Blackfeet Indian Tribal Council on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a
The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a
''Indian Country Today,'' 22 November 2016; accessed 23 November 2016 This sacred part of the Rocky Mountain Front was excluded from Blackfeet lands in a
 The 2010 census reported a population of 10,405 living on the reservation lands. The population density is 3.47 people per square mile (1.34 people/km²).
The Blackfeet Nation has 16,500 enrolled members. The main community is Browning, Montana, which is the seat of tribal government. Other towns serve the tourist economy along the edge of the park:
The 2010 census reported a population of 10,405 living on the reservation lands. The population density is 3.47 people per square mile (1.34 people/km²).
The Blackfeet Nation has 16,500 enrolled members. The main community is Browning, Montana, which is the seat of tribal government. Other towns serve the tourist economy along the edge of the park:
, Browning, Montana website In 2002, the Department of Interior declared roughly two-thirds — almost 90,000 acres (36,000 ha) — of the Badger-Two Medicine area along the Rocky Mountain Front as eligible for listing as a Traditional Cultural District in the National Register of Historic Places. This was a recognition of its importance to the Blackfeet. They used an ethnographer to document their oral history of use and practices, and in 2014 used this information to negotiate with stakeholders over leases for drilling rights that had been made in the area. The nation celebrates North American Indian Days, an annual festival held on
 The Blackfeet Nation runs the sovereign government on the reservation through its elected Tribal Business Council. For many years
The Blackfeet Nation runs the sovereign government on the reservation through its elected Tribal Business Council. For many years
''Indian Country Today,'' 19 November 2015; accessed 24 November 2016 It provides most services, including courts, child welfare, employment assistance, wildlife management, health care, education, land management, and senior services, as well as garbage collection and water systems. They worked with the federal
Blackfeet Tribal Land Department
Official tribe website
Blackfeet Reservation and Off-Reservation Trust Land, Montana
United States Census Bureau
Singer/songwriter/storyteller/lecturer Jack Gladstone
University of Montana Library {{Coord, 48, 39, 31, N, 112, 52, 18, W, scale:1000000, display=title American Indian reservations in Montana Blackfoot tribe Federally recognized tribes in the United States Geography of Glacier County, Montana Geography of Pondera County, Montana Montana articles lacking sources
 The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a
The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a federally recognized tribe
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United ...
of Siksikaitsitapi people with an Indian reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it ...
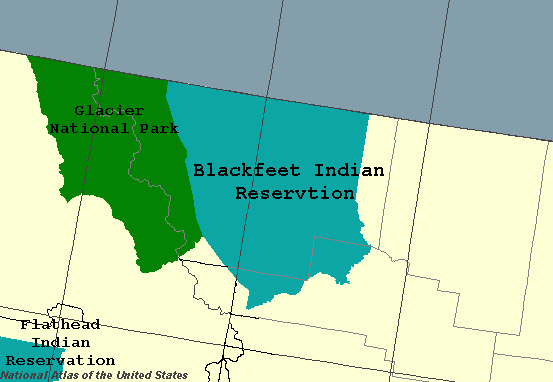
in Montana. Tribal members primarily belong to the Piegan Blackfeet (Ampskapi Piikani) band of the larger Blackfoot Confederacy that spans Canada and the United States.
The Blackfeet Indian Reservation is located east of Glacier National Park and borders the Canadian province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North ...
of Alberta. Cut Bank Creek and Birch Creek form part of its eastern and southern borders. The reservation contains 3,000 square miles (7,800 km2), twice the size of the national park and larger than the state of Delaware. It is located in parts of Glacier and Pondera counties.
History
The Blackfeet settled in the region around Montana beginning in the17th century
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural moveme ...
. Previously, they resided in an area of the woodlands north and west of the Great Lakes. Pressure exerted by British traders at James Bay in present day Canada on the Algonquin-speaking tribes in the area drove the Blackfeet out onto the Northern Plains. They eventually acquired firearms and horses, and became a formidable example of the classic Plains Indian culture. They were a powerful force, controlling an area that extended from current day Edmonton, Alberta Province, nearly to Yellowstone National Park, and from Glacier Park to the Black Hills of South Dakota. The Badger-Two Medicine area is a significant sacred site for the tribe.
In the late 19th century, Blackfeet territory was encroached on by European Americans and Canadians, and various branches of the people were forced to cede lands and ultimately move to smaller Indian reservations in the United States and reserves in Canada. Adjacent to their reservation, established by Treaty of 1896, are two federally controlled areas: the Lewis and Clark National Forest
Lewis and Clark National Forest is located in west central Montana, United States. Spanning , the forest is managed as two separate zones. The eastern sections, under the Jefferson Division, is a mixture of grass and shrublands dotted with "islan ...
, set up in 1896, which contains the Badger-Two Medicine area, an area of ; and Glacier National Park, both part of the tribal nation's former territory. The Badger-Two Medicine area is sacred to the Blackfeet people.Renae Ditmer, "On Eve of Film Premier, Interior Cancels Oil and Gas Leases in Blackfeet ‘Cathedral’"''Indian Country Today,'' 22 November 2016; accessed 23 November 2016 This sacred part of the Rocky Mountain Front was excluded from Blackfeet lands in a
Treaty of 1896
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
, but they reserved access, hunting and fishing rights. Since the early 1980s, when the Bureau of Land Management
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior responsible for administering federal lands. Headquartered in Washington DC, and with oversight over , it governs one eighth of the country's la ...
approved drilling rights leases without consultation with the tribe, the Blackfeet have worked to protect this sacred area, where they practiced their traditional religious rituals.
The United States federal government suspended all leasing activities for drilling in this area in the 1990s, and in 2007 the Bush administration made permanent a moratorium on issuing new permits. Many leaseholders had already relinquished their leases, and in November 2016 the Department of Interior announced the cancellation of the 15 drilling rights leases held by Devon Energy Corporation in the Badger-Two Medicine area. The Blackfeet had documented that the area was not a "wilderness," as the Bob Marshall Wilderness Complex
The Bob Marshall Wilderness Complex consists of three wilderness areas, all within the U.S. state of Montana totalling over 1.5 million acres (6,100 km²). The largest wilderness area is the Bob Marshall Wilderness Area consisting of 1 millio ...
was designated in 1964, but a "human landscape" shaped by and integral to their culture.
Geography
Elevations in the reservation range from a low of to a high of atChief Mountain
Chief Mountain ('' Blackfoot: Ninaistako'') () is located in the U.S. state of Montana on the eastern border of Glacier National Park and the Blackfeet Indian Reservation. The mountain is one of the most prominent peaks and rock formations alon ...
. Adjacent mountains include Ninaki Mountain and Papoose. The eastern part of the reservation is mostly open hills of grassland, while a narrow strip along the western edge is covered by forests of fir
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family (biology), family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North America, North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The ...
and spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
. Free-ranging cattle are present in several areas, sometimes including on roadways.
Several waterways drain the area with the largest being the St. Mary River, Two Medicine River
The Two Medicine River is a tributary of the Marias River, approximately 60 mi (97 km) long, in northwestern Montana in the United States.
It rises in the Rocky Mountain Front in Glacier National Park at the continental divide and fl ...
, Milk River, Birch Creek and Cut Bank Creek. There are of streams and eight major lakes on the reservation.
The reservation is east of the Lewis and Clark National Forest
Lewis and Clark National Forest is located in west central Montana, United States. Spanning , the forest is managed as two separate zones. The eastern sections, under the Jefferson Division, is a mixture of grass and shrublands dotted with "islan ...
in Montana, which contains the Badger-Two Medicine area, sacred to the Blackfeet people. The Badger-Two Medicine area is at the Rocky Mountain Front of the national forest. The Blackfeet call the Rocky Mountains the "Backbone of the World". Their names for peaks include Morning Star, Poia, Little Plume, Running Crane, Spotted Eagle, Kiyo, Scarface, Elkcalf Bullshoe, and Curly Bear.
Demographics
 The 2010 census reported a population of 10,405 living on the reservation lands. The population density is 3.47 people per square mile (1.34 people/km²).
The Blackfeet Nation has 16,500 enrolled members. The main community is Browning, Montana, which is the seat of tribal government. Other towns serve the tourist economy along the edge of the park:
The 2010 census reported a population of 10,405 living on the reservation lands. The population density is 3.47 people per square mile (1.34 people/km²).
The Blackfeet Nation has 16,500 enrolled members. The main community is Browning, Montana, which is the seat of tribal government. Other towns serve the tourist economy along the edge of the park: St. Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
and East Glacier Park Village
East Glacier Park (Blackfeet: , "Big Tree Lodge") is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Glacier County, Montana, United States. The population was 363 on the 2010 United States Census.
The Great Northern Railway pla ...
, which has an Amtrak passenger station and the historic Glacier Park Lodge
Glacier Park Lodge is located just outside the boundaries of Glacier National Park in the village of East Glacier Park, Montana, United States. The lodge was built in 1913 by the Glacier Park Company, a subsidiary of the Great Northern Railw ...
. Small communities include Babb, Kiowa, Blackfoot, Seville, Heart Butte, Starr School, and Glacier Homes.
Communities
* Babb * Browning *East Glacier Park Village
East Glacier Park (Blackfeet: , "Big Tree Lodge") is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Glacier County, Montana, United States. The population was 363 on the 2010 United States Census.
The Great Northern Railway pla ...
* Heart Butte
* Little Browning
* North Browning
*St. Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
* South Browning
* Starr School
Culture
The tribe has an oral history of 10,000 years in this region. It recounts the sacred nature of their central place, the Badger-Two Medicine area, known as their site of creation and origin. The Rocky Mountain Front near Birch Creek The Badger-Two Medicine is "covered by the Treaty of 1896, which gives Blackfeet tribal members the right to hunt and fish in any portion of the area in accordance with state law and cut wood for domestic use. Blackfeet treaty claims as well as spiritual and cultural uses of the Badger-Two Medicine are pre-existing rights ... Blackfeet tribal members have used the Badger-Two Medicine and its waters for hundreds of years for vision quests and for other religious and cultural purposes."Rocky Mountain Front, Browning, Montana website In 2002, the Department of Interior declared roughly two-thirds — almost 90,000 acres (36,000 ha) — of the Badger-Two Medicine area along the Rocky Mountain Front as eligible for listing as a Traditional Cultural District in the National Register of Historic Places. This was a recognition of its importance to the Blackfeet. They used an ethnographer to document their oral history of use and practices, and in 2014 used this information to negotiate with stakeholders over leases for drilling rights that had been made in the area. The nation celebrates North American Indian Days, an annual festival held on
pow wow
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native American and First Nations communities. Powwows today allow Indigenous people to socialize, dance, sing, and honor their cultures. Powwows may be private or pu ...
grounds, near the Museum of the Plains Indian in Browning. Adjacent to the reservation's eastern edge is the city of Cut Bank
A cut bank, also known as a river cliff or river-cut cliff, is the outside bank of a curve or meander in a water channel (stream), which is continually undergoing erosion.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak Cut banks are found in abu ...
.
Economy
Because of its isolated location, residents of the reservation have suffered high unemployment. As of May 2016, the Montana Local Area Unemployment Statistics (LAUS) Program Preliminary Non-Seasonally Adjusted Data reports the rate is 11.0% on the reservation (for comparison, at the same time, unemployment was 3.6% for Montana and 4.5% for the U.S.). In 2001, the BIA reported 69 percent unemployment among registered members of the tribe. Among those who were employed that year, 26% earned less than the poverty guideline. The major income source of the reservation is petroleum and natural gas leases on the oil fields on tribal lands. In 1982, there were 643 producing oil wells and 47 producing gas wells. The reservation also has a significant tourist industry. Other economic activities include ranching and a small lumber industry, which supported the Blackfeet Indian Writing Company pencil factory in Browning. Farms located at least partially on the reservation reported a total income of $9 million in 2002. A total of 354 farms covered , the majority of the reservation's land. Most of these farms or ranches were family-owned, including the 198 farms owned by Native Americans. Eighty percent of the land was used for raising beef cattle, which produced eighty percent of farm income. Other livestock included hogs, and chickens, with only small numbers of dairy cattle,bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
, horses, and sheep.
Of the used for growing crops, only , or 13%, were irrigated
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
. Crops raised included wheat, barley, and hay with a smaller amount of oats.
Members of the tribe work seasonally in wildfire firefighting, a source of considerable individual income. In 2000, some 1,000 Blackfeet worked as firefighters, including the elite Chief Mountain Hotshots team. Firefighting income brought in $6.1 million that year. However, this income is highly variable depending on the severity of the wildfire season.
On April 30, 2010, the Blackfeet Tribal Business Council (BTBC) approved three major initiatives totaling $5.5 million. The revenue was to be derived from payments for oil exploration from Newfield Production Co. The BTBC approved a $200 special per capita payments for all 16,500 members, initial funding for a new grocery store in Browning, and more than $1 million for land acquisition within the reservation to return property to tribal control.
Government
Earl Old Person
Earl Old Person ( Blackfeet names , "Cold Wind", and , "Charging Home"; April 13, 1929 – October 13, 2021) was an American Indian political leader and the honorary lifetime chief of the Blackfeet Nation () in Montana, United States.William ...
led the council. Old Person was also the honorary chief of the tribe.Jack McNeel, "10 Things You Should Know about the Blackfeet Nation"''Indian Country Today,'' 19 November 2015; accessed 24 November 2016 It provides most services, including courts, child welfare, employment assistance, wildlife management, health care, education, land management, and senior services, as well as garbage collection and water systems. They worked with the federal
Bureau of Indian Affairs
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States federal agency within the Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing federal laws and policies related to American Indians and A ...
to replace native police with federal officers in 2003 because of problems in the local force.
The reservation includes several types of land use. Of the total , are held in trust for enrolled tribal members, are held directly by the tribe, and are ''Government Reserve'', mostly irrigation projects and the Cut Bank Boarding School Reserve. The remaining are ''Fee lands,'' which is taxable and may be privately owned by the tribe, tribe members or non-tribe members.
The tribe leases some of its communal land for homes, farms, grazing, and commercial uses. They offer leases to tribe members prior to non-members. The tribe has the right of first refusal; all private land offered for sale within the reservation must be offered to the tribe first. If they decline to purchase it, they grant a waiver permitting purchase by non-Native parties.
Transportation
There are no paved north-south roads in Glacier National Park. Access to sites on the east side of the park is provided by U.S. Route 89, which runs through the reservation to the Canada–US border, crossing nearChief Mountain
Chief Mountain ('' Blackfoot: Ninaistako'') () is located in the U.S. state of Montana on the eastern border of Glacier National Park and the Blackfeet Indian Reservation. The mountain is one of the most prominent peaks and rock formations alon ...
. It provides access to the Canadian sister national park, Waterton Lakes. Both east-west routes for the park travel through the reservation, as does the passenger train service on Amtrak's '' Empire Builder''. Several hiking trails continue out of the park and across the reservation; they require Blackfeet-issued permits for use.
Notable people
* Gordon Belcourt (1945–2013), Executive Director of the Montana-Wyoming Tribal Leaders Council *Black Lodge Singers The Black Lodge Singers of White Swan, Washington are a Native American northern drum group led by Kenny ScabbyRobe, of the Blackfeet Nation. The Black Lodge Singers are largely drawn from his twelve sons. They have released twenty albums for Canyo ...
, powwow singers and drum group
* Elouise P. Cobell
Elouise Pepion Cobell, also known as Yellow Bird Woman (November 5, 1945 – October 16, 2011) (''Niitsítapi'' Blackfoot Confederacy), was a tribal elder and activist, banker, rancher, and lead plaintiff in the groundbreaking class-action sui ...
(1945–2011), tribal treasurer and founder of Blackfeet Nation Bank. She identified mismanagement of trust land fees by the departments of Interior and Treasury, and sought corrections in Washington. In 1996 she filed a class-action suit against the government in what is known as ''Cobell v. Salazar
''Cobell v. Salazar'' (previously ''Cobell v. Kempthorne'' and ''Cobell v. Norton'' and ''Cobell v. Babbitt'') is a class-action lawsuit brought by Elouise Cobell (Blackfeet) and other Native American representatives in 1996 against two departm ...
,'' settled by the federal government for $3.4 billion in 2009. The settlement provides for payment to potentially more than 250,000 plaintiffs, repurchase of lands across the country for transfer to tribal management, and a scholarship fund for Native American and Alaskan Native students.
* Richie Havens
Richard Pierce Havens (January 21, 1941 – April 22, 2013) was an American singer-songwriter and guitarist. His music encompassed elements of folk, soul (both of which he frequently covered), and rhythm and blues. He had a rhythmic guitar style ...
(1941–2013), singer-songwriter and guitarist
* Joe Hipp (born 1962), professional boxer
* Donna Hutchinson
Donna Jean King Hutchinson (born August 23, 1949) is a Republican Party (United States), Republican former member of the Arkansas House of Representatives from District 98, which includes part of fast-growing Benton County, Arkansas, Benton County ...
(born 1949), elected as member of the Arkansas House of Representatives
The Arkansas State House of Representatives is the lower house of the Arkansas General Assembly, the state legislature of the US state of Arkansas. The House is composed of 100 members elected from an equal amount of constituencies across the ...
from Bella Vista, Arkansas, served from 2007 to 2013
* Mountain Chief
Mountain Chief (''Ninna-stako'' in the Blackfoot language; – 1942) was a South Piegan warrior of the Blackfoot Tribe. Mountain Chief was also called Big Brave (Omach-katsi) and adopted the name Frank Mountain Chief. Mountain Chief was involved ...
(1848–1942)
* Earl Old Person
Earl Old Person ( Blackfeet names , "Cold Wind", and , "Charging Home"; April 13, 1929 – October 13, 2021) was an American Indian political leader and the honorary lifetime chief of the Blackfeet Nation () in Montana, United States.William ...
(1929-2021), tribal chief and political leader
* Steve Reevis
Steve Reevis (August 14, 1962 – December 7, 2017) was a Native American actor and member of the Blackfeet Tribe known for his roles in the films '' Fargo'', ''Last of the Dogmen'', and ''Dances with Wolves''.
Early life and education
Steve ...
(1962–2017), actor ('' Geronimo: An American Legend,'' '' The Missing,'' ''Fargo Fargo usually refers to:
* Fargo, North Dakota, United States
* ''Fargo'' (1996 film), a crime film by the Coen brothers
* ''Fargo'' (TV series), an American black comedy–crime drama anthology television series
Fargo may also refer to:
Othe ...
'')
* Misty Upham (1982–2014), actor
* Stephen Graham Jones (born 1972), author
* Rickey Medlocke (born 1950), guitarist for Blackfoot and Lynyrd Skynyrd bands
See also
* Tipi ring, with information about study of tipi ring sites on the Blackfeet Indian Reservation * Darrell "Dusty" Crawford learned that he has what may be the oldest DNA native to the Americas. The test revealed the origins of his Blackfeet ancestors who may have already been in the Americas about 17,000 years ago.References
References
*Farr, William E. ''The Reservation Blackfeet: A Photographic History of Cultural Survival''. Foreword by James Welch. Seattle: University of Washington Press, 1984. *McFee, Malcolm. ''Modern Blackfeet: Montanans on a Reservation''. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1972.External links
Blackfeet Tribal Land Department
Official tribe website
Blackfeet Reservation and Off-Reservation Trust Land, Montana
United States Census Bureau
Singer/songwriter/storyteller/lecturer Jack Gladstone
University of Montana Library {{Coord, 48, 39, 31, N, 112, 52, 18, W, scale:1000000, display=title American Indian reservations in Montana Blackfoot tribe Federally recognized tribes in the United States Geography of Glacier County, Montana Geography of Pondera County, Montana Montana articles lacking sources