Bishopric Of Caithness on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
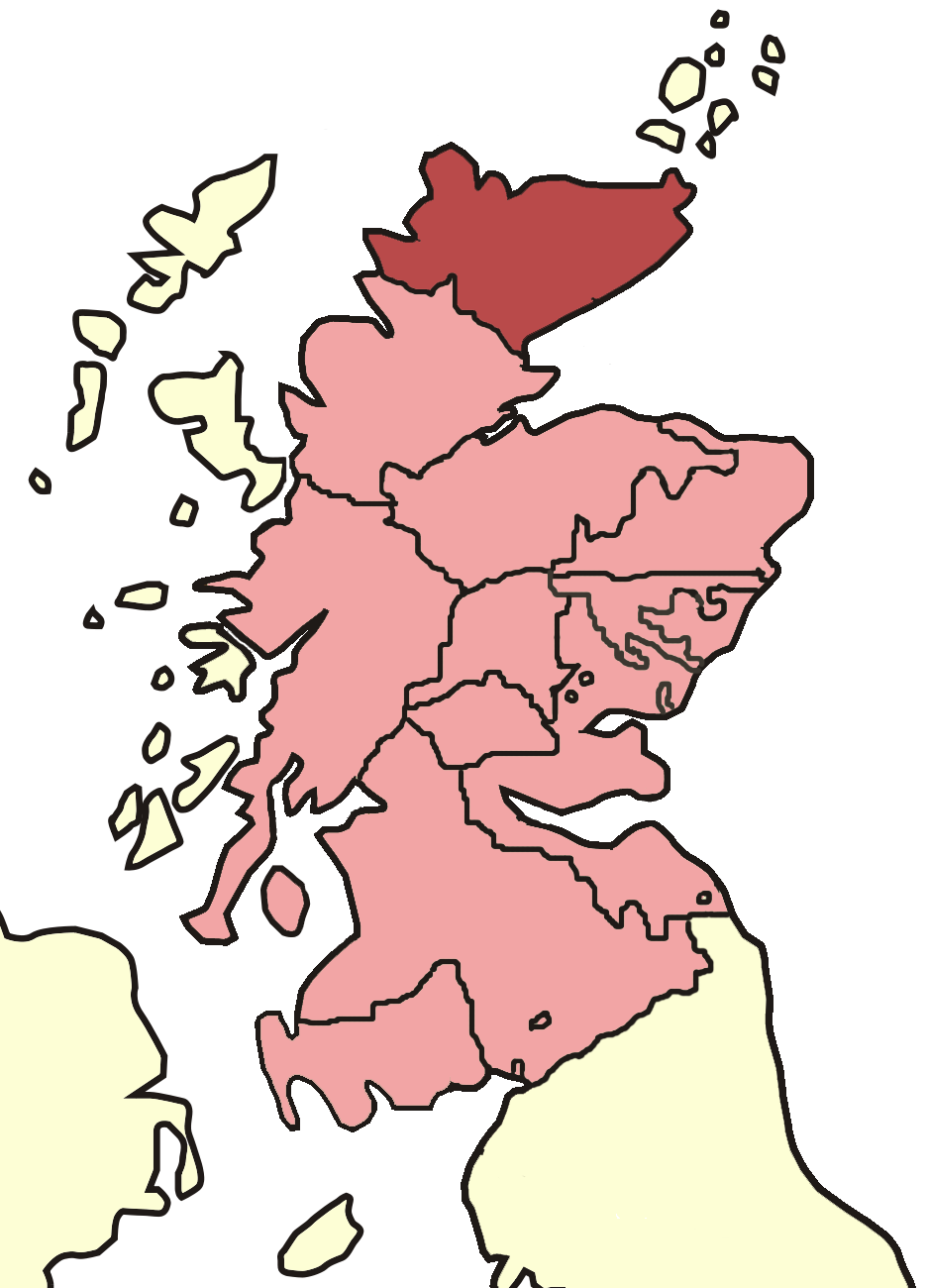 The Bishop of Caithness was the ecclesiastical head of the
The Bishop of Caithness was the ecclesiastical head of the
 The Bishop of Caithness was the ecclesiastical head of the
The Bishop of Caithness was the ecclesiastical head of the Diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
of Caithness
Caithness ( gd, Gallaibh ; sco, Caitnes; non, Katanes) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland.
Caithness has a land boundary with the historic county of Sutherland to the west and is otherwise bounded b ...
, one of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
's 13 medieval bishoprics. The first referenced bishop of Caithness was Aindréas, a Gael
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languag ...
who appears in sources between 1146 and 1151 as bishop. Aindréas spent much if not all of his career outside his see.
Other bishops before Aindréas are possible, but none is documented. King David I of Scotland
David I or Dauíd mac Maíl Choluim ( Modern: ''Daibhidh I mac haoilChaluim''; – 24 May 1153) was a 12th-century ruler who was Prince of the Cumbrians from 1113 to 1124 and later King of Scotland from 1124 to 1153. The youngest son of Malco ...
, is credited with founding many bishoprics, and it is possible that Caithness was one of them. Little documented history exists before the reign of King David.
The earliest bishops resided at Halkirk
Halkirk ( gd, Hàcraig) is a village on the River Thurso in Caithness, in the Highland council area of Scotland. From Halkirk the B874 road runs towards Thurso in the north and towards Georgemas in the east. The village is within the parish ...
, with a castle at Scrabster. Bishop Gilbert de Moravia
Gilbert de Moravia (died 1245), later known as Saint Gilbert of Dornoch, or Gilbert of Caithness, was the most famous Bishop of Caithness and founder of Dornoch Cathedral. His name may suggest that he came from the semi- Gaelicized family of ...
moved the episcopal seat to Dornoch
Dornoch (; gd, Dòrnach ; sco, Dornach) is a town, seaside resort, parish and former royal burgh in the county of Sutherland in the Highlands of Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Dornoch Firth, near to where it opens into the M ...
in what is now Sutherland
Sutherland ( gd, Cataibh) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in the Highlands of Scotland. Its county town is Dornoch. Sutherland borders Caithness and Moray Firth to the east, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire ( ...
(then regarded as part of Caithness), and the bishopric remained at Dornoch Cathedral
Dornoch Cathedral is a former Roman Catholic cathedral and is currently a Church of Scotland parish church serving the small Sutherland town of Dornoch, in the Scottish Highlands. As a congregation of the Church of Scotland, which is Presbyterian ...
for the remainder of its existence. The Bishopric of Caithness' links with Rome ceased to exist after the Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was the process by which Scotland broke with the Papacy and developed a predominantly Calvinist national Kirk (church), which was strongly Presbyterian in its outlook. It was part of the wider European Protestant Refor ...
, but the bishopric continued, saving temporary abolition between 1638 and 1661, under the episcopal Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from t ...
until the Revolution of 1688 led to the permanent abolition of episcopacy in the established church in Scotland (now Presbyterian in government) in 1689.
List of parishes
#Assynt
Assynt ( gd, Asainn or ) is a sparsely populated area in the south-west of Sutherland, lying north of Ullapool on the west coast of Scotland. Assynt is known for its landscape and its remarkable mountains, which have led to the area, along with ...
# Bower
# Canisbay
# Clyne
# Creich
# Dornoch
Dornoch (; gd, Dòrnach ; sco, Dornach) is a town, seaside resort, parish and former royal burgh in the county of Sutherland in the Highlands of Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Dornoch Firth, near to where it opens into the M ...
(Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
)
# Dunbeath
# Dunnet
# Durness
Durness ( gd, Diùranais) is a village and civil parish in the north-west Highlands of Scotland. It lies on the north coast of the country in the traditional county of Sutherland, around north of Inverness. The area is remote, and the parish is ...
# Farr
# Halkirk
Halkirk ( gd, Hàcraig) is a village on the River Thurso in Caithness, in the Highland council area of Scotland. From Halkirk the B874 road runs towards Thurso in the north and towards Georgemas in the east. The village is within the parish ...
# Kildonan
# Kilmalie (later Golspie
Golspie ( , gd, Goillspidh) is a village and parish in Sutherland, Highland, Scotland, which lies on the North Sea coast in the shadow of Ben Bhraggie. It has a population of around 1,350.
History
The name derives from the Norse for "gully ...
)
# Lairg
Lairg ( gd, An Luirg, meaning "the shank/shin") is a village and parish in Sutherland, Scotland. It has a population of 891 and is at the south-eastern end of Loch Shin.
Lairg is unusual in the northern Highlands in being a large settlement t ...
# Latheron
Latheron () is a small village and civil parish in Caithness, in the Highland area of Scotland, centred on the junction of the A9 with the A99.
The Clan Gunn Heritage Centre and Museum is housed in the old Parish Church (built in 1734). The ch ...
# Loth
# Olrig
Olrig is a parish in Caithness, Scotland. The main settlement in the parish is Castletown. Prior to the 19th century, the parish was sub-divided into ten townlands or "fermlands". Townland boundaries were mostly disregarded and lost during the a ...
# Reay
# Rogart
# Skinnet
# Thurso
Thurso (pronounced ; sco, Thursa, gd, Inbhir Theòrsa ) is a town and former burgh on the north coast of the Highland council area of Scotland. Situated in the historical County of Caithness, it is the northernmost town on the island of Great ...
# Watten
# Wick
List of Bishops
List of bishopric seats
*Bishop's Palace, Halwick * Bishop's Palace, Scrabster * Bishop's Palace, DornochReferences
* Broun, Dauvit, "The Seven Kingdoms in De Situ Albanie: A Record of Pictish political geography or imaginary Map of ancient Alba", in E.J. Cowan & R. Andrew McDonald (eds.), ''Alba: Celtic Scotland in the Medieval Era'', (Edinburgh, 2000, rev. 2005). * Crawford, Barbara, "The Earldom of Caithness and the Kingdom of Scotland, 1150-1266" in Keith Stringer (ed.), ''Essays on the Nobility of Medieval Scotland'', (Edinburgh, 1985), pp. 25-43 * Dowden, John, ''The Bishops of Scotland'', ed. J. Maitland Thomson, (Glasgow, 1912) * Jackson, Kenneth H. (ed), ''The Gaelic Notes in the Book of Deer'', (Cambridge, 1972) * Keith, Robert, ''An Historical Catalogue of the Scottish Bishops: Down to the Year 1688'', (London, 1924) * Lawrie, Sir Archibald, ''Early Scottish Charters Prior to A.D. 1153'', (Glasgow, 1905) * Watt, D.E.R., ''Fasti Ecclesiae Scoticanae Medii Aevi ad annum 1638'', 2nd Draft, (St Andrews, 1969) {{Catholic Church in Scotland 1689 disestablishments in Scotland