Battle of Beaufort on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Beaufort, also known as the Battle of Port Royal Island, was fought on February 3, 1779, near
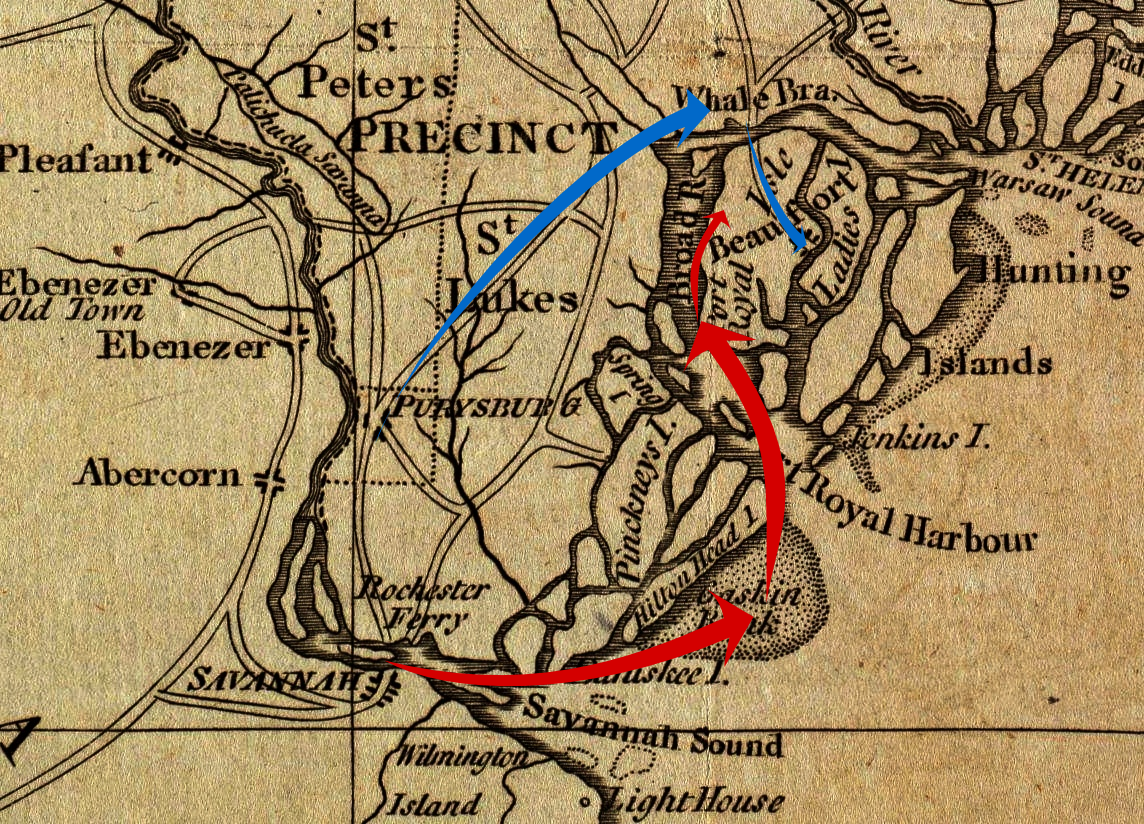 The only major defense establishment on Port Royal Island was Fort Lyttelton, which was garrisoned by a company of Continental Army troops under Captain John DeTreville. When he learned that a comparatively large British force was moving in his direction, he spiked the fort's cannons and blew up its main bastion in order to deny their use to the superior force. When General Lincoln learned that communications with Port Royal Island had been cut off by the British advance, he sent South Carolina Brigadier General
The only major defense establishment on Port Royal Island was Fort Lyttelton, which was garrisoned by a company of Continental Army troops under Captain John DeTreville. When he learned that a comparatively large British force was moving in his direction, he spiked the fort's cannons and blew up its main bastion in order to deny their use to the superior force. When General Lincoln learned that communications with Port Royal Island had been cut off by the British advance, he sent South Carolina Brigadier General
Beaufort, South Carolina
Beaufort ( , a different pronunciation from that used by the city with the same name in North Carolina) is a city in and the county seat of Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. Chartered in 1711, it is the second-oldest city in South ...
, during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. The battle took place not long after British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
forces consolidated control around Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and is the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Br ...
, which they had captured in December 1778.
Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
Augustine Prevost
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North A ...
sent 200 British regulars to seize Port Royal Island
Port Royal Island (historically Port Royal) is an island located in Beaufort County, South Carolina. It is considered one of the Sea Islands in the Lowcountry region and is the most populous island in northern Beaufort County, containing most of ...
at the mouth of the Broad River in South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
in late January 1779. Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Benjamin Lincoln
Benjamin Lincoln (January 24, 1733 ( O.S. January 13, 1733) – May 9, 1810) was an American army officer. He served as a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. Lincoln was involved in three major surrender ...
, the American commander in the south, sent South Carolina Brigadier General William Moultrie
William Moultrie (; November 23, 1730 – September 27, 1805) was an American planter and politician who became a general in the American Revolutionary War. As colonel leading a state militia, in 1776 he prevented the British from taking Charle ...
from Purrysburg, South Carolina
Purrysburg is an unincorporated community in Jasper County, South Carolina. While the town itself was abandoned, the settlers were successful. The town was located on the South Carolina bank of the Savannah River on 40,000 acres.
Purrysburg (aka ...
with a mixed force composed mainly of militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
, but with a few Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
men, to meet the British advance. The battle was inconclusive, but the British withdrew first and suffered heavier casualties than the Americans.
Background
The British began their "southern strategy" by sending expeditions fromNew York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and Saint Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Af ...
, East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of ...
to capture Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and is the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Br ...
late in 1778. The New York expedition, under the command of Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colone ...
Archibald Campbell Archibald Campbell may refer to:
Peerage
* Archibald Campbell of Lochawe (died before 1394), Scottish peer
* Archibald Campbell, 2nd Earl of Argyll (died 1513), Lord Chancellor of Scotland
* Archibald Campbell, 4th Earl of Argyll (c. 1507–1558) ...
, arrived first, and successfully captured the town on December 29, 1778. Remnants of Savannah's defenders combined with South Carolina militia under Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Benjamin Lincoln
Benjamin Lincoln (January 24, 1733 ( O.S. January 13, 1733) – May 9, 1810) was an American army officer. He served as a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. Lincoln was involved in three major surrender ...
at an encampment at Purrysburg, South Carolina
Purrysburg is an unincorporated community in Jasper County, South Carolina. While the town itself was abandoned, the settlers were successful. The town was located on the South Carolina bank of the Savannah River on 40,000 acres.
Purrysburg (aka ...
to oppose the British.
When Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
Augustine Prevost
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North A ...
arrived from Saint Augustine in mid-January 1779, he assumed command of the garrison there, and on the 22nd sent a force under Campbell to take control of Augusta and raise Loyalist militia companies.Russell, p. 104 Prevost decided thereafter to send a force to occupy Port Royal Island
Port Royal Island (historically Port Royal) is an island located in Beaufort County, South Carolina. It is considered one of the Sea Islands in the Lowcountry region and is the most populous island in northern Beaufort County, containing most of ...
just up the coast in South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, where he had been led to believe that Loyalist sentiment was strong. On January 29 , an unseaworthy
Seakeeping ability or seaworthiness is a measure of how well-suited a watercraft is to conditions when underway. A ship or boat which has good seakeeping ability is said to be very seaworthy and is able to operate effectively even in high sea stat ...
ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two colu ...
that had been converted to a floating battery
A floating battery is a kind of armed watercraft, often improvised or experimental, which carries heavy armament but has few other qualities as a warship.
History
Use of timber rafts loaded with cannon by Danish defenders of Copenhagen a ...
, was towed by Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
crews in longboat
A longboat is a type of ship's boat that was in use from ''circa'' 1500 or before. Though the Royal Navy replaced longboats with launches from 1780, examples can be found in merchant ships after that date. The longboat was usually the largest boa ...
s through the channel separating Hilton Head Island
Hilton Head Island, sometimes referred to as simply Hilton Head, is a South Carolina Lowcountry, Lowcountry resort town and barrier island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. It is northeast of Savannah, Georgia, and southwest of C ...
from the mainland. She was accompanied by a flotilla of smaller ships that carried 200 infantry from the 16th
16 (sixteen) is the natural number following 15 and preceding 17. 16 is a composite number, and a square number, being 42 = 4 × 4. It is the smallest number with exactly five divisors, its proper divisors being , , and .
In English speech, ...
and 60th Regiments under Major William Gardner, who had orders to take control of Beaufort, the island's main settlement.Rowland et al, p. 216
 The only major defense establishment on Port Royal Island was Fort Lyttelton, which was garrisoned by a company of Continental Army troops under Captain John DeTreville. When he learned that a comparatively large British force was moving in his direction, he spiked the fort's cannons and blew up its main bastion in order to deny their use to the superior force. When General Lincoln learned that communications with Port Royal Island had been cut off by the British advance, he sent South Carolina Brigadier General
The only major defense establishment on Port Royal Island was Fort Lyttelton, which was garrisoned by a company of Continental Army troops under Captain John DeTreville. When he learned that a comparatively large British force was moving in his direction, he spiked the fort's cannons and blew up its main bastion in order to deny their use to the superior force. When General Lincoln learned that communications with Port Royal Island had been cut off by the British advance, he sent South Carolina Brigadier General William Moultrie
William Moultrie (; November 23, 1730 – September 27, 1805) was an American planter and politician who became a general in the American Revolutionary War. As colonel leading a state militia, in 1776 he prevented the British from taking Charle ...
, who had distinguished himself in the 1776 Battle of Sullivan's Island
The Battle of Sullivan's Island or the Battle of Fort Sullivan was fought on June 28, 1776, during the American Revolutionary War. It took place near Charleston, South Carolina, during the first British attempt to capture the city from American ...
, and 300 men to counter the move. Moultrie's force was composed mostly of South Carolina militia from the Beaufort area, but it was accompanied by a few Continental Army regulars, and two companies of artillery from Charleston, which were headed by former Congressmen Edward Rutledge and Thomas Heyward, Jr. This force arrived at the main Port Royal ferry on the 31st, not long after DeTreville had finished destroying the fort. They crossed over to the island on February 1 and occupied Beaufort.Rowland et al, p. 217
Battle
Gardner's men landed on Port Royal Island at the plantation of Andrew Deveaux (present-day Laurel Bay), a Loyalist who may have guided them, on February 2. Gardner sent a detachment to secure the island side of the ferry. These men retreated when they encountered Patriot troops, and Gardner began to move his main force toward Beaufort to face the Americans. Early on February 3 General Moultrie was alerted to the British presence, and moved his forces out of town. The two forces met near the highest ground on Port Royal Island, a rise called Gray's Hill that was about south of the ferry and in the middle of the island. Gardner lined his men up at the edge of some woods near the top of the hill and advanced withbayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustr ...
s fixed. The Americans approached and lined up in an open field outside musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually d ...
range. General Moultrie positioned two six-pound field cannons in the center of his line, with a smaller two-pounder on the right. The Americans then advanced on the British, Moultrie observing that the action was "reversed from the usual way of fighting between British and Americans; they taking the bushes and we taking the open ground." The Americans opened fire first with the artillery, and then with musket volleys. The battle continued for about 45 minutes, at which point the Americans were running low on ammunition. Moultrie had begun a withdrawal when the British were also observed to retreat, leaving the field to the Americans.Rowland et al, p. 218 A company of light horse militia chased after the British, very nearly cutting them off from their boats. They successfully captured 26 men, but were unable to hold all of them due to their small numbers.
Aftermath
In addition to the prisoners taken (sources cite either seven or twelve were retained), the British reportedly suffered 40 killed or wounded, although deserters reported that nearly half of Gardner's men had been hit by American fire. The Americans, in contrast, suffered only 8 killed and 22 wounded. Gardner was criticized by Prevost for the mauling his detachment received because he strayed too far from his boats. It was not Gardner's fault, however, that he had no Loyalist support.Wilson, p. 101 The victory of a largely militia force over British regulars was a boost to the Americans' morale. However, severe losses incurred in early March at Brier Creek delayed American plans to move against Prevost's forces in Georgia. When Lincoln began moving troops toward Augusta in April, Prevost moved in force toward Charleston, but was able to do little more than briefly blockade the city before retreating back to Savannah. Port Royal Island was again occupied by the British during this campaign. The battle is commemorated by a highway marker on U. S. Route 21 near the battle site. Fort Lyttelton's remains are listed on theNational Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
.
Footnotes
References
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Beaufort, Battle of Conflicts in 1779 Battles involving the United States Battles involving Great Britain Beaufort Beaufort County, South Carolina BeaufortBattle of Beaufort
The Battle of Beaufort, also known as the Battle of Port Royal Island, was fought on February 3, 1779, near Beaufort, South Carolina, during the American Revolutionary War. The battle took place not long after British forces consolidated contr ...
Beaufort, South Carolina