, such as alcoholic beverages.
Signs and symptoms
Screening
 Breast cancer screening refers to testing otherwise-healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to diagnose breast tumors early when treatments are more successful. The most common screening test for breast cancer is low-dose X-ray imaging of the breast, called mammography. Each breast is pressed between two plates and imaged. Tumors can appear unusually dense within the breast, distort the shape of surrounding tissue, or cause small dense flecks called microcalcifications. Radiologists generally report mammogram results on a standardized scale – the six-point Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is the most common globally – where a higher number corresponds to a greater risk of a cancerous tumor.
A mammogram also reveals breast density; dense breast tissue appears opaque on a mammogram and can obscure tumors. BI-RADS categorizes breast density into four categories. Mammography can detect around 90% of breast tumors in the least dense breasts (called "fatty" breasts), but just 60% in the most dense breasts (called "extremely dense"). Women with particularly dense breasts can instead be screened by ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or tomosynthesis, all of which more sensitively detect breast tumors.
Breast cancer screening refers to testing otherwise-healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to diagnose breast tumors early when treatments are more successful. The most common screening test for breast cancer is low-dose X-ray imaging of the breast, called mammography. Each breast is pressed between two plates and imaged. Tumors can appear unusually dense within the breast, distort the shape of surrounding tissue, or cause small dense flecks called microcalcifications. Radiologists generally report mammogram results on a standardized scale – the six-point Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is the most common globally – where a higher number corresponds to a greater risk of a cancerous tumor.
A mammogram also reveals breast density; dense breast tissue appears opaque on a mammogram and can obscure tumors. BI-RADS categorizes breast density into four categories. Mammography can detect around 90% of breast tumors in the least dense breasts (called "fatty" breasts), but just 60% in the most dense breasts (called "extremely dense"). Women with particularly dense breasts can instead be screened by ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or tomosynthesis, all of which more sensitively detect breast tumors.
 Regular screening mammography reduces breast cancer deaths by at least 20%. Most medical guidelines recommend annual screening mammograms for women aged 50–70. Screening also reduces breast cancer mortality in women aged 40–49, and some guidelines recommend annual screening in this age group as well. For women at high risk for developing breast cancer, most guidelines recommend adding MRI screening to mammography, to increase the chance of detecting potentially dangerous tumors. Regularly feeling one's own breasts for lumps or other abnormalities, called breast self-examination, does not reduce a person's chance of dying from breast cancer. Clinical breast exams, where a health professional feels the breasts for abnormalities, are common; whether they reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer is not known. Regular breast cancer screening is commonplace in most wealthy nations, but remains uncommon in the world's poorer countries.
Regular screening mammography reduces breast cancer deaths by at least 20%. Most medical guidelines recommend annual screening mammograms for women aged 50–70. Screening also reduces breast cancer mortality in women aged 40–49, and some guidelines recommend annual screening in this age group as well. For women at high risk for developing breast cancer, most guidelines recommend adding MRI screening to mammography, to increase the chance of detecting potentially dangerous tumors. Regularly feeling one's own breasts for lumps or other abnormalities, called breast self-examination, does not reduce a person's chance of dying from breast cancer. Clinical breast exams, where a health professional feels the breasts for abnormalities, are common; whether they reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer is not known. Regular breast cancer screening is commonplace in most wealthy nations, but remains uncommon in the world's poorer countries.
Diagnosis
 Those who have a suspected tumor from a mammogram or physical exam first undergo additional imaging – typically a second "diagnostic" mammogram and ultrasound – to confirm its presence and location. A breast biopsy, biopsy is then taken of the suspected tumor. Breast biopsy is typically done by core needle biopsy, with a hollow needle used to collect tissue from the area of interest. Suspected tumors that appear to be filled with fluid are often instead sampled by fine-needle aspiration. Around 10–20% of breast biopsies are positive for cancer. Most biopsied breast masses are instead caused by fibrocystic breast changes, a term that encompasses benign pockets of fluid, cell growth, or fibrous tissue.
Those who have a suspected tumor from a mammogram or physical exam first undergo additional imaging – typically a second "diagnostic" mammogram and ultrasound – to confirm its presence and location. A breast biopsy, biopsy is then taken of the suspected tumor. Breast biopsy is typically done by core needle biopsy, with a hollow needle used to collect tissue from the area of interest. Suspected tumors that appear to be filled with fluid are often instead sampled by fine-needle aspiration. Around 10–20% of breast biopsies are positive for cancer. Most biopsied breast masses are instead caused by fibrocystic breast changes, a term that encompasses benign pockets of fluid, cell growth, or fibrous tissue.
Classification
Breast cancers are classified by several grading systems, each of which assesses a tumor characteristic that impacts a person's prognosis. First, a tumor is classified by the tissue it arises from, or the appearance of the tumor tissue under a microscope. Most breast cancers (85%) are ductal carcinoma – derived from the lining of the mammary ducts. 10% are lobular carcinoma – derived from the Mammary gland#Structure, mammary lobes – or mixed ductal/lobular carcinoma. Rarer types include Mucinous neoplasm, mucinous carcinoma (around 2.5% of cases; surrounded by mucin), tubular carcinoma (1.5%; full of small tubes of epithelial cells), medullary breast carcinoma, medullary carcinoma (1%; resembling "medullary" or middle-layer tissue), and Papillary carcinomas of the breast, papillary carcinoma (1%; covered in finger-like growths). Oftentimes a biopsy reveals cells that are cancerous but have not yet spread beyond their original location. This condition, called carcinoma in situ, is often considered "precancerous" rather than a dangerous cancer itself. Those with ductal carcinoma in situ (in the mammary ducts) are at increased risk for developing true invasive breast cancer – around a third develop breast cancer within five years. Lobular carcinoma in situ (in the mammary lobes) rarely causes a noticeable lump, and is often found incidentally during a biopsy for another reason. It is commonly spread throughout both breasts. Those with lobular carcinoma in situ also have an increased risk of developing breast cancer – around 1% develop breast cancer each year. However, their risk of dying of breast cancer is no higher than the rest of the population. Invasive tumor tissue is assigned a Grading (tumors), grade based on how distinct it appears from healthy breast. Breast tumors are graded on three features: the proportion of cancer cells that form tubules, the appearance of the cell nucleus, and how many cells are actively replicating. Each feature is scored on a three-point scale, with a higher score indicating less healthy looking tissue. A grade is assigned based on the sum of the three scores. Combined scores of 3, 4, or 5 represent grade 1, a slower-growing cancer. Scores of 6 or 7 represent grade 2. Scores of 8 or 9 represent grade 3, a faster-growing, more aggressive cancer. In addition to grading, tumor biopsy samples are tested by immunohistochemistry to determine if the tissue contains the proteins estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). Tumors containing either ER or PR are called "hormone receptor-positive" and can be treated with hormone therapies. Around 15 to 20% of tumors contain HER2; these can be treated with HER2-targeted therapies. The remainder that do not contain ER, PR, or HER2 are called "triple-negative" tumors, and tend to grow more quickly than other breast cancer types. After the tumor is evaluated, the breast cancer case is staged using the American Joint Committee on Cancer and Union for International Cancer Control's TNM staging system. Scores are assigned based on characteristics of the tumor (T), lymph nodes (N), and any metastases (M). T scores are determine by the size and extent of the tumor. Tumors less than 2 centimeters (cm) across are designated T1. Tumors 2–5 cm across are T2. A tumor greater than 5 cm across is T3. Tumors that extend to the chest wall or to the skin are designated T4. N scores are based on whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. N0 indicates no spread to the lymph nodes. N1 is for tumors that have spread to the closest axillary lymph nodes (called "level I" and "level II" axillary lymph nodes, in the armpit). N2 is for spread to the intramammary lymph nodes (on the other side of the breast, near the chest center), or for axillary lymph nodes that appear attached to each other or to the tissue around them (a sign of more severely affected tissue). N3 designates tumors that have spread to the highest axillary lymph nodes (called "level 3" axillary lymph nodes, above the armpit near the shoulder), to the supraclavicular lymph nodes (along the neck), or to both the axillary and intramammary lymph nodes. The M score is binary: M0 indicates no evidence metastases; M1 indicates metastases have been detected. TNM scores are then combined with tumor grades and ER/PR/HER2 status to calculate a cancer case's "prognostic stage group". Stage groups range from I (best prognosis) to IV (worst prognosis), with groups I, II, and III further divided into subgroups IA, IB, IIA, IIB, IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC. In general, tumors of higher T and N scores and higher grades are assigned higher stage groups. Tumors that are ER, PR, and HER2 positive are slightly lower stage group than those that are negative. Tumors that have metastasized are stage IV, regardless of the other scored characteristics.Management
The management of breast cancer depends on the affected person's health, the cancer case's molecular characteristics, and how far the tumor has spread at the time of diagnosis.Local tumors
 Those whose tumors have not spread beyond the breast often undergo surgery to remove the tumor and some surrounding breast tissue. The surgery method is typically chosen to spare as much healthy breast tissue as possible, removing just the tumor (lumpectomy) or a larger part of the breast (partial mastectomy). Those with large or multiple tumors, high genetic risk of subsequent cancers, or who are unable to receive radiotherapy, radiation therapy may instead opt for full removal of the affected breast(s) (full mastectomy). To reduce the risk of cancer spreading, women will often have the nearest lymph node removed in a procedure called sentinel lymph node biopsy. Dye is injected near the tumor site, and several hours later the lymph node the dye accumulates in is removed.
After surgery, many undergo radiotherapy to decrease the chance of cancer recurrence. Those who had lumpectomies receive radiation to the whole breast. Those who had a mastectomy and are at elevated risk of tumor spread – tumor greater than five centimeters wide, or cancerous cells in nearby lymph nodes – receive radiation to the mastectomy scar and chest wall. If cancerous cells have spread to nearby lymph nodes, those lymph nodes will be irradiated as well. Radiation is typically given five days per week, for up to seven weeks. Radiotherapy for breast cancer is typically delivered via external beam radiotherapy, where a device focuses radiation beams onto the targeted parts of the body. Instead, some undergo brachytherapy, where radioactive material is placed into a device inserted at the surgical site the tumor was removed from. Fresh radioactive material is added twice a day for five days, then the device is removed. Surgery plus radiation typically eliminates a person's breast tumor. Less than 5% of those treated have their breast tumor grow back. After surgery and radiation, the breast can be breast reconstruction, surgically reconstructed, either by adding a breast implant or transferring excess tissue from another part of the body.
Chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurring in the next ten years by around a third. However, 1-2% of those on chemotherapy experience life-threatening or permanent side effects. To balance these benefits and risks, chemotherapy is typically offered to those with a higher risk of cancer recurrence. There is no established risk cutoff for offering chemotherapy; determining who should receive chemotherapy is controversial. Chemotherapy drugs are typically given in two- to three-week cycles, with periods of drug treatment interspersed with rest periods to recover from the therapies' side effects. Four to six cycles are given in total. Many classes of chemotherapeutic agents are effective for breast cancer treatment, including the Alkylating antineoplastic agent, DNA alkylating drugs (cyclophosphamide), anthracyclines (doxorubicin and epirubicin), antimetabolites (fluorouracil, capecitabine, and methotrexate), taxanes (docetaxel and paclitaxel), and platinum-based chemotherapy, platinum-based chemotherapies (cisplatin and carboplatin).
Chemotherapies from different classes are typically given in combination, with particular chemotherapy drugs selected based on the affected person's health and the different chemotherapeutics' side effects. Anthrocyclines and cyclophosphamide cause leukemia in up to 1% of those treated. Anthrocyclines also cause congestive heart failure in around 1% of people treated. Taxanes cause peripheral neuropathy, which is permanent in up to 5% of those treated. The same chemotherapy agents can be given before surgery – called neoadjuvant therapy – to shrink tumors, making them easier to safely remove.
For those whose tumors are HER2-positive, adding the HER2-targeted antibody trastuzumab to chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurrence and death by at least a third. Trastuzumab is given weekly or every three weeks for twelve months. Adding a second HER2-targeted antibody, pertuzumab slightly enhances treatment efficacy. In rare cases, trastuzumab can disrupt heart function, and so it is typically not given in conjunction with anthracyclines, which can also damage the heart.
After their chemotherapy course, those whose tumors are ER-positive or PR-positive benefit from endocrine therapy, which reduces the levels of estrogens and progesterones that hormone receptor-positive breast cancers require to survive. Tamoxifen treatment blocks the ER in the breast and some other tissues, and reduces the risk of breast cancer death by around 40% over the next ten years. Chemically blocking estrogen production with GnRH-targeted drugs (goserelin, leuprolide, or triptorelin) and aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane) slightly improves survival, but has more severe side effects. Side effects of estrogen depletion include hot flashes, vaginal discomfort, and muscle and joint pain. Endocrine therapy is typically recommended for at least five years after surgery and chemotherapy, and is sometimes continued for 10 years or longer.
Women with breast cancer who had a lumpectomy or a mastectomy and kept their other breast have similar survival rates to those who had a double mastectomy. There seems to be no survival advantage to removing the other breast, with only a 7% chance of cancer occurring in the other breast over 20 years.
Those whose tumors have not spread beyond the breast often undergo surgery to remove the tumor and some surrounding breast tissue. The surgery method is typically chosen to spare as much healthy breast tissue as possible, removing just the tumor (lumpectomy) or a larger part of the breast (partial mastectomy). Those with large or multiple tumors, high genetic risk of subsequent cancers, or who are unable to receive radiotherapy, radiation therapy may instead opt for full removal of the affected breast(s) (full mastectomy). To reduce the risk of cancer spreading, women will often have the nearest lymph node removed in a procedure called sentinel lymph node biopsy. Dye is injected near the tumor site, and several hours later the lymph node the dye accumulates in is removed.
After surgery, many undergo radiotherapy to decrease the chance of cancer recurrence. Those who had lumpectomies receive radiation to the whole breast. Those who had a mastectomy and are at elevated risk of tumor spread – tumor greater than five centimeters wide, or cancerous cells in nearby lymph nodes – receive radiation to the mastectomy scar and chest wall. If cancerous cells have spread to nearby lymph nodes, those lymph nodes will be irradiated as well. Radiation is typically given five days per week, for up to seven weeks. Radiotherapy for breast cancer is typically delivered via external beam radiotherapy, where a device focuses radiation beams onto the targeted parts of the body. Instead, some undergo brachytherapy, where radioactive material is placed into a device inserted at the surgical site the tumor was removed from. Fresh radioactive material is added twice a day for five days, then the device is removed. Surgery plus radiation typically eliminates a person's breast tumor. Less than 5% of those treated have their breast tumor grow back. After surgery and radiation, the breast can be breast reconstruction, surgically reconstructed, either by adding a breast implant or transferring excess tissue from another part of the body.
Chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurring in the next ten years by around a third. However, 1-2% of those on chemotherapy experience life-threatening or permanent side effects. To balance these benefits and risks, chemotherapy is typically offered to those with a higher risk of cancer recurrence. There is no established risk cutoff for offering chemotherapy; determining who should receive chemotherapy is controversial. Chemotherapy drugs are typically given in two- to three-week cycles, with periods of drug treatment interspersed with rest periods to recover from the therapies' side effects. Four to six cycles are given in total. Many classes of chemotherapeutic agents are effective for breast cancer treatment, including the Alkylating antineoplastic agent, DNA alkylating drugs (cyclophosphamide), anthracyclines (doxorubicin and epirubicin), antimetabolites (fluorouracil, capecitabine, and methotrexate), taxanes (docetaxel and paclitaxel), and platinum-based chemotherapy, platinum-based chemotherapies (cisplatin and carboplatin).
Chemotherapies from different classes are typically given in combination, with particular chemotherapy drugs selected based on the affected person's health and the different chemotherapeutics' side effects. Anthrocyclines and cyclophosphamide cause leukemia in up to 1% of those treated. Anthrocyclines also cause congestive heart failure in around 1% of people treated. Taxanes cause peripheral neuropathy, which is permanent in up to 5% of those treated. The same chemotherapy agents can be given before surgery – called neoadjuvant therapy – to shrink tumors, making them easier to safely remove.
For those whose tumors are HER2-positive, adding the HER2-targeted antibody trastuzumab to chemotherapy reduces the chance of cancer recurrence and death by at least a third. Trastuzumab is given weekly or every three weeks for twelve months. Adding a second HER2-targeted antibody, pertuzumab slightly enhances treatment efficacy. In rare cases, trastuzumab can disrupt heart function, and so it is typically not given in conjunction with anthracyclines, which can also damage the heart.
After their chemotherapy course, those whose tumors are ER-positive or PR-positive benefit from endocrine therapy, which reduces the levels of estrogens and progesterones that hormone receptor-positive breast cancers require to survive. Tamoxifen treatment blocks the ER in the breast and some other tissues, and reduces the risk of breast cancer death by around 40% over the next ten years. Chemically blocking estrogen production with GnRH-targeted drugs (goserelin, leuprolide, or triptorelin) and aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane) slightly improves survival, but has more severe side effects. Side effects of estrogen depletion include hot flashes, vaginal discomfort, and muscle and joint pain. Endocrine therapy is typically recommended for at least five years after surgery and chemotherapy, and is sometimes continued for 10 years or longer.
Women with breast cancer who had a lumpectomy or a mastectomy and kept their other breast have similar survival rates to those who had a double mastectomy. There seems to be no survival advantage to removing the other breast, with only a 7% chance of cancer occurring in the other breast over 20 years.
Metastatic disease
For around 1 in 5 people treated for localized breast cancer, their tumors eventually spread to distant body sites – most commonly the nearby bones (67% of cases), liver (41%), lungs (37%), brain (13%), and peritoneum (10%). Those with metastatic disease can receive further chemotherapy, typically starting with capecitabine, an anthracycline, or a taxane. As one chemotherapy drug fails to control the cancer, another is started. In addition to the chemotherapeutic drugs used for localized cancer, gemcitabine, vinorelbine, etoposide, and epothilones are sometimes effective. Those with bone metastases benefit from regular infusion of the bone-strengthening agents denosumab and the bisphosphonates; infusion every three months reduces the chance of bone pain, fractures, and bone hypercalcemia. Up to 70% of those with ER-positive metastatic breast cancer benefit from additional endocrine therapy. Therapy options include those used in localized cancer, plus toremifene and fulvestrant, often used in combination with CDK inhibitor, CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, ribociclib, or abemaciclib). When one endocrine therapy fails, most will benefit from transitioning to a second one. Some respond to a third sequential therapy as well. Adding an mTOR inhibitor, everolimus, can further slow the tumors' progression. Those with HER2-positive metastatic disease can benefit from continued use of trastuzumab, alone, in combination with pertuzumab, or in combination with chemotherapy. Those whose tumors continue to progress on trastuzumab benefit from HER2-targeted antibody drug conjugates (HER2 antibodies linked to chemotherapy drugs) trastuzumab emtansine or trastuzumab deruxtecan. The HER2-targeted antibody margetuximab can also prolong survival, as can HER2 inhibitors lapatinib, neratinib, or tucatinib. Certain therapies are targeted at those whose tumors have particular gene mutations: Alpelisib or capivasertib for those with mutations activating the protein PIK3CA. PARP inhibitors (olaparib and talazoparib) for those with mutations that inactivate BRCA1 or BRCA2. The immune checkpoint inhibitor antibody atezolizumab for those whose tumors express PD-L1. And the similar immunotherapy pembrolizumab for those whose tumors have mutations in various DNA repair pathways.Supportive care
 Many breast cancer therapies have side effects that can be alleviated with appropriate supportive care. Chemotherapy causes alopecia, hair loss, nausea, and vomiting in nearly everyone who receives it. Antiemetic drugs can alleviate nausea and vomiting; cooling the scalp with a cold cap during chemotherapy treatments may reduce hair loss. Many complain of Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, cognitive issues during chemotherapy treatment. These usually resolve within a few months of the end of chemotherapy treatment. Those on endocrine therapy often experience hot flashes, muscle and joint pain, and vaginal dryness/discomfort that can lead to issues having sex. Around half of women have their hot flashes alleviated by taking antidepressants; pain can be treated with physical therapy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; counseling and use of personal lubricants can improve sexual issues.
In women with non-metastatic breast cancer, psychological interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy can have positive effects on outcomes such as cognitive impairment, anxiety, depression and mood disturbance, and can also improve the quality of life. Physical activity interventions, yoga and meditation may also have beneficial effects on health related quality of life, cognitive impairment, anxiety, fitness and physical activity in women with breast cancer following adjuvant therapy.
Many breast cancer therapies have side effects that can be alleviated with appropriate supportive care. Chemotherapy causes alopecia, hair loss, nausea, and vomiting in nearly everyone who receives it. Antiemetic drugs can alleviate nausea and vomiting; cooling the scalp with a cold cap during chemotherapy treatments may reduce hair loss. Many complain of Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, cognitive issues during chemotherapy treatment. These usually resolve within a few months of the end of chemotherapy treatment. Those on endocrine therapy often experience hot flashes, muscle and joint pain, and vaginal dryness/discomfort that can lead to issues having sex. Around half of women have their hot flashes alleviated by taking antidepressants; pain can be treated with physical therapy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; counseling and use of personal lubricants can improve sexual issues.
In women with non-metastatic breast cancer, psychological interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy can have positive effects on outcomes such as cognitive impairment, anxiety, depression and mood disturbance, and can also improve the quality of life. Physical activity interventions, yoga and meditation may also have beneficial effects on health related quality of life, cognitive impairment, anxiety, fitness and physical activity in women with breast cancer following adjuvant therapy.
Prognosis
Breast cancer prognosis varies widely depending on how far the tumor has spread at the time of diagnosis. Overall, 91% of women diagnosed with breast cancer Five-year survival rate, survive at least five years from diagnosis. Those whose tumor(s) are completely confined to the breast (nearly two thirds of cases) have the best prognoses – over 99% survive at least five years. Those whose tumors have metastasized to distant sites have relatively poor prognoses – 31% survive at least five years from the time of diagnosis. Triple-negative breast cancer (up to 15% of cases) and inflammatory breast cancer (up to 5% of cases) are particularly aggressive and have relatively poor prognoses. Those with triple-negative breast cancer have an overall five-year survival rate of 77% – 91% for those whose tumors are confined to the breast; 12% for those with metastases. Those with inflammatory breast cancer are diagnosed after the cancer has already spread to the skin of the breast. They have an overall five-year survival rate of 39%; 19% for those with metastases. The relatively rare tumors with tubular, mucinous, or medullary growth tend to have better prognoses. In addition to the factors that influence cancer staging, a person's age can also impact prognosis. Breast cancer before age 35 is rare, and is more likely to be associated with genetic predisposition to aggressive cancer. Conversely, breast cancer in those aged over 75 is associated with poorer prognosis.Risk factors
Hormonal
Up to 80% of the variation in breast cancer frequency across countries is due to differences in reproductive history that impact a woman's levels of female sex hormones (estrogens). Women who menarche, begin menstruating earlier (before age 12) or who undergo menopause later (after 51) are at increased risk of developing breast cancer. Women who give birth early in life are protected from breast cancer – someone who gives birth as a teenager has around a 70% lower risk of developing breast cancer than someone who does not have children. That protection wanes with higher maternal age at first birth, and disappears completely by age 35. Breastfeeding also reduces one's chance of developing breast cancer, with an approximately 4% reduction in breast cancer risk for every 12 months of breastfeeding experience. Those who lack functioning ovaries have reduced levels of estrogens, and therefore greatly reduced breast cancer risk. Hormone replacement therapy for treatment of menopause symptoms can also increase a woman's risk of developing breast cancer, though the effect depends on the type and duration of therapy. Combined progesterone/estrogen therapy increases breast cancer risk – approximately doubling one's risk after 6–7 years of treatment (though the same therapy decreases the risk of colorectal cancer). Hormone treatment with estrogen alone has no effect on breast cancer risk, but increases one's risk of developing endometrial cancer, and therefore is only given to women who have undergone hysterectomies. In the 1980s, the abortion–breast cancer hypothesis posited that induced abortion increased the risk of developing breast cancer. This hypothesis was the subject of extensive scientific inquiry, which concluded that neither miscarriages nor abortions are associated with a heightened risk for breast cancer. The use of hormonal birth control does not cause breast cancer for most women; if it has an effect, it is small (on the order of 0.01% per user–year), temporary, and offset by the users' significantly reduced risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers. Among those with a family history of breast cancer, use of modern oral contraceptives does not appear to affect the risk of breast cancer.Lifestyle
 Drinking alcoholic beverages increases the risk of breast cancer, even among very light drinkers (women drinking less than half of one alcoholic drink per day). The risk is highest among heavy drinkers. Globally, about one in ten cases of breast cancer is caused by women drinking alcoholic beverages. Alcohol use is among the most common modifiable risk factors.
Obesity and diabetes increase the risk of breast cancer. A high body mass index (BMI) causes 7% of breast cancers while diabetes is responsible for 2%. At the same time the correlation between obesity and breast cancer is not at all linear. Studies show that those who rapidly gain weight in adulthood are at higher risk than those who have been overweight since childhood. Likewise, excess fat in the midriff seems to induce a higher risk than excess weight carried in the lower body. Dietary factors that may increase risk include a high-fat diet and obesity-related high cholesterol levels.
Dietary iodine deficiency may also play a role in the development of breast cancer.
Smoking tobacco appears to increase the risk of breast cancer, with the greater the amount smoked and the earlier in life that smoking began, the higher the risk. In those who are long-term smokers, the relative risk is increased by 35% to 50%.
A lack of physical activity has been linked to about 10% of cases. Sitting regularly for prolonged periods is associated with higher mortality from breast cancer. The risk is not negated by regular exercise, though it is lowered.
Actions to prevent breast cancer include not drinking alcoholic beverages, maintaining a healthy body composition, avoiding smoking and eating Healthy diet, healthy food. Combining all of these (leading the healthiest possible lifestyle) would make almost a quarter of breast cancer cases worldwide preventable. The remaining three-quarters of breast cancer cases cannot be prevented through lifestyle changes.
Other risk factors include circadian disruptions related to shift-work and routine late-night eating. A number of chemicals have also been linked, including polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and organic solvents. Although the radiation from mammography is a low dose, it is estimated that yearly screening from 40 to 80 years of age will cause approximately 225 cases of fatal breast cancer per million women screened.
Drinking alcoholic beverages increases the risk of breast cancer, even among very light drinkers (women drinking less than half of one alcoholic drink per day). The risk is highest among heavy drinkers. Globally, about one in ten cases of breast cancer is caused by women drinking alcoholic beverages. Alcohol use is among the most common modifiable risk factors.
Obesity and diabetes increase the risk of breast cancer. A high body mass index (BMI) causes 7% of breast cancers while diabetes is responsible for 2%. At the same time the correlation between obesity and breast cancer is not at all linear. Studies show that those who rapidly gain weight in adulthood are at higher risk than those who have been overweight since childhood. Likewise, excess fat in the midriff seems to induce a higher risk than excess weight carried in the lower body. Dietary factors that may increase risk include a high-fat diet and obesity-related high cholesterol levels.
Dietary iodine deficiency may also play a role in the development of breast cancer.
Smoking tobacco appears to increase the risk of breast cancer, with the greater the amount smoked and the earlier in life that smoking began, the higher the risk. In those who are long-term smokers, the relative risk is increased by 35% to 50%.
A lack of physical activity has been linked to about 10% of cases. Sitting regularly for prolonged periods is associated with higher mortality from breast cancer. The risk is not negated by regular exercise, though it is lowered.
Actions to prevent breast cancer include not drinking alcoholic beverages, maintaining a healthy body composition, avoiding smoking and eating Healthy diet, healthy food. Combining all of these (leading the healthiest possible lifestyle) would make almost a quarter of breast cancer cases worldwide preventable. The remaining three-quarters of breast cancer cases cannot be prevented through lifestyle changes.
Other risk factors include circadian disruptions related to shift-work and routine late-night eating. A number of chemicals have also been linked, including polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and organic solvents. Although the radiation from mammography is a low dose, it is estimated that yearly screening from 40 to 80 years of age will cause approximately 225 cases of fatal breast cancer per million women screened.
Genetics
Around 10% of those with breast cancer have a family history of the disease or genetic factors that put them at higher risk. Women who have had a first-degree relative (mother or sister) diagnosed with breast cancer are at a 30–50% increased risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer themselves. In those with zero, one or two affected relatives, the risk of breast cancer before the age of 80 is 7.8%, 13.3%, and 21.1% with a subsequent mortality from the disease of 2.3%, 4.2%, and 7.6% respectively. Women with certain genetic variants are at higher risk of developing breast cancer. The most well known are variants of the BRCA mutation, BRCA genes ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2''. Women with pathogenic variants in either gene have around a 70% chance of developing breast cancer in their lifetime, as well as an approximately 33% chance of developing ovarian cancer. Pathogenic variants in ''PALB2'' – a gene whose product directly interacts with that of ''BRCA2'' – also increase breast cancer risk; a woman with such a variant has around a 50% increased risk of developing breast cancer. Variants in other tumor suppressor genes can also increase one's risk of developing breast cancer, namely ''p53'' (causes Li–Fraumeni syndrome), ''PTEN (gene), PTEN'' (causes Cowden syndrome), and ''PALB1''.Medical conditions
Breast changes like atypical ductal hyperplasia found in benign breast conditions such as fibrocystic breast changes, are correlated with an increased breast cancer risk. Diabetes mellitus might also increase the risk of breast cancer. Autoimmune diseases such as lupus erythematosus seem also to increase the risk for the acquisition of breast cancer. Women whose breasts have been exposed to substantial radiation doses before the age of 30 – typically due to repeated chest fluoroscopies or treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma – are at increased risk for developing breast cancer. Radioactive iodine therapy (used to treat thyroid disease) and radiation exposures after age 30 are not associated with breast cancer risk.Pathophysiology

Prevention

Lifestyle
Women can reduce their risk of breast cancer by maintaining a healthy weight, reducing alcohol use, increasing physical activity, and breastfeeding. These modifications might prevent 38% of breast cancers in the US, 42% in the UK, 28% in Brazil, and 20% in China. The benefits with moderate exercise such as brisk walking are seen at all age groups including postmenopausal women. High levels of physical activity reduce the risk of breast cancer by about 14%. Strategies that encourage regular physical activity and reduce obesity could also have other benefits, such as reduced risks of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. A study that included data from 130,957 women of European ancestry found "strong evidence that greater levels of physical activity and less sedentary time are likely to reduce breast cancer risk, with results generally consistent across breast cancer subtypes". The American Cancer Society and the American Society of Clinical Oncology advised in 2016 that people should eat a diet high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes. Eating foods rich in soluble fiber contributes to reducing breast cancer risk. High intake of citrus fruit has been associated with a 10% reduction in the risk of breast cancer. Marine omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids appear to reduce the risk. High consumption of soy-based foods may reduce risk.Preventive surgery
Removal of the breasts before breast cancer develops (called preventive mastectomy) reduces the risk of developing breast cancer by more than 95%. In women genetically predisposed to developing breast cancer, preventive mastectomy reduces their risk of dying from breast cancer. For those at normal risk, preventive mastectomy does not reduce their chance of dying, and so is generally not recommended. Removing the second breast in a person who has breast cancer (contralateral risk-reducing mastectomy or CRRM) may reduce the risk of cancer in the second breast, but it is not clear whether removing the second breast improves the chance of survival. An increasing number of women who test positive for faulty ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' genes choose to have Prophylactic surgery, risk-reducing surgery. The average waiting time for undergoing the procedure is two years, which is much longer than recommended.Medications
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) reduce the risk of breast cancer but increase the risk of thromboembolism and endometrial cancer. There is no overall change in the risk of death. They are thus not recommended for the prevention of breast cancer in women at average risk but it is recommended they be offered for those at high risk and over the age of 35. The benefit of breast cancer reduction continues for at least five years after stopping a course of treatment with these medications. Aromatase inhibitors (such as exemestane and anastrozole) may be more effective than SERMs (such as tamoxifen) at reducing breast cancer risk and they are not associated with an increased risk of endometrial cancer and thromboembolism.Epidemiology
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women in most countries, accounting for 30% of cancer cases in women. In 2022, an estimated 2.3 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer, and 670,000 died of the disease. The incidence (epidemiology), incidence of breast cancer is rising by around 3% per year, as populations in many countries are getting older. Rates of breast cancer vary across the world, but generally correlate with wealth. Around 1 in 12 women are diagnosed with breast cancer in wealthier countries, compared to 1 in 27 in lower income countries. Most of that difference is due to differences in menstrual and reproductive histories – women in wealthier countries tend to menarche, begin menstruating earlier and have children later, both factors that increase risk of developing breast cancer. People in lower income countries tend to have less access to breast cancer screening and treatments, and so breast cancer death rates tend to be higher. 1 in 71 women die of breast cancer in wealthy countries, while 1 in 48 die of the disease in lower income countries. Breast cancer predominantly affects women; less than 1% of those with breast cancer are men. Women can develop breast cancer as early as adolescence, but risk increases with age, and 75% of cases are in women over 50 years old. The risk over a woman's lifetime is approximately 1.5% at age 40, 3% at age 50, and more than 4% risk at age 70.History
 Because of its visibility, breast cancer was the form of cancer most often described in ancient documents. Because autopsies were rare, cancers of the internal organs were essentially invisible to ancient medicine. Breast cancer, however, could be felt through the skin, and in its advanced state often developed into fungating lesions: the tumor would become necrotic (die from the inside, causing the tumor to appear to break up) and Ulcer (dermatology), ulcerate through the skin, weeping fetid, dark fluid.
The oldest discovered evidence of breast cancer is from Egypt and dates back 4200 years, to the Sixth Dynasty. The study of a woman's remains from the necropolis of Qubbet el-Hawa showed the typical destructive damage due to metastatic spread. The Edwin Smith Papyrus describes eight cases of tumors or ulcers of the breast that were treated by cauterization. The writing says about the disease, "There is no treatment." For centuries, physicians described similar cases in their practices, with the same conclusion. Ancient medicine, from the time of the Greeks through the 17th century, was based on humoralism, and thus believed that breast cancer was generally caused by imbalances in the fundamental fluids that controlled the body, especially an excess of black bile. Alternatively it was seen as divine punishment.
Mastectomy for breast cancer was performed at least as early as AD 548, when it was proposed by the court physician Aetios of Amida to Theodora (wife of Justinian I), Theodora. It was not until doctors achieved greater understanding of the circulatory system in the 17th century that they could link breast cancer's spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit. In the early 18th century the French surgeon Jean Louis Petit performed total mastectomies that included removing the axillary lymph nodes, as he recognized that this reduced recurrence. Petit's work built on the methods of the surgeon Bernard Peyrilhe, who in the 17th century additionally removed the pectoralis major, pectoral muscle underlying the breast, as he judged that this greatly improved the prognosis. But poor results and the considerable risk to the patient meant that physicians did not share the opinion of surgeons such as Nicolaes Tulp, who in the 17th century proclaimed "the sole remedy is a timely operation." The eminent surgeon Richard Wiseman (surgeon), Richard Wiseman documented in the mid-17th century that following 12 mastectomies, two patients died during the operation, eight patients died shortly after the operation from progressive cancer and only two of the 12 patients were cured. Physicians were conservative in the treatment they prescribed in the early stages of breast cancer. Patients were treated with a mixture of Detoxification (alternative medicine), detox purges, blood letting and traditional remedies that were supposed to lower acidity, such as the alkaline arsenic.
When in 1664 Anne of Austria was diagnosed with breast cancer, the initial treatment involved compresses saturated with Conium, hemlock juice. When the lumps increased the King's physician commenced a treatment with arsenic ointments. The royal patient died 1666 in atrocious pain. Each failing treatment for breast cancer led to the search for new treatments, spurring a market in remedies that were advertised and sold by quackery, quacks, herbalists, chemists and apothecaries. The lack of anesthesia and antiseptics made mastectomy a painful and dangerous ordeal. In the 18th century, a wide variety of anatomical discoveries were accompanied by new theories about the cause and growth of breast cancer. The investigative surgeon John Hunter (surgeon), John Hunter claimed that neural fluid generated breast cancer. Other surgeons proposed that milk within the mammary ducts led to cancerous growths. Theories about trauma to the breast as cause for malignant changes in breast tissue were advanced. The discovery of breast lumps and swellings fueled controversies about hard tumors and whether lumps were benign stages of cancer. Medical opinion about necessary immediate treatment varied. The surgeon Benjamin Bell advocated removal of the entire breast, even when only a portion was affected.
Because of its visibility, breast cancer was the form of cancer most often described in ancient documents. Because autopsies were rare, cancers of the internal organs were essentially invisible to ancient medicine. Breast cancer, however, could be felt through the skin, and in its advanced state often developed into fungating lesions: the tumor would become necrotic (die from the inside, causing the tumor to appear to break up) and Ulcer (dermatology), ulcerate through the skin, weeping fetid, dark fluid.
The oldest discovered evidence of breast cancer is from Egypt and dates back 4200 years, to the Sixth Dynasty. The study of a woman's remains from the necropolis of Qubbet el-Hawa showed the typical destructive damage due to metastatic spread. The Edwin Smith Papyrus describes eight cases of tumors or ulcers of the breast that were treated by cauterization. The writing says about the disease, "There is no treatment." For centuries, physicians described similar cases in their practices, with the same conclusion. Ancient medicine, from the time of the Greeks through the 17th century, was based on humoralism, and thus believed that breast cancer was generally caused by imbalances in the fundamental fluids that controlled the body, especially an excess of black bile. Alternatively it was seen as divine punishment.
Mastectomy for breast cancer was performed at least as early as AD 548, when it was proposed by the court physician Aetios of Amida to Theodora (wife of Justinian I), Theodora. It was not until doctors achieved greater understanding of the circulatory system in the 17th century that they could link breast cancer's spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit. In the early 18th century the French surgeon Jean Louis Petit performed total mastectomies that included removing the axillary lymph nodes, as he recognized that this reduced recurrence. Petit's work built on the methods of the surgeon Bernard Peyrilhe, who in the 17th century additionally removed the pectoralis major, pectoral muscle underlying the breast, as he judged that this greatly improved the prognosis. But poor results and the considerable risk to the patient meant that physicians did not share the opinion of surgeons such as Nicolaes Tulp, who in the 17th century proclaimed "the sole remedy is a timely operation." The eminent surgeon Richard Wiseman (surgeon), Richard Wiseman documented in the mid-17th century that following 12 mastectomies, two patients died during the operation, eight patients died shortly after the operation from progressive cancer and only two of the 12 patients were cured. Physicians were conservative in the treatment they prescribed in the early stages of breast cancer. Patients were treated with a mixture of Detoxification (alternative medicine), detox purges, blood letting and traditional remedies that were supposed to lower acidity, such as the alkaline arsenic.
When in 1664 Anne of Austria was diagnosed with breast cancer, the initial treatment involved compresses saturated with Conium, hemlock juice. When the lumps increased the King's physician commenced a treatment with arsenic ointments. The royal patient died 1666 in atrocious pain. Each failing treatment for breast cancer led to the search for new treatments, spurring a market in remedies that were advertised and sold by quackery, quacks, herbalists, chemists and apothecaries. The lack of anesthesia and antiseptics made mastectomy a painful and dangerous ordeal. In the 18th century, a wide variety of anatomical discoveries were accompanied by new theories about the cause and growth of breast cancer. The investigative surgeon John Hunter (surgeon), John Hunter claimed that neural fluid generated breast cancer. Other surgeons proposed that milk within the mammary ducts led to cancerous growths. Theories about trauma to the breast as cause for malignant changes in breast tissue were advanced. The discovery of breast lumps and swellings fueled controversies about hard tumors and whether lumps were benign stages of cancer. Medical opinion about necessary immediate treatment varied. The surgeon Benjamin Bell advocated removal of the entire breast, even when only a portion was affected.
 Breast cancer was uncommon until the 19th century, when improvements in sanitation and control of deadly infectious diseases resulted in dramatic increases in lifespan. Previously, most women had died too young to have developed breast cancer. In 1878, an article in ''Scientific American'' described historical treatment by pressure intended to induce local ischemia in cases when surgical removal were not possible. William Stewart Halsted started performing radical mastectomies in 1882, helped greatly by advances in general surgical technology, such as aseptic technique and anesthesia. The Halsted radical mastectomy often involved removing both breasts, associated lymph nodes, and the underlying chest muscles. This often led to long-term pain and disability, but was seen as necessary to prevent the cancer from recurring. Before the advent of the Halsted radical mastectomy, 20-year survival rates were only 10%; Halsted's surgery raised that rate to 50%.
Cancer staging, Breast cancer staging systems were developed in the 1920s and 1930s to determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. The first case-controlled study on breast cancer epidemiology was done by Janet Lane-Claypon, who published a comparative study in 1926 of 500 breast cancer cases and 500 controls of the same background and lifestyle for the British Ministry of Health. Radical mastectomies remained the standard of care in the USA until the 1970s, but in Europe, breast-sparing procedures, often followed by radiation therapy, were generally adopted in the 1950s. In 1955 George Crile Jr. published ''Cancer and Common Sense'' arguing that cancer patients needed to understand available treatment options. Crile became a close friend of the environmentalist Rachel Carson, who had undergone a Halsted radical mastectomy in 1960 to treat her malign breast cancer. The US oncologist Jerome Urban promoted super radical mastectomies, taking even more tissue, until 1963, when the ten-year survival rates proved equal to the less-damaging radical mastectomy. Carson died in 1964 and Crile went on to published a wide variety of articles, both in the popular press and in medical journals, challenging the widespread use of the Halsted radical mastectomy. In 1973 Crile published ''What Women Should Know About the Breast Cancer Controversy''. When in 1974 Betty Ford was diagnosed with breast cancer, the options for treating breast cancer were openly discussed in the press. During the 1970s, a new understanding of metastasis led to perceiving cancer as a systemic illness as well as a localized one, and more sparing procedures were developed that proved equally effective.
In the 1980s and 1990s, thousands of women who had successfully completed standard treatment then demanded and received high-dose bone marrow transplants, thinking this would lead to better long-term survival. However, it proved completely ineffective, and 15–20% of women died because of the brutal treatment. The 1995 reports from the Nurses' Health Study and the 2002 conclusions of the Women's Health Initiative trial conclusively proved that Hormone replacement therapy, HRT significantly increased the incidence of breast cancer.
Breast cancer was uncommon until the 19th century, when improvements in sanitation and control of deadly infectious diseases resulted in dramatic increases in lifespan. Previously, most women had died too young to have developed breast cancer. In 1878, an article in ''Scientific American'' described historical treatment by pressure intended to induce local ischemia in cases when surgical removal were not possible. William Stewart Halsted started performing radical mastectomies in 1882, helped greatly by advances in general surgical technology, such as aseptic technique and anesthesia. The Halsted radical mastectomy often involved removing both breasts, associated lymph nodes, and the underlying chest muscles. This often led to long-term pain and disability, but was seen as necessary to prevent the cancer from recurring. Before the advent of the Halsted radical mastectomy, 20-year survival rates were only 10%; Halsted's surgery raised that rate to 50%.
Cancer staging, Breast cancer staging systems were developed in the 1920s and 1930s to determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. The first case-controlled study on breast cancer epidemiology was done by Janet Lane-Claypon, who published a comparative study in 1926 of 500 breast cancer cases and 500 controls of the same background and lifestyle for the British Ministry of Health. Radical mastectomies remained the standard of care in the USA until the 1970s, but in Europe, breast-sparing procedures, often followed by radiation therapy, were generally adopted in the 1950s. In 1955 George Crile Jr. published ''Cancer and Common Sense'' arguing that cancer patients needed to understand available treatment options. Crile became a close friend of the environmentalist Rachel Carson, who had undergone a Halsted radical mastectomy in 1960 to treat her malign breast cancer. The US oncologist Jerome Urban promoted super radical mastectomies, taking even more tissue, until 1963, when the ten-year survival rates proved equal to the less-damaging radical mastectomy. Carson died in 1964 and Crile went on to published a wide variety of articles, both in the popular press and in medical journals, challenging the widespread use of the Halsted radical mastectomy. In 1973 Crile published ''What Women Should Know About the Breast Cancer Controversy''. When in 1974 Betty Ford was diagnosed with breast cancer, the options for treating breast cancer were openly discussed in the press. During the 1970s, a new understanding of metastasis led to perceiving cancer as a systemic illness as well as a localized one, and more sparing procedures were developed that proved equally effective.
In the 1980s and 1990s, thousands of women who had successfully completed standard treatment then demanded and received high-dose bone marrow transplants, thinking this would lead to better long-term survival. However, it proved completely ineffective, and 15–20% of women died because of the brutal treatment. The 1995 reports from the Nurses' Health Study and the 2002 conclusions of the Women's Health Initiative trial conclusively proved that Hormone replacement therapy, HRT significantly increased the incidence of breast cancer.
Society and culture
Before the 20th century, breast cancer was feared and discussed in hushed tones, as if it were shameful. As little could be safely done with primitive surgical techniques, women tended to suffer silently rather than seeking care. When surgery advanced, and long-term survival rates improved, women began raising awareness of the disease and the possibility of successful treatment. The "Women's Field Army", run by the American Society for the Control of Cancer (later the American Cancer Society) during the 1930s and 1940s was one of the first organized campaigns. In 1952, the first peer-to-peer support group, called "Reach to Recovery", began providing post-mastectomy, in-hospital visits from women who had survived breast cancer. The breast cancer movement of the 1980s and 1990s developed out of the larger feminist movements and Women's health movement in the United States, women's health movement of the 20th century. This series of political and educational campaigns, partly inspired by the politically and socially effective AIDS awareness campaigns, resulted in the widespread acceptance of second opinions before surgery, less invasive surgical procedures, support groups, and other advances in care.Pink ribbon
Breast cancer culture
In her 2006 book ''Pink Ribbons, Inc.: Breast Cancer and the Politics of Philanthropy'' Samantha King claimed that breast cancer has been transformed from a serious disease and individual tragedy to a market-driven industry of survivorship and corporate sales pitch. In 2010 Gayle Sulik argued that the primary purposes or goals of breast cancer culture are to maintain breast cancer's dominance as the pre-eminent women's health issue, to promote the appearance that society is doing something effective about breast cancer, and to sustain and expand the social, political, and financial power of breast cancer activists. In the same year Barbara Ehrenreich published an opinion piece in ''Harper's Magazine'', lamenting that in breast cancer culture, breast cancer therapy is viewed as a rite of passage rather than a disease. To fit into this mold, the woman with breast cancer needs to normalize and feminize her appearance, and minimize the disruption that her health issues cause anyone else. Anger, sadness, and negativity must be silenced. As with most cultural models, people who conform to the model are given social status, in this case as cancer survivors. Women who reject the model are shunned, punished and shamed. The culture is criticized for treating adult women like little girls, as evidenced by "baby" toys such as pink teddy bears given to adult women.Emphasis
In 2009 the US science journalist Christie Aschwanden criticized that the emphasis on breast cancer screening may be harming women by subjecting them to unnecessary radiation, biopsies, and surgery. One-third of diagnosed breast cancers might recede on their own. Screening mammography efficiently finds non-life-threatening, asymptomatic breast cancers and precancers, even while overlooking serious cancers. According to the cancer researcher H. Gilbert Welch, screening mammography has taken the "brain-dead approach that says the best test is the one that finds the most cancers" rather than the one that finds dangerous cancers. In 2002 it was noted that as a result of breast cancer's high visibility, the statistical results can be misinterpreted, such as the claim that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lives – a claim that depends on the unrealistic assumption that no woman will die of any other disease before the age of 95. By 2010 the breast cancer survival rate in Europe was 91% at one years and 65% at five years. In the USA the five-year survival rate for localized breast cancer was 96.8%, while in cases of metastases it was only 20.6%. Because the prognosis for breast cancer was at this stage relatively favorable, compared to the prognosis for other cancers, breast cancer as cause of death among women was 13.9% of all cancer deaths. The second most common cause of death from cancer in women was lung cancer, the most common cancer worldwide for men and women. The improved survival rate made breast cancer the most prevalent cancer in the world. In 2010 an estimated 3.6 million women worldwide have had a breast cancer diagnosis in the past five years, while only 1.4 million male or female survivors from lung cancer were alive.Health disparities in breast cancer
There are ethnic disparities in the Mortality rate, mortality rates for breast cancer as well as in breast cancer treatment. Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer affecting women of every ethnic group in the United States. Breast cancer incidence among Black women aged 45 and older is higher than that of white women in the same age group. White women aged 60–84 have higher incidence rates of breast cancer than Black women. Despite this, Black women at every age are more likely to succumb to breast cancer. Breast cancer treatment has improved greatly over the years, but Black women are still less likely to obtain treatment compared to white women. Risk factors such as socioeconomic status, late-stage, or breast cancer at diagnosis, genetic differences in tumor subtypes, and differences in healthcare access all contribute to these disparities. Socioeconomic determinants affecting the disparity in breast cancer illness include poverty, culture, and social injustice. In Hispanic women, the incidence of breast cancer is lower than in non-Hispanic women, but is often diagnosed at a later stage than white women with larger tumors. Black women are usually diagnosed with breast cancer at a younger age than white women. The median age of diagnosis for Black women is 59, in comparison to 62 in White women. The incidence of breast cancer in Black women has increased by 0.4% per year since 1975 and 1.5% per year among Asian/Pacific Islander women since 1992. Incidence rates were stable for non-Hispanic White, Hispanics, and Native American women. The five-year survival rate is noted to be 81% in Black women and 92% in White women. Chinese and Japanese women have the highest survival rates. Poverty is a major driver for disparities related to breast cancer. Low-income women are less likely to undergo breast cancer screening and thus are more likely to have a late-stage diagnosis. Ensuring women of all ethnic groups receive equitable health care including breast screening can positively affect these disparities.Special populations
Men
Breast cancer is relatively uncommon in men, but it can occur. Typically, a breast tumor appears as a lump in the breast. Men who develop gynecomastia (enlargement of the breast tissue due to hormone imbalance) are at increased risk, as are men with disease-associated variations in the ''BRCA2'' gene, high exposure to estrogens, or men with Klinefelter syndrome (who have two copies of the X chromosome, and naturally high estrogen levels). Treatment typically involves surgery, followed by radiation if needed. Around 90% men's tumors are ER-positive, and are treated with endocrine therapy, typically tamoxifen. The disease course and prognosis is similar to that in women of similar age with similar disease characteristics.Pregnant women
Diagnosing breast cancer in pregnant women is often delayed as symptoms can be masked by pregnancy-related breast changes. The diagnostic path is the same as in non-pregnant women, except that radiography of the abdomen is avoided. Chemotherapy is avoided during the first trimester, but can be safely administered through the rest of the pregnancy term. anti-HER2 treatments and endocrine therapies are delayed until after delivery. These treatments given after delivery can cross into the breast milk, and so breast feeding is generally not possible. The prognosis for pregnant women with breast cancer is similar to non-pregnant women of similar age.Research
Treatments are being evaluated in clinical trials. This includes individual drugs, combinations of drugs, and surgical and radiation techniques Investigations include new types of targeted therapy, cancer vaccines, oncolytic virotherapy, gene therapy and immunotherapy. The latest research is reported annually at scientific meetings such as that of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, and the St. Gallen Oncology Conference in St. Gallen, Switzerland. These studies are reviewed by professional societies and other organizations, and formulated into guidelines for specific treatment groups and risk category. Fenretinide, a retinoid, is also being studied as a way to reduce the risk of breast cancer. In particular, combinations of ribociclib plus endocrine therapy have been the subject of clinical trials. A 2019 review found moderate certainty evidence that giving people antibiotics before breast cancer surgery helped to prevent Perioperative mortality, surgical site infection (SSI). Further study is required to determine the most effective antibiotic protocol and use in women undergoing immediate breast reconstruction. Andrographolide is the main bioactive compound found in the Andrographis paniculata plant, which is traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine and herbal medicine in Asia. This compound is known to have a variety of health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties. In recent years, attention has turned to the potential of andrographolide as an anticancer agent.Cryoablation
As of 2014 cryoablation is being studied to see if it could be a substitute for a lumpectomy in small cancers. There is tentative evidence in those with tumors less than 2 centimeters across. It may also be used in those in who surgery is not possible. Another review states that cryoablation looks promising for early breast cancer of small size.Breast cancer cell lines
Part of the current knowledge on breast carcinomas is based on in vivo and in vitro studies performed with cell lines derived from breast cancers. These provide an unlimited source of homogenous self-replicating material, free of contaminating stroma (animal tissue), stromal cells, and often easily cultured in simple standard growth medium, media. The first breast cancer cell line described, BT-20 (cell line), BT-20, was established in 1958. Since then, and despite sustained work in this area, the number of permanent lines obtained has been strikingly low (about 100). Indeed, attempts to culture breast cancer cell lines from primary tumors have been largely unsuccessful. This poor efficiency was often due to technical difficulties associated with the extraction of viable tumor cells from their surrounding stroma. Most of the available breast cancer cell lines issued from metastatic tumors, mainly from pleural effusions. Effusions provided generally large numbers of dissociated, viable tumor cells with little or no contamination by fibroblasts and other tumor stroma cells. Many of the currently used BCC lines were established in the late 1970s. A very few of them, namely MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3, account for more than two-thirds of all abstracts reporting studies on mentioned breast cancer cell lines, as concluded from a Medline-based survey.Molecular markers
Metabolic markers
Clinically, the most useful metabolic markers in breast cancer are the estrogen and progesterone receptors that are used to predict response to hormone therapy. New or potentially new markers for breast cancer include BRCA1 and BRCA2 to identify people at high risk of developing breast cancer, HER-2, and SCD1, for predicting response to therapeutic regimens, and urokinase plasminogen activator, PA1-1 and SCD1 for assessing prognosis.Other animals
* Mammary tumor for breast cancer in other animals * Mouse models of breast cancer metastasisSee also
* Metaplastic breast cancer (MBC) * Vasculogenic mimicryReferences
Works cited
* * * * * * * * *External links
{{Authority control Breast cancer, Hereditary cancers Human female endocrine system