Battle Of Fisher's Hill on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Fisher's Hill was fought September 21–22, 1864, near
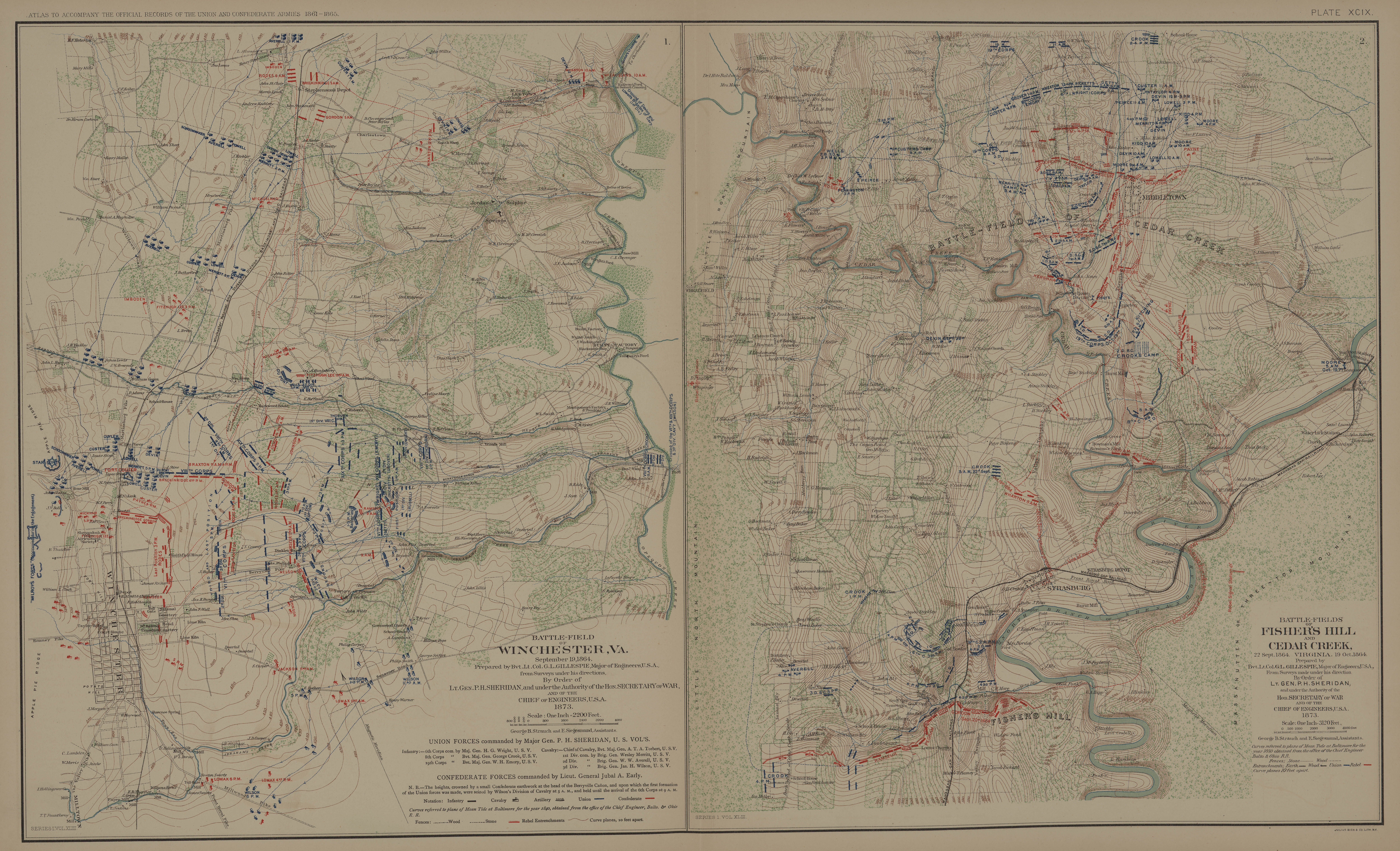 Crook's attack began about 4 p.m. on September 22, 1864. The infantry attack pushed the Confederate troopers out of their way. Maj. Gen. Stephen Dodson Ramseur tried refusing the left flank of his division. Crook and Brig. Gen. James B. Ricketts's division, of Horatio G. Wright's VI Corps struck Ramseur's line, pushing it in. Wright's remaining divisions and XIX Corps broke the Southern line.
Crook's attack began about 4 p.m. on September 22, 1864. The infantry attack pushed the Confederate troopers out of their way. Maj. Gen. Stephen Dodson Ramseur tried refusing the left flank of his division. Crook and Brig. Gen. James B. Ricketts's division, of Horatio G. Wright's VI Corps struck Ramseur's line, pushing it in. Wright's remaining divisions and XIX Corps broke the Southern line.
American Battlefield Trust Fisher's Hill Battlefield page. Accessed May 28, 2018.
National Park Service battle description
CWSAC Report Update and Resurvey: Individual Battlefield Profiles
Personal Memoirs of P. H. Sheridan, General, United States Army in Two Volumes
', Vol. II. New York, New York: Charles L. Webster & Company, 1888. * U.S. War Department
''The War of the Rebellion''
''a Compilation of the
Strasburg, Virginia
Strasburg is a town in Shenandoah County, Virginia, United States, which was founded in 1761 by Peter Stover. It is the largest town by population in the county and is known for its grassroots art culture, pottery, antiques, and American Civil ...
, as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. Despite its strong defensive position, the Confederate
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
army of Lt. Gen. Jubal Early
Jubal Anderson Early (November 3, 1816 – March 2, 1894) was an American lawyer, politician and military officer who served in the Confederate States Army during the Civil War. Trained at the United States Military Academy, Early resigned his ...
was defeated by the Union Army of the Shenandoah, commanded by Maj. Gen. Philip Sheridan
Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close association with General-i ...
.
Background
Military situation
Sheridan had almost 35,000 men in the Shenandoah Valley opposing Early, with just under 10,000. Early, following the Third Battle of Winchester, took a strong position. His right rested on the North Branch of theShenandoah River
The Shenandoah River is the principal tributary of the Potomac River, long with two River fork, forks approximately long each,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August ...
. The left flank of his infantry was on Fisher's Hill. Confederate cavalry was expected to hold the ground from there to Little North Mountain. Maj. Gen. George Crook
George R. Crook (September 8, 1828 – March 21, 1890) was a career United States Army officer who served in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars. He is best known for commanding U.S. forces in the Geronimo Campaign, 1886 campaign that ...
advised Sheridan to flank this position. His command was assigned to move along the wooded slopes of the mountain to attack the cavalry.
Opposing forces
Union
Confederate
Battle
 Crook's attack began about 4 p.m. on September 22, 1864. The infantry attack pushed the Confederate troopers out of their way. Maj. Gen. Stephen Dodson Ramseur tried refusing the left flank of his division. Crook and Brig. Gen. James B. Ricketts's division, of Horatio G. Wright's VI Corps struck Ramseur's line, pushing it in. Wright's remaining divisions and XIX Corps broke the Southern line.
Crook's attack began about 4 p.m. on September 22, 1864. The infantry attack pushed the Confederate troopers out of their way. Maj. Gen. Stephen Dodson Ramseur tried refusing the left flank of his division. Crook and Brig. Gen. James B. Ricketts's division, of Horatio G. Wright's VI Corps struck Ramseur's line, pushing it in. Wright's remaining divisions and XIX Corps broke the Southern line.
Aftermath
The Confederates fell back toWaynesboro, Virginia
Waynesboro (; formerly Flack) is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. It is a principal city of the Staunton-Waynesboro micropolitan area, Staunton-Waynesboro Metropoli ...
. Brig. Gen. Alfred Torbert was sent into the Luray Valley with 6,000 cavalrymen to force his way through the 1,200 Confederate cavalrymen under Brigadier General Williams Wickham. Torbert was then supposed to move through the New Market and Luray Gap in Massanutten Mountain and come up behind Early and cut-off his retreat at Fisher's Hill. Torbert fell back after making a token effort against Wickham's force at Milford (present day Overall) and Early escaped.
Four Union Army enlisted men and one officer received the Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest Awards and decorations of the United States Armed Forces, military decoration and is awarded to recognize American United States Army, soldiers, United States Navy, sailors, Un ...
in the action at Fisher's Hill.
* Private James Connors, 43rd New York Infantry
* Private John Creed, 23rd Illinois Infantry
* Private George G. Moore, 11th West Virginia Infantry
* Sergeant Sylvester D. Rhodes, 61st Pennsylvania Infantry
* First Lieutenant Edward N. Whittier, 5th Battery Maine Light Artillery
Battlefield preservation
TheCivil War Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, and the American Civil War, through the acquisition of battlefield lan ...
(a division of the American Battlefield Trust) and its partners have acquired and preserved of the battlefield. The preserved portion of the battlefield is marked by trails and interpretive signs.American Battlefield Trust Fisher's Hill Battlefield page. Accessed May 28, 2018.
See also
*Troop engagements of the American Civil War, 1864
The following engagements took place in the year 1864 during the American Civil War. The Union armies, under the command of U.S. Grant, launched multiple offenses in all theaters of the war, in an attempt to prevent Confederate forces from transfe ...
* List of costliest American Civil War land battles
This is a list of the costliest land battles of the American Civil War, measured by casualties (killed, wounded, captured, and missing) on both sides.
Highest casualty battles
See also
* List of American Civil War battles
* Timeline of events ...
* List of American Civil War battles
Battles of the American Civil War were fought between April 12, 1861, and May 12–13, 1865 in 19 states, mostly Confederate (Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Ohio ...
* Army of West Virginia
* Jackson's Valley Campaign
Notes
References
National Park Service battle description
CWSAC Report Update and Resurvey: Individual Battlefield Profiles
Memoirs and primary sources
*Early, Jubal A. ''A Memoir of the Last Year of the War for Independence in the Confederate States of America''. Edited by Gary W. Gallagher. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press, 2001. . * Sheridan, Philip Henry.Personal Memoirs of P. H. Sheridan, General, United States Army in Two Volumes
', Vol. II. New York, New York: Charles L. Webster & Company, 1888. * U.S. War Department
''The War of the Rebellion''
''a Compilation of the
Official Records
The ''Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies in the War of the Rebellion'', commonly known as the ''Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies'' or Official Records (OR or ORs), is the most extensive collection of Americ ...
of the Union and Confederate Armies''. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1880–1901.
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fishers Hill, Battle Of Battle of Fisher's Hill Fisher's Hill 1864 Battles of the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War Union victories of the American Civil War Fisher's Hill Battle of Fisher's Hill Conflicts in 1864 September 1864