Botanical Gardens In West Virginia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the
Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the
 Botany originated as
Botany originated as
 During the 18th century, systems of
During the 18th century, systems of 
 20th century developments in plant biochemistry have been driven by modern techniques of organic chemistry, organic chemical analysis, such as spectroscopy, chromatography and electrophoresis. With the rise of the related molecular-scale biological approaches of molecular biology,
20th century developments in plant biochemistry have been driven by modern techniques of organic chemistry, organic chemical analysis, such as spectroscopy, chromatography and electrophoresis. With the rise of the related molecular-scale biological approaches of molecular biology,
 Virtually all staple foods come either directly from primary production by plants, or indirectly from animals that eat them. Plants and other photosynthetic organisms are at the base of most food chains because they use the energy from the sun and nutrients from the soil and atmosphere, converting them into a form that can be used by animals. This is what ecologists call the first trophic level. The modern forms of the major staple foods, such as hemp, teff, maize, rice, wheat and other cereal grasses, Pulse (legume), pulses, bananas and plantains, as well as hemp, flax and cotton grown for their fibres, are the outcome of prehistoric selection over thousands of years from among Neolithic founder crops, wild ancestral plants with the most desirable characteristics.
Botanists study how plants produce food and how to increase yields, for example through plant breeding, making their work important to humanity's ability to feed the world and provide food security for future generations. Botanists also study weeds, which are a considerable problem in agriculture, and the biology and control of Plant pathology, plant pathogens in agriculture and natural ecosystems. Ethnobotany is the study of the relationships between plants and people. When applied to the investigation of historical plant–people relationships ethnobotany may be referred to as archaeobotany or paleoethnobotany, palaeoethnobotany. Some of the earliest plant-people relationships arose between the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people of Canada in identifying edible plants from inedible plants. This relationship the indigenous people had with plants was recorded by ethnobotanists.
Virtually all staple foods come either directly from primary production by plants, or indirectly from animals that eat them. Plants and other photosynthetic organisms are at the base of most food chains because they use the energy from the sun and nutrients from the soil and atmosphere, converting them into a form that can be used by animals. This is what ecologists call the first trophic level. The modern forms of the major staple foods, such as hemp, teff, maize, rice, wheat and other cereal grasses, Pulse (legume), pulses, bananas and plantains, as well as hemp, flax and cotton grown for their fibres, are the outcome of prehistoric selection over thousands of years from among Neolithic founder crops, wild ancestral plants with the most desirable characteristics.
Botanists study how plants produce food and how to increase yields, for example through plant breeding, making their work important to humanity's ability to feed the world and provide food security for future generations. Botanists also study weeds, which are a considerable problem in agriculture, and the biology and control of Plant pathology, plant pathogens in agriculture and natural ecosystems. Ethnobotany is the study of the relationships between plants and people. When applied to the investigation of historical plant–people relationships ethnobotany may be referred to as archaeobotany or paleoethnobotany, palaeoethnobotany. Some of the earliest plant-people relationships arose between the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people of Canada in identifying edible plants from inedible plants. This relationship the indigenous people had with plants was recorded by ethnobotanists.
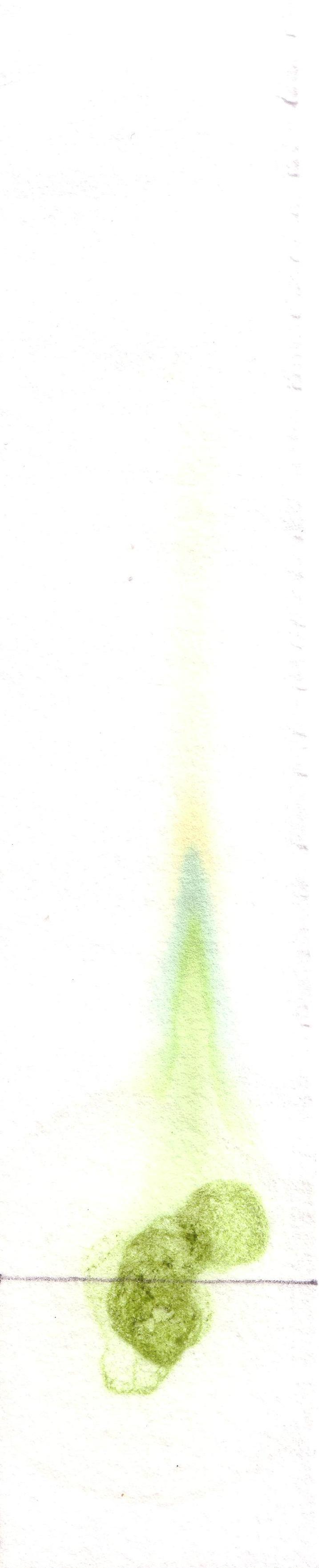 Plants and various other groups of photosynthetic eukaryotes collectively known as "
Plants and various other groups of photosynthetic eukaryotes collectively known as "
 Plant ecology is the science of the functional relationships between plants and their habitats – the environments where they complete their Biological life cycle, life cycles. Plant ecologists study the composition of local and regional floras, their
Plant ecology is the science of the functional relationships between plants and their habitats – the environments where they complete their Biological life cycle, life cycles. Plant ecologists study the composition of local and regional floras, their
 A considerable amount of new knowledge about plant function comes from studies of the molecular genetics of model organism#Plants, model plants such as the Thale cress, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', a weedy species in the mustard family (Brassicaceae). The genome or hereditary information contained in the genes of this species is encoded by about 135 million base pairs of DNA, forming one of the smallest genomes among
A considerable amount of new knowledge about plant function comes from studies of the molecular genetics of model organism#Plants, model plants such as the Thale cress, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', a weedy species in the mustard family (Brassicaceae). The genome or hereditary information contained in the genes of this species is encoded by about 135 million base pairs of DNA, forming one of the smallest genomes among
 The chloroplasts of plants have a number of biochemical, structural and genetic similarities to cyanobacteria, (commonly but incorrectly known as "blue-green algae") and are thought to be derived from an ancient endosymbiotic theory, endosymbiotic relationship between an ancestral eukaryote, eukaryotic cell and a Chloroplast#Parent group: Cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial resident.
The
The chloroplasts of plants have a number of biochemical, structural and genetic similarities to cyanobacteria, (commonly but incorrectly known as "blue-green algae") and are thought to be derived from an ancient endosymbiotic theory, endosymbiotic relationship between an ancestral eukaryote, eukaryotic cell and a Chloroplast#Parent group: Cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial resident.
The
 Plant physiology encompasses all the internal chemical and physical activities of plants associated with life. Chemicals obtained from the air, soil and water form the basis of all metabolism, plant metabolism. The energy of sunlight, captured by oxygenic photosynthesis and released by cellular respiration, is the basis of almost all life. Phototroph, Photoautotrophs, including all green plants, algae and cyanobacteria gather energy directly from sunlight by photosynthesis. Heterotrophs including all animals, all fungi, all completely parasitic plants, and non-photosynthetic bacteria take in organic molecules produced by photoautotrophs and respire them or use them in the construction of cells and tissues. Cellular respiration, Respiration is the oxidation of carbon compounds by breaking them down into simpler structures to release the energy they contain, essentially the opposite of photosynthesis.
Molecules are moved within plants by transport processes that operate at a variety of spatial scales. Subcellular transport of ions, electrons and molecules such as water and
Plant physiology encompasses all the internal chemical and physical activities of plants associated with life. Chemicals obtained from the air, soil and water form the basis of all metabolism, plant metabolism. The energy of sunlight, captured by oxygenic photosynthesis and released by cellular respiration, is the basis of almost all life. Phototroph, Photoautotrophs, including all green plants, algae and cyanobacteria gather energy directly from sunlight by photosynthesis. Heterotrophs including all animals, all fungi, all completely parasitic plants, and non-photosynthetic bacteria take in organic molecules produced by photoautotrophs and respire them or use them in the construction of cells and tissues. Cellular respiration, Respiration is the oxidation of carbon compounds by breaking them down into simpler structures to release the energy they contain, essentially the opposite of photosynthesis.
Molecules are moved within plants by transport processes that operate at a variety of spatial scales. Subcellular transport of ions, electrons and molecules such as water and
 Plants are not passive, but respond to signal transduction, external signals such as light, touch, and injury by moving or growing towards or away from the stimulus, as appropriate. Tangible evidence of touch sensitivity is the almost instantaneous collapse of leaflets of ''Mimosa pudica'', the insect traps of Venus flytrap and bladderworts, and the pollinia of orchids.
The hypothesis that plant growth and development is coordinated by plant hormones or plant growth regulators first emerged in the late 19th century. Darwin experimented on the movements of plant shoots and roots towards heliotropism, light and geotropism, gravity, and concluded "It is hardly an exaggeration to say that the tip of the radicle . . acts like the brain of one of the lower animals . . directing the several movements". About the same time, the role of auxins (from the Greek , to grow) in control of plant growth was first outlined by the Dutch scientist Frits Went. The first known auxin, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which promotes cell growth, was only isolated from plants about 50 years later. This compound mediates the tropic responses of shoots and roots towards light and gravity. The finding in 1939 that plant callus (cell biology), callus could be maintained in culture containing IAA, followed by the observation in 1947 that it could be induced to form roots and shoots by controlling the concentration of growth hormones were key steps in the development of plant biotechnology and genetic modification.
Cytokinins are a class of plant hormones named for their control of cell division (especially cytokinesis). The natural cytokinin zeatin was discovered in corn, ''Zea mays'', and is a derivative of the purine adenine. Zeatin is produced in roots and transported to shoots in the xylem where it promotes cell division, bud development, and the greening of chloroplasts. The gibberelins, such as gibberelic acid are diterpenes synthesised from Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, acetyl CoA via the mevalonate pathway. They are involved in the promotion of germination and dormancy-breaking in seeds, in regulation of plant height by controlling stem elongation and the control of flowering. Abscisic acid (ABA) occurs in all land plants except liverworts, and is synthesised from carotenoids in the chloroplasts and other plastids. It inhibits cell division, promotes seed maturation, and dormancy, and promotes stomatal closure. It was so named because it was originally thought to control abscission. Ethylene#Ethylene as a plant hormone, Ethylene is a gaseous hormone that is produced in all higher plant tissues from methionine. It is now known to be the hormone that stimulates or regulates fruit ripening and abscission, and it, or the synthetic growth regulator ethephon which is rapidly metabolised to produce ethylene, are used on industrial scale to promote ripening of cotton, pineapples and other climacteric (botany), climacteric crops.
Another class of phytohormones is the jasmonates, first isolated from the oil of ''Jasminum grandiflorum'' which regulates wound responses in plants by unblocking the expression of genes required in the systemic acquired resistance response to pathogen attack.
In addition to being the primary energy source for plants, light functions as a signalling device, providing information to the plant, such as how much sunlight the plant receives each day. This can result in adaptive changes in a process known as photomorphogenesis. Phytochromes are the Photoreceptor protein, photoreceptors in a plant that are sensitive to light.
Plants are not passive, but respond to signal transduction, external signals such as light, touch, and injury by moving or growing towards or away from the stimulus, as appropriate. Tangible evidence of touch sensitivity is the almost instantaneous collapse of leaflets of ''Mimosa pudica'', the insect traps of Venus flytrap and bladderworts, and the pollinia of orchids.
The hypothesis that plant growth and development is coordinated by plant hormones or plant growth regulators first emerged in the late 19th century. Darwin experimented on the movements of plant shoots and roots towards heliotropism, light and geotropism, gravity, and concluded "It is hardly an exaggeration to say that the tip of the radicle . . acts like the brain of one of the lower animals . . directing the several movements". About the same time, the role of auxins (from the Greek , to grow) in control of plant growth was first outlined by the Dutch scientist Frits Went. The first known auxin, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which promotes cell growth, was only isolated from plants about 50 years later. This compound mediates the tropic responses of shoots and roots towards light and gravity. The finding in 1939 that plant callus (cell biology), callus could be maintained in culture containing IAA, followed by the observation in 1947 that it could be induced to form roots and shoots by controlling the concentration of growth hormones were key steps in the development of plant biotechnology and genetic modification.
Cytokinins are a class of plant hormones named for their control of cell division (especially cytokinesis). The natural cytokinin zeatin was discovered in corn, ''Zea mays'', and is a derivative of the purine adenine. Zeatin is produced in roots and transported to shoots in the xylem where it promotes cell division, bud development, and the greening of chloroplasts. The gibberelins, such as gibberelic acid are diterpenes synthesised from Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, acetyl CoA via the mevalonate pathway. They are involved in the promotion of germination and dormancy-breaking in seeds, in regulation of plant height by controlling stem elongation and the control of flowering. Abscisic acid (ABA) occurs in all land plants except liverworts, and is synthesised from carotenoids in the chloroplasts and other plastids. It inhibits cell division, promotes seed maturation, and dormancy, and promotes stomatal closure. It was so named because it was originally thought to control abscission. Ethylene#Ethylene as a plant hormone, Ethylene is a gaseous hormone that is produced in all higher plant tissues from methionine. It is now known to be the hormone that stimulates or regulates fruit ripening and abscission, and it, or the synthetic growth regulator ethephon which is rapidly metabolised to produce ethylene, are used on industrial scale to promote ripening of cotton, pineapples and other climacteric (botany), climacteric crops.
Another class of phytohormones is the jasmonates, first isolated from the oil of ''Jasminum grandiflorum'' which regulates wound responses in plants by unblocking the expression of genes required in the systemic acquired resistance response to pathogen attack.
In addition to being the primary energy source for plants, light functions as a signalling device, providing information to the plant, such as how much sunlight the plant receives each day. This can result in adaptive changes in a process known as photomorphogenesis. Phytochromes are the Photoreceptor protein, photoreceptors in a plant that are sensitive to light.
 Plant anatomy is the study of the structure of plant cells and tissues, whereas plant morphology is the study of their external form.
All plants are multicellular eukaryotes, their DNA stored in nuclei. The characteristic features of
Plant anatomy is the study of the structure of plant cells and tissues, whereas plant morphology is the study of their external form.
All plants are multicellular eukaryotes, their DNA stored in nuclei. The characteristic features of
 Systematic botany is part of systematic biology, which is concerned with the range and diversity of organisms and their relationships, particularly as determined by their evolutionary history. It involves, or is related to, biological classification, scientific taxonomy and phylogenetics. Biological classification is the method by which botanists group organisms into categories such as genus, genera or
In 1998, the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group published a phylogenetics, phylogeny for flowering plants based on an analysis of DNA sequences from most families of flowering plants. As a result of this work, many questions, such as which families represent the earliest branches of angiosperms, have now been answered. Investigating how plant species are related to each other allows botanists to better understand the process of evolution in plants. Despite the study of model plants and increasing use of DNA evidence, there is ongoing work and discussion among taxonomists about how best to classify plants into various Taxon, taxa. Technological developments such as computers and electron microscopes have greatly increased the level of detail studied and speed at which data can be analysed.
Systematic botany is part of systematic biology, which is concerned with the range and diversity of organisms and their relationships, particularly as determined by their evolutionary history. It involves, or is related to, biological classification, scientific taxonomy and phylogenetics. Biological classification is the method by which botanists group organisms into categories such as genus, genera or
In 1998, the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group published a phylogenetics, phylogeny for flowering plants based on an analysis of DNA sequences from most families of flowering plants. As a result of this work, many questions, such as which families represent the earliest branches of angiosperms, have now been answered. Investigating how plant species are related to each other allows botanists to better understand the process of evolution in plants. Despite the study of model plants and increasing use of DNA evidence, there is ongoing work and discussion among taxonomists about how best to classify plants into various Taxon, taxa. Technological developments such as computers and electron microscopes have greatly increased the level of detail studied and speed at which data can be analysed.
Supporting Information
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
 Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the
Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
of plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
life and a branch of biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts Scientific method, scientific research to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, ...
who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
word (') meaning "pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or swine ...
", "herb
In general use, herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal ...
s" "grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns an ...
", or "fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agriculture, agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, domestic rabbit, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food g ...
"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
and algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
by mycologists
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans, including as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogens, as w ...
and phycologists
Phycology () is the scientific study of algae. Also known as algology, phycology is a branch of life science.
Algae are important as primary producers in aquatic ecosystems. Most algae are eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms that live in a w ...
respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress
International Botanical Congress (IBC) is an international meeting of botanists in all scientific fields, authorized by the International Association of Botanical and Mycological Societies (IABMS) and held every six years, with the location rotat ...
. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of land plants
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as siste ...
of which some 391,000 species are vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They al ...
s (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s), and approximately 20,000 are bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in ...
s.
Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern reme ...
with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – plants that were edible, poisonous, and possibly medicinal, making it one of the first endeavours of human investigation. Medieval physic garden
A physic garden is a type of herb garden with medicinal plants. Botanical gardens developed from them.
History
Modern botanical gardens were preceded by medieval physic gardens, often monastic gardens, that existed by 800 at least. Gardens of ...
s, often attached to monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
, contained plants possibly having medicinal benefit. They were forerunners of the first botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
s attached to universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy
Plant taxonomy is the science that finds, identifies, describes, classifies, and names plants. It is one of the main branches of taxonomy (the science that finds, describes, classifies, and names living things).
Plant taxonomy is closely allied ...
, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of nomenclature of Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
that remains in use to this day for the naming of all biological species.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviole ...
and live cell imaging
Live-cell imaging is the study of living cells using time-lapse microscopy. It is used by scientists to obtain a better understanding of biological function through the study of cellular dynamics. Live-cell imaging was pioneered in the first de ...
, electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, analysis of chromosome number
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively ...
, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s and other protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
and proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In ...
and DNA sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequences are usua ...
to classify plants more accurately.
Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with contributions and insights from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
, growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
and differentiation, reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
, biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
and primary metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, chemical products, development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
*Photographi ...
, diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that ar ...
, evolutionary relationships
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
, systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre ...
, and plant taxonomy
Plant taxonomy is the science that finds, identifies, describes, classifies, and names plants. It is one of the main branches of taxonomy (the science that finds, describes, classifies, and names living things).
Plant taxonomy is closely allied ...
. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is a sub-field of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the ...
and epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
, which study the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capabi ...
s and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and ...
, materials such as timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, rubber, fibre
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
and drugs, in modern horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. Th ...
, plant propagation
Plant propagation is the process by which new plants grow from a variety of sources: seeds, cuttings, and other plant parts. Plant propagation can also refer to the man-made or natural dispersal of seeds.
Propagation typically occurs as a step i ...
, breeding
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant.
Breeding may refer to:
* Animal husbandry, through selected specimens such as dogs, horses, and rab ...
and genetic modification
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including t ...
, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management
Environmental resource management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environmental resources management aims ...
, and the maintenance of biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
.
History
Early botany
 Botany originated as
Botany originated as herbalism
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern reme ...
, the study and use of plants for their possible medicinal properties. The early recorded history of botany includes many ancient writings and plant classifications. Examples of early botanical works have been found in ancient texts from India dating back to before 1100 BCE, Ancient Egypt, in archaic Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
writings, and in works from China purportedly from before 221 BCE.
Modern botany traces its roots back to Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
specifically to Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routledge ...
(–287 BCE), a student of Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
who invented and described many of its principles and is widely regarded in the scientific community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many " sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional activities are als ...
as the "Father of Botany". His major works, ''Enquiry into Plants
Theophrastus's ''Enquiry into Plants'' or ''Historia Plantarum'' ( grc-gre, Περὶ φυτῶν ἱστορία, ''Peri phyton historia'') was, along with his mentor Aristotle's ''History of Animals'', Pliny the Elder's '' Natural History'' an ...
'' and ''On the Causes of Plants'', constitute the most important contributions to botanical science until the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, almost seventeen centuries later.
Another work from Ancient Greece that made an early impact on botany is , a five-volume encyclopedia about preliminary herbal medicine written in the middle of the first century by Greek physician and pharmacologist Pedanius Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of ''De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vol ...
. was widely read for more than 1,500 years. Important contributions from the medieval Muslim world include Ibn Wahshiyya
( ar, ابن وحشية), died , was a Nabataean (Aramaic-speaking, rural Iraqi) agriculturalist, toxicologist, and alchemist born in Qussīn, near Kufa in Iraq. He is the author of the ''Nabataean Agriculture'' (), an influential Arabic work on ...
's ''Nabatean Agriculture
''The Nabataean Agriculture'' (), also written ''The Nabatean Agriculture'', is a 10th-century text on agronomy by Ibn Wahshiyya (died ), from Qussīn in present-day Iraq. It contains information on plants and agriculture, as well as on magic an ...
'', Abū Ḥanīfa Dīnawarī
Abū Ḥanīfa Aḥmad ibn Dāwūd Dīnawarī ( fa, ابوحنيفه دينوری; died 895) was a Persian Islamic Golden Age polymath, astronomer, agriculturist, botanist, metallurgist, geographer, mathematician, and historian.
Life
Dinawar ...
's (828–896) the ''Book of Plants'', and Ibn Bassal
Ibn Bassal ( ar, ابن بصال) was an 11th-century Andalusian Arab botanist and agronomist in Toledo and Seville, Spain who wrote about horticulture and arboriculture. He is best known for his book on agronomy, the ''Dīwān al-filāha'' (An ...
's ''The Classification of Soils''. In the early 13th century, Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati
Ahmad bin Muhammad bin Mufarraj bin Ani al-Khalil, better known as Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati, Ibn al-Rumiya or al-Ashshab, ( ar, أبو العباس النباتي, ''Abu’l-ʿAbbās al-Nabātī'') (c. 1200) was an Andalusian scientist, botan ...
, and Ibn al-Baitar
Diyāʾ al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Aḥmad al-Mālaqī, commonly known as Ibn al-Bayṭār () (1197–1248 AD) was an Andalusian Arab physician, botanist, pharmacist and scientist. His main contribution was to systematically record ...
(d. 1248) wrote on botany in a systematic and scientific manner.
In the mid-16th century, botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
s were founded in a number of Italian universities. The Padua botanical garden in 1545 is usually considered to be the first which is still in its original location. These gardens continued the practical value of earlier "physic gardens", often associated with monasteries, in which plants were cultivated for suspected medicinal uses. They supported the growth of botany as an academic subject. Lectures were given about the plants grown in the gardens. Botanical gardens came much later to northern Europe; the first in England was the University of Oxford Botanic Garden
The University of Oxford Botanic Garden is the oldest botanic garden in Great Britain and one of the oldest scientific gardens in the world. The garden was founded in 1621 as a physic garden growing plants for medicinal research. Today it conta ...
in 1621.
German physician Leonhart Fuchs
Leonhart Fuchs (; 17 January 1501 – 10 May 1566), sometimes spelled Leonhard Fuchs and cited in Latin as ''Leonhartus Fuchsius'', was a German physician and botanist. His chief notability is as the author of a large book about plants and th ...
(1501–1566) was one of "the three German fathers of botany", along with theologian Otto Brunfels
Otto Brunfels (also known as Brunsfels or Braunfels) (believed to be born in 1488 – 23 November 1534) was a German theologian and botanist. Carl von Linné listed him among the "Fathers of Botany".
Life
After studying theology and philosophy ...
(1489–1534) and physician Hieronymus Bock
Hieronymus Bock ( Latinised Hieronymus Tragus; c. 1498 – 21 February 1554) was a German botanist, physician, and Lutheran minister who began the transition from medieval botany to the modern scientific worldview by arranging plants by their re ...
(1498–1554) (also called Hieronymus Tragus). Fuchs and Brunfels broke away from the tradition of copying earlier works to make original observations of their own. Bock created his own system of plant classification.
Physician Valerius Cordus
Valerius Cordus (18 February 1515 – 25 September 1544) was a German physician, botanist and pharmacologist who authored the first pharmacopoeia North of the Alps and one of the most celebrated herbals in history. He is also widely credited with ...
(1515–1544) authored a botanically and pharmacologically important herbal ''Historia Plantarum'' in 1544 and a pharmacopoeia
A pharmacopoeia, pharmacopeia, or pharmacopoea (from the obsolete typography ''pharmacopœia'', meaning "drug-making"), in its modern technical sense, is a book containing directions for the identification of compound medicines, and published by ...
of lasting importance, the ''Dispensatorium'' in 1546. Naturalist Conrad von Gesner
Conrad Gessner (; la, Conradus Gesnerus 26 March 1516 – 13 December 1565) was a Swiss physician, naturalist, bibliographer, and philologist. Born into a poor family in Zürich, Switzerland, his father and teachers quickly realised his tale ...
(1516–1565) and herbalist John Gerard
John Gerard (also John Gerarde, c. 1545–1612) was an English herbalist with a large garden in Holborn, now part of London. His 1,484-page illustrated ''Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes'', first published in 1597, became a popular gard ...
(1545–) published herbals covering the supposed medicinal uses of plants. Naturalist Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi (11 September 1522 – 4 May 1605) was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carl Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history st ...
(1522–1605) was considered the ''father of natural history'', which included the study of plants. In 1665, using an early microscope, Polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
discovered cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, a term he coined, in cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
, and a short time later in living plant tissue.
Early modern botany
 During the 18th century, systems of
During the 18th century, systems of plant identification
In biology, determination is the process of matching a specimen of an organism to a known taxon, for example identifying a plant. The term is also used in cellular biology, where it means the act of the differentiation of stem cells becoming fixe ...
were developed comparable to dichotomous keys
In phylogenetics, a single-access key (also called dichotomous key, sequential key, analytical key, or pathway key) is an identification key where the sequence and structure of identification steps is fixed by the author of the key. At each point i ...
, where unidentified plants are placed into taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
omic groups (e.g. family, genus and species) by making a series of choices between pairs of characters
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to The ...
. The choice and sequence of the characters may be artificial in keys designed purely for identification ( diagnostic keys) or more closely related to the natural or phyletic order
Taxonomic sequence (also known as systematic, phyletic or taxonomic order) is a sequence followed in listing of taxa which aids ease of use and roughly reflects the evolutionary relationships among the taxa. Taxonomic sequences can exist for taxa ...
of the taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
in synoptic keys. By the 18th century, new plants for study were arriving in Europe in increasing numbers from newly discovered countries and the European colonies worldwide. In 1753, Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
published his Species Plantarum
' (Latin for "The Species of Plants") is a book by Carl Linnaeus, originally published in 1753, which lists every species of plant known at the time, classified into genera. It is the first work to consistently apply binomial names and was the ...
, a hierarchical classification of plant species that remains the reference point for modern botanical nomenclature. This established a standardised binomial or two-part naming scheme where the first name represented the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
and the second identified the species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
within the genus. For the purposes of identification, Linnaeus's ''Systema Sexuale'' classified plants into 24 groups according to the number of their male sexual organs. The 24th group, ''Cryptogamia'', included all plants with concealed reproductive parts, mosses, liverworts, ferns, algae and fungi.
Botany was originally a hobby for upper class women. These women would collect and paint flowers and plants from around the world with scientific accuracy. The paintings were used to record many species that could not be transported or maintained in other environments. Marianne North
Marianne North (24 October 1830 – 30 August 1890) was a prolific English Victorian biologist and botanical artist, notable for her plant and landscape paintings, her extensive foreign travels, her writings, her plant discoveries and the ...
illustrated over 900 species in extreme detail with watercolor and oil paintings. Her work and many other women's botany work was the beginning of popularizing botany to a wider audience.
Increasing knowledge of plant anatomy
Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Originally it included plant morphology, the description of the physical form and external structure of plants, but since the mid-20th century plant ...
, morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
and life cycles led to the realisation that there were more natural affinities between plants than the artificial sexual system of Linnaeus. Adanson (1763), de Jussieu
De Jussieu, the name of a French family which came into prominence towards the close of the sixteenth century, and was known for a century and a half for the botanists it produced. The following are its more eminent members:
*Antoine de Jussieu ( ...
(1789), and Candolle
Augustin Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (, , ; 4 February 17789 September 1841) was a Swiss botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at a herbarium. Within a couple of years de Candolle ...
(1819) all proposed various alternative natural systems of classification that grouped plants using a wider range of shared characters and were widely followed. The Candollean system reflected his ideas of the progression of morphological complexity and the later Bentham & Hooker system
A taxonomic system, the Bentham & Hooker system for seed plants, was published in Bentham and Hooker's ''Genera plantarum ad exemplaria imprimis in herbariis kewensibus servata definita'' in three volumes between 1862 and 1883.
George Bentham (18 ...
, which was influential until the mid-19th century, was influenced by Candolle's approach. Darwin's publication of the ''Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'' in 1859 and his concept of common descent required modifications to the Candollean system to reflect evolutionary relationships as distinct from mere morphological similarity.
Botany was greatly stimulated by the appearance of the first "modern" textbook, Matthias Schleiden
Matthias Jakob Schleiden (; 5 April 1804 – 23 June 1881) was a German botanist and co-founder of cell theory, along with Theodor Schwann and Rudolf Virchow.
Career
Matthias Jakob Schleiden was born in Hamburg. on 5 April 1804. His father was ...
's ', published in English in 1849 as ''Principles of Scientific Botany''. Schleiden was a microscopist and an early plant anatomist who co-founded the cell theory
In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory first formulated in the mid-nineteenth century, that living organisms are made up of Cell (biology), cells, that they are the basic structural/organizational unit of all organisms, and that all cell ...
with Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann (; 7 December 181011 January 1882) was a German physician and physiologist. His most significant contribution to biology is considered to be the extension of cell theory to animals. Other contributions include the discovery of ...
and Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder ...
and was among the first to grasp the significance of the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
that had been described by Robert Brown in 1831. In 1855, Adolf Fick
Adolf Eugen Fick (3 September 1829 – 21 August 1901) was a German-born physician and physiologist.
Early life and education
Fick began his work in the formal study of mathematics and physics before realising an aptitude for medicine. He th ...
formulated Fick's laws that enabled the calculation of the rates of molecular diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often simply called diffusion, is the thermal motion of all (liquid or gas) particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size (mass) of ...
in biological systems.

Late modern botany
Building upon the gene-chromosome theory of heredity that originated withGregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel, Augustinians, OSA (; cs, Řehoř Jan Mendel; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was a biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinians, Augustinian friar and abbot of St Thomas's Abbey, Brno, St. Thomas' Abbey in Br� ...
(1822–1884), August Weismann
August Friedrich Leopold Weismann FRS (For), HonFRSE, LLD (17 January 18345 November 1914) was a German evolutionary biologist. Fellow German Ernst Mayr ranked him as the second most notable evolutionary theorist of the 19th century, after Cha ...
(1834–1914) proved that inheritance only takes place through gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce t ...
s. No other cells can pass on inherited characters. The work of Katherine Esau
Katherine Esau (3 April 1898 – 4 June 1997) was a German-American botanist who received the National Medal of Science for her work on plant anatomy.
Personal life and education
Esau was born on 3 April 1898 in Yekaterinoslav, Russian Empire ...
(1898–1997) on plant anatomy is still a major foundation of modern botany. Her books ''Plant Anatomy'' and ''Anatomy of Seed Plants'' have been key plant structural biology texts for more than half a century.
The discipline of plant ecology
Plant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples o ...
was pioneered in the late 19th century by botanists such as Eugenius Warming
Eugenius (died 6 September 394) was a usurper in the Western Roman Empire (392–394) against Emperor Theodosius I. While Christian himself, Eugenius capitalized on the discontent in the West caused by Theodosius' religious policies targeting p ...
, who produced the hypothesis that plants form communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place (geography), place, Norm (social), norms, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Identity (social science), identity. Communiti ...
, and his mentor and successor Christen C. Raunkiær
Christen Christensen Raunkiær (29 March 1860 – 11 March 1938) was a Danish botanist, who was a pioneer of plant ecology. He is mainly remembered for his scheme of plant strategies to survive an unfavourable season ("life forms") and his demons ...
whose system for describing plant life forms is still in use today. The concept that the composition of plant communities such as temperate broadleaf forest changes by a process of ecological succession
Ecological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades (for example, after a wildfire) or more or less.
Bacteria allows for the cycling of nutrients such as ca ...
was developed by Henry Chandler Cowles
Henry Chandler Cowles (February 27, 1869 – September 12, 1939) was an American botanist and ecological pioneer (see History of ecology). A professor at the University of Chicago, he studied ecological succession in the Indiana Dunes of Northwes ...
, Arthur Tansley
Sir Arthur George Tansley FLS, FRS (15 August 1871 – 25 November 1955) was an English botanist and a pioneer in the science of ecology.
Educated at Highgate School, University College London and Trinity College, Cambridge, Tansley taught a ...
and Frederic Clements. Clements is credited with the idea of climax vegetation as the most complex vegetation that an environment can support and Tansley introduced the concept of ecosystems to biology. Building on the extensive earlier work of Alphonse Pyramus de Candolle, Alphonse de Candolle, Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov, Nikolai Vavilov (1887–1943) produced accounts of the biogeography, Center of origin, centres of origin, and evolutionary history of economic plants.
Particularly since the mid-1960s there have been advances in understanding of the physics of Plant physiology, plant physiological processes such as transpiration (the transport of water within plant tissues), the temperature dependence of rates of water evaporation from the leaf surface and the molecular diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often simply called diffusion, is the thermal motion of all (liquid or gas) particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size (mass) of ...
of water vapour and carbon dioxide through stomatal apertures. These developments, coupled with new methods for measuring the size of stomatal apertures, and the rate of photosynthesis have enabled precise description of the rates of gas exchange between plants and the atmosphere. Innovations in Statistics, statistical analysis by Ronald Fisher, Frank Yates and others at Rothamsted Research#Statistical science, Rothamsted Experimental Station facilitated rational experimental design and data analysis in botanical research. The discovery and identification of the auxin plant hormones by Kenneth V. Thimann in 1948 enabled regulation of plant growth by externally applied chemicals. Frederick Campion Steward pioneered techniques of micropropagation and plant tissue culture controlled by Plant physiology#Plant hormones, plant hormones. The synthetic auxin 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid or 2,4-D was one of the first commercial synthetic herbicides.
 20th century developments in plant biochemistry have been driven by modern techniques of organic chemistry, organic chemical analysis, such as spectroscopy, chromatography and electrophoresis. With the rise of the related molecular-scale biological approaches of molecular biology,
20th century developments in plant biochemistry have been driven by modern techniques of organic chemistry, organic chemical analysis, such as spectroscopy, chromatography and electrophoresis. With the rise of the related molecular-scale biological approaches of molecular biology, genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
, proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In ...
and metabolomics, the relationship between the plant genome and most aspects of the biochemistry, physiology, morphology and behaviour of plants can be subjected to detailed experimental analysis. The concept originally stated by Gottlieb Haberlandt in 1902 that all plant cells are Cell potency#Totipotency, totipotent and can be grown ''in vitro'' ultimately enabled the use of genetic engineering experimentally to knock out a gene or genes responsible for a specific trait, or to add genes such as Green fluorescent protein, GFP that reporter gene, report when a gene of interest is being expressed. These technologies enable the biotechnological use of whole plants or plant cell cultures grown in bioreactors to synthesise Bt corn, pesticides, Biopharmaceutics, antibiotics or other pharming (genetics), pharmaceuticals, as well as the practical application of genetically modified crops designed for traits such as improved yield.
Modern morphology recognises a continuum between the major morphological categories of root, stem (caulome), leaf (phyllome) and trichome. Furthermore, it emphasises structural dynamics. Modern systematics aims to reflect and discover Phylogenetic nomenclature, phylogenetic relationships between plants. Modern Molecular phylogenetics largely ignores morphological characters, relying on DNA sequences as data. Molecular analysis of nucleic acid sequence, DNA sequences from most families of flowering plants enabled the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group to publish in 1998 a phylogenetics, phylogeny of flowering plants, answering many of the questions about relationships among angiosperm families and species. The theoretical possibility of a practical method for identification of plant species and commercial varieties by DNA barcoding is the subject of active current research.
Branches of botany
Botany is divided along several axes. Some subfields of botany relate to particular groups of organisms. Divisions related to the broader historical sense of botany include bacteriology, mycology (or fungology) and phycology - the study of bacteria, fungi and algae respectively - with lichenology as a subfield of mycology. The narrower sense of botany in the sense of the study of embryophytes (land plants) is disambiguated as phytology. Bryology is the study of mosses (and in the broader sense also liverworts and hornworts). Pteridology (or filicology) is the study of ferns and allied plants. A number of other taxa of ranks varying from family to subgenus have terms for their study, including agrostology (or graminology) for the study of grasses, synantherology for the study of composites, and batology for the study of brambles. Study can also be divided by guild (ecology), guild rather than clade or evolutionary grade, grade. Dendrology is the study of woody plants. Many divisions ofbiology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
have botanical subfields. These are commonly denoted by prefixing the word plant (e.g. plant taxonomy, plant ecology, plant anatomy, plant morphology, plant systematics, plant ecology), or prefixing or substituting the prefix phyto- (e.g. phytochemistry, phytogeography). The study of fossil plants is palaeobotany. Other fields are denoted by adding or substituting the word botany (e.g. systematic botany).
Phytosociology is a subfield of plant ecology that classifies and studies communities of plants.
The intersection of fields from the above pair of categories gives rise to fields such as bryogeography (the study of the distribution of mosses).
Different parts of plants also give rise to their own subfields, including xylology, carpology (or fructology) and palynology, these been the study of wood, fruit and pollen/spores respectively.
Botany also overlaps on the one hand with agriculture, horticulture and silviculture, and on the other hand with medicine and pharmacology, giving rise to fields such as agronomy, horticultural botany, phytopathology and phytopharmacology.
Scope and importance
The study of plants is vital because they underpin almost all animal life on Earth by generating a large proportion of the oxygen and food that provide humans and other organisms with cellular respiration, aerobic respiration with the chemical energy they need to exist. Plants,algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
and cyanobacteria are the major groups of organisms that carry out photosynthesis, a process that uses the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars that can be used both as a source of chemical energy and of organic molecules that are used in the structural components of cells. As a by-product of photosynthesis, plants release oxygen into the atmosphere, a gas that is required by anaerobic organism, nearly all living things to carry out cellular respiration. In addition, they are influential in the global carbon cycle, carbon and water cycle, water cycles and plant roots bind and stabilise soils, preventing soil erosion. Plants are crucial to the future of human society as they provide food, oxygen, biochemistry, biochemicals, and products for people, as well as creating and preserving soil.
Historically, all living things were classified as either animals or plants and botany covered the study of all organisms not considered animals. Botanists examine both the internal functions and processes within plant organelles, cells, tissues, whole plants, plant populations and plant communities. At each of these levels, a botanist may be concerned with the classification (Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy), phylogeny and evolution, structure (Plant anatomy, anatomy and Plant morphology, morphology), or function (Plant physiology, physiology) of plant life.
The strictest definition of "plant" includes only the "land plants" or embryophytes, which include seed plants (gymnosperms, including the Pinophyta, pines, and flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s) and the free-sporing cryptogams including ferns, Lycopodiopsida, clubmosses, Marchantiophyta, liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Embryophytes are multicellular eukaryotes descended from an ancestor that obtained its energy from sunlight by photosynthesis. They have life cycles with alternation of generations, alternating haploid and diploid phases. The sexual haploid phase of embryophytes, known as the gametophyte, nurtures the developing diploid embryo sporophyte within its tissues for at least part of its life, even in the seed plants, where the gametophyte itself is nurtured by its parent sporophyte. Other groups of organisms that were previously studied by botanists include bacteria (now studied in bacteriology), fungi (mycology) – including lichen-forming fungi (lichenology), non-Chlorophyta, chlorophyte algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
(phycology), and viruses (virology). However, attention is still given to these groups by botanists, and fungi (including lichens) and photosynthetic protists are usually covered in introductory botany courses.
Paleobotany, Palaeobotanists study ancient plants in the fossil record to provide information about the evolutionary history of plants. Cyanobacteria, the first oxygen-releasing photosynthetic organisms on Earth, are thought to have given rise to the ancestor of plants by entering into an endosymbiotic relationship with an early eukaryote, ultimately becoming the chloroplasts in plant cells. The new photosynthetic plants (along with their algal relatives) accelerated the rise in atmospheric oxygen started by the cyanobacteria, great oxygenation event, changing the ancient oxygen-free, Redox, reducing, atmosphere to one in which free oxygen has been abundant for more than 2 billion years.
Among the important botanical questions of the 21st century are the role of plants as primary producers in the global cycling of life's basic ingredients: energy, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and water, and ways that our plant stewardship can help address the global environmental issues of resource management, Conservation (ethic), conservation, food security, human food security, introduced species, biologically invasive organisms, carbon sequestration, climate change, and sustainability.
Human nutrition
 Virtually all staple foods come either directly from primary production by plants, or indirectly from animals that eat them. Plants and other photosynthetic organisms are at the base of most food chains because they use the energy from the sun and nutrients from the soil and atmosphere, converting them into a form that can be used by animals. This is what ecologists call the first trophic level. The modern forms of the major staple foods, such as hemp, teff, maize, rice, wheat and other cereal grasses, Pulse (legume), pulses, bananas and plantains, as well as hemp, flax and cotton grown for their fibres, are the outcome of prehistoric selection over thousands of years from among Neolithic founder crops, wild ancestral plants with the most desirable characteristics.
Botanists study how plants produce food and how to increase yields, for example through plant breeding, making their work important to humanity's ability to feed the world and provide food security for future generations. Botanists also study weeds, which are a considerable problem in agriculture, and the biology and control of Plant pathology, plant pathogens in agriculture and natural ecosystems. Ethnobotany is the study of the relationships between plants and people. When applied to the investigation of historical plant–people relationships ethnobotany may be referred to as archaeobotany or paleoethnobotany, palaeoethnobotany. Some of the earliest plant-people relationships arose between the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people of Canada in identifying edible plants from inedible plants. This relationship the indigenous people had with plants was recorded by ethnobotanists.
Virtually all staple foods come either directly from primary production by plants, or indirectly from animals that eat them. Plants and other photosynthetic organisms are at the base of most food chains because they use the energy from the sun and nutrients from the soil and atmosphere, converting them into a form that can be used by animals. This is what ecologists call the first trophic level. The modern forms of the major staple foods, such as hemp, teff, maize, rice, wheat and other cereal grasses, Pulse (legume), pulses, bananas and plantains, as well as hemp, flax and cotton grown for their fibres, are the outcome of prehistoric selection over thousands of years from among Neolithic founder crops, wild ancestral plants with the most desirable characteristics.
Botanists study how plants produce food and how to increase yields, for example through plant breeding, making their work important to humanity's ability to feed the world and provide food security for future generations. Botanists also study weeds, which are a considerable problem in agriculture, and the biology and control of Plant pathology, plant pathogens in agriculture and natural ecosystems. Ethnobotany is the study of the relationships between plants and people. When applied to the investigation of historical plant–people relationships ethnobotany may be referred to as archaeobotany or paleoethnobotany, palaeoethnobotany. Some of the earliest plant-people relationships arose between the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people of Canada in identifying edible plants from inedible plants. This relationship the indigenous people had with plants was recorded by ethnobotanists.
Plant biochemistry
Plant biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes used by plants. Some of these processes are used in their primary metabolism like the photosynthetic Calvin cycle and crassulacean acid metabolism. Others make specialised materials like the cellulose and lignin used to build their bodies, and Secondary metabolism, secondary products like resins and aroma compounds.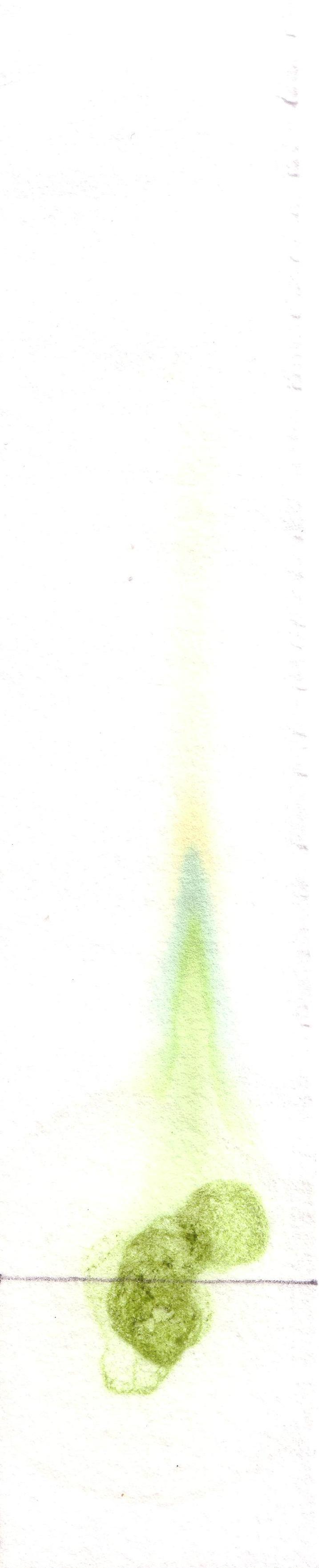
Plants make various photosynthetic pigments, some of which can be seen here through paper chromatography.
Xanthophylls, Xanthophylls
Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll ''a''
Chlorophyll b, Chlorophyll ''b''
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
" have unique organelles known as chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are thought to be descended from cyanobacteria that formed endosymbiotic relationships with ancient plant and algal ancestors. Chloroplasts and cyanobacteria contain the blue-green pigment chlorophyll a, chlorophyll ''a''. Chlorophyll ''a'' (as well as its plant and green algal-specific cousin chlorophyll b, chlorophyll ''b'') absorbs light in the blue-violet and orange/red parts of the visible spectrum, spectrum while reflecting and transmitting the green light that we see as the characteristic colour of these organisms. The energy in the red and blue light that these pigments absorb is used by chloroplasts to make energy-rich carbon compounds from carbon dioxide and water by Carbon fixation#Oxygenic photosynthesis, oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that generates molecular oxygen (O2) as a by-product.
The light energy captured by chlorophyll a, chlorophyll ''a'' is initially in the form of electrons (and later a proton gradient) that's used to make molecules of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP and NADPH which temporarily store and transport energy. Their energy is used in the light-independent reactions of the Calvin cycle by the enzyme rubisco to produce molecules of the 3-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is the first product of photosynthesis and the raw material from which glucose and almost all other organic molecules of biological origin are synthesised. Some of the glucose is converted to starch which is stored in the chloroplast. Starch is the characteristic energy store of most land plants and algae, while inulin, a polymer of fructose is used for the same purpose in the sunflower family Asteraceae. Some of the glucose is converted to sucrose (common table sugar) for export to the rest of the plant.
Unlike in animals (which lack chloroplasts), plants and their eukaryote relatives have delegated many biochemical roles to their chloroplasts, including synthesising all their fatty acids, and most amino acids. The fatty acids that chloroplasts make are used for many things, such as providing material to build cell membranes out of and making the polymer cutin which is found in the plant cuticle that protects land plants from drying out.
Plants synthesise a number of unique polymers like the polysaccharide molecules cellulose, pectin and xyloglucan from which the land plant cell wall is constructed.
Vascular land plants make lignin, a polymer used to strengthen the secondary cell walls of xylem tracheids and Xylem vessel element, vessels to keep them from collapsing when a plant sucks water through them under water stress. Lignin is also used in other cell types like Ground tissue#Sclerenchyma, sclerenchyma fibres that provide structural support for a plant and is a major constituent of wood. Sporopollenin is a chemically resistant polymer found in the outer cell walls of spores and pollen of land plants responsible for the survival of early land plant spores and the pollen of seed plants in the fossil record. It is widely regarded as a marker for the start of land plant evolution during the Ordovician period.
The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today is much lower than it was when plants emerged onto land during the Ordovician and Silurian periods. Many monocots like maize and the pineapple and some dicots like the Asteraceae have since independently evolved pathways like Crassulacean acid metabolism and the C4 carbon fixation, carbon fixation pathway for photosynthesis which avoid the losses resulting from photorespiration in the more common C3 carbon fixation, carbon fixation pathway. These biochemical strategies are unique to land plants.
Medicine and materials
Phytochemistry is a branch of plant biochemistry primarily concerned with the chemical substances produced by plants during secondary metabolism. Some of these compounds are toxins such as the alkaloid coniine from conium, hemlock. Others, such as the essential oils Peppermint#Oil, peppermint oil and lemon oil are useful for their aroma, as flavourings and spices (e.g., capsaicin), and in medicine as pharmaceuticals as in opium from Papaver somniferum, opium poppies. Many medication, medicinal and recreational drugs, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (active ingredient in Cannabis (drug), cannabis), caffeine, morphine and nicotine come directly from plants. Others are simple Derivative (chemistry), derivatives of botanical natural products. For example, the pain killer aspirin is the acetyl ester of salicylic acid, originally isolated from the Bark (botany), bark of willow trees, and a wide range of opiate analgesics, painkillers like diamorphine, heroin are obtained by chemical modification of morphine obtained from the opium poppy. Popular stimulants come from plants, such as caffeine from coffee, tea and chocolate, and nicotine from tobacco. Most alcoholic beverages come from fermentation (food), fermentation of carbohydrate-rich plant products such as barley (beer), rice (sake) and grapes (wine). Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans have used various plants as ways of treating illness or disease for thousands of years. This knowledge Native Americans have on plants has been recorded by Ethnobotany, enthnobotanists and then in turn has been used by Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical companies as a way of drug discovery. Plants can synthesise coloured dyes and pigments such as the anthocyanins responsible for the red colour of red wine, yellow Reseda luteola, weld and blue Isatis tinctoria, woad used together to produce Lincoln green, indoxyl, source of the blue dye indigo traditionally used to dye denim and the artist's pigments gamboge and rose madder. Sugar, starch, cotton, linen, hemp, some types of rope, wood and particle boards, papyrus and paper, vegetable oils, epicuticular wax, wax, and natural rubber are examples of commercially important materials made from plant tissues or their secondary products. Charcoal, a pure form of carbon made by pyrolysis of wood, has a long charcoal#History, history as a metal-smelting fuel, as a filter material and activated carbon#Applications, adsorbent and as an artist's material and is one of the three ingredients of gunpowder. Cellulose, the world's most abundant organic polymer, can be converted into energy, fuels, materials and chemical feedstock. cellulose#products, Products made from cellulose include rayon and cellophane, methyl cellulose, wallpaper paste, Butanol fuel#Using Alternate Carbon Sources, biobutanol and nitrocellulose, gun cotton. Sugarcane, rapeseed and soy are some of the plants with a highly fermentable sugar or oil content that are used as sources of biofuels, important alternatives to fossil fuels, such as biodiesel. Sweetgrass was used by Native Americans to ward off bugs like mosquitoes. These bug repelling properties of sweetgrass were later found by the American Chemical Society in the molecules phytol and coumarin.Plant ecology
biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, genetic diversity and Fitness (biology), fitness, the adaptation of plants to their environment, and their competitive or mutualism (biology), mutualistic interactions with other species. Some ecologists even rely on Empirical evidence, empirical data from indigenous people that is gathered by ethnobotanists. This information can relay a great deal of information on how the land once was thousands of years ago and how it has changed over that time. The goals of plant ecology are to understand the causes of their distribution patterns, productivity, environmental impact, evolution, and responses to environmental change.
Plants depend on certain edaphic (soil) and climatic factors in their environment but can modify these factors too. For example, they can change their environment's albedo, increase Surface runoff, runoff interception, stabilise mineral soils and develop their organic content, and affect local temperature. Plants compete with other organisms in their ecosystem for resources. They interact with their neighbours at a variety of spatial scales in groups, populations and Community (ecology), communities that collectively constitute vegetation. Regions with characteristic Holdridge life zones, vegetation types and dominant plants as well as similar Abiotic component, abiotic and Biotic components, biotic factors, climate, and geography make up biomes like tundra or tropical rainforest.
Herbivores eat plants, but plants can plant defence against herbivory, defend themselves and some species are parasitic plant, parasitic or even carnivorous plant, carnivorous. Other organisms form mutualism (biology), mutually beneficial relationships with plants. For example, mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia provide plants with nutrients in exchange for food, ants are recruited by myrmecophyte, ant plants to provide protection, honey bees, bats and other animals pollinate flowers and seed dispersal#Humans, humans and seed dispersal#Dispersal by animals, other animals act as dispersal vectors to spread spores and seeds.
Plants, climate and environmental change
Plant responses to climate and other environmental changes can inform our understanding of how these changes affect ecosystem function and productivity. For example, plant phenology can be a useful proxy (climate), proxy for temperature in historical climatology, and the biological effects of climate change, impact of climate change and global warming. Palynology, the analysis of fossil pollen deposits in sediments from geologic timescale, thousands or millions of years ago allows the reconstruction of past climates. Estimates of atmospheric concentrations since the Palaeozoic have been obtained from stomatal densities and the leaf shapes and sizes of ancient land plants. Ozone depletion can expose plants to higher levels of Ultraviolet, ultraviolet radiation-B (UV-B), resulting in lower growth rates. Moreover, information from studies of community (ecology), community ecology, plantsystematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre ...
, and taxonomy (biology), taxonomy is essential to understanding climate change#Vegetation, vegetation change, habitat destruction and endangered species, species extinction.
Genetics
Inheritance in plants follows the same fundamental principles of genetics as in other multicellular organisms.Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel, Augustinians, OSA (; cs, Řehoř Jan Mendel; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was a biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinians, Augustinian friar and abbot of St Thomas's Abbey, Brno, St. Thomas' Abbey in Br� ...
discovered the Mendelian inheritance, genetic laws of inheritance by studying inherited traits such as shape in ''Pisum sativum'' (peas). What Mendel learned from studying plants has had far-reaching benefits outside of botany. Similarly, "transposon, jumping genes" were discovered by Barbara McClintock while she was studying maize. Nevertheless, there are some distinctive genetic differences between plants and other organisms.
Species boundaries in plants may be weaker than in animals, and cross species hybrid (biology), hybrids are often possible. A familiar example is peppermint, ''Mentha'' × ''piperita'', a Sterility (physiology), sterile hybrid between ''Mentha aquatica'' and spearmint, ''Mentha spicata''. The many cultivated varieties of wheat are the result of multiple inter- and intra-species, specific crosses between wild species and their hybrids. Angiosperms with monoecious flowers often have Self-incompatibility in plants, self-incompatibility mechanisms that operate between the pollen and stigma (botany), stigma so that the pollen either fails to reach the stigma or fails to germinate and produce male gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce t ...
s. This is one of several methods used by plants to promote plant reproductive morphology, outcrossing. In many land plants the male and female gametes are produced by separate individuals. These species are said to be Plant reproductive morphology#Terminology, dioecious when referring to vascular plant sporophytes and monoecious, dioicous when referring to bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in ...
gametophytes.
Charles Darwin in his 1878 book The Effects of Cross and Self-Fertilization in the Vegetable KingdomDarwin, C. R. 1878. The effects of cross and self fertilisation in the vegetable kingdom. London: John Murray". darwin-online.org.uk at the start of chapter XII noted "The first and most important of the conclusions which may be drawn from the observations given in this volume, is that generally cross-fertilisation is beneficial and self-fertilisation often injurious, at least with the plants on which I experimented." An important adaptive benefit of outcrossing is that it allows the masking of deleterious mutations in the genome of progeny. This beneficial effect is also known as hybrid vigor or heterosis. Once outcrossing is established, subsequent switching to inbreeding becomes disadvantageous since it allows expression of the previously masked deleterious recessive mutations, commonly referred to as inbreeding depression.
Unlike in higher animals, where parthenogenesis is rare, asexual reproduction may occur in plants by several different mechanisms. The formation of stem tubers in potato is one example. Particularly in arctic or alpine climate, alpine habitats, where opportunities for fertilisation of flowers zoophily, by animals are rare, plantlets or bulbs, may develop instead of flowers, replacing sexual reproduction with asexual reproduction and giving rise to cloning, clonal populations genetically identical to the parent. This is one of several types of apomixis that occur in plants. Apomixis can also happen in a seed, producing a seed that contains an embryo genetically identical to the parent.
Most sexually reproducing organisms are diploid, with paired chromosomes, but doubling of their chromosome number may occur due to errors in cytokinesis. This can occur early in development to produce an autopolyploid or partly autopolyploid organism, or during normal processes of cellular differentiation to produce some cell types that are polyploid (endopolyploidy), or during gamete formation. An allopolyploid plant may result from a hybridization event, hybridisation event between two different species. Both autopolyploid and allopolyploid plants can often reproduce normally, but may be unable to cross-breed successfully with the parent population because there is a mismatch in chromosome numbers. These plants that are reproductively isolated from the parent species but live within the same geographical area, may be sufficiently successful to form a new sympatric speciation, species. Some otherwise sterile plant polyploids can still reproduce vegetative propagation, vegetatively or by seed apomixis, forming clonal populations of identical individuals. Durum wheat is a fertile tetraploid allopolyploid, while common wheat, bread wheat is a fertile hexaploid. The commercial banana is an example of a sterile, seedless triploid hybrid. Taraxacum officinale, Common dandelion is a triploid that produces viable seeds by apomictic seed.
As in other eukaryotes, the inheritance of endosymbiotic organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts in plants is non-Mendelian. Chloroplasts are inherited through the male parent in gymnosperms but often through the female parent in flowering plants.
Molecular genetics
 A considerable amount of new knowledge about plant function comes from studies of the molecular genetics of model organism#Plants, model plants such as the Thale cress, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', a weedy species in the mustard family (Brassicaceae). The genome or hereditary information contained in the genes of this species is encoded by about 135 million base pairs of DNA, forming one of the smallest genomes among
A considerable amount of new knowledge about plant function comes from studies of the molecular genetics of model organism#Plants, model plants such as the Thale cress, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', a weedy species in the mustard family (Brassicaceae). The genome or hereditary information contained in the genes of this species is encoded by about 135 million base pairs of DNA, forming one of the smallest genomes among flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s. ''Arabidopsis'' was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, in 2000. The sequencing of some other relatively small genomes, of rice (''Oryza sativa'') and ''Brachypodium distachyon'', has made them important model species for understanding the genetics, cellular and molecular biology of cereals, grasses and monocots generally.
Model organism#Plants, Model plants such as ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' are used for studying the molecular biology of plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capabi ...
s and the chloroplast. Ideally, these organisms have small genomes that are well known or completely sequenced, small stature and short generation times. Corn has been used to study mechanisms of photosynthesis and phloem loading of sugar in C4 plants, plants. The single celled green alga ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'', while not an embryophyte itself, contains a chlorophyll b, green-pigmented Chloroplast#Chloroplastida (green algae and plants), chloroplast related to that of land plants, making it useful for study. A red alga ''Cyanidioschyzon merolae'' has also been used to study some basic chloroplast functions. Spinach, peas, soybeans and a moss ''Physcomitrella patens'' are commonly used to study plant cell biology.
''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'', a soil rhizosphere bacterium, can attach to plant cells and infect them with a Callus (cell biology), callus-inducing Ti plasmid by horizontal gene transfer, causing a callus infection called crown gall disease. Schell and Van Montagu (1977) hypothesised that the Ti plasmid could be a natural vector for introducing the Nif gene responsible for nitrogen fixation in the root nodules of Fabaceae, legumes and other plant species. Today, genetic modification of the Ti plasmid is one of the main techniques for introduction of transgenes to plants and the creation of genetically modified crops.
Epigenetics
Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression, gene function that cannot be explained by changes in the underlying DNA sequence but cause the organism's genes to behave (or "express themselves") differently. One example of epigenetic change is the marking of the genes by DNA methylation which determines whether they will be expressed or not. Gene expression can also be controlled by repressor proteins that attach to silencer (DNA), silencer regions of the DNA and prevent that region of the DNA code from being expressed. Epigenetic marks may be added or removed from the DNA during programmed stages of development of the plant, and are responsible, for example, for the differences between anthers, petals and normal leaves, despite the fact that they all have the same underlying genetic code. Epigenetic changes may be temporary or may remain through successive cell divisions for the remainder of the cell's life. Some epigenetic changes have been shown to be Heritability, heritable, while others are reset in the germ cells. Epigenetic changes in Eukaryote, eukaryotic biology serve to regulate the process of cellular differentiation. During morphogenesis, totipotent stem cells become the various pluripotent cell lines of the embryo, which in turn become fully differentiated cells. A single fertilised egg cell, the zygote, gives rise to the many differentplant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capabi ...
types including parenchyma, vessel element, xylem vessel elements, phloem sieve tubes, guard cells of the epidermis (botany), epidermis, etc. as it continues to mitosis, divide. The process results from the epigenetic activation of some genes and inhibition of others.
Unlike animals, many plant cells, particularly those of the ground tissue#Parenchyma, parenchyma, do not terminally differentiate, remaining totipotent with the ability to give rise to a new individual plant. Exceptions include highly lignified cells, the ground tissue#Sclerenchyma, sclerenchyma and xylem which are dead at maturity, and the phloem sieve tubes which lack nuclei. While plants use many of the same epigenetic mechanisms as animals, such as chromatin remodeling, chromatin remodelling, an alternative hypothesis is that plants set their gene expression patterns using positional information from the environment and surrounding cells to determine their developmental fate.
Epigenetic changes can lead to paramutations, which do not follow the Mendelian heritage rules. These epigenetic marks are carried from one generation to the next, with one allele inducing a change on the other.
Plant evolution
 The chloroplasts of plants have a number of biochemical, structural and genetic similarities to cyanobacteria, (commonly but incorrectly known as "blue-green algae") and are thought to be derived from an ancient endosymbiotic theory, endosymbiotic relationship between an ancestral eukaryote, eukaryotic cell and a Chloroplast#Parent group: Cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial resident.
The
The chloroplasts of plants have a number of biochemical, structural and genetic similarities to cyanobacteria, (commonly but incorrectly known as "blue-green algae") and are thought to be derived from an ancient endosymbiotic theory, endosymbiotic relationship between an ancestral eukaryote, eukaryotic cell and a Chloroplast#Parent group: Cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial resident.
The algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
are a Polyphyly, polyphyletic group and are placed in various divisions, some more closely related to plants than others. There are many differences between them in features such as cell wall composition, biochemistry, pigmentation, chloroplast structure and nutrient reserves. The algal division Charophyta, sister to the green algal division Chlorophyta, is considered to contain the ancestor of true plants. The Charophyte class Charophyceae and the land plant sub-kingdom Embryophyta together form the monophyletic group or clade Streptophytina.
Nonvascular land plants are embryophytes that lack the vascular tissues xylem and phloem. They include mosses, Marchantiophyta, liverworts and hornworts. Pteridophyte, Pteridophytic vascular plants with true xylem and phloem that reproduced by spores germinating into free-living gametophytes evolved during the Silurian period and diversified into several lineages during the late Silurian and early Devonian. Representatives of the lycopods have survived to the present day. By the end of the Devonian period, several groups, including the Lycopodiophyta, lycopods, Sphenophyllales, sphenophylls and progymnosperms, had independently evolved "megaspory" – their spores were of two distinct sizes, larger megaspores and smaller microspores. Their reduced gametophytes developed from megaspores retained within the sporangium, spore-producing organs (megasporangia) of the sporophyte, a condition known as endospory. Seeds consist of an endosporic megasporangium surrounded by one or two sheathing layers (integuments). The young sporophyte develops within the seed, which on germination splits to release it. The earliest known seed plants date from the latest Devonian Famennian stage. Following the evolution of the seed habit, Spermatophyte, seed plants diversified, giving rise to a number of now-extinct groups, including Pteridospermatophyta, seed ferns, as well as the modern gymnosperms and angiosperms. Gymnosperms produce "naked seeds" not fully enclosed in an ovary; modern representatives include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and Gnetophyta, Gnetales. Angiosperms produce seeds enclosed in a structure such as a Gynoecium, carpel or an ovary. Ongoing research on the molecular phylogenetics of living plants appears to show that the angiosperms are a sister clade to the gymnosperms.
Plant physiology
 Plant physiology encompasses all the internal chemical and physical activities of plants associated with life. Chemicals obtained from the air, soil and water form the basis of all metabolism, plant metabolism. The energy of sunlight, captured by oxygenic photosynthesis and released by cellular respiration, is the basis of almost all life. Phototroph, Photoautotrophs, including all green plants, algae and cyanobacteria gather energy directly from sunlight by photosynthesis. Heterotrophs including all animals, all fungi, all completely parasitic plants, and non-photosynthetic bacteria take in organic molecules produced by photoautotrophs and respire them or use them in the construction of cells and tissues. Cellular respiration, Respiration is the oxidation of carbon compounds by breaking them down into simpler structures to release the energy they contain, essentially the opposite of photosynthesis.
Molecules are moved within plants by transport processes that operate at a variety of spatial scales. Subcellular transport of ions, electrons and molecules such as water and
Plant physiology encompasses all the internal chemical and physical activities of plants associated with life. Chemicals obtained from the air, soil and water form the basis of all metabolism, plant metabolism. The energy of sunlight, captured by oxygenic photosynthesis and released by cellular respiration, is the basis of almost all life. Phototroph, Photoautotrophs, including all green plants, algae and cyanobacteria gather energy directly from sunlight by photosynthesis. Heterotrophs including all animals, all fungi, all completely parasitic plants, and non-photosynthetic bacteria take in organic molecules produced by photoautotrophs and respire them or use them in the construction of cells and tissues. Cellular respiration, Respiration is the oxidation of carbon compounds by breaking them down into simpler structures to release the energy they contain, essentially the opposite of photosynthesis.
Molecules are moved within plants by transport processes that operate at a variety of spatial scales. Subcellular transport of ions, electrons and molecules such as water and enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s occurs across cell membranes. Minerals and water are transported from roots to other parts of the plant in the transpiration stream. Diffusion, osmosis, and active transport and Mass flow (life sciences), mass flow are all different ways transport can occur. Examples of plant nutrition, elements that plants need to transport are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. In vascular plants, these elements are extracted from the soil as soluble ions by the roots and transported throughout the plant in the xylem. Most of the elements required for plant nutrition come from the chemical breakdown of soil minerals. Sucrose produced by photosynthesis is transported from the leaves to other parts of the plant in the phloem and Plant physiology#Plant hormones, plant hormones are transported by a variety of processes.
Plant hormones
Plant anatomy and morphology
 Plant anatomy is the study of the structure of plant cells and tissues, whereas plant morphology is the study of their external form.
All plants are multicellular eukaryotes, their DNA stored in nuclei. The characteristic features of
Plant anatomy is the study of the structure of plant cells and tissues, whereas plant morphology is the study of their external form.
All plants are multicellular eukaryotes, their DNA stored in nuclei. The characteristic features of plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capabi ...
s that distinguish them from those of animals and fungi include a primary cell wall composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, larger vacuoles than in animal cells and the presence of plastids with unique photosynthetic and biosynthetic functions as in the chloroplasts. Other plastids contain storage products such as starch (amyloplasts) or lipids (elaioplasts). Uniquely, streptophyte cells and those of the green algal order Trentepohliales divide by construction of a phragmoplast as a template for building a cell plate late in cell division.
The bodies of vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They al ...
s including Lycopodiopsida, clubmosses, ferns and spermatophyte, seed plants (gymnosperms and angiosperms) generally have aerial and subterranean subsystems. The Shoot (botany), shoots consist of Plant stem, stems bearing green photosynthesising Leaf, leaves and reproductive structures. The underground vascularised roots bear root hairs at their tips and generally lack chlorophyll. Non-vascular plants, the Marchantiophyta, liverworts, hornworts and mosses do not produce ground-penetrating vascular roots and most of the plant participates in photosynthesis. The sporophyte generation is nonphotosynthetic in liverworts but may be able to contribute part of its energy needs by photosynthesis in mosses and hornworts.
The root system and the shoot system are interdependent – the usually nonphotosynthetic root system depends on the shoot system for food, and the usually photosynthetic shoot system depends on water and minerals from the root system. Cells in each system are capable of creating cells of the other and producing adventitious shoots or roots. Stolons and tubers are examples of shoots that can grow roots. Roots that spread out close to the surface, such as those of willows, can produce shoots and ultimately new plants. In the event that one of the systems is lost, the other can often regrow it. In fact it is possible to grow an entire plant from a single leaf, as is the case with plants in Streptocarpus sect. Saintpaulia, ''Streptocarpus'' sect. ''Saintpaulia'', or even a single Cell (biology), cell – which can dedifferentiate into a Callus (cell biology), callus (a mass of unspecialised cells) that can grow into a new plant.
In vascular plants, the xylem and phloem are the conductive tissues that transport resources between shoots and roots. Roots are often adapted to store food such as sugars or starch, as in sugar beets and carrots.
Stems mainly provide support to the leaves and reproductive structures, but can store water in succulent plants such as Cactus, cacti, food as in potato tubers, or vegetative reproduction, reproduce vegetatively as in the stolons of strawberry#Cultivation, strawberry plants or in the process of layering. Leaves gather sunlight and carry out photosynthesis. Large, flat, flexible, green leaves are called foliage leaves. Gymnosperms, such as conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophyta, gnetophytes are seed-producing plants with open seeds. Angiosperms are Spermatophyte, seed-producing plants that produce flowers and have enclosed seeds. Woody plants, such as azaleas and oaks, undergo a secondary growth phase resulting in two additional types of tissues: wood (secondary xylem) and bark (secondary phloem and Cork cambium, cork). All gymnosperms and many angiosperms are woody plants. Some plants reproduce sexually, some asexually, and some via both means.
Although reference to major morphological categories such as root, stem, leaf, and trichome are useful, one has to keep in mind that these categories are linked through intermediate forms so that a continuum between the categories results. Furthermore, structures can be seen as processes, that is, process combinations.
Systematic botany
 Systematic botany is part of systematic biology, which is concerned with the range and diversity of organisms and their relationships, particularly as determined by their evolutionary history. It involves, or is related to, biological classification, scientific taxonomy and phylogenetics. Biological classification is the method by which botanists group organisms into categories such as genus, genera or
Systematic botany is part of systematic biology, which is concerned with the range and diversity of organisms and their relationships, particularly as determined by their evolutionary history. It involves, or is related to, biological classification, scientific taxonomy and phylogenetics. Biological classification is the method by which botanists group organisms into categories such as genus, genera or species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
. Biological classification is a form of Taxonomy (biology), scientific taxonomy. Modern taxonomy is rooted in the work of Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
, who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics. These groupings have since been revised to align better with the Charles Darwin, Darwinian principle of common descent – grouping organisms by ancestry rather than phenotype, superficial characteristics. While scientists do not always agree on how to classify organisms, molecular phylogenetics, which uses DNA sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequences are usua ...
as data, has driven many recent revisions along evolutionary lines and is likely to continue to do so. The dominant classification system is called Linnaean taxonomy. It includes ranks and binomial nomenclature. The nomenclature of botanical organisms is codified in the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and administered by the International Botanical Congress
International Botanical Congress (IBC) is an international meeting of botanists in all scientific fields, authorized by the International Association of Botanical and Mycological Societies (IABMS) and held every six years, with the location rotat ...
.
Kingdom Plantae belongs to Domain (biology), Domain Eukaryota and is broken down recursively until each species is separately classified. The order is: Kingdom (biology), Kingdom; Phylum (or Division); Class (biology), Class; Order (biology), Order; Family (biology), Family; Genus (plural ''genera''); Species. The scientific name of a plant represents its genus and its species within the genus, resulting in a single worldwide name for each organism. For example, the tiger lily is ''Lilium columbianum''. ''Lilium'' is the genus, and ''columbianum'' the Botanical name#Binary name, specific epithet. The combination is the name of the species. When writing the scientific name of an organism, it is proper to capitalise the first letter in the genus and put all of the specific epithet in lowercase. Additionally, the entire term is ordinarily italicised (or underlined when italics are not available).
The evolutionary relationships and heredity of a group of organisms is called its Phylogenetics, phylogeny. Phylogenetic studies attempt to discover phylogenies. The basic approach is to use similarities based on shared inheritance to determine relationships. As an example, species of ''Pereskia'' are trees or bushes with prominent leaves. They do not obviously resemble a typical leafless cactus such as an ''Echinocactus''. However, both ''Pereskia'' and ''Echinocactus'' have spines produced from areoles (highly specialised pad-like structures) suggesting that the two genera are indeed related.
Judging relationships based on shared characters requires care, since plants may resemble one another through convergent evolution in which characters have arisen independently. Some euphorbias have leafless, rounded bodies adapted to water conservation similar to those of globular cacti, but characters such as the structure of their flowers make it clear that the two groups are not closely related. The Cladistics, cladistic method takes a systematic approach to characters, distinguishing between those that carry no information about shared evolutionary history – such as those evolved separately in different groups (homoplasies) or those left over from ancestors (plesiomorphies) – and derived characters, which have been passed down from innovations in a shared ancestor (apomorphies). Only derived characters, such as the spine-producing areoles of cacti, provide evidence for descent from a common ancestor. The results of cladistic analyses are expressed as cladograms: tree-like diagrams showing the pattern of evolutionary branching and descent.
From the 1990s onwards, the predominant approach to constructing phylogenies for living plants has been molecular phylogenetics, which uses molecular characters, particularly DNA sequences, rather than morphological characters like the presence or absence of spines and areoles. The difference is that the genetic code itself is used to decide evolutionary relationships, instead of being used indirectly via the characters it gives rise to. Clive A. Stace, Clive Stace describes this as having "direct access to the genetic basis of evolution." As a simple example, prior to the use of genetic evidence, fungi were thought either to be plants or to be more closely related to plants than animals. Genetic evidence suggests that the true evolutionary relationship of multicelled organisms is as shown in the cladogram below – fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Symbols
A few symbols are in current use in botany. A number of others are obsolete; for example, Linnaeus used planetary symbols (Mars) for biennial plants, (Jupiter) for herbaceous perennials and (Saturn) for woody perennials, based on the planets' orbital periods of 2, 12 and 30 years; and Willd used (Saturn) for neuter in addition to (Mercury) for hermaphroditic. The following symbols are still used: :♀ female :♂ male :⚥ Hermaphrodite#Plants, hermaphrodite/bisexual :⚲ vegetative (asexual) reproduction :◊ sex unknown :☉ annual :⚇ Biennial plant, biennial :♾ Perennial plant, perennial :☠ poisonous :🛈 further information :× crossbred hybrid :+ grafted hybridSee also
* Branches of botany * Evolution of plants * Glossary of botanical terms * Glossary of plant morphology * List of botany journals * List of botanists * List of botanical gardens * List of botanists by author abbreviation * List of domesticated plants * List of flowers * List of systems of plant taxonomy * Outline of botany * Timeline of British botanyNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Supporting Information
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
External links
* {{Authority control Botany, Articles containing video clips