Biting (embouchure) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Biting is an action involving a set of teeth closing down on an object. It is a common zoological behavior, being found in toothed animals such as
 The types of teeth that organisms use to bite vary throughout the animal kingdom. Different types of teeth are seen in
The types of teeth that organisms use to bite vary throughout the animal kingdom. Different types of teeth are seen in
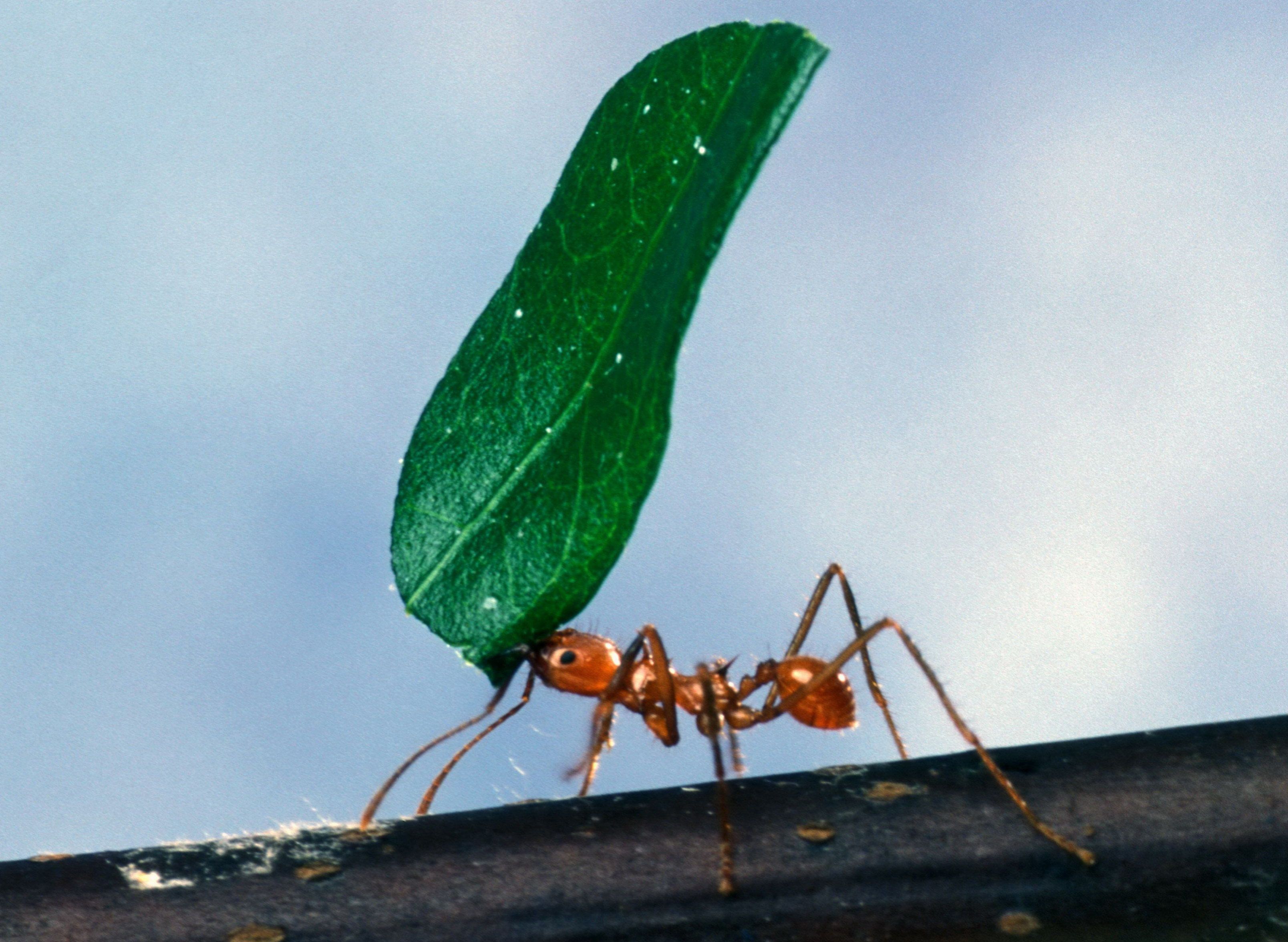 Biting can serve as a carrying mechanism for species such as
Biting can serve as a carrying mechanism for species such as
 Criminally, Forensic Dentistry is involved in bite-mark analysis. Because bite-marks change significantly over time, investigators must call for an expert as soon as possible. Bites are then analyzed to determine whether the biter was
Criminally, Forensic Dentistry is involved in bite-mark analysis. Because bite-marks change significantly over time, investigators must call for an expert as soon as possible. Bites are then analyzed to determine whether the biter was
"How Forensic Dentistry Works"
''How Stuff Works'', accessed June 28, 2019 Human bites have historically been viewed superstitiously, particularly in the
mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, and arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s. Biting is also an action humans participate in, most commonly when chewing food. Myocytic contraction of the muscles of mastication
There are four classical muscles of mastication. During mastication, three muscles of mastication (''musculi masticatorii'') are responsible for adduction of the jaw, and one (the lateral pterygoid) helps to abduct it. All four move the jaw late ...
is responsible for generating the force that initiates the preparatory jaw abduction (opening), then rapidly adducts (closes) the jaw and moves the top and bottom teeth towards each other, resulting in the forceful action of a bite. Biting is one of the main functions in the lives of larger organisms, providing them the ability to forage, hunt
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, et ...
, eat
Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food, typically to provide a heterotrophic organism with energy and to allow for growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive — carnivores eat other animals, herbi ...
, build, play, fight
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
, protect, and much more. Biting may be a form of physical aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
due to predatory or territorial intentions. In animals, biting can also be a normal activity, being used for eating, scratching, carrying objects, preparing food for young, removing ectoparasites or irritating foreign objects, and social grooming
Social grooming is a behavior in which social animals, including humans, clean or maintain one another's body or appearance. A related term, allogrooming, indicates social grooming between members of the same species. Grooming is a major soci ...
. Humans can have the tendency to bite each other whether they are children or adults.
Bites often result in serious puncture wound
Penetrating trauma is an open wound injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating a deep but relatively narrow entry wound. In contrast, a blunt or ''non-penetrating'' trauma may have some deep dama ...
s, avulsion injuries
In medicine, an avulsion is an injury in which a body structure is torn off by either trauma or surgery (from the Latin ''avellere'', meaning "to tear off"). The term most commonly refers to a surface trauma where all layers of the skin have been ...
, fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
s, hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
s, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
s, envenomation, and death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
. In modern human societies, dog bites
A dog bite is a bite upon a person or other animal by a dog, including from a rabid dog. More than one successive bite is often called a dog attack, although dog attacks can include knock-downs and scratches. Though some dog bites do not result ...
are the most common type of bite, with children being the most common victims and faces being the most common target. Some other species that may bite humans include urban animals such as feral cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens ...
s, spider
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species ...
s, and snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
s. Other common bites to humans are inflicted by hematophagous insects and arthropods, such as mosquitoes, flea
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, a ...
s, lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result o ...
, bedbug
Bed bugs are insects from the genus ''Cimex'' that feed on blood, usually at night. Their bites can result in a number of health impacts including skin rashes, psychological effects, and allergy, allergic symptoms. Bed bug bites may lead to ski ...
s, and tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s (whose "bites" are actually a form of stinging
Sting may refer to:
* Stinger or sting, a structure of an animal to inject venom, or the injury produced by a stinger
* Irritating hairs or prickles of a stinging plant, or the plant itself
Fictional characters and entities
* Sting (Middle-earth ...
rather than true biting).
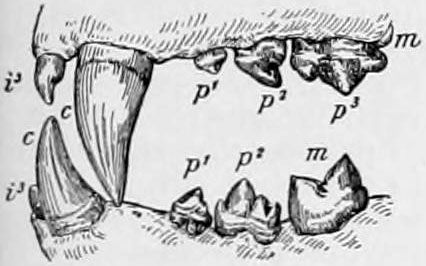
Types of teeth
 The types of teeth that organisms use to bite vary throughout the animal kingdom. Different types of teeth are seen in
The types of teeth that organisms use to bite vary throughout the animal kingdom. Different types of teeth are seen in herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s, carnivores, and omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutr ...
s as they are adapted over many years to better fit their diets. Carnivores possess canine, carnassial, and molar teeth
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
, while herbivores are equipped with incisor teeth and wide-back molars.Animal Teeth , Types of Teeth , DK Find Out. (2018). Retrieved October 28, 2018, from https://www.dkfindout.com/us/animals-and-nature/food-chains/types-teeth/ In general, tooth shape has traditionally been used to predict dieting habits. Carnivores have long, extremely sharp teeth for both gripping prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
and cutting meat into chunks. They lack flat chewing teeth because they swallow food in chunks. An example of this is shown by the broad, serrated teeth of great white sharks
The great white shark (''Carcharodon carcharias''), also known as the white shark, white pointer, or simply great white, is a species of large mackerel shark which can be found in the coastal surface waters of all the major oceans. It is nota ...
which prey on large marine animals. On the other hand, herbivores have rows of wide, flat teeth to bite and chew grass and other plants. Cows spend up to eleven hours a day biting off grass and grinding it with their molars. Omnivores consume both meat and plants, so they possess a mixture of flat teeth and sharp teeth.
Carrying mechanism
 Biting can serve as a carrying mechanism for species such as
Biting can serve as a carrying mechanism for species such as beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
s and ants, the raw power of their species-specific teeth allowing them to carry large objects. Beavers have a large tooth adapted for gnawing wood. Their jaw muscles are tuned to power through big trees and carry them back to their dam. Ants use their powerful jaws to lift material back to the colony. They can carry several thousand times their weight due to their bite and are adapted to use this to forage for their colonies. Fire ants use their strong bite to get a grip on prey, then inject a toxin via their stinger and carry the prey back to their territory.
Dangers
Some organisms have dangerous bites that injectvenom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
. Many snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
s carry a venomous saliva containing at least one of the major groups of toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849– ...
s, which include cytotoxins, hemotoxins, myotoxins, and neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature ner ...
s. Spider venom
The pathophysiology of a spider bite is due to the effect of its venom. A spider envenomation occurs whenever a spider injects venom into the skin. Not all spider bites inject venom – a dry bite, and the amount of venom injected can vary based on ...
polypeptides target specific ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
s, which excites components of the peripheral
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by the ...
, central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control ...
s, causing hyperactive neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
release and subsequently refractory
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase, ...
paralysis. Spider bite
A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin wound ...
s, or arachnidism
A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin wound ...
, are mainly a form of predation, but also means of self-defense — when trapped or accidentally tampered with by humans, spiders retaliate by biting. The recluse spider
The recluse spiders (''Loxosceles'' (), also known as brown spiders, fiddle-backs, violin spiders, and reapers, is a genus of spiders that was first described by R. T. Lowe in 1832. They are venomous spiders known for their bite, which sometimes ...
and widow species have neurotoxins and necrotizing agents that paralyze and digest prey.
Humans biting each other can cause a number of diseases with streptococci, staphylococci, and anaerobic organisms being very severe causing infections. These bites are typically deep cutting into the skin where the infection forms.
There are several creatures with non-lethal bites that may cause discomfort or diseases. Mosquito bites may cause allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derma ...
wheals that are itchy and may last a few days; in some areas, they can spread blood-borne diseases (e.g. malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
and West Nile fever) via transmission
Transmission may refer to:
Medicine, science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual transmission
*** ...
of protozoic
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histor ...
or viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s. Similarly, tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
bites spread diseases endemic to their location, most famously Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
, but ticks also serve as disease vector
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen to another living organism; agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as parasites or microbes. The first major discovery of a disease vec ...
s for Colorado tick fever, African tick bite fever
African tick bite fever (ATBF) is a bacterial infection spread by the bite of a tick. Symptoms may include fever, headache, muscle pain, and a rash. At the site of the bite there is typically a red skin sore with a dark center. The onset of sympto ...
, Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infectious disease involving the central nervous system. The disease most often manifests as meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis and spinal paralysis also occurs. In about one third ...
, etc.
In humans
Young children who bite others do so out of play or aggression whereas adults bite others out of aggression. Bites that occur from adults fighting are usually on the hands and the skeletal section. Infections are a result of bacteria from the mouth spread to another human and are the third common types of bites that require a hospital visit. Biting in children is common however, it may be prevented by methods including redirection, change in the environment and responding to biting by talking about appropriate ways to express anger and frustration. School-age children, those older than 30 months, who habitually bite may require professional intervention. Some discussion of human biting appears in '' The Kinsey Report on Sexual Behavior in the Human Female.'' Biting may also occur in physical fights or in self-defense. Criminally, Forensic Dentistry is involved in bite-mark analysis. Because bite-marks change significantly over time, investigators must call for an expert as soon as possible. Bites are then analyzed to determine whether the biter was
Criminally, Forensic Dentistry is involved in bite-mark analysis. Because bite-marks change significantly over time, investigators must call for an expert as soon as possible. Bites are then analyzed to determine whether the biter was human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, self-inflicted or not, and whether DNA was left behind from the biter. All measurements must be extremely precise, as small errors in measurement
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events.
In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared ...
can lead to large errors in legal judgment.Shanna Freeman"How Forensic Dentistry Works"
''How Stuff Works'', accessed June 28, 2019 Human bites have historically been viewed superstitiously, particularly in the
American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
where there was once a common belief that the bite of a "blue-gum negro
In the English language, ''negro'' is a term historically used to denote persons considered to be of Black African heritage. The word ''negro'' means the color black in both Spanish and in Portuguese, where English took it from. The term can be ...
" (i.e., a Black person
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in s ...
with darkly pigmented gums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue linin ...
) was lethally poisonous.
See also
* Chewing *Bite force quotient
Bite force quotient (BFQ) is a numerical value commonly used to represent the bite force of an animal, while also taking factors like the animal's size into account.
The BFQ is calculated as the regression of the quotient of an animal's bite f ...
* Animal bite
References
External links
* {{Animal bites and stings Ethology