Blackburn L.1 Bluebird on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Blackburn L.1 Bluebird was a British single-engine biplane Trainer (aircraft), light trainer/tourer with side-by-side seating, built in small numbers by Blackburn Aircraft in the 1920s.
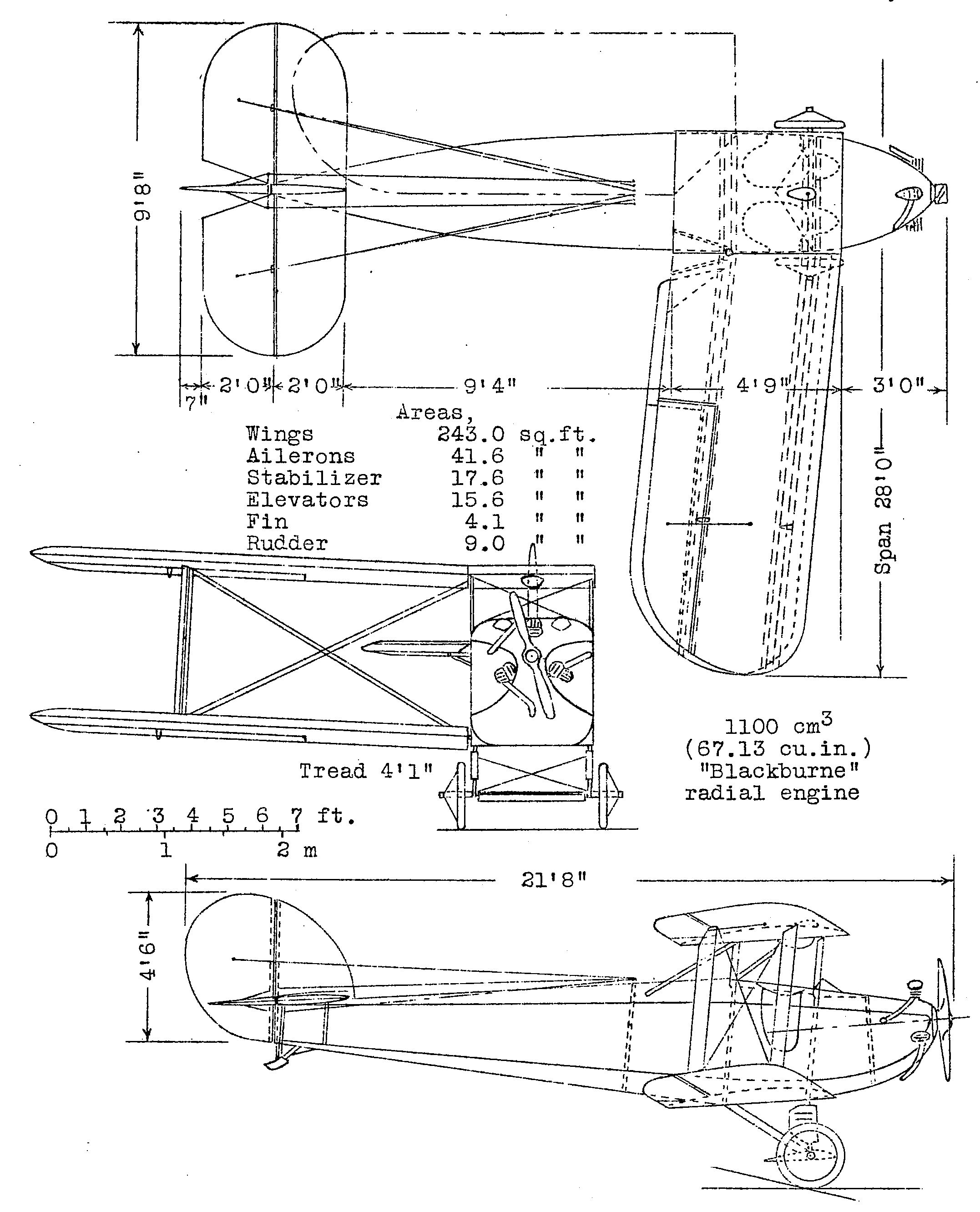
Design and development
The Bluebird L.1 was initially designed as a competitor in the Lympne light aircraft trials to be held in September 1924 for a low-powered two-seater, fitted with a 67 in³ (1,100 cc) Blackburne Thrush three-cylinder radial engine. The Bluebird was a wooden single-bay biplane, with folding wings and was fitted with a single side-by-side cockpit.Jackson 1974, p. 208. Although first flying in 1924,Taylor 1989, p. 157 problems with the engine, which failed to give the expected power, meant that it could not compete in the 1924 competition.Jackson 1968, pp. 190–191. It was realised that the machines that resulted from the 1923 and 1924 light aircraft trials were too low-powered for serious use. The Daily Mail sponsored a similar competition in September 1926, this time allowing the use of heavier and more powerful engines. The prototype Bluebird was then fitted with an Armstrong Siddeley Genet radial engine and dual controls for entry into the competition. Interest in the Bluebird following the competition and its success in the 1926 Grosvenor Cup air race, which it won, resulted in Blackburn manufacturing a batch of 13 production aircraft, known as the L.1A Bluebird II, which were similar to the prototype, and a further seven modified L.1B Bluebird IIIs.Jackson 1974, p. 209. The Bluebird formed the basis for the all-metal Blackburn Bluebird IV.Operational history
The wooden Bluebirds were used mainly by flying clubs, and were heavily used, but several were quickly written off, with only three surviving for more than four years.Jackson 1974, p. 210. One Bluebird II was fitted with floats and another, the Bluebird III prototype, was fitted with an Cirrus Engine, ADC Cirrus engine as a testbed for the Bluebird IV.Jackson 1974, pp. 209–210. The last wooden Bluebird was destroyed in a firefighting demonstration in 1937.Variants
;L.1 Bluebird I: Prototype. Originally powered by Blackburne Thrush engine, later refitted with Armstrong Siddeley Genet I radial engine and dual controls. ;L.1A Bluebird II: Production. Powered by Genet II engine. 13 built.Jackson 1968, p. 250. ;L.1.B Bluebird III: Modified internal structure. One prototype and six production aircraft.Jackson 1968, pp. 253–254.Operators
; *Royal Air ForceSpecifications (Bluebird II, III)

See also
Notes
References
* * * {{Blackburn aircraft 1920s British sport aircraft Blackburn aircraft, Bluebird Single-engined tractor aircraft Biplanes Aircraft first flown in 1924