Braunschweig Hauptbahnhof Innenansicht 2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( , from Low German ''Brunswiek'' , Braunschweig dialect: ''Bronswiek'') is a


 Up to the 12th century, Brunswick was ruled by the Saxon noble family of the
Up to the 12th century, Brunswick was ruled by the Saxon noble family of the
 In 1806, the city was captured by the French during the
In 1806, the city was captured by the French during the

 On 8 November 1918, at the end of
On 8 November 1918, at the end of
File:Braunschweiger Burgplatz.jpg, ''Burgplatz'', with Castle, Cathedral, lion, and Town Hall.
File:Braunschweiger Loewe Original Brunswick Lion.jpg, Brunswick Lion, original on display in castle museum.
File:Braunschweig, Rathaus (1).jpg, Town Hall
File:Braunschweig, Handwerkskammer.jpg, ''Veltheimsches Haus'' (left) and ''Gildehaus'' (right)
File:Braunschweig Brunswick Gewandhaus Ostfassade.jpg, ''Gewandhaus''
File:Braunschweig Altstadtrathaus mit Brunnen.jpg, ''Altstadtmarkt'', with Old Town town hall (left) and ''Stechinelli-Haus''
File:Braunschweig St.Martini 2005-01-23 (south).jpg, Church of St. Martin
File:Braunschweig Brunswick Ritter St Georg (2006).JPG, ''Altstadt'' ("Old Town")
File:Braunschweig Brunswick Haus zum Stern (2004).JPG, ''Haus zum Stern'' on ''Kohlmarkt''
File:Braunschweig, St. Katharinen, Heinrichsbrunnen (2).jpg, Church of St. Catherine and Henry the Lion's Fountain
File:Braunschweig Brunswick Magni-Kirche Turm Suedosten (2006).JPG, St. Magnus' Church
File:Braunschweig fachwerk 02.jpg, ''Magniviertel''
File:Happy RIZZI House Braunschweig von Süden.jpg, :de:Happy Rizzi House, Happy Rizzi House
File:Braunschweig, St. Andreaskirche (2).jpg, ''Andreaskirche''
File:Braunschweig, Alte Waage (1).jpg, ''Alte Waage''
File:Aegidienkirche 03 1a.jpg, Church of St. Giles
File:TheaterBS.jpg, State Theatre
File:ECE Schloss 06u07 1b.jpg, Rebuilt exterior of Brunswick Palace
File:Braunschweig Brunswick Schloss Richmond Frontansicht.jpg, ''Schloss Richmond'' (Richmond Palace)
File:Braunschweig Brunswick Klosterkirche Riddagshausen Osten (2006).jpg, Riddagshausen Abbey
File:Braunschweig Stadtbezirke.png, Boroughs of Braunschweig
File:Braunschweig Stadtteile.png, ''Stadtteile'' of Braunschweig
File:Braunschweig Luftaufnahme Innenstadt (2011).JPG, ''Innenstadt''
File:Braunschweig Luftaufnahme Oestliches Ringgebiet (2011).JPG, ''Östliches Ringgebiet''
File:Braunschweig Madamenweg (2010).JPG, ''Westliches Ringgebiet''
File:Braunschweig Weststadt Luftbild.jpg, ''Weststadt''
File:Riddagshausen 5.jpg, ''Riddagshausen'' (''Wabe-Schunter-Beberbach'')
1Formed in 2011 out of the former boroughs of Wabe-Schunter and Bienrode-Waggum-Bevenrode.
City of Braunschweig
 The Braunschweig city council governs the city alongside the Mayor. The most recent city council election was held on 12 September 2021, and the results were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD)
, 93,546
, 29.5
, 3.5
, 16
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens (Grüne)
, 71,880
, 22.7
, 10.6
, 12
, 5
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union of Germany, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, 69,670
, 22.0
, 4.2
, 12
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Free Democratic Party (Germany), Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, 18,704
, 5.9
, 1.4
, 3
, 1
, -
,
, align=left, Citizens' Initiative Braunschweig
, 16,778
, 5.3
, 0.7
, 3
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alternative for Germany (AfD)
, 13,512
, 4.3
, 4.6
, 2
, 3
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, The Left (Germany), The Left (Die Linke)
, 12,428
, 3.9
, 0.7
, 2
, 1
, -
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Volt Germany (Volt)
, 6,467
, 2.0
, New
, 1
, New
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Die PARTEI (PARTEI)
, 6,302
, 2.0
, 0.5
, 1
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Pirate Party Germany, Pirate Party (Piraten)
, 3,261
, 1.0
, 1.4
, 1
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Grassroots Democratic Party of Germany, Grassroots Democratic Party (dieBasis)
, 2,999
, 0.9
, New
, 1
, New
, -
, colspan=7 bgcolor=lightgrey,
, -
, bgoclor=,
, align=left, Alliance for Innovation and Justice (BIG)
, 1,646
, 0.5
, New
, 0
, New
, -
! colspan=2, Total
! 317,193
! 100.0
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Valid votes
! 107,850
! 98.5
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Invalid votes
! 1,606
! 1.5
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Total
! 109,456
! 100.0
!
! 54
! ±0
, -
! colspan=2, Electorate/voter turnout
! 197,728
! 55.4
! 0.2
!
!
, -
, colspan=7, Source
The Braunschweig city council governs the city alongside the Mayor. The most recent city council election was held on 12 September 2021, and the results were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD)
, 93,546
, 29.5
, 3.5
, 16
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens (Grüne)
, 71,880
, 22.7
, 10.6
, 12
, 5
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union of Germany, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, 69,670
, 22.0
, 4.2
, 12
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Free Democratic Party (Germany), Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, 18,704
, 5.9
, 1.4
, 3
, 1
, -
,
, align=left, Citizens' Initiative Braunschweig
, 16,778
, 5.3
, 0.7
, 3
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alternative for Germany (AfD)
, 13,512
, 4.3
, 4.6
, 2
, 3
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, The Left (Germany), The Left (Die Linke)
, 12,428
, 3.9
, 0.7
, 2
, 1
, -
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Volt Germany (Volt)
, 6,467
, 2.0
, New
, 1
, New
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Die PARTEI (PARTEI)
, 6,302
, 2.0
, 0.5
, 1
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Pirate Party Germany, Pirate Party (Piraten)
, 3,261
, 1.0
, 1.4
, 1
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Grassroots Democratic Party of Germany, Grassroots Democratic Party (dieBasis)
, 2,999
, 0.9
, New
, 1
, New
, -
, colspan=7 bgcolor=lightgrey,
, -
, bgoclor=,
, align=left, Alliance for Innovation and Justice (BIG)
, 1,646
, 0.5
, New
, 0
, New
, -
! colspan=2, Total
! 317,193
! 100.0
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Valid votes
! 107,850
! 98.5
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Invalid votes
! 1,606
! 1.5
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Total
! 109,456
! 100.0
!
! 54
! ±0
, -
! colspan=2, Electorate/voter turnout
! 197,728
! 55.4
! 0.2
!
!
, -
, colspan=7, Source
City of Braunschweig
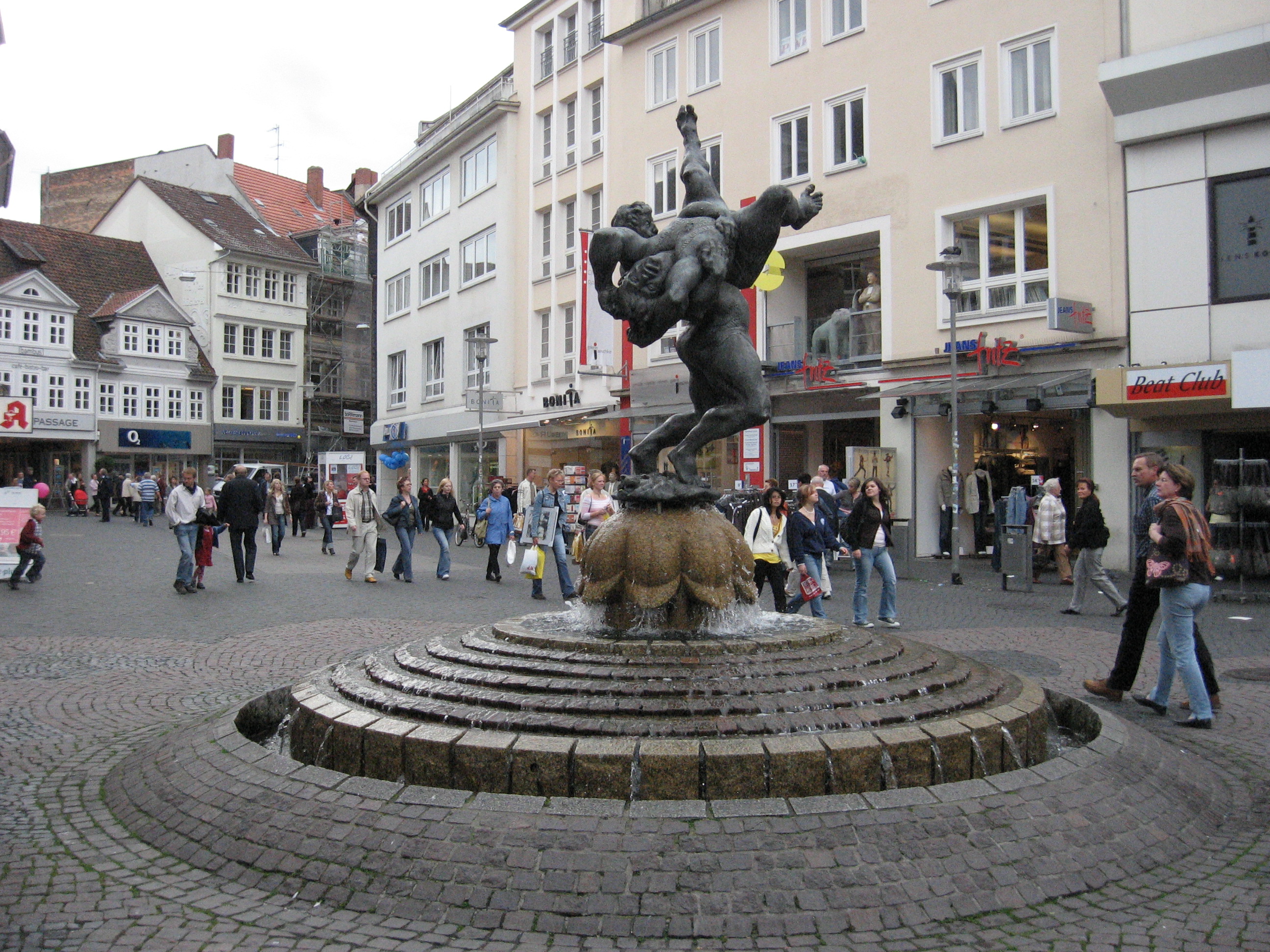 Braunschweig's city centre is mostly a car-free pedestrian zone.
Braunschweig's city centre is mostly a car-free pedestrian zone.
 The Trams in Braunschweig, Braunschweig tramway network is an inexpensive and extensive long electric tramway system. First opened in 1897, it has been modernized, including a extension in 2007. The network has an Track gauge, gauge, unique for a European railway or tramway network. However, it is being supplemented in stages by a third rail, to allow future joint working with the main railway network.
The municipally owned Braunschweiger Verkehrs-AG currently operates five tram lines and several bus lines. The tram lines are:
The Trams in Braunschweig, Braunschweig tramway network is an inexpensive and extensive long electric tramway system. First opened in 1897, it has been modernized, including a extension in 2007. The network has an Track gauge, gauge, unique for a European railway or tramway network. However, it is being supplemented in stages by a third rail, to allow future joint working with the main railway network.
The municipally owned Braunschweiger Verkehrs-AG currently operates five tram lines and several bus lines. The tram lines are:
 Braunschweig has been an important industrial area.
Today it is known for its Braunschweig University of Technology, University and research institutes, mainly the ''Johann Heinrich von Thuenen Institute'', the ''Julius Kühn-Institut'', and the ''Institute for Animal Food'' of the Friedrich Loeffler Institute, until the end of 2007 all part of the Federal Agricultural Research Centre, the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen, German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, and the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The PTB Braunschweig maintains the atomic clock responsible for the DCF77 time signal and the official German time. In 2006 the region of Braunschweig was the most R&D-intensive area in the whole European Economic Area investing 7.1% of its GDP for research & technology. In 2014, the figure had risen to 7.7%, making Braunschweig retain its ranking as the most R&D-intensive region in Germany. Braunschweig was named Germany's ''City of Science 2007'' (german: Stadt der Wissenschaft 2007).
Braunschweig University of Technology (German: ''Technische Universität Braunschweig'') was founded in 1745 and is the oldest member of TU9, an incorporated society of the nine most prestigious, oldest, and largest universities focusing on engineering and technology in Germany. With approximately 18,000 students, Braunschweig University of Technology is the third largest university in Lower Saxony.
Braunschweig has been an important industrial area.
Today it is known for its Braunschweig University of Technology, University and research institutes, mainly the ''Johann Heinrich von Thuenen Institute'', the ''Julius Kühn-Institut'', and the ''Institute for Animal Food'' of the Friedrich Loeffler Institute, until the end of 2007 all part of the Federal Agricultural Research Centre, the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen, German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, and the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The PTB Braunschweig maintains the atomic clock responsible for the DCF77 time signal and the official German time. In 2006 the region of Braunschweig was the most R&D-intensive area in the whole European Economic Area investing 7.1% of its GDP for research & technology. In 2014, the figure had risen to 7.7%, making Braunschweig retain its ranking as the most R&D-intensive region in Germany. Braunschweig was named Germany's ''City of Science 2007'' (german: Stadt der Wissenschaft 2007).
Braunschweig University of Technology (German: ''Technische Universität Braunschweig'') was founded in 1745 and is the oldest member of TU9, an incorporated society of the nine most prestigious, oldest, and largest universities focusing on engineering and technology in Germany. With approximately 18,000 students, Braunschweig University of Technology is the third largest university in Lower Saxony.

 Braunschweig is famous for ''Till Eulenspiegel'', a medieval jester who played many practical jokes on its citizens.
It also had many breweries, and still a very peculiar kind of beer is made called ''Brunswick Mum, Mumme'', first quoted in 1390, a malt-extract that was shipped all over the world. Two major breweries still produce in Braunschweig, the , founded in 1627, and the former brewery, founded in 1871, now operated by Oettinger Beer.
Braunschweiger (sausage), Braunschweiger Mettwurst, a soft, spreadable smoked pork sausage, is named after the city. Other traditional local dishes include Asparagus, white asparagus, ''Braunschweiger Lebkuchen'', ''Braunkohl'' (a variant of kale served with Bregenwurst), and ''Uhlen un Apen'' (Low German for "Owls and Guenons", a pastry).
Braunschweig is famous for ''Till Eulenspiegel'', a medieval jester who played many practical jokes on its citizens.
It also had many breweries, and still a very peculiar kind of beer is made called ''Brunswick Mum, Mumme'', first quoted in 1390, a malt-extract that was shipped all over the world. Two major breweries still produce in Braunschweig, the , founded in 1627, and the former brewery, founded in 1871, now operated by Oettinger Beer.
Braunschweiger (sausage), Braunschweiger Mettwurst, a soft, spreadable smoked pork sausage, is named after the city. Other traditional local dishes include Asparagus, white asparagus, ''Braunschweiger Lebkuchen'', ''Braunkohl'' (a variant of kale served with Bregenwurst), and ''Uhlen un Apen'' (Low German for "Owls and Guenons", a pastry).

 The city's most important museum is the Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum, a well known art museum and the oldest public museum in Germany, founded in 1754. It houses a collection of masters of Western art, including Albrecht Dürer, Dürer, Giorgione, Lucas Cranach the Elder, Cranach, Hans Holbein the Younger, Holbein, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Jan Vermeer, Vermeer, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, and Rembrandt.
The Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum, State Museum of Brunswick (''Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum''), founded in 1891, houses a permanent collection documenting the history of the Brunswick Land, Brunswick area ranging from its early history to the present.
The Municipal Museum of Brunswick (''Städtisches Museum Braunschweig''), founded in 1861, is a museum for art and cultural history, documenting the history of the city of Braunschweig.
The Naturhistorisches Museum (Braunschweig), State Natural History Museum is a zoology museum founded in 1754.
Other museums in the city include the Museum of Photography (''Museum für Photographie''), the Jewish Museum (''Jüdisches Museum''), the Museum for Agricultural Technology ''Gut Steinhof'', and the Friedrich Gerstäcker, Gerstäcker-Museum. Frequent exhibitions of contemporary art are also held by the Art Society of Braunschweig (German: ''Kunstverein Braunschweig''), housed in the ''Villa Salve Hospes'', a classicist villa built between 1805 and 1808.
The city's most important museum is the Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum, a well known art museum and the oldest public museum in Germany, founded in 1754. It houses a collection of masters of Western art, including Albrecht Dürer, Dürer, Giorgione, Lucas Cranach the Elder, Cranach, Hans Holbein the Younger, Holbein, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Jan Vermeer, Vermeer, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, and Rembrandt.
The Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum, State Museum of Brunswick (''Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum''), founded in 1891, houses a permanent collection documenting the history of the Brunswick Land, Brunswick area ranging from its early history to the present.
The Municipal Museum of Brunswick (''Städtisches Museum Braunschweig''), founded in 1861, is a museum for art and cultural history, documenting the history of the city of Braunschweig.
The Naturhistorisches Museum (Braunschweig), State Natural History Museum is a zoology museum founded in 1754.
Other museums in the city include the Museum of Photography (''Museum für Photographie''), the Jewish Museum (''Jüdisches Museum''), the Museum for Agricultural Technology ''Gut Steinhof'', and the Friedrich Gerstäcker, Gerstäcker-Museum. Frequent exhibitions of contemporary art are also held by the Art Society of Braunschweig (German: ''Kunstverein Braunschweig''), housed in the ''Villa Salve Hospes'', a classicist villa built between 1805 and 1808.

 Braunschweig's major local Association football, football team is Eintracht Braunschweig. Founded in 1895, Eintracht Braunschweig can look back on a long and chequered history. Eintracht Braunschweig won the List of German football champions, German football championship in 1967, and currently plays in the 2. Bundesliga, the second tier of German football, and attracts a large number of supporters. Braunschweig was also arguably the city in which the first ever game of football in Germany took place. The game had been brought to Germany by the local school teacher Konrad Koch, also the first to write down a German version of the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football,However, Koch's original German version of the rules of football, published in 1875, still resembled Rugby football—the unmodified rules of The Football Association were not commonly used in Germany before the 1900s. who organized the first match between pupils from his school ''Martino-Katharineum'' in 1874. The 2011 German drama film Lessons of a Dream is based on Koch.
Eintracht Braunschweig also fields a successful women's field hockey team that claimed nine national championship titles between 1965 and 1978. In the past, the club also had first or second-tier teams in the sports of ice hockey, field handball, and water polo.
The New Yorker Lions (formerly Braunschweig Lions) are the city's American football team, winning a record number of 12 German Bowl titles, as well as five Eurobowls (a shared record).
The city's professional basketball team, the Basketball Löwen Braunschweig, plays in the Basketball Bundesliga, the highest level in Germany. The Löwen's predecessor SG Braunschweig had previously played in the Bundesliga as well. Eintracht Braunschweig's women's basketball team plays in the , the second tier of women's basketball in Germany.
In handball, MTV Braunschweig, the city's oldest sports club (founded in 1847), plays in the semi-professional :de:3. Liga (Handball), 3. Liga.
Other sports clubs from Braunschweig that play or have played at the Bundesliga (disambiguation), Bundesliga or 2nd Bundesliga (disambiguation), 2nd Bundesliga level include (baseball), (field hockey), (handball), Rugby-Welfen Braunschweig (rugby union), and (volleyball).
Annual sporting events held in Braunschweig include the international Equestrianism, equestrian tournament ''Löwen Classics'', ''Rund um den Elm'', Germany's oldest Road bicycle racing, road bicycle race, and the professional tennis tournament ''Sparkassen Open''.
Braunschweig's major local Association football, football team is Eintracht Braunschweig. Founded in 1895, Eintracht Braunschweig can look back on a long and chequered history. Eintracht Braunschweig won the List of German football champions, German football championship in 1967, and currently plays in the 2. Bundesliga, the second tier of German football, and attracts a large number of supporters. Braunschweig was also arguably the city in which the first ever game of football in Germany took place. The game had been brought to Germany by the local school teacher Konrad Koch, also the first to write down a German version of the Laws of the Game (association football), rules of football,However, Koch's original German version of the rules of football, published in 1875, still resembled Rugby football—the unmodified rules of The Football Association were not commonly used in Germany before the 1900s. who organized the first match between pupils from his school ''Martino-Katharineum'' in 1874. The 2011 German drama film Lessons of a Dream is based on Koch.
Eintracht Braunschweig also fields a successful women's field hockey team that claimed nine national championship titles between 1965 and 1978. In the past, the club also had first or second-tier teams in the sports of ice hockey, field handball, and water polo.
The New Yorker Lions (formerly Braunschweig Lions) are the city's American football team, winning a record number of 12 German Bowl titles, as well as five Eurobowls (a shared record).
The city's professional basketball team, the Basketball Löwen Braunschweig, plays in the Basketball Bundesliga, the highest level in Germany. The Löwen's predecessor SG Braunschweig had previously played in the Bundesliga as well. Eintracht Braunschweig's women's basketball team plays in the , the second tier of women's basketball in Germany.
In handball, MTV Braunschweig, the city's oldest sports club (founded in 1847), plays in the semi-professional :de:3. Liga (Handball), 3. Liga.
Other sports clubs from Braunschweig that play or have played at the Bundesliga (disambiguation), Bundesliga or 2nd Bundesliga (disambiguation), 2nd Bundesliga level include (baseball), (field hockey), (handball), Rugby-Welfen Braunschweig (rugby union), and (volleyball).
Annual sporting events held in Braunschweig include the international Equestrianism, equestrian tournament ''Löwen Classics'', ''Rund um den Elm'', Germany's oldest Road bicycle racing, road bicycle race, and the professional tennis tournament ''Sparkassen Open''.
Official website
Daily newspaper Braunschweiger Zeitung
{{Authority control Braunschweig, Capitals of former nations Duchy of Brunswick Members of the Hanseatic League
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Germany, north of the Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker
The Oker is a river in Lower Saxony, Germany, that has historically formed an important political boundary. It is a left tributary of the River Aller, in length and runs in a generally northerly direction.
Origin and meaning of the name
The ...
, which connects it to the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
via the rivers Aller
Aller may refer to:
Places Rivers
* Aller (Germany), a major river in North Germany
*Aller (Asturian river), a river in Asturias, Spain
*River Aller, a small river on Exmoor in Somerset, England
Inhabited places in the United Kingdom
*Aller, Devo ...
and Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
. In 2016, it had a population of 250,704.
A powerful and influential centre of commerce in medieval Germany, Brunswick was a member of the Hanseatic League from the 13th until the 17th century. It was the capital city of three successive states: the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1269–1432, 1754–1807, and 1813–1814), the Duchy of Brunswick
The Duchy of Brunswick (german: Herzogtum Braunschweig) was a historical German state. Its capital was the city of Brunswick ().
It was established as the successor state of the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel by the Congress of Vienna ...
(1814–1918), and the Free State of Brunswick
The Free State of Brunswick () was a state of the German Reich in the time of the Weimar Republic. It was formed after the abolition of the Duchy of Brunswick in the course of the German Revolution of 1918–19. Its capital was Braunschweig (Bru ...
(1918–1946).
Today, Brunswick is the second-largest city in Lower Saxony and a major centre of scientific research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific m ...
and development.
History

Foundation and early history
The date and circumstances of the town's foundation are unknown. Tradition maintains that Brunswick was created through the merger of two settlements, one founded by Brun(o), a Saxon count who died in 880, on one side of the River Oker – the legend gives the year 861 for the foundation – and the other the settlement of a legendary Count Dankward, after whomDankwarderode Castle
Dankwarderode Castle (german: Burg Dankwarderode) on the ''Burgplatz'' ("castle square") in Braunschweig (Brunswick) is a Saxon lowland castle. It was the residence of the Brunswick dukes for centuries and, today, is part of the Herzog Anton Ulric ...
("Dankward's clearing"), which was reconstructed in the 19th century, is named.
The town's original name of ''Brunswik'' is a combination of the name Bruno and Low German ''wik'' (related to the Latin ''vicus''), a place where merchants rested and stored their goods. The town's name, therefore, indicates an ideal resting place, as it lay by a ford across the Oker River. Another explanation of the city's name is that it comes from ''Brand'', or burning, indicating a place which developed after the landscape was cleared through burning. The city was first mentioned in documents from the St. Magni Church from 1031, which give the city's name as ''Brunesguik''.
Middle Ages and early modern period

Brunonids The Brunonids (or Brunonians, german: Brunonen, la, Brunones, i.e. "Brunos") were a Saxon noble family in the 10th and 11th centuries, who owned property in Eastphalia (around Brunswick) and Frisia.
The Brunonids are assumed to be descendants o ...
, then, through marriage, it fell to the House of Welf. In 1142, Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
of the House of Welf became duke of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
and made Braunschweig the capital of his state (which, from 1156 on, also included the Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria ( German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under ...
). He turned Dankwarderode Castle, the residence of the counts of Brunswick, into his own ''Pfalz
Pfalz, Pfälzer, or Pfälzisch are German words referring to Palatinate.
They may refer to:
Places
*Pfalz, the Palatinate (region) of Germany
**Nordpfalz, the North Palatinate
**Vorderpfalz, the Anterior Palatinate
**Südpfalz, the South P ...
'' and developed the city further to represent his authority. Under Henry's rule, the Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
of St. Blasius was built and he also had the statue of a lion, his heraldic animal, erected in front of the castle. The lion subsequently became the city's landmark.
Henry the Lion became so powerful that he dared to refuse military aid to the Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt o ...
, which led to his banishment in 1182. Henry went into exile in England. He had previously established ties to the English crown in 1168, through his marriage to King Henry II of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin king ...
's daughter Matilda
Matilda or Mathilda may refer to:
Animals
* Matilda (chicken) (1990–2006), World's Oldest Living Chicken record holder
* Matilda (horse) (1824–1846), British Thoroughbred racehorse
* Matilda, a dog of the professional wrestling tag-team The ...
, sister of Richard the Lionheart
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was overl ...
. However, his son Otto
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', '' Odo'', ''Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity".
The name is recorded f ...
, who could regain influence and was eventually crowned Holy Roman Emperor, continued to foster the city's development.
During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Brunswick was an important center of trade, one of the economic and political centers in Northern Europe and a member of the Hanseatic League from the 13th century to the middle of the 17th century. By the year 1600, Brunswick was the seventh largest city in Germany. Although formally one of the residences of the rulers of the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg, a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, Brunswick was ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' ruled independently by a powerful class of patricians
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after ...
and the guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s throughout much of the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
and the Early modern period. Because of the growing power of Brunswick's burghers, the Princes of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, who ruled over one of the subdivisions of Brunswick-Lüneburg, finally moved their ''Residenz
Residenz () is a German word for "place of living", now obsolete except in the formal sense of an official residence. A related term, Residenzstadt, denotes a city where a sovereign ruler resided, therefore carrying a similar meaning as the modern ...
'' out of the city and to the nearby town of Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel (; nds, Wulfenbüddel) is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, the administrative capital of Wolfenbüttel District. It is best known as the location of the internationally renowned Herzog August Library and for having the largest ...
in 1432. The Princes of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel didn't regain control over the city until the late 17th century, when Rudolph Augustus, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, took the city by siege.
In the 18th century Brunswick was not only a political, but also a cultural centre. Influenced by the philosophy of the Enlightenment, dukes like Anthony Ulrich and Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
became patrons of the arts and sciences. In 1745, Charles I founded the ''Collegium Carolinum'', predecessor of the Brunswick University of Technology
The Technische Universität Braunschweig (unofficially University of Braunschweig – Institute of Technology), commonly referred to as TU Braunschweig, is the oldest ' (comparable to an institute of technology in the American system) in Germany. ...
, and in 1753 he moved the ducal residence back to Brunswick. With this he attracted poets and thinkers such as Lessing, Leisewitz, and Jakob Mauvillon to his court and the city. '' Emilia Galotti'' by Lessing and Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as tr ...
's ''Faust
Faust is the protagonist of a classic German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust ( 1480–1540).
The erudite Faust is highly successful yet dissatisfied with his life, which leads him to make a pact with the Devil at a crossroa ...
'' were performed for the first time in Brunswick.
19th century
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
and became part of the short-lived Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
ic Kingdom of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a kingdom in Germany, with a population of 2.6 million, that existed from 1807 to 1813. It included territory in Hesse and other parts of present-day Germany. While formally independent, it was a vassal state of the ...
in 1807. The exiled Duke Frederick William raised a volunteer corps, the Black Brunswickers, who fought the French in several battles.
After the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815, Brunswick was made capital of the re-established independent Duchy of Brunswick
The Duchy of Brunswick (german: Herzogtum Braunschweig) was a historical German state. Its capital was the city of Brunswick ().
It was established as the successor state of the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel by the Congress of Vienna ...
, later a constituent state of the German Empire from 1871. In the aftermath of the July Revolution
The French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution (french: révolution de Juillet), Second French Revolution, or ("Three Glorious ays), was a second French Revolution after the first in 1789. It led to the overthrow of King ...
in 1830, in Brunswick duke Charles II was forced to abdicate. His absolutist governing style had previously alienated the nobility and bourgeoisie, while the lower classes were disaffected by the bad economic situation. During the night of 7–8 September 1830, the ducal palace in Brunswick was stormed by an angry mob, set on fire, and destroyed completely. Charles was succeeded by his brother William VIII. During William's reign, liberal reforms were made and Brunswick's parliament was strengthened.
During the 19th century, industrialisation caused a rapid growth of population in the city, eventually causing Brunswick to be for the first time significantly enlarged beyond its medieval fortifications
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
and the River Oker. On 1 December 1838, the first section of the Brunswick–Bad Harzburg railway
The Brunswick–Bad Harzburg railway is a 47 km long German main line railway in the northern foothills of the Harz. It is one of the oldest lines in Germany and the first government-owned railway in Germany.
History
On 1 December 1838 t ...
line connecting Brunswick and Wolfenbüttel opened as the first railway line in Northern Germany, operated by the Duchy of Brunswick State Railway
The Duchy of Brunswick State Railway (''Herzoglich Braunschweigische Staatseisenbahn'') was the first state railway in Germany. The first section of its Brunswick–Bad Harzburg railway line between Brunswick and Wolfenbüttel opened on 1 Decembe ...
.
Early to mid-20th century

 On 8 November 1918, at the end of
On 8 November 1918, at the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, a socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
workers' council
A workers' council or labor council is a form of political and economic organization in which a workplace or municipality is governed by a council made up of workers or their elected delegates. The workers within each council decide on what thei ...
forced Duke Ernest Augustus to abdicate. On 10 November, the council proclaimed the Socialist Republic of Brunswick under one-party government by the Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Unabhängige Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, USPD) was a short-lived political party in Germany during the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. The organization was establish ...
(USPD); however, the subsequent Landtag election on 22 December 1918 was won by the Social Democratic Party of Germany (MSPD), and the USPD and MSPD formed a coalition government. An uprising in Braunschweig in 1919, led by the communist Spartacus League, was defeated when ''Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European military volunteer units, or paramilitary, that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenary or private armies, rega ...
'' troops under Georg Ludwig Rudolf Maercker
Georg Ludwig Rudolf Maercker (21 September 1865 in Baldenburg – 31 December 1924 in Dresden) was a German general of World War I.
Following the Armistice of 1918 that saw the end of fighting and of the Bolshevik revolution that led to the cre ...
took over the city on order of the German Minister of Defence, Gustav Noske
Gustav Noske (9 July 1868 – 30 November 1946) was a German politician of the Social Democratic Party (SPD). He served as the first Minister of Defence (''Reichswehrminister'') of the Weimar Republic between 1919 and 1920. Noske has been a cont ...
. An SPD-led government was subsequently established; in December 1921, a new constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
was approved for the Free State of Brunswick
The Free State of Brunswick () was a state of the German Reich in the time of the Weimar Republic. It was formed after the abolition of the Duchy of Brunswick in the course of the German Revolution of 1918–19. Its capital was Braunschweig (Bru ...
, now a parliamentary republic within the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is ...
, again with Braunschweig as its capital.
After the Landtag election of 1930, Brunswick became the second state in Germany where the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
participated in government, when the National Socialist German Workers' Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported th ...
(NSDAP) formed a coalition government with several conservative and right-wing parties. With the support of Dietrich Klagges
Dietrich Klagges () (1 February 1891 – 12 November 1971) was a Nazi Party politician and from 1933 to 1945 the appointed premier (''Ministerpräsident'') of the now abolished Free State of Brunswick. He also went by the pseudonym Rudolf Berg.c ...
, Brunswick's minister of the interior, the NSDAP organized a large SA rally in Braunschweig. On 17–18 October 1931, 100,000 SA stormtroopers marched through the city; street fights between Nazis, socialists, and communists left several dead or injured. On 25 February 1932, the state of Brunswick granted Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
German citizenship to allow him to run in the 1932 German presidential election. In Braunschweig, Nazis carried out several attacks on political enemies, with the acquiescence of the state government.
After the Nazi seizure of power in 1933, several state institutions were placed in Braunschweig, including the '' Luftfahrtforschungsanstalt'' in Völkenrode
Völkenrode is a quarter (''Stadtteil'') of Braunschweig, Lower Saxony, Germany. Formerly a municipality in its own right and part of the district of Braunschweig, it was incorporated into the city of Braunschweig in 1974. Today, it is part of t ...
, the Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
Academy for Youth Leadership, and the SS- Junkerschule Braunschweig. With the Reichswerke Hermann Göring
Reichswerke Hermann Göring was an industrial conglomerate in Nazi Germany from 1937 until 1945. It was established to extract and process domestic iron ores from Salzgitter that were deemed uneconomical by the privately held steel mills. The sta ...
in Salzgitter
Salzgitter (; Eastphalian: ''Soltgitter'') is an independent city in southeast Lower Saxony, Germany, located between Hildesheim and Braunschweig. Together with Wolfsburg and Braunschweig, Salzgitter is one of the seven ''Oberzentren'' of Lower ...
and the Stadt des KdF-Wagens, as well as several factories in the city itself (including Büssing
Büssing AG was a German bus and truck manufacturer, established in 1903 by Heinrich Büssing (1843–1929) in Braunschweig. It quickly evolved to one of the largest European producers, whose utility vehicles with the Brunswick Lion emblem were w ...
and the Volkswagenwerk Braunschweig), the Braunschweig region became one of the centres of the German arms industry
The arms industry, also known as the arms trade, is a global industry classification, industry which manufacturing, manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. It consists of a commerce, commercial Private industry, industry involved ...
.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Braunschweig was a sub-area headquarters of Wehrkreis XI
The military districts, also known in some English-language publications by their German name as Wehrkreise (singular: ''Wehrkreis''), were administrative territorial units in Nazi Germany before and during World War II. The task of military distr ...
(one of Germany's military districts), and was the garrison city of the 31st Infantry Division that took part in the invasions of Poland, Belgium, and France, largely being destroyed during its retreat following the invasion of Russia. In this period, thousands of Eastern workers were brought to the city as forced labor
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
, and in the 1943–1945 period at least 360 children taken away from such workers died in the '' Entbindungsheim für Ostarbeiterinnen'' ("Maternity Ward for Eastern Workers").
In 1944, a subcamp of the concentration camp Neuengamme was established in Braunschweig. Hundreds of prisoners, mostly Jews, lived in brutal conditions and hundreds died from hunger, disease, and overwork. Piera Sonnino (1922-1999), an Italian author, writes of her imprisonment in that camp in her book, ''This Has Happened'', published in English in 2006 by MacMillan Palgrave.
The Allied air raid on October 15, 1944, destroyed most of the city's churches, and the ''Altstadt'' (old town), the largest homogeneous ensemble of half-timbered houses in Germany.
The city's cathedral, which had been converted to a ''Nationale Weihestätte'' (national shrine) by the Nazi government, still stood.
Postwar period to the 21st century
Small sections of the city survived Allied bombing, so remain to represent its distinctive architecture. The cathedral was restored to its function as aProtestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
church.
Politically, after the war, the Free State of Brunswick was dissolved by the Allied occupying authorities, Braunschweig ceased to be a capital, and most of its lands were incorporated in the newly formed state of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
.
During the Cold War, Braunschweig, then part of West Germany, suffered economically due to its proximity to the Iron Curtain. The city lost its historically strong economic ties to what was then East Germany; for decades, economic growth remained, on average, below the rest of the country while unemployment was above-average for West Germany.
On 28 February 1974, as part of a district reform in Lower Saxony, the Landkreis, rural district of Braunschweig (district), Braunschweig, which had surrounded the city, was disestablished. The major part of the former district was incorporated into the city of Braunschweig, increasing its population by roughly 52,000 people.
In the 1990s, efforts increased to reconstruct historic buildings that had been destroyed in the air raid. The façade of the ''Brunswick Palace, Braunschweiger Schloss'' was rebuilt, and buildings such as the ''Alte Waage'' (originally built in 1534) now stand again.
Demographics
Population development
, the population of Braunschweig was 252,768. Today, Braunschweig is among the twenty German cities found to be most attractive to young people between the ages of 25 and 34, leading to an influx of younger residents.Religion
In 2015, 91,785 people or 36.3% of the population were Evangelical Church in Germany, Protestant and 34,604 (13.7%) people were Catholic Church, Roman Catholic; 126,379 people (50.0%) either adhered to other denominations or followed no religion.Immigration
A total of 64,737 of Braunschweig's residents, including German citizens, had an immigrant background in 2015 (25.6% of the total population). Among those, 25,676 were non-German citizens (10.2%); the following table lists up the largest minority groups:Main sights
*The ''Burgplatz'' (Castle Square), comprising a group of buildings of great historical and cultural significance: theCathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
(Saint Blaise, St Blasius, built at the end of the 12th century); the ''Burg Dankwarderode'' (Dankwarderode Castle) (a 19th-century reconstruction of the old castle of Henry the Lion); the Neo-Gothic Town Hall (built in 1893–1900); as well as some picturesque timber framing, half-timbered houses, such as the ''Gildehaus'' (Guild House), today the seat of the Craftsman's Association. In the centre of the square stands a copy of the ''Brunswick Lion, Burglöwe'' (Brunswick Lion), a Romanesque art, Romanesque statue of a lion, cast in bronze in 1166. The original statue can be seen in the museum of Dankwarderode Castle. The lion remains the symbol of Braunschweig today.
*The ''Altstadtmarkt'' ("Old Town market"), surrounded by the Old Town town hall (built between the 13th and the 15th centuries in Gothic style), and the ''Martinikirche'' (Church of Martin of Tours, Saint Martin, from 1195), with important historical houses including the ''Cloth hall, Gewandhaus'' (the former house of the drapers' guild, built sometime before 1268) and the ''Stechinelli-Haus'' (built in 1690) and a fountain from 1408.
*The ''Kohlmarkt'' ("coal market"), a market with many historical houses and a fountain from 1869.
*The ''Hagenmarkt'' (":wiktionary:Hag, Hagen market"), with the 13th-century ''Katharinenkirche'' (Church of Catherine of Alexandria, Saint Catherine) and the ''Heinrichsbrunnen'' ("Henry the Lion's Fountain") from 1874.
*The ''Magniviertel'' (Magnus of Anagni, St Magnus' Quarter), a remainder of ancient Braunschweig, lined with cobblestoned streets, little shops and cafés, centred on the 13th-century ''Magnikirche'' (St Magnus' Church). Here is also the ''Rizzi-Haus'', a highly distinctive, cartoonish office building designed by architect James Rizzi for the Expo 2000.
*The Romanesque architecture, Romanesque and Gothic architecture, Gothic ''Andreaskirche'' (Church of Saint Andrew), built mainly between the 13th and 16th centuries with stained glass by Charles Crodel. Surrounding the church are the ''List of Brick Gothic buildings#Lower Saxony and Bremen, Liberei'', the oldest surviving freestanding library building in Germany, and the reconstructed ''Alte Waage''.
*The Gothic ''Aegidienkirche, Braunschweig, Aegidienkirche'' (Church of Saint Giles), built in the 13th century, with an adjoining monastery, which is today a museum.
*The ''Staatstheater Braunschweig, Staatstheater'' (State Theatre), newly built in the 19th century, goes back to the first standing public theatre in Germany, founded in 1690 by Duke Anthony Ulrich.
*The Brunswick Palace, ducal palace of Braunschweig was bombed in World War II and demolished in 1960. The exterior was rebuilt to contain a palace museum, library and shopping centre, which opened in 2007.
*The baroque palace ''Schloss Richmond'' ("Richmond Palace"), built between 1768 and 1769 with a surrounding English garden for Princess Augusta of Great Britain, wife of Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, to remind her of her home in England.
*Riddagshausen Abbey (German: ''Kloster Riddagshausen''), a former Cistercian monastery, with the surrounding nature reserve and arboretum. The nature reserve ''Riddagshäuser Teiche'' is designated as an Important Bird Area and Special Protection Area.
Parks and gardens
Parks and gardens in the city include the botanical garden ''Botanischer Garten der Technischen Universität Braunschweig'', founded in 1840 by Johann Heinrich Blasius, the ''Bürgerpark'', the ''Löwenwall'' with an obelisk from 1825, the ''Prinz-Albrecht-Park'', and the ''Inselwallpark''. Other parks and recreation areas are ''Stadtpark'', ''Westpark'', ''Theaterpark'', ''Museumpark'', ''Heidbergsee'', ''Südsee'', ''Ölpersee'', the zoo, zoological garden ''Arche Noah Zoo Braunschweig'' and the nearby Essehof Zoo.Politics
Subdivisions
Braunschweig is made up of 19 boroughs (German: ''Stadtbezirke''), which themselves may consist of several quarters (German: ''Stadtteile'') each. The 19 boroughs, with their official numbers, are: *112: Wabe-Schunter-Beberbach1 *113: Hondelage *114: Volkmarode *120: Östliches Ringgebiet *131: Innenstadt (Braunschweig), Innenstadt *132: Viewegsgarten-Bebelhof *211: Stöckheim-Leiferde *212: Heidberg-Melverode *213: Südstadt-Rautheim-Mascherode *221: Weststadt (Braunschweig), Weststadt *222: Timmerlah-Geitelde-Stiddien *223: Broitzem *224: Rüningen *310: Westliches Ringgebiet *321: Lehndorf-Watenbüttel *322: Veltenhof-Rühme *323: Wenden-Thune-Harxbüttel *331: Nordstadt *332: SchunteraueMayor
The current mayor of Braunschweig is Thorsten Kornblum of the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) since 2021. The most recent mayoral election was held on 12 September 2021, with a runoff held on 26 September, and the results were as follows: ! rowspan=2 colspan=2, Candidate ! rowspan=2, Party ! colspan=2, First round ! colspan=2, Second round , - ! Votes ! % ! Votes ! % , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Thorsten Kornblum , align=left, Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party , 41,734 , 38.4 , 79,861 , 65.9 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Kaspar Haller , align=left, Christian Democratic Union of Germany, Christian Democratic Union , 29,011 , 26.7 , 41,401 , 34.1 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Tatjana Schneider , align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens , 24,802 , 22.8 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Mirco Hanker , align=left, Alternative for Germany , 4,704 , 4.3 , - , , align=left, Birgit Huvendieck , align=left, Citizens' Initiative Braunschweig , 3,215 , 3.0 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Anke Schneider , align=left, The Left (Germany), The Left , 2,827 , 2.6 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Thomas Hofmann , align=left, Die PARTEI , 1,904 , 1.7 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left, Erdmann Gust , align=left, Independent politician, Independent , 614 , 0.6 , - ! colspan=3, Valid votes ! 108,811 ! 99.3 ! 121,262 ! 98.1 , - ! colspan=3, Invalid votes ! 721 ! 0.7 ! 2,407 ! 1.9 , - ! colspan=3, Total ! 109,532 ! 100.0 ! 123,669 ! 100.0 , - ! colspan=3, Electorate/voter turnout ! 197,728 ! 55.4 ! 197,414 ! 62.6 , - , colspan=7, SourceCity of Braunschweig
City council
City of Braunschweig
Twin towns – sister cities
Braunschweig is Sister city, twinned with: * Bandung, Indonesia (1960) * Nîmes, France (1962) * Bath, Somerset, Bath, England (1971) * Sousse, Tunisia (1980) * Kiryat Tiv'on, Israel (1985) * Magdeburg, Germany (1987) * Kazan, Russia (1988) * Omaha, Nebraska, Omaha, United States (1992) * Zhuhai, China (2011)Transport
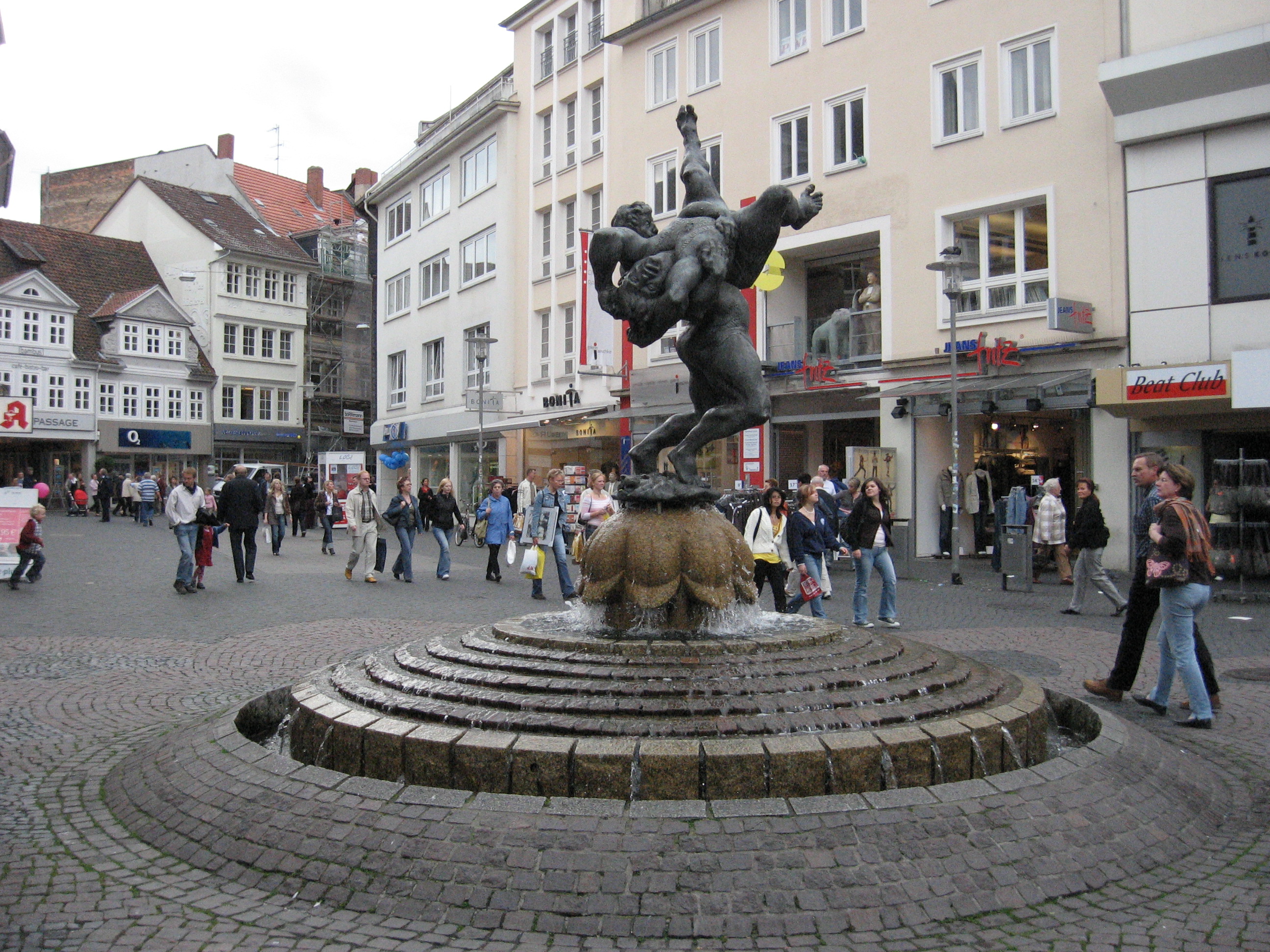 Braunschweig's city centre is mostly a car-free pedestrian zone.
Braunschweig's city centre is mostly a car-free pedestrian zone.
Road
Two main autobahns serve Braunschweig, the Bundesautobahn 2, A2 (Berlin—Hanover—Dortmund) and the Bundesautobahn 39, A39 (Salzgitter
Salzgitter (; Eastphalian: ''Soltgitter'') is an independent city in southeast Lower Saxony, Germany, located between Hildesheim and Braunschweig. Together with Wolfsburg and Braunschweig, Salzgitter is one of the seven ''Oberzentren'' of Lower ...
—Wolfsburg). City roads are generally wide, built after World War II to support the anticipated use of the car. There are several car parks in the city.
Bicycle
Many residents travel around town by bicycle using an extensive system of bicycle-only lanes. The main train station includes a bicycle parking area.Train
The city is on the main rail line between Frankfurt and Berlin. Deutsche Bahn (German Railways) serves the city with local, inter-city and high-speed InterCityExpress (ICE) trains, with frequent stops at Braunschweig Central Station (German: ''Braunschweig Hauptbahnhof'').Tram and bus
 The Trams in Braunschweig, Braunschweig tramway network is an inexpensive and extensive long electric tramway system. First opened in 1897, it has been modernized, including a extension in 2007. The network has an Track gauge, gauge, unique for a European railway or tramway network. However, it is being supplemented in stages by a third rail, to allow future joint working with the main railway network.
The municipally owned Braunschweiger Verkehrs-AG currently operates five tram lines and several bus lines. The tram lines are:
The Trams in Braunschweig, Braunschweig tramway network is an inexpensive and extensive long electric tramway system. First opened in 1897, it has been modernized, including a extension in 2007. The network has an Track gauge, gauge, unique for a European railway or tramway network. However, it is being supplemented in stages by a third rail, to allow future joint working with the main railway network.
The municipally owned Braunschweiger Verkehrs-AG currently operates five tram lines and several bus lines. The tram lines are:
Air
Braunschweig Airport (BWE / EDVE) is located north of the city at , elev. .Name
Many other geographical locations around the world are named Brunswick, after the historical English name of Braunschweig. Between 1714 and 1837, the House of Hanover ruled Great Britain in personal union with the Electorate of Hanover. The House of Hanover was formally known as the House of Welf, House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Hanover line. As a result, many places in British Empire, the British colonies were named after Brunswick, such as the province of New Brunswick in Canada. Ironically, the city of Braunschweig was not ruled by the Hanoverians while its name was being given to other Brunswicks around the world. Starting in 1269, the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg underwent a series of divisions and mergers, with parts of the territory being transferred between various branches of the family. The city of Braunschweig went to the senior branch of the house, the List of rulers of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Wolfenbüttel line, while Lüneburg eventually ended up with the House of Hanover, Hanover line. Although the territory had been split, all branches of the family continued to style themselves as the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg. In 1884, the senior branch of the House of Welf became extinct. The Hanover line, being the last surviving line of the family, subsequently held the throne of the Duchy of Brunswick from November 1913 until November 1918.Government offices
The offices of the Luftfahrt-Bundesamt (LBA, "Federal Aviation Office") and the German Federal Bureau of Aircraft Accident Investigation (BFU) are located in Braunschweig.Research and science
 Braunschweig has been an important industrial area.
Today it is known for its Braunschweig University of Technology, University and research institutes, mainly the ''Johann Heinrich von Thuenen Institute'', the ''Julius Kühn-Institut'', and the ''Institute for Animal Food'' of the Friedrich Loeffler Institute, until the end of 2007 all part of the Federal Agricultural Research Centre, the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen, German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, and the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The PTB Braunschweig maintains the atomic clock responsible for the DCF77 time signal and the official German time. In 2006 the region of Braunschweig was the most R&D-intensive area in the whole European Economic Area investing 7.1% of its GDP for research & technology. In 2014, the figure had risen to 7.7%, making Braunschweig retain its ranking as the most R&D-intensive region in Germany. Braunschweig was named Germany's ''City of Science 2007'' (german: Stadt der Wissenschaft 2007).
Braunschweig University of Technology (German: ''Technische Universität Braunschweig'') was founded in 1745 and is the oldest member of TU9, an incorporated society of the nine most prestigious, oldest, and largest universities focusing on engineering and technology in Germany. With approximately 18,000 students, Braunschweig University of Technology is the third largest university in Lower Saxony.
Braunschweig has been an important industrial area.
Today it is known for its Braunschweig University of Technology, University and research institutes, mainly the ''Johann Heinrich von Thuenen Institute'', the ''Julius Kühn-Institut'', and the ''Institute for Animal Food'' of the Friedrich Loeffler Institute, until the end of 2007 all part of the Federal Agricultural Research Centre, the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen, German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, and the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The PTB Braunschweig maintains the atomic clock responsible for the DCF77 time signal and the official German time. In 2006 the region of Braunschweig was the most R&D-intensive area in the whole European Economic Area investing 7.1% of its GDP for research & technology. In 2014, the figure had risen to 7.7%, making Braunschweig retain its ranking as the most R&D-intensive region in Germany. Braunschweig was named Germany's ''City of Science 2007'' (german: Stadt der Wissenschaft 2007).
Braunschweig University of Technology (German: ''Technische Universität Braunschweig'') was founded in 1745 and is the oldest member of TU9, an incorporated society of the nine most prestigious, oldest, and largest universities focusing on engineering and technology in Germany. With approximately 18,000 students, Braunschweig University of Technology is the third largest university in Lower Saxony.
Education
Also located in Braunschweig is the , a secondary school founded in 1415. It had such famous pupils as Carl Friedrich Gauss, Hoffmann von Fallersleben, Richard Dedekind and Louis Spohr. Since 2004, Braunschweig also has an ''International School''. Other notable secondary schools include the Gymnasium Neue Oberschule, Gymnasium Gaussschule, , , , and .Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
's only university of art, founded in 1963, can be found in Braunschweig, the ''Hochschule für Bildende Künste Braunschweig'' (Braunschweig College of Fine Arts). The HBK is an institution of higher artistic and scientific education and offers the opportunity to study for interdisciplinary artistic and scientific qualifications. Additionally, one of the campuses of the Ostfalia Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften, Eastphalia University of Applied Sciences (German: ''Ostfalia Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften'', formerly ''Fachhochschule Braunschweig/Wolfenbüttel'') was located in the city until 2010.
Economy
In 2015, the German weekly business news magazine ''Wirtschaftswoche'' ranked Braunschweig as one of the most dynamic economic spaces in all of Germany. Braunschweig was one of the centres of the industrialization in Northern Germany. During the 19th and early 20th century the canning and railroad industries and the sugar production were of great importance for Braunschweig's economy, but eventually other branches such as the automotive industry became more important, while especially the canning industry began to vanish from the city after the end of World War II. The defunct truck and bus manufacturerBüssing
Büssing AG was a German bus and truck manufacturer, established in 1903 by Heinrich Büssing (1843–1929) in Braunschweig. It quickly evolved to one of the largest European producers, whose utility vehicles with the Brunswick Lion emblem were w ...
was headquartered in Braunschweig. Current factory, factories in the city include Volkswagenwerk Braunschweig, Volkswagen, Siemens, Bombardier Transportation, and Robert Bosch GmbH, Bosch.
The fashion label NewYorker, the publishing house Westermann Verlag, Nordzucker, Volkswagen Group, Volkswagen Financial Services and Volkswagen Group, Volkswagen Bank have their headquarters in the city as well as the Volkswagen utility vehicle holding. Also two major optical companies were headquartered in Braunschweig: Voigtländer and Rollei.
During the 1980s and early 1990s the computer companies Atari and Commodore International both had branches for development and production within the city.
Braunschweig is the home of two piano companies, both known worldwide for the high quality of their instruments: Wilhelm Schimmel, Schimmel and Grotrian-Steinweg. Both companies were founded in the 19th century. Additionally :de:Sandberg Guitars, Sandberg Guitars is based in Braunschweig.
Culture
 Braunschweig is famous for ''Till Eulenspiegel'', a medieval jester who played many practical jokes on its citizens.
It also had many breweries, and still a very peculiar kind of beer is made called ''Brunswick Mum, Mumme'', first quoted in 1390, a malt-extract that was shipped all over the world. Two major breweries still produce in Braunschweig, the , founded in 1627, and the former brewery, founded in 1871, now operated by Oettinger Beer.
Braunschweiger (sausage), Braunschweiger Mettwurst, a soft, spreadable smoked pork sausage, is named after the city. Other traditional local dishes include Asparagus, white asparagus, ''Braunschweiger Lebkuchen'', ''Braunkohl'' (a variant of kale served with Bregenwurst), and ''Uhlen un Apen'' (Low German for "Owls and Guenons", a pastry).
Braunschweig is famous for ''Till Eulenspiegel'', a medieval jester who played many practical jokes on its citizens.
It also had many breweries, and still a very peculiar kind of beer is made called ''Brunswick Mum, Mumme'', first quoted in 1390, a malt-extract that was shipped all over the world. Two major breweries still produce in Braunschweig, the , founded in 1627, and the former brewery, founded in 1871, now operated by Oettinger Beer.
Braunschweiger (sausage), Braunschweiger Mettwurst, a soft, spreadable smoked pork sausage, is named after the city. Other traditional local dishes include Asparagus, white asparagus, ''Braunschweiger Lebkuchen'', ''Braunkohl'' (a variant of kale served with Bregenwurst), and ''Uhlen un Apen'' (Low German for "Owls and Guenons", a pastry).
Media
Braunschweig's major local newspaper is the ''Braunschweiger Zeitung'', first published in 1946. Papers formerly published in Braunschweig include the ''Braunschweigische Anzeigen''/''Braunschweigische Staatszeitung'' (1745–1934), the ''Braunschweigische Landeszeitung'' (1880–1936) and the ''Braunschweiger Stadtanzeiger''/''Braunschweiger Allgemeiner Anzeiger'' (1886–1941), and the social-democratic ' (1871–1933). Near Braunschweig at Cremlingen-Abbenrode, there is a large medium wave transmitter, which transmits the program of ''Deutschlandfunk'' on 756 kHz, the Cremlingen transmitter.Festivals
'':de:Schoduvel, Schoduvel'', a medieval Northern German form of Carnival in Germany, Switzerland and Austria, carnival was celebrated in Braunschweig as early as the 13th century. Since 1979 an annual Rosenmontag parade is held in Braunschweig, the largest in Northern Germany, which is named Schoduvel in honour of the medieval custom. An annual ''Weihnachtsmarkt'' (Christmas market) is held in late November and December on the Burgplatz in the centre of Braunschweig. In 2008 the market had 900,000 visitors.Museums and galleries

 The city's most important museum is the Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum, a well known art museum and the oldest public museum in Germany, founded in 1754. It houses a collection of masters of Western art, including Albrecht Dürer, Dürer, Giorgione, Lucas Cranach the Elder, Cranach, Hans Holbein the Younger, Holbein, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Jan Vermeer, Vermeer, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, and Rembrandt.
The Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum, State Museum of Brunswick (''Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum''), founded in 1891, houses a permanent collection documenting the history of the Brunswick Land, Brunswick area ranging from its early history to the present.
The Municipal Museum of Brunswick (''Städtisches Museum Braunschweig''), founded in 1861, is a museum for art and cultural history, documenting the history of the city of Braunschweig.
The Naturhistorisches Museum (Braunschweig), State Natural History Museum is a zoology museum founded in 1754.
Other museums in the city include the Museum of Photography (''Museum für Photographie''), the Jewish Museum (''Jüdisches Museum''), the Museum for Agricultural Technology ''Gut Steinhof'', and the Friedrich Gerstäcker, Gerstäcker-Museum. Frequent exhibitions of contemporary art are also held by the Art Society of Braunschweig (German: ''Kunstverein Braunschweig''), housed in the ''Villa Salve Hospes'', a classicist villa built between 1805 and 1808.
The city's most important museum is the Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum, a well known art museum and the oldest public museum in Germany, founded in 1754. It houses a collection of masters of Western art, including Albrecht Dürer, Dürer, Giorgione, Lucas Cranach the Elder, Cranach, Hans Holbein the Younger, Holbein, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Jan Vermeer, Vermeer, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, and Rembrandt.
The Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum, State Museum of Brunswick (''Braunschweigisches Landesmuseum''), founded in 1891, houses a permanent collection documenting the history of the Brunswick Land, Brunswick area ranging from its early history to the present.
The Municipal Museum of Brunswick (''Städtisches Museum Braunschweig''), founded in 1861, is a museum for art and cultural history, documenting the history of the city of Braunschweig.
The Naturhistorisches Museum (Braunschweig), State Natural History Museum is a zoology museum founded in 1754.
Other museums in the city include the Museum of Photography (''Museum für Photographie''), the Jewish Museum (''Jüdisches Museum''), the Museum for Agricultural Technology ''Gut Steinhof'', and the Friedrich Gerstäcker, Gerstäcker-Museum. Frequent exhibitions of contemporary art are also held by the Art Society of Braunschweig (German: ''Kunstverein Braunschweig''), housed in the ''Villa Salve Hospes'', a classicist villa built between 1805 and 1808.
Music and dance
The ''Braunschweig Classix Festival'' was an annual classical music festival. It is the largest promoter of classical music in the region and one of the most prominent music festivals inLower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
.
From 2001 to 2009, and again since 2013, the annual finals of the international breakdance competition Battle of the Year have been held at the Volkswagen Halle in Braunschweig.
''Braunschweiger TSC'' is among the leading competitive formation dance teams in the world and has won multiple World and European championship titles.
Sports

Notable people
Alphabetical list of some notable people associated with Braunschweig:See also
*Hannover–Braunschweig–Göttingen–Wolfsburg Metropolitan RegionNotes
References
Bibliography
*Richard Andree: ''Braunschweiger Volkskunde.'' 2nd edition. Vieweg, Braunschweig 1901. *Reinhard Bein, Ernst-August Roloff (eds.): ''Der Löwe unterm Hakenkreuz. Reiseführer durch Braunschweig und Umgebung 1930–1945.'' MatrixMedia Verlag, Göttingen 2010, . *Luitgard Camerer, Manfred Garzmann, Wolf-Dieter Schuegraf (eds.): ''Braunschweiger Stadtlexikon.'' Joh. Heinr. Meyer Verlag, Braunschweig 1992, . *Oskar Doering: ''Braunschweig.'' E. A. Seemann, Leipzig 1905. *Hermann Dürre: ''Geschichte der Stadt Braunschweig im Mittelalter.'' Grüneberg, Braunschweig 1861. *Reinhard Dorn: ''Mittelalterliche Kirchen in Braunschweig.'' Niemeyer, Hameln 1978, . *F. Fuhse (ed.): ''Vaterländische Geschichten und Denkwürdigkeiten der Lande Braunschweig und Hannover, Band 1: Braunschweig.'' 3rd edition. Appelhans Verlag, Braunschweig 1925. *Manfred Garzmann, Wolf-Dieter Schuegraf (eds.): ''Braunschweiger Stadtlexikon. Ergänzungsband.'' Joh. Heinr. Meyer Verlag, Braunschweig 1996, . *Otto Hohnstein: ''Braunschweig am Ende des Mittelalters.'' Ramdohr, Braunschweig 1886. *Horst-Rüdiger Jarck, Gerhard Schildt (eds.): ''Die Braunschweigische Landesgeschichte. Jahrtausendrückblick einer Region.'' 2nd edition. Appelhans Verlag, Braunschweig 2001, . *Horst-Rüdiger Jarck, Dieter Lent et al. (eds.): ''Braunschweigisches Biographisches Lexikon – 8. bis 18. Jahrhundert.'' Appelhans Verlag, Braunschweig 2006, . *Horst-Rüdiger Jarck, Günter Scheel (eds.): ''Braunschweigisches Biographisches Lexikon – 19. und 20. Jahrhundert.'' Hahnsche Buchhandlung, Hannover 1996, . *Jörg Leuschner, Karl Heinrich Kaufhold, Claudia Märtl (eds.): ''Die Wirtschafts- und Sozialgeschichte des Braunschweigischen Landes vom Mittelalter bis zur Gegenwart.'' 3 vols. Georg Olms Verlag, Hildesheim 2008, . *Richard Moderhack (ed.): ''Braunschweigische Landesgeschichte im Überblick.'' 3rd edition, Braunschweigischer Geschichtsverein, Braunschweig 1979. *Richard Moderhack: ''Braunschweiger Stadtgeschichte.'' Wagner, Braunschweig 1997, . *E. Oppermann: ''Landeskunde des Herzogtums Braunschweig. Geschichte und Geographie.'' E. Appelhans, Braunschweig 1911. *Rudolf Prescher: ''Der Rote Hahn über Braunschweig.'' Waisenhaus-Buchdruckerei und Verlag, Braunschweig 1955. *Birte Rogacki-Thiemann: ''Braunschweig. Eine kleine Stadtgeschichte.'' Sutton Verlag, Erfurt 2005, . *Ernst-August Roloff: ''Braunschweig und der Staat von Weimar.'' Waisenhaus-Buchdruckerei und Verlag, Braunschweig 1964. *Ernst-August Roloff: ''Wie braun war Braunschweig? Hitler und der Freistaat Braunschweig.'' Braunschweiger Zeitung, Braunschweig 2003. *Gerd Spies (ed.): ''Braunschweig – Das Bild der Stadt in 900 Jahren. Geschichte und Ansichten.'' 2 vols., Städtisches Museum Braunschweig, Braunschweig 1985. *Gerd Spies (ed.): ''Brunswiek 1031 – Braunschweig 1981. Die Stadt Heinrichs des Löwen von den Anfängen bis zur Gegenwart.'' 2 vols., Städtisches Museum Braunschweig, Braunschweig 1982. *Werner Spieß: ''Geschichte der Stadt Braunschweig im Nachmittelalter. Vom Ausgang des Mittelalters bis zum Ende der Stadtfreiheit 1491–1671.'' 2 vols., Waisenhaus-Buchdruckerei und Verlag, Braunschweig 1966, . *Henning Steinführer, Gerd Biegel (eds.): ''1913 – Braunschweig zwischen Monarchie und Moderne.'' Appelhans Verlag, Braunschweig 2015, .External links
Official website
{{Authority control Braunschweig, Capitals of former nations Duchy of Brunswick Members of the Hanseatic League