Beersheba Peak on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beersheba or Beer Sheva, officially Be'er-Sheva ( he, ūæų░ų╝ūÉųĄū© ū®ųČūüūæųĘūó, ''B╔Ö╩Š─ōr ┼Āeva╩┐'', ; ar, ž©ž”ž▒ ž¦┘äž│ž©ž╣, Bi╩Šr as-Sab╩┐, Well of the Oath or Well of the Seven), is the largest city in the



 The present-day city was built to serve as an administrative center by the Ottoman administration for the benefit of the Bedouin at the outset of the 20th century and was given the name of ''Bir al-Sabi'' (well of the seven). Until
The present-day city was built to serve as an administrative center by the Ottoman administration for the benefit of the Bedouin at the outset of the 20th century and was given the name of ''Bir al-Sabi'' (well of the seven). Until
online
(pdf, 28 MB) The 1945 village survey conducted by the Palestine Mandate government found 5,360 Muslims, 200 Christians and 10 others (total 5,570).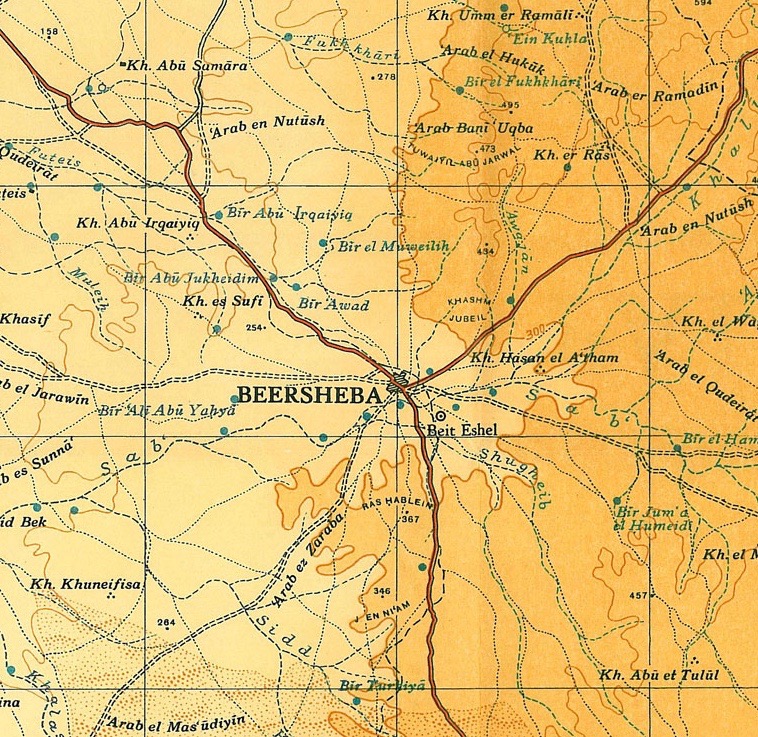

File:Beersheba from the air.jpg, Beersheba 1948
File:Beersheba i.jpg, Beersheba police station. 1948. Original building Ottoman with British Mandate addition.
File:Beersheba ii.jpg, Beersheba mosque. 1948
File:Beersheva mosque.jpg, A mosque in Be'ersheva photographed during


 In 1947, the
In 1947, the
A/364, Add. 1
. UNGA Resolution 181 (Nov 27, 1947
. See boundaries :File:UN Palestine Partition Versions 1947.jpg, here. However, when the UN's Ad Hoc Committee revised the plan, they moved Beersheva to the Arab state on account of it being primarily Arab. Egyptian forces had been stationed at Beersheva since May 1948. It was
''Cities of the Middle East and North Africa: A Historical Encyclopedia,''
ABC-CLIO, 2007 p.80. At 4:00 am on October 21, the 8th Brigade's 89th
''Contested Holy Places in IsraelŌĆōPalestine: Sharing and Conflict Resolution''
, Blueprint Negev

 Four new shopping malls were also built. Among them is Kanyon Beersheba, a ecologically planned mall with pools for collecting rainwater and lighting generated by solar panels on the roof. It will be situated next to an 8,000-meter park with bicycle paths. In addition, the first ever farmer's market in Israel was established as an enclosed, circular complex with 400 spaces for vendors surrounded by parks and greenery.
A new central bus station was built in the city. The station has a glass-enclosed complex also containing shops and caf├®s.
Some $10.5 million was also invested in renovating Beersheba's Old City, preserving historical buildings and upgrading infrastructure. The Turkish Quarter was also redeveloped with newly cobbled streets, widened sidewalks, and the restoration of Turkish homes into areas for dining and shopping.
In 2011, city hall announced plans to turn Beersheba into the "water city" of Israel. One of the projects, "Beersheva beach," is a 7-Dunam#Syria, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon and Turkey, dunam fountain opposite city hall. Other projects included fountains near the Soroka Medical Center and in front of the Shamoon College of Engineering.
In the 1990s, as skyscrapers began to appear in Israel, the construction of high-rise buildings began in Beersheba. Today, downtown Beersheba has been described as a "clean, compact, and somewhat sterile-looking collection of high-rise office and residential towers." The city's tallest building is Rambam Square 2, a 32-story apartment building. Many additional high-rise buildings are planned or are under construction, including skyscrapers. There are further plans to build luxury residential towers in the city.
In December 2012, a plan to build 16,000 new housing units in the Ramot Gimel neighborhood was scrapped in favor of creating a new urban forest, which spans and serves as the area's "green lung", as part of the plans to develop a "green band" around the city. The forest includes designated picnic areas, biking trails, and walking trails. According to Mayor Ruvik Danilovich, Beersheba still has an abundance of open, underdeveloped spaces that can be used for urban development.
In 2017, a new urban building plan was approved for the city, designed to raise the city's population to 340,000 by 2030. Under the plan, 13,000 more housing units will be built, along with industrial and business developments occupying a total of four million square meters. A second public hospital is also planned. Planning for a light rail system also began. In 2019, the construction of a new public hospital, which will be named after Shimon Peres, was approved. The hospital will be a complex that will feature 1,900 beds, commerce, hotel, alternative medicine, and paramedical services, and research centers, with the possibility of apartment units for medical faculty employees, students, and senior housing. It will be linked to the rest of the city by a light rail system.
Four new shopping malls were also built. Among them is Kanyon Beersheba, a ecologically planned mall with pools for collecting rainwater and lighting generated by solar panels on the roof. It will be situated next to an 8,000-meter park with bicycle paths. In addition, the first ever farmer's market in Israel was established as an enclosed, circular complex with 400 spaces for vendors surrounded by parks and greenery.
A new central bus station was built in the city. The station has a glass-enclosed complex also containing shops and caf├®s.
Some $10.5 million was also invested in renovating Beersheba's Old City, preserving historical buildings and upgrading infrastructure. The Turkish Quarter was also redeveloped with newly cobbled streets, widened sidewalks, and the restoration of Turkish homes into areas for dining and shopping.
In 2011, city hall announced plans to turn Beersheba into the "water city" of Israel. One of the projects, "Beersheva beach," is a 7-Dunam#Syria, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon and Turkey, dunam fountain opposite city hall. Other projects included fountains near the Soroka Medical Center and in front of the Shamoon College of Engineering.
In the 1990s, as skyscrapers began to appear in Israel, the construction of high-rise buildings began in Beersheba. Today, downtown Beersheba has been described as a "clean, compact, and somewhat sterile-looking collection of high-rise office and residential towers." The city's tallest building is Rambam Square 2, a 32-story apartment building. Many additional high-rise buildings are planned or are under construction, including skyscrapers. There are further plans to build luxury residential towers in the city.
In December 2012, a plan to build 16,000 new housing units in the Ramot Gimel neighborhood was scrapped in favor of creating a new urban forest, which spans and serves as the area's "green lung", as part of the plans to develop a "green band" around the city. The forest includes designated picnic areas, biking trails, and walking trails. According to Mayor Ruvik Danilovich, Beersheba still has an abundance of open, underdeveloped spaces that can be used for urban development.
In 2017, a new urban building plan was approved for the city, designed to raise the city's population to 340,000 by 2030. Under the plan, 13,000 more housing units will be built, along with industrial and business developments occupying a total of four million square meters. A second public hospital is also planned. Planning for a light rail system also began. In 2019, the construction of a new public hospital, which will be named after Shimon Peres, was approved. The hospital will be a complex that will feature 1,900 beds, commerce, hotel, alternative medicine, and paramedical services, and research centers, with the possibility of apartment units for medical faculty employees, students, and senior housing. It will be linked to the rest of the city by a light rail system.
 Since 1950, Beersheba has changed its municipal emblem several times.
The 1950 emblem, designed by Abraham Khalili, featured a tamarix tree, a factory and water flowing from a pipeline. In 1972 the emblem was modernized with the symbolic representation of the Twelve Tribes and a tower. Words from the Bible are inscribed: Abraham "planted a tamarix tree in Beersheba." (Genesis 21:33) Since 2012, it has incorporated the number seven as part of the city rebranding.
Since 1950, Beersheba has changed its municipal emblem several times.
The 1950 emblem, designed by Abraham Khalili, featured a tamarix tree, a factory and water flowing from a pipeline. In 1972 the emblem was modernized with the symbolic representation of the Twelve Tribes and a tower. Words from the Bible are inscribed: Abraham "planted a tamarix tree in Beersheba." (Genesis 21:33) Since 2012, it has incorporated the number seven as part of the city rebranding.
 Beersheba is located on the northern edge of the Negev desert south-east of Tel Aviv and south-west of Jerusalem. The city is located on the main route from the center and north of the country to Eilat in the far south. The Beersheba Valley has been populated for thousands of years, as it has available water, which flows from the Hebron hills in the winter and is stored underground in vast quantities. The main river in Beersheba is ''Nahal Beersheva'', a ''wadi'' that floods in the winter. The Kovshim and Katef streams are other important wadis that pass through the city. Beersheba is surrounded by a number of satellite towns, including Omer, Israel, Omer, Lehavim, and Meitar, and the Bedouin localities of Rahat, Tel as-Sabi, and Lakiya.
Just north west of the city (near Ramot neighborhood ) is a region called Goral hills (heb:ūÆūæūóūĢū¬ ūÆūĢū©ū£ lit: hills of fate), the area has hills with up to above sea level and low as above sea level. Due to heavy construction the flora unique to the area is endangered.
North east of the city (north to the Neve Menahem neighborhood) there are Loess plains and dry river bands.
Beersheba is located on the northern edge of the Negev desert south-east of Tel Aviv and south-west of Jerusalem. The city is located on the main route from the center and north of the country to Eilat in the far south. The Beersheba Valley has been populated for thousands of years, as it has available water, which flows from the Hebron hills in the winter and is stored underground in vast quantities. The main river in Beersheba is ''Nahal Beersheva'', a ''wadi'' that floods in the winter. The Kovshim and Katef streams are other important wadis that pass through the city. Beersheba is surrounded by a number of satellite towns, including Omer, Israel, Omer, Lehavim, and Meitar, and the Bedouin localities of Rahat, Tel as-Sabi, and Lakiya.
Just north west of the city (near Ramot neighborhood ) is a region called Goral hills (heb:ūÆūæūóūĢū¬ ūÆūĢū©ū£ lit: hills of fate), the area has hills with up to above sea level and low as above sea level. Due to heavy construction the flora unique to the area is endangered.
North east of the city (north to the Neve Menahem neighborhood) there are Loess plains and dry river bands.
 The largest employers in Beersheba are Soroka Medical Center, the municipality,
The largest employers in Beersheba are Soroka Medical Center, the municipality,
 The mayor of Beersheba is Ruvik Danilovich, who was deputy mayor under Yaakov Turner.
The mayor of Beersheba is Ruvik Danilovich, who was deputy mayor under Yaakov Turner.
 According to the Municipality CBS, in 2022, Beersheba has a ca.8,975 preschoolers in ca.300 preschools & kindergartens. A total of 99 schools teaching a student population of ca.45,291: 60 elementary schools with an enrollment of 19,617 (ca.3,200 of whom are entering the 1st grade), and 39 high schools with an enrollment of 16,699. Of Beersheba's 12th graders, 90% earned a Bagrut matriculation certificate in 2022. The city also has several private schools and Yeshiva, yeshivot in the religious sector with 3,000 or more students.
According to the Municipality CBS, in 2022, Beersheba has a ca.8,975 preschoolers in ca.300 preschools & kindergartens. A total of 99 schools teaching a student population of ca.45,291: 60 elementary schools with an enrollment of 19,617 (ca.3,200 of whom are entering the 1st grade), and 39 high schools with an enrollment of 16,699. Of Beersheba's 12th graders, 90% earned a Bagrut matriculation certificate in 2022. The city also has several private schools and Yeshiva, yeshivot in the religious sector with 3,000 or more students.
 Beersheba is home to one of Israel's major universities,
Beersheba is home to one of Israel's major universities,
"Magic Carpet: The Carpet-Style Patio Homes of Be'er Sheva"], ''Haaretz'' ''Mishol Girit,'' a neighborhood built in the late 1950s, was the first attempt to create an alternative to the standard public housing projects in Israel. ''Hashatiah'' (literally, "the carpet"), also known as (the model neighborhood), was hailed by architects around the world. Today, Beersheba is divided into seventeen residential neighborhoods in addition to the Old City and Ramot, an umbrella neighborhood of four sub-districts. Many of the neighbourhoods are named after letters of the Hebrew alphabet, which also have numerical value, but descriptive place names have been given to some of the newer neighborhoods.
 In 1953, Cinema Keren, the Negev's first movie theater, opened in Beersheba. It was built by the Histadrut and had seating for 1,200 people.
Beersheba is the home base of the Israel Sinfonietta, founded in 1973. Over the years, the Sinfonietta has developed a broad repertoire of symphonic works, concerti for solo instruments and large choral productions, among them Handel's ''Israel in Egypt,'' masses by Schubert and Mozart, Rossini's "Stabat Mater" and Vivaldi's "Gloria." World-famous artists have appeared as soloists with the Sinfonietta, including Pinchas Zukerman, Jean-Pierre Rampal, Shlomo Mintz, Gary Karr, and Paul Tortelier. In the 1970s, a memorial commemorating fallen Israeli soldiers designed by the sculptor Dani Karavan, Danny Karavan was erected on a hill north-east of the city. The Beersheba Theater opened in 1973. The Light Opera Group of the Negev, established in 1980, performs musicals in English every year.
Landmarks in the city include "Abraham's well", a well dating to at least the 12th century CE (now inside a visitors center), and the old Turkish railway station, now the focus of development plans. The Artists House of the Negev, in a Mandate-era building, showcases artwork connected in some way to the Negev.
The Negev Museum of Art reopened in 2004 in the Ottoman Governor's House, and an art and media center for young people was established in the Old City.
In 2009, a new tourist and Visitor center, information center, Gateway to the Negev, was built.
In 1953, Cinema Keren, the Negev's first movie theater, opened in Beersheba. It was built by the Histadrut and had seating for 1,200 people.
Beersheba is the home base of the Israel Sinfonietta, founded in 1973. Over the years, the Sinfonietta has developed a broad repertoire of symphonic works, concerti for solo instruments and large choral productions, among them Handel's ''Israel in Egypt,'' masses by Schubert and Mozart, Rossini's "Stabat Mater" and Vivaldi's "Gloria." World-famous artists have appeared as soloists with the Sinfonietta, including Pinchas Zukerman, Jean-Pierre Rampal, Shlomo Mintz, Gary Karr, and Paul Tortelier. In the 1970s, a memorial commemorating fallen Israeli soldiers designed by the sculptor Dani Karavan, Danny Karavan was erected on a hill north-east of the city. The Beersheba Theater opened in 1973. The Light Opera Group of the Negev, established in 1980, performs musicals in English every year.
Landmarks in the city include "Abraham's well", a well dating to at least the 12th century CE (now inside a visitors center), and the old Turkish railway station, now the focus of development plans. The Artists House of the Negev, in a Mandate-era building, showcases artwork connected in some way to the Negev.
The Negev Museum of Art reopened in 2004 in the Ottoman Governor's House, and an art and media center for young people was established in the Old City.
In 2009, a new tourist and Visitor center, information center, Gateway to the Negev, was built.
 In 1906, during the Ottoman era, the Great Mosque of Beersheba was built with donations collected from the Bedouin residents in the Negev. It was used actively as a mosque until the city fell to Israeli forces in 1948. The mosque was used until 1953 as the city's courthouse. From then until the 1990s, when it was closed for renovations, the building housed an archeological museum, which the city intended to turn into the archeological branch of the Negev Museum. In 2011, however, the Supreme Court of Israel, sitting as the Supreme Court of Israel#High Court of Justice, High Court of Justice, ordered the property to be turned into a museum of Islam without reverting to a place of worship.
In 1906, during the Ottoman era, the Great Mosque of Beersheba was built with donations collected from the Bedouin residents in the Negev. It was used actively as a mosque until the city fell to Israeli forces in 1948. The mosque was used until 1953 as the city's courthouse. From then until the 1990s, when it was closed for renovations, the building housed an archeological museum, which the city intended to turn into the archeological branch of the Negev Museum. In 2011, however, the Supreme Court of Israel, sitting as the Supreme Court of Israel#High Court of Justice, High Court of Justice, ordered the property to be turned into a museum of Islam without reverting to a place of worship.
 Israel Railways operates two stations in the city that form part of the railway to Beersheba: the old Be'er Sheva North Railway Station, Be'er Sheva North University station, adjacent to Ben Gurion University and Soroka Medical Center, and the new Be'er Sheva Center Railway Station, Be'er Sheva Central station, adjacent to the central bus station. Between the two stations, the railway splits into two, and also continues to Dimona and Dead Sea, the Dead Sea factories. An extension is planned to Eilat and Arad, Israel, Arad.
The Be'er Sheva North University station is the terminus of the line to Dimona. All stations of Israel Railways can be accessed from Beersheba using Interchange station, transfer stations in Tel Aviv and Lod. Until 2012, the Railway to Beersheba, railway line to Beersheba used a slow single-track configuration with sharp curves and many level crossings which limited train speed. Between 2004 and 2012 the line was double tracked and rebuilt using an improved alignment and all its level crossings were grade separation, grade separated. The rebuilding effort cost Israeli new shekel, NIS 2.8 billion and significantly reduced the travel time and greatly increased the train frequency to and from Tel Aviv and Kiryat Motzkin to Beersheba. In addition, Beersheba will be linked to Tel Aviv and Eilat by a new passenger and freight High speed railway to Eilat, high-speed railway system.
There have been plans for a light rail system in Beersheba for many years, and a light rail system appears in the master plan for the city. An agreement was signed for the construction of a light rail system in 1998, but was not implemented. In 2008, the Ministry of Finance (Israel), Israeli Finance Ministry contemplated freezing the Tel Aviv Light Rail project and building a light rail system in Beersheba instead, but that did not happen. In 2014, mayor Ruvik Danilovich announced that the light rail system will be built in the city. In 2017, the Ministry of Transport gave the Beersheba municipality approval to proceed with preliminary planning on a light rail system.
Israel Railways operates two stations in the city that form part of the railway to Beersheba: the old Be'er Sheva North Railway Station, Be'er Sheva North University station, adjacent to Ben Gurion University and Soroka Medical Center, and the new Be'er Sheva Center Railway Station, Be'er Sheva Central station, adjacent to the central bus station. Between the two stations, the railway splits into two, and also continues to Dimona and Dead Sea, the Dead Sea factories. An extension is planned to Eilat and Arad, Israel, Arad.
The Be'er Sheva North University station is the terminus of the line to Dimona. All stations of Israel Railways can be accessed from Beersheba using Interchange station, transfer stations in Tel Aviv and Lod. Until 2012, the Railway to Beersheba, railway line to Beersheba used a slow single-track configuration with sharp curves and many level crossings which limited train speed. Between 2004 and 2012 the line was double tracked and rebuilt using an improved alignment and all its level crossings were grade separation, grade separated. The rebuilding effort cost Israeli new shekel, NIS 2.8 billion and significantly reduced the travel time and greatly increased the train frequency to and from Tel Aviv and Kiryat Motzkin to Beersheba. In addition, Beersheba will be linked to Tel Aviv and Eilat by a new passenger and freight High speed railway to Eilat, high-speed railway system.
There have been plans for a light rail system in Beersheba for many years, and a light rail system appears in the master plan for the city. An agreement was signed for the construction of a light rail system in 1998, but was not implemented. In 2008, the Ministry of Finance (Israel), Israeli Finance Ministry contemplated freezing the Tel Aviv Light Rail project and building a light rail system in Beersheba instead, but that did not happen. In 2014, mayor Ruvik Danilovich announced that the light rail system will be built in the city. In 2017, the Ministry of Transport gave the Beersheba municipality approval to proceed with preliminary planning on a light rail system.
 In Be'er Sheva there are over 250 roundabouts, giving the city its nickname of "Roundabout Capital of Israel". Many roundabouts, part of Be'er-Sheva's urban oasis project, include fountains, landscaping and sculptures by well-known artists (such as Menashe Kadishman's The Horse Circle and Jeremy Langford (sculptor), Jeremy Langford's The Drip Circle). Some commemorate famous people and international and local organizations, or mark important events. Some are named after the twin cities of Beer Sheva.
Well-known roundabouts are: Ilan Ramon Circle, McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, Phantom Circle near the Air Force Technical School, Champions Square near Terner Stadium and Conch Arena, Chess Circle, Harp Circle near the Municipal Conservatory and the Be'er-Sheva Performing Arts Center, College Circle, Ben Gurion Circle, Light Circle, Freemasons Circle, Shofar, Shofarot Circle, World Trade Center (1973ŌĆō2001), Twin Towers Circle.
In Be'er Sheva there are over 250 roundabouts, giving the city its nickname of "Roundabout Capital of Israel". Many roundabouts, part of Be'er-Sheva's urban oasis project, include fountains, landscaping and sculptures by well-known artists (such as Menashe Kadishman's The Horse Circle and Jeremy Langford (sculptor), Jeremy Langford's The Drip Circle). Some commemorate famous people and international and local organizations, or mark important events. Some are named after the twin cities of Beer Sheva.
Well-known roundabouts are: Ilan Ramon Circle, McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, Phantom Circle near the Air Force Technical School, Champions Square near Terner Stadium and Conch Arena, Chess Circle, Harp Circle near the Municipal Conservatory and the Be'er-Sheva Performing Arts Center, College Circle, Ben Gurion Circle, Light Circle, Freemasons Circle, Shofar, Shofarot Circle, World Trade Center (1973ŌĆō2001), Twin Towers Circle.
 * Orna Banai (born 1966), actress, comedian, and entertainer
* Elyaniv Barda (born 1981), footballer
* Zehava Ben (born 1968), singer
* Avishay Braverman (born 1948), professor and politician, president of the
* Orna Banai (born 1966), actress, comedian, and entertainer
* Elyaniv Barda (born 1981), footballer
* Zehava Ben (born 1968), singer
* Avishay Braverman (born 1948), professor and politician, president of the
Be'er Sheva Municipal WebsiteMy Be'er-Sheva
* Battle of Beersheba (First World War) * Beer Sheva Park (Seattle), Beer Sheva Park, Seattle * :File:BeershevaRegion1940s.jpg, Map of Beersheba and surrounds in the 1940s and 1950s
Beersheba City Council
Selection of photos from Beer Sheva
from flickr
Ben-Gurion University
The city of Beersheba: a tourist's guide
nbsp;ŌĆō Historical article from the Catholic Encyclopedia, Catholic Encyclopaedia
Light Horse charges again
Article written by Martin Chulov, published in The Australian, November 1, 2007, the descendants of the Australian light-horsemen rode into the centre of Beersheva, re-enacting the gallant gallop of October 31, 1917
Expansion and architecture of Beersheva in the 1960s and 1970s
Blueprint for Beersheba
* * Tsagai Asamain
Be'er Sheva-Compound C:Conservation measures during the excavationIsrael Antiquities Authority Site
ŌĆ
Conservation Department
* Yardena Etgar and Ofer Cohen
Tel BeŌĆÖer Sheva: The Underground Water Reservoir SystemIsrael Antiquities Authority Site
ŌĆ
Conservation Department
* Shauli Sela and Fuad Abu-Taa
The Turkish Mosque and the Governor's House: Conservation of the stone and plasterIsrael Antiquities Authority Site
ŌĆ
Conservation Department
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 24
IAA
:commons:File:Survey_of_Western_Palestine_1880.24.jpg, Wikimedia commons
BeerSheva.city
the first French portal of the city {{Authority control Beersheba, Cities in Southern District (Israel) History of Israel by location, Beersheba Chess in Israel Hebrew Bible cities Torah cities Establishments in the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy) 1900s establishments in Ottoman Syria
Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, ūöųĘūĀųČų╝ūÆųČūæ, hanNeg├®v; ar, ┘▒┘ä┘å┘Ä┘æ┘é┘Äž©, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
desert of southern Israel
Israel (; he, ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, ; ar, žź┘Éž│┘Æž▒┘Äž¦ž”┘É┘Ŗ┘ä, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, ū×ų░ūōų┤ūÖūĀųĘū¬ ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, label=none, translit=Med─½nat Y─½sr─ü╩Š─ōl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. Often referred to as the "Capital of the Negev", it is the centre of the fourth-most populous metropolitan area in Israel, the eighth-most populous Israeli city with a population of , and the second-largest city in area (after Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, ūÖų░ū©ūĢų╝ū®ųĖūüū£ųĘūÖų┤ūØ ; ar, ž¦┘ä┘é┘Åž»ž│ ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, ß╝╣╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽģŽā╬▒╬╗╬«╬╝/ß╝Ė╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽāŽī╬╗Žģ╬╝╬▒, HierousalßĖŚm/Hieros├│luma; hy, įĄųĆšĖųéšĮšĪš▓šźš┤, Erusa┼é─ōm. i ...
), with a total area of 117,500 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; tr, d├Čn├╝m; he, ūōūĢūĀūØ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount ...
s.
The Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
site of Beersheba is Tel Be'er Sheva
Tel Sheva ( he, ū¬ū£ ū®ūæūó, translit=) or Tel Be'er Sheva (), also known as Tell es-Seba (), is an archaeological site in the Southern District of Israel, believed to be the site of the ancient biblical town of Beer-sheba. The site lies east o ...
, lying some 4 km distant from the modern city, which was established at the start of the 20th century by the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanl─▒ T├╝rkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302ŌĆō1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
. The city was captured by the British-led Australian Light Horse
Australian Light Horse were mounted troops with characteristics of both cavalry and mounted infantry, who served in the Second Boer War and World War I. During the inter-war years, a number of regiments were raised as part of Australia's part-ti ...
in the Battle of Beersheba during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
The population of the town was completely changed in 1948ŌĆō49. ''Bir Seb'a'' ( ar, ž©ž”ž▒ ž¦┘äž│ž©ž╣), as it was then known, had been almost entirely Muslim and Christian, and was designated to be part of the Arab state in the 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Re ...
. Following the declaration of Israel's independence, the Egyptian army amassed its forces in Beersheba as a strategic and logistical base. In October 1948 it was captured by the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, ū”ų░ūæųĖūÉ ūöųĘūöų▓ūÆųĖūĀųĖūö ū£ų░ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£ , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the Israel, State of Israel. It consists of three servic ...
, and the Arab population was expelled. Today, the population is almost exclusively Jewish, with a large portion of the population made up of the descendants of Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djud├Łos Sefard├Łes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: S╔Öp╠ä─üradd├«m, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Jud├Łos sefard├Łes (or ), pt, Judeus sefar ...
and Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews ( he, ūÖūöūĢūōūÖ ūöū×ų┤ū¢ų░ū©ųĖūŚ), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained i ...
who immigrated from Arab countries after 1948, as well as smaller communities of Bene Israel
The Bene Israel (), also referred to as the "Shanivar Teli" () or " Native Jew" caste, are a community of Jews in India. It has been suggested that they are the descendants of one of the Ten Lost Tribes via their ancestors who had settled there ce ...
and Cochin Jews
Cochin Jews (also known as Malabar Jews or Kochinim, from ) are the oldest group of Jews in India, with roots that are claimed to date back to the time of King Solomon. The Cochin Jews settled in the Kingdom of Cochin in South India, now pa ...
from India. Second and third waves of immigration have taken place since 1990, bringing Russian-speaking Ashkenazi Jewish
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōųĄūÖ ūÉųĘū®ų░ūüūøų░ų╝ūĀųĘū¢, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, ūÉųĘū®ūøų╝ūĀū¢ūÖū®ūó ūÖūÖų┤ūōū¤, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
immigrants from the former Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, as well as Beta Israel
The Beta Israel ( he, ūæųĄų╝ūÖū¬ųČūÉ ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, ''B─ōte╩Š Y─½sr─ü╩Š─ōl''; gez, ßēżßē░ ßŖźßłĄßł½ßŖżßłŹ, , modern ''B─ōte 'Isr─ü'─ōl'', EAE: "Bet├ż ŲÄsra╩Šel", "House of Israel" or "Community of Israel"), also known as Ethiopian Jews ...
immigrants from Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ßŖóßēĄßŗ«ßīĄßŗ½, ├Źtiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. The Soviet immigrants have made the game of chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to disti ...
a major sport in Beersheba, and it is now Israel's national chess center, with more chess grandmasters
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black in chess, White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's King (chess), king. It is sometimes called interna ...
per capita than any other city in the world.
Beersheba is home to Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) ( he, ūÉūĢūĀūÖūæū©ūĪūÖūśū¬ ūæū¤-ūÆūĢū©ūÖūĢū¤ ūæūĀūÆūæ, ''Universitat Ben-Guriyon baNegev'') is a public research university in Beersheba, Israel. Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has five campuses: the ...
. This city also serves as a center for Israel's high-tech and developing technology industry.
The city has constructed over 250 roundabouts, earning its moniker as the "Roundabouts Capital of the Israel" and apparently the largest number in the world.
Etymology
TheBook of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: ūæų░ų╝ū©ųĄūÉū®ų┤ūüūÖū¬ ''B╔Öre╩Š┼Ī─½t'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning") ...
gives two etymologies
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) ŌĆō p. 633 "Etymology /╦ī╔øt╔¬╦łm╔Æl╔Öd╩Æi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and ...
for the name ''Be'er Sheba''. Genesis 21:28-31 relates:Then Abraham set seven ewes apart. AndAbimelech Abimelech (also spelled Abimelek or Avimelech; ) was the generic name given to all Philistine kings in the Hebrew Bible from the time of Abraham through King David. In the Book of Judges, Abimelech, son of Gideon, of the Tribe of Manasseh, is ...said to Abraham, "What mean these seven ewes, which you have set apart? Andbraham Braham may refer to: * Braham (surname) * Braham, Minnesota, a city in the United States *Braham Murray Braham Sydney Murray, OBE (12 February 1943 ŌĆō 25 July 2018) was an English theatre director. In 1976, he was one of five founding Artistic ...said, "That you are to take these seven (''sheba'') ewes from me, to be for me a witness that I have dug this well (''bŪØ'er'')." Therefore the name of that place was Be'er Sheba, for there the two of them had sworn (''nishbŪØ'u'').
Genesis 26
Toledot, Toldot, Toldos, or Toldoth (ŌĆöHebrew for "generations" or "descendants," the second word and the first distinctive word in the ''parashah'') is the sixth weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. T ...
relates:And Isaac redug the wells which had been dug in the days of Abraham his father, and which the Philistines had sealed after the death of Abraham, and he used the same names as had his father . . . And they arose in the morning, and they swore (''wa-yishabŪØ'u'') each to his fellow, and Isaac sent them off, and they departed him in peace. On that same day, Isaac's men came to him to tell him of the well which they had dug, and they said to him, "We found water." And he called it ''Shib'a'' ("seven" normally, possibly "oath" or a proper noun); therefore the name of the city is Be'er Sheba to this day.The original name could therefore relate to the oath of
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
and Abimelech
Abimelech (also spelled Abimelek or Avimelech; ) was the generic name given to all Philistine kings in the Hebrew Bible from the time of Abraham through King David. In the Book of Judges, Abimelech, son of Gideon, of the Tribe of Manasseh, is ...
('well of the oath') or the seven ewes in that oath ('well of the seven'), as related in , and/or to the oath of Isaac
Isaac; grc, ß╝ĖŽā╬▒╬¼╬║, Isa├Īk; ar, žźž│žŁ┘░┘é/žźž│žŁž¦┘é, IsßĖź─üq; am, ßŗŁßłĄßłÉßēģ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the ...
and Abimelech in . Alternatively, Obadiah Sforno
Ovadia ben Jacob Sforno (Obadja Sforno, Hebrew: ūóūĢūæūōūÖūö ūĪūżūĢū©ūĀūĢ) was an Italian rabbi, Jewish commentaries on the Bible, Biblical commentator, philosopher and physician. A member of the Sforno (family), Sforno family, he was born in Ce ...
suggested that the well is called Seven because it was the seventh dug; the narrative of Genesis 26 includes three wells dug by Abraham which are reopened by Isaac (Esek
This is a list of places mentioned in the Bible, which do not have their own Wikipedia articles. See also the list of biblical places for locations which do have their own article.
A Abana
Abana, according to 2 Kings 5:12, was one of the " rive ...
, Sitnah, Rehoboth), for a total of six, after which Isaac goes to Beersheba, the seventh well.
The double name of Shib'a and Beersheba is referenced again by the Masoretic Text
The Masoretic Text (MT or ØĢĖ; he, ūĀų╗ūĪųĖų╝ūŚ ūöųĘū×ųĖų╝ūĪūĢų╣ū©ųĖūö, N┼½ss─üßĖź Hamm─üs┼Źr─ü, lit. 'Text of the Tradition') is the authoritative Hebrew and Aramaic text of the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) in Rabbinic Judaism. ...
in Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Y╔Öh┼Ź┼Īua╩┐'', Tiberian: ''Y┼Åh┼Ź┼Īua╩┐,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Y─ō┼Ī┼½a╩┐''; syr, ▄Ø▄½▄ś▄ź ▄Æ▄¬ ▄ó▄ś▄ó ''Y╔Ö┼Ī┼½╩┐ bar N┼Źn''; el, ß╝Ė╬ĘŽā╬┐ß┐”Žé, ar , ┘Ŗ┘Å┘łž┤┘Äž╣┘Å ┘▒ž©┘Æ┘å┘Å ┘å┘Å┘ł┘å┘Ź '' Y┼½┼Īa╩┐ ...
19:2, usually translated "Beersheba or Sheba"; however the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
reads "Beersheba and Samaa (╬Ż╬▒╬╝╬▒ßĮ░)" which fits with MT 1 Chron. 4:28.
Abraham ibn Ezra and Samuel b. Meir suggest the two etymologies refer to two different cities.
During Ottoman administration the city was referred as (''Belediye Bir├╝sseb'').
Hebrew Bible
Beersheba is mainly dealt with in theHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''T─ün ...
in connection with the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''T─ün ...
Patriarchs
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate (bishop), primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholicism, Independent Catholic Chur ...
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
and Isaac
Isaac; grc, ß╝ĖŽā╬▒╬¼╬║, Isa├Īk; ar, žźž│žŁ┘░┘é/žźž│žŁž¦┘é, IsßĖź─üq; am, ßŗŁßłĄßłÉßēģ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the ...
, who both dig a well and close peace treaties with King Abimelech
Abimelech (also spelled Abimelek or Avimelech; ) was the generic name given to all Philistine kings in the Hebrew Bible from the time of Abraham through King David. In the Book of Judges, Abimelech, son of Gideon, of the Tribe of Manasseh, is ...
of Gerar
Gerar ( ''Gərār'', "lodging-place") was a Philistine town and district in what is today south central Israel, mentioned in the Book of Genesis and in the Second Book of Chronicles of the Hebrew Bible.
Identification
According to the Internatio ...
at the site. Hence it receives its name twice, first after Abraham's dealings with Abimelech (), and again from Isaac
Isaac; grc, ß╝ĖŽā╬▒╬¼╬║, Isa├Īk; ar, žźž│žŁ┘░┘é/žźž│žŁž¦┘é, IsßĖź─üq; am, ßŗŁßłĄßłÉßēģ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the ...
who closes his own covenant with Abimelech of Gerar and whose servants also dig a well there (). The place is thus connected to two of the three WifeŌĆōsister narratives in the Book of Genesis
In biblical studies, the term wifeŌĆōsister narratives in Genesis refers to three strikingly similar stories in chapters 12, 20, and 26 of the Book of Genesis (part of the Torah and Old Testament). At the core of each is the story of a biblical ...
.
According to the Hebrew Bible, Beersheba was founded when Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
and Abimelech
Abimelech (also spelled Abimelek or Avimelech; ) was the generic name given to all Philistine kings in the Hebrew Bible from the time of Abraham through King David. In the Book of Judges, Abimelech, son of Gideon, of the Tribe of Manasseh, is ...
settled their differences over a well of water and made a covenant (see ). Abimelech's men had taken the well from Abraham after he had previously dug it so Abraham brought sheep and cattle to Abimelech to get the well back. He set aside seven lambs to swear that it was he that had dug the well and no one else. Abimelech conceded that the well belonged to Abraham and, in the Bible, Beersheba means "Well of Seven" or "Well of the Oath".
Beersheba is further mentioned in following Bible passages: Isaac built an altar in Beersheba (Genesis 26:23ŌĆō33). Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, ┘Ŗ┘Äž╣┘Æ┘é┘Å┘łž©, Ya╩┐q┼½b; gr, ß╝Ė╬▒╬║ŽÄ╬▓, Iakß╣ōb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
had his dream about a stairway to heaven after leaving Beersheba. (Genesis 28:10ŌĆō15 and 46:1ŌĆō7). Beersheba was the territory of the tribe of Simeon
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Simeon (; he, ''┼Ā─½mŌĆś┼Źn'', "hearkening/listening/understanding/empathizing") was one of the twelve tribes of Israel. The Book of Judges locates its territory inside the boundaries of the Tribe of ...
and Judah (Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Y╔Öh┼Ź┼Īua╩┐'', Tiberian: ''Y┼Åh┼Ź┼Īua╩┐,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Y─ō┼Ī┼½a╩┐''; syr, ▄Ø▄½▄ś▄ź ▄Æ▄¬ ▄ó▄ś▄ó ''Y╔Ö┼Ī┼½╩┐ bar N┼Źn''; el, ß╝Ė╬ĘŽā╬┐ß┐”Žé, ar , ┘Ŗ┘Å┘łž┤┘Äž╣┘Å ┘▒ž©┘Æ┘å┘Å ┘å┘Å┘ł┘å┘Ź '' Y┼½┼Īa╩┐ ...
15:28 and 19:2). The sons of the prophet Samuel
Samuel ''┼Ā╔Öm┼½╩Š─ōl'', Tiberian: ''┼Ā─ām┼½╩Š─ōl''; ar, ž┤┘ģ┘łž”┘Ŗ┘ä or žĄ┘ģ┘łž”┘Ŗ┘ä '; el, ╬Ż╬▒╬╝╬┐Žģ╬«╬╗ ''SamoußĖŚl''; la, Sam┼½─ōl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bibl ...
were judges in Beersheba (I Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1ŌĆō2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Joshu ...
8:2). Saul
Saul (; he, , ; , ; ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first monarch of the United Kingdom of Israel. His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked the transition of Israel and Judah from a scattered tri ...
, Israel's first king, built a fort there for his campaign against the Amalek
Amalek (; he, ūóų▓ū×ųĖū£ųĄū¦, , ar, ž╣┘ģž¦┘ä┘Ŗ┘é ) was a nation described in the Hebrew Bible as a staunch enemy of the Israelites. The name "Amalek" can refer to the nation's founder, a grandson of Esau; his descendants, the Amalekites; or the ...
ites (I Samuel 14:48 and 15:2ŌĆō9). The prophet Elijah
Elijah ( ; he, ūÉųĄū£ų┤ūÖųĖų╝ūöūĢų╝, ╩Š─Æl─½yy─üh┼½, meaning "My God is Yahweh/YHWH"; Greek form: Elias, ''El├Łas''; syr, ▄É▄Ė▄Ā▄Ø▄╝▄Ą▄É, ''Ely─üe''; Arabic: žź┘ä┘Ŗž¦ž│ or žź┘ä┘Ŗž¦, ''Ily─üs'' or ''Ily─ü''. ) was, according to the Books of ...
took refuge in Beersheba when Jezebel
Jezebel (;"Jezebel"
(US) and ) was the daughte ...
ordered him killed ((US) and ) was the daughte ...
I Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' S─ōfer M╔Öl─üßĖĄ─½m'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1ŌĆō2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books ...
19:3). The prophet Amos
Amos or AMOS may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Amos Records, an independent record label established in Los Angeles, California, in 1968
* Amos (band), an American Christian rock band
* ''Amos'' (album), an album by Michael Ray
* ''Amos' ...
mentions the city in regard to idolatry (Amos
Amos or AMOS may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Amos Records, an independent record label established in Los Angeles, California, in 1968
* Amos (band), an American Christian rock band
* ''Amos'' (album), an album by Michael Ray
* ''Amos' ...
5:5 and 8:14). Following the Babylonian conquest and subsequent enslavement
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slaveŌĆösomeone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
of many Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
, the town was abandoned. After the Israelite slaves returned from Babylon
''B─übili(m)''
* sux, ÆåŹÆĆŁÆŖÅÆåĀ
* arc, ÉĪüÉĪüÉĪŗ ''B─üßĖćel''
* syc, ▄Æ▄Æ▄Ā ''B─üßĖćel''
* grc-gre, ╬Æ╬▒╬▓Žģ╬╗ŽÄ╬Į ''Babylß╣ōn''
* he, ūæųĖų╝ūæųČū£ ''B─üvel''
* peo, ÉÄ▓ÉÄĀÉÄ▓ÉÄĪÉÄĮÉÄó ''B─übiru''
* elx, ÆĆĖÆüĆÆē┐ÆćĘ ''Babi ...
, they resettled the town. According to the Hebrew Bible, Beersheba was the southernmost city of the territories settled by Israelites, hence the expression "from Dan to Beersheba
From Dan to Beersheba is a biblical phrase used nine times in the Hebrew Bible to refer to the settled areas of the Tribes of Israel between Dan in the North and Beersheba in the South. The term contributed to the position that was used by Britis ...
" to describe the whole kingdom.
Zibiah Zibiah, or Sibia, ( he, ū”ų┤ūæų░ūÖųĖūö; ''ß╣ó─½ßĖć╔Öy─ü'', "gazelle") was the consort of King Ahaziah of Judah, and the mother of King Jehoash of Judah.2 Kings 12:1 She was from Beersheba. She is mentioned only in 2 Kings 12:1 and 2 Chronicles 24 ...
, the consort __NOTOC__
Consort may refer to:
Music
* "The Consort" (Rufus Wainwright song), from the 2000 album ''Poses''
* Consort of instruments, term for instrumental ensembles
* Consort song (musical), a characteristic English song form, late 16thŌĆōearl ...
of King Ahaziah of Judah Ahaziah ( he, ūÉų▓ūŚųĘū¢ų░ūÖųĖūöūĢų╝, "held by Yah(-weh)"; DouayŌĆōRheims: Ochozias) was the name of two kings mentioned in the Hebrew Bible:
*Ahaziah of Israel
*Ahaziah of Judah Ahaziah ( he, ūÉų▓ūŚųĘū¢ų░ūÖųĖūöūĢų╝, "held by Yah(-weh)"; DouayŌĆō ...
and the mother of King Jehoash of Judah
Jehoash (; el, ╬ÖŽē╬▒Žé; la, Joas), also known as Joash (in King James Version), Joas (in DouayŌĆōRheims) or Jo├Īs (), was the eighth king of Judah, and the sole surviving son of Ahaziah after the massacre of the royal family ordered by his gr ...
,2 Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' S─ōfer M╔Öl─üßĖĄ─½m'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1ŌĆō2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books ...
12:1 was from Beersheba.
History
The city has been destroyed and rebuilt many times over the centuries. Unimportant for centuries, BeŌĆÖer Sheva regained importance under Byzantine rule (in the 4thŌĆō7th century), when it was a key point on the Limes Palestinae, a defense line built against the desert tribes; however, it fell to the Arabs in the 7th century and to the Turks in the 16th. It long remained a watering place and small trade centre for the nomadic Bedouin tribes of the Negev, despite Turkish efforts at town planning and development around 1900. Its capture in 1917 by the British Army opened the way for their conquest of Palestine and Syria. After being taken by Israeli troops in October 1948, Beersheba was rapidly settled by new immigrants and has since developed as the administrative, cultural, and industrial centre of the Negev. It is one of the largest cities in Israel outside of metropolitan Tel Aviv, Jerusalem, and Haifa.Chalcolithic
Human settlement in the area dates from theCopper Age
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, Žć╬▒╬╗╬║ŽīŽé ''khalk├│s'', "copper" and ''l├Łthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
. The inhabitants lived in caves, crafting metal tools and raising cattle. Findings unearthed at Tel Sheva
Tel Sheva ( he, ū¬ųĄų╝ū£ ū®ųČūüūæųĘūó) or Tel as-Sabi ( ar, ž¬┘ä ž¦┘äž│ž©ž╣) is a Bedouin town in the Southern District of Israel, bordering the city of Beersheba. In it had a population of .
History
The first Bedouin township in Israel, Tel a ...
, an archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
east of modern-day Beersheba, suggest the region has been inhabited since the 4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
.
Iron Age Israelite town
Tel Be'er Sheva
Tel Sheva ( he, ū¬ū£ ū®ūæūó, translit=) or Tel Be'er Sheva (), also known as Tell es-Seba (), is an archaeological site in the Southern District of Israel, believed to be the site of the ancient biblical town of Beer-sheba. The site lies east o ...
, an archaeological site containing the ruins of an ancient town believed to have been the Biblical Beersheba, lies a few kilometers east of the modern city. The town dates to the early Israelite period, around the 10th century BCE. The site was probably chosen due to the abundance of water, as evidenced by the numerous wells in the area. According to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''T─ün ...
, the wells were dug by ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''T─ün ...
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
and Isaac
Isaac; grc, ß╝ĖŽā╬▒╬¼╬║, Isa├Īk; ar, žźž│žŁ┘░┘é/žźž│žŁž¦┘é, IsßĖź─üq; am, ßŗŁßłĄßłÉßēģ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the ...
when they arrived there. The streets were laid out in a grid, with separate areas for administrative, commercial, military, and residential use. It is believed to have been the first planned settlement in the region, and is also noteworthy for its elaborate water system; in particular, a huge cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by t ...
carved out of the rock beneath the town.
Persian period
During the Persian rule 539 BCŌĆōc. 332 BC Beersheba was at the south ofYehud Medinata
Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta (), was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a Autonomy, self-governing region under its local Jews, Jewish po ...
autonomous province of the Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, ÉĦÉÅüÉÅé, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. During that era the city was rebuilt and a citadel had been built. Archeological finds from between 359 and 338 BC have been made and include pottery and Ostracon
An ostracon (Greek: ''ostrakon'', plural ''ostraka'') is a piece of pottery, usually broken off from a vase or other earthenware vessel. In an archaeological or epigraphical context, ''ostraca'' refer to sherds or even small pieces of ston ...
.
Hellenistic period
During the Hasmonean rule, the city did not take importance as it was not mentioned when conquered fromEdom
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, ūÉų▒ūōūĢų╣ūØ , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
or described in the Hasmonean wars.
Roman and Byzantine periods
DuringRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
rule the city was in the Coele-Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, ╬Ü╬┐╬»╬╗╬Ę ╬ŻŽģŽü╬»╬▒, ''Ko├Łl─ō Syr├Ła'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, C┼ōl─ō Syria or ), was a region of Syria (region), Syria in cl ...
region. During the Roman era and later Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
periods, the town served as a front-line defense against Nabatean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, ╬Ø╬▒╬▓╬▒Žä╬▒ß┐¢╬┐Žé, translit=Nabata├«os; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Lev ...
attacks. Around 64-63 BC Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC ŌĆō 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
made Be'er Sheva the southern part of the Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, ūÖūöūĢūōūö, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard ''Y╔Öh┼½da'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Yeh┼½ßĖÅ─ü''; el, ß╝Ė╬┐Žģ╬┤╬▒╬»╬▒, ; la, I┼½daea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous L ...
province, in the following years the city was on the limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
* the Latin word for ''limit'' which refers to:
** Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin, singular; plural: ) is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting ...
belt, which in this region is attributed to the time of Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 ŌĆō 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
,"The Origin of the Limes Palaestinae and the Major Phases in its Development", in ''Studien zu den Milit├żrgrenzen Roms'', 1967 The city become centre of an eparchy
Eparchy ( gr, ß╝ÉŽĆ╬▒ŽüŽć╬»╬▒, la, eparch├Ła / ''overlordship'') is an ecclesiastical unit in Eastern Christianity, that is equivalent to a diocese in Western Christianity. Eparchy is governed by an ''eparch'', who is a bishop. Depending on th ...
in around 268.
Beersheba was described in the Madaba Map and Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, ╬ĢßĮÉŽā╬Ł╬▓╬╣╬┐Žé ; 260/265 ŌĆō 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, ╬ĢßĮÉŽā╬Ł╬▓╬╣╬┐Žé Žä╬┐ß┐” ╬Ā╬▒╬╝Žå╬»╬╗╬┐Žģ), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christia ...
as a large village with a Roman garrison.
Mamluk period
In 1483, during the lateMamluk
Mamluk ( ar, ┘ģ┘ģ┘ä┘ł┘ā, maml┼½k (singular), , ''mam─ül─½k'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
era, the pilgrim Felix Fabri
Felix Fabri (also spelt Faber; 1441 ŌĆō 1502) was a Swiss Dominican theologian. He left vivid and detailed descriptions of his pilgrimages to Palestine and also in 1489 authored a book on the history of Swabia, entitled ''Historia Suevorum''.
H ...
noted Beersheba as a city. Fabri also noted that Beersheba marked the southern-most border of "the Holy Land".
Ottoman period


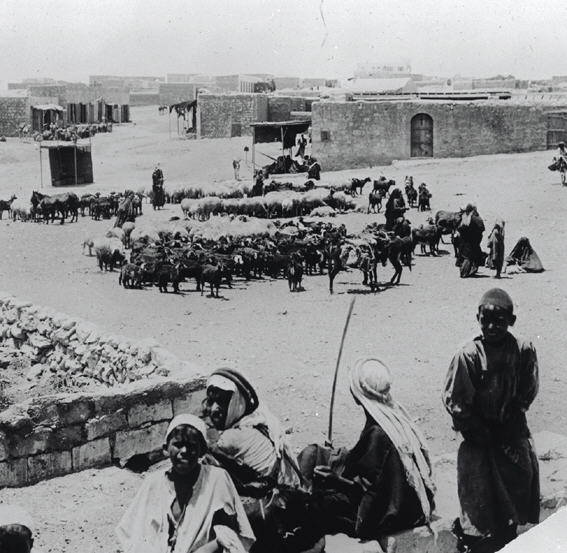
 The present-day city was built to serve as an administrative center by the Ottoman administration for the benefit of the Bedouin at the outset of the 20th century and was given the name of ''Bir al-Sabi'' (well of the seven). Until
The present-day city was built to serve as an administrative center by the Ottoman administration for the benefit of the Bedouin at the outset of the 20th century and was given the name of ''Bir al-Sabi'' (well of the seven). Until World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, it was an overwhelmingly Muslim township, with some 1,000 residents. Ben-David and Kressel have argued that the Bedouin traditional market was the cornerstone for the founding of Beersheba as capital of the Negev during this period, and Negev Bedouin anthropologist and educationalist, Aref Abu-Rabia, who worked for the Israeli Ministry of Education and Culture, described it as "the first Bedouin city."
In June 1899, the Ottoman government ordered the creation of the Beersheba sub-district (''kaza'') of the district (''mutasarr─▒fl─▒k'') of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, ūÖų░ū©ūĢų╝ū®ųĖūüū£ųĘūÖų┤ūØ ; ar, ž¦┘ä┘é┘Åž»ž│ ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, ß╝╣╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽģŽā╬▒╬╗╬«╬╝/ß╝Ė╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽāŽī╬╗Žģ╬╝╬▒, HierousalßĖŚm/Hieros├│luma; hy, įĄųĆšĖųéšĮšĪš▓šźš┤, Erusa┼é─ōm. i ...
, with Beersheba to be developed as its capital. Implementation was entrusted to a special bureau of the Ministry of the Interior. There were multiple reasons for the decision. The British incorporation of Sinai
Sinai commonly refers to:
* Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Biblical Mount Sinai, the site in the Bible where Moses received the Law of God
Sinai may also refer to:
* Sinai, South Dakota, a place ...
into Egypt
Egypt ( ar, ┘ģžĄž▒ , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
led to a need for the Ottomans to consolidate their hold on southern Palestine. There was also a desire to encourage the Bedouin to become sedentary, with a predicted increase of tranquility and tax revenue. The first governor (''kaymakam
Kaymakam, also known by many other romanizations, was a title used by various officials of the Ottoman Empire, including acting grand viziers, governors of provincial sanjaks, and administrators of district kazas. The title has been retained an ...
''), Isma'il Kamal Bey, lived in a tent lent by the local sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, ž┤┘Ŗž« ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )ŌĆöalso transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shakŌĆöis an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a ...
until the government house (''Saraya'') was built. Kamal was replaced by Muhammed Carullah Efendi in 1901, who in turn was replaced by Hamdi Bey in 1903. The governor in 1908 was promoted to 'adjoint' (''mutassarr─▒f muavin'') to the governor of the Jerusalem district, which placed him above the other sub-district governors.
A visitor to Beersheba in May 1900 found only a ruin, a two-storey stone khan, and several tents. By the start of 1901 there was a barracks with a small garrison and other buildings. The Austro-Hungaria
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
n-Czech orientalist Alois Musil
Alois Musil (30 June 1868 – 12 April 1944) was a Czech theologian, orientalist, explorer and bilingual Czech and German writer.
Biography
Musil was the oldest son born in 1868 into an poor farming family in Moravia (then Cisleithanian pa ...
noted in August 1902:
: Bir es-Seba grows from day to day; This year, instead of the tents, we found stately houses along a beautiful road from the Sarayah to the bed of the wadi. In the government building a garden has been laid out, and all sorts of trees have been planted which are sure to prosper, for the few shrubs planted two years ago by the steam mill at the south-east end of the road have grown considerably. The lively construction activity is also causing a lively exploitation of the ruins.
By 1907 there was a large village and military post, with a residence for the ''kaymakam'' and a large mosque. The population increased from 300 to 800 between 1902 and 1911, and by 1914 there were 1,000 people living in 200 houses.
A plan for the town in the form of a grid
Grid, The Grid, or GRID may refer to:
Common usage
* Cattle grid or stock grid, a type of obstacle is used to prevent livestock from crossing the road
* Grid reference, used to define a location on a map
Arts, entertainment, and media
* News g ...
was developed by a Swiss and a German architect and two others. The grid pattern can be seen today in Beersheba's Old City. Most of the residents at the time were Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘ī┘æ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s from Hebron
Hebron ( ar, ž¦┘äž«┘ä┘Ŗ┘ä or ; he, ūŚųČūæų░ū©ūĢų╣ū¤ ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after East J ...
and the Gaza area, although Jews
Jews ( he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōų┤ūÖūØ, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
also began settling in the city. Many Bedouin abandoned their nomadic lives and built homes in Beersheba.
First World War and British Mandate
DuringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Ottomans built a military railroad from the Hejaz line to Beersheba, inaugurating the station on October 30, 1915. The celebration was attended by the Ottoman army commander Jamal Pasha
Ahmed Djemal ( ota, ž¦žŁ┘ģž» ž¼┘ģž¦┘ä ┘Šž¦ž┤ž¦, Ahmet Cem├ól Pa┼¤a; 6 May 1872 ŌĆō 21 July 1922), also known as Cemal Pasha, was an Ottoman military leader and one of the Three Pashas that ruled the Ottoman Empire during World War I.
Djemal wa ...
and other senior government officials. The train line was captured by Allied forces in 1917, towards the end of the war. Today, it forms part of the Israeli railway network.
Beersheba played an important role in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign in World War I. The Battle of Beersheba was part of a wider British offensive in aimed at breaking the Turkish defensive line from Gaza to Beersheba. On October 31, 1917, three months after taking Rafah
Rafah ( ar, ž▒┘üžŁ, RafaßĖź) is a Palestinian city in the southern Gaza Strip. It is the district capital of the Rafah Governorate, located south of Gaza City. Rafah's population of 152,950 (2014) is overwhelmingly made up of former Palestinian ...
, General Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 ŌĆō 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and Imperial Governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in the First World War, in which he led th ...
's troops breached the line of Turkish defense between Gaza and Beersheba. Approximately five-hundred soldiers of the Australian
Australian(s) may refer to:
Australia
* Australia, a country
* Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia
** European Australians
** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists
** Aboriginal Au ...
4th Light Horse Regiment and the 12th Light Horse Regiment of the 4th Light Horse Brigade, led by Brigadier General William Grant, with only horses and bayonets, charged the Turkish trenches, overran them and captured the wells in what has become known as the Battle of Beersheba, called the "last successful cavalry charge in British military history." On the edge of Beersheba's Old City is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) is an intergovernmental organisation of six independent member states whose principal function is to mark, record and maintain the graves and places of commemoration of Commonwealth of Nations mil ...
Cemetery containing the graves of Australian, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmassesŌĆöthe North Island () and the South Island ()ŌĆöand over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
and British soldiers. The town also contains a memorial park dedicated to them.
During the Palestine Mandate, Beersheba was a major administrative center. The British constructed a railway between Rafah
Rafah ( ar, ž▒┘üžŁ, RafaßĖź) is a Palestinian city in the southern Gaza Strip. It is the district capital of the Rafah Governorate, located south of Gaza City. Rafah's population of 152,950 (2014) is overwhelmingly made up of former Palestinian ...
and Beersheba in October 1917; it opened to the public in May 1918, serving the Negev and settlements south of Mount Hebron
The Hebron Hills, also known as Mount Hebron ( ar, ž¼ž©┘ä ž¦┘äž«┘ä┘Ŗ┘ä, translit=Jabal al-Khal─½l, he, ūöū© ūŚūæū©ūĢū¤, translit=Har Hevron), are a mountain ridge, geographic region, and geologic formation, comprising the southern part of the J ...
. In 1928, at the beginning of the tension between the Jews and the Arabs over control of Palestine, and wide-scale rioting which left 133 Jews dead and 339 wounded, many Jews abandoned Beersheba, although some returned occasionally. After an Arab attack on a Jewish bus in 1936, which escalated into the 1936ŌĆō39 Arab revolt in Palestine, the remaining Jews left.
At the time of the 1922 census of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922.
The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The divisi ...
, Beersheba had a population of 2,012 Muslims, 235 Christians, 98 Jews and 11 Druze
The Druze (; ar, ž»┘Äž▒┘Æž▓┘É┘Ŗ┘ī┘æ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
(total 2,356). At the time of the 1931 census, Beersheba had 545 occupied houses and a population of 2,791 Muslim
Muslims ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘ģž│┘ä┘ģ┘ł┘å, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s, 152 Christians, 11 Jews and 5 Bah├Ī╩╝├Ł (total 2,959).online
(pdf, 28 MB) The 1945 village survey conducted by the Palestine Mandate government found 5,360 Muslims, 200 Christians and 10 others (total 5,570).


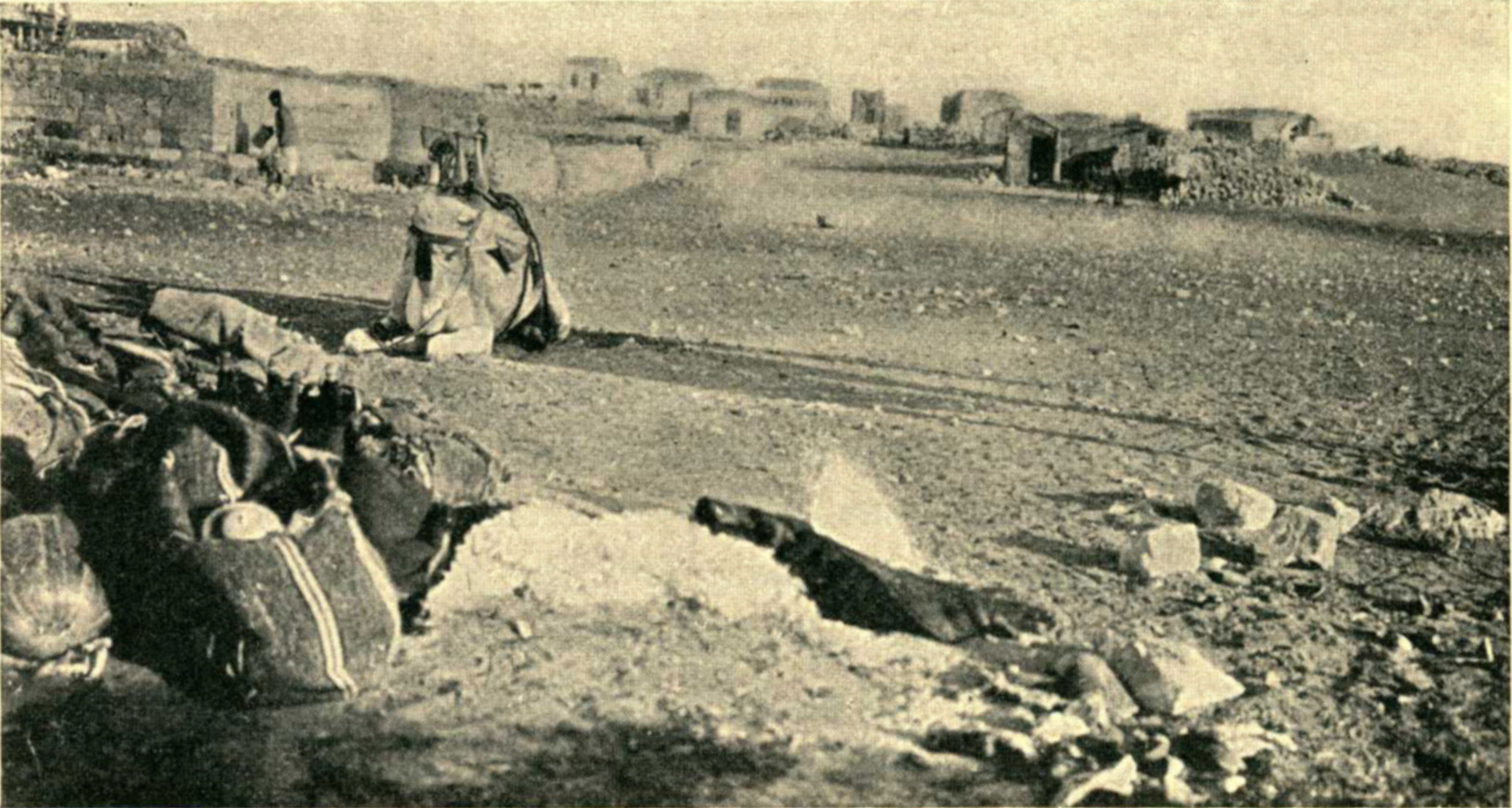
Operation Yoav
Operation Yoav (also called ''Operation Ten Plagues'' or ''Operation Yo'av'') was an Israeli military operation carried out from 15ŌĆō22 October 1948 in the Negev Desert, during the 1948 ArabŌĆōIsraeli War. Its goal was to drive a wedge between th ...
, 1948
File:Beersheba iv.jpg, Harel Brigade assembling in Beersheba prior to Operation Horev, 25 December 1948
File:Beersheba v.jpg, Nahal Beersheba in flood, 1948
State of Israel
1947ŌĆō1949 war


United Nations Special Committee on Palestine
The United Nations Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) was created on 15 May 1947 in response to a United Kingdom government request that the General Assembly "make recommendations under article 10 of the Charter, concerning the future govern ...
(UNSCOP) proposed that Beersheba be included within the Jewish state in their partition plan for Palestine.United Nations Special Committee on Palestine, Report to the General Assembly, September 3, 1947, Volume IIA/364, Add. 1
. UNGA Resolution 181 (Nov 27, 1947
. See boundaries :File:UN Palestine Partition Versions 1947.jpg, here. However, when the UN's Ad Hoc Committee revised the plan, they moved Beersheva to the Arab state on account of it being primarily Arab. Egyptian forces had been stationed at Beersheva since May 1948. It was
Yigal Allon
Yigal Allon ( he, ūÖūÆūÉū£ ūÉū£ūĢū¤; 10 October 1918 ŌĆō 29 February 1980) was an Israeli politician, commander of the Palmach, and general in the Israel Defense Forces, IDF. He served as one of the leaders of Ahdut HaAvoda party and the Labor P ...
who proposed the conquest of Beersheba, which was approved by Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion
David Ben-Gurion ( ; he, ūōųĖų╝ūĢų┤ūō ūæųČų╝ū¤-ūÆų╝ūĢų╝ū©ų┤ūÖų╝ūĢų╣ū¤ ; born David Gr├╝n; 16 October 1886 ŌĆō 1 December 1973) was the primary national founder of the State of Israel and the first prime minister of Israel. Adopting the name ...
. According to Israeli historian Benny Morris
Benny Morris ( he, ūæūĀūÖ ū×ūĢū©ūÖūĪ; born 8 December 1948) is an Israeli historian. He was a professor of history in the Middle East Studies department of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in the city of Beersheba, Israel. He is a member of t ...
, he ordered the "conquest of Beersheba, occupation of outposts around it, nddemolition of most of the town."Morris, Benny. ''The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited'', Cambridge University Press, p. 467. The objective was to break the Egyptian blockade of Israeli convoys to the Negev. The Egyptian army did not expect an offensive and fled en masse. Israel bombed the town on October 16,Alef Abu-Rabia, 'Beersheva,' in Michael Dumper, Bruce E. Stanley (eds.)''Cities of the Middle East and North Africa: A Historical Encyclopedia,''
ABC-CLIO, 2007 p.80. At 4:00 am on October 21, the 8th Brigade's 89th
battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions are ...
and the Negev Brigade
The 12th Negev Brigade ( he, ūŚūśūÖūæū¬ ūöūĀūÆūæ, ''Hativat HaNegev'') is an Israeli reserve infantry brigade under the Sinai Division, that originally served in the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
History
Founding and organization
The brigade was fou ...
's 7th and 9th battalions moved in, some troops advancing from Mishmar HaNegev
Mishmar HaNegev ( he, ū×ų┤ū®ų░ūüū×ųĘū© ūöųĘūĀųČų╝ūÆųČūæ, ''lit.'' Guard of the Negev) is a kibbutz in the northern fringe of the Negev desert in Israel. Located on Road 264, about two kilometres south of the Bedouin city of Rahat and around ten ...
junction, north of Beersheba, others from the Turkish train station and Hatzerim
Hatzerim ( he, ūŚų▓ū”ųĄū©ų┤ūÖūØ, ''lit.'' Farmyards) is a kibbutz located 8 kilometers west of Beersheba in the Negev desert in Israel. It is named after the Bible (Deuteronomy 2:23), mentioning a site nearby: "the Avvites who lived in farmyards ...
. By 9:45, Beersheba was in Israeli hands. Around 120 Egyptian soldiers were taken prisoner. All of the Arab inhabitants who had resisted, were expelled Yitzhak Reiter''Contested Holy Places in IsraelŌĆōPalestine: Sharing and Conflict Resolution''
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in England that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, Routledge, F1000 (publisher), F1000 Research or Dovepress. It is a division of Informa ...
, 2017 p.209. with the remaining Arab civilians, 200 men and 150 women and children, taken to the police fort and, on October 25, the women, children, disabled and elderly were driven by truck to the Gaza border. The Egyptian soldiers were interned in POW
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war ...
camps. Some men lived in the local mosque and were put to work cleaning but when it was discovered that they were supplying information to the Egyptian army they were also deported. The town was subject to large-scale looting by the Haganah
Haganah ( he, ūöųĘūöų▓ūÆųĖūĀųĖūö, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the ...
, and by December, in one calculation, the total number of Arabs driven out from Beersheva and surrounding areas reached 30,000 with many ending up in Jordan as refugees. Following Operation Yoav
Operation Yoav (also called ''Operation Ten Plagues'' or ''Operation Yo'av'') was an Israeli military operation carried out from 15ŌĆō22 October 1948 in the Negev Desert, during the 1948 ArabŌĆōIsraeli War. Its goal was to drive a wedge between th ...
, a 10-kilometer radius exclusion zone around Beersheba was enforced into which no Bedouin were allowed. In response, the United Nations Security Council passed two resolutions on the 4th and 16 November demanding that Israel withdraw from the area.
First four decades
Following the conclusion of the war, the 1949 Armistice Agreements formally granted Beersheba to Israel. The town was then transformed into an Israeli city with only an exiguous Arab minority. Beersheba was deemed strategically important due to its location with a reliable water supply and at a major crossroads, northwest to Hebron andJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, ūÖų░ū©ūĢų╝ū®ųĖūüū£ųĘūÖų┤ūØ ; ar, ž¦┘ä┘é┘Åž»ž│ ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, ß╝╣╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽģŽā╬▒╬╗╬«╬╝/ß╝Ė╬ĄŽü╬┐ŽāŽī╬╗Žģ╬╝╬▒, HierousalßĖŚm/Hieros├│luma; hy, įĄųĆšĖųéšĮšĪš▓šźš┤, Erusa┼é─ōm. i ...
, east to the Dead Sea and al Karak, south to Aqaba, west to Gaza and southwest to Auja al-Hafir, Al-Auja and the border with Egypt
Egypt ( ar, ┘ģžĄž▒ , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
.
After a few months, the town's war-damaged houses were repaired. As a post-independence wave of Jewish immigration to Israel began, Beersheba experienced a population boom as thousands of immigrants moved in. The city rapidly expanded beyond its core, which became known as the "Old City," as new neighborhoods were built around it, complete with various housing projects such as apartment buildings and houses with auxiliary farms, as well as shopping centers and schools. The Old City was turned into a city center, with shops, restaurants, and government and utility offices. An industrial area and one of the largest cinemas in Israel were also built in the city. By 1956, Beersheba was a booming city of 22,000. In 1959, during the Wadi Salib riots, riots spread quickly to other parts of the country, including Beersheba.
Soroka Medical Center, Soroka Hospital opened its doors in 1960. By 1968, the population had grown to 80,000. The University of the Negev, which would later become Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, was established in 1969. The then List of Presidents of Egypt, Egyptian president Anwar Sadat visited Beersheba in 1979. In 1983, its population was more than 110,000. During the 1990s post-Soviet aliyah, the city's population greatly increased as many immigrants from the former Soviet Union settled there.
Urban development in the 21st century
As part of its Blueprint Negev project, the Jewish National Fund funded major redevelopment projects in Beersheba. One project was the Beersheba River Walk, a riverfront district with green spaces, hiking trails, a 3,000-seat sports hall, a boating lake filled with recycled waste water, promenades, restaurants, caf├®s, galleries, boat rentals, a 12,000-seat amphitheater, playgrounds, and a bridge along the route of the city's Mekorot water pipes. At the official entrance to the river park is the Beit Eshel Park, which consists of a park built around a courtyard with historic remains from the settlement of Beit Eshel."Beit Eshel Park, Beersheba", Blueprint Negev


Security incidents in the city
On October 19, 1998, sixty four people were wounded in a grenade attack. On August 31, 2004, sixteen people were killed in Beersheba bus bombings, two suicide bombings on commuter buses in Beersheba for which Hamas claimed responsibility. On August 28, 2005, another suicide bomber attacked the central bus station, seriously injuring two security guards and 45 bystanders. During Gaza War (2008ŌĆō09), Operation Cast Lead, which began on December 27, 2008, and lasted until the ceasefire on January 18, 2009, Hamas fired 2,378 rockets (such as BM-21 Grad, Grad rockets) and mortars, from Gaza into southern Israel, including Beersheba. The List of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, rocket attacks have continued, but have been only partially effective since the introduction of the Iron Dome rocket defense system. In 2010, an Arab attacked and injured two people with an axe. In 2012, a Palestinian from Jenin was stopped before a stabbing attack in a "safe house." On October 18, 2015, a lone gunman Beersheva bus station shooting, shot and killed a soldier guarding the Beersheva bus station before being gunned down by police. In September 2016, the Shin Bet thwarted a Palestinian Islamic Jihad terror attack at a wedding hall in Beersheba. On March 22, 2022, a convicted Islamic State supporter carried out a 2022 Beersheba attack, stabbing and vehicle-ramming attack, killing four people and injuring two others.Emblem of Beersheba
 Since 1950, Beersheba has changed its municipal emblem several times.
The 1950 emblem, designed by Abraham Khalili, featured a tamarix tree, a factory and water flowing from a pipeline. In 1972 the emblem was modernized with the symbolic representation of the Twelve Tribes and a tower. Words from the Bible are inscribed: Abraham "planted a tamarix tree in Beersheba." (Genesis 21:33) Since 2012, it has incorporated the number seven as part of the city rebranding.
Since 1950, Beersheba has changed its municipal emblem several times.
The 1950 emblem, designed by Abraham Khalili, featured a tamarix tree, a factory and water flowing from a pipeline. In 1972 the emblem was modernized with the symbolic representation of the Twelve Tribes and a tower. Words from the Bible are inscribed: Abraham "planted a tamarix tree in Beersheba." (Genesis 21:33) Since 2012, it has incorporated the number seven as part of the city rebranding.
Geography
 Beersheba is located on the northern edge of the Negev desert south-east of Tel Aviv and south-west of Jerusalem. The city is located on the main route from the center and north of the country to Eilat in the far south. The Beersheba Valley has been populated for thousands of years, as it has available water, which flows from the Hebron hills in the winter and is stored underground in vast quantities. The main river in Beersheba is ''Nahal Beersheva'', a ''wadi'' that floods in the winter. The Kovshim and Katef streams are other important wadis that pass through the city. Beersheba is surrounded by a number of satellite towns, including Omer, Israel, Omer, Lehavim, and Meitar, and the Bedouin localities of Rahat, Tel as-Sabi, and Lakiya.
Just north west of the city (near Ramot neighborhood ) is a region called Goral hills (heb:ūÆūæūóūĢū¬ ūÆūĢū©ū£ lit: hills of fate), the area has hills with up to above sea level and low as above sea level. Due to heavy construction the flora unique to the area is endangered.
North east of the city (north to the Neve Menahem neighborhood) there are Loess plains and dry river bands.
Beersheba is located on the northern edge of the Negev desert south-east of Tel Aviv and south-west of Jerusalem. The city is located on the main route from the center and north of the country to Eilat in the far south. The Beersheba Valley has been populated for thousands of years, as it has available water, which flows from the Hebron hills in the winter and is stored underground in vast quantities. The main river in Beersheba is ''Nahal Beersheva'', a ''wadi'' that floods in the winter. The Kovshim and Katef streams are other important wadis that pass through the city. Beersheba is surrounded by a number of satellite towns, including Omer, Israel, Omer, Lehavim, and Meitar, and the Bedouin localities of Rahat, Tel as-Sabi, and Lakiya.
Just north west of the city (near Ramot neighborhood ) is a region called Goral hills (heb:ūÆūæūóūĢū¬ ūÆūĢū©ū£ lit: hills of fate), the area has hills with up to above sea level and low as above sea level. Due to heavy construction the flora unique to the area is endangered.
North east of the city (north to the Neve Menahem neighborhood) there are Loess plains and dry river bands.
Climate
Beersheba has a hot Semi-arid climate, semi arid (K├Čppen climate classification ''Bsh'') with Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean influences. The city has both characteristics of Mediterranean and desert climates. Summers are hot and dry, and winters are mild. Rainfall is highly concentrated in the winter season. In summer, the temperatures are high in daytime and nighttime with an average high of and an average low of . Winters have an average high of and average low of . Snow is very rare; a snowfall on February 20, 2015, was the first such occurrence in the city since 2000. Precipitation in summer is rare, the most rainfalls come in winter between September to May, but the annual amount is low, averaging per year. Sandstorms, haze and fog are common, especially in winter, as a result of the high humidity.Demography
Beersheba is one of the fastest-growing cities in Israel. Though it has a population of about 200,000, the city is larger in area than Tel Aviv, and its urban plan calls for an eventual population of 450,000ŌĆō500,000. It is planned to have a population of 340,000 by 2030. In 2010, the National Council for Planning and Construction approved a master plan with the goal of increasing the population of Beersheba and its metropolitan area to 1 million by 2020. The population of Beersheba is predominantly Jewish. Jews and others represent 97.3% of the population, of whom Jews are 86.5%. Arabs constitute around 2.69% of city population. The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics divides the Beersheba metropolitan area into two areas:Economy
Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, ū”ų░ūæųĖūÉ ūöųĘūöų▓ūÆųĖūĀųĖūö ū£ų░ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£ , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the Israel, State of Israel. It consists of three servic ...
and Ben-Gurion University. A major Israel Aerospace Industries complex is located in the main industrial zone, north of Highway 60 (Israel), Highway 60. Numerous electronics and chemical plants, including Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, are located in and around the city.
Beersheba is emerging as a high-tech center, with an emphasis on cyber security. A large high-tech park is being built near the Be'er Sheva North Railway Station. Deutsche Telekom, Elbit Systems, EMC Corporation, EMC, Lockheed Martin, Ness Technologies, WeWork and RAD Data Communications have already opened facilities there, as has a cyberincubator run by Jerusalem Venture Partners. A Science park funded by the RASHI-SACTA Foundation, Beersheba Municipality and private donors was completed in 2008. Another high-tech park is located north of the city near Omer, Israel, Omer.
An additional three industrial zones are located on the southeastern side of the city ŌĆō Makhteshim, Emek Sara and Kiryat Yehudit ŌĆō and a light industry zone between Kiryat Yehudit and the Old City.
Local government
 The mayor of Beersheba is Ruvik Danilovich, who was deputy mayor under Yaakov Turner.
The mayor of Beersheba is Ruvik Danilovich, who was deputy mayor under Yaakov Turner.
Educational institutions
 According to the Municipality CBS, in 2022, Beersheba has a ca.8,975 preschoolers in ca.300 preschools & kindergartens. A total of 99 schools teaching a student population of ca.45,291: 60 elementary schools with an enrollment of 19,617 (ca.3,200 of whom are entering the 1st grade), and 39 high schools with an enrollment of 16,699. Of Beersheba's 12th graders, 90% earned a Bagrut matriculation certificate in 2022. The city also has several private schools and Yeshiva, yeshivot in the religious sector with 3,000 or more students.
According to the Municipality CBS, in 2022, Beersheba has a ca.8,975 preschoolers in ca.300 preschools & kindergartens. A total of 99 schools teaching a student population of ca.45,291: 60 elementary schools with an enrollment of 19,617 (ca.3,200 of whom are entering the 1st grade), and 39 high schools with an enrollment of 16,699. Of Beersheba's 12th graders, 90% earned a Bagrut matriculation certificate in 2022. The city also has several private schools and Yeshiva, yeshivot in the religious sector with 3,000 or more students.
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) ( he, ūÉūĢūĀūÖūæū©ūĪūÖūśū¬ ūæū¤-ūÆūĢū©ūÖūĢū¤ ūæūĀūÆūæ, ''Universitat Ben-Guriyon baNegev'') is a public research university in Beersheba, Israel. Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has five campuses: the ...
, located on an urban campus in the city (Dalet neighborhood). Other schools in Beersheva are the Open University of Israel, Shamoon College of Engineering (SCE), Kaye Academic College of Education, Practical Engineering College of Beersheba (), and a campus of the Israeli Air and Space College (''Beersheba Tehni School, Techni Be'er sheva '').
Neighborhoods
After Israeli independence, Beersheba became a "laboratory" for Architecture of Israel, Israeli architecture.Haaretz.com"Magic Carpet: The Carpet-Style Patio Homes of Be'er Sheva"], ''Haaretz'' ''Mishol Girit,'' a neighborhood built in the late 1950s, was the first attempt to create an alternative to the standard public housing projects in Israel. ''Hashatiah'' (literally, "the carpet"), also known as (the model neighborhood), was hailed by architects around the world. Today, Beersheba is divided into seventeen residential neighborhoods in addition to the Old City and Ramot, an umbrella neighborhood of four sub-districts. Many of the neighbourhoods are named after letters of the Hebrew alphabet, which also have numerical value, but descriptive place names have been given to some of the newer neighborhoods.
Art and cultural institutions
 In 1953, Cinema Keren, the Negev's first movie theater, opened in Beersheba. It was built by the Histadrut and had seating for 1,200 people.
Beersheba is the home base of the Israel Sinfonietta, founded in 1973. Over the years, the Sinfonietta has developed a broad repertoire of symphonic works, concerti for solo instruments and large choral productions, among them Handel's ''Israel in Egypt,'' masses by Schubert and Mozart, Rossini's "Stabat Mater" and Vivaldi's "Gloria." World-famous artists have appeared as soloists with the Sinfonietta, including Pinchas Zukerman, Jean-Pierre Rampal, Shlomo Mintz, Gary Karr, and Paul Tortelier. In the 1970s, a memorial commemorating fallen Israeli soldiers designed by the sculptor Dani Karavan, Danny Karavan was erected on a hill north-east of the city. The Beersheba Theater opened in 1973. The Light Opera Group of the Negev, established in 1980, performs musicals in English every year.
Landmarks in the city include "Abraham's well", a well dating to at least the 12th century CE (now inside a visitors center), and the old Turkish railway station, now the focus of development plans. The Artists House of the Negev, in a Mandate-era building, showcases artwork connected in some way to the Negev.
The Negev Museum of Art reopened in 2004 in the Ottoman Governor's House, and an art and media center for young people was established in the Old City.
In 2009, a new tourist and Visitor center, information center, Gateway to the Negev, was built.
In 1953, Cinema Keren, the Negev's first movie theater, opened in Beersheba. It was built by the Histadrut and had seating for 1,200 people.
Beersheba is the home base of the Israel Sinfonietta, founded in 1973. Over the years, the Sinfonietta has developed a broad repertoire of symphonic works, concerti for solo instruments and large choral productions, among them Handel's ''Israel in Egypt,'' masses by Schubert and Mozart, Rossini's "Stabat Mater" and Vivaldi's "Gloria." World-famous artists have appeared as soloists with the Sinfonietta, including Pinchas Zukerman, Jean-Pierre Rampal, Shlomo Mintz, Gary Karr, and Paul Tortelier. In the 1970s, a memorial commemorating fallen Israeli soldiers designed by the sculptor Dani Karavan, Danny Karavan was erected on a hill north-east of the city. The Beersheba Theater opened in 1973. The Light Opera Group of the Negev, established in 1980, performs musicals in English every year.
Landmarks in the city include "Abraham's well", a well dating to at least the 12th century CE (now inside a visitors center), and the old Turkish railway station, now the focus of development plans. The Artists House of the Negev, in a Mandate-era building, showcases artwork connected in some way to the Negev.
The Negev Museum of Art reopened in 2004 in the Ottoman Governor's House, and an art and media center for young people was established in the Old City.
In 2009, a new tourist and Visitor center, information center, Gateway to the Negev, was built.
Great Mosque of Beersheba
 In 1906, during the Ottoman era, the Great Mosque of Beersheba was built with donations collected from the Bedouin residents in the Negev. It was used actively as a mosque until the city fell to Israeli forces in 1948. The mosque was used until 1953 as the city's courthouse. From then until the 1990s, when it was closed for renovations, the building housed an archeological museum, which the city intended to turn into the archeological branch of the Negev Museum. In 2011, however, the Supreme Court of Israel, sitting as the Supreme Court of Israel#High Court of Justice, High Court of Justice, ordered the property to be turned into a museum of Islam without reverting to a place of worship.
In 1906, during the Ottoman era, the Great Mosque of Beersheba was built with donations collected from the Bedouin residents in the Negev. It was used actively as a mosque until the city fell to Israeli forces in 1948. The mosque was used until 1953 as the city's courthouse. From then until the 1990s, when it was closed for renovations, the building housed an archeological museum, which the city intended to turn into the archeological branch of the Negev Museum. In 2011, however, the Supreme Court of Israel, sitting as the Supreme Court of Israel#High Court of Justice, High Court of Justice, ordered the property to be turned into a museum of Islam without reverting to a place of worship.
Transportation
Beersheba is the central transport hub of southern Israel, served by roads, railways and air. Beersheba is connected to Tel Aviv via Highway 40 (Israel), Highway 40, the second longest highway in Israel, which passes to the east of the city and is called the Beersheba bypass because it allows travellers from the north to go to southern locations, avoiding the more congested city center. From west to east, the city is divided by Highway 25 (Israel), Highway 25, which connects to Ashkelon and the Gaza Strip to the northwest, and Dimona to the east. Finally, Highway 60 connects Beersheba with Jerusalem and the Shoket Junction, and goes through the West Bank. On the local level, a partial Beltway, ring road surrounds the city from the north and east, and Road 406 (Rager Blvd.) goes through the city center from north to south. Metrodan Beersheba, established in 2003, had a fleet of 90 buses and operates 19 lines in the city between 2003 and 2016, most of which depart from the Beersheba Central Bus Station. These lines were formerly operated by the municipality as the 'Be'er Sheva Urban Bus Services'. Inter-city buses to and from Beersheba are operated by Egged Bus Cooperative, Egged, Dan BaDarom and Metropoline. The intercity bus service was transferred to Dan Be'er Sheva in 25'th of November 2016 and Metrodan Beersheva had been shut down. With the change to Dan Be'er Sheva the company introduced electronic payment stopping pay at the driver which was common in Beersheba.Roundabouts
 In Be'er Sheva there are over 250 roundabouts, giving the city its nickname of "Roundabout Capital of Israel". Many roundabouts, part of Be'er-Sheva's urban oasis project, include fountains, landscaping and sculptures by well-known artists (such as Menashe Kadishman's The Horse Circle and Jeremy Langford (sculptor), Jeremy Langford's The Drip Circle). Some commemorate famous people and international and local organizations, or mark important events. Some are named after the twin cities of Beer Sheva.
Well-known roundabouts are: Ilan Ramon Circle, McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, Phantom Circle near the Air Force Technical School, Champions Square near Terner Stadium and Conch Arena, Chess Circle, Harp Circle near the Municipal Conservatory and the Be'er-Sheva Performing Arts Center, College Circle, Ben Gurion Circle, Light Circle, Freemasons Circle, Shofar, Shofarot Circle, World Trade Center (1973ŌĆō2001), Twin Towers Circle.
In Be'er Sheva there are over 250 roundabouts, giving the city its nickname of "Roundabout Capital of Israel". Many roundabouts, part of Be'er-Sheva's urban oasis project, include fountains, landscaping and sculptures by well-known artists (such as Menashe Kadishman's The Horse Circle and Jeremy Langford (sculptor), Jeremy Langford's The Drip Circle). Some commemorate famous people and international and local organizations, or mark important events. Some are named after the twin cities of Beer Sheva.
Well-known roundabouts are: Ilan Ramon Circle, McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, Phantom Circle near the Air Force Technical School, Champions Square near Terner Stadium and Conch Arena, Chess Circle, Harp Circle near the Municipal Conservatory and the Be'er-Sheva Performing Arts Center, College Circle, Ben Gurion Circle, Light Circle, Freemasons Circle, Shofar, Shofarot Circle, World Trade Center (1973ŌĆō2001), Twin Towers Circle.
Hiking
Beersheba is linked to ''Hilvan'' by the Abraham Path.Sports
Hapoel Be'er Sheva F.C., Hapoel Be'er Sheva plays in the Israeli Premier League, the top tier of Football in Israel, Israeli football, having been promoted in the 2008ŌĆō09 Liga Leumit, 2008ŌĆō2009 Liga Leumit season. The club has won the Israeli championship five times, in 1975, 1976, 2016, 2017 and 2018, as well as the Israel State Cup, State Cup in 1997, 2020 and 2022. Beersheba has two other local clubs, Maccabi Be'er Sheva F.C., Maccabi Be'er Sheva (based in Neighborhoods of Beersheba#Neve Noy, Neve Noy) and F.C. Be'er Sheva (based in the north of Neighborhoods of Beersheba#Dalet, Dalet), a continuation of the defunct Beitar Avraham Be'er Sheva F.C., Beitar Avraham Be'er Sheva. Hapoel play at the Turner Stadium. Beersheba has a basketball club, Hapoel Be'er Sheva B.C., Hapoel Be'er Sheva. The team plays at The Conch Arena, which seats 3,000. Beersheba has become Israel's nationalchess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to disti ...
center; thanks to Soviet immigration, it is home to the largest number of chess grandmasters
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black in chess, White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's King (chess), king. It is sometimes called interna ...
of any city in the world. The city hosted the World Team Chess Championship in 2005, and chess is taught in the city's kindergartens. The Israeli chess team won the silver medal at the 38th Chess Olympiad, 2008 Chess Olympiad and the bronze at the 39th Chess Olympiad, 2010 Olympiad. The chess club was founded in 1973 by Eliyahu Levant, who is still the driving spirit behind it.
The city has the second largest wrestling center (AMI wrestling school) in Israel. The center is run by Leonid Shulman and has approximately 2,000 students, most of whom are from Russian immigrant families since the origins of the club are in the Neighborhoods of Beersheba#Nahal Beka, Nahal Beka immigrant absorption center. Maccabi Be'er Sheva has a freestyle wrestling team, whilst Hapoel Be'er Sheva has a Greco-Roman wrestling team. In the 2010 World Wrestling Championships, AMI students won five medals. Cricket is played under the auspices of Israel Cricket Association. Beersheba is also home to a Rugby union, rugby team, whose senior and youth squads have won several national titles (including the recent Senior National League 2004ŌĆō2005 championship). Beersheba's tennis center, which opened in 1991, features eight lighted courts, and the Beersheba (Teyman) airfield is used for gliding.
Environmental awards
In 2012, the Beersheba "ring trail", a 42-kilometer hiking trail around the city, won third place in the annual environmental competition of the European Travelers Association.Notable people
 * Orna Banai (born 1966), actress, comedian, and entertainer
* Elyaniv Barda (born 1981), footballer
* Zehava Ben (born 1968), singer
* Avishay Braverman (born 1948), professor and politician, president of the
* Orna Banai (born 1966), actress, comedian, and entertainer
* Elyaniv Barda (born 1981), footballer
* Zehava Ben (born 1968), singer
* Avishay Braverman (born 1948), professor and politician, president of the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) ( he, ūÉūĢūĀūÖūæū©ūĪūÖūśū¬ ūæū¤-ūÆūĢū©ūÖūĢū¤ ūæūĀūÆūæ, ''Universitat Ben-Guriyon baNegev'') is a public research university in Beersheba, Israel. Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has five campuses: the ...
* Almog Cohen (born 1988), footballer
* Ruvik Danilovich (born 1971), 8th mayor of Be'er - Sheva
* Anat Draigor (born 1960), basketball player
* Eli Alaluf (born 1945), politician
* Ronit Elkabetz (1964ŌĆō2016), actress
* Velvl Greene (1928ŌĆō2011), CanadianŌĆōAmericanŌĆōIsraeli scientist and academic
* Zvika Hadar (born 1966), comedian and show host
* Boaz Huss (born 1959), professor of Kabbalah at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) ( he, ūÉūĢūĀūÖūæū©ūĪūÖūśū¬ ūæū¤-ūÆūĢū©ūÖūĢū¤ ūæūĀūÆūæ, ''Universitat Ben-Guriyon baNegev'') is a public research university in Beersheba, Israel. Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has five campuses: the ...
*Ron Kaplan (born 1970), Olympic gymnast
* Victor Mikhalevski (born 1972), chess grandmaster
* David Naccache (born 1967), cryptologist, professor at France's Ecole normale sup├®rieure
* David Newman (political geographer), David Newman (born 1956), professor and Dean of Social Science and Humanities, BGU
* Ilan Ramon (1954ŌĆō2003), Israel's first astronaut; died in the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, Columbia disaster
* Yehudit Ravitz (born 1956), singer
*Idan Tal (born 1975), footballer
* Eli Zizov (born 1991), footballer
* Ze'ev Zrizi (1916ŌĆō2011), second mayor of Beersheba
Twin towns ŌĆō sister cities
Beersheba is Sister city, twinned with: * Adana, Turkey * Addis Ababa, Ethiopia * Cluj-Napoca, Romania * Lyon, France * Ni┼Ī, Serbia * Oni, Georgia, Oni, Georgia * City of Parramatta, Parramatta, Australia * La Plata, Argentina * Seattle, United States * Winnipeg, Canada * Wuppertal, Germany * Munich, GermanySee also
Be'er Sheva Municipal Website
* Battle of Beersheba (First World War) * Beer Sheva Park (Seattle), Beer Sheva Park, Seattle * :File:BeershevaRegion1940s.jpg, Map of Beersheba and surrounds in the 1940s and 1950s
References
Bibliography
* *External links
Beersheba City Council
Selection of photos from Beer Sheva
from flickr
Ben-Gurion University
The city of Beersheba: a tourist's guide
nbsp;ŌĆō Historical article from the Catholic Encyclopedia, Catholic Encyclopaedia
Light Horse charges again
Article written by Martin Chulov, published in The Australian, November 1, 2007, the descendants of the Australian light-horsemen rode into the centre of Beersheva, re-enacting the gallant gallop of October 31, 1917
Expansion and architecture of Beersheva in the 1960s and 1970s
Blueprint for Beersheba
* * Tsagai Asamain
Be'er Sheva-Compound C:Conservation measures during the excavation
ŌĆ
Conservation Department
* Yardena Etgar and Ofer Cohen
Tel BeŌĆÖer Sheva: The Underground Water Reservoir System
ŌĆ
Conservation Department
* Shauli Sela and Fuad Abu-Taa
The Turkish Mosque and the Governor's House: Conservation of the stone and plaster
ŌĆ
Conservation Department
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 24
IAA
:commons:File:Survey_of_Western_Palestine_1880.24.jpg, Wikimedia commons
BeerSheva.city
the first French portal of the city {{Authority control Beersheba, Cities in Southern District (Israel) History of Israel by location, Beersheba Chess in Israel Hebrew Bible cities Torah cities Establishments in the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy) 1900s establishments in Ottoman Syria