Blueprint Cafe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A blueprint is a reproduction of a
A blueprint is a reproduction of a
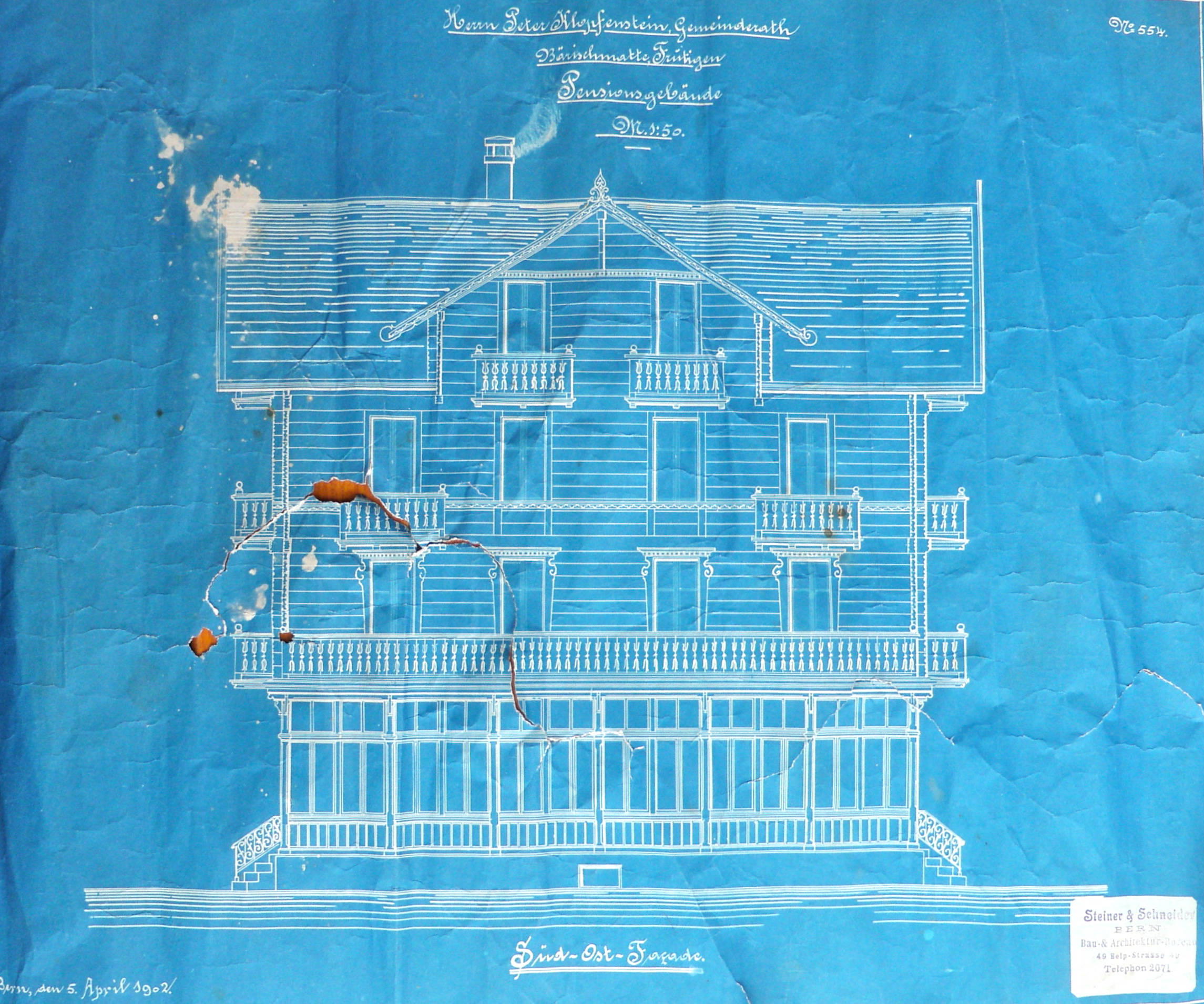
 The blueprint process is based on a photosensitive ferric compound. The best known is a process using ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide. The paper is impregnated with a solution of ammonium ferric citrate and dried. When the paper is illuminated, a photoreaction turns the trivalent ferric iron into divalent ferrous iron. The image is then developed using a solution of potassium ferricyanide forming insoluble ferroferricyanide ( Prussian blue or Turnbull's blue) with the divalent iron. Excess ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide are then washed away. The process is also known as
The blueprint process is based on a photosensitive ferric compound. The best known is a process using ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide. The paper is impregnated with a solution of ammonium ferric citrate and dried. When the paper is illuminated, a photoreaction turns the trivalent ferric iron into divalent ferrous iron. The image is then developed using a solution of potassium ferricyanide forming insoluble ferroferricyanide ( Prussian blue or Turnbull's blue) with the divalent iron. Excess ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide are then washed away. The process is also known as
 Traditional blueprints became obsolete when less expensive printing methods and digital displays became available.
In the early 1940s, cyanotype blueprint began to be supplanted by diazo prints, also known as
Traditional blueprints became obsolete when less expensive printing methods and digital displays became available.
In the early 1940s, cyanotype blueprint began to be supplanted by diazo prints, also known as
 A blueprint is a reproduction of a
A blueprint is a reproduction of a technical drawing
Technical drawing, drafting or drawing, is the act and Academic discipline, discipline of composing Plan (drawing), drawings that Visual communication, visually communicate how something functions or is constructed.
Technical drawing is essent ...
or engineering drawing
An engineering drawing is a type of technical drawing that is used to convey information about an object. A common use is to specify the geometry necessary for the construction of a component and is called a detail drawing. Usually, a number of ...
using a contact print
A contact print is a photographic image produced from film; sometimes from a film negative, and sometimes from a film positive or paper negative. In a darkroom an exposed and developed piece of film or photographic paper is placed emulsion si ...
process on light-sensitive sheets. Introduced by Sir John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical wor ...
in 1842, the process allowed rapid and accurate production of an unlimited number of copies. It was widely used for over a century for the reproduction of specification drawings used in construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and com ...
and industry. The blueprint process was characterized by white lines on a blue background, a negative of the original. The process was not able to reproduce color or shades of grey.
The process is now obsolete. It was first largely displaced by the diazo whiteprint
Whiteprint describes a document reproduction produced by using the diazo chemical process. It is also known as the blue-line process since the result is blue lines on a white background. It is a contact printing process which accurately reproduc ...
process, and later by large-format xerographic
Xerography is a dry photocopying technique. Originally called electrophotography, it was renamed xerography—from the roots el, ξηρός, label=none ''xeros'', meaning "dry" and -γραφία ''-graphia'', meaning "writing"—to emphasize ...
photocopiers.
The term ''blueprint
A blueprint is a reproduction of a technical drawing or engineering drawing using a contact print process on light-sensitive sheets. Introduced by Sir John Herschel in 1842, the process allowed rapid and accurate production of an unlimited number ...
'' continues to be used less formally to refer to any floor plan
In architecture and building engineering, a floor plan is a technical drawing to scale, showing a view from above, of the relationships between rooms, spaces, traffic patterns, and other physical features at one level of a structure.
Dimensio ...
(and even less formally, any type of plan). Practicing engineers, architects, and drafters often call them "drawings", “prints”, or “plans”.
It has almost entirely been replaced with digital computer-aided construction drawings.
The blueprint process
 The blueprint process is based on a photosensitive ferric compound. The best known is a process using ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide. The paper is impregnated with a solution of ammonium ferric citrate and dried. When the paper is illuminated, a photoreaction turns the trivalent ferric iron into divalent ferrous iron. The image is then developed using a solution of potassium ferricyanide forming insoluble ferroferricyanide ( Prussian blue or Turnbull's blue) with the divalent iron. Excess ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide are then washed away. The process is also known as
The blueprint process is based on a photosensitive ferric compound. The best known is a process using ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide. The paper is impregnated with a solution of ammonium ferric citrate and dried. When the paper is illuminated, a photoreaction turns the trivalent ferric iron into divalent ferrous iron. The image is then developed using a solution of potassium ferricyanide forming insoluble ferroferricyanide ( Prussian blue or Turnbull's blue) with the divalent iron. Excess ammonium ferric citrate and potassium ferricyanide are then washed away. The process is also known as cyanotype
The cyanotype (from Ancient Greek κυάνεος - ''kuáneos'', “dark blue” + τύπος - ''túpos'', “mark, impression, type”) is a slow-reacting, economical photographic printing formulation sensitive to a limited near ultraviolet ...
.
This is a simple process for the reproduction of any light transmitting document. Engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the l ...
s and architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
s drew their designs on cartridge paper Cartridge paper is a type of high-quality heavy paper used for illustration and drawing. The term "cartridge" refers to the history of the paper originally being used for making paper cartridges for early breechloading firearm
A firearm is any ...
; these were then traced on to tracing paper
Tracing paper is paper made to have low opacity, allowing light to pass through. It was originally developed for architects and design engineers to create drawings that could be copied precisely using the diazo copy process; it then found ma ...
using India ink for reproduction whenever needed. The tracing paper drawing is placed on top of the sensitized paper, and both are clamped under glass, in a daylight exposure frame, which is similar to a picture frame. The frame is put out into daylight, requiring a minute or two under a bright sun, or about ten minutes under an overcast sky to complete the exposure. Where ultra-violet light is transmitted through the tracing paper, the light-sensitive coating converts to a stable blue or black dye. Where the India ink blocks the ultra-violet light the coating does not convert and remains soluble. The image can be seen forming. When a strong image is seen the frame is brought indoors to stop the process. The unconverted coating is washed away, and the paper is then dried. The result is a copy of the original image with the clear background area rendered dark blue and the image reproduced as a white line.
This process has several features:
Introduction of the blueprint process eliminated the expense of photolithographic reproduction or of hand-tracing of original drawings. By the later 1890s in American architectural offices, a blueprint was one-tenth the cost of a hand-traced reproduction. The blueprint process is still used for special artistic and photographic effects, on paper and fabrics.
Various base materials have been used for blueprints. Paper was a common choice; for more durable prints linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
was sometimes used, but with time, the linen prints would shrink slightly. To combat this problem, printing on imitation vellum and, later, polyester film (Mylar
BoPET (biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aro ...
) was implemented.
Whiteprints
 Traditional blueprints became obsolete when less expensive printing methods and digital displays became available.
In the early 1940s, cyanotype blueprint began to be supplanted by diazo prints, also known as
Traditional blueprints became obsolete when less expensive printing methods and digital displays became available.
In the early 1940s, cyanotype blueprint began to be supplanted by diazo prints, also known as whiteprint
Whiteprint describes a document reproduction produced by using the diazo chemical process. It is also known as the blue-line process since the result is blue lines on a white background. It is a contact printing process which accurately reproduc ...
s. This technique produces blue lines on a white background. The drawings are also called ''blue-lines'' or bluelines. Other comparable dye-based prints were known as blacklines. Diazo prints remained in use until they were replaced by xerographic
Xerography is a dry photocopying technique. Originally called electrophotography, it was renamed xerography—from the roots el, ξηρός, label=none ''xeros'', meaning "dry" and -γραφία ''-graphia'', meaning "writing"—to emphasize ...
print processes.
Xerography is standard copy machine technology using toner
Toner is a powder mixture used in laser printers and photocopiers to form the printed text and images on paper, in general through a toner cartridge. Mostly granulated plastic, early mixtures only added carbon powder and iron oxide, however, ...
on bond paper
Bond paper is a high-quality durable writing paper similar to bank paper but having a weight greater than 50 g/m2. The most common weights are 60 g/m2 (16 lb), 75 g/m2 (20 lb) and 90 g/m2 (24 lb). The name comes from ...
. When large size xerography machines became available, 1975, they replaced the older printing methods. As computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
techniques came into use, the designs were printed directly using a computer printer
In computing, a printer is a peripheral machine which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text, usually on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers. Differ ...
or plotter
A plotter is a machine that produces vector graphics drawings. Plotters draw lines on paper using a pen, or in some applications, use a knife to cut a material like vinyl or leather. In the latter case, they are sometimes known as a cutting pl ...
.
Digital
In most computer-aided design of parts to be machined, paper is avoided altogether, and the finished design is an image on the computer display. The computer-aided design program generates acomputer numerical control
Numerical control (also computer numerical control, and commonly called CNC) is the automated control of machining tools (such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers) by means of a computer. A CNC machine processes a pie ...
sequence from the approved design. The sequence is a computer file which will control the operation of the machine tools
A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, boring, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some sort of tool that does the cutting or shaping. All m ...
used to make the part.
In the case of construction plans, such as road work or erecting a building, the supervising workers may view the "blueprints" directly on displays, rather than using printed paper sheets. These displays include mobile devices, such as smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
s or tablets. Software allows users to view and annotate electronic drawing files. Construction crews use software in the field to edit, share, and view blueprint documents in real-time.
Many of the original paper blueprints are archived since they are still in use. In many situations their conversion to digital form is prohibitively expensive. Most buildings and roads constructed before 1990 will only have paper blueprints, not digital. These originals have significant importance to the repair and alteration of constructions still in use, e.g. bridges, buildings, sewer systems, roads, railroads, etc., and sometimes in legal matters concerning the determination of, for example, property boundaries, or who owns (and/or is responsible for) a boundary wall.
See also
*Architectural reprography
Architectural reprography, the reprography of architectural drawings, covers a variety of technologies, media, and supports typically used to make multiple copies of original technical drawings and related records created by architects, landsca ...
*Floor plan
In architecture and building engineering, a floor plan is a technical drawing to scale, showing a view from above, of the relationships between rooms, spaces, traffic patterns, and other physical features at one level of a structure.
Dimensio ...
*Graph paper
Graph paper, coordinate paper, grid paper, or squared paper is writing paper that is printed with fine lines making up a regular grid. The lines are often used as guides for plotting graphs of functions or experimental data and drawing curves. I ...
*Technical drawing
Technical drawing, drafting or drawing, is the act and Academic discipline, discipline of composing Plan (drawing), drawings that Visual communication, visually communicate how something functions or is constructed.
Technical drawing is essent ...
*Heliographic copier A heliographic copier or heliographic duplicator is an apparatus used in the world of reprography for making contact prints on paper from original drawings made with that purpose on tracing paper, parchment paper or any other transparent or transl ...
*Whiteprint
Whiteprint describes a document reproduction produced by using the diazo chemical process. It is also known as the blue-line process since the result is blue lines on a white background. It is a contact printing process which accurately reproduc ...
*Cyanotype
The cyanotype (from Ancient Greek κυάνεος - ''kuáneos'', “dark blue” + τύπος - ''túpos'', “mark, impression, type”) is a slow-reacting, economical photographic printing formulation sensitive to a limited near ultraviolet ...
References
Further reading
* {{Visualization 1842 introductions Non-impact printing Infographics Publications by format Technical drawing