Boundary-value Analysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Boundary-value analysis is a
class Safe
On the basis of the code, the input vectors of are partitioned. The blocks we need to cover are the overflow statement
and the underflow statement and neither of these 2. That gives rise to 3 equivalent classes, from the code review itself.
 we note that there is a fixed size of
we note that there is a fixed size of
The Testing Standards Working Party
website Software testing
software testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.
Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computin ...
technique in which tests are designed to include representatives of boundary values in a range. The idea comes from the boundary. Given that there is a set of test vector In computer science and engineering, a test vector is a set of inputs provided to a system in order to test that system. In software development, test vectors are a methodology of software testing and software verification and validation.
Rationa ...
s to test the system, a topology can be defined on that set. Those inputs which belong to the same equivalence class
In mathematics, when the elements of some set S have a notion of equivalence (formalized as an equivalence relation), then one may naturally split the set S into equivalence classes. These equivalence classes are constructed so that elements ...
as defined by the equivalence partitioning
Equivalence partitioning or equivalence class partitioning (ECP) is a software testing technique that divides the input data of a software unit into partitions of equivalent data from which test cases can be derived. In principle, test cases are ...
theory would constitute the basis. Given that the basis sets are neighbors, there would exist a boundary between them. The test vectors on either side of the boundary are called boundary values. In practice, this would require that the test vectors can be ordered, and that the individual parameters follows some kind of order (either partial order
In mathematics, especially order theory, a partial order on a set is an arrangement such that, for certain pairs of elements, one precedes the other. The word ''partial'' is used to indicate that not every pair of elements needs to be comparable ...
or total order
In mathematics, a total order or linear order is a partial order in which any two elements are comparable. That is, a total order is a binary relation \leq on some set X, which satisfies the following for all a, b and c in X:
# a \leq a ( re ...
).
Formal definition
Formally, the boundary values can be defined as below: :Let the set of thetest vector In computer science and engineering, a test vector is a set of inputs provided to a system in order to test that system. In software development, test vectors are a methodology of software testing and software verification and validation.
Rationa ...
s be .
:Let's assume that there is an ordering relation defined over them, as .
:Let be two equivalent classes.
:Assume that test vector and .
:If or then the classes are in the same neighborhood
A neighbourhood (Commonwealth English) or neighborhood (American English) is a geographically localized community within a larger town, city, suburb or rural area, sometimes consisting of a single street and the buildings lining it. Neigh ...
and the values are boundary values.
In plainer English, values on the minimum and maximum edges of an equivalence partition are tested. The values could be input or output ranges of a software component, can also be the internal implementation. Since these boundaries are common locations for errors that result in software faults they are frequently exercised in test case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise ...
s.
Application
The expected input and output values to the software component should be extracted from the component specification. The values are then grouped into sets with identifiable boundaries. Each set, or partition, contains values that are expected to be processed by the component in the same way. Partitioning of test data ranges is explained in theequivalence partitioning
Equivalence partitioning or equivalence class partitioning (ECP) is a software testing technique that divides the input data of a software unit into partitions of equivalent data from which test cases can be derived. In principle, test cases are ...
test case design technique. It is important to consider both valid and invalid partitions when designing test cases.
The demonstration can be done using a function written in Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
.
 we note that there is a fixed size of
we note that there is a fixed size of integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
hence:-
:
We note that the input parameter ''a'' and ''b'' both are integers, hence total order
In mathematics, a total order or linear order is a partial order in which any two elements are comparable. That is, a total order is a binary relation \leq on some set X, which satisfies the following for all a, b and c in X:
# a \leq a ( re ...
exists on them.
When we compute the equalities:-
:
:
we get back the values which are on the boundary, inclusive, that is these pairs of are valid combinations,
and no underflow or overflow would happen for them.
On the other hand:-
:
gives pairs of which are invalid combinations,
Overflow would occur for them. In the same way:-
:
gives pairs of which are invalid combinations,
Underflow would occur for them.
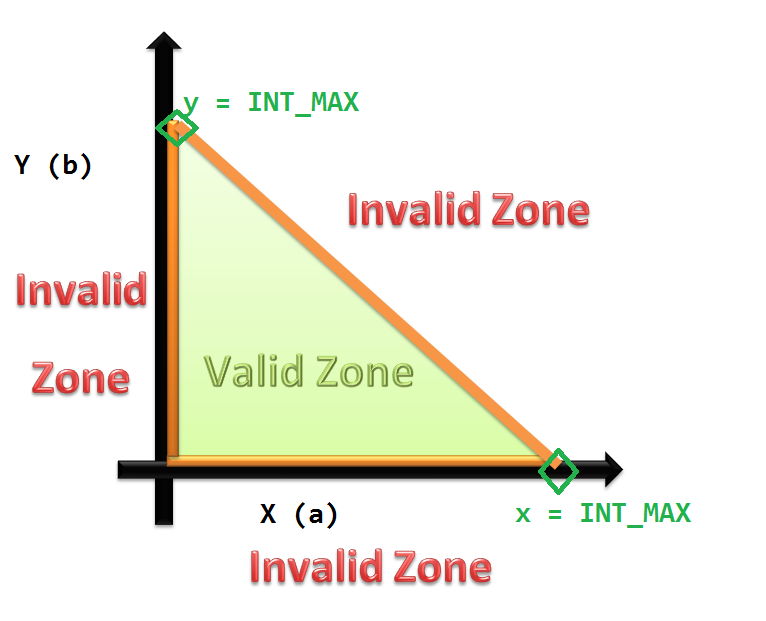
Boundary values (drawn only for the overflow case) are being shown as the orange line in the right hand side figure.
For another example, if the input values were months of the year, expressed as integers, the input parameter 'month' might have the following partitions:
... -2 -1 0 1 .............. 12 13 14 15 .....
--------------, -------------------, -------------------
invalid partition 1 valid partition invalid partition 2
The boundary between two partitions is the place where the behavior of the application changes and is not a real number itself. The boundary value is the minimum (or maximum) value that is at the boundary. The number 0 is the maximum number in the first partition, the number 1 is the minimum value in the second partition, both are boundary values. Test cases should be created to generate inputs or outputs that will fall on and to either side of each boundary, which results in two cases per boundary. The test cases on each side of a boundary should be in the smallest increment possible for the component under test, for an integer this is 1, but if the input was a decimal with 2 places then it would be .01. In the example above there are boundary values at 0,1 and 12,13 and each should be tested.
Boundary value analysis does not require invalid partitions. Take an example where a heater is turned on if the temperature is 10 degrees or colder. There are two partitions (temperature≤10, temperature>10) and two boundary values to be tested (temperature=10, temperature=11).
Where a boundary value falls within the invalid partition the test case is designed to ensure the software component handles the value in a controlled manner. Boundary value analysis can be used throughout the testing cycle and is equally applicable at all testing phases.
References
{{ReflistExternal links
The Testing Standards Working Party
website Software testing