Belgium Under-21 International Footballers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in
Belgium
'. Benchmark Books. p. 27. the
*
*
*
* Belgium's linguistic diversity and related political conflicts are reflected in its complex system of governance, made up of six different governments. Since the
chapter 46
Belgium has also been the battleground of European powers, earning the moniker the "Battlefield of Europe",—The book reviewer, Haß, attributes the expression in English to
*—and as such coined for Belgium:
* (See also
 According to
According to
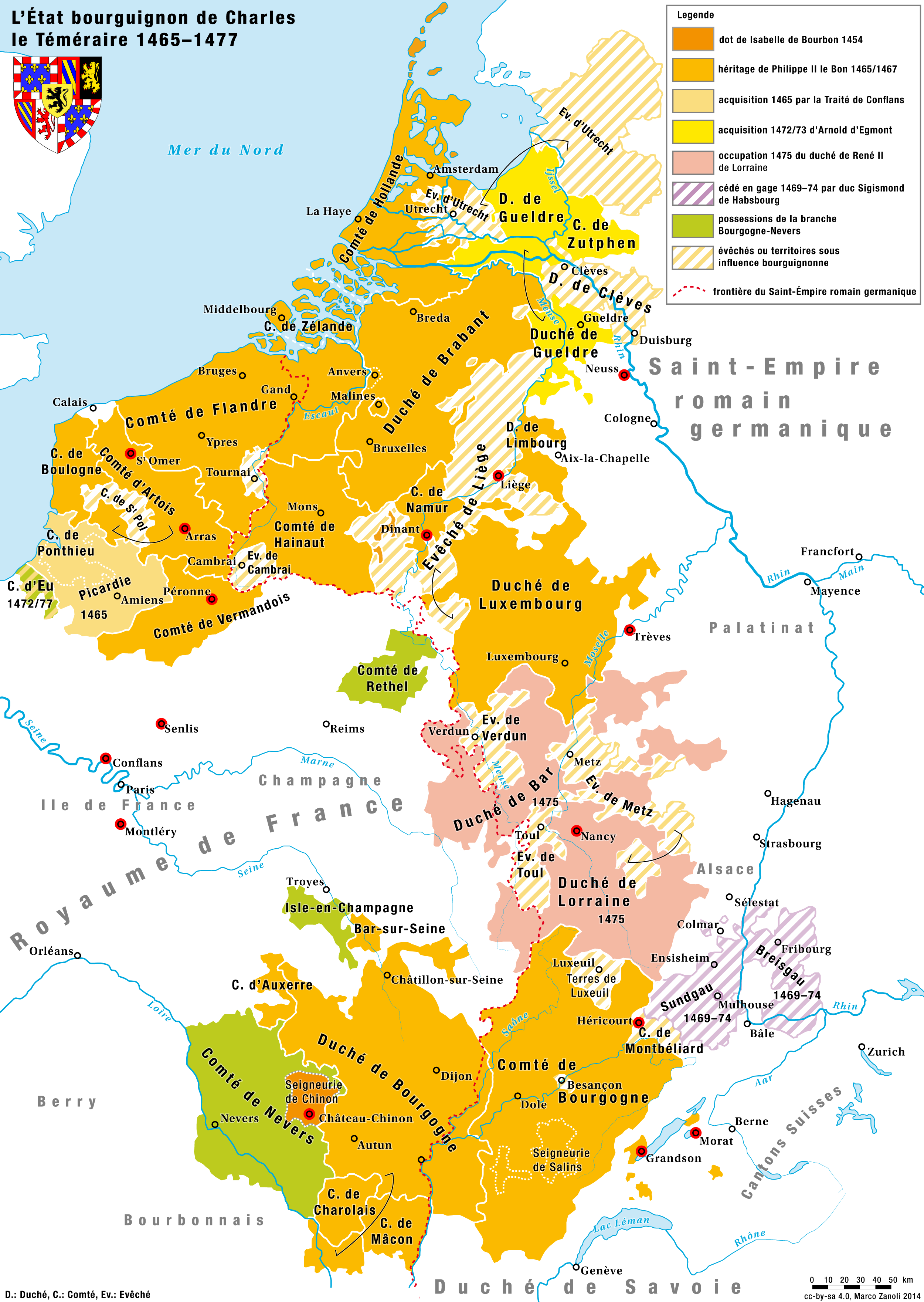 In the 15th century, the Duke of Burgundy in France took control of Flanders, and from there they proceeded to unite much of what is now the Benelux, the so-called
In the 15th century, the Duke of Burgundy in France took control of Flanders, and from there they proceeded to unite much of what is now the Benelux, the so-called
 Belgium shares borders with
Belgium shares borders with
. Belgium.be. Retrieved 12 August 2013. Belgium has three main geographical regions; the coastal plain in the northwest and the central plateau both belong to the Anglo-Belgian Basin, and the
Final Revised Paper
)'' The average temperature is lowest in January at and highest in July at . The average precipitation per month varies between for February and April, to for July. Averages for the years 2000 to 2006 show daily temperature minimums of and maximums of and monthly rainfall of ; these are about 1 °C and nearly 10 millimetres above last century's normal values, respectively.
 Belgium is a
Belgium is a
 A string of Christian Democrat coalition governments from 1958 Belgian federal election, 1999, was broken in 1999 after the first dioxine affair, dioxin crisis, a major Food contaminant, food contamination scandal.ElAmin, Ahmed (31 January 2006
A string of Christian Democrat coalition governments from 1958 Belgian federal election, 1999, was broken in 1999 after the first dioxine affair, dioxin crisis, a major Food contaminant, food contamination scandal.ElAmin, Ahmed (31 January 2006
Belgium, Netherlands meat sectors face dioxin crisis
. foodproductiondaily.com A "rainbow coalition" emerged from six parties: the Flemish and the French-speaking Liberals, Social Democrats and Greens. Later, a "Purple (government), purple coalition" of Liberals and Social Democrats formed after the Greens lost most of their seats in the Belgian federal election, 2003, 2003 election. The government led by Prime Minister Guy Verhofstadt from 1999 to 2007 achieved a balanced budget, some tax reforms, a labor-market reform, scheduled Nuclear energy policy#Europe, nuclear phase-out and instigated legislation allowing more stringent War Crimes Law (Belgium), war crime and more lenient drug harmfulness, soft drug usage prosecution. Restrictions on withholding euthanasia were reduced and same-sex marriage in Belgium, same-sex marriage legalized. The government promoted active diplomacy in Africa The article shows an example of Belgium's recent African policies. and Governmental positions on the Iraq War prior to the 2003 invasion of Iraq, opposed the invasion of Iraq. It is the only country that does not have age restrictions on euthanasia. Verhofstadt's coalition fared badly in the Belgian federal election, 2007, June 2007 elections. For more than a year, the country experienced a 2007 Belgian government formation, political crisis. This crisis was such that many observers speculated on a possible partition of Belgium. From 2007 until 2008 the temporary Verhofstadt III Government was in office. This was a coalition of the Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams, Flemish and Humanist Democratic Centre, Francophone Christian Democrats, the Open Vlaamse Liberalen en Democraten, Flemish and Mouvement Réformateur, Francophone Liberals together with the Socialist Party (francophone Belgium), Francophone Social Democrats. On that day a Leterme I Government, new government, led by Flemish Christian Democrat Yves Leterme, the actual winner of the federal elections of , was sworn in by the king. On 2008 Leterme announced the resignation of the cabinet to the king, as no progress in state reform in Belgium, constitutional reforms had been made. In December 2008, he once more offered his resignation to the king after a 2008–2009 Belgian financial crisis, crisis surrounding the sale of Fortis (finance), Fortis to BNP Paribas.CNN.com
, "Belgium Prime Minister offers resignation over banking deal" At this juncture, his resignation was accepted and Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams, Christian Democratic and Flemish Herman Van Rompuy was sworn in as Prime Minister on 2008.Belgian king asks Van Rompuy to form government
Reuters. After Herman Van Rompuy was designated the first permanent President of the European Council on 2009, he offered the resignation of his government to King Albert II on 2009. A few hours later, the Leterme II Government, new government under Prime Minister Yves Leterme was sworn in. On 2010, Leterme again offered the resignation of his cabinet to the king after one of the coalition partners, the OpenVLD, withdrew from the government, and on 2010 King Albert officially accepted the resignation. The Parliamentary elections in Belgium on 2010 saw the Flemish nationalist New Flemish Alliance, N-VA become the largest party in Flanders, and the Socialist Party PS the largest party in Wallonia. Until December 2011, Belgium was governed by Leterme's caretaker government awaiting the end of the deadlocked negotiations for 2010–2011 Belgian government formation, formation of a new government. By 30 March 2011, this set a new world record for the elapsed time without an official government, previously held by war-torn Iraq. Finally, in December 2011 the Di Rupo Government led by Walloon socialist Prime Minister Elio Di Rupo was sworn in. The Belgian federal election, 2014, 2014 federal election (coinciding with the Belgian regional elections, 2014, regional elections) resulted in a further electoral gain for the Flemish nationalist N-VA, although the incumbent coalition (composed of Flemish and French-speaking Social Democrats, Liberals, and Christian Democrats) maintains a solid majority in Parliament and in all electoral constituencies. On 22 July 2014, King Philippe nominated Charles Michel (MR) and Kris Peeters (CD&V) to 2014 Belgian government formation, lead the formation of a new federal cabinet composed of the Flemish parties N-VA, CD&V, Open Vld and the French-speaking MR, which resulted in the Michel I Government, Michel Government. It was the first time N-VA was part of the federal cabinet, while the French-speaking side was represented only by the MR, which achieved a minority of the public votes in Wallonia. In May 2019 Belgian federal election, 2019 federal elections in the Flemish-speaking northern region of Flanders far-right Vlaams Belang party made major gains. In the French-speaking southern area of Wallonia the Socialists were strong. The moderate Flemish nationalist party the N-VA remained the largest party in parliament. In July 2019 prime minister Charles Michel was selected to hold the post of President of the

 Following a usage which can be traced back to the Burgundian and Habsburg courts, in the 19th century it was necessary to speak French to belong to the governing upper class, and those who could only speak Dutch were effectively second-class citizens. Late that century, and continuing into the 20th century, Flemish movements evolved to counter this situation.#Fitzmaurice, Fitzmaurice (1996), p. 31.
While the people in Southern Belgium spoke French or dialects of French, and Frenchification of Brussels, most Brusselers adopted French as their first language, the Flemings refused to do so and succeeded progressively in making Dutch an equal language in the education system. Following World War II, Belgian politics became increasingly dominated by the autonomy of its two main linguistic communities. Intercommunal tensions rose and the constitution was amended to minimize the potential for conflict.
Based on the four language areas defined in 1962–63 (the Dutch, bilingual, French and German language areas), consecutive state reform in Belgium, revisions of Constitution of Belgium, the country's constitution in 1970, 1980, 1988 and 1993 established a unique form of a federal state with segregated political power into three levels:
# The Belgian federal government, federal government, based in Brussels.
# The three language communities:
#* the
Following a usage which can be traced back to the Burgundian and Habsburg courts, in the 19th century it was necessary to speak French to belong to the governing upper class, and those who could only speak Dutch were effectively second-class citizens. Late that century, and continuing into the 20th century, Flemish movements evolved to counter this situation.#Fitzmaurice, Fitzmaurice (1996), p. 31.
While the people in Southern Belgium spoke French or dialects of French, and Frenchification of Brussels, most Brusselers adopted French as their first language, the Flemings refused to do so and succeeded progressively in making Dutch an equal language in the education system. Following World War II, Belgian politics became increasingly dominated by the autonomy of its two main linguistic communities. Intercommunal tensions rose and the constitution was amended to minimize the potential for conflict.
Based on the four language areas defined in 1962–63 (the Dutch, bilingual, French and German language areas), consecutive state reform in Belgium, revisions of Constitution of Belgium, the country's constitution in 1970, 1980, 1988 and 1993 established a unique form of a federal state with segregated political power into three levels:
# The Belgian federal government, federal government, based in Brussels.
# The three language communities:
#* the
 Because of its location at the crossroads of Western Europe, Belgium has historically been the route of invading armies from its larger neighbors. With virtually defenseless borders, Belgium has traditionally sought to avoid domination by the more powerful nations which surround it through a policy of mediation. The Belgians have been strong advocates of European integration. The headquarters of
Because of its location at the crossroads of Western Europe, Belgium has historically been the route of invading armies from its larger neighbors. With virtually defenseless borders, Belgium has traditionally sought to avoid domination by the more powerful nations which surround it through a policy of mediation. The Belgians have been strong advocates of European integration. The headquarters of
 Belgium's strongly globalized economyBelgium ranked first in the KOF Globalization Index 2009 and its transport in Belgium, transport infrastructure are integrated with the rest of Europe. Its location at the heart of a highly industrialized region helped make it the world's 15th largest trading nation in 2007. The economy is characterized by a highly productive work force, high Gross national product, GNP and high exports per capita. Belgium's main imports are raw materials, machinery and equipment, chemicals, raw diamonds, pharmaceuticals, foodstuffs, transportation equipment, and oil products. Its main exports are machinery and equipment, chemicals, finished diamonds, metals and metal products, and foodstuffs.
The Belgian economy is heavily service-oriented and shows a dual nature: a dynamic Flemish economy and a Walloon economy that lags behind. One of the founding members of the European Union, Belgium strongly supports an open economy and the extension of the powers of EU institutions to integrate member economies. Since 1922, through the Belgium-Luxembourg Economic Union, Belgium and Luxembourg have been a single trade market with customs and currency union.
Belgium's strongly globalized economyBelgium ranked first in the KOF Globalization Index 2009 and its transport in Belgium, transport infrastructure are integrated with the rest of Europe. Its location at the heart of a highly industrialized region helped make it the world's 15th largest trading nation in 2007. The economy is characterized by a highly productive work force, high Gross national product, GNP and high exports per capita. Belgium's main imports are raw materials, machinery and equipment, chemicals, raw diamonds, pharmaceuticals, foodstuffs, transportation equipment, and oil products. Its main exports are machinery and equipment, chemicals, finished diamonds, metals and metal products, and foodstuffs.
The Belgian economy is heavily service-oriented and shows a dual nature: a dynamic Flemish economy and a Walloon economy that lags behind. One of the founding members of the European Union, Belgium strongly supports an open economy and the extension of the powers of EU institutions to integrate member economies. Since 1922, through the Belgium-Luxembourg Economic Union, Belgium and Luxembourg have been a single trade market with customs and currency union.
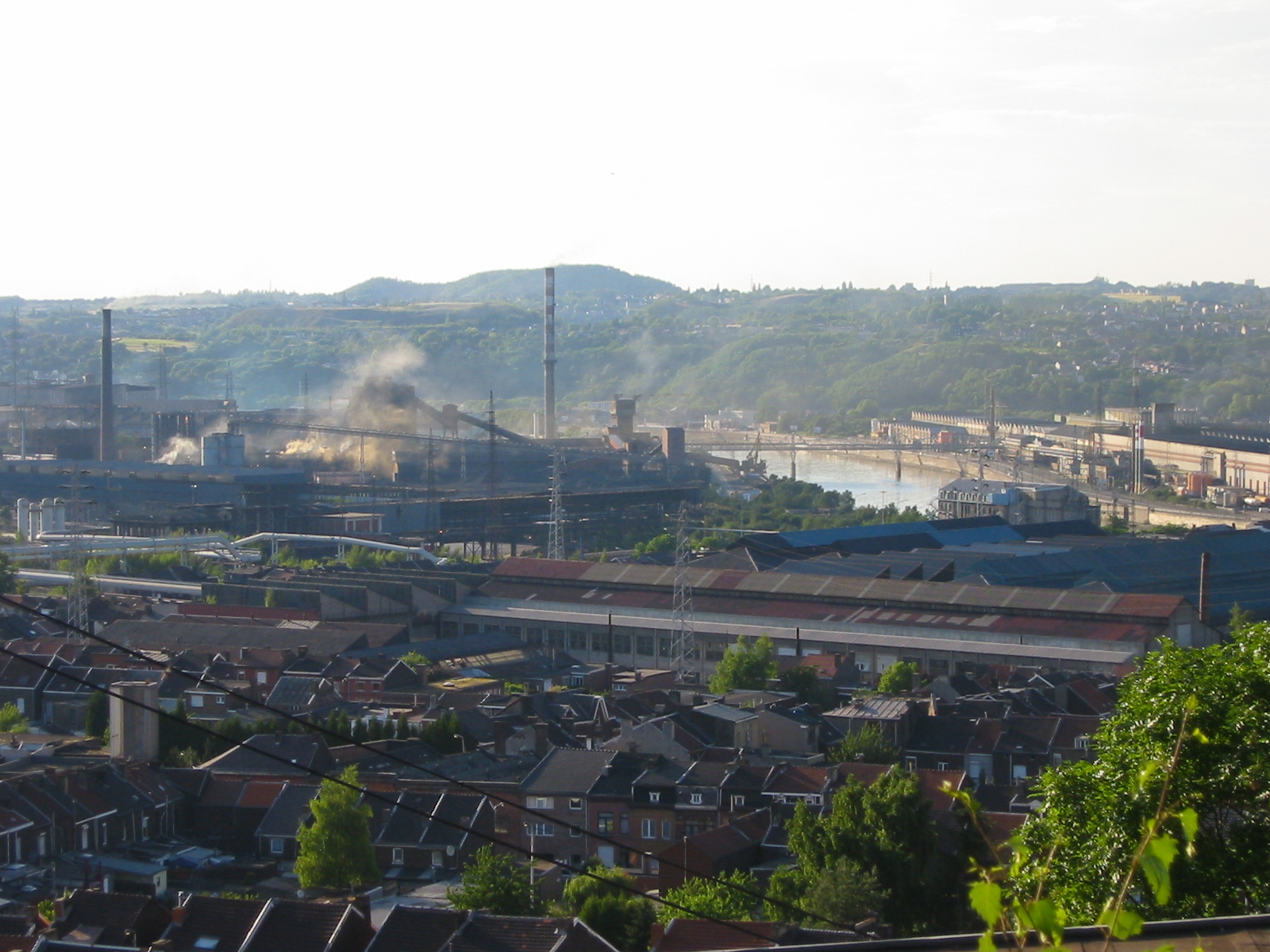 Belgium was the first continental European country to undergo the
Belgium was the first continental European country to undergo the  From a biological resource perspective, Belgium has a low endowment: Belgium's biocapacity adds up to only 0.8 global hectares in 2016, just about half of the 1.6 global hectares of biocapacity available per person worldwide. In contrast, in 2016, Belgians used on average 6.3 global hectares of biocapacity - their ecological footprint of consumption. This means they required about eight times as much biocapacity as Belgium contains. As a result, Belgium was running a biocapacity deficit of 5.5 global hectares per person in 2016.
Belgium experiences some of the most congested traffic in Europe. In 2010, commuters to the cities of Brussels and Antwerp spent respectively 65 and 64 hours a year in traffic jams. Like in most small European countries, more than 80% of the airways traffic is handled by a single airport, the Brussels Airport. The port of Antwerp, ports of Antwerp and port of Zeebrugge, Zeebrugge (Bruges) share more than 80% of Belgian maritime traffic, Antwerp being the second European harbor with a gross weight of goods handled of 115 988 000 t in 2000 after a growth of 10.9% over the preceding five years.Another comparative study on transportation in Belgium: In 2016, the port of Antwerp handled 214 million tons after a year-on-year growth of 2.7%.
There is a large economic gap between Flanders and Wallonia. Wallonia was historically wealthy compared to Flanders, mostly due to its heavy industry, heavy industries, but the decline of the steel industry post-World War II led to the region's rapid decline, whereas Flanders rose swiftly. Since then, Flanders has been prosperous, among the wealthiest regions in Europe, whereas Wallonia has been languishing. As of 2007, the unemployment rate of Wallonia is over double that of Flanders. The divide has played a key part in the tensions between the Flemish and Walloons in addition to the already-existing language divide. Flemish Movement, Pro-independence movements have gained high popularity in Flanders as a consequence. The separatist New Flemish Alliance (N-VA) party, for instance, is the largest party in Belgium.
From a biological resource perspective, Belgium has a low endowment: Belgium's biocapacity adds up to only 0.8 global hectares in 2016, just about half of the 1.6 global hectares of biocapacity available per person worldwide. In contrast, in 2016, Belgians used on average 6.3 global hectares of biocapacity - their ecological footprint of consumption. This means they required about eight times as much biocapacity as Belgium contains. As a result, Belgium was running a biocapacity deficit of 5.5 global hectares per person in 2016.
Belgium experiences some of the most congested traffic in Europe. In 2010, commuters to the cities of Brussels and Antwerp spent respectively 65 and 64 hours a year in traffic jams. Like in most small European countries, more than 80% of the airways traffic is handled by a single airport, the Brussels Airport. The port of Antwerp, ports of Antwerp and port of Zeebrugge, Zeebrugge (Bruges) share more than 80% of Belgian maritime traffic, Antwerp being the second European harbor with a gross weight of goods handled of 115 988 000 t in 2000 after a growth of 10.9% over the preceding five years.Another comparative study on transportation in Belgium: In 2016, the port of Antwerp handled 214 million tons after a year-on-year growth of 2.7%.
There is a large economic gap between Flanders and Wallonia. Wallonia was historically wealthy compared to Flanders, mostly due to its heavy industry, heavy industries, but the decline of the steel industry post-World War II led to the region's rapid decline, whereas Flanders rose swiftly. Since then, Flanders has been prosperous, among the wealthiest regions in Europe, whereas Wallonia has been languishing. As of 2007, the unemployment rate of Wallonia is over double that of Flanders. The divide has played a key part in the tensions between the Flemish and Walloons in addition to the already-existing language divide. Flemish Movement, Pro-independence movements have gained high popularity in Flanders as a consequence. The separatist New Flemish Alliance (N-VA) party, for instance, is the largest party in Belgium.
 Contributions to the development of science and technology have appeared throughout the country's history. The 16th century Early Modern flourishing of Western Europe included cartography, cartographer Gerardus Mercator, anatomy, anatomist Andreas Vesalius, herbalist Rembert Dodoens (*) Free abstract for pay-per-view article by and mathematician Simon Stevin among the most influential scientists.
Chemist Ernest Solvay and engineer Zenobe Gramme (École industrielle de Liège) gave their names to the Solvay process and the Gramme dynamo, respectively, in the 1860s. Bakelite was developed in 1907–1909 by Leo Baekeland. Ernest Solvay also acted as a major philanthropist and gave his name to the Solvay Institute of Sociology, the Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management and the International Solvay Institutes for Physics and Chemistry which are now part of the Université libre de Bruxelles. In 1911, he started a series of conferences, the Solvay Conferences on Physics and Chemistry, which have had a deep impact on the evolution of quantum physics and chemistry. A major contribution to fundamental science was also due to a Belgian, Monsignor Georges Lemaître (Catholic University of Leuven (1834–1968), Catholic University of Louvain), who is credited with proposing the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe in 1927.
Three Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine were awarded to Belgians: Jules Bordet (Université libre de Bruxelles) in 1919, Corneille Heymans (University of Ghent) in 1938 and Albert Claude (Université libre de Bruxelles) together with Christian de Duve (Université catholique de Louvain) in 1974. François Englert (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2013. Ilya Prigogine (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1977. Two Belgian mathematicians have been awarded the Fields Medal: Pierre Deligne in 1978 and Jean Bourgain in 1994. (Retrieved 10 November 2011) (Retrieved 10 November 2011) Belgium was ranked 22nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 23rd in 2019.
Contributions to the development of science and technology have appeared throughout the country's history. The 16th century Early Modern flourishing of Western Europe included cartography, cartographer Gerardus Mercator, anatomy, anatomist Andreas Vesalius, herbalist Rembert Dodoens (*) Free abstract for pay-per-view article by and mathematician Simon Stevin among the most influential scientists.
Chemist Ernest Solvay and engineer Zenobe Gramme (École industrielle de Liège) gave their names to the Solvay process and the Gramme dynamo, respectively, in the 1860s. Bakelite was developed in 1907–1909 by Leo Baekeland. Ernest Solvay also acted as a major philanthropist and gave his name to the Solvay Institute of Sociology, the Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management and the International Solvay Institutes for Physics and Chemistry which are now part of the Université libre de Bruxelles. In 1911, he started a series of conferences, the Solvay Conferences on Physics and Chemistry, which have had a deep impact on the evolution of quantum physics and chemistry. A major contribution to fundamental science was also due to a Belgian, Monsignor Georges Lemaître (Catholic University of Leuven (1834–1968), Catholic University of Louvain), who is credited with proposing the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe in 1927.
Three Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine were awarded to Belgians: Jules Bordet (Université libre de Bruxelles) in 1919, Corneille Heymans (University of Ghent) in 1938 and Albert Claude (Université libre de Bruxelles) together with Christian de Duve (Université catholique de Louvain) in 1974. François Englert (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2013. Ilya Prigogine (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1977. Two Belgian mathematicians have been awarded the Fields Medal: Pierre Deligne in 1978 and Jean Bourgain in 1994. (Retrieved 10 November 2011) (Retrieved 10 November 2011) Belgium was ranked 22nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 23rd in 2019.

 As of 1 January 2020, the total population of Belgium according to its population register was 11,492,641. The population density of Belgium is as of January 2019, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world, and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe. The most densely populated province is Antwerp province, Antwerp, the least densely populated province is Luxembourg (Belgium), Luxembourg. As of January 2019, the
As of 1 January 2020, the total population of Belgium according to its population register was 11,492,641. The population density of Belgium is as of January 2019, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world, and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe. The most densely populated province is Antwerp province, Antwerp, the least densely populated province is Luxembourg (Belgium), Luxembourg. As of January 2019, the
ecodata.mineco.fgov.be In 2007, there were 1.38 million foreign-born residents in Belgium, corresponding to 12.9% of the total population. Of these, 685,000 (6.4%) were born outside the EU and 695,000 (6.5%) were born in another EU Member State.L'IMMIGRATION EN BELGIQUE. EFFECTIFS, MOUVEMENTS. ET MARCHE DU TRAVAIL
. Rapport 2009. Direction générale Emploi et marché du travai At the beginning of 2012, people of foreign background and their descendants were estimated to have formed around 25% of the total population i.e. 2.8 million ''new Belgians''.
. npdata.be (1 January 2012). Of these new Belgians, 1,200,000 are of European ancestry and 1,350,000
. npdata.be (7 May 2012). are from non-Western countries (most of them from Morocco, Turkey, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DR Congo). Since the modification of the Belgian nationality law in 1984 more than Demographics of Belgium, 1.3 million migrants have acquired Belgian citizenship. The largest group of immigrants and their descendants in Belgium are Moroccan people, Moroccans. 89.2% of inhabitants of Turkish people, Turkish origin have been naturalized, as have 88.4% of people of Moroccan background, 75.4% of Italians, 56.2% of the French and 47.8% of Dutch people. Statistics Belgium, Statbel released figures of the Belgian population in relation to the origin of people in Belgium. According to the data, as of 1 January 2021, 67.3% of the Belgian population was of ethnic Belgian origin and 32.7% were of foreign origin or nationality, with 20.3% of those of a foreign nationality or ethnic group originating from neighbouring countries. The study also found that 74.5% of the Brussels, Brussels Capital Region were of non-Belgian origin, of which 13.8% originated from neighbouring countries.
 Belgium has three official languages: Dutch, French and German. A number of non-official minority languages are spoken as well.
As no census exists, there are no official statistical data regarding the distribution or usage of Belgium's three official languages or their dialects. However, various criteria, including the language(s) of parents, of education, or the second-language status of foreign born, may provide suggested figures. An estimated 60% of the Belgian population are native speakers of Dutch (often referred to as Flemish), and 40% of the population speaks French natively. French-speaking Belgians are often referred to as Walloons, although the French speakers in Brussels are not Walloons.
The total number of native Dutch speakers is estimated to be about 6.23 million, concentrated in the northern Flanders region, while native French speakers number 3.32 million in Wallonia and an estimated 870,000 (or 85%) in the officially bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.—Strictly, the capital is the municipality Brussels, (City of) Brussels, though the Brussels-Capital Region might be intended because of its name and also its other municipalities housing institutions typical for a capital. The
Belgium has three official languages: Dutch, French and German. A number of non-official minority languages are spoken as well.
As no census exists, there are no official statistical data regarding the distribution or usage of Belgium's three official languages or their dialects. However, various criteria, including the language(s) of parents, of education, or the second-language status of foreign born, may provide suggested figures. An estimated 60% of the Belgian population are native speakers of Dutch (often referred to as Flemish), and 40% of the population speaks French natively. French-speaking Belgians are often referred to as Walloons, although the French speakers in Brussels are not Walloons.
The total number of native Dutch speakers is estimated to be about 6.23 million, concentrated in the northern Flanders region, while native French speakers number 3.32 million in Wallonia and an estimated 870,000 (or 85%) in the officially bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.—Strictly, the capital is the municipality Brussels, (City of) Brussels, though the Brussels-Capital Region might be intended because of its name and also its other municipalities housing institutions typical for a capital. The
version in German language
(already) mentions 73,000 instead of 71,500 inhabitants. Both Belgian Dutch and Belgian French have Cognate, minor differences in vocabulary and semantic nuances from the varieties spoken respectively in the Netherlands and France. Many Flemish people still speak Dutch dialects, dialects of Dutch in their local environment. Walloon language, Walloon, considered either as a dialect of French or a distinct Romance language,According to Le Petit Larousse, Walloon is a dialect of the langue d'oïl. According to the ''Meyers grosses Taschenlexikon'' is now only understood and spoken occasionally, mostly by elderly people. Walloon is divided into four dialects, which along with those of Picard language, Picard,Among Belgium native German speakers many are familiar with the local dialect varieties of their region, that include dialects that spill over into neighboring Luxembourg and Germany. (Online version
Sixteenth edition
) are rarely used in public life and have largely been replaced by French.
 Since the country's independence, Roman Catholicism has had an important role in Belgium's politics.See for example s:en:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Belgium, Belgium entry of the Catholic Encyclopedia However Belgium is largely a secular country as the Constitution of Belgium, constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. During the reigns of Albert I of Belgium, Albert I and Baudouin I of Belgium, Baudouin, the Belgian royal family had a reputation of deeply rooted Catholicism.
Roman Catholicism has traditionally been Belgium's majority religion; being especially strong in Flanders. However, by 2009 Sunday church attendance was 5% for Belgium in total; 3% in Brussels, and 5.4% in Flanders. Church attendance in 2009 in Belgium was roughly half of the Sunday church attendance in 1998 (11% for the total of Belgium in 1998).Kerken lopen zeer geleidelijk helemaal leeg – Dutch news article describing church attendance in Flanders
Since the country's independence, Roman Catholicism has had an important role in Belgium's politics.See for example s:en:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Belgium, Belgium entry of the Catholic Encyclopedia However Belgium is largely a secular country as the Constitution of Belgium, constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. During the reigns of Albert I of Belgium, Albert I and Baudouin I of Belgium, Baudouin, the Belgian royal family had a reputation of deeply rooted Catholicism.
Roman Catholicism has traditionally been Belgium's majority religion; being especially strong in Flanders. However, by 2009 Sunday church attendance was 5% for Belgium in total; 3% in Brussels, and 5.4% in Flanders. Church attendance in 2009 in Belgium was roughly half of the Sunday church attendance in 1998 (11% for the total of Belgium in 1998).Kerken lopen zeer geleidelijk helemaal leeg – Dutch news article describing church attendance in Flanders
. Standaard.be (25 November 2010). Retrieved 26 September 2011. Despite the drop in church attendance, Catholic identity nevertheless remains an important part of Belgium's culture. According to the Eurobarometer 2010,
Eurobarometer Biotechnology report 2010
'' p.381. 37% of Belgian citizens responded that they believe there is a God. 31% answered that they believe there is some sort of spirit or life-force. 27% answered that they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God, or life-force. 5% did not respond. According to the Eurobarometer 2015, 60.7% of the total population of Belgium adhered to Christianity, with Roman Catholicism being the largest denomination with 52.9%. Protestants comprised 2.1% and Orthodox Christians were the 1.6% of the total. Non-religious people comprised 32.0% of the population and were divided between atheists (14.9%) and agnostics (17.1%). A further 5.2% of the population was Muslim and 2.1% were believers in other religions. The same survey held in 2012 found that Christianity was the largest religion in Belgium, accounting for 65% of Belgians. Symbolically and materially, the Roman Catholic Church remains in a favorable position. Belgium officially recognizes three religions: Christianity (Catholic, Protestantism, Orthodox churches and Anglicanism), Islam and Judaism. In the early 2000s, there were approximately 42,000 Jews in Belgium. The Jewish Community of Antwerp (numbering some 18,000) is one of the largest in Europe, and one of the last places in the world where Yiddish is the primary language of a large Jewish community (mirroring certain Orthodox and Hasidic communities in New York, New Jersey, and Israel). In addition, most Jewish children in Antwerp receive a Jewish education.Ghiuzeli, Haim F
In the early 2000s, there were approximately 42,000 Jews in Belgium. The Jewish Community of Antwerp (numbering some 18,000) is one of the largest in Europe, and one of the last places in the world where Yiddish is the primary language of a large Jewish community (mirroring certain Orthodox and Hasidic communities in New York, New Jersey, and Israel). In addition, most Jewish children in Antwerp receive a Jewish education.Ghiuzeli, Haim F
The Jewish Community of Antwerp, Belgium
. Beit Hatfutsot, the Museum of the Jewish People There are several Jewish newspapers and more than 45 active synagogues (30 of which are in Antwerp) in the country. A 2006 inquiry in Flanders, considered to be a more religious region than Wallonia, showed that 55% considered themselves religious and that 36% believed that God created the universe.Inquiry by 'Vepec', 'Vereniging voor Promotie en Communicatie' (Organization for Promotion and Communication), published in Knack magazine 2006 p. 14 [The Dutch language term 'gelovig' is in the text translated as 'religious'. More precisely it is a very common word for believing in particular in any kind of God in a monotheism, monotheistic sense or in some afterlife], or both. On the other hand, Wallonia has become one of Europe's most secular/least religious regions. Most of the French-speaking region's population does not consider religion an important part of their lives, and as much as 45% of the population identifies as irreligious. This is particularly the case in eastern Wallonia and areas along the French border. A 2008 estimate found that approximately 6% of the Belgian population (628,751 people) is Islam in Belgium, Muslim. Muslims constitute 23.6% of the population of Brussels, 4.9% of Wallonia and 5.1% of Flanders. The majority of Belgian Muslims live in the major cities, such as
A 2008 estimate found that approximately 6% of the Belgian population (628,751 people) is Islam in Belgium, Muslim. Muslims constitute 23.6% of the population of Brussels, 4.9% of Wallonia and 5.1% of Flanders. The majority of Belgian Muslims live in the major cities, such as
. hbvl.be. 2007
 The Belgians enjoy good health. According to 2012 estimates, the average life expectancy is 79.65 years. Since 1960, life expectancy has, in line with the European average, grown by two months per year. Death in Belgium is mainly due to heart and vascular disorders, neoplasms, disorders of the respiratory system and unnatural causes of death (accidents, suicide). Non-natural causes of death and cancer are the most common causes of death for females up to age 24 and males up to age 44.
Healthcare in Belgium is financed through both social security contributions and taxation. Health insurance is compulsory. Health care is delivered by a mixed public and private system of independent medical practitioners and public, university and semi-private hospitals. Health care service are payable by the patient and reimbursed later by health insurance institutions, but for ineligible categories (of patients and services) so-called 3rd party payment systems exist. The Belgian health care system is supervised and financed by the federal government, the Flemish and Walloon Regional governments; and the German Community also has (indirect) oversight and responsibilities.
For the first time in Belgian history, the first child was euthanized following the 2-year mark of the removal of the euthanization age restrictions. The child had been euthanized due to an incurable disease that was inflicted upon the child. Although there may have been some support for the euthanization there is a possibility of controversy due to the issue revolving around the subject of assisted suicide. Excluding assisted suicide, Belgium has the highest suicide rate in Western Europe and one of the suicide rate by country, highest suicide rates in the developed countries, developed world (exceeded only by Lithuania, South Korea, and Latvia).
The Belgians enjoy good health. According to 2012 estimates, the average life expectancy is 79.65 years. Since 1960, life expectancy has, in line with the European average, grown by two months per year. Death in Belgium is mainly due to heart and vascular disorders, neoplasms, disorders of the respiratory system and unnatural causes of death (accidents, suicide). Non-natural causes of death and cancer are the most common causes of death for females up to age 24 and males up to age 44.
Healthcare in Belgium is financed through both social security contributions and taxation. Health insurance is compulsory. Health care is delivered by a mixed public and private system of independent medical practitioners and public, university and semi-private hospitals. Health care service are payable by the patient and reimbursed later by health insurance institutions, but for ineligible categories (of patients and services) so-called 3rd party payment systems exist. The Belgian health care system is supervised and financed by the federal government, the Flemish and Walloon Regional governments; and the German Community also has (indirect) oversight and responsibilities.
For the first time in Belgian history, the first child was euthanized following the 2-year mark of the removal of the euthanization age restrictions. The child had been euthanized due to an incurable disease that was inflicted upon the child. Although there may have been some support for the euthanization there is a possibility of controversy due to the issue revolving around the subject of assisted suicide. Excluding assisted suicide, Belgium has the highest suicide rate in Western Europe and one of the suicide rate by country, highest suicide rates in the developed countries, developed world (exceeded only by Lithuania, South Korea, and Latvia).
 Education is compulsory from 6 to 18 years of age for Belgians. Extracts
Education is compulsory from 6 to 18 years of age for Belgians. Extracts
p. 97
p. 105
Among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD countries in 2002, Belgium had the third highest proportion of 18- to 21-year-olds enrolled in postsecondary education, at 42%. Though an estimated 99% of the adult population is literate, concern is rising over functional illiteracy. The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), coordinated by the OECD, currently ranks Belgium's education as the 19th best in the world, being significantly higher than the OECD average. Education being organized separately by each, the Flemish Community scores noticeably above the French and German-speaking Communities. Mirroring the dual structure of the 19th-century Belgian political landscape, characterized by the Liberal Party (Belgium), Liberal and the Catholic Party (Belgium), Catholic parties, the educational system is segregated within a secular and a religious segment. The secular branch of schooling is controlled by the communities, the provinces, or the municipalities, while religious, mainly Catholic school, Catholic branch education, is organized by religious authorities, although subsidized and supervised by the communities.
 Contributions to painting and architecture have been especially rich. The Mosan art, the Early Netherlandish painting, Early Netherlandish, the Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, Flemish Renaissance and Flemish Baroque painting, Baroque painting and major examples of Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Gothic architecture, Gothic, Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Baroque architectureSeveral examples of major architectural realizations in Belgium belong to UNESCO's World Heritage List: are milestones in the history of art. While the 15th century's art in the Low Countries is dominated by the religious paintings of Jan van Eyck and Rogier van der Weyden, the 16th century is characterized by a broader panel of styles such as Pieter Brueghel the Elder, Peter Breughel's landscape paintings and Lambert Lombard's representation of the antique. Though the Baroque style of Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck flourished in the early 17th century in the Southern Netherlands, it gradually declined thereafter.—A general presentation of the Flemish artistic movement with a list of its artists, linking to their biographies and artworks
During the 19th and 20th centuries many original romanticism, romantic, expressionism, expressionist and surrealism, surrealist Belgian painters emerged, including James Ensor and other artists belonging to the Les XX group, Constant Permeke, Paul Delvaux and René Magritte. The avant-garde COBRA (avant-garde movement), CoBrA movement appeared in the 1950s, while the sculptor Panamarenko remains a remarkable figure in contemporary art.—List of Belgian painters, linking to their biographies and artworks Multidisciplinary artists Jan Fabre, Wim Delvoye and the painter Luc Tuymans are other internationally renowned figures on the contemporary art scene.
Belgian contributions to architecture also continued into the 19th and 20th centuries, including the work of Victor Horta and Henry van de Velde, who were major initiators of the Art Nouveau style.Brussels, capital of Art Nouveau (page 1)
Contributions to painting and architecture have been especially rich. The Mosan art, the Early Netherlandish painting, Early Netherlandish, the Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, Flemish Renaissance and Flemish Baroque painting, Baroque painting and major examples of Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Gothic architecture, Gothic, Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Baroque architectureSeveral examples of major architectural realizations in Belgium belong to UNESCO's World Heritage List: are milestones in the history of art. While the 15th century's art in the Low Countries is dominated by the religious paintings of Jan van Eyck and Rogier van der Weyden, the 16th century is characterized by a broader panel of styles such as Pieter Brueghel the Elder, Peter Breughel's landscape paintings and Lambert Lombard's representation of the antique. Though the Baroque style of Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck flourished in the early 17th century in the Southern Netherlands, it gradually declined thereafter.—A general presentation of the Flemish artistic movement with a list of its artists, linking to their biographies and artworks
During the 19th and 20th centuries many original romanticism, romantic, expressionism, expressionist and surrealism, surrealist Belgian painters emerged, including James Ensor and other artists belonging to the Les XX group, Constant Permeke, Paul Delvaux and René Magritte. The avant-garde COBRA (avant-garde movement), CoBrA movement appeared in the 1950s, while the sculptor Panamarenko remains a remarkable figure in contemporary art.—List of Belgian painters, linking to their biographies and artworks Multidisciplinary artists Jan Fabre, Wim Delvoye and the painter Luc Tuymans are other internationally renowned figures on the contemporary art scene.
Belgian contributions to architecture also continued into the 19th and 20th centuries, including the work of Victor Horta and Henry van de Velde, who were major initiators of the Art Nouveau style.Brussels, capital of Art Nouveau (page 1)
, (for example) The vocal music of the Franco-Flemish School developed in the southern part of the Low Countries and was an important contribution to Renaissance culture. In the 19th and 20th centuries, there was an emergence of major violinists, such as Henri Vieuxtemps, Eugène Ysaÿe and Arthur Grumiaux, while Adolphe Sax invented the saxophone in 1846. The composer César Franck was born in Liège in 1822. Contemporary popular music in Belgium is also of repute. Jazz musicians Django Reinhardt and Toots Thielemans and singer Jacques Brel have achieved global fame. Nowadays, singer Stromae has been a musical revelation in Europe and beyond, having great success. In rock/pop music, Telex (band), Telex, Front 242, K's Choice, Hooverphonic, Zap Mama, Soulwax and Deus (band), dEUS are well known. In the heavy metal scene, bands like Machiavel (band), Machiavel, Channel Zero (band), Channel Zero and Enthroned have a worldwide fan-base.Two comprehensive discussions of rock and pop music in Belgium since the 1950s:
Belgium has produced several well-known Belgian literature, authors, including the poets Emile Verhaeren, Guido Gezelle, Robert Goffin and novelists Hendrik Conscience, Stijn Streuvels, Georges Simenon, Suzanne Lilar, Hugo Claus and Amélie Nothomb. The poet and playwright Maurice Maeterlinck won the Nobel Prize in literature in 1911. ''The Adventures of Tintin'' by Hergé is the best known of Franco-Belgian comics, but many other major authors, including Peyo (''The Smurfs''), André Franquin (''Gaston Lagaffe''), Dupa (''Cubitus''), Morris (comics), Morris (''Lucky Luke''), Greg (comics), Greg (''Achille Talon''), Lambil (''Les Tuniques Bleues''), Edgar P. Jacobs and Willy Vandersteen brought the Belgian cartoon strip industry a worldwide fame. Additionally, famous crime author Agatha Christie created the character Hercule Poirot, a Belgian detective, who has served as a protagonist in a number of her acclaimed mystery novels. Cinema of Belgium, Belgian cinema has brought a number of mainly Flemish novels to life on-screen. Other Belgian directors include André Delvaux, Stijn Coninx, Luc Dardenne, Luc and Jean-Pierre Dardenne; well-known actors include Jean-Claude Van Damme, Jan Decleir and Marie Gillain; and successful films include ''Bullhead (film), Bullhead, Man Bites Dog (film), Man Bites Dog'' and ''The Alzheimer Affair''.A review of the Belgian cinema till about 2000 can be found at Belgium is also home to a number of successful fashion designers :Belgian fashion designers.
 Folklore plays a major role in Belgium's cultural life; the country has a comparatively high number of processions, cavalcades, parades, ommegangs, ducasses, kermesse (festival), kermesses, and other local festivals, nearly always with an originally religious or mythology of the Low Countries, mythological background. The three-day Carnival of Binche, near Mons, with its famous Gilles (men dressed in high, plumed hats and bright costumes) is held just before Lent (the 40 days between Ash Wednesday and Easter). Together with the 'Processional Giants and Dragons' of Ath, Brussels, Dendermonde, Mechelen and Mons, it is recognized by UNESCO as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity.
Other examples are the three-day Carnival of Aalst in February or March; the still very religious processions of procession of the Holy Blood, the Holy Blood taking place in
Folklore plays a major role in Belgium's cultural life; the country has a comparatively high number of processions, cavalcades, parades, ommegangs, ducasses, kermesse (festival), kermesses, and other local festivals, nearly always with an originally religious or mythology of the Low Countries, mythological background. The three-day Carnival of Binche, near Mons, with its famous Gilles (men dressed in high, plumed hats and bright costumes) is held just before Lent (the 40 days between Ash Wednesday and Easter). Together with the 'Processional Giants and Dragons' of Ath, Brussels, Dendermonde, Mechelen and Mons, it is recognized by UNESCO as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity.
Other examples are the three-day Carnival of Aalst in February or March; the still very religious processions of procession of the Holy Blood, the Holy Blood taking place in
 Belgium is famous for beer, chocolate, waffles and French fries. The national dishes are "Steak frites, steak and fries", and "moules-frites, mussels with fries". Republished from Republished from Many highly ranked Belgian restaurants can be found in the most influential restaurant guides, such as the Michelin Guide. One of the many beers with the high prestige is that of the Trappists, Trappist monks. Technically, it is an ale and traditionally each abbey's beer is served in its own glass (the forms, heights and widths are different). There are only eleven breweries (six of them are Belgian) that are allowed to brew Trappist beer.
Although Belgian gastronomy is connected to French cuisine, some recipes were reputedly invented there, such as French fries (despite the name, although their exact place of origin is uncertain), Flemish Stew (a beef stew with beer, mustard and bay laurel), speculaas (or ''speculoos'' in French, a sort of cinnamon and ginger-flavoured shortcrust pastry, shortcrust biscuit), Brussels waffles (and their variant, Liège waffles), waterzooi (a broth made with chicken or fish, cream and vegetables), endive with bechamel sauce, Brussels sprouts, Belgian pralines (Belgium has some of the most renowned chocolate houses), ''charcuterie'' (deli meats) and ''Paling in 't groen'' (river eels in a sauce of green herbs).
Brands of Belgian chocolate and pralines, like Côte d'Or (brand), Côte d'Or, Chocolatier Neuhaus, Neuhaus, Leonidas (chocolate maker), Leonidas and Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva are famous, as well as independent producers such as Burie and Del Rey in Antwerp and Mary's in Brussels. Belgium produces over Belgian beer, 1100 varieties of beer. The Trappist beer of the Westvleteren Brewery, Abbey of Westvleteren has repeatedly been rated the world's best beer.
The biggest brewer in the world by volume is Anheuser-Busch InBev, based in
Belgium is famous for beer, chocolate, waffles and French fries. The national dishes are "Steak frites, steak and fries", and "moules-frites, mussels with fries". Republished from Republished from Many highly ranked Belgian restaurants can be found in the most influential restaurant guides, such as the Michelin Guide. One of the many beers with the high prestige is that of the Trappists, Trappist monks. Technically, it is an ale and traditionally each abbey's beer is served in its own glass (the forms, heights and widths are different). There are only eleven breweries (six of them are Belgian) that are allowed to brew Trappist beer.
Although Belgian gastronomy is connected to French cuisine, some recipes were reputedly invented there, such as French fries (despite the name, although their exact place of origin is uncertain), Flemish Stew (a beef stew with beer, mustard and bay laurel), speculaas (or ''speculoos'' in French, a sort of cinnamon and ginger-flavoured shortcrust pastry, shortcrust biscuit), Brussels waffles (and their variant, Liège waffles), waterzooi (a broth made with chicken or fish, cream and vegetables), endive with bechamel sauce, Brussels sprouts, Belgian pralines (Belgium has some of the most renowned chocolate houses), ''charcuterie'' (deli meats) and ''Paling in 't groen'' (river eels in a sauce of green herbs).
Brands of Belgian chocolate and pralines, like Côte d'Or (brand), Côte d'Or, Chocolatier Neuhaus, Neuhaus, Leonidas (chocolate maker), Leonidas and Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva are famous, as well as independent producers such as Burie and Del Rey in Antwerp and Mary's in Brussels. Belgium produces over Belgian beer, 1100 varieties of beer. The Trappist beer of the Westvleteren Brewery, Abbey of Westvleteren has repeatedly been rated the world's best beer.
The biggest brewer in the world by volume is Anheuser-Busch InBev, based in
 Since the 1970s, sports clubs and federations are organized separately within each Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, language community. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
Association football is the most popular sport in both parts of Belgium; also very popular are cycling, tennis, swimming, judo and basketball. The Belgium national football team has been on the top spot of the FIFA World Rankings ever since September 2018 (it reached this rank for the first time in November 2015). Since the 1990s, the team has been the world's number one for the most years in history, only behind the records of Brazil National Football Team, Brazil and Spain National Football Team, Spain.
Since the 1970s, sports clubs and federations are organized separately within each Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, language community. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
Association football is the most popular sport in both parts of Belgium; also very popular are cycling, tennis, swimming, judo and basketball. The Belgium national football team has been on the top spot of the FIFA World Rankings ever since September 2018 (it reached this rank for the first time in November 2015). Since the 1990s, the team has been the world's number one for the most years in history, only behind the records of Brazil National Football Team, Brazil and Spain National Football Team, Spain.''Team of the Year Award 2010''
on the FIFA website The team's golden generations with the world class players in the squad, namely Eden Hazard, Kevin De Bruyne, Jean-Marie Pfaff, Jan Ceulemans achieved the bronze medals at 2018 FIFA World Cup, World Cup 2018, and silver medals at UEFA Euro 1980, Euro 1980. Belgium hosted the UEFA Euro 1972, Euro 1972, and co-hosted the UEFA Euro 2000, Euro 2000 with the Netherlands. Belgians hold List of Tour de France winners, the most Tour de France victories of any country except France. They have also the most victories on the UCI Road World Championships. With five victories in the Tour de France and numerous other cycling records, Belgian cyclist Eddy Merckx is regarded as one of the greatest cyclists of all time. Philippe Gilbert is the 2012 world champion. Another well-known Belgian cyclist is Tom Boonen. Kim Clijsters and Justine Henin both were WTA Awards, Player of the Year in the Women's Tennis Association as they were ranked the number one female tennis player. The Spa-Francorchamps motor-racing circuit hosts the Formula One World Championship Belgian Grand Prix. The Belgian driver, Jacky Ickx, won eight Grands Prix and six 24 Hours of Le Mans and finished twice as runner-up in the Formula One World Championship. Belgium also has a strong reputation in, motocross with the riders Joël Robert, Roger De Coster, Georges Jobé, Eric Geboers and Stefan Everts, among others. Sporting events annually held in Belgium include the Memorial Van Damme athletics competition, the Belgian Grand Prix Formula One, and a number of classic cycle races such as the Tour of Flanders and Liège–Bastogne–Liège. The 1920 Summer Olympics were held in Antwerp. The 1977 European Basketball Championship was held in
Belgium
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved on 7 June 2007. * * * * * * * —Reflections on nations and nation-state developments regarding Belgium
[Also editions [1913], London, ; (1921) D. Unwin and Co., New York also published (1921) as ''Belgium from the Roman invasion to the present day'', The Story of the nations, 67, T. Fisher Unwin, London, ] * Facsimile reprint of a 1902 edition by the author, London
Facsimile reprint of a 1909 edition by the author, London * * (Several editions in English, incl. (1997) 7th ed.)
Official site of the Belgian monarchy
Official site of the Belgian federal government
Belgium
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Belgium
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
Belgium
information from the United States Department of State *
Portals to the World
from the United States Library of Congress
Belgium profile
from the BBC News
FAO Country Profiles: Belgium
Statistical Profile of Belgium at the Association of Religion Data Archives
*
Key Development Forecasts for Belgium
from International Futures
Official Site of the Belgian Tourist Office in the Americas and GlobeScope
{{Authority control Belgium Benelux Dutch-speaking countries and territories Federal monarchies French-speaking countries and territories German-speaking countries and territories Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of NATO Member states of the Dutch Language Union Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Member states of the Council of Europe States and territories established in 1830 Northwestern European countries Countries in Europe, Geographical articles missing image alternative text Kingdoms Countries of Europe with multiple official languages OECD members
Northwestern Europe
Northwestern Europe, or Northwest Europe, is a loosely defined subregion of Europe, overlapping Northern and Western Europe. The region can be defined both geographically and ethnographically.
Geographic definitions
Geographically, North ...
. The country is bordered by the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
to the north, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
to the east, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
to the southeast, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
to the southwest, and the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a politico- economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe ...
group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
; other major cities are Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
, Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
, Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far fro ...
, Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
, Namur
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration.
Na ...
, and Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic c ...
.
Belgium is a sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined ter ...
and a federal constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
with a parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of th ...
. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional and linguistic grounds. It is divided into three highly autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
:Pateman, Robert and Elliott, Mark (2006). Belgium
'. Benchmark Books. p. 27. the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and ...
(Flanders) in the north, the Walloon Region
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
(Wallonia) in the south, and the Brussels-Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. Brussels is the smallest and most densely populated region, as well as the richest region in terms of GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflo ...
. Belgium is also home to two main linguistic communities: the Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
, which constitutes about 60 percent of the population, and the French Community
The French Community (1958–1960; french: Communauté française) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
, which constitutes about 40 percent of the population. A small German-speaking Community
The German-speaking Community (german: links=no, Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft, or DG; french: links=no, Communauté germanophone; nl, links=no, Duitstalige Gemeenschap), since 2017 also known as East Belgium (german: links=no, Ostbelgien), is ...
, numbering around one percent, exists in the East Cantons
Eupen-Malmedy is a small, predominantly German-speaking region in eastern Belgium. It consists of three administrative cantons around the towns of Eupen, Malmedy, and Sankt Vith which encompass some . Elsewhere in Belgium, the region is common ...
. The Brussels-Capital Region is officially bilingual in French and Dutch, although French is the dominant language.*
*
*
* Belgium's linguistic diversity and related political conflicts are reflected in its complex system of governance, made up of six different governments. Since the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Belgium's central location near several major rivers has meant that the area has been relatively prosperous, connected commercially and politically to its bigger neighbours. The country as it exists today was established following the 1830 Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
T ...
, when it seceded from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
, which had incorporated the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
(which comprised most of modern-day Belgium) after the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
in 1815. The name chosen for the new state is derived from the Latin word ', used in Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
's "Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
", to describe a nearby region in the period around 55 BCE.C. Julius Caesar, ''De Bello Gallico'', book 8chapter 46
Belgium has also been the battleground of European powers, earning the moniker the "Battlefield of Europe",—The book reviewer, Haß, attributes the expression in English to
James Howell
James Howell (c. 1594 – 1666) was a 17th-century Anglo-Welsh historian and writer who is in many ways a representative figure of his age. The son of a Welsh clergyman, he was for much of his life in the shadow of his elder brother Thomas Ho ...
in 1640. Howell's original phrase "the cockpit of Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwin ...
" became modified afterwards, as shown by:*—and as such coined for Belgium:
* (See also
The Nuttall Encyclopaedia
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the ...
) a reputation reinforced in the 20th century by both world war
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
s.
Belgium participated in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, and during the course of the 20th century, possessed a number of colonies in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. Between 1885 and 1908, the Congo Free State
''(Work and Progress)
, national_anthem = Vers l'avenir
, capital = Vivi Boma
, currency = Congo Free State franc
, religion = Catholicism (''de facto'')
, leader1 = Leop ...
, which was privately owned by King Leopold II of Belgium
* german: link=no, Leopold Ludwig Philipp Maria Viktor
, house = Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
, father = Leopold I of Belgium
, mother = Louise of Orléans
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Brussels, Belgium
, death_date = ...
, was characterized by widespread atrocities and disease, leading to a population decline of millions; amid public outcry in Europe, Belgium annexed the territory as a colony. The Belgian colonial empire gained independence between 1960 and 1962.
The second half of the 20th century was marked by rising tensions between the Dutch-speaking and the French-speaking citizens fuelled by differences in language and culture and the unequal economic development of Flanders and Wallonia. This continuing antagonism has led to several far-reaching state reforms, resulting in the transition from a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation In mathematics, a unitary representation of a grou ...
to a federal arrangement between 1970 and 1993. Despite the reforms, tensions between the groups have remained, if not increased; there is significant separatism particularly among the Flemish; controversial language laws exist such as the municipalities with language facilities
There are 27 municipalities with language facilities ( nl, faciliteitengemeenten; french: communes à facilités; german: Fazilitäten-Gemeinden) in Belgium which must offer linguistic services to residents in Dutch, French, or German in addit ...
; and the formation of a coalition government took 18 months following the June 2010 federal election, a world record. Unemployment in Wallonia is more than double that of Flanders, which boomed after the Second World War.
Belgium is one of the six founding countries of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
, and its capital, Brussels, is also the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' capital of the European Union itself, hosting the official seats of the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
, the Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as ...
, and the European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body that defines the overall political direction and priorities of the European Union. It is composed of the heads of state or government of the EU member states, the President of the ...
, as well as one of two seats of the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
(the other being Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
). Belgium is also a founding member of the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU pol ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
, OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
, and WTO, and a part of the trilateral Benelux Union and the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and ...
. Brussels also hosts the headquarters of many major international organizations, such as NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
.
Belgium is a developed country
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, with an advanced high-income economy
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a nation with a gross national income per capita of US$12,696 or more in 2020, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with " First Worl ...
. It has very high standards of living
Living or The Living may refer to:
Common meanings
*Life, a condition that distinguishes organisms from inorganic objects and dead organisms
** Living species, one that is not extinct
*Personal life, the course of an individual human's life
* H ...
, quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health pr ...
, education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
, and is categorized as "very high" on the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, w ...
. It also ranks relatively high on the Global Peace Index
Global Peace Index (GPI) is a report produced by the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) which measures the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. The GPI ranks 163 independent states and territories (collectively accountin ...
.
History
Antiquity
 According to
According to Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
, the ''Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Ju ...
'' were the inhabitants of the northernmost part of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, which was much bigger than modern Belgium. He also specifically used the Latin word "''Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
''", to refer to a politically dominant part of that larger region, which is now in northernmost France. Modern Belgium corresponds to the lands of the Morini
The Morini (Gaulish: "sea folk, sailors") were a Belgic coastal tribe dwelling in the modern Pas de Calais region, around present-day Boulogne-sur-Mer, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name
They are mentioned as ''Morini'' by Caesar ( ...
, Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name Attestations
They are mentioned as ''Menapii'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Orosius (early 5th c. AD ...
, Nervii
The Nervii were one of the most powerful Belgic tribes of northern Gaul at the time of its conquest by Rome. Their territory corresponds to the central part of modern Belgium, including Brussels, and stretched southwards into French Hainault. ...
, Germani Cisrhenani
The ''Germani cisrhenani'' (Latin '' cis- rhenanus'' "on this side of the Rhine", referring to the Roman or western side), or "Left bank ''Germani''", were a group of Germanic peoples who lived west of the Lower Rhine at the time of the Gallic W ...
, Aduatuci
The Atuatuci (or Aduatuci) were a Gallic- Germanic tribe, dwelling in the eastern part of modern-day Belgium during the Iron Age.
They fought the Roman armies of Julius Caesar during the Gallic Wars (58–50 BC). In the Battle of the Sabis ( ...
, and, around Arlon
Arlon (; lb, Arel ; nl, Aarlen ; german: Arel ; wa, Årlon; la, Orolaunum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in and capital of the province of Luxembourg in the Ardennes, Belgium. With a population of just over 28,000, it is th ...
, a part of the country of the Treveri
The Trēverī (Gaulish: *''Trēueroi'') were a Celtic tribe of the Belgae group who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle from around 150 BCE, if not earlier, until their displacement by the Franks. Their domain lay within the southern fring ...
. Caesar described these regions as a less economically developed transition zone, which had links to the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
over the Rhine.
After Caesar's conquests, ''Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, a ...
'' came to be the Latin name of a large Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
covering most of Northern Gaul, including the Treveri. Areas closer to the lower Rhine frontier, including the eastern part of modern Belgium, eventually became part of the frontier province of ''Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agripp ...
'', which continued to interact with their neighbours outside the empire. At the time when central government collapsed in the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
, the Roman provinces of Belgica and Germania were inhabited by a mix of a Romanized population and Germanic-speaking Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
who came to dominate the military and political class.
Middle Ages
During the 5th century, the area came under the rule of the FrankishMerovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaul ...
kings, who established a kingdom ruling over the Romanized population in what is northern France, and then conquered the other Frankish kingdoms. During the 8th century, this kingdom of the Franks came to be ruled by the Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pi ...
, whose centre of power included the area which is now eastern Belgium. Over the centuries, the kingdom was divided up in many ways, but the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
in 843 divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms whose borders had a lasting impact on medieval political boundaries. Most of modern Belgium was in the Middle Kingdom, later known as Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable ...
, but the coastal county of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges a ...
, west of the Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to ...
, became the northernmost part of West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from ab ...
, the predecessor of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. In 870 in the Treaty of Meerssen
The Treaty of Mersen or Meerssen, concluded on 8 August 870, was a treaty to partition the realm of Lothair II, known as Lotharingia, by his uncles Louis the German of East Francia and Charles the Bald of West Francia, the two surviving sons of ...
, modern Belgium lands all became part of the western kingdom for a period, but in 880 in the Treaty of Ribemont, Lotharingia returned to the lasting control of the Eastern king, or Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. The lordships and bishoprics along the "March" (frontier) between the two great kingdoms maintained important connections between each other. For example, the county of Flanders expanded over the Scheldt into the empire, and during several periods was ruled by the same lords as the county of Hainaut
The County of Hainaut (french: Comté de Hainaut; nl, Graafschap Henegouwen; la, comitatus hanoniensis), sometimes spelled Hainault, was a territorial lordship within the medieval Holy Roman Empire that straddled what is now the border of Belg ...
.
In the 13th and 14th centuries, the cloth industry and commerce boomed especially in the County of Flanders and it became one of the richest areas in Europe. This prosperity played a role in conflicts between Flanders and the king of France. Famously, Flemish militias scored a surprise victory at the Battle of the Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemis ...
against a strong force of mounted knights in 1302, but France soon regained control of the rebellious province.
Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands
 In the 15th century, the Duke of Burgundy in France took control of Flanders, and from there they proceeded to unite much of what is now the Benelux, the so-called
In the 15th century, the Duke of Burgundy in France took control of Flanders, and from there they proceeded to unite much of what is now the Benelux, the so-called Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
. "Belgium" and "Flanders" were the first two common names used for the Burgundian Netherlands which was the predecessor of the Austrian Netherlands, the predecessor of modern Belgium. The union, technically stretching between two kingdoms, gave the area economic and political stability which led to an even greater prosperity and artistic creation.
Born in Belgium, the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
Emperor Charles V was heir of the Burgundians, but also of the royal families of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Castile and Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
. With the Pragmatic Sanction of 1549
The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 was an edict, promulgated by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, reorganising the Seventeen Provinces of the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg into one indivisible territory, while retaining existing custo ...
he gave the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (F ...
more legitimacy as a stable entity, rather than just a temporary personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
. He also increased the influence of these Netherlands over the Prince-Bishopric of Liège
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial Estate, so the bishop of Liège, as its prince, ...
, which continued to exist as a large semi-independent enclave.
Spanish and Austrian Netherlands
TheEighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Ref ...
(1568–1648), was triggered by the Spanish government's policy towards Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, which was becoming popular in the Low Countries. The rebellious northern United Provinces (''Belgica Foederata'' in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, the "Federated Netherlands") eventually separated from the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
(''Belgica Regia'', the "Royal Netherlands"). The latter were ruled successively by the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
(Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
) and the Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s (Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
) and comprised most of modern Belgium. This was the theatre of several more protracted conflicts during much of the 17th and 18th centuries involving France, including the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
(1672–1678), the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between Kingdom of France, France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by t ...
(1688–1697), the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
(1701–1714), and part of the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George ...
(1740–1748).
The French revolution and the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Following thecampaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars continued from 1793 with few immediate changes in the diplomatic situation as France fought the First coalition.
On the Alpine frontier, there was little change, with the French invasion of Piedmont failing. On the ...
, the Low Countriesincluding territories that were never nominally under Habsburg rule, such as the Prince-Bishopric of Liègewere annexed by the French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 ...
, ending Austrian rule in the region. A reunification of the Low Countries as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
occurred at the dissolution of the First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
in 1814, after the abdication of Napoleon.
Independent Belgium
In 1830, theBelgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
T ...
led to the separation of the Southern Provinces from the Netherlands and to the establishment of a Catholic and bourgeois, officially French-speaking and neutral, independent Belgium under a provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
and a national congress ''National Congress'' is a term used in the names of various political parties and legislatures .
Political parties
*Ethiopia: Oromo National Congress
*Guyana: People's National Congress (Guyana)
*India: Indian National Congress
*Iraq: Iraqi Nati ...
. Since the installation of Leopold I as king on 1831, now celebrated as Belgium's National Day, Belgium has been a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
and parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of t ...
, with a laicist constitution based on the Napoleonic code. Although the franchise was initially restricted, universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political sta ...
for men was introduced after the general strike of 1893 (with plural voting
Plural voting is the practice whereby one person might be able to vote multiple times in an election. It is not to be confused with a plurality voting system which does not necessarily involve plural voting. Weighted voting is a generalisation of p ...
until 1919) and for women in 1949.
The main political parties of the 19th century were the Catholic Party and the Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
, with the Belgian Labour Party
The Belgian Labour Party ( nl, Belgische Werkliedenpartij, BWP; french: Parti ouvrier belge, POB) was the first major socialist party in Belgium. Founded in 1885, the party was officially disbanded in 1940 and superseded by the Belgian Socialist ...
emerging towards the end of the 19th century. French was originally the single official language adopted by the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The character ...
and the bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. Th ...
. It progressively lost its overall importance as Dutch became recognized as well. This recognition became official in 1898, and in 1967, the parliament accepted a Dutch version of the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these pr ...
.
The Berlin Conference
The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, also known as the Congo Conference (, ) or West Africa Conference (, ), regulated European colonisation and trade in Africa during the New Imperialism period and coincided with Germany's sudden emergenc ...
of 1885 ceded control of the Congo Free State
''(Work and Progress)
, national_anthem = Vers l'avenir
, capital = Vivi Boma
, currency = Congo Free State franc
, religion = Catholicism (''de facto'')
, leader1 = Leop ...
to King Leopold II as his private possession. From around 1900 there was growing international concern for the extreme and savage treatment of the Congolese population under Leopold II, for whom the Congo was primarily a source of revenue from ivory and rubber production. Many Congolese were killed by Leopold's agents for failing to meet production quotas for ivory and rubber. In 1908, this outcry led the Belgian state to assume responsibility for the government of the colony, henceforth called the Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (french: Congo belge, ; nl, Belgisch-Congo) was a Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960. The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964.
Colo ...
. A Belgian commission in 1919 estimated that Congo's population was half what it was in 1879.
Germany invaded Belgium in August 1914 as part of the Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (german: Schlieffen-Plan, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on ...
to attack France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and much of the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
fighting of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
occurred in western parts of the country. The opening months of the war were known as the Rape of Belgium
The Rape of Belgium was a series of systematic war crimes, especially mass murder and deportation and enslavement, by German troops against Belgian civilians during the invasion and occupation of Belgium in World War I.
The neutrality ...
due to German excesses. Belgium assumed control of the German colonies
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
of Ruanda-Urundi
Ruanda-Urundi (), later Rwanda-Burundi, was a colonial territory, once part of German East Africa, which was occupied by troops from the Belgian Congo during the East African campaign in World War I and was administered by Belgium under milita ...
(modern-day Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
and Burundi
Burundi (, ), officially the Republic of Burundi ( rn, Repuburika y’Uburundi ; Swahili: ''Jamuhuri ya Burundi''; French: ''République du Burundi'' ), is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley at the junction between the African Gr ...
) during the war, and in 1924 the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
mandated them to Belgium. In the aftermath of the First World War, Belgium annexed the Prussian districts of Eupen and Malmedy in 1925, thereby causing the presence of a German-speaking minority.
German forces again invaded the country in May 1940, and 40,690 Belgians, over half of them Jews, were killed during the subsequent occupation
Occupation commonly refers to:
*Occupation (human activity), or job, one's role in society, often a regular activity performed for payment
*Occupation (protest), political demonstration by holding public or symbolic spaces
*Military occupation, th ...
and the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. From September 1944 to February 1945 the Allies liberated Belgium. After World War II, a general strike forced King Leopold III to abdicate in 1951 in favour of his son, Prince Baudouin, since many Belgians felt he had collaborated with Germany during the war. The Belgian Congo gained independence in 1960 during the Congo Crisis
The Congo Crisis (french: Crise congolaise, link=no) was a period of political upheaval and conflict between 1960 and 1965 in the Republic of the Congo (today the Democratic Republic of the Congo). The crisis began almost immediately after ...
; Ruanda-Urundi followed with its independence two years later. Belgium joined NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
as a founding member and formed the Benelux group of nations with the Netherlands and Luxembourg.
Belgium became one of the six founding members of the European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a European organization created after World War II to regulate the coal and steel industries. It was formally established in 1951 by the Treaty of Paris, signed by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembo ...
in 1951 and of the European Atomic Energy Community
The European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom) is an international organisation established by the Euratom Treaty on 25 March 1957 with the original purpose of creating a specialist market for nuclear power in Europe, by developing nucl ...
and European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
, established in 1957. The latter has now become the European Union, for which Belgium hosts major administrations and institutions, including the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
, the Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as ...
and the extraordinary and committee sessions of the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
.
In the early 1990s, Belgium saw several large corruption scandals notably surrounding Marc Dutroux
Marc Paul Alain Dutroux (; born 6 November 1956) is a Belgian convicted serial killer, serial rapist, and child molester. Initially convicted for the abduction and rape of five young girls in 1989, Dutroux was released on parole after just thr ...
, Andre Cools, the Dioxin Affair, Agusta Scandal
The Agusta scandal (french: Affaire Agusta, nl, Agustaschandaal), alternatively known as the Agusta–Dassault Case, was a major political scandal which occurred in Belgium during the 1990s, based on allegations that two multinational companies ...
and the murder of Karel van Noppen.
Geography
 Belgium shares borders with
Belgium shares borders with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
(), Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
(), Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
() and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
(). Its total surface, including water area, is . Before 2018, its total area was believed to be . However, when the country's statistics were measured in 2018, a new calculation method was used. Unlike previous calculations, this one included the area from the coast to the low-water line, revealing the country to be larger in surface area than previously thought. Its land area alone is 30,278 km2. It lies between latitudes 49°30' and 51°30' N, and longitudes 2°33' and 6°24' E.Geografische beschrijving van België – Over Belgie – Portaal Belgische Overheid. Belgium.be. Retrieved 12 August 2013. Belgium has three main geographical regions; the coastal plain in the northwest and the central plateau both belong to the Anglo-Belgian Basin, and the
Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Be ...
uplands in the southeast to the Hercynian orogenic belt. The Paris Basin
The Paris Basin is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny (Hercynian orogeny). The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in the cr ...
reaches a small fourth area at Belgium's southernmost tip, Belgian Lorraine
Belgian Lorraine is the part of Lorraine that lies in the south of the Belgian province of Luxembourg, in Wallonia.
The term is used solely in a geological context, as the region borders the geologically-distinct Ardennes, to the north.
Cultural ...
.
The coastal plain consists mainly of sand dunes and polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
s. Further inland lies a smooth, slowly rising landscape irrigated by numerous waterways, with fertile valleys and the northeastern sandy plain of the Campine
The Campine ( French ) or De Kempen (Dutch ) is a natural region situated chiefly in north-eastern Belgium and parts of the south-eastern Netherlands which once consisted mainly of extensive moors, tracts of sandy heath, and wetlands. It encom ...
(''Kempen''). The thickly forested hills and plateaus of the Ardennes are more rugged and rocky with caves and small gorges. Extending westward into France, this area is eastwardly connected to the Eifel
The Eifel (; lb, Äifel, ) is a low mountain range in western Germany and eastern Belgium. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Community of ...
in Germany by the High Fens
The High Fens (german: Hohes Venn; french: Hautes Fagnes; nl, Hoge Venen), which were declared a nature reserve in 1957, are an upland area, a plateau region in Liège Province, in the east of Belgium and adjoining parts of Germany, between the ...
plateau, on which the Signal de Botrange
Signal de Botrange is the highest point in Wallonia and in Belgium, located in the ''High Fens'' (''Hautes Fagnes'' in French, ''Hohes Venn'' in German, ''Hoge Venen'' in Dutch), at . It is the top of a broad plateau and a road crosses the summi ...
forms the country's highest point at .
The climate is maritime temperate with significant precipitation in all seasons (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
: ''Cfb''), like most of northwest Europe. ''(directFinal Revised Paper
)'' The average temperature is lowest in January at and highest in July at . The average precipitation per month varies between for February and April, to for July. Averages for the years 2000 to 2006 show daily temperature minimums of and maximums of and monthly rainfall of ; these are about 1 °C and nearly 10 millimetres above last century's normal values, respectively.
Phytogeographically
Phytogeography (from Greek language, Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographi ...
, Belgium is shared between the Atlantic European and Central European provinces of the Circumboreal Region
The Circumboreal Region in phytogeography is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan.
It is the largest floristic region in ...
within the Boreal Kingdom
The Boreal Kingdom or Holarctic Kingdom (Holarctis) is a floristic kingdom identified by botanist Ronald Good (and later by Armen Takhtajan), which includes the temperate to Arctic portions of North America and Eurasia. Its flora is inherited f ...
.Takhtajan, Armen, 1986. ''Floristic Regions of the World''. (translated by T.J. Crovello and A. Cronquist). University of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty ...
, Berkeley
Berkeley most often refers to:
*Berkeley, California, a city in the United States
**University of California, Berkeley, a public university in Berkeley, California
* George Berkeley (1685–1753), Anglo-Irish philosopher
Berkeley may also refer ...
. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor ...
, the territory of Belgium belongs to the terrestrial ecoregions
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecology, ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large a ...
of Atlantic mixed forests
The Atlantic mixed forests is a terrestrial ecoregion in western Europe. It extends along the western edge of continental Europe, from southwestern France through northern France, Belgium, the Netherlands, northwestern Germany, and western Denmar ...
and Western European broadleaf forests
The Western European broadleaf forests is an ecoregion in Western Europe, and parts of the Alps. It comprises temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, that cover large areas of France, Germany and the Czech Republic and more moderately sized parts ...
. Belgium had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 1.36/10, ranking it 163rd globally out of 172 countries.
Provinces
The territory of Belgium is divided into three Regions, two of which, theFlemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and ...
and Walloon Region
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
, are in turn subdivided into provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
; the third Region, the Brussels Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, is neither a province nor a part of a province.
Politics
constitutional
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
, popular monarchy
Popular monarchy is a term used by Kingsley Martin (1936) for monarchical titles referring to a people rather than a territory.
This was the norm in classical antiquity and throughout much of the Middle Ages, and such titles were retained in some ...
and a federal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
. The bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
federal parliament
The Parliament of Australia (officially the Federal Parliament, also called the Commonwealth Parliament) is the legislative branch of the government of Australia. It consists of three elements: the monarch (represented by the governor-gen ...
is composed of a Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and a Chamber of Representatives. The former is made up of 50 senators appointed by the parliaments of the communities and regions and 10 co-opted senators. Prior to 2014, most of the Senate's members were directly elected. The Chamber
Chamber or the chamber may refer to:
In government and organizations
* Chamber of commerce, an organization of business owners to promote commercial interests
*Legislative chamber, in politics
* Debate chamber, the space or room that houses delib ...
's 150 representatives are elected under a proportional voting
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
system from 11 electoral districts
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity ...
. Belgium has compulsory voting
Compulsory voting, also called mandatory voting, is the requirement in some countries that eligible citizens register and vote in elections. Penalties might be imposed on those who fail to do so without a valid reason. According to the CIA World F ...
and thus maintains one of the highest rates of voter turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford Unive ...
in the world.
The King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
(currently Philippe) is the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
, though with limited prerogatives
In law, a prerogative is an exclusive right bestowed by a government or state and invested in an individual or group, the content of which is separate from the body of rights enjoyed under the general law. It was a common facet of feudal law. The ...
. He appoints ministers, including a Prime Minister, that have the confidence of the Chamber of Representatives to form the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
. The Council of Ministers is composed of no more than fifteen members. With the possible exception of the Prime Minister, the Council of Ministers is composed of an equal number of Dutch-speaking members and French-speaking members.
The judicial system is based on civil law and originates from the Napoleonic code. The Court of Cassation
A court of cassation is a high-instance court that exists in some judicial systems. Courts of cassation do not re-examine the facts of a case, they only interpret the relevant law. In this they are appellate courts of the highest instance. In th ...
is the court of last resort, with the courts of appeal
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of ...
one level below.
Political culture
Belgium's political institutions are complex; most political power rests on representation of the main cultural communities. Since about 1970, the significant national Belgian political parties have split into distinct components that mainly represent the political and linguistic interests of these communities. The major parties in each community, though close to the political center, belong to three main groups:Christian Democrats
__NOTOC__
Christian democratic parties are political parties that seek to apply Christian principles to public policy. The underlying Christian democracy movement emerged in 19th-century Europe, largely under the influence of Catholic social ...
, Liberals, and Social Democrats
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote so ...
.
Further notable parties came into being well after the middle of last century, mainly to represent linguistic
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
, nationalist, or environmental interests, and recently smaller ones of some specific liberal nature.
 A string of Christian Democrat coalition governments from 1958 Belgian federal election, 1999, was broken in 1999 after the first dioxine affair, dioxin crisis, a major Food contaminant, food contamination scandal.ElAmin, Ahmed (31 January 2006
A string of Christian Democrat coalition governments from 1958 Belgian federal election, 1999, was broken in 1999 after the first dioxine affair, dioxin crisis, a major Food contaminant, food contamination scandal.ElAmin, Ahmed (31 January 2006Belgium, Netherlands meat sectors face dioxin crisis
. foodproductiondaily.com A "rainbow coalition" emerged from six parties: the Flemish and the French-speaking Liberals, Social Democrats and Greens. Later, a "Purple (government), purple coalition" of Liberals and Social Democrats formed after the Greens lost most of their seats in the Belgian federal election, 2003, 2003 election. The government led by Prime Minister Guy Verhofstadt from 1999 to 2007 achieved a balanced budget, some tax reforms, a labor-market reform, scheduled Nuclear energy policy#Europe, nuclear phase-out and instigated legislation allowing more stringent War Crimes Law (Belgium), war crime and more lenient drug harmfulness, soft drug usage prosecution. Restrictions on withholding euthanasia were reduced and same-sex marriage in Belgium, same-sex marriage legalized. The government promoted active diplomacy in Africa The article shows an example of Belgium's recent African policies. and Governmental positions on the Iraq War prior to the 2003 invasion of Iraq, opposed the invasion of Iraq. It is the only country that does not have age restrictions on euthanasia. Verhofstadt's coalition fared badly in the Belgian federal election, 2007, June 2007 elections. For more than a year, the country experienced a 2007 Belgian government formation, political crisis. This crisis was such that many observers speculated on a possible partition of Belgium. From 2007 until 2008 the temporary Verhofstadt III Government was in office. This was a coalition of the Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams, Flemish and Humanist Democratic Centre, Francophone Christian Democrats, the Open Vlaamse Liberalen en Democraten, Flemish and Mouvement Réformateur, Francophone Liberals together with the Socialist Party (francophone Belgium), Francophone Social Democrats. On that day a Leterme I Government, new government, led by Flemish Christian Democrat Yves Leterme, the actual winner of the federal elections of , was sworn in by the king. On 2008 Leterme announced the resignation of the cabinet to the king, as no progress in state reform in Belgium, constitutional reforms had been made. In December 2008, he once more offered his resignation to the king after a 2008–2009 Belgian financial crisis, crisis surrounding the sale of Fortis (finance), Fortis to BNP Paribas.CNN.com
, "Belgium Prime Minister offers resignation over banking deal" At this juncture, his resignation was accepted and Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams, Christian Democratic and Flemish Herman Van Rompuy was sworn in as Prime Minister on 2008.Belgian king asks Van Rompuy to form government
Reuters. After Herman Van Rompuy was designated the first permanent President of the European Council on 2009, he offered the resignation of his government to King Albert II on 2009. A few hours later, the Leterme II Government, new government under Prime Minister Yves Leterme was sworn in. On 2010, Leterme again offered the resignation of his cabinet to the king after one of the coalition partners, the OpenVLD, withdrew from the government, and on 2010 King Albert officially accepted the resignation. The Parliamentary elections in Belgium on 2010 saw the Flemish nationalist New Flemish Alliance, N-VA become the largest party in Flanders, and the Socialist Party PS the largest party in Wallonia. Until December 2011, Belgium was governed by Leterme's caretaker government awaiting the end of the deadlocked negotiations for 2010–2011 Belgian government formation, formation of a new government. By 30 March 2011, this set a new world record for the elapsed time without an official government, previously held by war-torn Iraq. Finally, in December 2011 the Di Rupo Government led by Walloon socialist Prime Minister Elio Di Rupo was sworn in. The Belgian federal election, 2014, 2014 federal election (coinciding with the Belgian regional elections, 2014, regional elections) resulted in a further electoral gain for the Flemish nationalist N-VA, although the incumbent coalition (composed of Flemish and French-speaking Social Democrats, Liberals, and Christian Democrats) maintains a solid majority in Parliament and in all electoral constituencies. On 22 July 2014, King Philippe nominated Charles Michel (MR) and Kris Peeters (CD&V) to 2014 Belgian government formation, lead the formation of a new federal cabinet composed of the Flemish parties N-VA, CD&V, Open Vld and the French-speaking MR, which resulted in the Michel I Government, Michel Government. It was the first time N-VA was part of the federal cabinet, while the French-speaking side was represented only by the MR, which achieved a minority of the public votes in Wallonia. In May 2019 Belgian federal election, 2019 federal elections in the Flemish-speaking northern region of Flanders far-right Vlaams Belang party made major gains. In the French-speaking southern area of Wallonia the Socialists were strong. The moderate Flemish nationalist party the N-VA remained the largest party in parliament. In July 2019 prime minister Charles Michel was selected to hold the post of President of the
European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body that defines the overall political direction and priorities of the European Union. It is composed of the heads of state or government of the EU member states, the President of the ...
. His successor Sophie Wilmès was Belgium's first female prime minister. She led the caretaker government since October 2019. The Flemish Liberal party politician Alexander De Croo became new prime minister in October 2020. The parties had agreed on federal government 16 months after the elections.
Communities and regions
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
(Dutch-speaking);
#* the French Community
The French Community (1958–1960; french: Communauté française) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
(French-speaking);
#* the German-speaking Community
The German-speaking Community (german: links=no, Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft, or DG; french: links=no, Communauté germanophone; nl, links=no, Duitstalige Gemeenschap), since 2017 also known as East Belgium (german: links=no, Ostbelgien), is ...
.
# The three regions:
#* the Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and ...
, subdivided into five provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
;
#* the Walloon Region
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
, subdivided into five provinces;
#* the Brussels-Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
.
The Language legislation in Belgium, constitutional language areas determine the official languages in their municipalities, as well as the geographical limits of the empowered institutions for specific matters.#Fitzmaurice, Fitzmaurice (1996), p. 121 Although this would allow for seven parliaments and governments when the Communities and Regions were created in 1980, Flemish politicians decided to merge both.#Fitzmaurice, Fitzmaurice (1996), p. 122. Thus the Flemings just have one single institutional body of parliament and government is empowered for all except federal and specific municipal matters.
The overlapping boundaries of the Regions and Communities have created two notable peculiarities: the territory of the Brussels-Capital Region (which came into existence nearly a decade after the other regions) is included in both the Flemish and French Communities, and the territory of the German-speaking Community lies wholly within the Walloon Region. Conflicts about jurisdiction between the bodies are resolved by the Constitutional Court of Belgium. The structure is intended as a compromise to allow different cultures to live together peacefully.
Locus of policy jurisdiction
The Federal State's authority includes justice, defense, federal police, social security, nuclear energy, monetary policy and public debt, and other aspects of public finances. State-owned companies include the Belgian Post Group and National Railway Company of Belgium, Belgian Railways. The Federal Government is responsible for the obligations of Belgium and its federalized institutions towards the European Union and NATO. It controls substantial parts of public health, home affairs and foreign affairs. The budget—without the debt—controlled by the federal government amounts to about 50% of the national fiscal income. The federal government employs around 12% of the civil servants. Communities exercise their authority only within linguistically determined geographical boundaries, originally oriented towards the individuals of a Community's language: culture (including audiovisual media), education and the use of the relevant language. Extensions to personal matters less directly connected with language comprise health policy (curative and preventive medicine) and assistance to individuals (protection of youth, social welfare, aid to families, immigrant assistance services, and so on.). Regions have authority in fields that can be broadly associated with their territory. These include economy, employment, agriculture, water policy, housing, public works, energy, transport, the environment, town and country planning, nature conservation, credit and foreign trade. They supervise the provinces, municipalities and intercommunal utility companies. In several fields, the different levels each have their own say on specifics. With education, for instance, the autonomy of the Communities neither includes decisions about the compulsory aspect nor allows for setting minimum requirements for awarding qualifications, which remain federal matters. Each level of government can be involved in scientific research and international relations associated with its powers. The treaty-making power of the Regions' and Communities' Governments is the broadest of all the Federating units of all the Federations all over the world.Foreign relations
 Because of its location at the crossroads of Western Europe, Belgium has historically been the route of invading armies from its larger neighbors. With virtually defenseless borders, Belgium has traditionally sought to avoid domination by the more powerful nations which surround it through a policy of mediation. The Belgians have been strong advocates of European integration. The headquarters of
Because of its location at the crossroads of Western Europe, Belgium has historically been the route of invading armies from its larger neighbors. With virtually defenseless borders, Belgium has traditionally sought to avoid domination by the more powerful nations which surround it through a policy of mediation. The Belgians have been strong advocates of European integration. The headquarters of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
and of several of the institutions of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
are located in Belgium.
Armed forces
The Belgian Armed Forces have about 47,000 active troops. In 2019, Belgium's defense budget totaled €4.303 billion ($4.921 billion) representing .93% of its GDP. They are organized into one unified structure which consists of four main components: Belgium Land Component, Land Component or the Army, Belgium Air Component, Air Component or the Air Force, Belgium Marine Component, Marine Component or the Navy and the Belgium Medical Component, Medical Component. The operational commands of the four components are subordinate to the Staff Department for Operations and Training of the Ministry of Defence (Belgium), Ministry of Defense, which is headed by the ACOS Operations and Training, Assistant Chief of Staff Operations and Training, and to the Chief of Defence (Belgium), Chief of Defense. The effects of the Second World War made collective security a priority for Foreign relations of Belgium, Belgian foreign policy. In March 1948 Belgium signed the Treaty of Brussels and then joinedNATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
in 1948. However, the integration of the armed forces into NATO did not begin until after the Korean War.David Isby and Charles Kamps Jr, 'Armies of NATO's Central Front,' Jane's Publishing Company, 1985, p.59 The Belgians, along with the Luxembourg government, sent a detachment of battalion strength to fight in Korea known as the Belgian United Nations Command. This mission was the first in a long line of UN missions which the Belgians supported. Currently, the Belgian Marine Component is working closely together with the Dutch Navy under the command of the Admiral Benelux.
Economy
 Belgium was the first continental European country to undergo the
Belgium was the first continental European country to undergo the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, in the early 19th century. Areas in Liège Province and around Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
rapidly developed mining and steelmaking, which flourished until the mid-20th century in the Sillon industriel, Sambre and Meuse valley and made Belgium one of the three most industrialized nations in the world from 1830 to 1910. However, by the 1840s the textile industry of Flanders was in severe crisis, and the region experienced European Potato Failure, famine from 1846 to 1850.
After World War II, Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
and Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
experienced a rapid expansion of the chemical and petroleum industries. The 1973 and 1979 oil crisis, 1979 oil crises sent the economy into a recession; it was particularly prolonged in Wallonia, where the steel industry had become less competitive and experienced a serious decline. In the 1980s and 1990s, the economic center of the country continued to shift northwards and is now concentrated in the populous Flemish Diamond area.
By the end of the 1980s, Belgian macroeconomic policies had resulted in a cumulative government debt of about 120% of GDP. , the budget was balanced and public debt was equal to 90.30% of GDP. In 2005 and 2006, real GDP growth rates of 1.5% and 3.0%, respectively, were slightly above the average for the Euro area. Unemployment rates of 8.4% in 2005 and 8.2% in 2006 were close to the area average. By , this had grown to 8.5% compared to an average rate of 9.6% for the European Union as a whole (EU 27). From 1832 until 2002, Belgium's currency was the Belgian franc. Belgium switched to the euro in 2002, with the first sets of euro coins being minted in 1999. The standard Belgian euro coins designated for circulation show the portrait of the monarch (first King Albert II, since 2013 King Philippe).
Despite an 18% decrease observed from 1970 to 1999, Belgium still had in 1999 the highest Rail transport in Belgium, rail network density within the European Union with 113.8 km/1 000 km2. On the other hand, the same period, 1970–1999, has seen a huge growth (+56%) of the List of motorways in Belgium, motorway network. In 1999, the density of km motorways per 1000 km2 and 1000 inhabitants amounted to 55.1 and 16.5 respectively and were significantly superior to the EU's means of 13.7 and 15.9.
Science and technology
 Contributions to the development of science and technology have appeared throughout the country's history. The 16th century Early Modern flourishing of Western Europe included cartography, cartographer Gerardus Mercator, anatomy, anatomist Andreas Vesalius, herbalist Rembert Dodoens (*) Free abstract for pay-per-view article by and mathematician Simon Stevin among the most influential scientists.
Chemist Ernest Solvay and engineer Zenobe Gramme (École industrielle de Liège) gave their names to the Solvay process and the Gramme dynamo, respectively, in the 1860s. Bakelite was developed in 1907–1909 by Leo Baekeland. Ernest Solvay also acted as a major philanthropist and gave his name to the Solvay Institute of Sociology, the Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management and the International Solvay Institutes for Physics and Chemistry which are now part of the Université libre de Bruxelles. In 1911, he started a series of conferences, the Solvay Conferences on Physics and Chemistry, which have had a deep impact on the evolution of quantum physics and chemistry. A major contribution to fundamental science was also due to a Belgian, Monsignor Georges Lemaître (Catholic University of Leuven (1834–1968), Catholic University of Louvain), who is credited with proposing the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe in 1927.
Three Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine were awarded to Belgians: Jules Bordet (Université libre de Bruxelles) in 1919, Corneille Heymans (University of Ghent) in 1938 and Albert Claude (Université libre de Bruxelles) together with Christian de Duve (Université catholique de Louvain) in 1974. François Englert (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2013. Ilya Prigogine (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1977. Two Belgian mathematicians have been awarded the Fields Medal: Pierre Deligne in 1978 and Jean Bourgain in 1994. (Retrieved 10 November 2011) (Retrieved 10 November 2011) Belgium was ranked 22nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 23rd in 2019.
Contributions to the development of science and technology have appeared throughout the country's history. The 16th century Early Modern flourishing of Western Europe included cartography, cartographer Gerardus Mercator, anatomy, anatomist Andreas Vesalius, herbalist Rembert Dodoens (*) Free abstract for pay-per-view article by and mathematician Simon Stevin among the most influential scientists.
Chemist Ernest Solvay and engineer Zenobe Gramme (École industrielle de Liège) gave their names to the Solvay process and the Gramme dynamo, respectively, in the 1860s. Bakelite was developed in 1907–1909 by Leo Baekeland. Ernest Solvay also acted as a major philanthropist and gave his name to the Solvay Institute of Sociology, the Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management and the International Solvay Institutes for Physics and Chemistry which are now part of the Université libre de Bruxelles. In 1911, he started a series of conferences, the Solvay Conferences on Physics and Chemistry, which have had a deep impact on the evolution of quantum physics and chemistry. A major contribution to fundamental science was also due to a Belgian, Monsignor Georges Lemaître (Catholic University of Leuven (1834–1968), Catholic University of Louvain), who is credited with proposing the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe in 1927.
Three Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine were awarded to Belgians: Jules Bordet (Université libre de Bruxelles) in 1919, Corneille Heymans (University of Ghent) in 1938 and Albert Claude (Université libre de Bruxelles) together with Christian de Duve (Université catholique de Louvain) in 1974. François Englert (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2013. Ilya Prigogine (Université libre de Bruxelles) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1977. Two Belgian mathematicians have been awarded the Fields Medal: Pierre Deligne in 1978 and Jean Bourgain in 1994. (Retrieved 10 November 2011) (Retrieved 10 November 2011) Belgium was ranked 22nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, up from 23rd in 2019.
Demographics

 As of 1 January 2020, the total population of Belgium according to its population register was 11,492,641. The population density of Belgium is as of January 2019, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world, and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe. The most densely populated province is Antwerp province, Antwerp, the least densely populated province is Luxembourg (Belgium), Luxembourg. As of January 2019, the
As of 1 January 2020, the total population of Belgium according to its population register was 11,492,641. The population density of Belgium is as of January 2019, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world, and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe. The most densely populated province is Antwerp province, Antwerp, the least densely populated province is Luxembourg (Belgium), Luxembourg. As of January 2019, the Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and ...
had a population of 6,589,069 (57.6% of Belgium), its most populous cities being Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
(523,248), Ghent (260,341) and Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
(118,284). Wallonia had a population of 3,633,795 (31.8% of Belgium) with Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
(201,816), Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far fro ...
(197,355) and Namur
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration.
Na ...
(110,939), its most populous cities. The Brussels-Capital Region
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
has 1,208,542 inhabitants (10.6% of Belgium) in the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities, three of which have over 100,000 residents.
In 2017 the average total fertility rate (TFR) across Belgium was 1.64 children per woman, below the replacement rate of 2.1; it remains considerably below the high of 4.87 children born per woman in 1873. Belgium subsequently has one of the oldest populations in the world, with an average age of 41.6 years.
Migration
, nearly 92% of the population had Belgian citizenship,This number evolved to 89% in 2011. and other European Union member citizens account for around 6%. The prevalent foreign nationals were Italian (171,918), French (125,061), Dutch (116,970), Morocco, Moroccan (80,579), Portuguese people, Portuguese (43,509), Spanish (42,765), Turkish people, Turkish (39,419) and German (37,621).De vreemde bevolkingecodata.mineco.fgov.be In 2007, there were 1.38 million foreign-born residents in Belgium, corresponding to 12.9% of the total population. Of these, 685,000 (6.4%) were born outside the EU and 695,000 (6.5%) were born in another EU Member State.L'IMMIGRATION EN BELGIQUE. EFFECTIFS, MOUVEMENTS. ET MARCHE DU TRAVAIL
. Rapport 2009. Direction générale Emploi et marché du travai At the beginning of 2012, people of foreign background and their descendants were estimated to have formed around 25% of the total population i.e. 2.8 million ''new Belgians''.
. npdata.be (1 January 2012). Of these new Belgians, 1,200,000 are of European ancestry and 1,350,000
. npdata.be (7 May 2012). are from non-Western countries (most of them from Morocco, Turkey, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DR Congo). Since the modification of the Belgian nationality law in 1984 more than Demographics of Belgium, 1.3 million migrants have acquired Belgian citizenship. The largest group of immigrants and their descendants in Belgium are Moroccan people, Moroccans. 89.2% of inhabitants of Turkish people, Turkish origin have been naturalized, as have 88.4% of people of Moroccan background, 75.4% of Italians, 56.2% of the French and 47.8% of Dutch people. Statistics Belgium, Statbel released figures of the Belgian population in relation to the origin of people in Belgium. According to the data, as of 1 January 2021, 67.3% of the Belgian population was of ethnic Belgian origin and 32.7% were of foreign origin or nationality, with 20.3% of those of a foreign nationality or ethnic group originating from neighbouring countries. The study also found that 74.5% of the Brussels, Brussels Capital Region were of non-Belgian origin, of which 13.8% originated from neighbouring countries.
Languages
 Belgium has three official languages: Dutch, French and German. A number of non-official minority languages are spoken as well.
As no census exists, there are no official statistical data regarding the distribution or usage of Belgium's three official languages or their dialects. However, various criteria, including the language(s) of parents, of education, or the second-language status of foreign born, may provide suggested figures. An estimated 60% of the Belgian population are native speakers of Dutch (often referred to as Flemish), and 40% of the population speaks French natively. French-speaking Belgians are often referred to as Walloons, although the French speakers in Brussels are not Walloons.
The total number of native Dutch speakers is estimated to be about 6.23 million, concentrated in the northern Flanders region, while native French speakers number 3.32 million in Wallonia and an estimated 870,000 (or 85%) in the officially bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.—Strictly, the capital is the municipality Brussels, (City of) Brussels, though the Brussels-Capital Region might be intended because of its name and also its other municipalities housing institutions typical for a capital. The
Belgium has three official languages: Dutch, French and German. A number of non-official minority languages are spoken as well.
As no census exists, there are no official statistical data regarding the distribution or usage of Belgium's three official languages or their dialects. However, various criteria, including the language(s) of parents, of education, or the second-language status of foreign born, may provide suggested figures. An estimated 60% of the Belgian population are native speakers of Dutch (often referred to as Flemish), and 40% of the population speaks French natively. French-speaking Belgians are often referred to as Walloons, although the French speakers in Brussels are not Walloons.
The total number of native Dutch speakers is estimated to be about 6.23 million, concentrated in the northern Flanders region, while native French speakers number 3.32 million in Wallonia and an estimated 870,000 (or 85%) in the officially bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.—Strictly, the capital is the municipality Brussels, (City of) Brussels, though the Brussels-Capital Region might be intended because of its name and also its other municipalities housing institutions typical for a capital. The German-speaking Community
The German-speaking Community (german: links=no, Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft, or DG; french: links=no, Communauté germanophone; nl, links=no, Duitstalige Gemeenschap), since 2017 also known as East Belgium (german: links=no, Ostbelgien), is ...
is made up of 73,000 people in the east of the Walloon Region
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
; around 10,000 German and 60,000 Belgian nationals are speakers of German. Roughly 23,000 more German speakers live in municipalities near the official Community. The (originalversion in German language
(already) mentions 73,000 instead of 71,500 inhabitants. Both Belgian Dutch and Belgian French have Cognate, minor differences in vocabulary and semantic nuances from the varieties spoken respectively in the Netherlands and France. Many Flemish people still speak Dutch dialects, dialects of Dutch in their local environment. Walloon language, Walloon, considered either as a dialect of French or a distinct Romance language,According to Le Petit Larousse, Walloon is a dialect of the langue d'oïl. According to the ''Meyers grosses Taschenlexikon'' is now only understood and spoken occasionally, mostly by elderly people. Walloon is divided into four dialects, which along with those of Picard language, Picard,Among Belgium native German speakers many are familiar with the local dialect varieties of their region, that include dialects that spill over into neighboring Luxembourg and Germany. (Online version
Sixteenth edition
) are rarely used in public life and have largely been replaced by French.
Religion
 Since the country's independence, Roman Catholicism has had an important role in Belgium's politics.See for example s:en:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Belgium, Belgium entry of the Catholic Encyclopedia However Belgium is largely a secular country as the Constitution of Belgium, constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. During the reigns of Albert I of Belgium, Albert I and Baudouin I of Belgium, Baudouin, the Belgian royal family had a reputation of deeply rooted Catholicism.
Roman Catholicism has traditionally been Belgium's majority religion; being especially strong in Flanders. However, by 2009 Sunday church attendance was 5% for Belgium in total; 3% in Brussels, and 5.4% in Flanders. Church attendance in 2009 in Belgium was roughly half of the Sunday church attendance in 1998 (11% for the total of Belgium in 1998).Kerken lopen zeer geleidelijk helemaal leeg – Dutch news article describing church attendance in Flanders
Since the country's independence, Roman Catholicism has had an important role in Belgium's politics.See for example s:en:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Belgium, Belgium entry of the Catholic Encyclopedia However Belgium is largely a secular country as the Constitution of Belgium, constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. During the reigns of Albert I of Belgium, Albert I and Baudouin I of Belgium, Baudouin, the Belgian royal family had a reputation of deeply rooted Catholicism.
Roman Catholicism has traditionally been Belgium's majority religion; being especially strong in Flanders. However, by 2009 Sunday church attendance was 5% for Belgium in total; 3% in Brussels, and 5.4% in Flanders. Church attendance in 2009 in Belgium was roughly half of the Sunday church attendance in 1998 (11% for the total of Belgium in 1998).Kerken lopen zeer geleidelijk helemaal leeg – Dutch news article describing church attendance in Flanders. Standaard.be (25 November 2010). Retrieved 26 September 2011. Despite the drop in church attendance, Catholic identity nevertheless remains an important part of Belgium's culture. According to the Eurobarometer 2010,
Eurobarometer Biotechnology report 2010
'' p.381. 37% of Belgian citizens responded that they believe there is a God. 31% answered that they believe there is some sort of spirit or life-force. 27% answered that they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God, or life-force. 5% did not respond. According to the Eurobarometer 2015, 60.7% of the total population of Belgium adhered to Christianity, with Roman Catholicism being the largest denomination with 52.9%. Protestants comprised 2.1% and Orthodox Christians were the 1.6% of the total. Non-religious people comprised 32.0% of the population and were divided between atheists (14.9%) and agnostics (17.1%). A further 5.2% of the population was Muslim and 2.1% were believers in other religions. The same survey held in 2012 found that Christianity was the largest religion in Belgium, accounting for 65% of Belgians. Symbolically and materially, the Roman Catholic Church remains in a favorable position. Belgium officially recognizes three religions: Christianity (Catholic, Protestantism, Orthodox churches and Anglicanism), Islam and Judaism.
The Jewish Community of Antwerp, Belgium
. Beit Hatfutsot, the Museum of the Jewish People There are several Jewish newspapers and more than 45 active synagogues (30 of which are in Antwerp) in the country. A 2006 inquiry in Flanders, considered to be a more religious region than Wallonia, showed that 55% considered themselves religious and that 36% believed that God created the universe.Inquiry by 'Vepec', 'Vereniging voor Promotie en Communicatie' (Organization for Promotion and Communication), published in Knack magazine 2006 p. 14 [The Dutch language term 'gelovig' is in the text translated as 'religious'. More precisely it is a very common word for believing in particular in any kind of God in a monotheism, monotheistic sense or in some afterlife], or both. On the other hand, Wallonia has become one of Europe's most secular/least religious regions. Most of the French-speaking region's population does not consider religion an important part of their lives, and as much as 45% of the population identifies as irreligious. This is particularly the case in eastern Wallonia and areas along the French border.
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Brussels and Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
. The largest group of immigrants in Belgium are Moroccans, with 400,000 people. The Turks are the third largest group, and the second largest Muslim ethnic group, numbering 220,000.Voor het eerst meer Marokkaanse dan Italiaanse migranten. hbvl.be. 2007
Health
 The Belgians enjoy good health. According to 2012 estimates, the average life expectancy is 79.65 years. Since 1960, life expectancy has, in line with the European average, grown by two months per year. Death in Belgium is mainly due to heart and vascular disorders, neoplasms, disorders of the respiratory system and unnatural causes of death (accidents, suicide). Non-natural causes of death and cancer are the most common causes of death for females up to age 24 and males up to age 44.
Healthcare in Belgium is financed through both social security contributions and taxation. Health insurance is compulsory. Health care is delivered by a mixed public and private system of independent medical practitioners and public, university and semi-private hospitals. Health care service are payable by the patient and reimbursed later by health insurance institutions, but for ineligible categories (of patients and services) so-called 3rd party payment systems exist. The Belgian health care system is supervised and financed by the federal government, the Flemish and Walloon Regional governments; and the German Community also has (indirect) oversight and responsibilities.
For the first time in Belgian history, the first child was euthanized following the 2-year mark of the removal of the euthanization age restrictions. The child had been euthanized due to an incurable disease that was inflicted upon the child. Although there may have been some support for the euthanization there is a possibility of controversy due to the issue revolving around the subject of assisted suicide. Excluding assisted suicide, Belgium has the highest suicide rate in Western Europe and one of the suicide rate by country, highest suicide rates in the developed countries, developed world (exceeded only by Lithuania, South Korea, and Latvia).
The Belgians enjoy good health. According to 2012 estimates, the average life expectancy is 79.65 years. Since 1960, life expectancy has, in line with the European average, grown by two months per year. Death in Belgium is mainly due to heart and vascular disorders, neoplasms, disorders of the respiratory system and unnatural causes of death (accidents, suicide). Non-natural causes of death and cancer are the most common causes of death for females up to age 24 and males up to age 44.
Healthcare in Belgium is financed through both social security contributions and taxation. Health insurance is compulsory. Health care is delivered by a mixed public and private system of independent medical practitioners and public, university and semi-private hospitals. Health care service are payable by the patient and reimbursed later by health insurance institutions, but for ineligible categories (of patients and services) so-called 3rd party payment systems exist. The Belgian health care system is supervised and financed by the federal government, the Flemish and Walloon Regional governments; and the German Community also has (indirect) oversight and responsibilities.
For the first time in Belgian history, the first child was euthanized following the 2-year mark of the removal of the euthanization age restrictions. The child had been euthanized due to an incurable disease that was inflicted upon the child. Although there may have been some support for the euthanization there is a possibility of controversy due to the issue revolving around the subject of assisted suicide. Excluding assisted suicide, Belgium has the highest suicide rate in Western Europe and one of the suicide rate by country, highest suicide rates in the developed countries, developed world (exceeded only by Lithuania, South Korea, and Latvia).
Education
 Education is compulsory from 6 to 18 years of age for Belgians. Extracts
Education is compulsory from 6 to 18 years of age for Belgians. Extractsp. 97
p. 105
Among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD countries in 2002, Belgium had the third highest proportion of 18- to 21-year-olds enrolled in postsecondary education, at 42%. Though an estimated 99% of the adult population is literate, concern is rising over functional illiteracy. The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), coordinated by the OECD, currently ranks Belgium's education as the 19th best in the world, being significantly higher than the OECD average. Education being organized separately by each, the Flemish Community scores noticeably above the French and German-speaking Communities. Mirroring the dual structure of the 19th-century Belgian political landscape, characterized by the Liberal Party (Belgium), Liberal and the Catholic Party (Belgium), Catholic parties, the educational system is segregated within a secular and a religious segment. The secular branch of schooling is controlled by the communities, the provinces, or the municipalities, while religious, mainly Catholic school, Catholic branch education, is organized by religious authorities, although subsidized and supervised by the communities.
Culture
Despite its partition of Belgium, political and linguistic divisions, the region corresponding to today's Belgium has seen the flourishing of major artistic movements that have had tremendous influence on European art and culture. Nowadays, to a certain extent, cultural life is concentrated within each language Community, and a variety of barriers have made a shared cultural sphere less pronounced. Since the 1970s, there are no bilingual universities or colleges in the country except the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy and the Antwerp Maritime Academy.Fine arts
 Contributions to painting and architecture have been especially rich. The Mosan art, the Early Netherlandish painting, Early Netherlandish, the Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, Flemish Renaissance and Flemish Baroque painting, Baroque painting and major examples of Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Gothic architecture, Gothic, Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Baroque architectureSeveral examples of major architectural realizations in Belgium belong to UNESCO's World Heritage List: are milestones in the history of art. While the 15th century's art in the Low Countries is dominated by the religious paintings of Jan van Eyck and Rogier van der Weyden, the 16th century is characterized by a broader panel of styles such as Pieter Brueghel the Elder, Peter Breughel's landscape paintings and Lambert Lombard's representation of the antique. Though the Baroque style of Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck flourished in the early 17th century in the Southern Netherlands, it gradually declined thereafter.—A general presentation of the Flemish artistic movement with a list of its artists, linking to their biographies and artworks
During the 19th and 20th centuries many original romanticism, romantic, expressionism, expressionist and surrealism, surrealist Belgian painters emerged, including James Ensor and other artists belonging to the Les XX group, Constant Permeke, Paul Delvaux and René Magritte. The avant-garde COBRA (avant-garde movement), CoBrA movement appeared in the 1950s, while the sculptor Panamarenko remains a remarkable figure in contemporary art.—List of Belgian painters, linking to their biographies and artworks Multidisciplinary artists Jan Fabre, Wim Delvoye and the painter Luc Tuymans are other internationally renowned figures on the contemporary art scene.
Belgian contributions to architecture also continued into the 19th and 20th centuries, including the work of Victor Horta and Henry van de Velde, who were major initiators of the Art Nouveau style.Brussels, capital of Art Nouveau (page 1)
Contributions to painting and architecture have been especially rich. The Mosan art, the Early Netherlandish painting, Early Netherlandish, the Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, Flemish Renaissance and Flemish Baroque painting, Baroque painting and major examples of Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Gothic architecture, Gothic, Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Baroque architectureSeveral examples of major architectural realizations in Belgium belong to UNESCO's World Heritage List: are milestones in the history of art. While the 15th century's art in the Low Countries is dominated by the religious paintings of Jan van Eyck and Rogier van der Weyden, the 16th century is characterized by a broader panel of styles such as Pieter Brueghel the Elder, Peter Breughel's landscape paintings and Lambert Lombard's representation of the antique. Though the Baroque style of Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck flourished in the early 17th century in the Southern Netherlands, it gradually declined thereafter.—A general presentation of the Flemish artistic movement with a list of its artists, linking to their biographies and artworks
During the 19th and 20th centuries many original romanticism, romantic, expressionism, expressionist and surrealism, surrealist Belgian painters emerged, including James Ensor and other artists belonging to the Les XX group, Constant Permeke, Paul Delvaux and René Magritte. The avant-garde COBRA (avant-garde movement), CoBrA movement appeared in the 1950s, while the sculptor Panamarenko remains a remarkable figure in contemporary art.—List of Belgian painters, linking to their biographies and artworks Multidisciplinary artists Jan Fabre, Wim Delvoye and the painter Luc Tuymans are other internationally renowned figures on the contemporary art scene.
Belgian contributions to architecture also continued into the 19th and 20th centuries, including the work of Victor Horta and Henry van de Velde, who were major initiators of the Art Nouveau style.Brussels, capital of Art Nouveau (page 1), (for example) The vocal music of the Franco-Flemish School developed in the southern part of the Low Countries and was an important contribution to Renaissance culture. In the 19th and 20th centuries, there was an emergence of major violinists, such as Henri Vieuxtemps, Eugène Ysaÿe and Arthur Grumiaux, while Adolphe Sax invented the saxophone in 1846. The composer César Franck was born in Liège in 1822. Contemporary popular music in Belgium is also of repute. Jazz musicians Django Reinhardt and Toots Thielemans and singer Jacques Brel have achieved global fame. Nowadays, singer Stromae has been a musical revelation in Europe and beyond, having great success. In rock/pop music, Telex (band), Telex, Front 242, K's Choice, Hooverphonic, Zap Mama, Soulwax and Deus (band), dEUS are well known. In the heavy metal scene, bands like Machiavel (band), Machiavel, Channel Zero (band), Channel Zero and Enthroned have a worldwide fan-base.Two comprehensive discussions of rock and pop music in Belgium since the 1950s:
Belgium has produced several well-known Belgian literature, authors, including the poets Emile Verhaeren, Guido Gezelle, Robert Goffin and novelists Hendrik Conscience, Stijn Streuvels, Georges Simenon, Suzanne Lilar, Hugo Claus and Amélie Nothomb. The poet and playwright Maurice Maeterlinck won the Nobel Prize in literature in 1911. ''The Adventures of Tintin'' by Hergé is the best known of Franco-Belgian comics, but many other major authors, including Peyo (''The Smurfs''), André Franquin (''Gaston Lagaffe''), Dupa (''Cubitus''), Morris (comics), Morris (''Lucky Luke''), Greg (comics), Greg (''Achille Talon''), Lambil (''Les Tuniques Bleues''), Edgar P. Jacobs and Willy Vandersteen brought the Belgian cartoon strip industry a worldwide fame. Additionally, famous crime author Agatha Christie created the character Hercule Poirot, a Belgian detective, who has served as a protagonist in a number of her acclaimed mystery novels. Cinema of Belgium, Belgian cinema has brought a number of mainly Flemish novels to life on-screen. Other Belgian directors include André Delvaux, Stijn Coninx, Luc Dardenne, Luc and Jean-Pierre Dardenne; well-known actors include Jean-Claude Van Damme, Jan Decleir and Marie Gillain; and successful films include ''Bullhead (film), Bullhead, Man Bites Dog (film), Man Bites Dog'' and ''The Alzheimer Affair''.A review of the Belgian cinema till about 2000 can be found at Belgium is also home to a number of successful fashion designers :Belgian fashion designers.
Folklore
 Folklore plays a major role in Belgium's cultural life; the country has a comparatively high number of processions, cavalcades, parades, ommegangs, ducasses, kermesse (festival), kermesses, and other local festivals, nearly always with an originally religious or mythology of the Low Countries, mythological background. The three-day Carnival of Binche, near Mons, with its famous Gilles (men dressed in high, plumed hats and bright costumes) is held just before Lent (the 40 days between Ash Wednesday and Easter). Together with the 'Processional Giants and Dragons' of Ath, Brussels, Dendermonde, Mechelen and Mons, it is recognized by UNESCO as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity.
Other examples are the three-day Carnival of Aalst in February or March; the still very religious processions of procession of the Holy Blood, the Holy Blood taking place in
Folklore plays a major role in Belgium's cultural life; the country has a comparatively high number of processions, cavalcades, parades, ommegangs, ducasses, kermesse (festival), kermesses, and other local festivals, nearly always with an originally religious or mythology of the Low Countries, mythological background. The three-day Carnival of Binche, near Mons, with its famous Gilles (men dressed in high, plumed hats and bright costumes) is held just before Lent (the 40 days between Ash Wednesday and Easter). Together with the 'Processional Giants and Dragons' of Ath, Brussels, Dendermonde, Mechelen and Mons, it is recognized by UNESCO as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity.
Other examples are the three-day Carnival of Aalst in February or March; the still very religious processions of procession of the Holy Blood, the Holy Blood taking place in Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
in May, the Virga Jesse Basilica, Virga Jesse procession held every seven years in Hasselt, the Basilica of Our Lady of Hanswijk, annual procession of Hanswijk in Mechelen, the 15 August festivities in Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far fro ...
, and the Walloon festival in Namur
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration.
Na ...
. Originated in 1832 and revived in the 1960s, the Gentse Feesten (a music and theatre festival organised in Ghent around Belgian National Day, on 21 July) have become a modern tradition. Several of these festivals include sporting competitions, such as cycle sport, cycling, and many fall under the category of kermesses.
A major non-official holiday (which is however not an official public holiday) is Saint Nicholas Day (Dutch: ''Sinterklaas'', French: ''la Saint-Nicolas''), a festivity for children, and in Liège, for students. It takes place each year on 6 December and is a sort of early Christmas. On the evening of 5 December, before going to bed, children put their shoes by the hearth with water or wine and a carrot for Saint Nicholas's horse or donkey. According to tradition, Saint Nicholas comes at night and travels down the chimney. He then takes the food and water or wine, leaves presents, goes back up, feeds his horse or donkey, and continues on his course. He also knows whether children have been good or bad. This holiday is especially loved by children in Belgium and the Netherlands. Dutch immigrants imported the tradition into the United States, where Saint Nicholas is now known as Santa Claus.
Cuisine
 Belgium is famous for beer, chocolate, waffles and French fries. The national dishes are "Steak frites, steak and fries", and "moules-frites, mussels with fries". Republished from Republished from Many highly ranked Belgian restaurants can be found in the most influential restaurant guides, such as the Michelin Guide. One of the many beers with the high prestige is that of the Trappists, Trappist monks. Technically, it is an ale and traditionally each abbey's beer is served in its own glass (the forms, heights and widths are different). There are only eleven breweries (six of them are Belgian) that are allowed to brew Trappist beer.
Although Belgian gastronomy is connected to French cuisine, some recipes were reputedly invented there, such as French fries (despite the name, although their exact place of origin is uncertain), Flemish Stew (a beef stew with beer, mustard and bay laurel), speculaas (or ''speculoos'' in French, a sort of cinnamon and ginger-flavoured shortcrust pastry, shortcrust biscuit), Brussels waffles (and their variant, Liège waffles), waterzooi (a broth made with chicken or fish, cream and vegetables), endive with bechamel sauce, Brussels sprouts, Belgian pralines (Belgium has some of the most renowned chocolate houses), ''charcuterie'' (deli meats) and ''Paling in 't groen'' (river eels in a sauce of green herbs).
Brands of Belgian chocolate and pralines, like Côte d'Or (brand), Côte d'Or, Chocolatier Neuhaus, Neuhaus, Leonidas (chocolate maker), Leonidas and Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva are famous, as well as independent producers such as Burie and Del Rey in Antwerp and Mary's in Brussels. Belgium produces over Belgian beer, 1100 varieties of beer. The Trappist beer of the Westvleteren Brewery, Abbey of Westvleteren has repeatedly been rated the world's best beer.
The biggest brewer in the world by volume is Anheuser-Busch InBev, based in
Belgium is famous for beer, chocolate, waffles and French fries. The national dishes are "Steak frites, steak and fries", and "moules-frites, mussels with fries". Republished from Republished from Many highly ranked Belgian restaurants can be found in the most influential restaurant guides, such as the Michelin Guide. One of the many beers with the high prestige is that of the Trappists, Trappist monks. Technically, it is an ale and traditionally each abbey's beer is served in its own glass (the forms, heights and widths are different). There are only eleven breweries (six of them are Belgian) that are allowed to brew Trappist beer.
Although Belgian gastronomy is connected to French cuisine, some recipes were reputedly invented there, such as French fries (despite the name, although their exact place of origin is uncertain), Flemish Stew (a beef stew with beer, mustard and bay laurel), speculaas (or ''speculoos'' in French, a sort of cinnamon and ginger-flavoured shortcrust pastry, shortcrust biscuit), Brussels waffles (and their variant, Liège waffles), waterzooi (a broth made with chicken or fish, cream and vegetables), endive with bechamel sauce, Brussels sprouts, Belgian pralines (Belgium has some of the most renowned chocolate houses), ''charcuterie'' (deli meats) and ''Paling in 't groen'' (river eels in a sauce of green herbs).
Brands of Belgian chocolate and pralines, like Côte d'Or (brand), Côte d'Or, Chocolatier Neuhaus, Neuhaus, Leonidas (chocolate maker), Leonidas and Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva are famous, as well as independent producers such as Burie and Del Rey in Antwerp and Mary's in Brussels. Belgium produces over Belgian beer, 1100 varieties of beer. The Trappist beer of the Westvleteren Brewery, Abbey of Westvleteren has repeatedly been rated the world's best beer.
The biggest brewer in the world by volume is Anheuser-Busch InBev, based in Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic c ...
.
Sports
 Since the 1970s, sports clubs and federations are organized separately within each Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, language community. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
Association football is the most popular sport in both parts of Belgium; also very popular are cycling, tennis, swimming, judo and basketball. The Belgium national football team has been on the top spot of the FIFA World Rankings ever since September 2018 (it reached this rank for the first time in November 2015). Since the 1990s, the team has been the world's number one for the most years in history, only behind the records of Brazil National Football Team, Brazil and Spain National Football Team, Spain.
Since the 1970s, sports clubs and federations are organized separately within each Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, language community. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
Association football is the most popular sport in both parts of Belgium; also very popular are cycling, tennis, swimming, judo and basketball. The Belgium national football team has been on the top spot of the FIFA World Rankings ever since September 2018 (it reached this rank for the first time in November 2015). Since the 1990s, the team has been the world's number one for the most years in history, only behind the records of Brazil National Football Team, Brazil and Spain National Football Team, Spain.on the FIFA website The team's golden generations with the world class players in the squad, namely Eden Hazard, Kevin De Bruyne, Jean-Marie Pfaff, Jan Ceulemans achieved the bronze medals at 2018 FIFA World Cup, World Cup 2018, and silver medals at UEFA Euro 1980, Euro 1980. Belgium hosted the UEFA Euro 1972, Euro 1972, and co-hosted the UEFA Euro 2000, Euro 2000 with the Netherlands. Belgians hold List of Tour de France winners, the most Tour de France victories of any country except France. They have also the most victories on the UCI Road World Championships. With five victories in the Tour de France and numerous other cycling records, Belgian cyclist Eddy Merckx is regarded as one of the greatest cyclists of all time. Philippe Gilbert is the 2012 world champion. Another well-known Belgian cyclist is Tom Boonen. Kim Clijsters and Justine Henin both were WTA Awards, Player of the Year in the Women's Tennis Association as they were ranked the number one female tennis player. The Spa-Francorchamps motor-racing circuit hosts the Formula One World Championship Belgian Grand Prix. The Belgian driver, Jacky Ickx, won eight Grands Prix and six 24 Hours of Le Mans and finished twice as runner-up in the Formula One World Championship. Belgium also has a strong reputation in, motocross with the riders Joël Robert, Roger De Coster, Georges Jobé, Eric Geboers and Stefan Everts, among others. Sporting events annually held in Belgium include the Memorial Van Damme athletics competition, the Belgian Grand Prix Formula One, and a number of classic cycle races such as the Tour of Flanders and Liège–Bastogne–Liège. The 1920 Summer Olympics were held in Antwerp. The 1977 European Basketball Championship was held in
Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far fro ...
and Ostend.
See also
* Index of Belgium-related articles * Outline of BelgiumFootnotes
References
Online sources
* * (mentioning other original sources) *Belgium
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved on 7 June 2007. * * * * * * * —Reflections on nations and nation-state developments regarding Belgium
Bibliography
* * *[Also editions [1913], London, ; (1921) D. Unwin and Co., New York also published (1921) as ''Belgium from the Roman invasion to the present day'', The Story of the nations, 67, T. Fisher Unwin, London, ] * Facsimile reprint of a 1902 edition by the author, London
Facsimile reprint of a 1909 edition by the author, London * * (Several editions in English, incl. (1997) 7th ed.)
External links
Government
Official site of the Belgian monarchy
Official site of the Belgian federal government
General
Belgium
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Belgium
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
Belgium
information from the United States Department of State *
Portals to the World
from the United States Library of Congress
Belgium profile
from the BBC News
FAO Country Profiles: Belgium
Statistical Profile of Belgium at the Association of Religion Data Archives
*
Key Development Forecasts for Belgium
from International Futures
Official Site of the Belgian Tourist Office in the Americas and GlobeScope
{{Authority control Belgium Benelux Dutch-speaking countries and territories Federal monarchies French-speaking countries and territories German-speaking countries and territories Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of NATO Member states of the Dutch Language Union Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Member states of the Council of Europe States and territories established in 1830 Northwestern European countries Countries in Europe, Geographical articles missing image alternative text Kingdoms Countries of Europe with multiple official languages OECD members