Bilateral Frontoparietal Polymicrogyria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria is a genetic disorder with
 *Symptoms: Developmental delay, Psychomotor delay, Mental retardation - moderate to severe, Exaggerated reflexes and Seizures (epilepsy)
*Symptoms: Developmental delay, Psychomotor delay, Mental retardation - moderate to severe, Exaggerated reflexes and Seizures (epilepsy)

 There are different tests or methods used to determine
There are different tests or methods used to determine
autosomal recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
inheritance that causes a cortical malformation. Our brain has folds in the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
to increase surface area called gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ma ...
and patients with polymicrogyri have an increase number of folds and smaller folds than usual. Polymicrogyria is defined as a cerebral malformation of cortical development in which the normal gyral pattern of the surface of the brain is replaced by an excessive number of small, fused gyri separated by shallow sulci
Sulci or Sulki (in Greek , Steph. B., Ptol.; , Strabo; , Paus.), was one of the most considerable cities of ancient Sardinia, situated in the southwest corner of the island, on a small island, now called Isola di Sant'Antioco, which is, howev ...
and abnormal cortical lamination. From ongoing research, mutation in GPR56, a member of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, results in BFPP. These mutations are located in different regions of the protein without any evidence of a relationship between the position of the mutation and phenotypic severity. It is also found that GPR56 plays a role in cortical pattering.Presentation
 *Symptoms: Developmental delay, Psychomotor delay, Mental retardation - moderate to severe, Exaggerated reflexes and Seizures (epilepsy)
*Symptoms: Developmental delay, Psychomotor delay, Mental retardation - moderate to severe, Exaggerated reflexes and Seizures (epilepsy)
Associated conditions
BFPP is a cobblestone-like cortical malformation of the brain. Disruptions of cerebral cortical development due to abnormal neuronal migration and positioning usually lead to cortical disorders, which includes cobblestone lissencephaly. Cobblestone lissencephaly is typically seen in three different human congenital muscular dystrophy syndromes:Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy
Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD) is a rare, autosomal recessive form of muscular dystrophy (weakness and breakdown of muscular tissue) mainly described in Japan but also identified in Turkish and Ashkenazi Jewish patients; fifteen case ...
, Walker-Warburg syndrome, and muscle-eye-brain disease. In cobblestone lissencephaly, the brain surface actually has a bumpy contour caused by the presence of collections of misplaced neurons and glial cell
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myel ...
s that have migrated beyond the normal surface boundaries of the brain. Sometimes regions populated by these misplaced cells have caused a radiologic misdiagnosis of polymicrogyria. However, the presence of other abnormalities in these cobblestone lissencephaly syndromes, including ocular anomalies, congenital muscular dystrophy, ventriculomegaly
Ventriculomegaly is a brain condition that mainly occurs in the fetus when the lateral ventricles become dilated. The most common definition uses a width of the atrium of the lateral ventricle of greater than 10 mm. This occurs in around 1 ...
, and cerebellar dysplasia, usually distinguishes these disorders from polymicrogyria. There are no anatomopathologic studies that have characterized the pattern of cortical laminar alterations in patients with GPR56 gene mutations, but it has been suggested that the imaging characteristics of BFPP, including myelination
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be l ...
defects and cerebellar cortical dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic ...
, are reminiscent of those of the so-called cobblestone malformations (muscle-eye-brain disease and Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy) that are also associated with N-glycosylation defects in the developing brain.
Lissencephaly ("smooth brain") is the extreme form of pachygyria
Pachygyria (from the Greek "pachy" meaning "thick" or "fat" gyri) is a congenital malformation of the cerebral hemisphere. It results in unusually thick convolutions of the cerebral cortex. Typically, children have developmental delay and seizures, ...
. In lissencephaly, few or no sulci are seen on the cortical surface, resulting in a broad, smooth appearance to the entire brain. Lissencephaly can be radiologically confused with polymicrogyria, particularly with low-resolution imaging, but the smoothness and lack of irregularity in the gray-white junction, along with markedly increased cortical thickness, distinguishes lissencephaly.
GPR56 mutation also can cause a severe encelphalopathy which is associated with electro clinical features of the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome can be cryptogenic or symptomatic, but the symptomatic forms have been associated with multiple etiologies and abnormal cortical development. BFPP caused by GPR56 mutations is a manifestation of a malformation of cortical development that causes Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome.
Polymicrogyria is often confused with pachygyria; therefore, it needs to be distinguished from pachygyria, a distinct brain malformation in which the surface folds are excessively broad and sparse. Pachygyria and polymicrogyria may look similar on low-resolution neuroimaging such as CT because the cortical thickness can appear to be increased and the gyri can appear to be broad and smooth in both conditions. This is why higher resolution neuroimaging, such as an MRI, is necessary for proper diagnosis.

Genetics
The GPR56 is grouped in the B family of GPCRs. This GPCR group have long N termini characterized by an extracellular “cysteine box” and hydrophilic, potentiallymucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins (glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most ...
-rich. The cysteine box contains four conserved cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
s and two tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic ...
s arranged in a specific fashion (C-x2-W-x6-16-W-x4-C-x10-22-C-x-C) just before the first transmembrane domain and serves as a cleavage site in some members of this group of G protein–coupled receptors. Although, the molecular and cellular mechanisms of how GPR56 regulates brain development remain largely unknown. These types of receptors play an essential role in biological processes including embryonic development, central nervous system (CNS), immune system, and tumorigenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
.
Mode of inheritance
Parents of a proband :::::::::::*The parents of an affected individual are obligate heterozygotes and therefore carry onemutant
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It ...
allele.
:::::::::::*Heterozygotes (carriers) are asymptomatic.
Sibs of a proband
:::::::::::*At conception, each sibling of an affected individual has a 25% chance of being affected, a 50% chance of being an asymptomatic carrier, and a 25% chance of being unaffected and not a carrier.
:::::::::::*Once an at-risk sibling is known to be unaffected, the risk of his/her being a carrier is 2/3.
:::::::::::*Heterozygotes (carriers) are asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
.
Offspring of a proband
:::::::::::*Offspring of a proband are obligate heterozygotes and will therefore carry one mutant allele.
:::::::::::*In populations with a high rate of consanguinity, the offspring of a person with GPR56-related BFPP and a reproductive partner who is a carrier of GPR56-related BFPP have a 50% chance of inheriting two GPR56 disease-causing alleles and having BFPP and a 50% chance of being carriers.
Other family members of a proband In medical genetics and other medical fields, a proband, proposito (male proband), or proposita (female proband)Bennett, RL. The Language of the Pedigree. In: ''The Practical Guide to the Genetic Family History''. Wiley-Liss. is a particular subjec ...
.
:::::::::::*Each sibling of the proband's parents is at a 50% risk of being a carrier
Diagnosis
Diagnostic criteria for a BFPP patient entails aheterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
genotype for a deletion of chromosome 16q12.1-q21 region,
including GPR56 gene. To date the only gene known to be associated with polymicrogyria is GPR56. Testing for GPR56-related bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria is available clinically. Mutations in GPR56 hinders Collagen III, its specific ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
, to bind in a developing brain. To date, a total of fourteen BFPP-associated mutations have been identified, including one deletion, two splicing, and eleven missense mutation
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution.
Substitution of protein from DNA mutations
Missense m ...
s. Two mutations in the GPCR proteolytic site (GPS) domain, C346S and W349S, cause a brain malformation through trapping the mutated proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
.
GPR56 are a part of the B class of the GPCR
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
family, the largest cell surface gene family in the human genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
. Within this family there are different types of bio-active molecules that transduce their signal to the intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
compartment via interaction with this type of receptor. Children often present with developmental delay, spasticity, or seizures; they are also often microcephalic
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
. Some patients with polymicrogyria go undiagnosed until they produce children with the disorder who have more severe manifestations. Retrospectively, these patients will often report some difficulty in their medical or educational history. BFPP patients demonstrate mental retardation, language impairment, motor developmental delay, and seizure disorders such as epilepsy. The association of epilepsy is in approximately 50% to 85% of affected BFPP patients.
The clinical manifestations of polymicrogyria are stable neurologic deficits:
In the mildest form, polymicrogyria is unilateral
__NOTOC__
Unilateralism is any doctrine or agenda that supports one-sided action. Such action may be in disregard for other parties, or as an expression of a commitment toward a direction which other parties may find disagreeable. As a word, ''un ...
with only one small region of the brain involved; neurologic problems may not be evident.
In more severe forms, focal motor, sensory, visual, or cognitive problems may be present, depending on the location of the brain region affected.
In the most severe forms, polymicrogyria is bilateral
Bilateral may refer to any concept including two sides, in particular:
* Bilateria, bilateral animals
*Bilateralism, the political and cultural relations between two states
*Bilateral, occurring on both sides of an organism ( Anatomical terms of ...
and generalized, resulting in severe intellectual disability, cerebral palsy, and refractory epilepsy.
Individuals with the milder forms of polymicrogyria survive into adulthood, while those with the most severe forms, such as BFPP, may die at a young age as a result of such complications as seizures or pneumonia.
The prevalence of isolated polymicrogyria is unknown. Researchers believe that it may be relatively common overall, although BFPP is probably rare.
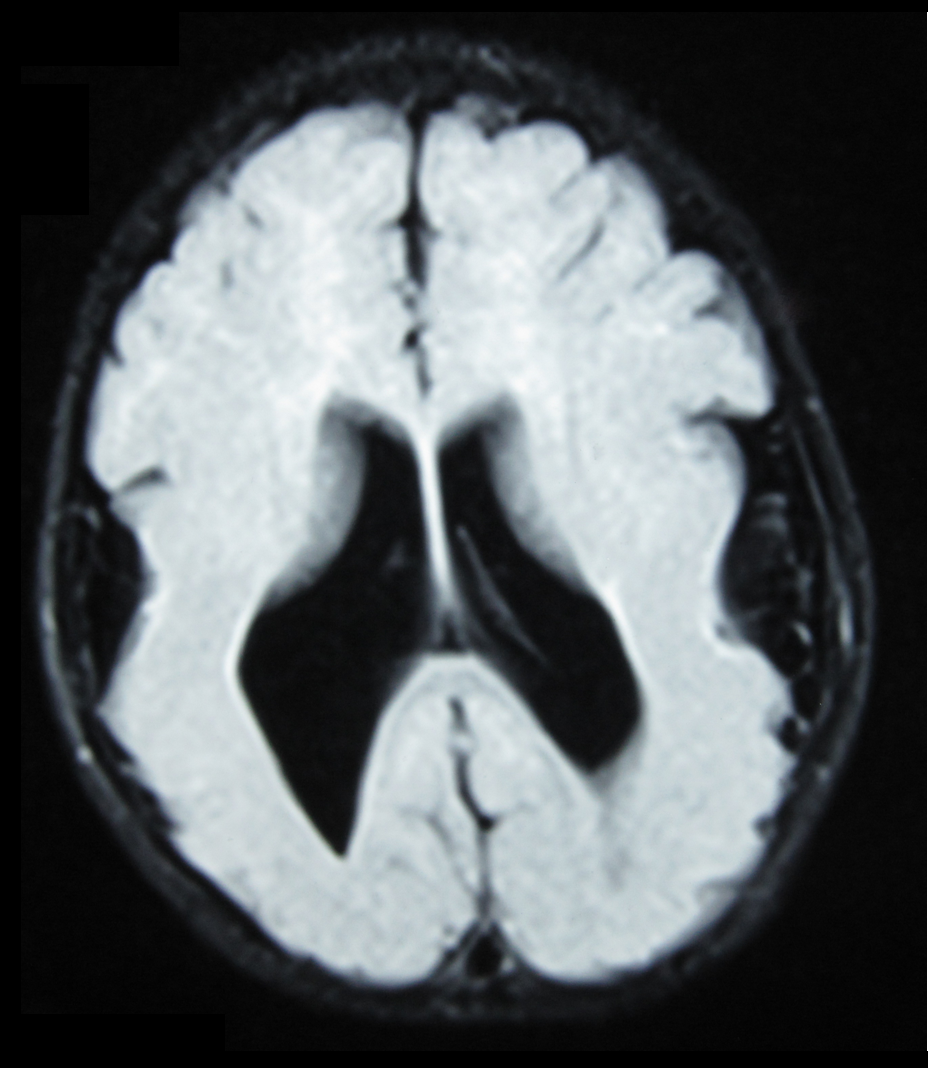
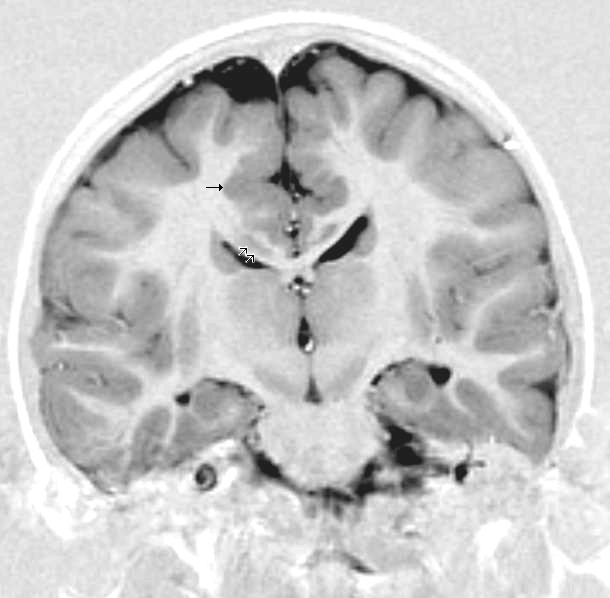
*Radiological findings (MRI) demonstrated symmetric generalized polymicrogyria with decreasing anterior-posterior gradient, most prominent in frontoparietal cortex.
*Numerous gyrus on the cortex
*Small gyri and sulci
*Thin cortexMethods/tests
GPR56
G protein-coupled receptor 56 also known as TM7XN1 is a protein encoded by the ''ADGRG1'' gene. GPR56 is a member of the adhesion GPCR family.
Adhesion GPCRs are characterized by an extended extracellular region often possessing N-terminal protei ...
expression or visuals of the brain to analyze the specific sections that are affected. These tests for example, using animals such as mice, RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by o ...
, Behavioral assay, Electron microscopy, CT scan, or MRI demonstrate different results that concludes an affected BFPP patient. MRI's reveal either irregularity to the cortical surface suggestive of multiple small folds or an irregular, scalloped appearance of the gray matter-white matter junction.
Neuroimaging The diagnosis of polymicrogyria
Polymicrogyria (PMG) is a condition that affects the development of the human brain by multiple small gyri ( microgyri) creating excessive folding of the brain leading to an abnormally thick cortex. This abnormality can affect either one region o ...
is typically made by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) since computed tomography (CT) and other imaging methods generally do not have high enough resolution
Resolution(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Resolution (debate), the statement which is debated in policy debate
* Resolution (law), a written motion adopted by a deliberative body
* New Year's resolution, a commitment that an individual mak ...
or adequate contrast to identify the small folds that define the condition. The cerebral cortex often appears abnormally thick as well because the multiple small gyri are fused, infolded, and superimposed in appearance.
Neuropathology Gross neuropathologic examination reveals a pattern of complex convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is ...
s to the cerebral cortex, with miniature gyri fused and superimposed together, often resulting in an irregular brain surface. The cortical ribbon can appear excessively thick as a result of the infolding and fusion of multiple small gyri.Chang B, Walsh CA, Apse K, et al. Polymicrogyria Overview. 2005 Apr 18 pdated 2007 Aug 6 In: Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, et al., editors. GeneReviews™ nternet Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1329/
Microscopic examination demonstrates that the cerebral cortex is in fact abnormally thin and has abnormal lamination; typically the cortex is unlayered or has four layers, in contrast to the normal six layers. The most superficial layers between adjacent small gyri appear fused, with the pia (layer of the meninges) bridging across multiple gyri. Prenatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
diagnosis for BFPP is also available for pregnancies at risk if the GPR56 mutations have been identified in an affected family member.
Treatment
Treatment plans will vary depending on the severity of the condition and its evidences in each patient. Areas that will probably need to be evaluated and assessed include speech, vision, hearing andEEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
. Treatment measures may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, Speech therapy, anti-seizure drugs and orthotic devices. Surgery may be needed to assuage spastic motor problems. Various supportive measures such as joint contractures that could prevent complications.
Genetic counseling may also be recommendedGuerrini, R., W. Dobyns, and A. Barkovich. "Abnormal Development of the Human Cerebral Cortex: Genetics, Functional Consequences and Treatment Options." Trends in Neurosciences 31.3 (2008): 154-62. Print.Prognosis
Once the diagnosis of polymicrogyria has been established in an individual, the following approach can be used for discussion of prognosis: A pregnancy history should be sought, with particular regard to infections, trauma, multiple gestations, and other documented problems. Screening for the commoncongenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
infections associated with polymicrogyria with standard TORCH testing may be appropriate. Other specific tests targeting individual neurometabolic disorders can be obtained if clinically suggested.
The following may help in determining a genetic etiology:
Family history
It is important to ask for the presence of neurologic problems in family members, including seizures, cognitive delay, motor impairment, pseudobulbar signs, and focal weakness because many affected family members, particularly those who are older, may not have had MRI performed, even if these problems came to medical attention. In addition, although most individuals with polymicrogyria do present with neurologic difficulties in infancy, childhood, or adulthood, those with mild forms may have no obvious deficit or only minor manifestations, such as a simple lisp or isolated learning disability. Therefore, if a familial polymicrogyria syndrome is suspected, it may be reasonable to perform MRI on relatives who are asymptomatic or have what appear to be minor findings. The presence of consanguinity in a child's parents may suggest an autosomal recessive familial polymicrogyria syndrome.
Physical examination
A general physical examination of the proband may identify associated craniofacial Craniofacial (''cranio-'' combining form meaning head or skull + ''-facial'' combining form referring to the facial structures grossly) is an adjective referring to the parts of the head enclosing the brain and the face.
The term is typically used ...
, musculoskeletal, or visceral
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
malformations that could indicate a particular syndrome. Neurologic examination should assess cognitive and mental abilities, cranial nerve function, motor function, deep tendon reflexes, sensory function, coordination, and gait (if appropriate).
Genetic testing
See also
* Epilepsy Phenome/Genome ProjectReferences
External links
*{{RareDiseases, 10784, Bilateral Frontalparietal Polymicrogyria Genetic diseases and disorders