Battle of Arcadiopolis (970) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Arcadiopolis was fought in 970 between a
 It was a clear declaration of war, but Nikephoros' forces were largely preoccupied in the East. Thus the emperor turned to the traditional Byzantine expedient of turning one of the peoples living further north, in modern-day
It was a clear declaration of war, but Nikephoros' forces were largely preoccupied in the East. Thus the emperor turned to the traditional Byzantine expedient of turning one of the peoples living further north, in modern-day
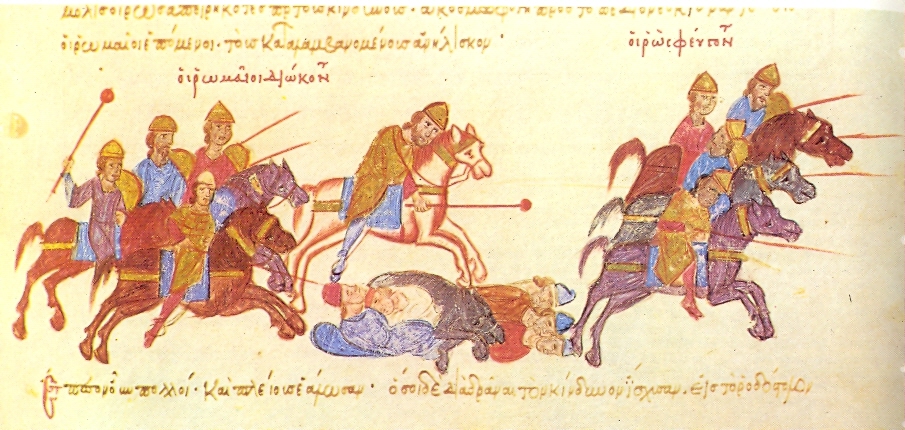 Skleros then quickly assembled a force of ten to twelve thousand men and set out to meet the Rus'. The two armies met near Arcadiopolis (modern
Skleros then quickly assembled a force of ten to twelve thousand men and set out to meet the Rus'. The two armies met near Arcadiopolis (modern
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
army under Bardas Skleros
Bardas Skleros (Greek: Βάρδας Σκληρός) or Sclerus was a Byzantine general who led a wide-scale Asian rebellion against Emperor Basil II during the years 976 to 979.
Background
Bardas belonged to the great family of the Skleroi, wh ...
and a Rus' army, the latter also including allied Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, Pecheneg
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, and Hungarian (Magyar) contingents. In the preceding years, the Rus' ruler Sviatoslav
Sviatoslav (russian: Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ; uk, Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ) is a Russian and Ukrainian given name of Slavic origin. Cognates include Svetoslav, Svatoslav, , Svetislav. It has a Pre-Christian pagan charact ...
had conquered northern Bulgaria, and was now menacing Byzantium as well. The Rus' force had been advancing through Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
towards Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
when it was met by Skleros' force. Having fewer men than the Rus', Skleros prepared an ambush and attacked the Rus' army with a portion of his force. The Byzantines then feigned retreat
A feigned retreat is a military tactic, a type of feint, whereby a military force pretends to withdraw or to have been routed, in order to lure an enemy into a position of vulnerability.
A feigned retreat is one of the more difficult tactics fo ...
, and succeeded in drawing off the Pecheneg contingent into the ambush, routing it. The remainder of the Rus' army then suffered heavy casualties from the pursuing Byzantines. The battle was important as it bought time for the Byzantine emperor John I Tzimiskes
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
to settle his internal problems and assemble a large expedition, which eventually defeated
Defeated may refer to:
* "Defeated" (Breaking Benjamin song)
* "Defeated" (Anastacia song)
*"Defeated", a song by Snoop Dogg from the album ''Bible of Love''
*Defeated, Tennessee, an unincorporated community
*''The Defeated
''The Defeated'', al ...
Sviatoslav the next year.
Background
In 965 or 966, aBulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
embassy visited the Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
(r. 963–969) at Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
to receive the annual tribute that had been agreed by the two powers as the price of peace in 927. Phokas, flush and self-confident from a series of victories against the Arabs in the East that had led to the recovery of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
, refused to comply, and even had the envoys beaten up. He followed this up with a show of military strength, by sending a small force to raze a number of Bulgarian border posts in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
..
 It was a clear declaration of war, but Nikephoros' forces were largely preoccupied in the East. Thus the emperor turned to the traditional Byzantine expedient of turning one of the peoples living further north, in modern-day
It was a clear declaration of war, but Nikephoros' forces were largely preoccupied in the East. Thus the emperor turned to the traditional Byzantine expedient of turning one of the peoples living further north, in modern-day Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, against Bulgaria. He sent an ambassador, the ''patrikios
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after ...
'' Kalokyros Kalokyros ( el, Καλοκυρός, died 971) was a pretender to the Byzantine throne during the Rus'–Byzantine War (970–971) in the reigns of Nikephoros II and John I Tzimiskes.
According to the historians John Skylitzes and Leo the Deacon, ...
, to Sviatoslav
Sviatoslav (russian: Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ; uk, Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ) is a Russian and Ukrainian given name of Slavic origin. Cognates include Svetoslav, Svatoslav, , Svetislav. It has a Pre-Christian pagan charact ...
, ruler of the Rus' with whom the Byzantines had maintained close relations.. Sviatoslav enthusiastically responded, and invaded Bulgaria in 967 or 968 in a devastating raid, before returning home to defend his capital against a Pecheneg
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
attack. This forced the Bulgarian tsar, Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholico ...
, to the negotiating table, agreeing to terms favourable to Byzantium. However, this brief sojourn also awakened in Sviatoslav the desire to conquer Bulgaria and establish his own realm there. He returned in force in July or August 969 and conquered the country within a few months..
Nikephoros' scheme had backfired dramatically: instead of peace, a new and formidable foe had appeared in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, and a large part of the Bulgarian nobility appeared to side with the Rus' prince. The emperor, however, was murdered in December 969, and it fell to his successor, John I Tzimiskes
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
(r. 969–976), to deal with the Rus' threat. Sviatoslav now turned his sights on Byzantium, and to John's entreaties for peace he allegedly answered that the Empire should abandon its European territories to him and withdraw to Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Tzimiskes himself was preoccupied with consolidating his position and with countering the unrest of the powerful Phokas clan and its adherents, and delegated the war in the Balkans to his brother-in-law, the Domestic of the Schools
The office of the Domestic of the Schools ( gr, δομέστικος τῶν σχολῶν, domestikos tōn scholōn) was a senior military post of the Byzantine Empire, extant from the 8th century until at least the early 14th century. Originally ...
Bardas Skleros
Bardas Skleros (Greek: Βάρδας Σκληρός) or Sclerus was a Byzantine general who led a wide-scale Asian rebellion against Emperor Basil II during the years 976 to 979.
Background
Bardas belonged to the great family of the Skleroi, wh ...
, and to the eunuch ''stratopedarches
''Stratopedarchēs'' ( el, στρατοπεδάρχης, , master of the camp), sometimes Anglicized as Stratopedarch, was a Greek term used with regard to high-ranking military commanders from the 1st century BC on, becoming a proper office in ...
'' Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a sur ...
. They were to winter in Thrace and raise an army, whilst sending spies to discover Sviatoslav's intentions..
At the news of this, a powerful Rus' force, along with many Bulgarians and a Pecheneg contingent, was sent south over the Balkan Mountains. After sacking the city of Philippopolis (modern Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
) in Thrace, they bypassed the heavily defended city of Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
and turned towards Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. The size of the Rus' army, and whether it comprised the entirety of Sviatoslav's forces or just a division, is unclear. John Skylitzes
John Skylitzes, commonly Latinized as Ioannes, la, Johannes, label=none, la, Iōannēs, label=none Scylitzes ( el, Ἰωάννης Σκυλίτζης, ''Iōánnēs Skylítzēs'', or el, Σκυλίτση, ''Skylítsē'', label=none ; la, ...
, for instance, implies that this was the entire Rus' army, numbering an incredible 308,000 men, but the contemporary Leo the Deacon Leo the Deacon ( el, Λέων ο Διάκονος) (born c. 950) was a Byzantine Greek historian and chronicler.
He was born around 950 at Kaloe in Asia Minor, and was educated in Constantinople, where he became a deacon in the imperial palace. Whi ...
reports that it was a detachment of "over 30,000 men"; conversely, the Russian ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'' gives the ''entire'' Rus' army under Sviatoslav at some 30,000, whilst numbering the Rus' at Arcadiopolis at only 10,000, faced with 100,000 Byzantines. It is clear, however, that the Byzantines were considerably outnumbered, and that the Rus' force at Arcadiopolis included significant numbers of Bulgarians, as well as allied contingents of Pechenegs and "Turks" (i.e. Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic ...
)..
The battle
 Skleros then quickly assembled a force of ten to twelve thousand men and set out to meet the Rus'. The two armies met near Arcadiopolis (modern
Skleros then quickly assembled a force of ten to twelve thousand men and set out to meet the Rus'. The two armies met near Arcadiopolis (modern Lüleburgaz
Lüleburgaz (, Modern Greek: Λουλέ Μπουργκάς ''Lule Burgas'', Bulgarian: Люлебургаз ''Lyuleburgaz''), Bergoulion (Ancient Greek: Βεργούλιον) or Arcadiopolis (Ancient Greek: Αρκαδιόυπολις ''Arkadiópol ...
in Turkish Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace ( tr, Doğu Trakya or simply ''Trakya''; el, Ανατολική Θράκη, ''Anatoliki Thraki''; bg, Източна Тракия, ''Iztochna Trakiya''), also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the pa ...
), some 80 km west of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. The two primary accounts on the Byzantine side differ on the preliminaries of the battle: Leo the Deacon reports that Skleros sent a scouting detachment ahead under the ''patrikios
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after ...
'' John Alakaseus, and then gave battle after only a day, but the later chronicle of Skylitzes reports that for a few days, Skleros with his men remained within the walls of Arcadiopolis as the Rus' encamped nearby, and refused to come out and meet them in battle despite their repeated challenges for him to do so. According to Skylitzes, the Rus' quickly became convinced that the imperial army was too afraid to face them; consequently they roamed about the countryside plundering, neglected their camp defences, and spent their nights in heedless revelry.
Skleros eventually set out from the city, and divided his forces into three groups: two divisions were placed in ambush on the wooded sides of the road leading towards the Rus' camp, while another, probably some 2,000–3,000 men, was placed under himself (or Alakaseus in Skylitzes' account) and went forth to attack the Rus' host. The Byzantine detachment quickly came into contact with the Rus' army, and charged the Pecheneg contingent. The Byzantines executed a gradual orderly retreat, turning at intervals to charge back at the pursuing Pechenegs, who had thus become separated from the main body of the Rus' army. This conflict was fierce and bloody, taxing the discipline and endurance of the small Byzantine force. According to Leo the Deacon, at one point one of the Pechenegs charged Bardas himself and delivered a sword blow on his helmet, which was deflected by the metal without doing harm. Bardas' young brother Constantine came to his rescue, killing the Pecheneg.
When the two opposing forces reached the place of the ambush, Bardas ordered the trumpets blown and the two concealed Byzantine divisions attacked the Pechenegs from the flanks and the rear. Cut off from aid and surrounded, the Pechenegs began to panic and flee. One of their leaders tried to rally his men, but he was attacked by Bardas Skleros himself, who killed him with a single sword-blow that reportedly cut him in two from his head down to the waist, through the Pecheneg's helmet and cuirass.. The loss of the Pecheneg commander turned the battle into a complete rout, and panic spread to the Bulgarian contingent following behind the Pechenegs, which also suffered heavy casualties in the general chaos. The Byzantine casualties in the battle were low (Skylitzes speaks of 25 dead and Leo of 55) although they lost many horses to the Pecheneg arrows, while the losses of the Rus' force, although certainly lower than Leo's claimed 20,000, were still significant, probably running into several thousands.
Aftermath
The Byzantines were unable to exploit this victory or pursue the remnants of the Rus' army, since Bardas Phokas rose in revolt in Asia Minor. Bardas Skleros and his men were consequently withdrawn to Asia Minor, whilst Sviatoslav restricted his forces to the north of the Balkan Mountains. In the spring of the next year, however, with Phokas' rebellion subdued, Tzimiskes himself, at the head of his army, advanced north into Bulgaria. The Byzantines took the Bulgarian capitalPreslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
, capturing the Bulgarian tsar Boris II
Boris II ( cu, Борисъ В҃; bg, Борис II; c. 931 – 977) was emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 969 to 977 (in Byzantine captivity from 971).
Boris II was the eldest surviving son of Emperor Peter I of Bulgaria and Maria (renamed Eiren ...
, and confined the Rus' in the fortress of Dorostolon (modern Silistra
Silistra ( bg, Силистра ; tr, Silistre; ro, Silistra) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Sil ...
). After a three-month siege and a series of pitched battles before the city walls, Sviatoslav conceded defeat and abandoned Bulgaria.
In Hungarian historiography, the Battle of Arcadiopolis is considered as the final chapter of the Hungarian invasions of Europe
The Hungarian invasions of Europe ( hu, kalandozások, german: Ungarneinfälle) took place in the 9th and 10th centuries,
the period of transition in the history of Europe in the Early Middle Ages, when the territory of the former Carolingian Em ...
, a series of plundering raids both westward and southward since the end of the 9th century. Following that the new Grand Prince, Géza Géza is a Hungarian given name and may refer to any of the following:
* Benjamin Géza Affleck
* Géza, Grand Prince of the Hungarians
* Géza I of Hungary, King of Hungary
* Géza II of Hungary, King of Hungary
* Géza, son of Géza II of Hungar ...
consolidated his authority and also supported Christian missionaries from Western Europe (experiencing the fate of the Bulgarian patriarchate
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
after John Tzimiskes's campaign against Bulgaria, when lost its independence), which led to the Christianization of the Magyars and the establishment of the Christian Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
by the beginning of the new millennium.
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Arcadiopolis (970) Battles involving Kievan Rus' Battles involving the Byzantine Empire Battles involving the First Bulgarian Empire Battles involving Hungary in the Middle Ages Battles of the Hungarian invasions of Europe Arcadiopolis History of Kırklareli Province Pechenegs 970s in the Byzantine Empire 970s conflicts 970 10th century in Kievan Rus'