Blood Pressure Meter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A sphygmomanometer ( ), a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure
/ref> They measure mean blood pressure and pulse rate, while systolic and diastolic pressures are obtained less accurately than with manual meters, and calibration is also a concern. Digital oscillometric monitors may not be advisable for some patients, such as those with
 In humans, the cuff is normally placed smoothly and snugly around an upper
In humans, the cuff is normally placed smoothly and snugly around an upper 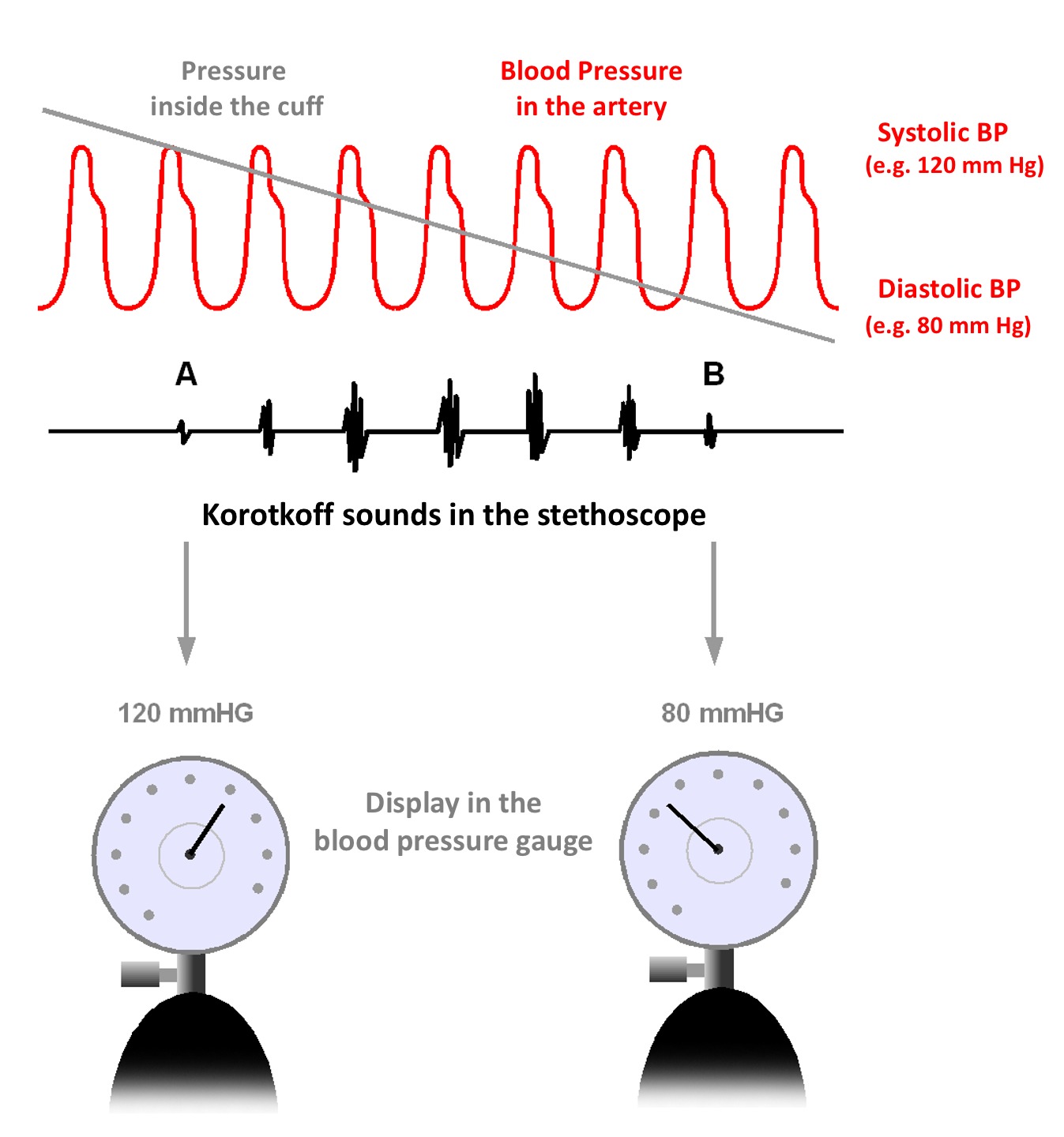
 The sphygmomanometer was invented by
The sphygmomanometer was invented by
blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
, composed of an inflatable cuff
A cuff is a layer of fabric at the lower edge of the sleeve of a garment (shirt, coat, jacket, etc.) at the wrist, or at the ankle end of a trouser leg. The function of turned-back cuffs is to protect the cloth of the garment from fraying, an ...
to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
or aneroid manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressur ...
to measure the pressure. Manual sphygmomanometers are used with a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
when using the auscultatory technique.
A sphygmomanometer consists of an inflatable cuff, a measuring unit (the mercury manometer, or aneroid gauge), and a mechanism for inflation which may be a manually operated bulb and valve or a pump operated electrically.
Types
Both manual and digital meters are currently employed, with different trade-offs in accuracy versus convenience.Manual
A stethoscope is required forauscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (hea ...
( see below). Manual meters are best used by trained practitioners, and, while it is possible to obtain a basic reading through palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
alone, this yields only the systolic pressure.
* Mercury sphygmomanometers are considered the gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
. They indicate pressure with a column of mercury, which does not require recalibration. Because of their accuracy, they are often used in clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietar ...
s of drugs and in clinical evaluations of high-risk patients, including pregnant women. A frequently used wall mounted mercury sphygmomanometer is also known as a Baumanometer.
* Aneroid sphygmomanometers (mechanical types with a dial) are in common use; they may require calibration checks, unlike mercury manometers. Aneroid sphygmomanometers are considered safer than mercury sphygmomanometers, although inexpensive ones are less accurate. A major cause of departure from calibration is mechanical jarring. Aneroids mounted on walls or stands are not susceptible to this particular problem.
Digital
Digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
meters employ oscillometric measurements and electronic calculations rather than auscultation. They may use manual or automatic inflation, but both types are electronic, easy to operate without training, and can be used in noisy environments. They measure systolic
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun ...
and diastolic pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
s by oscillometric detection, employing either deformable membranes that are measured using differential capacitance, or differential piezoresistance, and they include a microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
.Oscillometry, Explanation of oscillometric detection in Medical Electronics, N Townsend, p48-51/ref> They measure mean blood pressure and pulse rate, while systolic and diastolic pressures are obtained less accurately than with manual meters, and calibration is also a concern. Digital oscillometric monitors may not be advisable for some patients, such as those with
arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is the thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of Artery, arteries. This process gradually restricts the blood flow to one's organs and tissues and can lead to severe health risks brought on by atherosclerosis ...
, arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
, preeclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease ...
, ''pulsus alternans
Pulsus alternans is a physical finding with arterial pulse waveform showing alternating strong and weak beats. It is almost always indicative of left ventricular systolic impairment, and carries a poor prognosis.
Pathophysiology
One explanation ...
'', and ''pulsus paradoxus
Pulsus paradoxus, also paradoxic pulse or paradoxical pulse, is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration. The normal fall in pressure is less than 10 mmHg. When the drop i ...
'', as their calculations may not correct for these conditions, and in these cases, an analog sphygmomanometer is preferable when used by a trained person.
Digital instruments may use a cuff placed, in order of accuracy and inverse order of portability and convenience, around the upper arm, the wrist, or a finger. Recently, a group of researchers at Michigan State University developed a smartphone based device that uses oscillometry to estimate blood pressure. The oscillometric method of detection used gives blood pressure readings that differ from those determined by auscultation, and vary according to many factors, such as pulse pressure
Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It represents the force that the heart generates each time it contracts. Resting blood pressure is normally approx ...
, heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
and arterial stiffness
Arterial stiffness occurs as a consequence of biological aging and arteriosclerosis. Inflammation plays a major role in arteriosclerosis development, and consequently it is a major contributor in large arteries stiffening. Increased arterial stiff ...
, although some instruments are claimed also to measure arterial stiffness, and some can detect irregular heartbeats.
Operation
arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the ...
, at roughly the same vertical height as the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
while the subject is seated with the arm supported. Other sites of placement depend on species and may include the flipper or tail. It is essential that the correct size of cuff is selected for the patient. Too small a cuff results in too high a pressure, while too large a cuff results in too low a pressure. For clinical measurements it is usual to measure and record both arms in the initial consultation to determine if the pressure is significantly higher in one arm than the other. A difference of 10 mmHg may be a sign of coarctation of the aorta
Coarctation of the aorta (CoA or CoAo), also called aortic narrowing, is a congenital condition whereby the aorta is narrow, usually in the area where the ductus arteriosus (ligamentum arteriosum after regression) inserts. The word ''coarctation' ...
. If the arms read differently, the higher reading arm would be used for later readings. The cuff is inflated until the artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pul ...
is completely occluded.
With a manual instrument, listening with a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
to the brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa ...
, the examiner slowly releases the pressure in the cuff at a rate of approximately 2 mmHg per heart beat. As the pressure in the cuffs falls, a "whooshing" or pounding sound is heard (see Korotkoff sounds
Korotkoff sounds are the sounds that medical personnel listen for when they are taking blood pressure using a non-invasive procedure. They are named after Nikolai Korotkov, a Russian physician who discovered them in 1905, when he was working at th ...
) when blood flow first starts again in the artery. The pressure at which this sound began is noted and recorded as the systolic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
. The cuff pressure is further released until the sound can no longer be heard. This is recorded as the diastolic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
. In noisy environments where auscultation is impossible (such as the scenes often encountered in emergency medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for unsche ...
), systolic blood pressure alone may be read by releasing the pressure until a radial pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the nec ...
is palpated (felt). In veterinary medicine, auscultation is rarely of use, and palpation or visualization of pulse distal to the sphygmomanometer is used to detect systolic pressure.
Digital instruments use a cuff which may be placed, according to the instrument, around the upper arm, wrist, or a finger, in all cases elevated to the same height as the heart. They inflate the cuff and gradually reduce the pressure in the same way as a manual meter, and measure blood pressures by the oscillometric method.

Significance
By observing the mercury in the column, or the aneroid gauge pointer, while releasing the air pressure with a control valve, the operator notes the values of the blood pressure in mmHg. The peak pressure in the arteries during thecardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following ...
is the systolic pressure, and the lowest pressure (at the resting phase of the cardiac cycle) is the diastolic pressure. A stethoscope, applied lightly over the artery being measured, is used in the auscultatory method. Systolic pressure (first phase) is identified with the first of the continuous Korotkoff sounds. Diastolic pressure is identified at the moment the Korotkoff sounds disappear (fifth phase).
Measurement of the blood pressure is carried out in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
(high blood pressure), and in many other healthcare scenarios.
History
Samuel Siegfried Karl Ritter von Basch
Samuel Siegfried Karl ''Ritter'' von Basch (9 September 1837, Prague25 April 1905) was an Austrian-Jewish (Yekke) physician who was best known as the personal physician of emperor Maximilian of Mexico and the inventor of the blood pressure meter ( ...
in the year 1881. Scipione Riva-Rocci
Scipione Riva Rocci (7 August 1863 in Almese, Piedmont – 15 March 1937 in Rapallo, Liguria) was an Italian internist, Pathology, pathologist and pediatrician. He is best known for the invention of an easy-to-use cuff-based version of the me ...
introduced a more easily used version in 1896. In 1901, pioneering neurosurgeon
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peri ...
Dr. Harvey Cushing brought an example of Riva-Rocci's device to the US, modernized it and popularized it within the medical community. Further improvement came in 1905 when Russian physician Nikolai Korotkov
Nikolai Sergeyevich Korotkov (also romanized Korotkoff; russian: Никола́й Серге́евич Коротко́в) ( – 14 March 1920) was a Russian Empire surgeon, a pioneer of 20th-century vascular surgery, and the inventor of auscul ...
included diastolic
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricu ...
blood pressure measurement following his discovery of "Korotkoff sounds." William A. Baum invented the Baumanometer brand in 1916, while working for The Life Extension Institute which performed insurance and employment physicals. In 1981 the first fully automated oscillometric blood pressure cuff was invented by Donald Nunn.
Etymology
The word ''sphygmomanometer'' uses thecombining form
Neoclassical compounds are compound words composed from combining forms (which act as affixes or stems) derived from classical Latin or ancient Greek roots. New Latin comprises many such words and is a substantial component of the technical an ...
of '' sphygmo-'' + ''manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressur ...
''. The roots involved are as follows: Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''sphygmos'' "pulse", plus the scientific term ''manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressur ...
'' (from French ''manomètre''), i.e. "pressure meter", itself coined from ''manos'' "thin, sparse", and ''metron'' "measure"., , .
Most sphygmomanometers were mechanical gauges with dial faces, or mercury columns, during most of the 20th century. Since the advent of electronic medical device
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assura ...
s, names such as "meter" and "monitor" can also apply, as devices can automatically monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West Vir ...
blood pressure on an ongoing basis.
References
External links
* * * * {{US patent reference , number = 6752764 , inventor = Man S. Oh , title = Pocket sphygmomanometer , y = 2004, m = 06, d = 22 Medical equipment Pressure gauges Physiological instruments Blood pressure 1881 introductions 19th-century inventions Austrian inventions