Bowfin (ling) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species of the
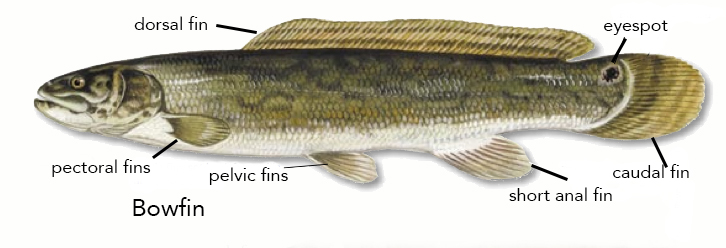 The body of the bowfin is elongated and cylindrical, with the sides and back
The body of the bowfin is elongated and cylindrical, with the sides and back  Bowfin are often referred to as " living fossils" or " primitive fish" because they retained some of the primitive characters common to their ancestors, including a modified (rounded externally) heterocercal caudal fin, a highly vascularized
Bowfin are often referred to as " living fossils" or " primitive fish" because they retained some of the primitive characters common to their ancestors, including a modified (rounded externally) heterocercal caudal fin, a highly vascularized 
 The bowfin is a member of
The bowfin is a member of
 Bowfin are
Bowfin are

 Bowfin are stalking, ambush predators that customarily move into the shallows at night to prey on fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates such as crawfish, other crustaceans, mollusks, and aquatic insects. Young bowfin feed mostly on small crustaceans, while adults are mostly piscivorous, but also known to be opportunistic. Some common examples of prey include frogs, bass, other bowfin, dragonflies, sunfish, crawfish, etc. Bowfin are remarkably agile, can move quickly through the water, and they have a voracious appetite. Their undulating dorsal fin propels them silently through the water while stalking their prey. The attack is straightforward and swift with a movement that lasts approximately 0.075 seconds. There were also some studies regarding the capacity of the bowfin to survive without food. In 1916, a female bowfin was starved for twenty months. It was the longest period that any vertebrate had been without food, as far the writer was aware during the observation. Some independent studies focus on the bowfin's ability to use organic material as a source of food and studied the structure of the gill raker. They concluded that it did not benefit from the organic material in the water because the gill rakers were short with blunt processes and a short space between them. Even bacteria could enter and exit through the gill easily. Its structure alone indicated that the ''Amia'' do not use microorganisms as a source of food.
Bowfin are stalking, ambush predators that customarily move into the shallows at night to prey on fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates such as crawfish, other crustaceans, mollusks, and aquatic insects. Young bowfin feed mostly on small crustaceans, while adults are mostly piscivorous, but also known to be opportunistic. Some common examples of prey include frogs, bass, other bowfin, dragonflies, sunfish, crawfish, etc. Bowfin are remarkably agile, can move quickly through the water, and they have a voracious appetite. Their undulating dorsal fin propels them silently through the water while stalking their prey. The attack is straightforward and swift with a movement that lasts approximately 0.075 seconds. There were also some studies regarding the capacity of the bowfin to survive without food. In 1916, a female bowfin was starved for twenty months. It was the longest period that any vertebrate had been without food, as far the writer was aware during the observation. Some independent studies focus on the bowfin's ability to use organic material as a source of food and studied the structure of the gill raker. They concluded that it did not benefit from the organic material in the water because the gill rakers were short with blunt processes and a short space between them. Even bacteria could enter and exit through the gill easily. Its structure alone indicated that the ''Amia'' do not use microorganisms as a source of food.
 Fossil deposits indicate amiiforms included freshwater and marine species that were once widely distributed in North America, South America, Eurasia and Africa. Today, bowfin (''Amia calva'') are the only remaining species in the order Amiiformes; they are
Fossil deposits indicate amiiforms included freshwater and marine species that were once widely distributed in North America, South America, Eurasia and Africa. Today, bowfin (''Amia calva'') are the only remaining species in the order Amiiformes; they are
 A common parasite of bowfin is the anchor worm (''Lernaea''). These small crustaceans infest the skin and bases of fins, with consequences ranging from slowed growth to death. The mollusk '' Megalonaias gigantea'' lays eggs in the bowfin gills, that are then externally fertilized by sperm passing in the water flow. The small glochidia larvae then hatch and develop in the gill tubes.
Bowfin with
A common parasite of bowfin is the anchor worm (''Lernaea''). These small crustaceans infest the skin and bases of fins, with consequences ranging from slowed growth to death. The mollusk '' Megalonaias gigantea'' lays eggs in the bowfin gills, that are then externally fertilized by sperm passing in the water flow. The small glochidia larvae then hatch and develop in the gill tubes.
Bowfin with
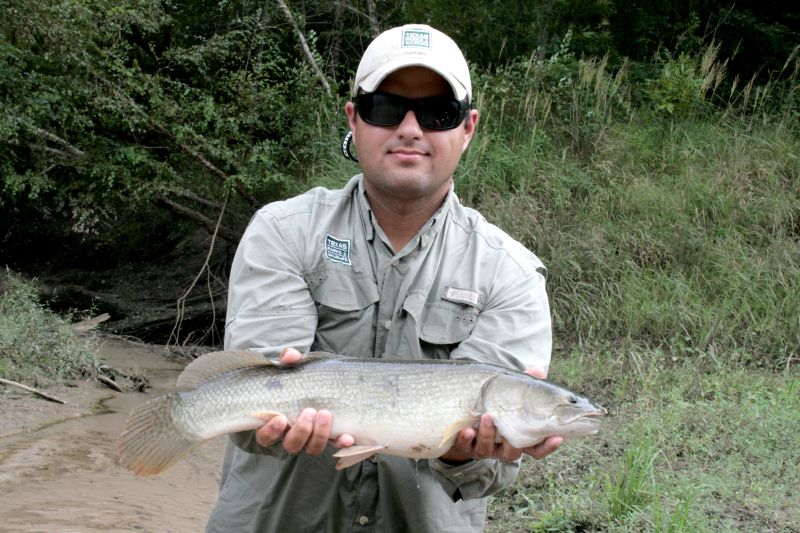 As a sport fish, bowfin are not considered desirable to many anglers. They were once considered a nuisance fish by anglers and early biologists who believed the bowfin's predatory nature was harmful to sport fish populations. As a result, efforts were taken to reduce their numbers. Research has since proven otherwise, and that knowledge together with a better understanding of maintaining overall balance of ecosystems, regulations were introduced to help protect and maintain viable populations of bowfin. Bowfin are strong fighters, a prized trait in game fish. However, they do have a jaw full of sharp teeth which requires careful handling. The current tackle record is
Bowfin were once considered to have little commercial value because of its poor-tasting meat which has been referred to as "soft, bland-tasting and of poor texture". However, it is considered quite palatable if cleaned properly and
As a sport fish, bowfin are not considered desirable to many anglers. They were once considered a nuisance fish by anglers and early biologists who believed the bowfin's predatory nature was harmful to sport fish populations. As a result, efforts were taken to reduce their numbers. Research has since proven otherwise, and that knowledge together with a better understanding of maintaining overall balance of ecosystems, regulations were introduced to help protect and maintain viable populations of bowfin. Bowfin are strong fighters, a prized trait in game fish. However, they do have a jaw full of sharp teeth which requires careful handling. The current tackle record is
Bowfin were once considered to have little commercial value because of its poor-tasting meat which has been referred to as "soft, bland-tasting and of poor texture". However, it is considered quite palatable if cleaned properly and
MN DNR
Bowfin Anglers' Group
FishBase info for Amiidae
{{Taxonbar, from=Q491934 Amiiformes Fish of North America
Halecomorphi
Halecomorphi is a taxon of ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The sole living Halecomorph is the bowfin (''Amia calva''), but the group contains many extinct species in several families (including Amiidae, Caturidae, Liodesmidae, S ...
, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a " primitive fish" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus ''Amia,'' along with '' Amia ocellicauda'', the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei.
Bowfins are demersal
The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) consisting of the part of the water column near to (and significantly affected by) the seabed and the benthos. The demersal zone is just above the benthic zone and forms a layer of ...
freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Now, their range is limited to much of the eastern United States and adjacent southern Canada, including the drainage basins of the Mississippi River, Great Lakes, and various rivers exiting in the Eastern Seaboard or Gulf of Mexico. Their preferred habitat includes vegetated sloughs, lowland rivers and lakes, swamps, and backwater areas; they are also occasionally found in brackish water. They are stalking, ambush predators known to move into the shallows at night to prey on fish and aquatic invertebrates such as crawfish, mollusks, and aquatic insects.
Like gars, bowfin are bimodal breathers—they have the capacity to breathe both water and air. Their gills exchange gases in the water allowing them to breathe, but they also have a gas bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
that serves to maintain buoyancy, and also allows them to breathe air by means of a small pneumatic duct
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth wit ...
connected from the foregut to the gas bladder. They can break the surface to gulp air, which allows them to survive conditions of aquatic hypoxia that would be lethal to most other species. The bowfin is long-lived, with age up to 33 years reported.
Morphology
The typical length of a bowfin is ; females typically grow to , males to . They can reach in length, and weigh . Young of the year typically grow to by October. Females tend to grow larger than males. The body of the bowfin is elongated and cylindrical, with the sides and back
The body of the bowfin is elongated and cylindrical, with the sides and back olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
to brown in color, often with vertical bars and dark reticulations or another camouflaged pattern. The dorsal fin has horizontal bars, and the caudal fin has irregular vertical bars. The underside is white or cream, and the paired fins and anal fin are bright green. During larval stage, hatchlings from about total length are black and tadpole-like in appearance. At approximately total length they have been described as looking like miniature placoderms
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate-skinned') is a Class (biology), class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devoni ...
. They grow quickly, and typically leave the nest within 4 to 6 weeks after hatching. Young males have a black eyespot on the base of the tail ( caudal peduncle) that is commonly encircled by an orange-yellowish border, while the female's is black, if present at all. It is thought the purpose of the eyespot is to confuse predators, deflecting attacks away from the head of the fish to its tail, which affords the bowfin an opportunity to escape predation. The bowfin is so named for its long, undulating dorsal fin consisting of 145 to 250 rays that runs from the middle of the back to the base of the tail.
The skull of the bowfin is made of two layers of skull, the dermatocranium and the chondrocranium
The chondrocranium (or ''cartilaginous neurocranium'') is the primitive cartilage, cartilaginous skeleton, skeletal structure of the fetal skull that grows to envelop the rapidly growing embryonic brain.Salentijn, L. ''Biology of Mineralized Tissue ...
. The chondrocranium layer cannot be seen because it is located below the dermal bones. The bowfin skull is made up of 28 fused bones, which compose the dermatocranium. The roof of the mouth is made up of three bones, the ectopterygoid, the palantine, and the vomer. They have two sets of teeth, including one set of larger sharp teeth coming out of the mandibular and premaxillary
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
bones to grasp and control the prey. The other set of teeth, located posteriorly and connected to the hyomandibula
The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular one( la, os hyomandibulare, from el, hyoeides, "upsilon-shaped" (υ), and Latin: mandibula, "jawbone") is a set of bones that is found in the hyoid region in most fishes. It usually plays ...
r bone, is made up of pharyngeal tooth patches, which are used for sorting out nutrients and grinding down larger pieces of food. '' ''Another three bones make up the lower jaw: the dentary, the angular, and the surangular. The cranial surface of the skull is made up of the nasals, the antorbital, the lacrimal, the parietal, the intertemporal, the post parietal, the supratemporal, the extra scapular, the post temporal, and the opercular. The entirety of the skull is attached to the girdle through another set of bones.
 Bowfin are often referred to as " living fossils" or " primitive fish" because they retained some of the primitive characters common to their ancestors, including a modified (rounded externally) heterocercal caudal fin, a highly vascularized
Bowfin are often referred to as " living fossils" or " primitive fish" because they retained some of the primitive characters common to their ancestors, including a modified (rounded externally) heterocercal caudal fin, a highly vascularized gas bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
lung, vestiges of a spiral valve, and a bony gular plate. The bony gular plate is located underneath the head on the exterior of the lower jaw between the two sides of the lower jaw bone. Other distinguishing characteristics include long, sharp teeth, and two protruding tube-like nostrils. Unlike all of the most primitive actinopterygians, the scales of bowfin differ in that they are not ganoid scales, rather they are large, single-layered cycloid scales closer in similarity to more derived teleosts.

Fish similar in appearance
Northern snakeheads (''Channa argus'') are commonly mistaken for bowfin because of similarities in appearance, most noticeably their elongated, cylindrical shape, and long dorsal fin that runs along their backs. Northern snakeheads are piscivorous fish native to the rivers and estuaries of China, Russia, and Korea that have been introduced and become established in parts of North America. However, unlike bowfin which are native to North America, the northern snakehead is considered aninvasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species ad ...
and environmentally harmful there. Some contrasting differences in bowfin include a black eyespot on their caudal peduncle, a tan and olive coloration, a shorter anal fin, a more rounded head, pelvic fins at a greater distance from the pectoral fins than in the northern snakehead and the presence of the gular plate on the ventral side of the lower jaw. Another noticeable difference is that bowfin scales do not continue uniformly from their body to their head. Bowfin heads are smooth and free of scales, whereas the northern snakehead has scales that uniformly continue from their body through to their head.
The burbot (''Lota lota''), a predatory fish native to streams and lakes of North America and Eurasia, is also commonly mistaken for bowfin. Burbots can be distinguished by their flat head and chin barbel, long anal fin, and pelvic fins situated beneath the pectoral fins.
Bowfin body-shape evolution and development
The first fish lacked jaws and used negative pressure to suck their food in through their mouths. The jaw in the bowfin is a result of their evolutionary need to be able to catch and eat bigger and more nutritious prey. As a result of being able to gather more nutrients, Bowfin are able to live a more active lifestyle. The jaw of a bowfin has several adaptations. The maxilla and premaxilla are fused and the posterior chondrocranium articulates with the vertebra which allows the jaw freedom to rotate. The suspensorium includes several bones and articulates with the snout, brain case, and the mandible. When the jaw opens epaxial muscles lift the chondrocranium, which is attached to the upper jaw, whileadductor muscles
The adductor muscles of the hip are a group of muscles mostly used for bringing the thighs together (called adduction).
Structure
The adductor group is made up of:
*Adductor brevis
*Adductor longus
*Adductor magnus
* Adductor minimus This is o ...
act to close the lower jaw. This ability to open and close the jaw helps the bowfin to be an active predator that can catch bigger prey and digest them.
The vertebral column in bowfin is ossified and in comparison to earlier fish, the centra are the major support for the body, whereas in earlier fish the notochord was the main form of support. In bowfin neural spines and ribs also increase in prominence, an evolutionary aspect that helps provide additional support and stabilize unpaired fins. The evolution of the vertebral column allows the bowfin to withstand lateral bending that puts the column under compression without breaking. This, in turn, allows the bowfin to have more controlled and powerful movements, in comparison to fish that had only a notochord. The bowfin has a rounded heterocercal tail that resembles a homocercal tail. This type of tail gives the body a streamlined shape which allows the bowfin to improve its swimming ability by reducing drag. These types of tails are common in fish with gas bladders, because the bladder supplies the fish with natural buoyancy.
 The bowfin is a member of
The bowfin is a member of actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or h ...
which means that the pectoral girdle is partly endochondral
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system by which bone tissue is produced. Unlike intramembranous ossification, the other process by which bone tissue is produced, ...
but mostly dermal bone. In this group of fish the fins function to maneuver, brake, and for slight positional adjustments. The pectoral girdle of the bowfin has six parts. The post temporal, supracleithrum, postcleithrum, cleithrum, scapulacoracoid, and the clavicle make up the pectoral girdle. The pectoral girdle is attached to the skull. The paired pectoral and pelvic fins of fish are homologous with the limbs of tetrapods.
Physiology
 Bowfin are
Bowfin are physostome
Physostomes are fishes that have a pneumatic duct connecting the gas bladder to the alimentary canal. This allows the gas bladder to be filled or emptied via the mouth. This not only allows the fish to fill their bladder by gulping air, but also ...
s, meaning they have a small "pneumatic duct
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth wit ...
" that connects their swim bladders
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth wi ...
to their digestrive tract. This allows them, like lungfish, to "breath" in two ways: they can extract oxygen from the water when breathing through their gills, but can also break the water's surface to breathe or gulp air through the pneumatic duct
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth wit ...
. When performing low-level physical activity, bowfin obtain more than half of their oxygen from breathing air. The fish have two distinct air-breathing mechanisms used to ventilate the gas bladder. Air breathing ''type I'' is consistent with the action of exhale / inhale exchange, stimulated by either air or water hypoxia, to regulate gas exchange; ''type II'' air breaths are inhalation alone, which is believed to regulate gas bladder volume, to control buoyancy. Bimodal respiration helps bowfin survive and maintain their metabolic rate in hypoxic (low-oxygen) conditions. Bowfin air breath more frequently when they are in darkness, and correspondingly more active.
Bowfin blood can adapt to warm, acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ic waters. The fish becomes inactive in waters below ; at this temperature they breathe almost no air; however, with increasing temperature their air breathing increases. Their preferred temperature range is between , with the temperature of maximum activity.
Air breathing is at a maximum in the range . Bowfin do not use central chemoreceptor regulation for respiration control. Experiments manipulating the oxygen content, carbon dioxide content, and pH of bowfin extradural fluid did not affect breathing rate, heart rate, or blood pressure pointing to a lack of central chemoreceptor regulation. Instead, bowfin respiratory patterns respond to water oxygen content and water temperature, as water temperatures play a role in oxygen content. In the lab, bowfin showed an increase in the breathing rate when the temperatures were raised above 10°C. Bowfin also showed an increase in breathing rate when exposed to lower oxygen levels in the water.
Herpetologist W. T. Neill Wilfred T. Neill (1922–2001) was an American herpetologist and author. His name survives in the scientific names of the central Florida crowned snake, ''Tantilla relicta neilli'', and a Central American snail-eating snake, ''Sibon sanniolus neilli ...
reported in 1950 that he unearthed a bowfin aestivating (in a dormant state) in a chamber below the ground surface, in diameter, from a river. It was further noted that flood levels had previously reached the area, and receded. It is not unusual for riverine species like bowfin to move into backwaters with flood currents, and become trapped when water levels recede. While aestivation is anecdotally documented by multiple researchers, laboratory experiments have suggested instead that bowfin are physiologically incapable of surviving more than three to five days of air exposure. However, no field manipulation has been performed. Regardless of the lack of evidence confirming the bowfin's ability to aestivate, it has been noted that bowfin can survive prolonged conditions of exposure to air because they have the ability to breathe air. Their gill filaments and lamellae are rigid in structure which helps prevent the lamellae from collapsing and aids gas exchange even during air exposure.
Evolution and phylogeny
Competinghypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obser ...
and debates continue over the evolution of ''Amia'' and relatives, including their relationship among basal extant teleosts, and organization of clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s. Bowfin are the last remaining member of Halecomorphi
Halecomorphi is a taxon of ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The sole living Halecomorph is the bowfin (''Amia calva''), but the group contains many extinct species in several families (including Amiidae, Caturidae, Liodesmidae, S ...
, a group that includes many extinct species in several families. Halecomorphs were generally accepted as the sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
to Teleostei
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest class (biology), infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of a ...
but not without question. While a halecostome pattern of neopterygian
Neopterygii (from Greek νέος ''neos'' 'new' and πτέρυξ ''pteryx'' 'fin') is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant f ...
clades was produced in morphology-based analyses of extant actinopterygian
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or ho ...
s, a different result was produced with fossil taxa which showed a monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
Holostei. Monophyletic Holostei were also recovered by at least two nuclear gene
A nuclear gene is a gene whose physical DNA nucleotide sequence is located in the cell nucleus of a eukaryote. The term is used to distinguish nuclear genes from genes found in mitochondria or chloroplasts. The vast majority of genes in eukaryote ...
analyses, in an independent study of fossil and extant fish, and in an analysis of ultraconserved genomic elements.
The extant ray-finned fish of the subclass Actinopterygii include 42 orders, 431 families and over 23,000 species. They are currently classified into two infraclasses, Chondrostei (holosteans
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by a single living species, the bowfin (''Amia calva''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Le ...
) and Neopterygii (teleost fishes). Sturgeons, paddlefish, bichirs and reed fish compose the thirty-eight species of chondrosteans, and are considered relict species. Included in the over 23,000 species of neopterygians are eight relict species comprising gars and the bowfin.

Infraclass Neopterygii
Neopterygians are the second major occurrence in the evolution of ray-finned fish and today include the majority of modern bony fish. They are distinguished from their earlier ancestors by major changes to the jaws, shape of the skull, and tail. They are divided into three divisions: * Division 1. Order Lepisosteiformes – the relict gars which include extant species of gars that first appeared in the Cretaceous. * Division 2. Order Amiiformes – the relict bowfin, (halecomorphi
Halecomorphi is a taxon of ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The sole living Halecomorph is the bowfin (''Amia calva''), but the group contains many extinct species in several families (including Amiidae, Caturidae, Liodesmidae, S ...
ds), the only extant species in the order Amiiformes which date back to the Triassic period.
* Division 3. Division Teleostei – the stem group of Teleostei
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest class (biology), infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of a ...
from which modern fish arose, including most of the bony fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilag ...
we are familiar with today.
Species
The following is a species listGenome evolution
The bowfin genome contains an intact ParaHox gene cluster, similar to the bichir and to most other vertebrates. This is in contrast, however, with teleost fish, which have a fragmented ParaHox cluster, probably because of a whole genome duplication event in their lineage. The presence of an intact ParaHox gene cluster suggests that bowfin ancestors separated from other fish before the last common ancestor of all teleosts appeared. Bowfin are thus possibly a better model to study vertebrate genome organization than common teleostmodel organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
s such as zebrafish.
Feeding behavior
 Bowfin are stalking, ambush predators that customarily move into the shallows at night to prey on fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates such as crawfish, other crustaceans, mollusks, and aquatic insects. Young bowfin feed mostly on small crustaceans, while adults are mostly piscivorous, but also known to be opportunistic. Some common examples of prey include frogs, bass, other bowfin, dragonflies, sunfish, crawfish, etc. Bowfin are remarkably agile, can move quickly through the water, and they have a voracious appetite. Their undulating dorsal fin propels them silently through the water while stalking their prey. The attack is straightforward and swift with a movement that lasts approximately 0.075 seconds. There were also some studies regarding the capacity of the bowfin to survive without food. In 1916, a female bowfin was starved for twenty months. It was the longest period that any vertebrate had been without food, as far the writer was aware during the observation. Some independent studies focus on the bowfin's ability to use organic material as a source of food and studied the structure of the gill raker. They concluded that it did not benefit from the organic material in the water because the gill rakers were short with blunt processes and a short space between them. Even bacteria could enter and exit through the gill easily. Its structure alone indicated that the ''Amia'' do not use microorganisms as a source of food.
Bowfin are stalking, ambush predators that customarily move into the shallows at night to prey on fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates such as crawfish, other crustaceans, mollusks, and aquatic insects. Young bowfin feed mostly on small crustaceans, while adults are mostly piscivorous, but also known to be opportunistic. Some common examples of prey include frogs, bass, other bowfin, dragonflies, sunfish, crawfish, etc. Bowfin are remarkably agile, can move quickly through the water, and they have a voracious appetite. Their undulating dorsal fin propels them silently through the water while stalking their prey. The attack is straightforward and swift with a movement that lasts approximately 0.075 seconds. There were also some studies regarding the capacity of the bowfin to survive without food. In 1916, a female bowfin was starved for twenty months. It was the longest period that any vertebrate had been without food, as far the writer was aware during the observation. Some independent studies focus on the bowfin's ability to use organic material as a source of food and studied the structure of the gill raker. They concluded that it did not benefit from the organic material in the water because the gill rakers were short with blunt processes and a short space between them. Even bacteria could enter and exit through the gill easily. Its structure alone indicated that the ''Amia'' do not use microorganisms as a source of food.
Distribution and habitat
 Fossil deposits indicate amiiforms included freshwater and marine species that were once widely distributed in North America, South America, Eurasia and Africa. Today, bowfin (''Amia calva'') are the only remaining species in the order Amiiformes; they are
Fossil deposits indicate amiiforms included freshwater and marine species that were once widely distributed in North America, South America, Eurasia and Africa. Today, bowfin (''Amia calva'') are the only remaining species in the order Amiiformes; they are demersal
The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) consisting of the part of the water column near to (and significantly affected by) the seabed and the benthos. The demersal zone is just above the benthic zone and forms a layer of ...
freshwater piscivores, and their range is restricted to freshwater environments in North America, including much of the eastern United States and adjacent southern Canada from the St. Lawrence River and Lake Champlain drainage of southern Ontario and Quebec westward around the Great Lakes in southern Ontario into Minnesota.
Historically, their distribution in North America included the drainage basins of the Mississippi River from Quebec to northern Minnesota, the St. Lawrence-Great Lakes, including Georgian Bay, Lake Nipissing
Lake Nipissing (; french: lac Nipissing, oj, Gichi-nibiinsing-zaaga’igan) is a lake in the Canadian province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under ...
and Simcoe Simcoe may refer to:
Geography Canada
* Simcoe, Ontario, a town in southwestern Ontario, near Lake Erie, Canada
* Simcoe County, a county in central Ontario, Canada
* Lake Simcoe, a lake in central Ontario, Canada
* Simcoe North, a federal and pro ...
, Ontario, south to the Gulf of Mexico; Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain from the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
drainage in southeastern Pennsylvania to the Colorado River in Texas.
Stocking
Research from the late 1800s to the 1980s suggests a trend of intentional stockings of non-indigenous fish into ponds, lakes and rivers in the United States. At that time, little was known about environmental impacts, or long-term effects of new species establishment and spread as a result of "fish rescue and transfer" efforts, or the importance of nongame fish to the ecological balance of aquatic ecosystems. Introductions of bowfin to areas they were considered a non-indigenous species included various lakes, rivers and drainages in Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Missouri, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. Many of the introductions were intentional stockings; however, there is no way to positively determine distribution resulting from flood transfers, or other inadvertent migrations. Bowfin are typically piscivorous, but as an introduced species are capable of being voracious predators that pose a threat to native fish and their prey.Preferred habitat
Bowfin prefer vegetated sloughs, lowland rivers and lakes, swamps, backwater areas, and are occasionally found in brackish water. They are well camouflaged, and not easy to spot in slow water with abundant vegetation. They often seek shelter under roots, and submerged logs. Oxygen-poor environments can be tolerated because of their ability to breathe air.Life cycle
Bowfin spawn in the spring or early summer, typically between April and June, more commonly at night in abundantly vegetated, clear shallow water in weed beds over sand bars, and also under stumps, logs, and bushes. Optimum temperatures for nesting and spawning range between . The males construct circular nests in fibrous root mats, clearing away leaves and stems. Depending on the density of surrounding vegetation there may be a tunnel-like entrance at one side. The diameter of the nests commonly range between , at a water depth of . During spawning season, the fins and underside of male bowfin often change in color to a bright lime green. The courtship/spawning sequence lasts one to three hours, and can repeat up to five times. Courtship begins when a female approaches the nest. The ritual consists of intermittent nose bites, nudges, and chasing behavior by the male until the female becomes receptive, at which time the pair lie side by side in the nest. She deposits her eggs while he shakes his fins in a vibratory movement, and releases his milt for fertilization to occur. A male often has eggs from more than one female in his nest, and a single female often spawns in several nests. Females vacate the nest after spawning, leaving the male behind to protect the eggs during the eight to ten days of incubation. A nest may contain 2,000 to 5,000 eggs, possibly more. Fecundity is usually related to size of the fish, so it is not unusual for the roe of a large gravid female to contain over 55,000 eggs. Bowfin eggs are adhesive, and will attach to aquatic vegetation, roots, gravel, and sand. After hatching, larval bowfin do not swim actively in search of food. During the seven to nine days required for yolk-sac absorption, they attach to vegetation by means of an adhesive organ on their snout, and remain protected by the parent male bowfin. Bowfin aggressively protect their spawn from the first day of incubation to a month or so after the eggs have hatched. When the fry are able to swim and forage on their own, they will form a school and leave the nest accompanied by the parent male bowfin who slowly circles them to prevent separation. Bowfin reach sexually maturity at two to three years of age. They can live up to 33 years in the wild, and 30 years in captivity. Bowfin may live decades at adult size.Diseases
 A common parasite of bowfin is the anchor worm (''Lernaea''). These small crustaceans infest the skin and bases of fins, with consequences ranging from slowed growth to death. The mollusk '' Megalonaias gigantea'' lays eggs in the bowfin gills, that are then externally fertilized by sperm passing in the water flow. The small glochidia larvae then hatch and develop in the gill tubes.
Bowfin with
A common parasite of bowfin is the anchor worm (''Lernaea''). These small crustaceans infest the skin and bases of fins, with consequences ranging from slowed growth to death. The mollusk '' Megalonaias gigantea'' lays eggs in the bowfin gills, that are then externally fertilized by sperm passing in the water flow. The small glochidia larvae then hatch and develop in the gill tubes.
Bowfin with liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
and with fatal leukemia have been reported.
Utilization
 As a sport fish, bowfin are not considered desirable to many anglers. They were once considered a nuisance fish by anglers and early biologists who believed the bowfin's predatory nature was harmful to sport fish populations. As a result, efforts were taken to reduce their numbers. Research has since proven otherwise, and that knowledge together with a better understanding of maintaining overall balance of ecosystems, regulations were introduced to help protect and maintain viable populations of bowfin. Bowfin are strong fighters, a prized trait in game fish. However, they do have a jaw full of sharp teeth which requires careful handling. The current tackle record is
Bowfin were once considered to have little commercial value because of its poor-tasting meat which has been referred to as "soft, bland-tasting and of poor texture". However, it is considered quite palatable if cleaned properly and
As a sport fish, bowfin are not considered desirable to many anglers. They were once considered a nuisance fish by anglers and early biologists who believed the bowfin's predatory nature was harmful to sport fish populations. As a result, efforts were taken to reduce their numbers. Research has since proven otherwise, and that knowledge together with a better understanding of maintaining overall balance of ecosystems, regulations were introduced to help protect and maintain viable populations of bowfin. Bowfin are strong fighters, a prized trait in game fish. However, they do have a jaw full of sharp teeth which requires careful handling. The current tackle record is
Bowfin were once considered to have little commercial value because of its poor-tasting meat which has been referred to as "soft, bland-tasting and of poor texture". However, it is considered quite palatable if cleaned properly and smoked
Smoking is the process of flavoring, browning, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Meat, fish, and ''lapsang souchong'' tea are often smoked.
In Europe, alder is the tradi ...
, or prepared fried, blackened, used in courtbouillion, or in fishballs or fishcakes. Over the years, global efforts have imposed strict regulations on the international trade of caviar, particularly on the harvest of sturgeons from the Caspian Sea where the highly prized caviar from the beluga sturgeon
The beluga (), also known as the beluga sturgeon or great sturgeon (''Huso huso''), is a species of anadromous fish in the sturgeon family (Acipenseridae) of order Acipenseriformes. It is found primarily in the Caspian and Black Sea basins, a ...
originates. The bans imposed on Caspian sturgeons have created lucrative markets for affordable substitutes in the United States including paddlefish, bowfin, and various species of sturgeon
Sturgeon is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretace ...
. In Louisiana, bowfin are harvested in the wild, and cultured commercially in hatcheries for their meat and roe. The roe is processed into caviar, and sold as "Cajun caviar", or marketed under the trade name "Choupiquet Royale".
Accumulation of toxic substances
In some areas of the United States where aquatic environments have tested positive for elevated levels oftoxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1 ...
, such as mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, arsenic, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
, and copper, there are posted signs with warnings about the consumption of fish caught in those areas. Concentration of mercury biomagnifies as it passes up the food chain from organisms on lower trophic levels to apex predators. It bioaccumulates in the tissues of larger, long-lived predatory fish. When compared to smaller, short-lived fish, bowfin tend to concentrate mercury at higher levels thereby making them less safe for human consumption.
See also
* Snakehead (fish)References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
MN DNR
Bowfin Anglers' Group
FishBase info for Amiidae
{{Taxonbar, from=Q491934 Amiiformes Fish of North America
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
Fish of the Great Lakes
Freshwater fish of the Southeastern United States
Articles containing video clips
Fish described in 1766
Freshwater fish